Wearing Quality of Ribbed Knits Made from Viscose and Lyocell Fibers for Underwear
Highlights
- Compared to viscose knits, lyocell rib knitwear has better structural uniformity, tensile properties, dimensional stability and air permeability but lower abrasion resistance and comparable moisture absorption and pilling tendency.
- The influence of unconventionally spun yarns is observed, and ribbed knits made from ring-spun yarns have better mechanical properties, while knits from air-jet-spun yarns have better comfort properties.
- Dry relaxation preserves bulkier structures with higher thickness and porosity but can result in slightly lower dimensional stability, while wet relaxation stabilizes the fabric and results in thinner, denser knitted fabrics with better structural uniformity, shrinkage resistance and, in some cases, improved abrasion resistance.
- The degree of relaxation of knitwear, the type of fiber and the type of yarn used in the design of novel knits affect the wearing quality of the underwear.
- Lyocell ribbed knits made from air-spun yarns, which have better contact comfort, esthetics and usage quality, can be used for the production of finer women’s underwear, while lyocell knitted fabrics made from ring-spun yarns are recommended for the production of underwear with a longer service life.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
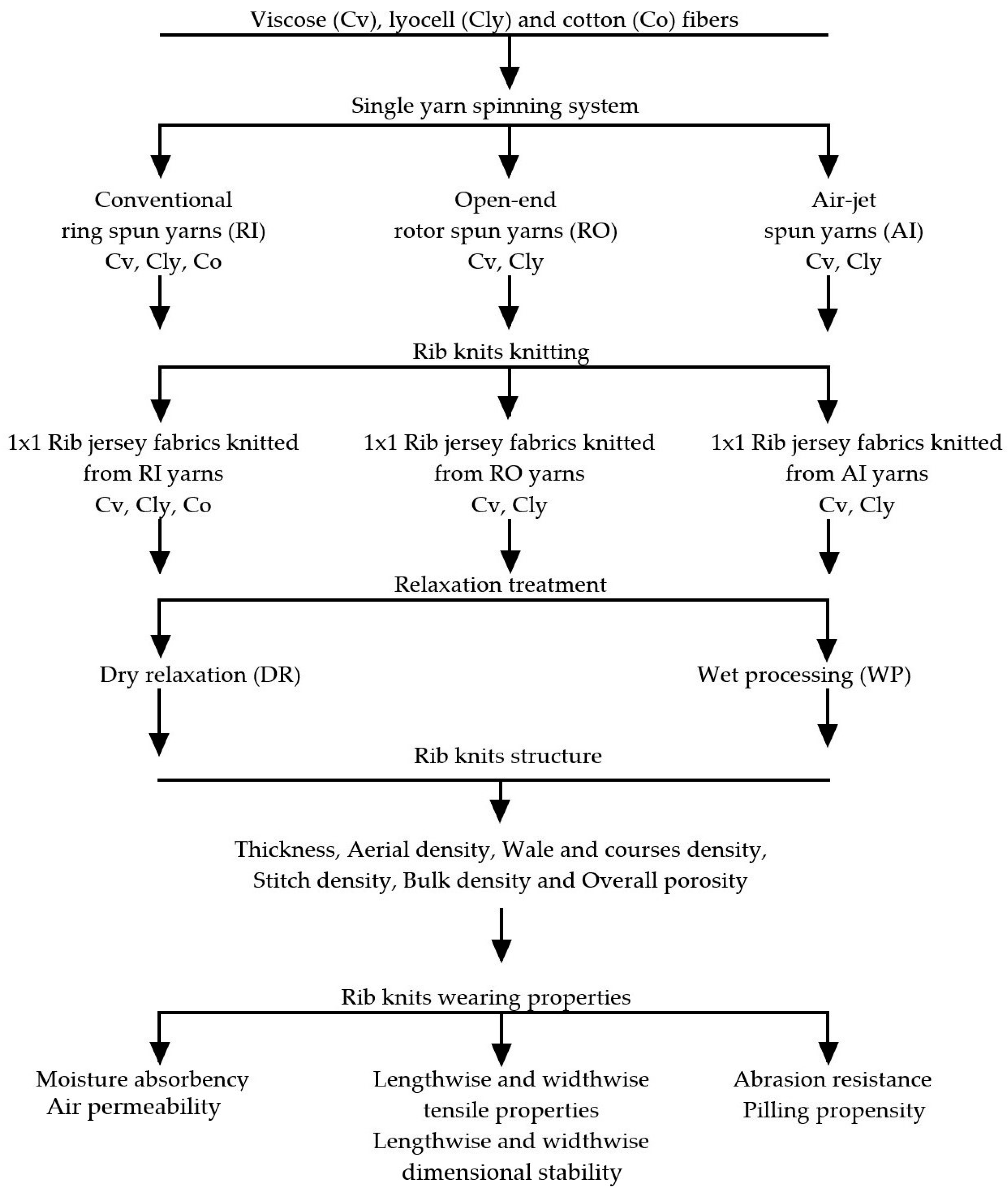
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rib Knits Fabrication
2.2. Rib Knits Wearing Quality Evaluation Methodology
2.2.1. Structure of 1 × 1 Rib Jersey Fabrics
- Rib knit thickness, expressed in millimeters, was tested at ten different points using the 2000-U thickness gauge from Hess MBV GmbH, Germany, in accordance with EN ISO 5084:2003 [47]. The pressure used for the measurement was 1 kPa;
- Areal density of rib knit, expressed in grams per square meter, was measured by cutting and weighing five round specimens of 100 square centimeters and multiplying the obtained value by 100, all in accordance with EN 12127:2003 [48];
- Rib knit wale, course, and stitch density, expressed as the number of wales per centimeter, courses per centimeter, and stitches per square centimeter, were determined in accordance with EN 14971:2008, for which five measurements were taken [49];
- Bulk density of rib knit fabrics, expressed in grams per cubic centimeter, was calculated by dividing the areal density and the thickness of the measured fabrics using the following Equation (1):Fabric bulk density (g/cm3) = Fabric areal density (g/m2)/1000 × Fabric thickness (mm)
- Total porosity of the rib knitted fabric, expressed as a percentage, defined as the ratio of the open space (both within and between the yarns) to the total volume of porous material [34,50], was calculated using the following Equation (2):Fabric overall porosity (%) = Fiber density (g/cm3) − Fabric bulk density (g/cm3)/Fiber density × 100
- where the fiber density values used are listed in Table 1.
