Municipal Solid Waste and Leachate Characterization in the Cairo Metropolitan Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Field and Experimental Investigation
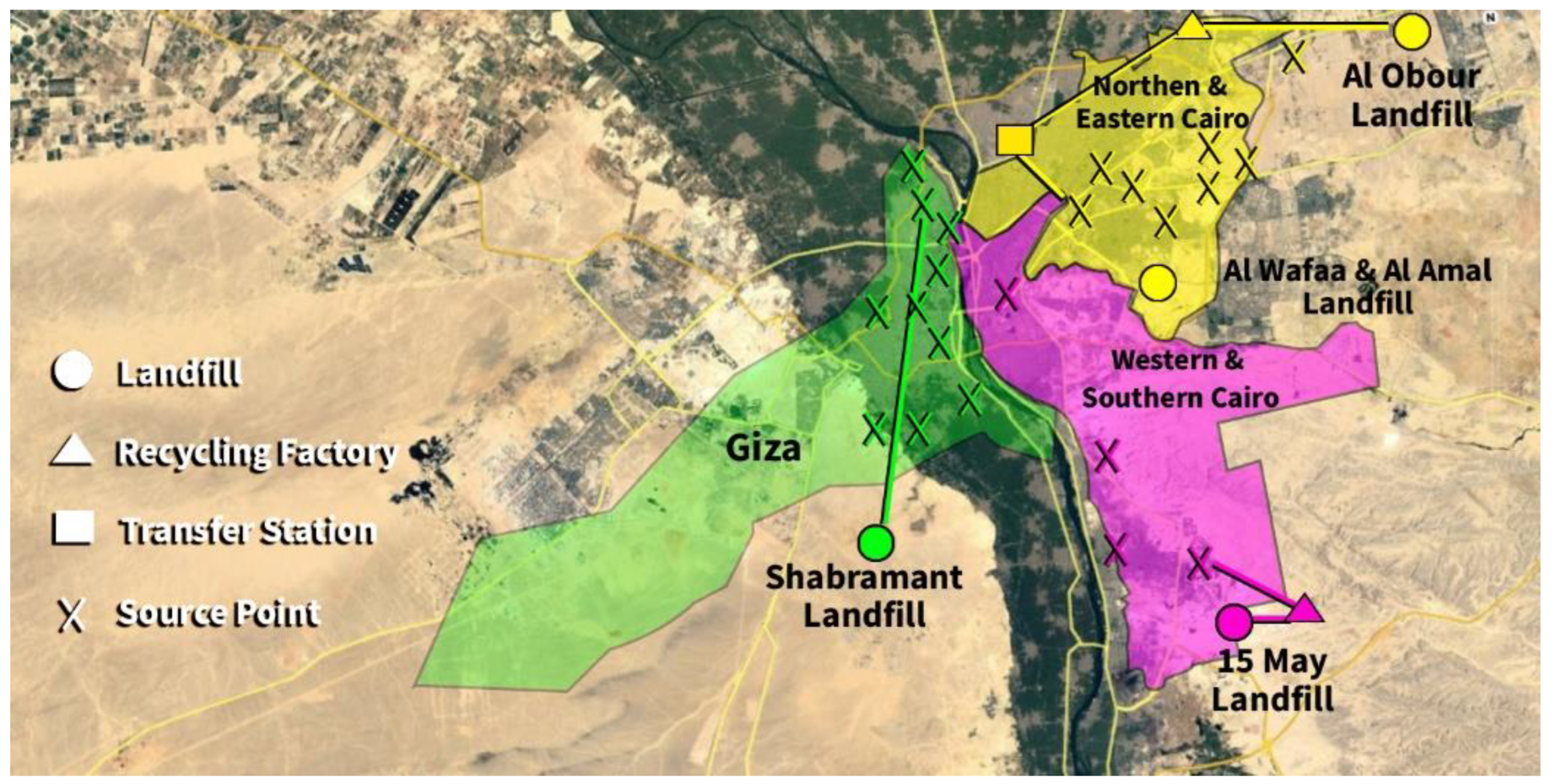
2.1. Study Scope
2.2. Waste Composition Analysis
2.3. Leachate Chemical Analysis
3. Results & Discussion
3.1. Waste Composition
3.2. Leachate Composition
| City or Region Country | Site 1 Zhejiang China | Site 2 Zhejiang China | Site 3 Zhejiang China | Site 1, Central area of Taiwan | Site 2, Central area of Taiwan | Site 3, Central area of Taiwan | Tsuen-Wan Hong Kong | Sai-Kung Hong Kong | Sulaibiyah Kuwait | Jaleeb AlShiookh Kuwait | Nova Scotia Canada | Ouled Fayet Algeria | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Unit | [57] | [59] | [60] | [61] | [48] | [62] | ||||||
| Study date | - | NA | NA | NA | Feb. 2001–July 2003 | March 1990–Jan. 1991 | May–Oct.2000 | NA | 2006 | ||||
| pH | - | 8.01 | 7.75 | 7.66 | 7.03–8.50 | 7.30–8.40 | 6.82–8.37 | 7.20–8.00 | 7.20–8.40 | 6.90–8.20 | 7.82–8.06 | 5.10 | 8.27 |
| BOD | mg/L | 1000 | 876 | 834 | 12–97 | 26.0–492 | 16.0–312 | - | - | 30–600 | 210–345 | - | 980 |
| COD | mg/L | 1490 | 1100 | 1900 | 320–1340 | 400–4300 | 840–4200 | 489–1670 | 147–1590 | 158–9440 | 6400–8800 | 11,6000 | 3790 |
| CaCO3 | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 85.8 |
| NH4+ | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Norg | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 58.2 |
| PO43- | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Cl- | mg/L | 1430 | 819 | 3150 | NA | NA | NA | 464–1340 | 140–1100 | NA | NA | 3720 | 4570 |
| SO42- | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | - | - | NA | NA | - | 3060 |
| Na+ | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | 320–1340 | 297–3530 | 431–3140 | 484–1190 | 132–743 | NA | NA | 3800 | NA |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | 27.8–103 | 23.0–163 | 15.7–157 | 35.0–63.0 | 9.00–26.0 | 5.20–20.8 | 86.0–268 | 1020 | NA |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | 47.2–137 | 67.2–133.7 | 15.9–61.0 | NA | NA | 5.60–67.6 | 52.0–122 | 6300 | NA |
| Zn2+ | mg/L | 17.2 | 533 | 1330 | 0.04–1.61 | 0.003–0.56 | 0.03–0.66 | 0.24–2.55 | 0.13–0.39 | 0.00–0.20 | 0.20–4.80 | 13.5 | NA |
| Mn2+ | mg/L | 0.54 | 2.39 | 5.98 | 0.18–5.27 | 0.02–0.74 | 0.02–0.75 | 0.05–0.24 | 0.05–1.30 | NA | NA | 51.0 | 0.41 |
| Fe2+ | mg/L | 1.94 | 15.5 | 38.6 | 0.26–5.44 | 0.26–15.3 | 0.39–28.0 | 1.14–3.25 | 1.26–5.00 | 0.30–18.1 | 1.40–54.6 | 297 | 8.23 |
