Interface Characterization of Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: A Molecular Dynamics Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
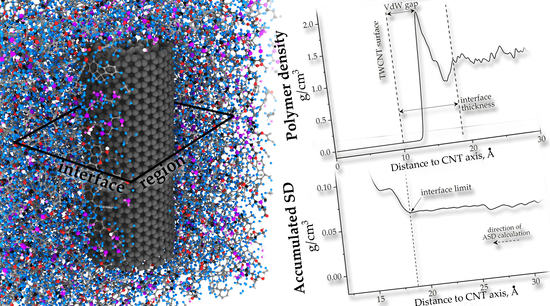
3.1. Interface Structure
3.2. Effect of Epoxy Resin and CNT Characteristics on Interface Structure
3.2.1. Effect of Cross-Linking Degree and Type of Epoxy Resin Hardener
3.2.2. Effect of CNT Diameter and Length
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adnan, A.; Sun, C.T.; Mahfuz, H. A molecular dynamics simulation study to investigate the effect of filler size on elastic properties of polymer nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Nelson, J.K.; MacCrone, R.K.; Schadler, L.S.; Reed, C.W.; Keefe, R. Polymer nanocomposite dielectrics-the role of the interface. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2005, 12, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Reed, C.W.; MacCrone, R.K.; Schadler, L.S.; Nelson, J.K.; Keefe, R.; Zenger, W. Evidence for the role of the interface in polyolefin nanocomposites. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Symposium on Electrical Insulating Materials, 2005 (ISEIM 2005), Kitakyushu, Japan, 5–9 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ndoro, T.V.M.; Voyiatzis, E.; Ghanbari, A.; Theodorou, D.N.; Böhm, M.C.; Müller-Plathe, F. Interface of Grafted and Ungrafted Silica Nanoparticles with a Polystyrene Matrix: Atomistic Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 2316–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, A.; Rahimi, M.; Dehghany, J. Influence of Surface Grafted Polymers on the Polymer Dynamics in a Silica–Polystyrene Nanocomposite: A Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Investigation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 25069–25076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, A.; Ndoro, T.V.M.; Leroy, F.; Rahimi, M.; Böhm, M.C.; Müller-Plathe, F. Interphase Structure in Silica–Polystyrene Nanocomposites: A Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Study. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, G.; Dhand, V.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, W.R. A review on carbon nanotubes and graphene as fillers in reinforced polymer nanocomposites. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvo, M.R.; Clary, G.J.; Ii, R.M.T.; Chi, V.; Brooks, F.P., Jr.; Washburn, S.; Superfine, R. Bending and buckling of carbon nanotubes under large strain. Nature 1997, 389, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoller, M.D.; Park, S.; Zhu, Y.; An, J.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-Based Ultracapacitors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3498–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbesen, T.W.; Lezec, H.J.; Hiura, H.; Bennett, J.W.; Ghaemi, H.F.; Thio, T. Electrical conductivity of individual carbon nanotubes. Nature 1996, 382, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balandin, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Miao, F.; Lau, C.N. Superior Thermal Conductivity of Single-Layer Graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the Elastic Properties and Intrinsic Strength of Monolayer Graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siochi, E.J.; Harrison, J.S. Structural nanocomposites for aerospace applications. Mrs Bull. 2015, 40, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AERO—Boeing 787 from the Ground up. Available online: http://www.boeing.com/commercial/aeromagazine/articles/qtr_4_06/article_04_2.html (accessed on 12 March 2018).
- Lee, J.H.; Marroquin, J.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.J.; Hui, D. Cryomilling application of graphene to improve material properties of graphene/chitosan nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 45, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, C.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Nanofibrous Materials and Their Applications. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2006, 36, 333–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jia, C.; He, J.; Zhao, F.; Fan, D.; Xing, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, Y. Interfacial characterization, control and modification of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 121, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshelby, J. The Determination of the Elastic Field of an Ellipsoidal Inclusion, and Related Problems. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1957, 241, 376–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Tanaka, K. Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusions. Acta Metall. 1973, 21, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpin, J.C.; Kardos, J.L. The Halpin-Tsai equations: a review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1976, 16, 344–352. [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste, Y. A new approach to the application of Mori-Tanaka’s theory in composite materials. Mech. Mater. 1987, 6, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.L.; Wang, J.; Huang, Z.P.; Karihaloo, B.L. Eshelby formalism for nano-inhomogeneities. Proc. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2005, 461, 3335–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arash, B.; Wang, Q.; Varadan, V.K. Mechanical properties of carbon nanotube/polymer composites. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odegard, G.M.; Clancy, T.C.; Gates, T.S. Modeling of the mechanical properties of nanoparticle/polymer composites. Polymer 2005, 46, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herasati, S.; Zhang, L.C.; Ruan, H.H. A new method for characterizing the interphase regions of carbon nanotube composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, S.F.; Sarker, M.F.; Adnan, A. Role of nanoparticle dispersion and filler-matrix interface on the matrix dominated failure of rigid C60-PE nanocomposites: A molecular dynamics simulation study. Polymer 2013, 54, 2565–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamm, M. Polymer surface and interface characterization techniques. In Polymer Surfaces and Interfaces; Springer: Bazel, Swuitzerland, 2008; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.H.; Yu, A.B.; Lu, G.Q. Multiscale modeling and simulation of polymer nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 191–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Minaie, B.; Wang, B.