2.2.2. Wearing Properties of 1 × 1 Rib Jersey Fabrics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure Evaluation of Rib Knits
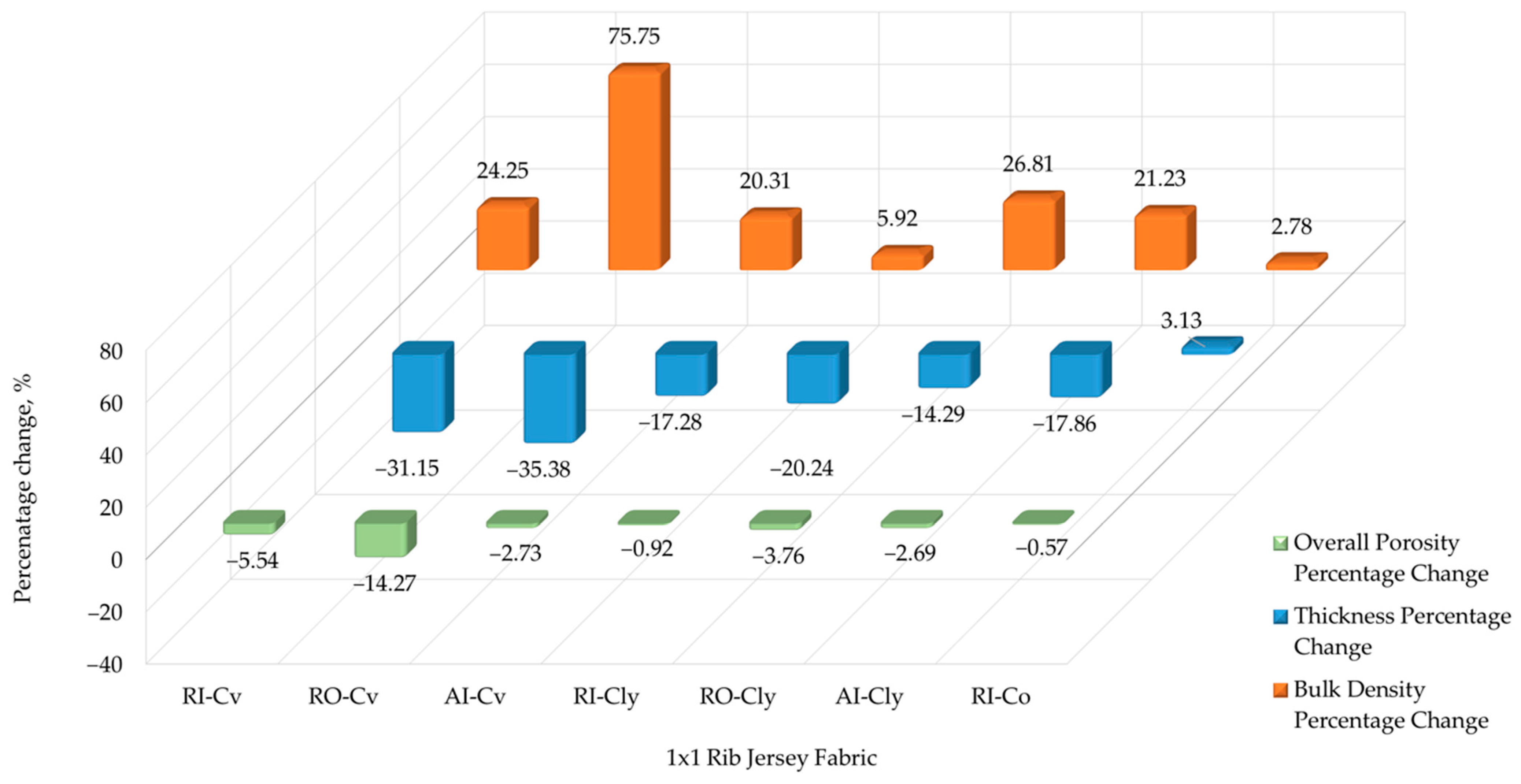
3.1.1. Thickness, Bulk Density, and Overall Porosity of Rib Knits
3.1.2. Areal Density, Wale and Course Density, and Stitch Density of Rib Knits
3.2. Wearing Properties Evaluation of Rib Knits
3.2.1. Air Permeability and Moisture Absorbency of Rib Knits
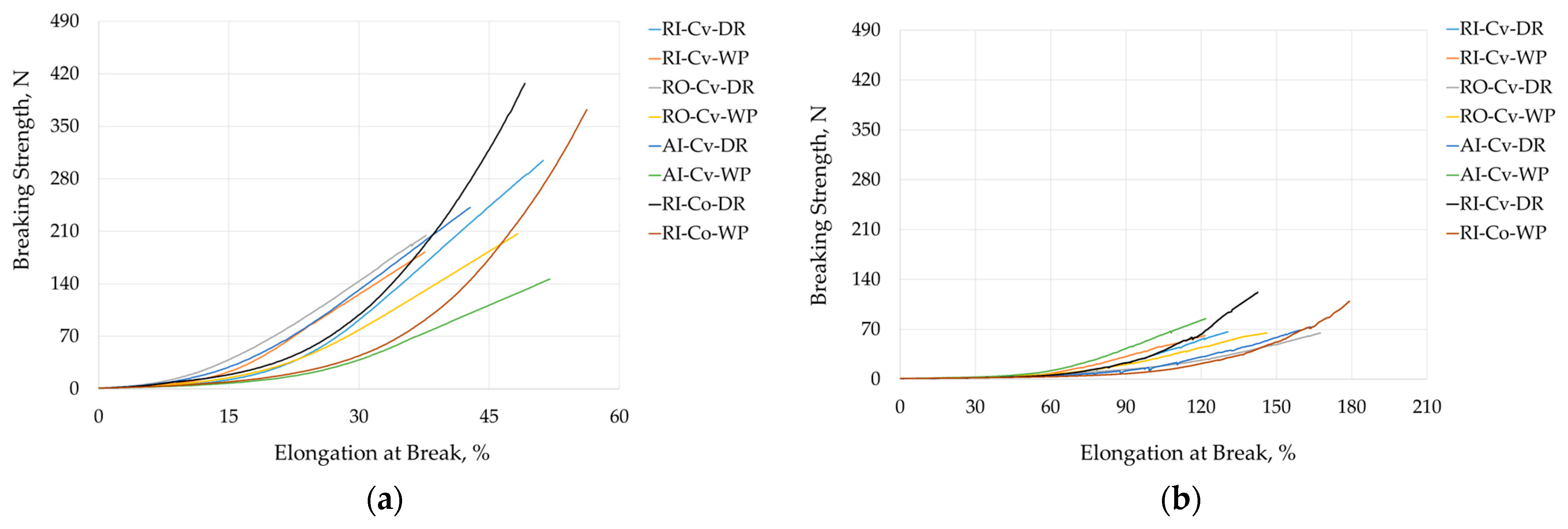
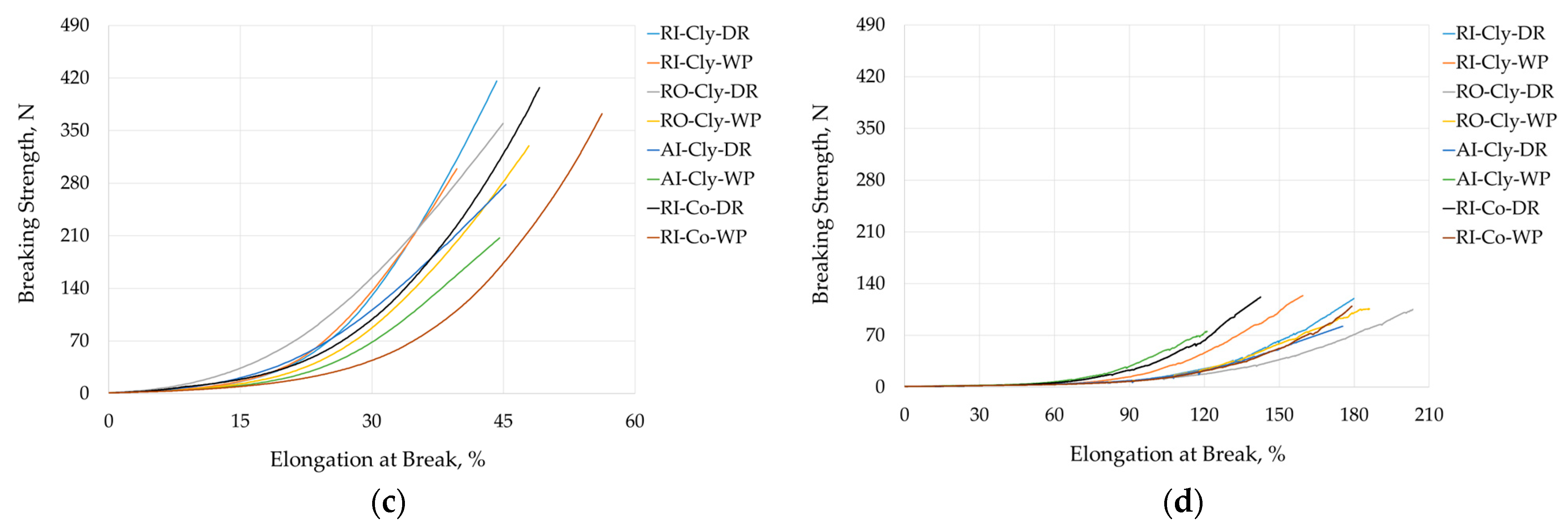
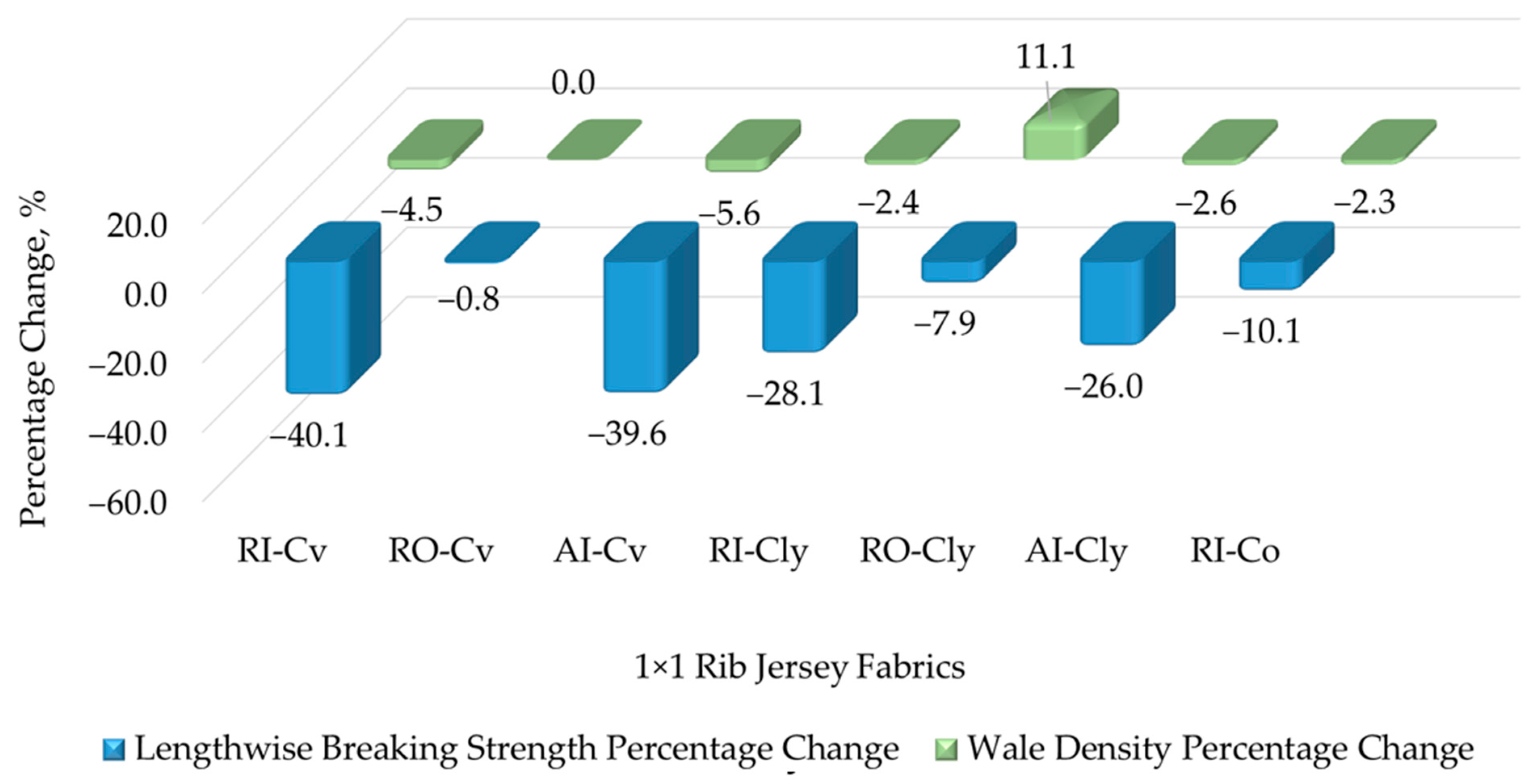
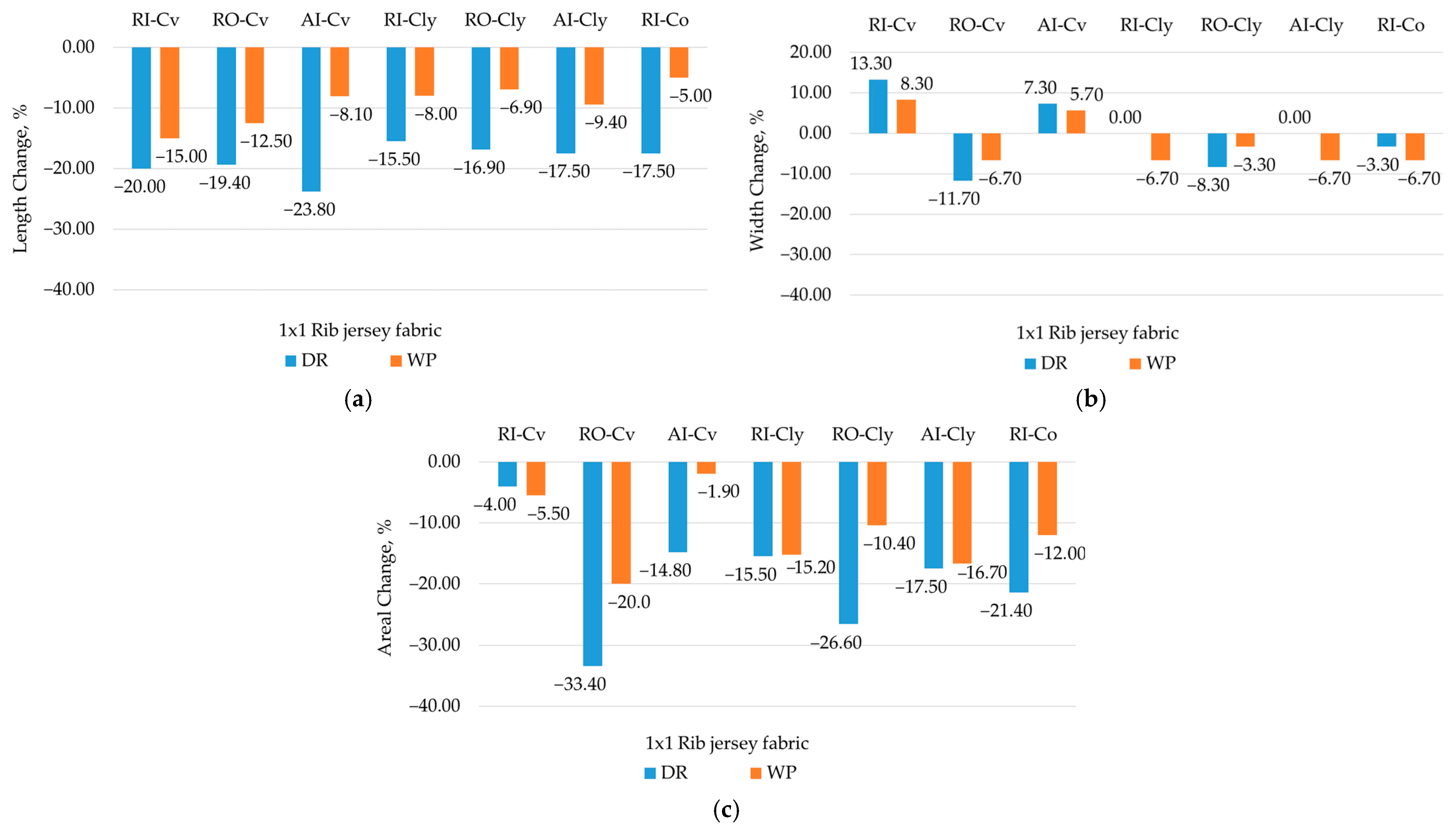
3.2.2. Tensile Properties and Dimensional Stability of Rib Knits
3.2.3. Abrasion and Pilling Properties of Rib Knits
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Björquist, S.; Aronsson, J.; Henriksson, G.; Persson, A. Textile qualities of regenerated cellulose fibers from cotton waste pulp. Text. Res. J. 2018, 88, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Worrell, E.; Patel, M.K. Environmental impact assessment of man-made cellulose fibres. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 55, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, I.S.F.; Prates, A.; Evtuguin, D.V. Production of rayon fibres from cellulosic pulps: State of the art and current developments. Carbohyd Polym. 2021, 273, 118466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Nagarkar, S.; Thakre, S.; Kumaraswamy, G. Structure–property relations in regenerated cellulose fibers: Comparison of fibers manufactured using viscose and lyocell processes. Cellulose 2019, 26, 3655–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciechanska, D.; Wesolowska, E.; Wawro, D. An introduction to cellulosic fibres. In Handbook of Textile Fibre Structure, 1st ed.; Eichhorn, S.J., Hearle, J.W.S., Jaffe, M., Kikutani, T., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, UK, 2009; Volume 66, pp. 3–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Lu, A.; Zhang, L. Recent advances in regenerated cellulose materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 53, 169–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Bai, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, W. A review on raw materials, commercial production and properties of lyocell fiber. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Rissanen, M.; You, X.; Moriam, K.; Hummel, M.; Sixta, H. New method for determining the degree of fibrillation of regenerated cellulose fibres. Cellulose 2020, 28, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Textile Exchange. Preferred Fiber & Materials Market Report 2022. Available online: https://textileexchange.org/knowledge-center/reports/materials-market-report-2022/ (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Kreze, T.; Malej, S. Structural characteristics of new and conventional regenerated cellulosic fibers. Text. Res. J. 2003, 73, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, W.; Wulfhorst, B.; Külter, H. Fiber tables according to P.