On the Management of Nature-Based Solutions in Open-Air Laboratories: New Insights and Future Perspectives
Abstract
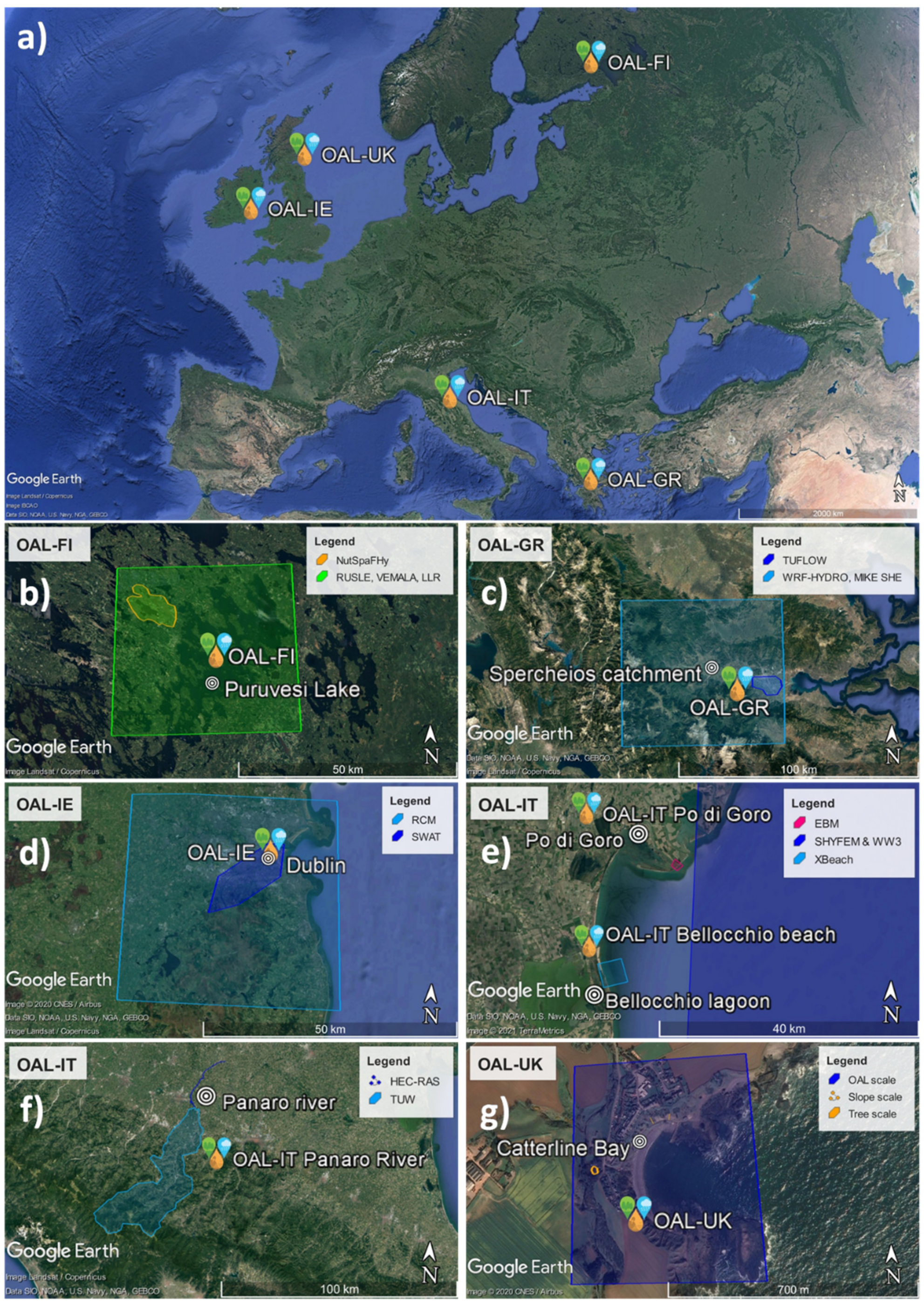
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. OAL Finland
3.2. OAL Greece
3.3. OAL Ireland
3.4. OAL Italy
3.5. OAL UK
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IUCN. The IUCN Programme 2013–2016; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2012; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Schacham, E.; Walters, G.; Janzen, C.; Maginnis, S. Nature-based Solutions to Address Global Societal Challenges; IUCN: Galnd, Switzerland, 2016; pp. xii + 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, C.M.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Kabisch, N.; Berry, P.; Breil, M.; Nita, M.R.; Geneletti, D.; Calfapietra, C. A framework for assessing and implementing the co-benefits of nature-based solutions in urban areas. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 77, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, A.; Carrus, G.; Lafortezza, R.; Marian, L.; Sanesi, G. Nature-based solutions to promote human resilience and wellbeing in cities during increasingly hot summers. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastenrath, S.; Bush, J.; Coenen, L. Scaling-up nature-based solutions. Lessons from the Living Melbourne strategy. Geoforum 2020, 116, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almenar, J.B.; Elliot, T.; Rugani, B.; Philippe, B.; Gutierrez, T.N.; Sonnemann, G.; Geneletti, D. Nexus between nature-based solutions, ecosystem services and urban challenges. Land Use Policy 2021, 100, 104898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.; Nunes, J.; Novara, A.; Finger, D.; Avelar, D.; Kalantari, Z.; Cedrà, A. The superior effect of nature-based solutions in land management for enhancing ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faivre, N.; Fritz, M.; Freitas, T.; de Boissezon, B.; Vandewoestijne, S. Nature-based solutions in the EU: Innovating with nature to address social, economic and environmental challenges. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accastello, C.; Blanc, S.; Brun, F. A Framework for the Integration of Nature-Based Solutions into Environmental Risk Management Strategies. Sustainability 2019, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Debele, S.E.; Kumar, P.; Sahani, J.; Marti-Cardona, B.; Mickovski, S.B.; Leo, L.S.; Porcù, F.; Bertini, F.; Montesi, D.; Vojinovic, Z.; et al. Nature-based solutions for hydro-meteorological hazards: Revised concepts, classification schemes and databases. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahani, J.; Kumar, P.; Debele, S.; Spyrou, C.; Loupis, M.; Aragão, L.; Porcù, F.; Shah, M.A.R.; Di Sabatino, S. Hydro-meteorological risk assessment methods and management by nature-based solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Debele, S.E.; Sahani, J.; Aragão, L.; Barisani, F.; Basu, B.; Bucchignani, E.; Charizopoulos, N.; Di Sabatino, S.; Domeneghetti, A.; et al. Towards an operationalisation of nature-based solutions for natural hazards. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 138855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.E.; Costa, M.M.; Manez, K.S. An operationalized classification of Nature Based Solutions for water-related hazards: From theory to practice. