Combined Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes (CNT) Fibers with H2SO4/HNO3 and Ca(OH)2 for Addition in Cementitious Matrix
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. CNT Treatment
2.3. Testing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
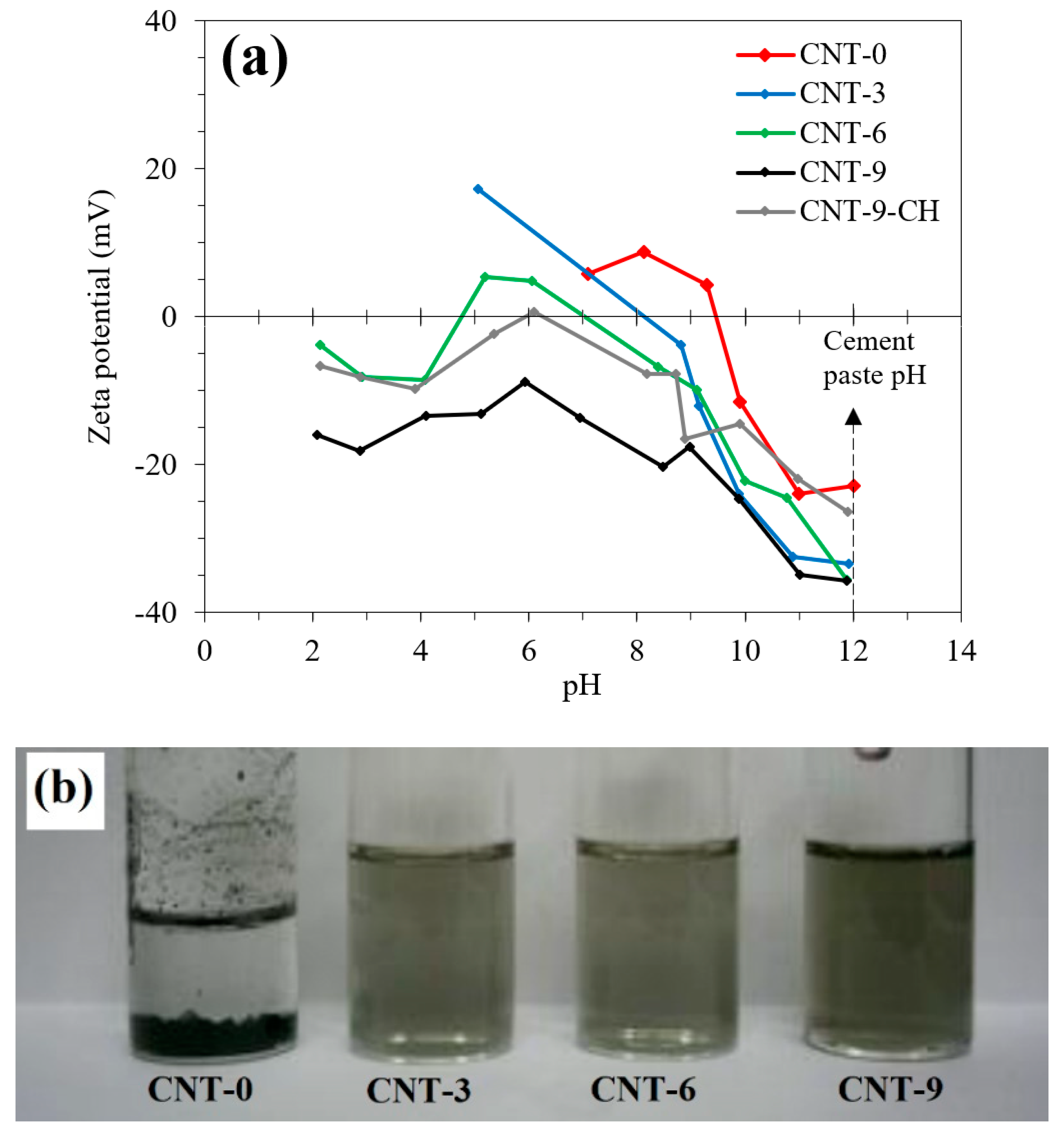
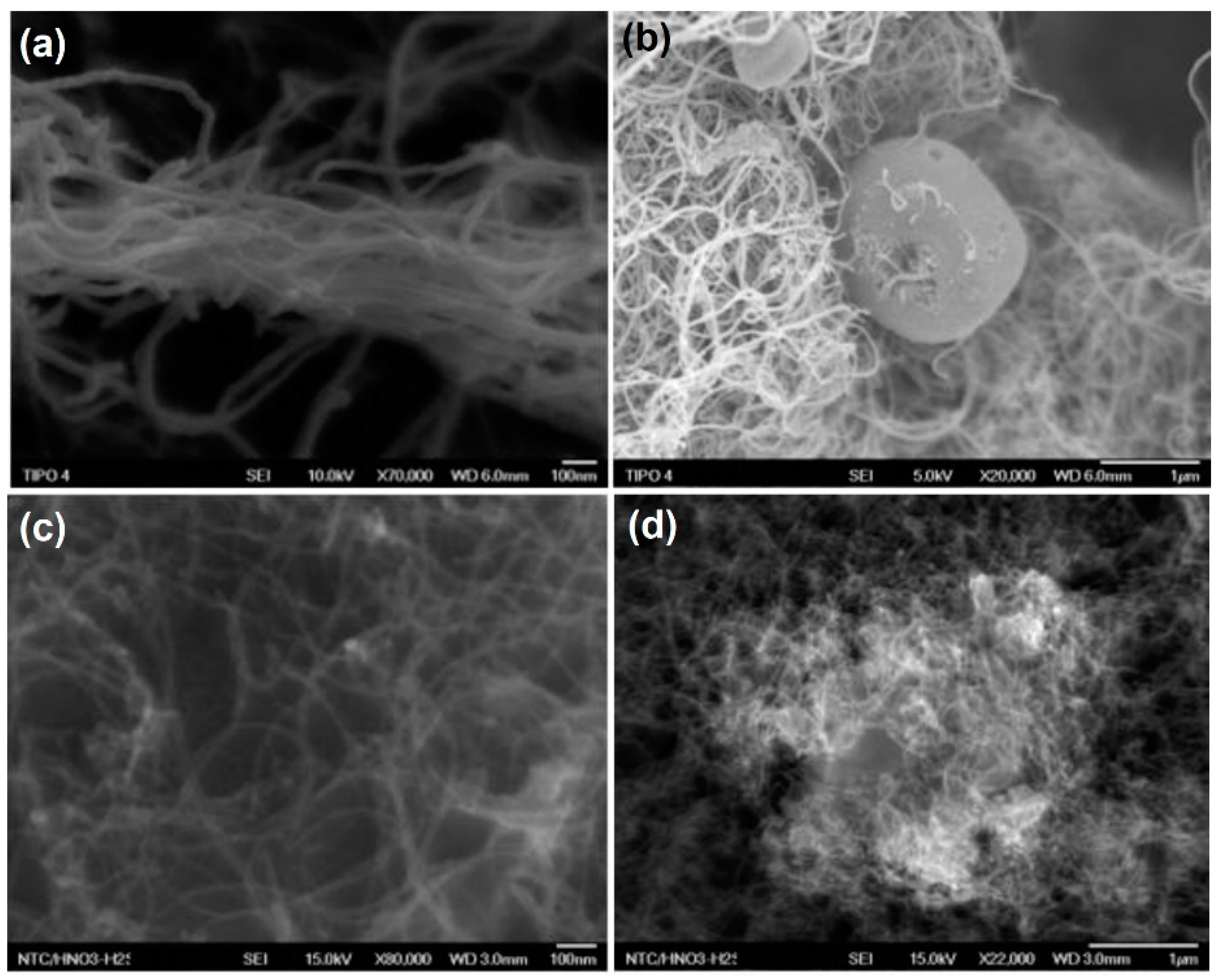
3.1. CNT Treatment
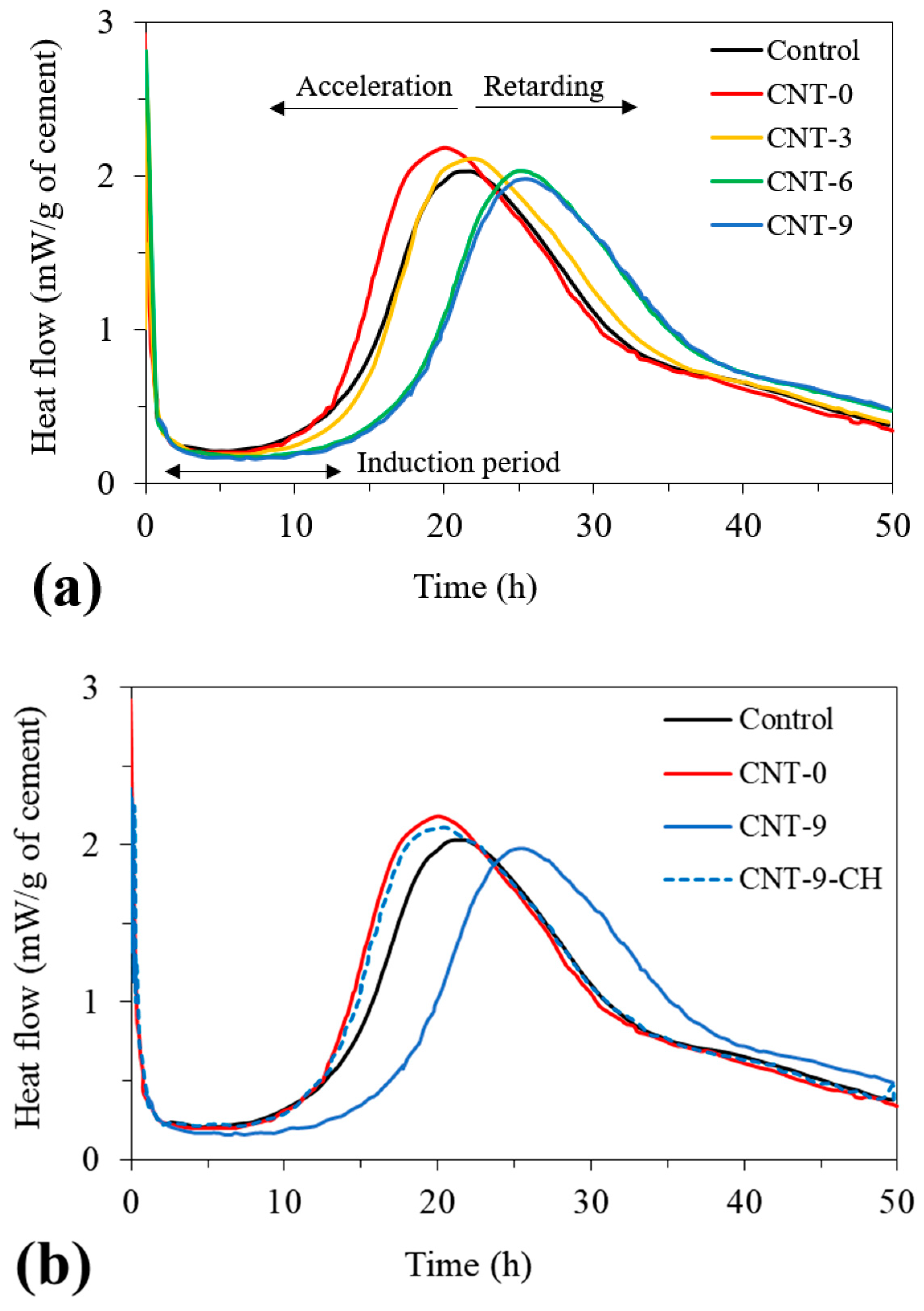
3.2. Cement Hydration Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Han, Y.; Liu, S. Effect of highly dispersed carbon nanotubes on the flexural toughness of cement-based composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 46, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyuev, S.V.; Klyuev, A.V.; Khezhev, T.A.; Pukharenko, Y.V. High-strength fine-grained fiber concrete with combined reinforcement by fiber. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2018, 13, 6407–6412. [Google Scholar]
- Pimenov, A.I.; Ibragimov, R.A.; Izotov, V.S. Research on the influence of the carbon nanotubes injection method on cement composite properties. ZKG Int. 2015, 68, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Klyuyev, A.; Sopin, D.; Netrebenko, A.; Kazlitin, S. Heavy loaded floors based on fine-grained fiber concrete. Mag. Civ. Eng. 2013, 38, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafesse, M.; Kim, H.-K. The role of carbon nanotube on hydration kinetics and shrinkage of cement composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 169, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, D. The algorithm of complex diagnostics of technical condition of building structures on thermograms analysis. Constr. Mater. Prod. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibragimov, R.R.; Izotov, V.S. Effect of carbon nanotubes on the structure and properties of cement composites. Inorg. Mater. 2015, 51, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Fediuk, R.; Vatin, N.; Lee, Y.H.; Murali, G.; Ozbakkaloglu, T.; Klyuev, S.; Alabduljabbar, H. Fibre-Reinforced Foamed Concretes: A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisman, L.; Wagner, H.D.; Marom, G. The role of surfactants in dispersion of carbon nanotubes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 128–130, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fediuk, R.S. Mechanical Activation of Construction Binder Materials by Various Mills. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Yurga, Russia, 26–28 November 2015; Volume 125, p. 012019. [Google Scholar]