| Cd2+ | mg/L | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.60 | <0.15 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.02 | NA | NA | 0.02 | NA |
| Cr3+ | mg/L | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.78 | 0.01–0.18 | 0.12–0.52 | 0.04–1.26 | 0.03–0.15 | 0.02–0.23 | NA | NA | 0.40 | 0.20 |
| Pb2+ | mg/L | 0.23 | 4.56 | 11.4 | <0.02 | <0.01–0.09 | 0.02–0.18 | 0.03–0.12 | <0.10 | 0–0.10 | NA | 0.81 | 3.49 |
| City or Region Country | Riyadh Saudi Arabia | USA | Italy | Germany | UK | Southern Italy | Thessaloniki Greece | Site 1 South Africa | Site 2 South Africa | Hong Kong | New Zealand | Alexandria Egypt | Cairo Egypt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Unit | [52] | [6] | [47] | [63] | [64] | [65] | [53] | Current study | |||||
| Study date | - | Feb.–May 2008 | 1972–1979 | 1987 | 1991 | Jan.–March 2000 | NA | NA | 1999–2003 | 1990–1991 | 1986–1987 | NA | March 2020–March 2021 | |
| pH | - | 5.94–6.32 | 5.10–6.90 | 6.00–8.50 | 5.70–8.10 | 6.70 | 8.20 | 7.90 | 7.50 | 8.20 | 7.80 | 7.00 | 7.00–7.80 | 6.14–8.14 |
| BOD | mg/L | NA | 13400 | 2130–10,400 | 400–45,900 | 18,600 | 2300 | 1050 | 170 | 550 | 117 | 737 | 10,824 ± 95 | 3880–4860 |
| COD | mg/L | 13,900–22,400 | 1340–18,100 | 7750–38,500 | 1630–63,700 | 36,800 | 10,500 | 5350 | 760 | 4560 | 873 | 1700 | 15,600 ± 206 | 23,300–29,500 |
| CaCO3 | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | NA | 7250 | 21,500 | 4950 | 2420 | 9650 | 4940 | NA | NA | 24,000–30,000 |
| NH4+ | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | NA | 922 | 5210 | 940 | 435 | 1550 | 1160 | NA | 321 ± 68.0 | 2250–2550 |
| Norg | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 340–390 |
| PO43- | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5.00 | 32.0 | 8.80 | 1.40 | 13.0 | 22.2 | NA | NA | 0.08–71.0 |
| Cl- | mg/L | NA | 180–2260 | 1870–3650 | 1490–21,700 | 1810 | 4900 | 4120 | 1690 | 4630 | 821 | 973 | 11,400 ± 119 | 11,000–28,000 |
| SO42- | mg/L | NA | NA | NA | NA | 676 | NA | 210 | NA | NA | NA | 1.00 | 596 ± 87 | 400–980 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 4140–7770 | 160–1380 | 1300–1400 | NA | 1370 | 3970 | NA | 590 | 2830 | 217 | 429 | NA | 12,500–22,000 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 693– 2610 | 233–410 | 830–1470 | 100–270 | 384 | 24.1 | 140 | 80.0 | 195 | 18.0 | 160 | NA | 530–6620 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 5300–8600 | 354–2300 | 70.0–290 | 130–4000 | 2240 | 15.7 | NA | 105 | 198 | 22.0 | NA | NA | 2320–13300 |
