Spring Water Quality in a Flood-Prone Area of Kampala City, Uganda: Insights Furnished by Sanitary and Limnochemical Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area and Choice of the Sampled Springs
2.2. Sanitary Inspection of the Springs
2.3. Water Sampling Protocol
2.4. Determination of Physicochemical Parameters of Water
2.4.1. Non-Conservable Parameters
2.4.2. Turbidity and Total Alkalinity
2.4.3. Nitrate-Nitrogen and Water Hardness
2.4.4. Determination of Sulphates, Phosphates, Fluoride, Sodium, and Potassium Contents
2.5. Assessment of Water Quality
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sanitary Risk Assessment Results
3.2. Temporal Variations in the Hydrochemistry of Spring Water
3.2.1. Electrical Conductivity
3.2.2. pH
3.2.3. Temperature
3.2.4. Turbidity
3.2.5. Total Dissolved Solids and Total Alkalinity
3.2.6. Nitrate-Nitrogen
3.2.7. Magnesium, Calcium, and Total Hardness
3.2.8. Sulphates and Phosphates
3.2.9. Sodium and Potassium Contents
3.2.10. Fluorides and Chlorides
3.2.11. Dissolved Oxygen
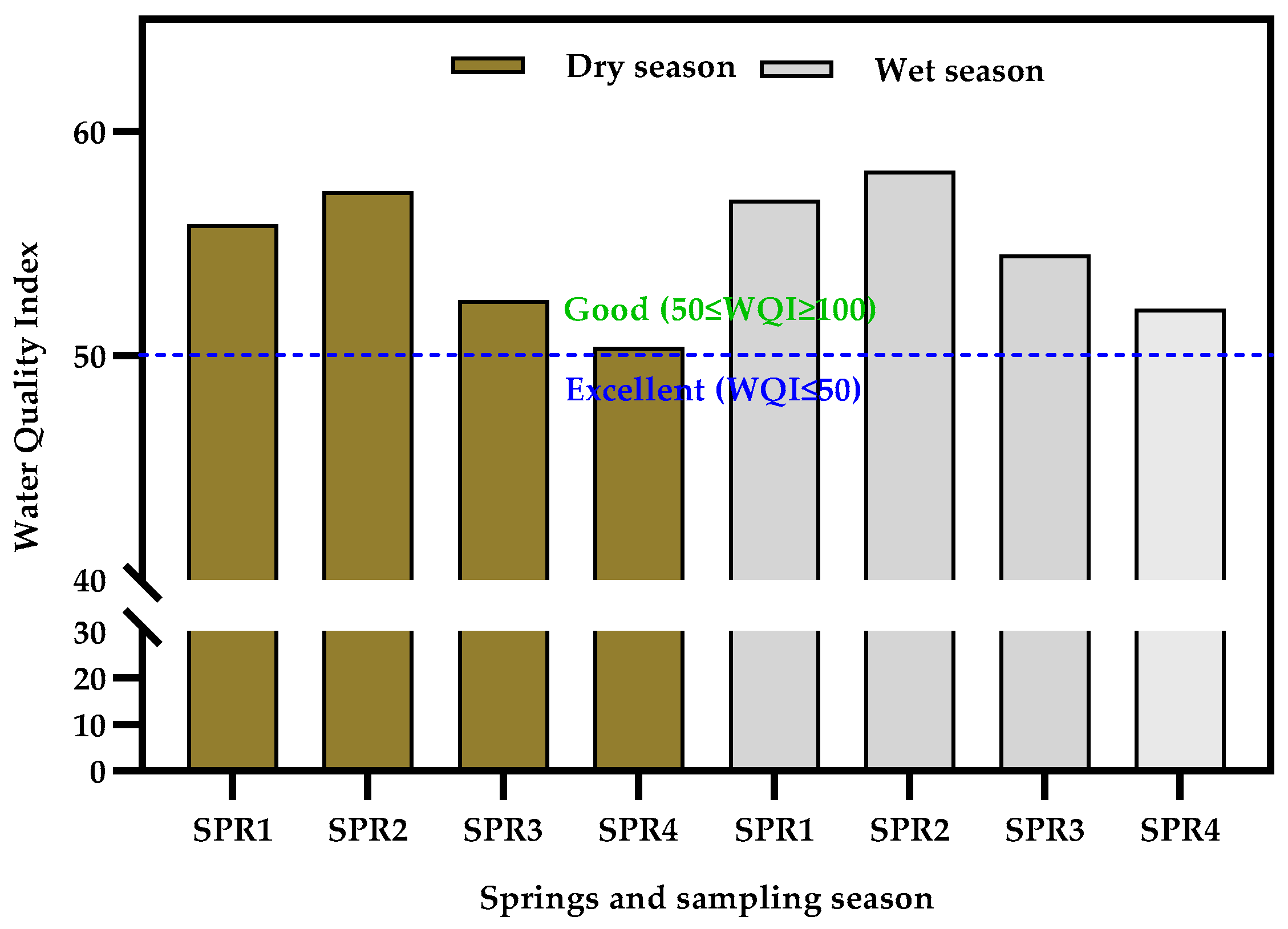
3.3. Water Quality Index of the Springs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Ensuring Safe Water and Sanitation for All: A Solution through Science, Technology and Innovation. Available online: https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/ecn162023d3_en.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- UN Water. Blueprint for Acceleration: Sustainable Development Goal 6 Synthesis Report on Water and Sanitation 2023. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/sites/default/files/2023-08/UN-Water_SDG6_SynthesisReport_2023.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Musie, W.; Gonfa, G. Fresh water resource, scarcity, water salinity challenges and possible remedies: A review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evaristo, J.; Jameel, Y.; Tortajada, C.; Wang, R.Y.; Horne, J.; Neukrug, H.; David, C.P.; Fasnacht, A.M.; Ziegler, A.D.; Biswas, A. Water woes: The institutional challenges in achieving SDG 6. Sustain. Earth Rev. 2023, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Bazin, J.; Strokal, M.; Ma, L.; Kroeze, C. Accounting for interactions between Sustainable Development Goals is essential for water pollution control in China. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Triple Threat. How Disease, Climate Risks, and Unsafe Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Create a Deadly Combination for Children. New York: United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). Available online: https://www.unicef.org/media/137206/file/triple-threat-wash-EN.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Onen, P.; Akemkwene, R.; Nakiguli, C.K.; Nimusiima, D.; Ruma, D.H.; Khanakwa, A.V.; Angiro, C.; Bamanya, G.; Opio, B.; Gonzaga, A.; et al. Health Risks from Intake and Contact with Toxic Metal-Contaminated Water from Pager River, Uganda. J. Xenobiot. 2023, 13, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. Npj Clean Water 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Assessment of Groundwater Challenges & Opportunities in Support of Sustainable Development in Sub-Saharan Africa. Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/420291533931251279/pdf/Assessment-of-groundwater-challenges-and-opportunities-in-Sub-Saharan-Africa.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Bonacci, O.; Roje-Bonacci, T. Water temperature and electrical conductivity as an indicator of karst aquifer: The case of Jadro Spring (Croatia). Carbonates Evaporites 2023, 38, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, A.F.; Husman, A.M.R. Bottled and Drinking Water. In Food Safety Management, 2nd ed.; A Practical Guide for the Food Industry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 339–362. [Google Scholar]
