Microfiltration of Submicron-Sized and Nano-Sized Suspensions for Particle Size Determination by Dynamic Light Scattering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Reference Materials
2.1.2. Representative Test Materials
2.1.3. Membranes
2.2. Desagglomeration
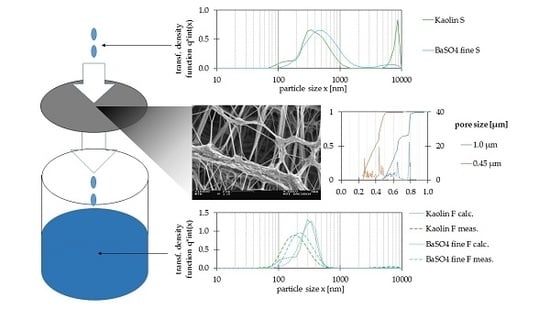
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.3.1. SEM Images
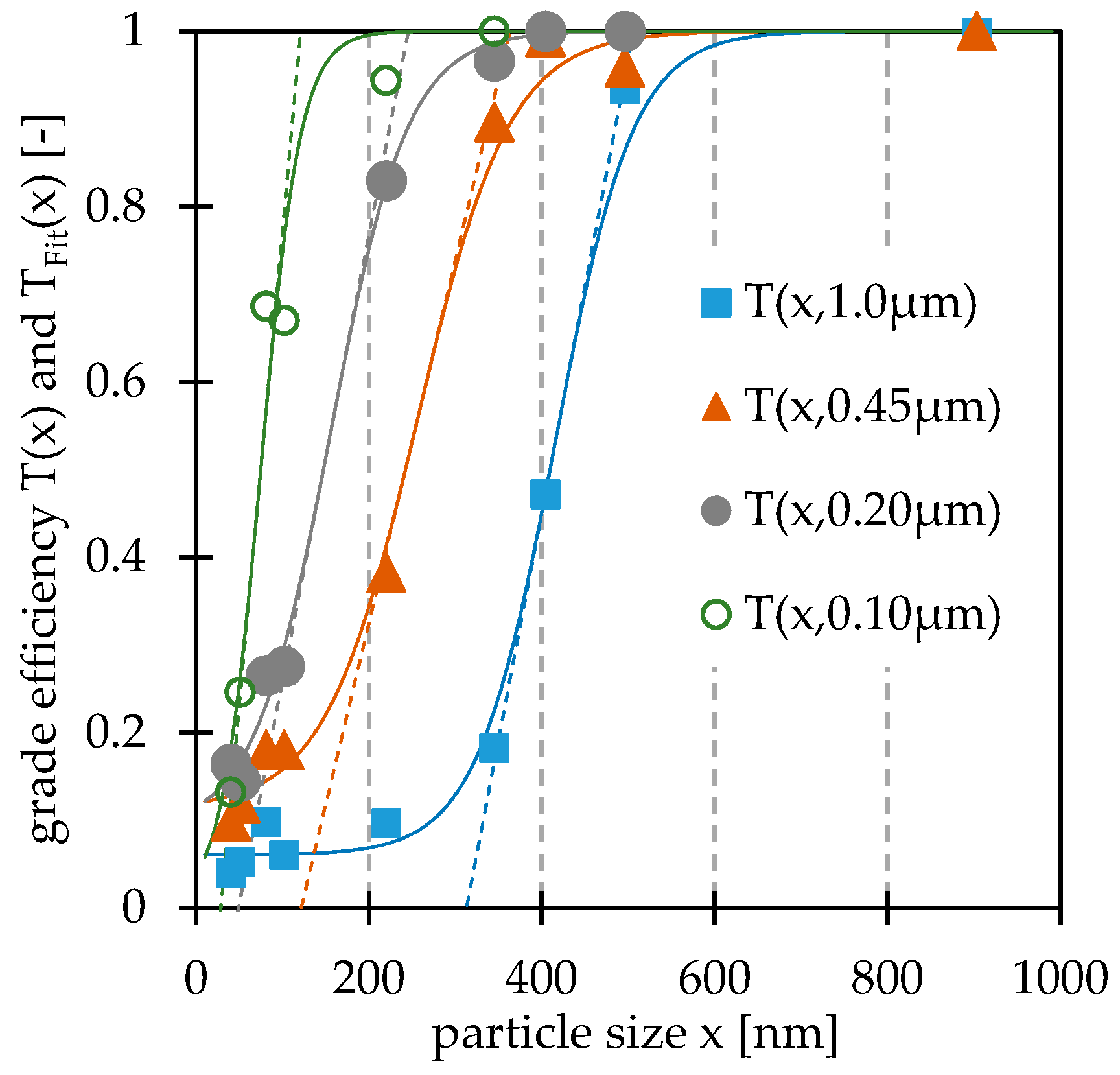
2.3.2. Pore Size Analysis
2.4. Sample Preparation Procedures
2.4.1. Blank Samples
2.4.2. Procedures for Reference Materials
2.4.3. Monomodal Material
2.4.4. Polydisperse Materials
2.5. Filtration Procedure
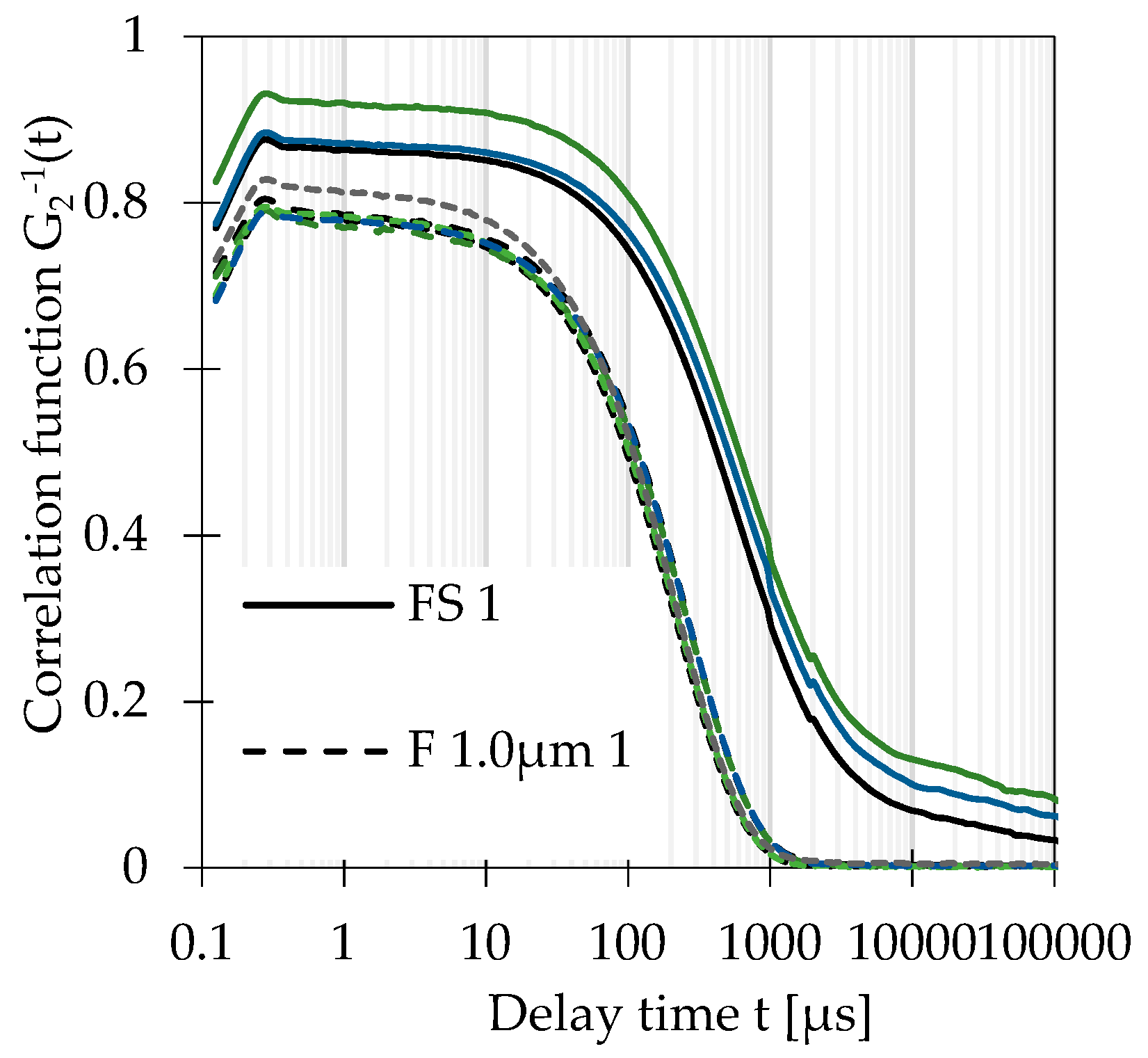
2.6. DLS Measurement Procedure and Analysis
2.7. Calculation Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membrane Characterization
3.2. Blank Samples
3.3. Suspension Samples with Reference Materials
3.4. Effect of Particle Concentration
3.5. Representative Materials
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasmussen, K.; Gonzales, M.; Kearns, P.; Sintes, J.R.; Rossi, F.; Sayre, P. Review of achievements of the OECD Working Party on Manufactured Nanomaterials’ Testing and Assessment Programme. From exploratory testing to test guidelines. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2016, 74, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, A.; Couteau, O.; Franks, K.; Kestens, V.; Roebben, G.; Lamberty, A.; Linsinger, T.P.J. Validation of dynamic light scattering and centrifugal liquid sedimentation methods for nanoparticle characterisation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2011, 22, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberty, A.; Franks, K.; Braun, A.; Kestens, V.; Roebben, G.; Linsinger, T.P.J. Interlaboratory comparison for the measurement of particle size and zeta potential of silica nanoparticles in an aqueous suspension. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 7317–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.; Kestens, V.; Franks, K.; Roebben, G.; Lamberty, A.; Linsinger, T.P.J. A new certified reference material for size analysis of nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestens, V.; Roebben, G.; Herrmann, J.; Jamting, A.; Coleman, V.; Minelli, C.; Clifford, C.; De Temmerman, P.J.; Mast, J.; Liu, J.J.; et al. Challenges in the size analysis of a silica nanoparticle mixture as candidate certified reference material. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franks, K.; Braun, A.; Charoud-Got, J.; Couteau, O.; Kestens, V.; Lamberty, A.; Linsinger, T.J.P.; Roebben, G. Certification Report—Certification of the Equivalent Spherical Diameters of Silica Nanoparticles in Aqueous Solution—Certified Reference Material ERM®-FD304; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Provencher, S.W. Inverse problems in polymer characterization. Direct analysis of polydispersity with photon correlation spectroscopy. Makromol. Chem. 1979, 180, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, S.W. Contin—a general-purpose constrained regularization program for inverting noisy linear algebraic and integral-equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1982, 27, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, D.E. Analysis of macromolecular polydispersity in intensity correlation spectroscopy—method of cumulants. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 57, 4814–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie, G. Beiträge zur Optik trüber Medien, speziell kolloidaler Metallösungen. Ann. Phys. 1908, 330, 377–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babick, F.; Gropp, S.; Katzel, U.; Vorbau, M. Dynamic light scattering of dispersed fumed silica aggregates. Powder Technol. 2012, 217, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babick, F.; Schiessl, K.; Stintz, M. Characterization of pyrogenic powders with conventional particle sizing technique: I. prediction of measured size distributions. Part. Part. Syst. Char. 2012, 29, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotti, A.; Liu, W.; Hyatt, J.S.; Herman, E.S.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, J.W.; Lyon, L.A.; Gasser, U.; Fernandez-Nieves, A. The CONTIN algorithm and its application to determine the size distribution of microgel suspensions. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 142, 234905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Committee for Standardization CEN/TS 17010:2016. Nanotechnologies—Guidance on Measurands for Characterising Nano-Objects and Materials that Contain them; Brussels, Belgium, 2016; Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/75190.html (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- Rauscher, H.; Roebben, G.; Amenta, V.; Sanfeliu, A.B.; Calzolai, L.; Emons, H.; Gaillard, C.; Gibson, N.; Linsinger, T.P.J.; Mech, Â.; et al. JRC Scientific and Policy Report—Towards A Review of the EC Recommendation for A Definition of the Term “Nanomaterial”—Part 1: Compilation of Information Concerning the Experience with the Definition; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Babick, F.; Mielke, J.; Wohlleben, W.; Weigel, S.; Hodoroaba, V.D. How reliably can a material be classified as a nanomaterial? Available particle-sizing techniques at work. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijman, E.J.; Merkus, H.G.; Marijnissen, J.C.M.; Scarlett, B. Simulations and experiments on number fluctuations in photon-correlation spectroscopy at low particle concentrations. Appl. Optics 2001, 40, 4058–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, C.; Babick, F.; Koeber, R.; Stintz, M. Performance of analytical centrifugation for the particle size analysis of real-world materials. Powder Technol. 2017, 319, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurozzi, J.S.; Hackley, V.A.; Wiesner, M.R. Ultrasonic dispersion of nanoparticles for environmental, health and safety assessment - issues and recommendations. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 711–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, T.; Oelschlagel, K.; Potthoff, A. Dispersion of nanomaterials used in toxicological studies: A comparison of sonication approaches demonstrated on TiO2 P25. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Pacek, A.W. Ultrasonic processing of suspensions of hematite nanopowder stabilized with sodium polyacrylate. AIChE J. 2009, 55, 2796–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, M.; Hogekamp, S.; Hoffmann, N.Q.; Schuchmann, H.P. Dispersion and deagglomeration of nanoparticles with ultrasound. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2004, 76, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, R.R.R.; Babick, F.; Stintz, M. Ultrasonic dispersion of nanostructured materials with probe sonication—practical aspects of sample preparation. Powder Technol. 2017, 318, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, R.R.R.; Babick, F.; Lindner, G.G.; Wiemann, M.; Stintz, M. Effects of sample preparation on particle size distributions of different types of silica in Suspensions. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 8070454. [Google Scholar]
- Mawson, R.; Rout, M.; Ripoll, G.; Swiergon, P.; Singh, T.; Knoerzer, K.; Juliano, P. Production of particulates from transducer erosion: Implications on food safety. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, K.; Rauscher, H.; Mech, A.; Riego Sintes, J.; Gilliland, D.; Gonzalez, M.; Kearns, P.; Moss, K.; Visser, M.; Groenewold, M.; et al. Physico-chemical properties of manufactured nanomaterials—Characterisation and relevant methods. An outlook based on the OECD Testing Programme. J. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 92, 8–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlleben, W. Validity range of centrifuges for the regulation of nanomaterials: from classification to as-tested coronas. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barahona, F.; Ojea-Jimenez, I.; Geiss, O.; Gilliland, D.; Barrero-Moreno, J. Multimethod approach for the detection and characterisation of food-grade synthetic amorphous silica nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1432, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiezorek, C. Fractionation of nanoparticles in food and cosmetics using “Nanosiebung” and their further chemical analysis. Deut. Lebensm.-Rund. 2011, 107, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Babick, F.; Ullmann, C. Error propagation at the conversion of particle size distributions. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babick, F. Report of the Potentials of the Transformation of Non-Counting Methods Size Distributions into Number-Weighted Size Distributions of the Constituent Particles Based on Instrument Manufacturers Algorithms—NanoDefine Technical Report D3.6; NanoDefine Consortium: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization ISO 9276-2:2014. Representation of Results of Particle Size Analysis—Part 2: Calculation of Average Particle Sizes/Diameters and Moments from Particle Size Distributions; Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/57641.html (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- Shiller, A.M. Syringe filtration methods for examining dissolved and colloidal trace element distributions in remote field locations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3953–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minning, T.; Lytle, D.A.; Pham, M.; Kelty, K. Systematic evaluation of dissolved lead sorption losses to particulate syringe filter materials. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G. On the challenge of quantifying man-made nanoparticles in the aquatic environment. J. Environ. Monitor. 2010, 12, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, C.; Müller, P. SOP, Applicability Range and Method Performance Description for DLS & MiniTEM —NanoDefine Technical Report D4.6; NanoDefine Consortium: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization ISO 14887:2000. Sample Preparation—Dispersing Procedures for Powders in Liquids; Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:14887:ed-1:v1:en (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- International Organization for Standardization ISO 22412:2017. Particle Size Analysis—Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS); Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/65410.html (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- ASTM E2490-09 (Reapproved 2015) Standard Guide for Measurement of Particle Size Distribution of Nanomaterials in Suspension by Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (PCS). West Conshohocken: PA, US. 2015. Available online: www.astm.org (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- International Organization for Standardization ISO 10304-1:2007. International Organization for Standardization ISO 10304-1:2007. Water Quality—Determination of Dissolved Anions by Liquid Chromatography of Ions—Part 1: Determination of Bromide, Chloride, Fluoride, Nitrate, Nitrite, Phosphate and Sulfate; Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/46004.html (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- Bin Darwis, N.; Kochkodan, V.; Hilal, N. Microfiltration of micro-sized suspensions of boron-selective resin with PVDF membranes. Desalination 2017, 403, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.Y.; Jung, M.Y. Ultra-High-Throughput Analytical Strategy Based on UHPLC-DAD in Combination with Syringe Filtration for the Quantitation of Nine Synthetic Colorants in Beverages: Impacts of Syringe Membrane Types and Sample pH on Recovery. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9916–9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roebben, G.; Rasmussen, K.; Kestens, V.; Linsinger, T.P.J.; Rauscher, H.; Emons, H.; Stamm, H. Reference materials and representative test materials: the nanotechnology case. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E1294-89(1999), Standard Test Method for Pore Size Characteristics of Membrane Filters Using Automated Liquid Porosimeter (Withdrawn 2008), ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA. 1999. Available online: www.astm.org (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- ASTM F316-03(2011), Standard Test Methods for Pore Size Characteristics of Membrane Filters by Bubble Point and Mean Flow Pore Test, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA. 2011. Available online: www.astm.org (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- Hernandez, A.; Calvo, J.I.; Pradanos, P.; Tejerina, F. Pore size distributions in microporous membranes. A critical analysis of the bubble point extended method. J. Membrane Sci. 1996, 112, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babick, F. Suspensions of Colloidal Particles and Aggregates; In particle Ttechnology Series; Valverde Millán, J.M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland, D.; Pianella, F.; Rio-Echevarria, I.M.; Loeschner, K.; Correia, M.; Mast, J.; Ullmann, C. Standardised Dispersion Protocols for High Priority Materials Groups—NanoDefine Technical Report D2.3; NanoDefine Consortium: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, M.J. Handbook of Optical Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, Florida, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jellison, G.E.; Boatner, L.A.; Budai, J.D.; Jeong, B.S.; Norton, D.P. Spectroscopic ellipsometry of thin film and bulk anatase (TiO2). J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 9537–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieß, M. Mechanische Verfahrenstechnik-Partikeltechnologie 1, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heideberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Linsinger, T.P.; Roebben, G.; Gilliland, D.; Calzolai, L.; Rossi, F.; Gibson, N.; Klein, C. Requirements on Measurements for the Implementation of the European Commission Definition of the Term “Nanomaterial”; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 2012. [Google Scholar]




| Material | Supplier | Reference diameter by AUC [nm] | Reference diameter by TEM [nm] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x50,0 | x50,3 | x50,0 | x50,3 | ||
| BaSO4 ultrafine grade (UF) (IRMM-387) | JRC | 24 | 49.3 | 33.4 | 69.3 |
| Levasil® 50/50% | H.C. Starck | - | - | - | - |
| Kaolin (IRMM-385) | JRC | 98 | 306 | 120.6 | 412.2 |
| Coated titania (IRMM-388) | JRC | 201 | 243 | 185.0 | 228.8 |
| BaSO4 fine grade (F) (IRMM-381) | JRC | 203 | 444 | 280.5 | 665.6 |
| Membrane Pore Size [µm] | Non-Treated Blank Samples | Sonicated Samples | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count Rate [kcps] | xcumulants [nm] | PI | Count Rate [kcps] | xcumulants [nm] | PI | x50,int [nm] | x50,0 [nm] | |