| Zn2+ | mg/L | 0.11–0.23 | 18.8–67.0 | 5.00–10.0 | NA | 17.4 | 0.16 | NA | 0.17 | NA | 0.90 | 1.65 | 0.75 ± 0.24 | <0.01–37.4 |
| Mn2+ | mg/L | 9.25–13.2 | NA | NA | NA | 32.9 | 0.04 | NA | 0.86 | NA | NA | 6.56 | 0.84 ± 0.17 | 0.25–20.6 |
| Fe2+ | mg/L | 134–190 | 4.20–1190 | 47.0–330 | 8.00–870 | 654 | 2.70 | 16.2 | 18.8 | 9.35 | 7.80 | 0.89 | 6.31 ± 1.83 | 9.50–317 |
| Cd2+ | mg/L | <0.002 | NA | NA | NA | 0.02 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.01–0.60 |
| Cr3+ | mg/L | 0.21–0.34 | NA | NA | NA | 0.13 | 2.21 | 1.91 | 0.08 | NA | NA | 0.07 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.21–1.00 |
| Pb2+ | mg/L | <0.04 | 0.00–0.46 | NA | NA | 0.28 | NA | NA | NA | 0.02 | NA | 0.15 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.70–0.86 |
4. Variation of Leachate Quality with Time
5. Practical Implications
6. Conclusions
- The main components of municipal solid waste in Cairo were organics (58–75%) and plastics (19–28%).
- The percentage of organics was higher in the waste disposed of in the landfills examined compared to the dumpsite since landfilling was accompanied by the recycling process that consumes plastics and paper/cardboard components.
- The leachate analyzed at different locations in Cairo contained ammonia concentrations higher than most of the values reported for MSW leachate from other countries. Hence, aerobic biological treatment of leachate with extended aeration is needed.
- The chloride concentration detected in the MSW leachate in Cairo is high but not exceptional. HDPE geomembrane base barrier shall be mandatory in landfills planned in Cairo since it has excellent resistance to chloride diffusibility.
- The high, but not exceptional, COD (23,250–24,570 mg/L) and BOD (3880–4860 mg/L) values of the MSW leachate examined in this study might indicate clogging in the leachate collection system of the two landfills examined. Consequently, the grain size distribution of the leachate collection system used in MSW landfills in Cairo shall be investigated.
- The relatively high concentration of Calcium (8470 mg/L) and magnesium (4260 mg/L) suggests an expected shorter service life for HDPE geomembranes used as baseliners in MSW landfills in Cairo, assuming every other factor is kept the same, compared to values reported in the literature.
