Multifunctional NaLnF4@MOF-Ln Nanocomposites with Dual-Mode Luminescence for Drug Delivery and Cell Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of NaLnF4 Nanocrystals
2.2. Synthesis of NaLnF4@MOF-Ln Nanocomposites
2.3. Preparation of PVP-Capped NaLnF4@MOF-Ln Nanocomposites
2.4. Preparation of [(NaLnF4@MOF-Ln)@PVP]-DOX Nanocomposites
2.5. Drug Storage/Delivery Studies
2.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assays of NaLnF4@MOF-Ln Nanocomposites
2.7. Materials Characterization
2.8. Anti-Stokes Luminescent Imaging of NaLnF4@MOF-Ln Nanocomposites
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of NaLnF4@MOF-Ln Nanocomposites
3.2. Luminescence Performance of NaYF4:Tm3+/Yb3+@MOF-Y:Eu3+ Nanocomposites
3.3. Drug Release from NaYF4:Tm3+/Yb3+@MOF-Y:Eu3+ Nanocomposites
3.4. Cell Imaging
3.5. In Vitro Cell Viability Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phua, S.Z.F.; Xue, C.; Lim, W.Q.; Yang, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wijaya, C.F.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, Y. Light-Responsive Prodrug-Based Supramolecular Nanosystems for Site-Specific Combination Therapy of Cancer. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 3349–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainshelboim, B.; Muller, J.; Lima, R.M.; Nead, K.T.; Chester, C.; Chan, K.; Kokkinos, P.; Myers, J. Cardiorespiratory fitness, physical activity and cancer mortality in men. Prev. Med. 2017, 100, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.; Gollavelli, G.; Ling, Y.-C. Exploring the photothermal hot spots of graphene in the first and second biological window to inactivate cancer cells and pathogens. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 63859–63866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, D.; Fu, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Shang, L.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Composite core-shell microparticles from microfluidics for synergistic drug delivery. Sci. China Mater. 