| no filtration | 32.3 ± 21.3 | 387 ± 351 | 0.77 ± 0.15 | 9497 ± 392 | 1352 ± 164 | 0.88 ± 0.07 | 446.6 ± 33.7 | 102.3 ± 12.3 |
| 1.0 | 30.4 ± 3.8 | 695 ± 308 | 0.77 ± 0.14 | 1362 ± 179 | 152.2 ± 1.6 | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 160.5 ± 1.8 | 66.9 ± 2.3 |
| 0.45 | 124 ± 68.3 | 342 ± 89 | 0.63 ± 0.16 | 820.8 ± 88 | 127.1 ± 4.3 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 136.7 ± 1.9 | 52.2 ± 2.6 |
| Denoted Pore Size [µm] | Bubble Point (Pressure) [µm, (mbar)] | Median Pore Size [µm] | Modal Pore Size = [µm] | Grade Efficiency Median µm] | Inflection Tangent at I(x) = 0 [µm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 1.03 (446) | 0.74 | 0.81 | 0.409 | 0.313 |
| 0.45 | 0.76 (606) | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.242 | 0.122 |
| 0.20 | 0.44 (1029) | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.147 | 0.049 |
| 0.10 | 0.30 (1535) | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.074 | 0.029 |
| Membrane Pore Size [µm] | 350 ppm | 1000 ppm | 3500 ppm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count Rate [kcps] | xcumulants [nm] | PI | Count Rate [kcps] | xcumulants [nm] | PI | Count Rate [kcps] | xcumulants [nm] | PI | |
| no filtration | 15806 ± 97 | 105 ± 2 | 0.092 ± 0.034 | 45399 ± 319 | 107 ± 1 | 0.056 ± 0.019 | 171361 ± 2056 | 106 ± 1 | 0.073 ± 0.015 |
| 1.0 | 16343 ± 133 | 104 ± 2 | 0.087 ± 0.029 | 43131 ± 728 | 105 ± 1 | 0.06 ± 0.017 | 154329 ± 2724 | 106 ± 0 | 0.077 ± 0.017 |
| 0.45 | 14898 ± 142 | 102 ± 1 | 0.106 ± 0.013 | 38985 ± 401 | 104 ± 1 | 0.073 ± 0.020 | 138787 ± 1047 | 105 ± 1 | 0.079 ± 0.020 |
| 0.20 | 13549 ± 59 | 101 ± 2 | 0.087 ± 0.047 | 32958 ± 223 | 102 ± 1 | 0.072 ± 0.012 | 127992 ± 573 | 105 ± 1 | 0.066 ± 0.016 |
| 0.10 | 11629 ± 69 | 98.4 ± 1 | 0.110 ± 0.027 | 27362 ± 279 | 101 ± 0 | 0.060 ± 0.013 | 116059 ± 750 | 104 ± 1 | 0.060 ± 0.018 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullmann, C.; Babick, F.; Stintz, M. Microfiltration of Submicron-Sized and Nano-Sized Suspensions for Particle Size Determination by Dynamic Light Scattering. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9060829
Ullmann C, Babick F, Stintz M. Microfiltration of Submicron-Sized and Nano-Sized Suspensions for Particle Size Determination by Dynamic Light Scattering. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(6):829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9060829
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllmann, Christian, Frank Babick, and Michael Stintz. 2019. "Microfiltration of Submicron-Sized and Nano-Sized Suspensions for Particle Size Determination by Dynamic Light Scattering" Nanomaterials 9, no. 6: 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9060829
APA StyleUllmann, C., Babick, F., & Stintz, M. (2019). Microfiltration of Submicron-Sized and Nano-Sized Suspensions for Particle Size Determination by Dynamic Light Scattering. Nanomaterials, 9(6), 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9060829