- The concentration of the soluble inorganic load, alkalinity, and COD of an MSW leachate in Cairo increased with time. For instance, the concentration of chloride for the two-year-age leachate analyzed was 325 ppm compared to 11,000 ppm for the sixteen-year-old specimen.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monavari, S.M.; Omrani, G.A.; Karbassi, A.; Raof, F.F. The effects of socioeconomic parameters on household solid-waste generation and composition in developing countries (a case study: Ahvaz, Iran). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klavenieks, K.; Dzene, K.P.; Blumberga, D. Optimal strategies for municipal solid waste treatment-environmental and socio-economic criteria assessment. Energy Procedia 2017, 128, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z. The impacts of social interaction-based factors on household waste-related behav-iors. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gounaris, V.; Anderson, P.R.; Holsen, T.M. Characteristics and environmental significance of colloids in landfill leachate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, P.; Barlaz, M.A.; Rooker, A.P.; Baun, A.; Ledin, A.; Christensen, T.H. Present and Long-Term Composition of MSW Landfill Leachate: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 32, 297–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, S.; Negi, P.; Khaiwal, R. Assessment of groundwater pollution by landfills in India using leachate pollution index and estimation of error. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 10, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.M.; Alfaia, R.G.D.S.M.; Campos, J.C. Landfill leachate treatment in Brazil–An overview. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.; Millar, G.J.; Altaee, A. Process design of a treatment system to reduce conductivity and ammoniacal ni-trogen content of landfill leachate. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrig, H.-J. Water and Element Balances of Landfills; The landfill: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 83–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Abdelaal, F.B.; Islam, M.Z. Aging of High-Density Polyethylene Geomembranes of Three Different Thicknesses. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, D.R.; McCreanor, P.T.; Townsend, T. The bioreactor landfill: Its status and future. Waste Manag. Res. J. A Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2002, 20, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K. Protecting the Environment with Geosynthetics: 53rd Karl Terzaghi Lecture. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T. Sanitary Landfilling: Process, Technology and Environmental Impact; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Damgaard, A.; Lü, F.; Shao, L.-M.; Brogaard, L.K.-S.; He, P.-J. Environmental impact assessment on the construction and operation of municipal solid waste sanitary landfills in developing countries: China case study. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khalil, C.; Al Hageh, C.; Korfali, S.; Khnayzer, R.S. Municipal leachates health risks: Chemical and cytotoxicity assessment from regulated and unregulated municipal dumpsites in Lebanon. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadder, S.; Prabhakar, R.; Khan, D.; Kishan, D.; Chauhan, M. Analysis of the contaminants released from municipal solid waste landfill site: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, J.L.; Yesiller, N.; Von Stockhausen, S.A.; Wong, W.W. Compaction characteristics of municipal solid waste. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2010, 136, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pohland, F.G. Landfill bioreactors: Fundamentals and practice. Water Qual. Int. 1996, 9, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Pohland, F.G.; Kim, J.C. In situ anaerobic treatment of leachate in landfill bioreactors. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P.M. Plastics recycling and waste management in the US. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2000, 28, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Lettieri, P.; Baeyens, J. Recycling and recovery routes of plastic solid waste (PSW): A review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2625–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaert, K.; Delva, L.; Van Geem, K. Mechanical and chemical recycling of solid plastic waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 24–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finstein, M.S.; Morris, M.L. Microbiology of Municipal Solid Waste Composting. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 19, 113–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamoda, M.; Abu Qdais, H.; Newham, J. Evaluation of municipal solid waste composting kinetics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 1998, 23, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, M.; Jones, D.L. Critical evaluation of municipal solid waste composting and potential compost mar-kets. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4301–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, L.F.; Savage, G.M.; Eggerth, L.L.; Golueke, C.G. Composting and Recycling: Municipal Solid Waste; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Waste Incineration and Public Health; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Sabbas, T.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Astrup, T.; Hjelmar, O.; Mostbauer, P.; Cappai, G.; Magel, G.; Salhofer, S.; Speiser, C.; et al. Management of municipal solid waste incineration residues. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelmar, O. Disposal strategies for municipal solid waste incineration residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 1996, 47, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, A.; Mahmood, A.; Aziz, H.A. Current practice of solid waste management in malaysia and its disposal. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2007, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; López-Acevedo, M. Zinc levels in vineyard soils from the Alt Penedès-Anoia region (NE Spain) after compost application. Adv. Environ. Res. 2004, 8, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, E.; Barton, J.; Stentiford, E. Sources and levels of potentially toxic elements in the biodegradable fraction of autoclaved non-segregated household waste and its compost/digestate. Waste Manag. Res. J. Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2008, 26, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, M.; Masaguer, A.; Moliner, A.; Arrigo, N.; Palma, R.M. Chemical and microbiological parameters for the characterisation of the stability and maturity of pruning waste compost. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 37, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, 312, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Elagroudy, S.; Warith, M.A.; El Zayat, M. Municipal Solid Waste Management and Green Economy; Global Young Academy: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, N.A.; El-Ata, G.A.A.; El-Hattab, M.M. Status, Problems and Challenges for Municipal Solid Waste Management in Assiut Governate. J. Environ. Stud. Res. 2020, 10, 362–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEAA. Environment Quality Report; Egyptian Environmental Agency: Cairo, Egypt, 2017.