- Petrunin, S.; Vaganov, V.; Reshetniak, V.; Zakrevskaya, L. Influence of Carbon Nanotubes on the Structure Formation of Cement Matrix; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2015; Volume 96, p. 012046. [Google Scholar]
- Fediuk, R.; Amran, M.; Mosaberpanah, M.A.; Danish, A.; El-Zeadani, M.; Klyuev, S.; Vatin, N. A Critical Review on the Properties and Applications of Sulfur-Based Concrete. Materials 2020, 13, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierard, N.; Fonseca, A.; Konya, Z.; Willems, I.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Nagy, J. Production of short carbon nanotubes with open tips by ball milling. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2001, 335, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Tu, J.; Kong, F.; Huang, W.; Chen, C. Preparation of short carbon nanotubes by mechanical ball milling and their hydrogen adsorption behavior. Carbon 2003, 41, 2527–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizina, T.; Ponomarev, A.; Balykov, A.; Pankin, N. Fine-grained fibre concretes modified by complexed nanoadditives. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 14, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharun, M.; Klyuev, S.; Koroteev, D.; Chiadighikaobi, P.C.; Fediuk, R.; Olisov, A.; Vatin, N.; Alfimova, N. Heat Treatment of Basalt Fiber Reinforced Expanded Clay Concrete with Increased Strength for Cast-In-Situ Construction. Fibers 2020, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Metaxa, Z.S.; Shah, S.P. Highly dispersed carbon nanotube reinforced cement based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Lee, Y.-S.; Hong, S.-G.; Moon, J. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): Dispersion, mechanical properties, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding effectiveness (SE). Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 131, 106017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoy, A.D.; Lesovik, V.S.; Glagolev, E.S.; Krymova, A.I. Synergetics of Hardening Construction Systems; IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 327, p. 032056. [Google Scholar]