- Cousteau, J. The Value of Water. Available online: https://opac.geologie.ac.at/wwwopacx/wwwopac.ashx?command=getcontent&server=images&value=EGU_Eonder%20Water.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Cantonati, M.; Lichtenwöhrer, K.; Leonhardt, G.; Seifert, L.; Mustoni, A.; Hotzy, R.; Schubert, E.; Blattner, L.; Bilous, O.; Lotz, A.; et al. Using Springs as Sentinels of Climate Change in Nature Parks North and South of the Alps: A Critical Evaluation of Methodological Aspects and Recommendations for Long-Term Monitoring. Water 2022, 14, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkurunziza, G.; Omara, T.; Nakiguli, C.K.; Mukasa, P.; Byamugisha, D.; Ntambi, E. Physicochemical Quality of Water from Chuho Springs, Kisoro District, Uganda. Fr. Ukr. J. Chem. 2021, 9, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June, A.; Mika, S. Metals in kitagata hot springs and water quality effect from Balneotherapy and Hydrotherapy. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2012, 16, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ndiba, J. Facts About African Great Lakes—Summary from the AGLI Website. Available online: https://www.africangreatlakesinform.org/article/facts-about-african-great-lakes-summary-agli-website (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- U.S. Department of State. About the Great Lakes Region. Available online: https://2009-2017.state.gov/s/greatlakes_drc/191417.htm (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Karp, T.; Scholz, C.A.; McGlue, M.M. Structure and stratigraphy of the Lake Albert rift, East Africa: Observations from seismic reflection and gravity data. In Lacustrine Sandstone Reservoirs and Hydrocarbon Systems: AAPG Memoir 95; Baganz, O.W., Bartov, Y., Bohacs, K., Nummedal, D., Eds.; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2012; pp. 299–318. [Google Scholar]
- Penny Africa Safaris. Hot Springs in East Africa. Available online: https://pennyafricasafaris.travel/hot-springs-in-east-africa/ (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Butturini, A.; Amalfitano, S.; Herzsprung, P.; Lechtenfeld, O.J.; Venturi, S.; Olaka, L.A.; Pacini, N.; Harper, D.M.; Tassi, F.; Fazi, S. Dissolved Organic Matter in Continental Hydro-Geothermal Systems: Insights from Two Hot Springs of the East African Rift Valley. Water 2020, 12, 3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, R.; Ejobi, F.; Kabagambe, E.K. The Quality of Water from Protected Springs in Katwe and Kisenyi Parishes, Kampala City, Uganda. Afr. Health Sci. 2005, 5, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uche, C.K.A.; Amgbara, T.O.; Birungi, M.; Taremwa, D. Quality Analysis of Water from Kitagata Hot Springs in Sheema District, Western Region, Uganda. Int. J. Eng. Inform. Syst. 2021, 5, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Omara, T.; Nassazi, W.; Adokorach, M.; Kagoya, S. Physicochemical and Microbiological Quality of Springs in Kyambogo University Propinquity. OALibJ 2019, 6, e5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakyayita, G.K.; Norrström, A.C.; Kulabako, R.N. Assessment of Levels, Speciation, and Toxicity of Trace Metal Contaminants in Selected Shallow Groundwater Sources, Surface Runoff, Wastewater, and Surface Water from Designated Streams in Lake Victoria Basin, Uganda. J. Environ. Public Health 2019, 2019, 6734017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabagyea, A.; Yatuha, J. Physico-chemical Parameters and Species’ Distribution Patterns of Extremophilic Bacteria in Kitagata and Ihimbo Hot Springs in South Western Uganda. Am. Acad. Sci. Res. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2022, 86, 157–173. [Google Scholar]