- ASTM Committee D-34 on Waste Management. Standard Test Method for Determination of the Composition of Unprocessed Municipal Solid Waste; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, M.; Arab, M.; Shabib, A.; El-Sherbiny, R.; El-Sheltawy, S. Characterization and sustainable management strategies of municipal solid waste in Egypt. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comere, E. The Evolving Ton and the Circular Economy, 2016. Available online: https://www.environmentalleader.com/2016/06/the-evolving-ton-and-the-circular-economy (accessed on 22 September 2022).
- Smith, K.K.; Tonjes, D.J. The evolving ton [Conference presentation]. In Proceedings of the NY Annual Solid Waste & Recycling Conference, New York, NY, USA, 23 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; He, D.; Pan, X. Recent advances in municipal landfill leachate: A review focusing on its characteristics, treatment, and toxicity assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 703, 135468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K. Leachate characteristics for MSW landfills. In Proceedings of the Sardinia 95, 5th International Landfill Sympo-sium, S. Margherita di Pula, Cagliari, Italy, 2–6 October 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, R.K.; Yu, Y. A practical technique for estimating service life of MSW leachate collection systems. Can. Geotech. J. 2013, 50, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Pacheco, M.; Ciríaco, L.; Lopes, A. Review on the electrochemical processes for the treatment of sanitary landfill leachates: Present and future. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2015, 176–177, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, H.D. A Review of the Composition of Leachates from Domestic Wastes in Landfill Sites; Department of the Environment. Wastes Technical Division: London, UK, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, K.; Ghoshdastidar, A.J.; Hanmore, J.; Frazee, J.; Tong, A.Z. Membrane bioreactor technology: A novel ap-proach to the treatment of compost leachate. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2188–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canziani, R.; Emondi, V.; Garavaglia, M.; Malpei, F.; Pasinetti, E.; Buttiglieri, G. Effect of oxygen concentration on biological nitrification and microbial kinetics in a cross-flow membrane bioreactor (MBR) and moving-bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) treating old landfill leachate. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 286, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Vigil, S.A. Integrated solid waste management: Engineering principles and management issues. Water Sci. Technol. Libr. 2000, 8, 63–90. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, S.Q.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Bashir, M.J.; Umar, M. Leachate characterization in semi-aerobic and anaerobic sanitary landfills: A comparative study. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2608–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wabel, M.; Al Yehya, W.; Al-Farraj, A.; El-Maghraby, S. Characteristics of landfill leachates and bio-solids of municipal solid waste (MSW) in Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2011, 10, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Salam, M.M.A.; Abu-Zuid, G.I. Impact of landfill leachate on the groundwater quality: A case study in Egypt. J. Adv. Res. 2014, 6, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brune, M.; Ramke, H.G.; Collins, H.J.; Hanert, H.H. Incrustation processes in drainage systems of sanitary landfills. In Proceedings of the 3rd Int. Landfill Symp., Cagliari, Italy, 14–18 October 1991; pp. 999–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Kiely, G. Environmental Engineering; Tata McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Raju, N.J.; RamaKrishna, C. Assessment of the effect of landfill leachate irrigation of different doses on wheat plant growth and harvest index: A laboratory simulation study. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 8, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Q.; Tian, B.-H.; Zhang, X.; Ghulam, A.; Fang, C.-R.; He, R. Investigation on characteristics of leachate and concentrated leachate in three landfill leachate treatment plants. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajoo, K.S.; Karam, D.S.; Ismail, A.; Arifin, A. Evaluating the leachate contamination impact of landfills and open dumpsites from developing countries using the proposed Leachate Pollution Index for Developing Countries (LPIDC). Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-J.; Shu, H.-Y.; Yang, H.-S.; Chen, W.-C. Characteristics of landfill leachates in central Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 361, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.M.; Cheung, K.C.; Wong, M.H. Variations in the chemical properties of landfill leachate. Environ. Manag. 1994, 18, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yaqout, A.; Hamoda, M. Evaluation of landfill leachate in arid climate—a case study. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, Z.; Hamouri, K.; Djemaa, R.; Allia, K. Evaluation of landfill leachate pollution and treat-ment. Desalination 2008, 220, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.; Pagano, M.; Volpe, A.; Di Pinto, A.C. Fenton’s pre-treatment of mature landfill leach-ate. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsi, A.; Zouboulis, A.; Matis, K.; Samaras, P. Coagulation–flocculation pretreatment of sanitary landfill leachates. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, H. The composition of leachates from very large landfills: An international review. Commun. Waste Resour. Manag. 2007, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Eid, M.M.; Abdelrahman, M.T.; Abdel-Aal, F.M.B. Sand bentonite mixture as a secondary liner in landfills. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering (Volumes 1, 2, 3 and 4), Alexandria, Egypt, 5–9 October 2009; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 225–228. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, H.J. Influences of Recycling Household Refuse upon Sanitary Landfills. 1991. Available online: https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10014712525/ (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Booker, J.; Brachman, R.; Quigley, R.; Rowe, R.K. Barrier Systems for Waste Disposal Facilities; Crc Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Flórez, E.; Cardona-Gallo, S.-A. Technologies applicable to the removal of heavy metals from landfill leachate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 15725–15753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Alappat, B.J. Evaluating leachate contamination potential of landfill sites using leachate pollution in-dex. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2005, 7, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copa, W.M.; Vollstedt, T.J.; Brown, S.J. Anaerobic and aerobic treatment technologies for leachate. In Landfill Closures-Environmental Protection and Land Recovery Session; ASCE Convention: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Jokela, J.; Kettunen, R.; Sormunen, K.; Rintala, J. Biological nitrogen removal from municipal landfill leachate: Low-cost nitrification in biofilters and laboratory scale in-situ denitrification. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4079–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.; Lo, W.; Chan, G. Physico-chemical treatments for removal of recalcitrant contaminants from landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, R.K.; Jefferis, S. Protecting the environment from contamination with barrier systems: Advances and chal-lenges, State-of-the-Art Lecture. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Sydney, Australia, 1–5 May 2022; pp. 187–293. [Google Scholar]
- Belevi, H.; Baccini, P. Long-term behavior of municipal solid waste landfills. Waste Manag. Res. 1989, 7, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheirs, J. A Guide to Polymeric Geomembranes: A Practical Approach. John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelaal, F.B.; Rowe, R.K.; Islam, M.Z. Effect of leachate composition on the long-term performance of a HDPE geomembrane. Geotext. Geomembr. 2014, 42, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Islam, M.Z.; Hsuan, Y.G. Leachate chemical composition effects on OIT depletion in an HDPE ge-omembrane. Geosynth. Int. 2008, 15, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowe, R.; Rimal, S.; Sangam, H. Ageing of HDPE geomembrane exposed to air, water and leachate at different temperatures. Geotext. Geomembr. 2008, 27, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewais, A.; Rowe, R.K.; Scheirs, J. Degradation behaviour of HDPE geomembranes with high and low initial high-pressure oxidative induction time. Geotext. Geomembr. 