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, C. Computational and experimental study of interfacial bonding of single-walled nanotube reinforced composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2004, 31, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Wang, K.W.; Bakis, C.E. Effect of functionalization of single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) on the damping characteristics of SWNT-based epoxy composites via multiscale analysis. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; Borodin, O.; Smith, G.D.; Kober, E.M. A molecular dynamics simulation and quantum chemistry study of poly(dimethylsiloxane)–silica nanoparticle interactions. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2007, 45, 1599–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, H.; Rahimi, M.; Müller-Plathe, F. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of a Silica Nanoparticle in Oligomeric Poly(methyl methacrylate): A Model System for Studying the Interphase Thickness in a Polymer–Nanocomposite via Different Properties. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 8680–8692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsafack, T.; Alred, J.M.; Wise, K.E.; Jensen, B.; Siochi, E.; Yakobson, B.I. Exploring the interface between single-walled carbon nanotubes and epoxy resin. Carbon 2016, 105, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H. COMPASS: An ab initio force-field optimized for condensed-phase applications—Overview with details on alkane and benzene compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 7338–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tersoff, J. Modeling solid-state chemistry: Interatomic potentials for multicomponent systems. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 1989, 39, 5566–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarovsky, I.; Evans, E. Computer simulation of structure and properties of crosslinked polymers: application to epoxy resins. Polymer 2002, 43, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-Range Molecular Dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ci, L.; Bai, J. The reinforcement role of carbon nanotubes in epoxy composites with different matrix stiffness. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goclon, J.; Panczyk, T.; Winkler, K. Investigation of the interfacial properties of polyurethane/carbon nanotube hybrid composites: A molecular dynamics study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 433, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaminpayma, E.; Mirabbaszadeh, K. Interaction between single-walled carbon nanotubes and polymers: A molecular dynamics simulation study with reactive force field. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 58, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| ID of Model 1 | Resin 2 | Filler | Chirality of Filler | Filler Diameter, Å | Filler Length, Å | Weight Fraction of Filler, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a/b | DGEBA/DETA | TWCNT | (5, 5) 3 | 20.3 | 50 | 9.02 |
| 2a/b | DGEBA/DETA | TWCNT | (5, 5) 3 | 20.3 | 240 | 20.57 |
| 3a/b | DGEBA/DETA | TWCNT | (65, 65) 3 | 101.7 | 80 | 44.85 |
| 4a/b | DGEBA/DETA | CF | Armchair | n.a. | 78 × 78 | 23.14 |
| 5a/b | DGEBA/MeTHPA | CF | Armchair | n.a. | 78 × 78 | 22.50 |
| Non-Cross-Linked Systems | Interface Thickness, Å | VdW Gap Thickness, Å | Peak Density, g/cm3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID of Model | Epoxy Resin | Reinforcement | ||||||
| Type | Chirality | Length, Å | Diameter, Å | |||||
| 1a | DGEBA-DETA | TWCNT | (5, 5) | 50 | 20.3 | 10.00 | 3.50 | 2.305 |
| 2a | DGEBA-DETA | TWCNT | (5, 5) | 240 | 20.3 | 9.75 | 3.75 | 2.101 |
| 3a | DGEBA-DETA | TWCNT | (65, 65) | 80 | 101.7 | 9.00 | 3.25 | 1.878 |
| 4a | DGEBA-DETA | CF | armchair | 78 × 78 | n.a. | 10.00 | 3.75 | 2.127 |
| 5a | DGEBA-MeTHPA | CF | armchair | 78 × 78 | n.a. | 10.50 | 4.00 | 1.881 |
| Cross-Linked Systems | Interface Thickness, Å | VdW Gap Thickness, Å | Peak Density, g/cm3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID of Model | Epoxy Resin | Reinforcement | ||||||
| Type | Chirality | Length, Å | Diameter, Å | |||||
| 1b | DGEBA-DETA | TWCNT | (5, 5) | 50 | 20.3 | 7.87 1 | 3.75 | 2.008 2 |
| 2b | DGEBA-DETA | TWCNT | (5, 5) | 240 | 20.3 | 7.50 | 3.50 | 2.248 |
| 3b | DGEBA-DETA | TWCNT | (65, 65) | 80 | 101.7 | 10.00 | 3.50 | 2.172 |
| 4b | DGEBA-DETA | CF | armchair | 78 × 78 | n.a. | 10.50 | 3.75 | 1.921 |
| 5b | DGEBA-MeTHPA | CF | armchair | 78 × 78 | n.a. | 9.75 | 3.75 | 1.853 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sáenz Ezquerro, C.; Laspalas, M.; Chiminelli, A.; Serrano, F.; Valero, C. Interface Characterization of Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: A Molecular Dynamics Approach. Fibers 2018, 6, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6030054
Sáenz Ezquerro C, Laspalas M, Chiminelli A, Serrano F, Valero C. Interface Characterization of Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: A Molecular Dynamics Approach. Fibers. 2018; 6(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleSáenz Ezquerro, Carlos, Manuel Laspalas, Agustín Chiminelli, Francisco Serrano, and Clara Valero. 2018. "Interface Characterization of Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: A Molecular Dynamics Approach" Fibers 6, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6030054
APA StyleSáenz Ezquerro, C., Laspalas, M., Chiminelli, A., Serrano, F., & Valero, C. (2018). Interface Characterization of Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: A Molecular Dynamics Approach. Fibers, 6(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6030054