- Onohuean, H.; Okoh, A.I.; Nwodo, U.U. Epidemiologic potentials and correlational analysis of Vibrio species and virulence toxins from water sources in greater Bushenyi districts, Uganda. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, V.; Kraml, M. Geochemistry of Rwenzori hot spring waters. In Proceedings of the 3rd East African Rift Geothermal Conference, Djibouti, Djibouti, 22–25 November 2010; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Bwire, G.; Sack, D.A.; Kagirita, A.; Obala, T.; Debes, A.K.; Ram, M.; Komakech, H.; George, C.M.; Orach, C.G. The quality of drinking and domestic water from the surface water sources (lakes, rivers, irrigation canals and ponds) and springs in cholera prone communities of Uganda: An analysis of vital physicochemical parameters. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apecu, R.O.; Ampaire, L.; Mulogo, E.M.; Bagenda, F.N.; Traore, A.; Potgieter, N. Quality of water sources in Southwestern Uganda using the compartment bag test (CBT): A cross-sectional descriptive study. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2019, 9, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukubye, B.; Andama, M. Bacterial Analysis of Selected Drinking Water Sources in Mbarara Municipality, Uganda. J. Water Resour. Protect. 2017, 9, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukubye, B.; Andama, M. Physico-Chemical Quality of Selected Drinking Water Sources in Mbarara Municipality, Uganda. J. Water Resour. Protect. 2017, 9, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulodi, S.; Thorsell, J. Evaluation of the Levels of Selected Trace Metal Pollutants in Groundwater and Soil from Protected Springs in Peri-Urban Kampala, Uganda. Master’s Thesis, TRITA-LWR Degree Project 13: 17. Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Stockholm, Sweden, 2013; 56p. [Google Scholar]
- Kiwanuka, M.; Mutanda, H.E.; Niyomukiza, J.B.; Nakasagga, E. Assessment of suitability of drinking water from the springs in Urban slums of Kampala. Environ. Chall. 2023, 10, 100667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okot, J.; Otim, J. The quality of drinking water used by the communities in some regions of Uganda. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2015, 9, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntuwa, R.; Onen, P.; Baguma, G.; Niringiyimana, E.; Byaruhanga, I.; Otema, T.; Ampaire, W.; Ogenrwot, D.A.; Ocira, D. Comparative Analysis of Some Trace Metals in Municipal and Spring Water from Makerere University and Selected Springs in Bunga, Uganda. Asian J. Fish. Aquat. Res. 2022, 18, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsubuga, F.B.; Kansiime, F.; Okot-Okumu, J. Pollution of protected springs in relation to high and low density settlements in Kampala—Uganda. Phys. Chem. Earth 2004, 29, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzanzu, T.; Barasa, J.; Nanyonga, S.K.; Binenwa, J. Water Quality in Selected Water Springs in Banda, Kampala-Uganda. SJHR-Africa 2022, 3, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Kampala City Guide. Kansanga. Available online: https://www.kampalacityguide.com/kampala-city/makindye/kansanga.html (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- The Independent. The Ghost Flood Villages of Kansanga. Available online: https://www.independent.co.ug/the-ghost-flood-villages-of-kansanga/ (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- James, M.K. Effects of Poor Sanitation Management on the Urban Population in Uganda: The Case of Kansanga Parish, Makindye Division, Kampala, Central Uganda. Bachelor’s Thesis, Kampala International University, Kampala, Uganda, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Akugizibwe, I. KIU General News: Water Crisis Hits Kansanga. Available online: https://kiu.ac.ug/news-page.php?i=kiu-general-news-water-crisis-hits-kansanga (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- WHO. Sanitary Inspection Package (Drinking-Water): Spring. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/wash-documents/water-safety-and-quality/water-safety-planning/sanitary-inspection-packages/3.-spring_web.pdf?sfvrsn=378469bb_5 (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; Rice, E.W., Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Omara, T.; Nteziyaremye, P.; Akaganyira, S.; Opio, D.W.; Karanja, L.N.; Nyangena, D.M.; Kiptui, B.J.; Ogwang, R.; Epiaka, S.M.; Jepchirchir, A.; et al. Physicochemical quality of water and health risks associated with consumption of African lung fish (Protopterus annectens) from Nyabarongo and Nyabugogo rivers, Rwanda. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimusiima, D.; Byamugisha, D.; Omara, T.; Ntambi, E. Physicochemical and Microbial Quality of Water from the Ugandan Stretch of the Kagera Transboundary River. Limnol. Rev. 2023, 23, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanadhia, K.C.; Ramavataram, D.V.; Nilakhe, S.P.; Patel, S. A study of water hardness and the prevalence of hypomagnesaemia and hypocalcaemia in healthy subjects of Surat district (Gujarat). Magnes. Res. 2014, 27, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangiah, A.S. Spectrophotometric determination of sulphate and nitrate in drinking water at Asia-Pacific International University Campus, Muak Lek, Thailand. Rasayan J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadeniz, S.; Ustaoğlu, F.; Aydın, H. Toxicological risk assessment using spring water quality indices in plateaus of Giresun Province/Türkiye: A holistic hydrogeochemical data analysis. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 38, pp. 1–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukisa, W.; Yatuha, J.; Andama, M.; Aventino, K. Heavy metal pollution in the main rivers of Rwenzori region, Kasese district South-western Uganda. Octa J. Environ. Res. 2020, 8, 78–90. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/352532/9789240045064-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Elambo, G.N.; Kinyuy, B.L.; Martel, J.; Aghaindum, A.G. An appraisal of some water ressources in the city of Yaoundé (Cameroon): Water adduction potentialities, physico-chemistry and consequent eco-sanitary repercussions. CJBBS 2020, 28, 67–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanem, M.; Jebreen, H.; Sege, J.; Rubin, Y. Investigation of spring water quality in the Natuv catchment, Palestine: A component for the regional environmental management system. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2019, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, G.; Kubiniok, J. Spring waters as an indicator of nitrate and pesticide pollution of rural watercourses from nonpoint sources: Results of repeated monitoring campaigns since the early 2000s in the low mountain landscape of Saarland, Germany. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmedenov, K.M.; Idrisova, G.Z. The importance of springs, self-flowing artesian wells, underground cave lakes of Western Kazakhstan in tourism. Geo. J. Tourism. Geosites 2021, 37, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; Liu, J. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of spring water in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Southwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 2061–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Tufail, M.; Ayaz, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Lei, M. Groundwater quality assessment and its vulnerability to pollution: A study of district Nowshera, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Available online: https://iris.who.int/rest/bitstreams/907844/retrieve (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- EPA 822-F-18-001; 2018 Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories Tables. United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 9–19.