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 167, 106460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangpan, L.; Vojinovic, Z.; Di Sabatino, S.; Leo, L.S.; Capobianco, V.; Oen, A.M.P.; McClain, M.E.; Lopez-Gunn, E. Nature-based solutions for hydro-meteorological risk reduction: A state-of-the-art review of the research area. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Fong, T.; Chui, M. Integrated hydro-environmental impact assessment and alternative selection of low impact development practices in small urban catchments. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, S.; Pluchinotta, I.; Pagano, A.; Pengal, P.; Cokan, B.; Giordano, R. Assessing stakeholders’ risk perception to promote Nature Based Solutions as flood protection strategies: The case of the Glinščica river (Slovenia). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, X. Do forests relieve crop thirst in the face of drought? Empirical evidence from South. China. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2019, 55, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalantari, Z.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; Keesstra, S.; Destouni, G. Nature-based solutions for flood-drought risk mitigation in vulnerable urbanizing parts of East.-Africa. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 5, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.; Fidélis, T.; Roebeling, P.; Teles, F. The Institutionalization of Nature-Based Solutions—A Discourse Analysis of Emergent Literature. Resources 2020, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ershad Sarabi, S.; Han, Q.L.; Romme, A.G.; de Vries, B.; Wendling, L. Key Enablers of and Barriers to the Uptake and Implementation of Nature-Based Solutions in Urban. Settings: A Review. Resources 2019, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nesshover, C.; Assmuth, T.; Irvine, K.N.; Rusch, G.M.; Waylen, K.A.; Delbaere, B.; Haase, D.; Jones-Walters, L.; Keune, H.; Kovacs, E.; et al. The science, policy and practice of nature-based solutions: An interdisciplinary perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, T.; Jordan, A. Climate Change Policy in the European Union. 2016. Available online: https://oxfordre.com/climatescience/view/10.1093/acrefore/9780190228620.001.0001/acrefore-9780190228620-e-47 (accessed on 4 September 2020). [CrossRef]
- Grafakos, S.; Viero, G.; Reckien, D.; Trigg, K.; Viguie, V.; Sudmant, A.; Graves, C.; Foley, A.; Heidrich, O.; Mirailles, J.M.; et al. Integration of mitigation and adaptation in urban climate change action plans in Europe: A systematic assessment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 121, 109623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, R.; Pluchinotta, I.; Pagano, A.; Scrieciuc, A.; Nanu, F. Enhancing nature-based solutions acceptance through stakeholders’ engagement in co-benefits identification and trade-offs analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calliari, E.; Staccione, A.; Mysiak, J. An assessment framework for climate-proof nature-based solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.E.; Giordano, R.; Pagano, A.; van der Keur, P.; Costa, M.M. Using a system thinking approach to assess the contribution of nature based solutions to sustainable development goals. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, L.; Bell, J.N.B.; Bone, J.; Head, M.; Hill, L.; Howard, C.; Hobbs, S.J.; Jones, D.T.; Power, S.A.; Rose, N.; et al. Open Air Laboratories (OPAL): A community-driven research programme. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakeman-Fraser, P.; Gosling, L.; Moffat, A.J.; West, S.E.; Fradera, R.; Davies, L.; Ayamba, M.A.; van der Wal, R. To have your citizen science cake and eat it? Delivering research and outreach through Open Air Laboratories (OPAL). BMC Ecol. 2016, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blöschl, G.; Blaschke, A.P.; Broer, M.; Bucher, C.; Carr, G.; Chen, X.; Eder, A.; Exner-Kittridge, M.; Farnleitner, A.; Flores-Orozco, A.; et al. The Hydrological Open Air Laboratory (HOAL) in Petzenkirchen: A hypothesis-driven observatory. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Széles, B.; Broer, M.; Parajka, J.; Hogan, P.; Eder, A.; Strauss, P.; Blöschl, G. Separation of scales in transpirationeffects on low flows: A spatial analysis in the Hydrological OpenAir Laboratory. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 6168–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, A.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Modeling and mitigating natural hazards: Stationarity is immortal! Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 9748–9756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.P.; Srivastava, P.K. Flood Hazards Mitigation Analysis Using Remote Sensing and GIS: Correspondence with Town Planning Scheme. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2353–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursanidis, D.; Chrysoulakis, N. Remote Sensing, natural hazards and the contribution of ESA Sentinels missions. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 6, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siagian, T.H.; Purhadi, P.; Suhartono, S.; Ritonga, H. Social vulnerability to natural hazards in Indonesia: Driving factors and policy implications. Nat. Hazards 2014, 70, 1603–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, I.; De Amicis, M. Mapping social vulnerability to natural hazards in Italy: A suitable tool for risk mitigation strategies. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 63, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreibich, H.; van den Bergh, J.C.J.M.; Bouwer, L.M.; Bubeck, P.; Ciavola, P.; Green, C.; Hallegatte, S.; Logar, I.; Meyer, V.; Schwarze, R.; et al. Costing natural hazards. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesalon, L.; Cretan, R. Mono-industrialism and the Struggle for Alternative Development: The Case of the Roşia Montană Gold-mining Project. J. Tijdschr. Econ. Soc. Geogr. 2013, 104, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesalon, L.; Cretan, R. ‘Cyanide kills!’ Environmental movements and the construction of environmental risk at Roşia Montană, Romania. Area 2013, 45, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Fan, Y. Robust climate change research: A review on multi-model analysis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, J.; Mejia, C.; Sorror, C.; Sylla, A.; Crépon, M.; Thiria, S. Towards an objective assessment of climate multi-model ensembles—a case study: The Senegalo-Mauritanian upwelling region. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 2723–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; Volume 703.