-A. Koch. Regenerated cellulose fibers. Chem. Fibers Int. 1991, 40, 26–44. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, W.; Reintjes, M.; Wulfhorst, B. Fiber tables according to P.-A. Koch. Lyocell fibers (Alternative regenerated cellulose fibers). Chem. Fibers Int. 1997, 47, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Wulfhorst, B.; Külter, H. Fiber tables according to P.-A. Koch. Cotton. Chem. Fibers Int. 1989, 39, 12–34. [Google Scholar]
- Tomljenović, A.; Živičnjak, J.; Skenderi, Z. Quality Assessment of Socks Produced from Viscose and Lyocell Fibers. Materials 2024, 17, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatkić, E.; Geršak, J.; Ujević, D. Influence of Knitting Parameters on the Mechanical Properties of Plain Jersey Weft Knitted Fabrics. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2011, 19, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Kim, K.O.; Hashimoto, K.; Takatera, M. Effect of Washing and Drying Conditions on Dimensional Change in Various Articles of Knitted Clothing. J. Fiber Bioeng. Inform. 2018, 11, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, N.; Yilmaz, T. Thermal properties of 1 × 1, 2 × 2, 3 × 3 rib knit fabrics. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2004, 12, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Mikučionienė, D.; Laureckienė, G. The Influence of Drying Conditions on Dimensional Stability of Cotton Weft Knitted Fabrics. Mater. Sci.-Medzg. 2009, 15, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, S.C.; Brown, K.S.M.; Higgins, L.G.; Holmes, D.A.; Hall, M.E.; Conrad, D. Effect of Laundering on the Dimensional Stability and Distortion of Knitted Fabrics. Autex Res. J. 2002, 2, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onal, L.; Candan, C. Contribution of fabric characteristics and laundering to shrinkage of weft knitted fabrics. Tex. Res. J. 2003, 73, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikučionienė, D.; Arbataitis, E. Comparative Analysis of the Influence of Bamboo and Other Cellulose Fibres on Selected Structural Parameters and Physical Properties of Knitted Fabrics. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2013, 21, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Badr, A.; Hassanin, A.; Moursey, M. Influence of Tencel/cotton blends on knitted fabric performance. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckinney, M.; Broome, E.R. The effects of laundering on the performance of open-end and ring-spun yarns in jersey knit fabrics. Tex. Res. J. 1977, 47, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomljenović, A.; Živičnjak, J.; Mihaljević, I. Usage Durability and Comfort Properties of Socks Made from Differently Spun Modal and Micro Modal Yarns. Materials 2023, 16, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Değirmenci, Z.; Coruh, E. The Influences of Loop Length and Raw Material on Bursting Strength Air Permeability and Physical Characteristics of Single Jersey Knitted Fabrics. J. Eng. Fiber. Fabr. 2017, 12, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.N.; Kong, F.R.; Xu, R.C. Comparative Study on Mechanical Properties of Jutecell, Cotton and Bamboo Fiber Knitted Fabrics. Adv. Mat. Res. 2012, 627, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitotaw, D.B.; Adamu, B.F. Tensile Properties of Single Jersey and 1×1 Rib Knitted Fabrics Made from 100% Cotton and Cotton/Lycra Yarns. J. Eng. 2017, 2017, 4310782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikučionienė, D. The Dimensional Change of Used Pure and Compound Cotton Knitwear. Mater. Sci.-Medzg. 2004, 10, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Manonmani, G.; Vigneswaran, C.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Ramachandran, T. Effect of Ring and Compact Cotton Spun Yarn characteristics on Physical and Comfort Properties of Knitted Fabrics. Res. J. Text. Appar. 2013, 17, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öner, E.; Atasağun, H.G.; Okur, A.; Beden, A.R.; Durur, G. Evaluation of Moisture Management Properties on Knitted Fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2013, 104, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.S.; Ajmeri, J.R. Air Permeability of Knitted fabrics made from Regenerated Cellulosic fibres. Int. J. Eng. Res. Dev. 2014, 10, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Oglakcioglu, N.; Marmaralı, A. Thermal comfort properties of some knitted structures. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2007, 15, 94–96. [Google Scholar]
- Özdil, N.; Marmaralı, A.; Kretzschmar, S.D. Effect of yarn properties on thermal comfort of knitted fabrics. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2007, 46, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, S.B.; Popović, D.; Poparić, G.B. Thermal properties of textile fabrics made of natural and regenerated cellulose fibers. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Yadav, R. Thermal properties of knitted fabrics made from cotton and regenerated bamboo cellulosic fibres. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 2042–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, J.; Anbumani, N. Dimensional properties of single jersey knitted fabrics made from new and regenerated celllosic fibers. J. Text. Appar. Technol. Manag. 2012, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Rameshkumar, C.; Anandkumar, P.; Senthilnathan, P.; Jeevitha, R.; Anbumani, N. “Comparitive Studies on Ring Rotor and Vortex Yarn Knitted Fabrics. Autex Res. J. 2008, 8, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kireçci, A.; Kaynak, H.K.; Ince, M.E. Comparative Study of the Quality Parameters of Knitted Fabrics Produced from Sirospun, Single and Two-ply Yarns. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2011, 19, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, L.; Behera, B.K. Comparative Studies on Ring, Compact and Vortex Yarns and Fabrics. J. Text. Sci. Fash. Technol. 2020, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, S.; Eldeeb, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Mazari, A. Comparative Study on Viscose Yarn and Knitted Fabric Made From Open End and Rieter Airjet Spinning System. Tekst. Ve Konfeksiyon 2017, 27, 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ortlek, H.G.; Onal, L. Comparative study on the characteristics of knitted fabrics made of vortex-spun viscose yarns. Fibers Polym. 2008, 9, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.A.; Kim, S.J. Mechanical Properties of Micro Modal Air Vortex Yarns and the Tactile Wear Comfort of Knitted Fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdumlu, N.; Ozipek, B.; Oztuna, A.S.; Cetinkaya, S. Investigation of Vortex Spun Yarn Properties in Comparison with Conventional Ring and Open-end Rotor Spun Yarns. Text. Res. J. 2009, 79, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Jiang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Xiang, H.; Yan, J. Study of knitted fabrics with ultra-low modulus based on geometrical deformation mechanism. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopitar, D.; Pavlović, Ž.; Skenderi, Z.; Vrljičak, Z. Comparison of Double Jersey Knitted Fabrics Made of Regenerated Cellulose Conventional and Unconventional Yarns. Tekstilec 2022, 65, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 139:2005/A1:2011; Textiles—Standard Atmospheres for Conditioning and Testing. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- EN ISO 5084:2003; Textiles—Determination of Thickness of Textiles and Textile Products. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- EN 12127:2003; Textiles—Fabrics—Determination of Mass per Unit Area Using Small Samples. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- EN 14971:2008; Textiles—Knitted Fabrics—Determination of Number of Stitches per Unit Length and Unit Area. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Camilli Duru, S.; Candan, C. Effect of repeated laundering on wicking and drying properties of fabrics of seamless garments. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 9237:1995; Textiles—Determination of the Permeability of Fabrics to Air. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- ASTM D 2654-89a; Standard Test Methods for Moisture in Textiles. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- EN ISO 13934-1:2013; Textiles—Tensile Properties of Fabrics—Part 1: Determination of Maximum Force and Elongation at Maximum Force Using the Strip Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- EN ISO 6330:2012; Textiles—Domestic Washing and Drying Procedures for Textile Testing. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- EN ISO 3759:2011; Textiles—Preparation, Marking and Measuring of Fabric Specimens and Garments in Tests for Determination of Dimensional Change. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- EN ISO 5077:2008; Textiles—Determination of Dimensional Change in Washing and Drying. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- EN ISO 12947-2:2016; Textiles—Determination of the Abrasion Resistance of Fabrics by the Martindale Method—Part 2: Determination of Specimen Breakdown. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- EN ISO 12945-2:2020; Textiles—Determination of Fabric Propensity to Surface Pilling, Fuzzing or Matting—Part 2: Modified Martindale Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- EN ISO 12945-4:2020; Textiles—Determination of Fabric Propensity to Surface Pilling, Fuzzing or Matting—Part 4: Assessment of Pilling, Fuzzing or Matting by Visual Analysis. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Morton, W.E.; Hearle, J.W.S. Flex Fatigue and Other Forms of Failure. In Physical Properties of Textile Fibres, 3rd ed.; The Textile Institute: Manchester, UK, 1997; pp. 678–706. [Google Scholar]
- Özdil, N.; Özçelik Kayseri, G.; Süpüren Mengüç, G. Analysis of Abrasion Characteristic in Textiles. In Abrasion Resistance of Materials; Adamiak, M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 119–146. [Google Scholar]
- Karypidis, Μ.; Wilding, Μ.A.; Carr, C.Μ. The Effect of Crosslinking Agents and Reactive Dyes on the Fibrillation of Lyocell. AATCC Rev. 2001, 1, 40–44. [Google Scholar]



| Cellulosic Fiber | Viscose | Lyocell | Cotton |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose degree of polymerization | 290–320 | 550–650 | 2000–3000 |
| Crystallinity | 0.39 | 0.62 | 0.74 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.50 | 1.52 | 1.54 |
| Regain (%) | 12–14 | 11–13 | 7–9 |
| Water retention (%) | 85–100 | 60–75 | 38–55 |
| Elongation, dry (%) Elongation, wet (%) | 17–25 | 10–17 | 7–10 |
| 21–23 | 17–19 | 12–14 | |
| Tenacity, dry (cN/tex) Tenacity, wet (cN/tex) | 20–27 | 35–42 | 24–36 |
| 10–15 | 26–38 | 26–40 |
| Single-Spun Yarn | Count, tex | Twist, m−1 | Tenacity, cN/tex | Hairiness | Irregularity, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RI-Cv | 19.9 ± 0.13 | 751 ± 12.00 | 16.80 ± 1.26 | 6.47 ± 0.25 | 11.50 ± 0.18 |
| RO-Cv | 20.1 ± 0.15 | rotor speed 753 | 13.98 ± 0.26 | 4.36 ± 0.08 | 14.63 ± 0.10 |
| AI-Cv | 20.2 ± 0.14 | air pressure 0.6 MPa | 14.52 ± 1.42 | 3.75 ± 0.21 | 13.31 ± 0.37 |
| RI-Cly | 20.1 ± 0.28 | 810 ± 14.60 | 26.86 ± 2.02 | 6.50 ± 0.21 | 12.21 ± 0.10 |
| RO-Cly | 19.8 ± 0.32 | rotor speed 753 | 19.07 ± 2.11 | 4.73 ± 0.14 | 14.77 ± 0.31 |
| AI-Cly | 20.2 ± 0.30 | air pressure 0.6 MPa | 25.26 ± 1.88 | 3.53 ± 0.05 | 11.93 ± 0.20 |
| 1st Part | ||||||