2017, 60, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Rajabi, M.; Mousa, S.A. Multifunctional Nanomaterials and Their Applications in Drug Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, W.; Li, R.Q.; Qiu, W.X.; Zhuang, Z.N.; Cheng, S.X.; Zhang, X.Z. Peptide-Based Multifunctional Nanomaterials for Tumor Imaging and Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.; Bai, L.; Dai, Y.; Yu, Z.; Pan, Y. Functional magnetic hybrid nanomaterials for biomedical diagnosis and treatment. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 10, e1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Hableel, G.; Zhao, E.R.; Jokerst, J.V. Multifunctional nanomedicine with silica: Role of silica in nanoparticles for theranostic, imaging, and drug monitoring. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 521, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Guo, J.; Ju, Y.; Serda, R.E.; Croissant, J.G.; Shang, J.; Coker, E.; Agola, J.O.; Zhong, Q.-Z.; Ping, Y.; et al. Modular Metal–Organic Polyhedra Superassembly: From Molecular-Level Design to Targeted Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanbakht, S.; Namazi, H. Doxorubicin loaded carboxymethyl cellulose/graphene quantum dot nanocomposite hydrogel films as a potential anticancer drug delivery system. Mater. Sci. Eng. C: Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 87, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, A.D.; Ivanova, A.A.; Zyuzin, M.V.; Timin, A.S. Porous Inorganic Carriers Based on Silica, Calcium Carbonate and Calcium Phosphate for Controlled/Modulated Drug Delivery: Fresh Outlook and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.X.; Yang, Y.W. Metal-Organic Framework (MOF)-Based Drug/Cargo Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.K.; Mishra, N.; Yadav, K.S.; Yadav, N.P. Nanoemulsion as pharmaceutical carrier for dermal and transdermal drug delivery: Formulation development, stability issues, basic considerations and applications. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, P.P.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Cao, R. Outstanding drug loading capacity by water stable microporous MOF: A potential drug carrier. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3669–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huo, F. Metal-organic framework composites: From fundamentals to applications. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7482–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Yarza, T.; Mielcarek, A.; Couvreur, P.; Serre, C. Nanoparticles of Metal-Organic Frameworks: On the Road to In Vivo Efficacy in Biomedicine. Adv. Mater. Process. 2018, 30, e1707365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Y.; Pan, D.L.; Chen, H.; Bu, X.B.; Gao, Y.X.; Gao, H.; Tian, Y.; Li, G.S.; Wang, G.; Cao, S.L.; et al. A Methylthio-Functionalized-MOF Photocatalyst with High Performance for Visible-Light-Driven H2 Evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 9864–9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lykourinou, V.; Vetromile, C.; Hoang, T.; Ming, L.J.; Larsen, R.W.; Ma, S. How can proteins enter the interior of a MOF? Investigation of cytochrome c translocation into a MOF consisting of mesoporous cages with microporous windows. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13188–13191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Song, Y.; Wang, L. Nanoscale luminescent lanthanide-based metal–organic frameworks: Properties, synthesis, and applications. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, L.; Fan, W.; Wang, K.Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Dai, F.; Sun, D.; et al. Topology Exploration in Highly Connected Rare-Earth Metal-Organic Frameworks via Continuous Hindrance Control. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6967–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.X.; Cairns, A.J.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Wojtas, L.; Liu, Y.; Alkordi, M.H.; Eddaoudi, M. Tunable rare-earth fcu-MOFs: A platform for systematic enhancement of CO2 adsorption energetics and uptake. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7660–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.X.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Yang, T.; Chen, B. Microporous Lanthanide Metal-Organic Framework Constructed from Lanthanide Metalloligand for Selective Separation of C2H2/CO2 and C2H2/CH4 at Room Temperature. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 7145–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, C.; Tao, L.; Zhu, H.; Hu, G. Synthesis, characterization and heterogeneous base catalysis of amino functionalized lanthanide metal-organic frameworks. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1146, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F.; Chu, T.; Yang, Y. A novel lanthanide MOF thin film: The highly performance self-calibrating luminescent sensor for detecting formaldehyde as an illegal preservative in aquatic product. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.-W.; Yan, B. Hybrids based on lanthanide ions activated yttrium metal–organic frameworks: Functional assembly, polymer film preparation and luminescence tuning. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 5098–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.S.; Li, J.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, K.; Ding, Y.; Xia, X.H. Lanthanide-based metal-organic framework nanosheets with unique fluorescence quenching properties for two-color intracellular adenosine imaging in living cells. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.M.; Jin, A.; Lin, W. Surfactant-assisted synthesis of nanoscale gadolinium metal-organic frameworks for potential multimodal imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 7722–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tong, R.; Shi, Z.; Yang, B.; Liu, H.; Ding, S.; Wang, X.; Lei, Q.; Wu, J.; Fang, W. MOF Nanoparticles with Encapsulated Autophagy Inhibitor in Controlled Drug Delivery System for Antitumor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Younus, H.A.; Gaoke, Z.; Van Hecke, K.; Verpoort, F. Direct Synthesis of the 2D Copper(II) 5-Prop-2-ynoxyisophthalate MOF: Comment on “Surface Functionalization of Porous Coordination Nanocages Via Click Chemistry and Their Application in Drug Delivery”. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1801399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Peng, Q.; Li, Y. Dual-Mode Luminescent Colloidal Spheres from Monodisperse Rare-Earth Fluoride Nanocrystals. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1945–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Song, X.; Zhu, M.; Meng, X.; Zhao, S.; Su, S.; Yang, W.; Song, S.; Zhang, H. One-dimensional channel-structured Eu-MOF for sensing small organic molecules and Cu2+ ion. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yang, L.; Petros, J.A.; Marshall, F.F.; Simons, J.W.; Nie, S. In vivo molecular and cellular imaging with quantum dots. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Mi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Mao, C.; Xu, S. NIR-responsive silica-coated NaYbF4:Er/Tm/Ho upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles with tunable emission colors and their applications in immunolabeling and fluorescent imaging of cancer cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 19021–19027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Miao, H.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Tang, B. Fabrication of NaYF4:Yb,Er Nanoprobes for Cell Imaging Directly by Using the Method of Hydrion Rivalry Aided by Ultrasonic. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, G.-S.; Chow, G.-M. Water-Soluble NaYF4:Yb,Er(Tm)/NaYF4/Polymer Core/Shell/Shell Nanoparticles with Significant Enhancement of Upconversion Fluorescence. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S. Multicolor Core/Shell-Structured Upconversion Fluorescent Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4765–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Gu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yin, W.; Liu, X.; Yan, L.; Jin, S.; Ren, W.; Xing, G.; Li, S.; et al. Mn2+ dopant-controlled synthesis of NaYF4:Yb/Er upconversion nanoparticles for in vivo imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Yan, B. A lanthanide metal–organic framework (MOF-76) for adsorbing dyes and fluorescence detecting aromatic pollutants. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 11570–11576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Mi, C.C.; Wang, W.X.; Liu, C.H.; Wu, Y.F.; Xu, Z.R.; Mao, C.B.; Xu, S.K. Immunolabeling and NIR-excited fluorescent imaging of HeLa cells by using NaYF4:Yb,Er upconversion nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollnau, M.; Gamelin, D.R.; Lüthi, S.R. Power dependence of upconversion luminescence in lanthanide and transition-metal-ion systems. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 3337–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xu, W.; Song, H.; Zhang, S. Temperature-dependent upconversion luminescence and dynamics of NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+ nanocrystals: Influence of particle size and crystalline phase. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 6139–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyver, J.F.; Grimm, J.; Krämer, K.W.; Güdel, H.U. Highly efficient near-infrared to visible up-conversion process in. J. Lumin. 2005, 114, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qin, W.; Wang, L.; Wei, G.; Zhu, P.; Kim, R. Intense ultraviolet upconversion luminescence from hexagonal NaYF4:Yb3+/Tm3+ microcrystals. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 11907–11914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renero-Lecuna, C.; Martín-Rodríguez, R.; Valiente, R.; González, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Krämer, K.W.; Güdel, H.U. Origin of the High Upconversion Green Luminescence Efficiency in β-NaYF4:2%Er3+,20%Yb3+. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3442–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.A.; Gibbs, W.E.; Collins, S.F.; Blanc, W.; Dussardier, B.; Monnom, G.; Peterka, P.; Baxter, G.W. Visible and near infra-red up-conversion in Tm3+/Yb3+ co-doped silica fibers under 980 nm excitation. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 13781–13799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wei, R.; Yan, G.H.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Shi, L.; Capobianco, J.A.; Sun, L. Smart Self-Assembled Nanosystem Based on Water-Soluble Pillararene and Rare-Earth-Doped Upconversion Nanoparticles for pH-Responsive Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 4910–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzabasaki, M.; Froudakis, G.E. Review of computer simulations on anti-cancer drug delivery in MOFs. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1255–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francés-Soriano, L.; Zakharko, M.A.; González-Béjar, M.; Panchenko, P.A.; Herranz-Pérez, V.; Pritmov, D.A.; Grin, M.A.; Mironov, A.F.