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The New Assessment of Soil Loss by Water Erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, I.; Huttunen, M.; Piirainen, V.; Korppoo, M.; Lepistö, A.; Räike, A.; Tattari, S.; Vehviläinen, B. A national-scale nutrient loading model for Finnish watersheds—VEMALA. Environ. Model Assess. 2016, 21, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotamäki, N.; Pätynen, A.; Taskinen, A.; Huttula, T.; Malve, O. Statistical dimensioning of nutrient loading reduction: LLR assessment tool for lake managers. Environ. Manag. 2015, 56, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veijalainen, N.; Korhonen, J.; Vehviläinen, B.; Koivusalo, H. Modelling and statistical analysis of catchment water balance and discharge in Finland in 1951–2099 using transient climate scenarios. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2012, 3, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Bremnes, J.B.; Haugen, J.E.; Engen-Skaugen, T. Technical Note: Downscaling RCM precipitation to the station scale using statistical transformations—A comparison of methods. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finnish Forest Centre. Forest Inventory Data, FDI. 2020. Available online: https://www.metsaan.fi/paikkatietoaineistot (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Mentzafou, A.; Varlas, G.; Dimitriou, E.; Papadopoulos, A.; Pytharoulis, I.; Katsafados, P. Modeling the Effects of Anthropogenic Land Cover Changes to the Main Hydrometeorological Factors in a Regional Watershed, Central Greece. Climate 2019, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- TUFLOW. Available online: https://www.tuflow.com/About.aspx (accessed on 26 March 2019).
- Gochis, D.J.; Yu, W.; Yates, D.N. The WRF-Hydro Model Technical Description and User’s Guide, Version 3.0. NCAR Technical Document; NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2015; Available online: https://ral.ucar.edu/sites/default/files/public/images/project/WRF_Hydro_User_Guide_v3.0.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Refsgaard, J.C.; Storm, B. MIKE SHE. In Computer Models of Watershed Hydrology; Singh, V.P., Ed.; Water Resources Publications, LLC: Littleton, CO, USA, 1995; pp. 809–846. [Google Scholar]
- DHI. MIKE SHE User Manual; Danish Hydraulic Institute: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Komar, P.D.; Allan, J.C. “Design with Nature” strategies for shore protection—The construction of a cobble berm and artificial dune in an Oregon State Park. In Puget Sound Shorelines and the Impacts of Armoring—Proceedings of a State of the Science Workshop, May 2009; Shipman, H., Dethier, M.N., Gelfenbaum, G., Fresh, K.L., Dinicola, R.S., Eds.; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2010; pp. 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ondiviela, B.; Losada, I.J.; Lara, J.L.; Maza, M.; Galván, C.; Bouma, T.J.; van Belzen, J. The role of seagrasses in coastal protection in a changing climate. Coast. Eng. 2014, 87, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umgiesser, G.; Melaku Canu, D.; Cucco, A.; Solidoro, C. A finite element model for the Venice Lagoon. Development, set up, calibration and validation. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 51, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, C.; Umgiesser, G.; Cucco, A.; Hsu, T.W.; Roland, A.; Amos, C.L. Development and validation of a finite element morphological model for shallow water basins. Coast. Eng. 2008, 55, 716–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellafiore, D.; Umgiesser, G. Hydrodynamic coastal processes in the North. Adriatic investigated with a 3D finite element model. Ocean Dyn. 2009, 60, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The WAVEWATCH III® Development Group (WW3DG). User Manual and System Documentation of WAVEWATCH III® Version 5.16. Tech. Note 329; NOAA/NWS/NCEP/MMAB: College Park, MD, USA, 2016. Available online: https://polar.ncep.noaa.gov/waves/wavewatch/manual.v5.16.