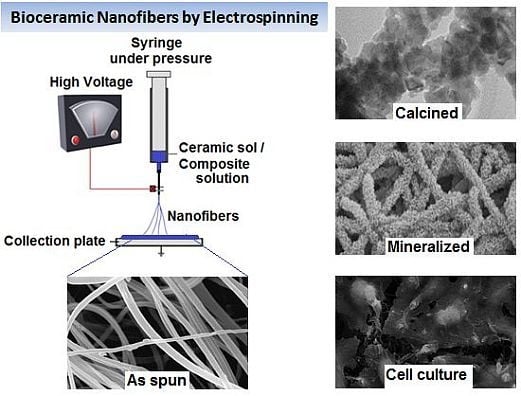
Bioceramic Nanofibres by Electrospinning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Electrospinning Bioceramic Nanofibres

2.1. Alumina Nanofibres

2.2. Zirconia Nanofibres

2.3. Titania Nanofibres

2.4. Pyrolytic Carbon Nanofibres

2.5. Calcium Phosphate Ceramic Nanofibres

2.6. Bioactive Glass Nanofibres

3. Conclusion and Future Perspective
Authors Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hench, L.L.; Wilson, J. An Introduction to BioceramicsAdvance Series in Bioceramics; 1st ed.; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Thamaraiselvi, T.V.; Rajeswari, S. Biological evaluation of bioceramic materials—A review. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2004, 18, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaseshan, R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Sundarrajan, S.; Jose, R. Nanostructured ceramics by electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Kim, M.J.; Balkus, K.J. TiO2 nanofibres and core-shell structures prepared using mesoporous molecular sieves as templates. Small 2006, 2, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lak, A.; Mazloumi, M.; Mohajerani, M.; Kajbafvala, A.; Zanganeh, S.; Arami, H.; Sadrnezhaad, S.K. Self-assembly of dandelion-like hydroxyapatite nanostructures via hydrothermal method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 3292–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Fabrication of titania nanofibers by electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fugihara, K.; Teo, W.E.; Lim, T.C.; Ma, Z. An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibres; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vendorf, J.H.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Electrospinning: Material Processing and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G. Electrically driven jets. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A 1969, 313, 453–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Koombhongse, S. Taylor cone and jetting from liquid droplets in electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 4836–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y.N. Electrospinning of nanofibers: Reinventing the wheel. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenot, A.; Chronakis, L.S. Polymer nanofibres assembled by electrospinning. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Hsiao, B.S. Functional electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1392–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, W.K.; Cho, D. Direct electrospinning of ultrafine titania fibres in the absence of polymer additives and formation of pure anatase titania fibres at low temperature. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Aviles, J.J.S. Synthesis of lead zirconate titanate nanofibres and the Fourier-transform infrared characterization of their metallo-organic decomposition process. Nanotechnology 2004, 15, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuh, J.; Perez, L.; Sigmund, W.M.; Nino, J.C. Sol-gel based synthesis of complex oxide nanofibers. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Boutin, P.; Blanquaert, D. A study of the mechanical properties of alumina-on-alumina total hip prosthesis. Rev. Chir. Orthop. Reparatrice Appar. Mot. 1981, 67, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Price, R.L.; Haberstroh, K.M.; Webster, T.J. Enhanced functions of osteoblasts on nanostructured surfaces of carbon and alumina. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2003, 41, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, A.M. Fabrication of transparent alumina (Al2O3) nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 435, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning of alumina nanofibers using different precursors. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2189–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuttle, R.W.; Chowdury, A.; Bender, E.T.; Ramsier, R.D.; Rapp, J.L.; Espe, M.P. Electrospun ceramic fibers: Composition, structure and the fate of precursors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 4925–4929. [Google Scholar]