- De Azevedo, A.R.; Klyuev, S.; Marvila, M.T.; Vatin, N.; Alfimova, N.; De Lima, T.E.; Fediuk, R.; Olisov, A. Investigation of the Potential Use of Curauá Fiber for Reinforcing Mortars. Fibers 2020, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Sandler, J.; Windle, A.; Schwarz, M.-K.; Bauhofer, W.; Schulte, K.; Shaffer, M. Electric field-induced aligned multi-wall carbon nanotube networks in epoxy composites. Polymer 2005, 46, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyuev, S.V.; Khezhev, T.; Pukharenko, Y.; Klyuev, A. To the Question of Fiber Reinforcement of Concrete. Mater. Sci. Forum 2019, 945, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artamonova, O.V.; Slavcheva, G.S.; Shvedova, M.A. Effectiveness of Nanotubular Additives in the Modification of Cement Systems. Inorg. Mater. 2020, 56, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Luz, G.; Gleize, P.J.; Batiston, E.R.; Pelisser, F. Effect of pristine and functionalized carbon nanotubes on microstructural, rheological, and mechanical behaviors of metakaolin-based geopolymer. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 104, 103332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuzin, A.; Ibragimov, R.R. Processes of structure formation and paste matrix hydration with multilayer carbon nanotubes additives. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 102030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lannoy, C.-F.; Soyer, E.; Wiesner, M.R. Optimizing carbon nanotube-reinforced polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes through carboxylic acid functionalization. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 447, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibragimov, R.; Fediuk, R. Improving the early strength of concrete: Effect of mechanochemical activation of the cementitious suspension and using of various superplasticizers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 226, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroganov, V.; Sagadeev, E.; Ibragimov, R.R.; Potapova, L. Mechanical activation effect on the biostability of modified cement