- Ward, M.H.; Jones, R.R.; Brender, J.D.; De Kok, T.M.; Weyer, P.J.; Nolan, B.T.; Villanueva, C.M.; Van Breda, S.G. Drinking Water Nitrate and Human Health: An Updated Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, N.H. Water Quality Parameters. In Water Quality—Science, Assessments and Policy; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Water Stewardship Information Series. Hardness in Groundwater. Available online: https://www.rdn.bc.ca/cms/wpattachments/wpID2284atID3802.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Pantha, S.; Timilsina, S.; Pantha, S.; Manjan, S.K.; Maharjan, M. Water quality index of springs in mid-hill of Nepal. Environ. Challenges 2022, 9, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonorova, I.; Ilyin, V.; Ilyina, A.; Nikitin, A. Increasing the ecological and recreational importance of the springs of the Chuvash Republic. BIO Web Conf. 2024, 116, 03013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, L.C. Assessing the acute gastrointestinal effects of ingesting naturally occurring, high levels of sulfate in drinking water. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2000, 37, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Water Research Center. Phosphate in Surface Water Streams, Lakes, and Ponds. Available online: https://www.knowyourh2o.com/outdoor-4/phosphate-in-surface-water-streams-lakes-ponds#google_vignette (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Macheyeki, A.S.; Kafumu, D.P. Hydrogeological (water) resources. In The East African Rift System. Geodynamics and Natural Resource Potentials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 241–296. [Google Scholar]
- Umer, M.F. A Systematic Review on Water Fluoride Levels Causing Dental Fluorosis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.U.; Nisa, A.U.; Sabha, I.; Mondal, N.C. Spring water quality assessment of Anantnag district of Kashmir Himalaya: Towards understanding the looming threats to spring ecosystem services. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikeogu, T.C.; Okeke, O.C.; Ogbekhiulu, L.O.; Ogbenna, P.C. Major ion chemistry and hydrochemical processes of Ngeneagu spring water at Akpugoeze, Oji river, Enugu, southeastern Nigeria. J. Adv. Acad. Res. 2018, 4, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Isunju, J.B.; Orach, C.G.; Kemp, J. Hazards and vulnerabilities among informal wetland communities in Kampala, Uganda. Environ. Urban 2016, 28, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