- Lamastra, F.R.; Bianco, A.; Meriggi, A.; Montesperelli, G.; Nanni, F.; Gusmano, G. Nanohybrid PVA/ZrO2 and PVA/Al2O3 electrospun mats. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 145, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.C.; Yang, R.J.; Tsai, Y.Y.; Sigmund, W.; Yen, F.S. Growth mechanism of single-crystal α-Al2O3 nanofibers fabricated by electrospinning techniques. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, J.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M. Preparation of continuous alumina nanofibers via electrospinning of PAN/DMF solution. Mater. Lett. 2012, 74, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.L.; Gutwein, L.G.; Kaledin, L.; Tepper, F.; Webster, T.J. Osteoblast function on nanophase alumina materials: Influence of chemistry, phase, and topography. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2003, 67, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Carlo, F.D.; Quaranta, M.; Piattelli, A. Bone response to zirconia ceramic implants: An experimental study in rabbits. J. Oral Implant. 2003, 29, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Guan, H.; Liu, Y.; Gong, J.; Yu, N.; Yang, X. A novel method for making ZrO2 nanofibres via an electrospinning technique. J. Cryst. Growth 2004, 267, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmaraj, N.; Kim, C.; Kim, H. Synthesis and characterisation of zirconium oxide nanofibers by electrospinning. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 2006, 36, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, J.A. Zirconium oxide and zirconium nitride coated biocompatible leads. US Patent 5496359, 5 March 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Y.; Sun, Y.; Tan, Y.; Xu, F.M.; Shi, X.L.; Ren, N. Zirconium nitride (ZrN) fibers prepared by carbothermal reduction and nitridation of electrospun PVP/zirconium oxychloride composite fibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I. Yttrium-partially stabilized zirconium dioxide posts: An approach to restoring coronally compromised nonvital teeth. Int. J. Periodont. Restor. Dent. 1998, 18, 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, A.M. Fabrication of yttria-stabilized zirconia nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Tan, Y.; Xu, F.M.; Sun, Y.; Cao, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.F. Hollow fibers of yttria-stabilized zirconia (8YSZ) prepared by calcination of electrospun composite fibers. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2396–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotha, S.; Li, C.; Schmid, S.; Mason, J. Reinforcement of bone cement using zirconia fibers with and without acrylic coating. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2009, 88, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, P.; Liang, J.; Guo, S.M. Phase transformation and morphological evolution of electrospun zirconia nanofibers during thermal annealing. Ceram. Int. 2010, 36, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Gu, A.; Liang, G.; Yuan, L. A facile method to prepare zirconia electrospun fibers with different morphologies and their novel composites based on cyanate ester resin. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guo, G.; Fan, Y. Fabrication and characterization of dense zirconia and zirconia-silica ceramic nanofibers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 5672–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Matsuguchi, N.; Uenoyama, K.; Kanemaru, T.; Sugioka, Y. Evaluation of metal implants coated with several types of ceramics as biomaterials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 1989, 23, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, S.; Greer, A.L. Fabrication and biocompatibility of nano-TiO2/titanium alloys biomaterials. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 3144–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Tekmen, C.; Sigmund, W.M. Three-point bending of electrospun TiO2 nanofibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 398, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.I.; Yu, B.; Woo, K.M.; Lee, Y.K. Immobilization of TiO2 nanofibers on titanium plates for implant applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2456–2460. [Google Scholar]
- Yuh, J.; Nino, J.C.; Sigmund, W.M. Synthesis of barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanofibers via electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 3645–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B. Bioactive nano-titania ceramics with biomechanical compatibility prepared by doping with piezoelectric BaTiO3. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young-taek, S. Osseoinductive magnesium-titanate implant and method of manufacturing the same. US Patent 7452566, 15 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dharmaraj, N.; Park, H.C.; Lee, B.M.; Viswanathamurthi, P.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, D.R. Preparation and morphology of magnesium titanate nanofibres via electrospinning. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2004, 7, 431–433. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, Y.U.; Choi, S.S.; Park, T.Y.; Joo, Y.L.; Lee, S.G. Preparation of SiO2/TiO2 composite fibers by sol-gel reaction and electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, N.F.; Morks, M.F.; Sekino, T. Electrochemical synthesis of silica-doped high aspect-ratio titania nanotubes as nanobioceramics for implant applications. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 3255–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmaraj, N.; Park, H.C.; Kim, C.