2014, 42, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewais, A.; Rowe, R.K. Effect of aging on the stress crack resistance of an HDPE geomembrane. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 109, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.S.; Rowe, R.K.; Brandon, T.L.; Valentine, R.J. Performance of Blended Polyolefin Geomembrane in Various Incubation Media Based on Std-OIT. Geotech. Front. 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Morsy, M.S.; Ewais, A. Representative stress crack resistance of polyolefin geomembranes used in waste management. Waste Manag. 2019, 100, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsy, M.S.; Rowe, R.K. Effect of texturing on the longevity of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) geomembranes in municipal solid waste landfills. Can. Geotech. J. 2020, 57, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Abdelaal, F.B.; Zafari, M.; Morsy, M.S.; Priyanto, D. An approach to high-density polyethylene (HDPE) geomembrane selection for challenging design requirements. Can. Geotech. J. 2020, 57, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.S.; Rowe, R.K.; Abdelaal, F. Longevity of 12 geomembranes in chlorinated water. Can. Geotech. J. 2021, 58, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrapovic, L. Laboratory Study of Intrinsic Degradation of Organic Pollutants in Compacted Clayey Soil. Faculty of Graduate Studies, University of Western Ontario: Ontario, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sangam, H.P.; Rowe, R.K. Effects of exposure conditions on the depletion of antioxidants from high-density poly-ethylene (HDPE) geomembranes. Can. Geotech. J. 2002, 39, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Armstrong, M.D.; Cullimore, D.R. Particle Size and Clogging of Granular Media Permeated with Leachate. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2000, 126, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, G.R.; Koerner, R.M.; Martin, J.P. Design of Landfill Leachate-Collection Filters. J. Geotech. Eng. 1994, 120, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Waste Composition a (%) | Northern & Eastern Cairo a | Southern & Western Cairo b | Giza c | Average Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organics | 71 ± 3.4 | 60± 2.9 | 61 ± 2.8 | 64 ± 3.0 |
| Plastics | 15 ± 1.7 | 25 ±2.8 | 25 ± 2.3 | 21 ± 2.3 |
| Textiles | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 7.4 ± 2.4 | 4.1 ± 1.1 |
| Paper & Cardboard | 4.0 ± 1.4 | 4.9 ± 1.7 | 3.1 ± 0.6 | 4.0 ± 1.2 |
| Diapers | 6.1 ± 2.6 | 7.5 ± 3.2 | 2.6 ± 0.8 | 5.4 ± 2.2 |
| Wood | 0.6 ± 1.1 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 1.4 | 0.6 ± 0.8 |
| Metals | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 0.4 ± 0.4 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.3 |
| Glass | 1.0 ± 1.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.5 | 0.5 ± 0.5 |
| Waste Composition a (%) | Source | Transfer Station | Recycling Plant | Landfill (El-Obour Landfill) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organics | 71 ± 3.4 | 63 ± 5.4 | 65 ± 3.4 | 75 ± 4.4 |
| Plastics | 15 ± 1.7 | 23 ± 6.5 | 17 ± 5.0 | 20 ± 3.6 |
| Textiles | 2.5 ± 0.4 | 3.9 ± 2.0 | 6.0 ± 7.0 | 5.2 ± 5.2 |
| Paper & Cardboard | 4.0 ± 1.4 | 3.3 ± 1.2 | 1.4 ± 1.4 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Diapers | 6.1 ± 2.6 | 5.3 ± 1.4 | 8.1 ± 4.0 | 0.2 ± 0.3 |
| Wood | 0.6 ± 1.1 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 2.3 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Metals | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.8 ± 0.8 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Glass | 1.0 ± 1.0 | 1.6 ± 1.4 | 0.9 ± 1.1 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Waste Composition a (%) | Source | Recycling Plant | Landfill b (15th May Landfill) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organics | 61 ± 2.9 | 74 ± 0.8 | 71 ± 7.3 |
| Plastics | 25 ± 2.8 | 19 ± 1.5 | 19 ± 5.9 |
| Textiles | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 0.7 ± 1.1 | 6.2 ± 5.7 |
| Paper & Cardboard | 4.9 ± 1.7 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Diapers | 7.5 ± 3.2 | 3.4 ± 1.4 | 4.1 ± 3.9 |
| Wood | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.7 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Metals | 0.4 ± 0.4 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Glass | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Waste Composition a (%) | Source | Dumpsite b |