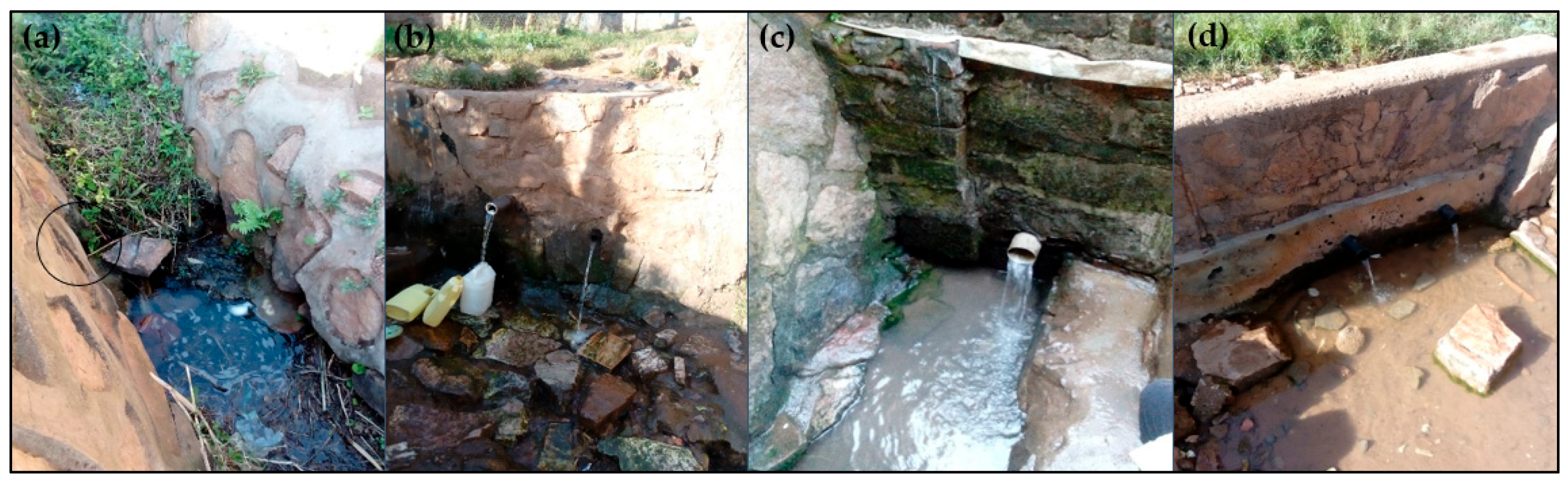
| Spring | Potential Risks Noted a | Risk Score (%) | Aggregate Risk Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPR1 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 9, 10 | 60 | High |
| SPR2 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 10 | 70 | High |
| SPR3 | 2, 3, 4, 9, 10 | 50 | Medium |
| SPR4 | 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10 | 60 | High |
| Parameter | SPR1 | SPR2 | SPR3 | SPR4 | WHO Guidelines [51] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity (µS/cm) | 233 ± 0.82 (231 ± 0.74) | 285 ± 1.50 (288 ± 3.14) | 220 ± 0.81 (221 ± 1.32) | 198 ± 0.77 (199 ± 1.30) | 1500 | 0.000 ** (0.000**) |
| pH | 6.10 ± 0.02 (6.30 ± 0.01) | 6.15 ± 0.31 (6.00 ± 0.05) | 6.13 ± 0.01 (6.10 ± 0.03) | 6.02 ± 0.15 (6.01 ± 0.04) | — | 0.746 (0.430) |
| ) | 23.0 ± 0.85 (22.4 ± 0.65) | 22.9 ± 1.20 (22.4 ± 0.75) | 22.7 ± 0.60 (22.3 ± 0.53) | 22.8 ± 0.25 (22.5 ± 0.51) | — | 0.847 (0.962) |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 3.2 ± 0.25 (3.8 ± 0.03) | 3.4 ± 0.30 (3.9 ± 0.42) | 3.3 ± 0.02 (3.7 ± 0.31) | 3.4 ± 0.20 (3.9 ± 0.25) | 5 | 0.501 (0.474) |
| Total alkalinity (mg/L) | 38.00 ± 0.35 (36.50 ± 0.77) | 5.10 ± 0.30 (3.81 ± 0.62) | 38.00 ± 0.42 (35.92 ± 0.40) | 34.00 ± 0.25 (32.63 ± 0.41) | 200 | 0.000 ** (0.000 **) |
| Total dissolved solids (mg/L) | 90.20 ± 0.38 (90.60 ± 0.41) | 90.40 ± 0.25 (90.60 ± 0.40) | 89.70 ± 0.35 (90.00 ± 0.31) | 89.90 ± 0.20 (90.10 ± 0.40) | 1000 | 0.040 (0.315) |
| Nitrate-nitrogen (mg/L) | 30.89 ± 0.05 (38.60 ± 0.15) | 30.63 ± 0.04 (31.31 ± 0.04) | 17.00 ± 0.06 (20.00 ± 050) | 5.14 ± 0.04 (5.80 ± 0.03) | 10 | 0.410 (0.000 **) |
| Total hardness (mg/L) | 75.00 ± 0.30 (76.30 ± 0.51) | 110.00 ± 0.76 (111.00 ± 0.65) | 83.20 ± 0.40 (84.00 ± 1.21) | 48.20 ± 0.52 (49.61 ± 0.53) | 500 | 0.000 ** (0.000 **) |
| Calcium hardness (mg/L) | 43.00 ± 0.25 (44.70 ± 0.64) | 60.10 ± 0.22 (61.80 ± 0.52) | 51.10 ± 0.52 (51.80 ± 0.25) | 30.00 ± 0.48 (32.20 ± 0.32) | 150 | 0.000 **(0.000 **) |
| Magnesium hardness (mg/L) | 32.00 ± 0.58 (33.30 ± 0.78) | 50.00 ± 0.68 (52.10 ± 0.62) | 32.00 ± 0.40 (33.90 ± 0.22) | 18.00 ± 0.20 (20.10 ± 0.01) | 250 | 0.000 ** (0.000 **) |