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, D.R. Nickel titanate nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 87, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansiddhi, A.; Sargeant, T.D.; Stupp, S.I.; Dunand, D.C. Porous NiTi for bone implants: A review. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadur, K.C.R.; Kim, C.K.; Khil, M.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, I.S. Synthesis of hydroxyapatite crystals using titanium oxide electrospun nanofibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amna, T.; Hassan, M.S.; Barakat, N.A.M.; Pandeya, D.R.; Hong, S.T.; Khil, M.S.; Kim, H.Y. Antibacterial activity and interaction mechanism of electrospun zinc-doped titania nanofibers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.S.; Amna, T.; Mishra, A.; Yun, S.I.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Khil, M.S. Fabrication, characterization and antibacterial effect of novel electrospun TiO2 nanorods on a panel of pathogenic bacteria. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yin, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Ao, Y.; Chen, H. Evaluation of the morphology and osteogenic potential of titania-based electrospun nanofibers. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, A.S.K.; Balu, R.; Kumar, T.S.S.J. Vero cell viability and human osteoblast cell response to electrospun phase controlled titania nanofibers. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2012, 2, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundarajan, V.M. Principles of Biomedical Engineering; Artech House: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago-Aviles, J.J.; Wang, Y. Magnetoconductance, carrier concentration and mobility measurement in electrospun carbon nanofibers. Carbon 2003, 41, 2665–2667. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, M.; Parsons, J.R.; Alexander, H.; Weiss, A.B. The electrical stimulation of bone using a filamentous carbon cathode. J. Biomed. Mat. Res. Part A 2004, 18, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zussman, E.; Chen, X.; Ding, W.; Calabri, L.; Dikin, D.A.; Quintana, J.P.; Ruoff, R.S. Mechanical and structural characterization of electrospun PAN-derived carbon nanofibers. Carbon 2005, 43, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, D.S.; Silva, A.N.R.; Morimoto, N.I.; Mendes, L.T.F.; Furlan, R.; Ramos, I. Characterization of an electrospinning process using different PAN/DMF concentrations. Polim. Cienc. Tecnol. 2007, 17, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Cho, Y.J.; Yun, W.Y.; Ngoc, B.T.N.; Yang, K.S.; Chang, D.R.; Lee, J.W.; Kojima, M.; Kim, Y.A.; Endo, M. Fabrications and structural characterization of ultra-fine carbon fibres by electrospinning of polymer blends. Solid State Commun. 2007, 142, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, F.; Gogotsi, Y.; Ali, A.; Naguib, N.; Ye, H.; Yang, G.L.; Li, C.; Willis, P. Electrospinning of continuous carbon nanotube-filled nanofibers yarns. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Duarte, M.A.; Wagner, N.; Rojas-Chapana, J.; Morsczeck, C.; Michael Thie, M.; Giersig, M. Fabrication and biocompatibility of carbon nanotube-based 3D networks as scaffolds for cell seeding and growth. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2233–2236. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, H.; Titchenal, N.; Naguib, N.; Ye, H.; Gogotsi, Y.; Ko, F. Electrospinning of carbon nanotube reinforced nanocomposite fibrils and yarns. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2003, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, S.K.; Cassady, A.I.; Lu, G.Q.; Martin, D.J. The biocompatibility of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2006, 44, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, L.Y.; Friend, J.R. Electrospinning carbon nanotube polymer composite nanofibers. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2006, 1, 177–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Mo, X.; Chen, D. Electrospun carbon nanotube composite nanofibers with uniaxially aligned arrays. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 115611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.Q.; He, J.H.; Yu, J.Y. Carbon nanotube-reinforced polyacrylonitrile nanofibres by vibration-electrospinning. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.A.; Zhang, L.; Webster, T.J. Carbon nanofibers and carbon nanotubes in regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1097–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavangarian, F.; Li, Y. Carbon nanostructures as nerve scaffolds for repairing large gaps in severed nerves. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 6075–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpato, F.Z.; Ramos, S.L.F.; Motta, A.; Migliaresi, C. Physical and in vitro biological evaluation of a PA 6/MWCNT electrospun composite for biomedical applications. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2011, 26, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Hasuda, H.; Kamitakahara, M.; Ohtsuki, C.; Tanihara, M.; Kang, I.K.; Kwon, O.H. A composite of hydroxyapatite with electrospun biodegradable nanofibres as a tissue engineering material. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 100, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, J.; Vadgama, P.; Kumar, T.S.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Biocomposite nanofibres and osteoblasts for bone tissue engineering. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 55101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.M.; Yuan, X.Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, W.C.; Wang, X.K. Formation of ultrafine apatite fibres by sol-gel/electrospinning. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2007, 23, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yao, C.; Sun, F.; Song, T.; Li, Y.; Pu, Y. Conjugate electrospinning of continuous nanofibre yarn of poly(L-lactide)/nanotricalcium phosphate nanocomposite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 3756–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisken, C.; Kalyon, D.M.; Wang, H. Functionally graded electrospun polycaprolactone and β-tricalcium phosphate nanocomposites for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4065–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, S.H.; Lee, E.J.; Wang, P.; Kim, H.E. Collagen/hydroxyapatite composite nanofibres by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3055–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Chen, Z.; Huang, C.; Lin, Y. Attachment, proliferation and differentiation of BMSCs on gas-jet/electrospun nHAP/PHB fibrous scaffolds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 324–327. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Venugopal, J.R.; El-Turki, A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Su, B.; Lim, C.T. Electrospun biomimetic nanocomposite nanofibers of hydroxyapatite/chitosan for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4314–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Murugan, R.; Chan, C.K.; Ramakrishna, S. Processing nanoengineered scaffolds through electrospinning and mineralization suitable for biomimetic bone tissue engineering. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 1, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Wolke, J.G.C.; Jansen, J.A. Biomimetic calcium phosphate coating on electrospun poly(ɛ-caprolactone) scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Tang, Q.L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wang, K.W.; Zhang, M.L.; Zhai, W.Y.; Chang, J. Hydroxyapatite nanorods/poly(vinyl pyrolidone) composite nanofibres, arrays and three-dimensional fabrics: Electrospun preparation and transformation to hydroxyapatite nanostructures. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3013–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.S.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, H.W. Surface-mineralized polymeric nanofiber for the population and osteogenic stimulation of rat bone-marrow stromal cells. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 873–877. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, M.V.; Thomas, V.; Johnson, K.T.; Dean, D.R.; Nyairo, E. Aligned PLGA/HA nanofibrous nanocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Liu, X.Y.; Hong, H. Cladding of titanium/hydroxyapatite composites onto Ti6Al4V for load-bearing implant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 2063–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Li, Y.; Kim, K.O.; Nakagawa, Y.; Kim, B.S.; Abe, K.; Chen, G.Q.; Kim, I.S. Fabrication of nano-hydroxyapatite on electrospun silk fibroin nanofibre and their effects in osteoblastic behavior. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2011, 97, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Ling, F.; Li, H.; Gao, Z.; Chen, X. Tuned morphological electrospun hydroxyapatite nanofibres via pH. J. Bionic Eng. 2012, 9, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. The story of bioglass. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Kim, H.E.; Knowles, J.C. Production and potential of bioactive glass nanofibres as a next-generation biomaterial. Adv. Funct. Mater 2006, 16, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Song, J.H.; Kim, H.E. Bioactive glass nanofibre-collagen nanocomposite as a novel bone regeneration matrix. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 79, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Lee, H.H.; Chun, G.S. Bioactivity and osteoblast responses of novel biomedical nanocomposites of bioactive glass nanofibre filled poly(lactic acid). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2008, 85, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Yu, H.S.