|---|---|---|
| Organics | 61 ± 2.8 | 58 ± 7.1 |
| Plastics | 25 ± 2.3 | 28 ± 6.6 |
| Textiles | 7.4 ± 2.4 | 4.2 ± 1.4 |
| Paper & Cardboard | 3.1 ± 0.6 | 3.2 ± 1.2 |
| Diapers | 2.6 ± 0.8 | 1.9 ± 1.9 |
| Wood | 1.0 ± 1.4 | 1.1 ± 1.9 |
| Metals | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 0.6 ± 0.5 |
| Glass | 0.5 ± 0.5 | 2.7 ± 1.2 |
| Parameter | Unit | Giza (Shabramant Dumpsite) a | Southern & Western Cairo Landfill (15th May Landfill) b | Northern & Eastern Cairo (El-Wafaa & El-amal Landfill) c | Range d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | mg/L | 29,500 ± 1470 | 24,600 ± 1230 | 23,300 ± 1160 | 23,300–29,500 |
| BOD | mg/L | 4530 ± 1380 | 3880 ± 660 | 4860 ± 830 | 3880–4860 |
| pH | - | 6.14 ± 0.06 | 6.30 ± 0.06 | 8.14 ± 0.08 | 6.14–8.14 |
| TFA | mg/L | 1.98 ± 0.10 | 1.74 ± 0.09 | 1.45 ± 0.07 | 1.45–1.98 |
| TDS | mg/L | 72,600 ± 4360 | 88,700 ± 5320 | 45,800 ± 2750 | 45,800–88,700 |
| NH4+ | mg/L | 2460 ± 120 | 2550 ± 130 | 2250 ± 110 | 2250–2550 |
| Norg | mg/L | 390 ± 20.0 | 380 ± 20.0 | 340 ± 20.0 | 340–390 |
| CaCO3 | mg/L | 26,000 ± 1300 | 30,000 ± 1500 | 24,000 ± 1200 | 24,000–30,000 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 18,900 ± 380 | 22,000 ± 440 | 12,500 ± 250 | 12,500–22,000 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 9800 ± 490 | 133,00 ± 660 | 2320 ± 120 | 2320–13,300 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 6620 ± 130 | 5640 ± 110 | 530 ± 10.0 | 530–6620 |
| Mn2+ | mg/L | 20.6 ± 0.41 | 9.90 ± 0.20 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 0.25–20.6 |
| Fe2+ | mg/L | 317 ± 6.34 | 129 ± 2.58 | 9.50 ± 0.19 | 9.50–317 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 14,000 ± 700 | 28,000 ± 1400 | 11,000 ± 550 | 11,000–28,000 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 400 ± 10.0 | 980 ± 20.0 | 770 ± 20.0 | 400–980 |
| PO43− | mg/L | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 71.0 ± 1.42 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.08–71.0 |
| Cr3+ | mg/L | 1.00 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.00 | 0.89 ± 0.02 | 0.21–1.00 |
| Cd2+ | mg/L | 0.60 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.01–0.60 |
| Pb2+ | mg/L | 0.70 ± 0.01 | 0.80 ± 0.02 | 0.86 ± 0.02 | 0.70–0.86 |
| Zn2+ | mg/L | 37.4 ± 0.75 | 0.50 ± 0.01 | <0.01 b | <0.01–37.4 |
| Parameter | Units | 2006 a (LCS) | 2020 b (Sump) |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD | mg/L | 7350 | 23,300 ± 1160 |
| BOD5 | mg/L | 18.6 | 4900 ± 830 |
| pH | - | 8.10 | 8.90 ± 0.08 |
| TFA | mg/L | NA | 1.45 |
| TS | mg/L | NA | 45,800 |
| TDS | mg/L | 32,900 | 54,000 |
| Norg | mg/L | NA | 340 ± 20 |
| NH4+ | mg/L | 12,100 | 2300 ± 110 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 301 | 12,500 ± 250 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 137 | 2300 ± 120 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 104 | 530 ± 10 |
| Mn2+ | mg/L | NA | 0.25 ± 0.01 |
| Fe2+ | mg/L | NA | 9.50 ± 0.19 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 325 | 11,000 ± 550 |
| SO42− | mg/L | NA | 770 ±20 |
| TA | mg/L | NA | 24,000 ± 1200 |
| PO43− | mg/L | 33.5 | 80.0 ± 0.0 |
| Cr3+ | mg/L | 2.26 | 890 ± 20 |
| Cd2+ | mg/L | NA | 10.0 ± 0.00 |
| Pb2+ | mg/L | 855 | 860 ± 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussieny, M.A.; Morsy, M.S.; Ahmed, M.; Elagroudy, S.; Abdelrazik, M.H. Municipal Solid Waste and Leachate Characterization in the Cairo Metropolitan Area. Resources 2022, 11, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources11110102
Hussieny MA, Morsy MS, Ahmed M, Elagroudy S, Abdelrazik MH. Municipal Solid Waste and Leachate Characterization in the Cairo Metropolitan Area. Resources. 2022; 11(11):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources11110102
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussieny, Maged A., Mohamed S. Morsy, Mostafa Ahmed, Sherien Elagroudy, and Mohamed H. Abdelrazik. 2022. "Municipal Solid Waste and Leachate Characterization in the Cairo Metropolitan Area" Resources 11, no. 11: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources11110102
APA StyleHussieny, M. A., Morsy, M. S., Ahmed, M., Elagroudy, S., & Abdelrazik, M. H. (2022). Municipal Solid Waste and Leachate Characterization in the Cairo Metropolitan Area. Resources, 11(11), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources11110102