| 1 × 1 Rib Jersey Fabric | Rib Knit Thickness, mm | Rib Knit Bulk Density, g/m3 | Rib Knit Overall Porosity, % | |||
| DR | WP | DR | WP | DR | WP | |
| RI-Cv | 0.61 ± 0.03 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 81.40 | 76.89 |
| RO-Cv | 0.65 ± 0.02 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.42 | 84.15 | 72.15 |
| AI-Cv | 0.81 ± 0.01 | 0.67 ± 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 88.16 | 85.76 |
| RI-Cly | 0.84 ± 0.01 | 0.67 ±0.01 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 86.58 | 85.78 |
| RO-Cly | 0.77 ± 0.02 | 0.66 ± 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 87.71 | 84.42 |
| AI-Cly | 0.84 ± 0.02 | 0.69 ± 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 88.77 | 86.38 |
| RI-Co | 0.64 ± 0.02 | 0.66 ± 0.03 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 83.04 | 82.57 |
| 2nd Part | ||||||
| 1 × 1 Rib Jersey Fabric | Rib Knit Areal Density, g/m2 | Rib Knit Wale/Course Density, cm−1 | Rib Knit Stitch Density, cm−2 | |||
| DR | WP | DR | WP | DR | WP | |
| RI-Cv | 170.2 ± 0.9 | 145.6 ± 1.5 | 22.0 ± 0.0/12.5 ± 0.5 | 21.0 ± 0.0/12.5 ± 0.5 | 275.0 | 262.5 |
| RO-Cv | 154.5 ± 1.1 | 175.5 ± 0.9 | 20.0 ± 0.0/12.5 ± 0.5 | 20.0 ± 0.0/13.5 ± 0.5 | 250.0 | 270.0 |
| AI-Cv | 143.8 ± 1.3 | 143.1 ± 1.1 | 18.0 ± 0.0/12.5 ± 0.5 | 17.0 ± 0.0/14.0 ± 0.0 | 225.0 | 238.0 |
| RI-Cly | 171.4 ± 1.5 | 144.8 ± 1.1 | 20.5 ± 0.5/12.0 ± 0.0 | 20.0 ± 0.0/13.0 ± 0.0 | 246.0 | 260.0 |
| RO-Cly | 143.8 ± 1.7 | 156.3 ± 1.4 | 18.0 ± 0.0/13.0 ± 0.0 | 20.0 ± 0.0/13.0 ± 0.0 | 234.0 | 260.0 |
| AI-Cly | 143.4 ± 1.1 | 142.8 ± 1.1 | 19.0 ± 0.0/13.0 ± 0.0 | 18.5 ± 0.5/13.0 ± 0.0 | 247.0 | 240.5 |
| RI-Co | 167.2 ± 1.1 | 177.2 ± 1.3 | 21.5 ± 0.5/12.5 ± 0.5 | 21.0 ± 0.0/13.0 ± 0.0 | 268.8 | 273.0 |
| 1 × 1 Rib Jersey Fabric | Rib Knit Air Permeability, dm3/min cm2 | Rib Knit Absorbency, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DR | WP | DR | WP | |
| RI-Cv | 52.47 ± 3.34 | 58.12 ± 2.83 | 10.12 ± 1.20 | 10.05 ± 1.28 |
| RO-Cv | 107.90 ± 3.29 | 74.19 ± 6.08 | 10.02 ± 1.18 | 10.31 ± 1.19 |
| AI-Cv | 97.31 ± 1.56 | 69.53 ± 3.22 | 9.90 ± 1.12 | 9.77 ± 1.31 |
| RI-Cly | 60.66 ± 2.78 | 77.62 ± 2.84 | 8.97 ± 1.17 | 8.83 ± 1.26 |
| RO-Cly | 115.83 ± 2.01 | 74.75 ± 3.85 | 8.71 ± 1.21 | 8.60 ± 1.42 |
| AI-Cly | 101.61 ± 3.72 | 73.39 ± 2.81 | 9.60 ± 1.34 | 9.42 ± 1.15 |
| RI-Co | 49.64 ± 1.84 | 28.45 ± 3.27 | 5.78 ± 1.21 | 6.07 ± 1.35 |
| 1 × 1 Rib Jersey Fabric | Rib Knit Breaking Strength, N | Rib Knit Elongation at Break, % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lengthwise | Widthwise | Lengthwise | Widthwise | |||||
| DR | WP | DR | WP | DR | WP | DR | WP | |
| RI-Cv | 304.8 ± 20.6 | 182.7 ± 18.3 | 65.1 ± 4.6 | 60.6 ± 2.1 | 50.8 ± 0.9 | 37.7 ± 2.2 | 131.3 ± 7.1 | 123.3 ± 5.8 |
| RO-Cv | 204.7 ± 12.6 | 203.0 ± 17.2 | 64.9 ± 4.1 | 63.7 ± 5.6 | 38.1 ± 1.3 | 47.7 ± 1.5 | 171.8 ± 5.7 | 146.1 ± 4.4 |