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Roelvink, D.; Reniers, A.; van Dongeren, A.; van Thiel de Vries, J.; McCall, R.; Lescinski, J. Modelling storm impacts on beaches, dunes and barrier islands. Coast. Eng. 2009, 56, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerman, E. Long-Term Morphological Modelling of the Mouth of the Columbia River. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 9 December 2010. Available online: http://resolver.tudelft.nl/uuid:0a39e67c-ec24-4264-b523-d3ece34f9da8 (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Van Bemmelen, C.W.T. Long Term Process-Based Morphological Modelling of Pocket Beaches. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 4 May 2017. Available online: http://resolver.tudelft.nl/uuid:8fad63f2-1994-4877-9627-4446eae21913 (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Ruti, P.; Somot, S.; Giorgi, F.; Dubois, C.; Flaounas, E.; Obermann, A.; Dell’Aquila, A.; Pisacane, G.; Harzallah, A.; Lombardi, E.; et al. Med.-CORDEX initiative for Mediterranean climate studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 1187–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viglione, A.; Parajka, J. TUWmodel: Lumped/Semi-Distributed Hydrological Model for Education Purposes. R Package Version 1.1-0. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=TUWmodel (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Switanek, M.B.; Troch, P.A.; Castro, C.L.; Leuprecht, A.; Chang, H.-I.; Mukherjee, R.; Demaria, E.M.C. Scaled distribution mapping: A bias correction method that preserves raw climate model projected changes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2649–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciervo, F.; Rianna, G.; Mercogliano, P.; Papa, M.N. Effects of climate change on shallow landslides in a small coastal catchment in southern Italy. Landslides 2016, 14, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkau, R.L. UNET One Dimensional Unsteady Flow through a Full Network of Open Channels; US Army Corps of Engineerings, Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Verri, G.; Pinardi, N.; Bryan, F.; Tseng, Y.H.; Coppini, G.; Clementi, E. A box model to represent estuarine dynamics in mesoscale resolution ocean models. Ocean Model. 2020, 148, 101587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ollauri, A.; Mickovski, S.B. Hydrological effect of vegetation against rainfall-induced landslides. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bishop, A.W. The use of the Slip Circle in the Stability Analysis of Slopes. Géotechnique 1955, 5, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardio, G.; Mickovski, S.B. Implementation of eco-engineering design into existing slope stability design practices. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 92, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ollauri, A.; Mickovski, S.B. Plant-Best: A novel plant selection tool for slope protection. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 154–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Ollauri, A.; Mickovski, S.B. Plant-soil reinforcement response under different soil hydrological regimes. Geoderma 2017, 285, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, B.M.; Sivakugan, N. Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Acharia, M.S. Analytical approach to design vegetative crib walls. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birkmann, J.; von Teichman, K. Integrating disaster risk reduction and climate change adaptation: Key challenges—scales, knowledge, and norms. Sustain. Sci. 2010, 5, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkmann, J.; Pardoe, J. Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction: Fundamentals, Synergies and Mismatches. In Adapting to Climate Change. Environmental Hazards; Glavovic, B., Smith, G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stults, M. Integrating climate change into hazard mitigation planning: Opportunities and examples in practice. Clim. Risk Manag. 