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; Fedorova, O.A.; et al. Nanohybrid for Photodynamic Therapy and Fluorescence Imaging Tracking without Therapy. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 3677–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ji, Y.; You, M.; Wang, S.; Dong, Y.; Jin, G.; Lin, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; et al. Labeling and long-term tracking of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro using NaYF4:Yb3+,Er3+ upconversion nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2016, 42, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




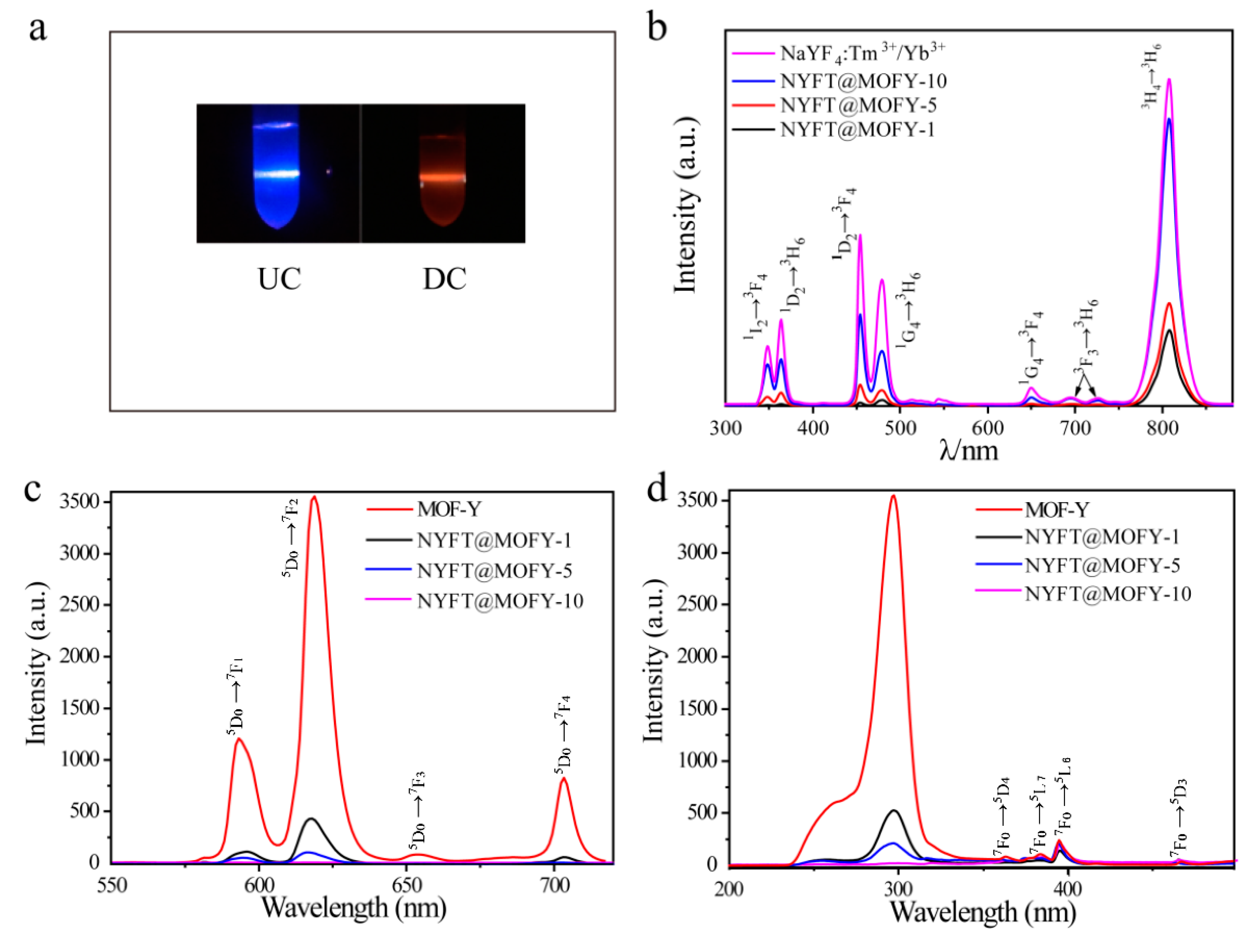

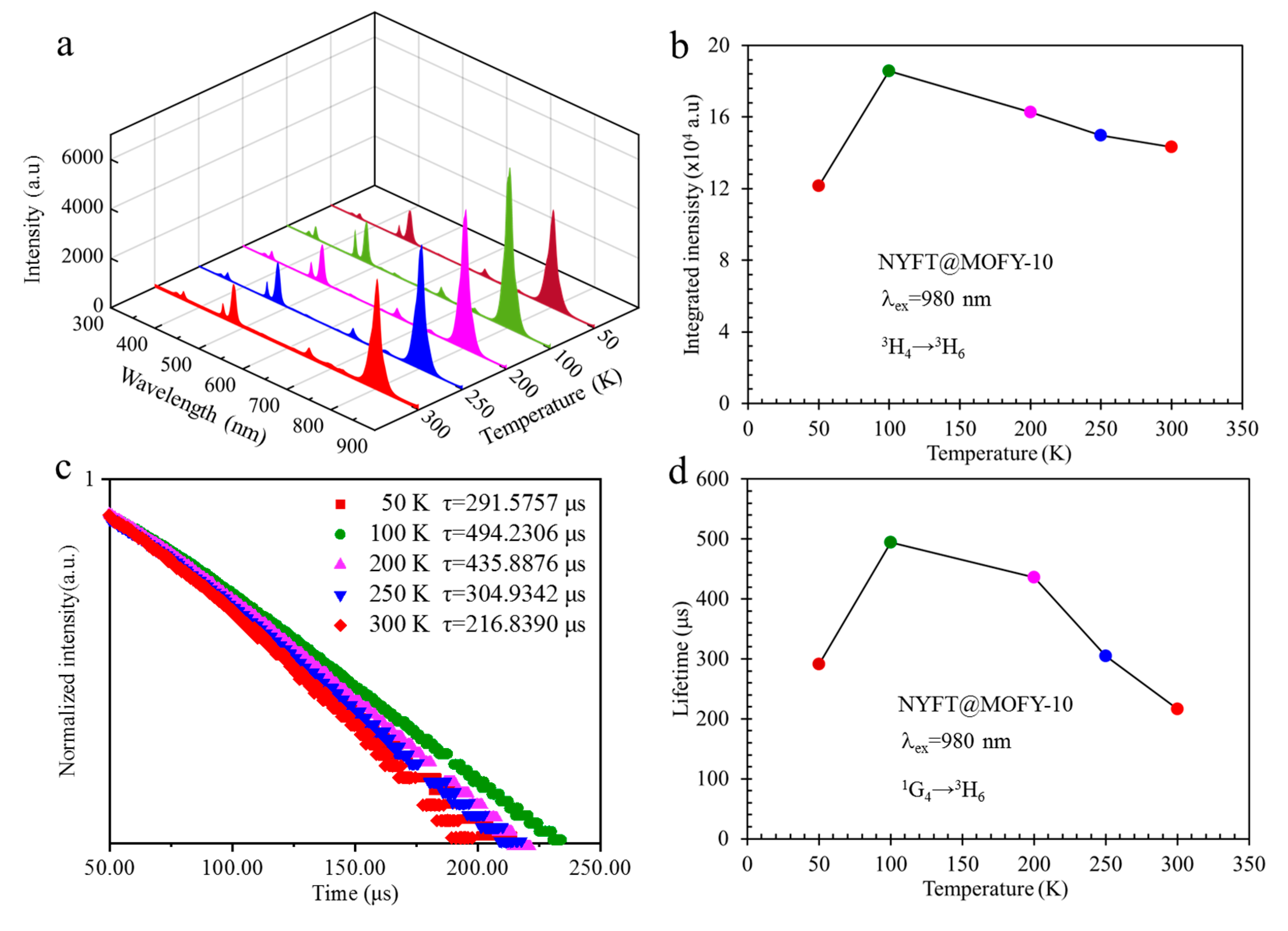
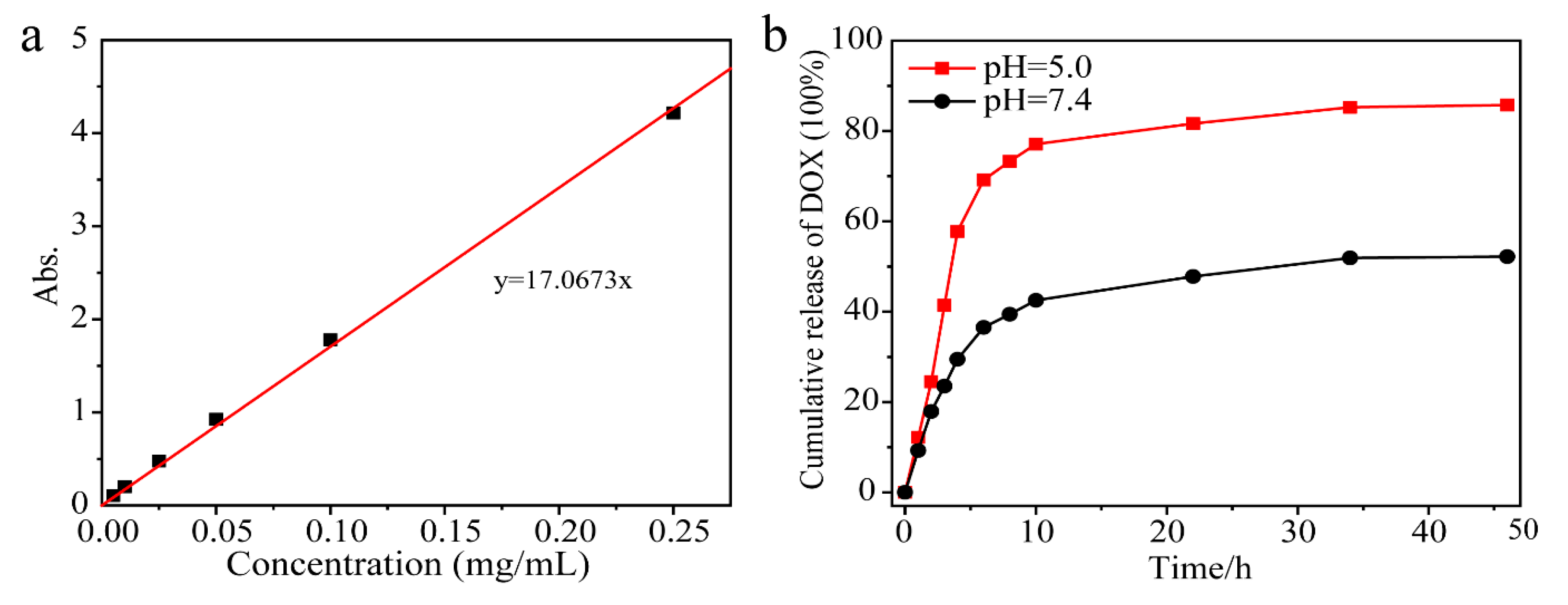
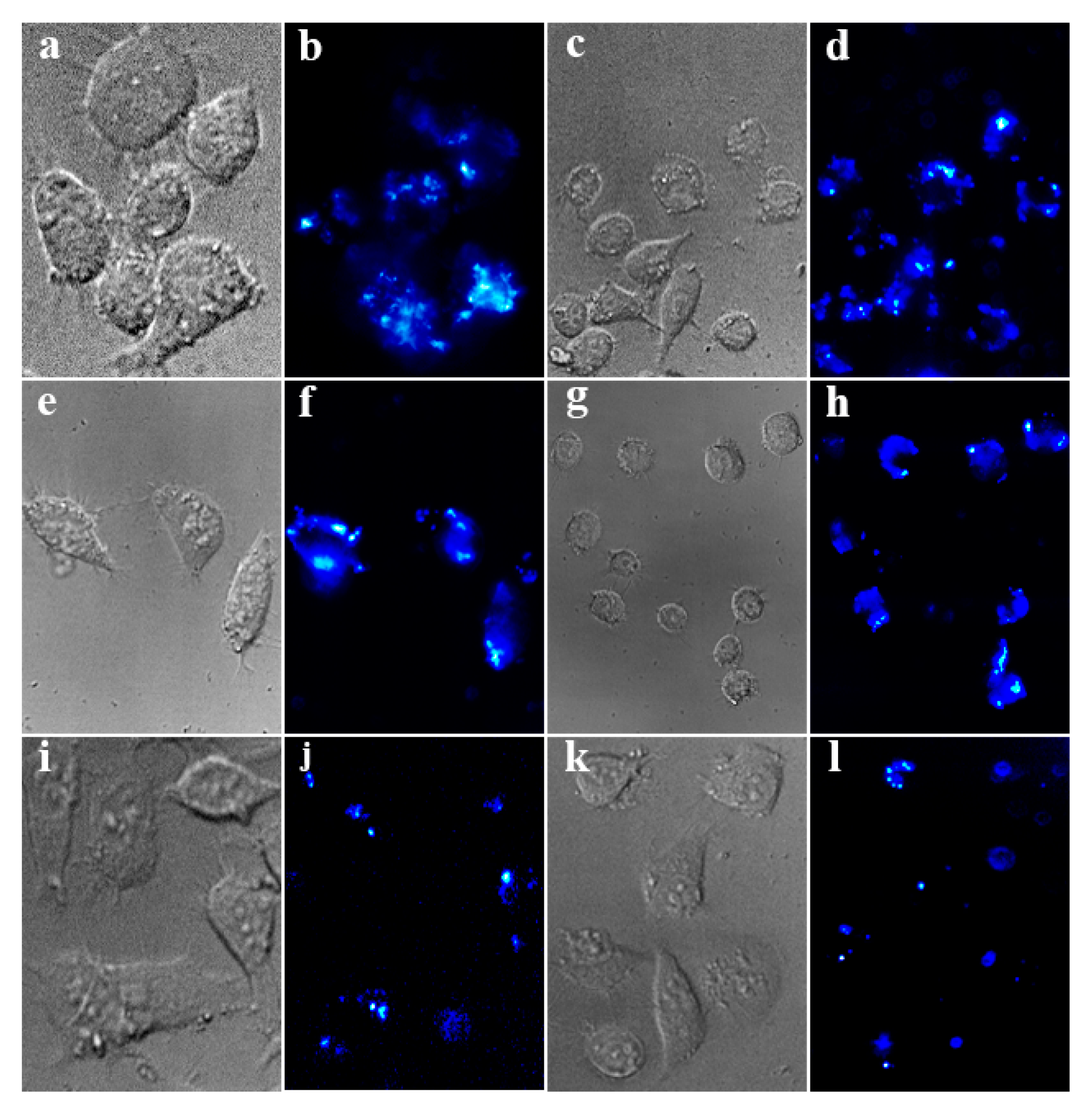
| Name | NaYF4: Tm3+/Yb3+ (g) | MOF-Y: Eu3+ (g) | Weight Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| NYFT@MOFY-1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1:1 |
| NYFT@MOFY-5 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 5:1 |
| NYFT@MOFY-10 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 10:1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Zhao, C.; Gao, G.; Xu, L.; Wang, G.; Zhu, P. Multifunctional NaLnF4@MOF-Ln Nanocomposites with Dual-Mode Luminescence for Drug Delivery and Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091274
Wang D, Zhao C, Gao G, Xu L, Wang G, Zhu P. Multifunctional NaLnF4@MOF-Ln Nanocomposites with Dual-Mode Luminescence for Drug Delivery and Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(9):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091274
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Dan, Chen Zhao, Guoyang Gao, Linna Xu, Guofeng Wang, and Peifen Zhu. 2019. "Multifunctional NaLnF4@MOF-Ln Nanocomposites with Dual-Mode Luminescence for Drug Delivery and Cell Imaging" Nanomaterials 9, no. 9: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091274
APA StyleWang, D., Zhao, C., Gao, G., Xu, L., Wang, G., & Zhu, P. (2019). Multifunctional NaLnF4@MOF-Ln Nanocomposites with Dual-Mode Luminescence for Drug Delivery and Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials, 9(9), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091274