| AI-Cv | 242.9 ± 21.6 | 146.8 ± 34.8 | 74.9 ± 2.7 | 82.8 ± 4.7 | 44.1 ± 2.7 | 51.1 ± 3.1 | 165.7 ± 5.3 | 119.3 ± 3.0 |
| RI-Cly | 418.1 ± 21.2 | 300.6 ± 28.6 | 119.2 ± 3.3 | 120.6 ± 2.6 | 45.9 ± 1.1 | 41.2 ± 1.5 | 180.1 ± 2.0 | 164.7 ± 4.3 |
| RO-Cly | 359.4 ± 19.5 | 330.9 ± 31.7 | 105.1 ± 3.1 | 106.9 ± 2.6 | 47.0 ± 0.9 | 49.4 ± 1.2 | 205.7 ± 2.4 | 185.8 ± 2.9 |
| AI-Cly | 278.0 ± 26.4 | 205.6 ± 15.2 | 81.1 ± 2.3 | 75.1 ± 5.1 | 45.8 ± 2.2 | 44.1 ± 2.4 | 175.7 ± 3.9 | 120.0 ± 5.0 |
| RI-Co | 415.7 ± 42.3 | 373.8 ± 35.6 | 121.2 ± 11.6 | 103.6 ± 13.0 | 50.6 ± 2.2 | 56.5 ± 1.3 | 142.4 ± 3.1 | 183.3 ± 6.7 |
| 1 × 1 Rib Jersey Fabric | RI-Cv-DR | RO-Cv-DR | AI-Cv-DR |
| Dry Relaxed |  |  |  |
| RI-Co-DR | RI-Cly-DR | RO-Cly-DR | AI-Cly-DR |
 |  |  |  |
| 1 × 1 Rib Jersey Fabric | RI-Cv-WP | RO-Cv-WP | AI-Cv-WP |
| Wet Processed | 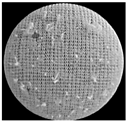 | 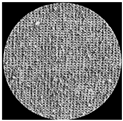 | 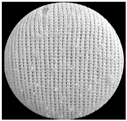 |
| RI-Co-WP | RI-Cly-WP | RO-Cly-WP | AI-Cly-WP |
 |  |  | 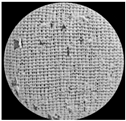 |
| 1 × 1 Rib Jersey Fabric | Dry Relaxed | Wet Processed | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Pilling Rubs | ||||||||||||
| 125 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 5000 | 7000 | 125 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 5000 | 7000 | |
| Pilling Ratings | ||||||||||||
| RI-Cv | 5.0 | 4.5 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| RO-Cv | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| AI-Cv | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 |
| RI-Cly | 4.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 2.5 |
| RO-Cly | 5.0 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 4.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| AI-Cly | 5.0 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| RI-Co | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 2.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomljenović, A.; Živičnjak, J.; Skenderi, Z. Wearing Quality of Ribbed Knits Made from Viscose and Lyocell Fibers for Underwear. Fibers 2024, 12, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12100083
Tomljenović A, Živičnjak J, Skenderi Z. Wearing Quality of Ribbed Knits Made from Viscose and Lyocell Fibers for Underwear. Fibers. 2024; 12(10):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12100083
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomljenović, Antoneta, Juro Živičnjak, and Zenun Skenderi. 2024. "Wearing Quality of Ribbed Knits Made from Viscose and Lyocell Fibers for Underwear" Fibers 12, no. 10: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12100083
APA StyleTomljenović, A., Živičnjak, J., & Skenderi, Z. (2024). Wearing Quality of Ribbed Knits Made from Viscose and Lyocell Fibers for Underwear. Fibers, 12(10), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12100083