2017, 17, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, H.J.; Blenkinsop, S.; Tebaldi, C. Linking climate change modelling to impacts studies: Recent advances in downscaling techniques for hydrological modelling. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 1547–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockel, B.; Castro, C.L.; Pielke, R.A., Sr.; von Storch, H.; Leoncini, G. Dynamical downscaling: Assessment of model system dependent retained and added variability for two different regional climate models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D21107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallard, M.S.; Nolte, C.G.; Bullock, O.R.; Spero, T.L.; Gula, J. Using a coupled lake model with WRF for dynamical downscaling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 7193–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F.J.; Navarro, A.; Moreno, R.; Sánchez, J.L.; García-Ortega, E. Regional climate models: 30 years of dynamical downscaling. Atm. Res. 2019, 235, 104785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, S.; Guiomar, N.; Machado, R.; Santos, P.; Sà-Sousa, P.; Fernandes, J.P.; Neves, N.; Pinto-Correia, P. Assessment of environment, land management, and spatial variables on recent changes in montado land cover in southern Portugal. Agrofor. Syst. 2016, 90, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, R.J.; Quillérou, E.; Stewart, N. The Rewards of Investing in Sustainable Land Management: Interim Report for the Economics of Land Degradation Initiative: A Global Strategy for Sustainable Land Management. [Research Report] Economics of Land Degradation (ELD) Initiative. 2013. ffhal-01954823f. Available online: www.eld-initiative.org (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Kumar, P.; Debele, S.E.; Sahani, J.; Rawat, N.; Marti-Cardona, B.; Alfieri, S.M.; Basu, B.; Basu, A.S.; Bowyer, P.; Charizopoulos, N.; et al. An overview of monitoring methods for assessing the performance of nature-based solutions against natural hazards. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 103603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Debele, S.E.; Sahani, J.; Rawat, N.; Marti-Cardona, B.; Alfieri, S.M.; Basu, B.; Basu, A.S.; Bowyer, P.; Charizopoulos, N.; et al. Nature-based solutions efficiency evaluation against natural hazards: Modelling methods, advantages, and limitations. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallotti, G.; Santo, M.A.; Apostolidou, I.; Alessandri, J.; Armigliato, A.; Basu, B.; Debele, S.; Domeneghetti, A.; Gonzalez-Ollauri, A.; Kumar, P.; et al. On the Management of Nature-Based Solutions in Open-Air Laboratories: New Insights and Future Perspectives. Resources 2021, 10, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources10040036
Gallotti G, Santo MA, Apostolidou I, Alessandri J, Armigliato A, Basu B, Debele S, Domeneghetti A, Gonzalez-Ollauri A, Kumar P, et al. On the Management of Nature-Based Solutions in Open-Air Laboratories: New Insights and Future Perspectives. Resources. 2021; 10(4):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources10040036
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallotti, Glauco, Marco Antonio Santo, Ilektra Apostolidou, Jacopo Alessandri, Alberto Armigliato, Bidroha Basu, Sisay Debele, Alessio Domeneghetti, Alejandro Gonzalez-Ollauri, Prashant Kumar, and et al. 2021. "On the Management of Nature-Based Solutions in Open-Air Laboratories: New Insights and Future Perspectives" Resources 10, no. 4: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources10040036
APA StyleGallotti, G., Santo, M. A., Apostolidou, I., Alessandri, J., Armigliato, A., Basu, B., Debele, S., Domeneghetti, A., Gonzalez-Ollauri, A., Kumar, P., Mentzafou, A., Pilla, F., Pulvirenti, B., Ruggieri, P., Sahani, J., Salmivaara, A., Basu, A. S., Spyrou, C., Pinardi, N., ... Di Sabatino, S. (2021). On the Management of Nature-Based Solutions in Open-Air Laboratories: New Insights and Future Perspectives. Resources, 10(4), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources10040036