| Sulphates (mg/L) | 13.50 ± 0.30 (13.90 ± 0.20) | 33.20 ± 0.21 (33.70 ± 0.90) | 19.00 ± 0.29 (19.30 ± 0.40) | 15.00 ± 0.50 (15.10 ± 0.25) | — | 0.000 * (0.000 **) |
| Total phosphorus (mg/L) | 0.23 ± 0.00 (0.07 ± 0.01) | 0.05 ± 0.01 (0.02 ± 0.01) | 0.05 ± 0.01 (0.02 ± 0.01) | 0.05 ± 0.01 (0.03 ± 0.02) | — | 0.000 ** (0.006 *) |
| Sodium (mg/L) | 23.00 ± 0.05 (23.50 ± 0.04) | 48.20 ± 0.03 (49.10 ± 0.35) | 26.20 ± 0.24 (26.80 ± 0.45) | 17.20 ± 0.04 (17.51 ± 0.05) | 200 | 0.000 ** (0.000 **) |
| Potassium (mg/L) | 6.80 ± 0.01 (7.00 ± 0.25) | 22.00 ± 0.02 (22.80 ± 0.04) | 8.10 ± 0.01 (8.50 ± 0.05) | 4.20 ± 0.03 (4.30 ± 0.06) | 12 | 0.000 ** (0.000 **) |
| Fluorides (mg/L) | 0.29 ± 0.02 (0.28 ± 0.01) | 0.17 ± 0.02 (0.17 ± 0.01) | 0.16 ± 0.03 (0.15 ± 0.02) | 0.39 ± 0.01 (0.39 ± 0.01) | 1.5 | 0.004 * (0.012) |
| Chlorides (mg/L) | 28.80 ± 0.50 (31.70 ± 0.41) | 61.20 ± 0.48 (62.80 ± 0.45) | 25.50 ± 0.55 (27.20 ± 0.31) | 18.00 ± 0.45 (20.10 ± 0.35) | 250 | 0.000 ** (0.000 **) |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) | 5.68 ± 0.18 (5.55 ± 0.21) | 5.70 ± 0.20 (5.80 ± 0.31) | 5.90 ± 0.21 (6.00 ± 0.22) | 6.20 ± 0.35 (6.00 ± 0.35) | 4 | 0.822 (0.657) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tenywa, R.; Omara, T.; Kwikiriza, G.; Angiro, C.; Ntambi, E. Spring Water Quality in a Flood-Prone Area of Kampala City, Uganda: Insights Furnished by Sanitary and Limnochemical Data. Resources 2024, 13, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13100133
Tenywa R, Omara T, Kwikiriza G, Angiro C, Ntambi E. Spring Water Quality in a Flood-Prone Area of Kampala City, Uganda: Insights Furnished by Sanitary and Limnochemical Data. Resources. 2024; 13(10):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13100133
Chicago/Turabian StyleTenywa, Ronald, Timothy Omara, Gerald Kwikiriza, Christopher Angiro, and Emmanuel Ntambi. 2024. "Spring Water Quality in a Flood-Prone Area of Kampala City, Uganda: Insights Furnished by Sanitary and Limnochemical Data" Resources 13, no. 10: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13100133
APA StyleTenywa, R., Omara, T., Kwikiriza, G., Angiro, C., & Ntambi, E. (2024). Spring Water Quality in a Flood-Prone Area of Kampala City, Uganda: Insights Furnished by Sanitary and Limnochemical Data. Resources, 13(10), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13100133