compositions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Gong, H.; Gu, C. Research progress on CNTs/CNFs-modified cement-based composites—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fediuk, R.S.; Lesovik, V.S.; Liseitsev, Y.L.; Timokhin, R.A.; Bituyev, A.V.; Zaiakhanov, M.Y.; Mochalov, A.V. Composite binders for concretes with improved shock resistance. Mag. Civ. Eng. 2019, 85, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyuyev, S.; Guryanov, Y. External reinforcing of fiber concrete constructions by carbon fiber tapes. Mag. Civ. Eng. 2013, 36, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, D.; Goetz-Neunhoeffer, F.; Lothenbach, B.; Neubauer, J. The early hydration of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC): An approach comparing measured heat flow with calculated heat flow from QXRD. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezhev, T.A.; Pukharenko, Y.V.; Khezhev, K.A.; Klyuev, S.V. Fiber gypsum concrete composites with using volcanic tuffsawing waste. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2018, 13, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, P.R.; Oliveira, J.C.; Medina, T.M.; Magalhães, D.C.; Gleize, P.J.; Schankoski, R.A.; Pilar, R. Use of air-cooled blast furnace slag as supplementary cementitious material for self-compacting concrete production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L.; Juilland, P.; Monteiro, P.J. Advances in understanding hydration of Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begich, Y.E.; Klyuev, S.V.; Jos, V.A.; Cherkashin, A.V. Fine-grained concrete with various types of fibers. Mag. Civ. Eng. 2020, 96, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matos, P.R.; Sakata, R.D.; Onghero, L.; Uliano, V.G.; De Brito, J.; Campos, C.E.; Gleize, P.J. Utilization of ceramic tile demolition waste as supplementary cementitious material: An early-age investigation. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 38, 102187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reales, O.A.M.; Pearl, W.C.; Paiva, M.D.M.; Miranda, C.R.; Filho, R.D.T. Effect of a commercial dispersion of multi walled carbon nanotubes on the hydration of an oil well cementing paste. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2015, 10, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isfahani, F.T.; Li, W.; Redaelli, E. Dispersion of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and its effects on the properties of cement composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 74, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Bogas, J.A.; Guedes, M.; Pereira, M.F.C.; Hawreen, A. Dispersion and reinforcement efficiency of carbon nanotubes in cementitious composites. Mag. Concr. Res. 2019, 71, 408–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. Norma Brasileira: NBR 16697-Cimento Portland—Requisitos; ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018. (in Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Wepasnick, K.A.; Smith, B.A.; Schrote, K.E.; Wilson, H.K.; Diegelmann, S.R.; Fairbrother, D.H. Surface and structural characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes following different oxidative treatments. Carbon 2011, 49, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Thomas, J.J.; Taylor, H.F.; Jennings, H.M. Solubility and structure of calcium silicate hydrate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1499–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Xiao, G.; Feng, C.; Xu, W.; Bai, B.; Yang, N.; Gao, Y.; Hou, X.; et al. Dispersing of functionalized CNTs in Si–O–C ceramics and electromagnetic wave absorbing and mechanical properties of CNTs/Si–O–C nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 5407–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, P. (Ed.) Spark Plasma Sintering of Materials: Advances in Processing and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Berodier, E.; Scrivener, K. Understanding the Filler Effect on the Nucleation and Growth of C-S-H. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 3764–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Wang, P.M.; Zhao, X. Mechanical behavior and microstructure of cement composites incorporating surface-treated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2005, 43, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usanova, K.; Barabanshchikov, Y.G. Cold-bonded fly ash aggregate concrete. Mag. Civ. Eng. 2020, 95, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsun, V.I.; Vatin, N.; Korsun, A.; Nemova, D. Physical-Mechanical Properties of the Modified Fine-Grained Concrete Subjected to Thermal Effects up to 200 °C. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 633, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical composition (wt. %) | |