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, H.W. Bioactivity improvement of poly(ε-caprolactone) membrane with the addition of nanofibrous bioactive glass. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Wei, G.; Huang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, C. Sol–gel derived mesoporous bioactive glass fibres as tissue-engineering scaffolds. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 45, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.P.; Fang, Q.F. Electrospun submicron bioactive glass fibres for bone tissue scaffold. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allo, B.A.; Rizkalla, A.S.; Mequanint, K. Synthesis and electrospinning of ε-polycaprolactone-bioactive glass hybrid biomaterials via a sol-gel process. Langmuir 2010, 26, 18340–18348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Blough, E.R.; Wang, C.H. Submicron bioactive glass tubes for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccaccini, A.R.; Erol, M.; Stark, W.J.; Mohn, D.; Hong, Z.; Mano, J.F. Polymer/Bioactive glass nanocomposites for biomedical applications: A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1764–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.N.; Day, D.E.; Bal, B.S.; Fu, Q.; Jung, S.B.; Bonewald, L.F.; Tomsia, A.P. Bioactive glass in tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2355–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Kang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, P.; Jia, Y.; Lin, J. Electrospinning preparation and drug delivery properties of Eu3+/Tb3+ doped mesoporous bioactive glass nanofibres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 387, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, X. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticle-strengthened bioactive glass nanofibres. Micro Nano Lett. 2013, 8, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalumon, K.T.; Sowmya, S.; Sathish, D.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Effect of incorporation of nanoscale bioactive glass and hydroxyapatite in PCL/chitosan nanofibres for bone and periodontal tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 430–440. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Sui, G.; Shi, Y.Z.; Duan, S.; Bao, J.Q.; Cai, Q.; Yang, X.P. Osteocompatibility characterization of polyacrylonitrile carbon nanofibres containing bioactive glass nanoparticles. Carbon 2013, 56, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Deng, X.; Cai, Q.; Jia, X.; Yang, X.; Wei, Y.; Li, G. Improved bioactivity of PAN-based carbon nanofibres decorated with bioglass nanoparticles. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegani, F.J.; Langroudi, L.; Ardeshirylajimi, A.; Dinarvand, P.; Dodel, M.; Doostmohammadi, A.; Rahimian, A.; Zohrabi, P.; Seyedjafari, E.; Soleimani, M. Coating of electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibres with willemite bioceramic: Improvement of bone reconstruction in rat model. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, T.; Yang, H.; Ko, F.; Troczynski, T. Bio-inspired dicalcium phosphate anhydrate/poly(lactic acid) nanocomposite fibrous scaffolds for hard tissue regeneration: In situ synthesis and electrospinning. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 102, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Suna, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Cui, W.; Li, B. Electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds of poly (L-lactic acid)-dicalcium silicate composite via ultrasonic-aging technique for bone regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 35, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjubala, I.; Sivakumar, M.; Kumar, T.S.S.; Rao, K.P. Synthesis and characterization of functional gradient materials using indian corals. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2000, 11, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krishna, D.S.R.; Siddharthan, A.; Seshadri, S.K.; Kumar, T.S.S. Nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite from eggshell waste by microwave processing and its sintering studies. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Balu, R.; Singaravelu, S.; Nagiah, N. Bioceramic Nanofibres by Electrospinning. Fibers 2014, 2, 221-239. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2030221
Balu R, Singaravelu S, Nagiah N. Bioceramic Nanofibres by Electrospinning. Fibers. 2014; 2(3):221-239. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2030221
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalu, Rajkamal, Sivakumar Singaravelu, and Naveen Nagiah. 2014. "Bioceramic Nanofibres by Electrospinning" Fibers 2, no. 3: 221-239. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2030221
APA StyleBalu, R., Singaravelu, S., & Nagiah, N. (2014). Bioceramic Nanofibres by Electrospinning. Fibers, 2(3), 221-239. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib2030221