| SiO2 | 20.17 |
| Al2O3 | 4.06 |
| Fe2O3 | 3.33 |
| CaO | 60.96 |
| MgO | 3.54 |
| SiO3 | 3.43 |
| K2O | 1.1 |
| Na2O | 0.09 |
| Loss on ignition | 3.05 |
| Insoluble residue | 0.27 |
| Physical property | |
| Fc 1 day (MPa) | 23.8 |
| Fc 3 day (MPa) | 29.2 |
| Fc 28 day (MPa) | 40.2 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 3.11 |
| Blaine fineness (cm2/g) | 3460 |
| Mix | Heat Flow Peak | |
|---|---|---|
| Value (mW/g Cement) | Occurrence Time (h) | |
| Control | 2.03 | 21.5 |
| CNT-0 | 2.18 | 20.2 |
| CNT-3 | 2.05 | 23.2 |
| CNT-6 | 2.03 | 24.8 |
| CNT-9 | 1.98 | 25.6 |
| CNT-9-CH | 2.11 | 20.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batiston, E.; de Matos, P.R.; Gleize, P.J.P.; Fediuk, R.; Klyuev, S.; Vatin, N.; Karelina, M. Combined Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes (CNT) Fibers with H2SO4/HNO3 and Ca(OH)2 for Addition in Cementitious Matrix. Fibers 2021, 9, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9030014
Batiston E, de Matos PR, Gleize PJP, Fediuk R, Klyuev S, Vatin N, Karelina M. Combined Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes (CNT) Fibers with H2SO4/HNO3 and Ca(OH)2 for Addition in Cementitious Matrix. Fibers. 2021; 9(3):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9030014
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatiston, Eduardo, Paulo Ricardo de Matos, Philippe Jean Paul Gleize, Roman Fediuk, Sergey Klyuev, Nikolai Vatin, and Maria Karelina. 2021. "Combined Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes (CNT) Fibers with H2SO4/HNO3 and Ca(OH)2 for Addition in Cementitious Matrix" Fibers 9, no. 3: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9030014
APA StyleBatiston, E., de Matos, P. R., Gleize, P. J. P., Fediuk, R., Klyuev, S., Vatin, N., & Karelina, M. (2021). Combined Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes (CNT) Fibers with H2SO4/HNO3 and Ca(OH)2 for Addition in Cementitious Matrix. Fibers, 9(3), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9030014









