1. Introduction
Common reed (
Phragmites australis) is one of the most widespread plants in the world and populates wetlands of various kinds [
1]. Since time immemorial, people made use of different parts of the plant as well as of the reedbed itself [
2]. A wide range of historical uses up to services appreciated only recently is described by Haslam [
2], Kiviat [
3], and Köbbing et al. [
4]. While reed is an important resource for the pulp and paper industry in China [
5,
6], in Europe it is appreciated as building material.
The utilization of the long and thin reed culms as roofing material, i.e., for thatching, is one of the best known and most common applications in many European countries. In Germany, evidence for the use of reed for thatching comes from as early as 4000 BC, when the first Neolithic farmers settled at the coastline of the North and Baltic Sea [
7]. Until today, thatched houses are commonly found in the coastal regions of Northern Germany and in regions with many inland lakes where they have a landscape-defining character. The thatcher’s craft is included in the German Inventory of Intangible Cultural Heritage [
8]. Thatched houses are valued for providing a pleasant living climate, for the renewable building material, and for its high aesthetic value [
8,
9]. An average estimate for the durability of a reed thatched roof is 40–50 years with possibly much longer lifetime for the Eastern or Northern side of the roof and very steep roofs [
7]. Single cases of considerably shorter lifetimes are known as early or premature decay and have been described for reed thatched houses at least since the 1970s [
10] but were increasingly observed in Germany at the turn to the 21st century [
11]. The lifetime of a roof is influenced by many factors starting from the quality of the reed, over the construction of the roof up to the maintenance of the thatched roof. Repair work can be necessary from time to time as well as renewing parts especially exposed to wind and weather, like the roof ridge, which needs to be conducted normally every 15–20 years [
12]. Every landscape has a traditional regional building and thatching culture with specific house types, roof shapes, or materials used for the roof ridge, e.g., variations of the Low German house, the Haubarg of the Eiderstedt peninsula, or log houses in the Spreewald [
12]. Today, reed is not only used for rethatching historical monuments but also on newly build (holiday) houses and even for modern architecture, e.g., exploring the use of thatch for covering walls [
13,
14].
Despite its long tradition as locally available roofing material, reed for thatching is nowadays an internationally traded commodity. A first analysis of the European market identified major importing countries (the Netherlands, Germany, the United Kingdom, and Denmark) relying on imports of up to 85% of the national consumption [
15]. One major reason of the low self-supply rate is the decline of reedbeds due to dyke construction, drainage, and cultivation of peatland and marsh land [
12]. Additionally, the remaining reedbeds are defined as legally protected habitat by the Federal Nature Conservation Act in Germany and partly located in designated nature conservation areas. While the use of domestic resources has been increasingly restricted, reed was imported from East and Southeast Europe (e.g., Hungary, Romania) and since 2005 even from China [
15]. The cultivation of reed as agricultural crop might improve the supply with domestic reed.
Common reed is considered as a promising paludicultural plant [
16]. Paludiculture is defined as agriculture and forestry on wet or rewetted peatlands; it combines a productive use with the preservation of the peat body as long-term carbon store [
17]. There is a high need to develop climate smart utilization options for rewetted peatlands. In Germany, drained peatlands encompass only 7% of the agricultural area but emit 37% of the national greenhouse gas emissions of agriculture and agricultural land use; in the EU 3% of the area are responsible for 25% of the emissions [
18]. Being an emergent wetland plant, reed grows well at water levels near surface, which are needed to ensure peat preservation. In addition to reducing a large source of soil born GHG emissions, below-ground biomass may form new peat thus acting as sink for carbon captured from the atmosphere. Comparing three utilization options for reed, the harvest for thatching was the most profitable option compared to combustion and biogas generation [
19]. When it comes to economic viability, the market potential of domestic reed plays an important role.
The research aimed at determining the market volume and market potential of reed of regional origin for thatching in Northern Germany. Specifically, it aimed to answer the following three research questions:
What is the current market volume of reed for thatching in Northern Germany?
What are the market shares of thatching reed from different origins?
What factors influence the demand and supply of reed of regional origin and how can its market potential be assessed?
In answering these questions, we add to the very sparse literature on reed markets and provide the first in-depth study on the market of thatching reed not only in Northern Germany but worldwide. The total quantity, the origin of reed, and quality attributes are investigated as key factors. The results are relevant beyond the scope of Northern Germany as similar situations, i.e., a high consumption of reed and a little self-supply rate, are found in other countries, in particular in the Netherlands, Denmark, and the United Kingdom. Furthermore, rewetting of peatlands and identifying economically viable utilization options is an issue worldwide in order to enhance nature-based climate solutions [
20,
21].
3. Results
3.1. Thatching Companies
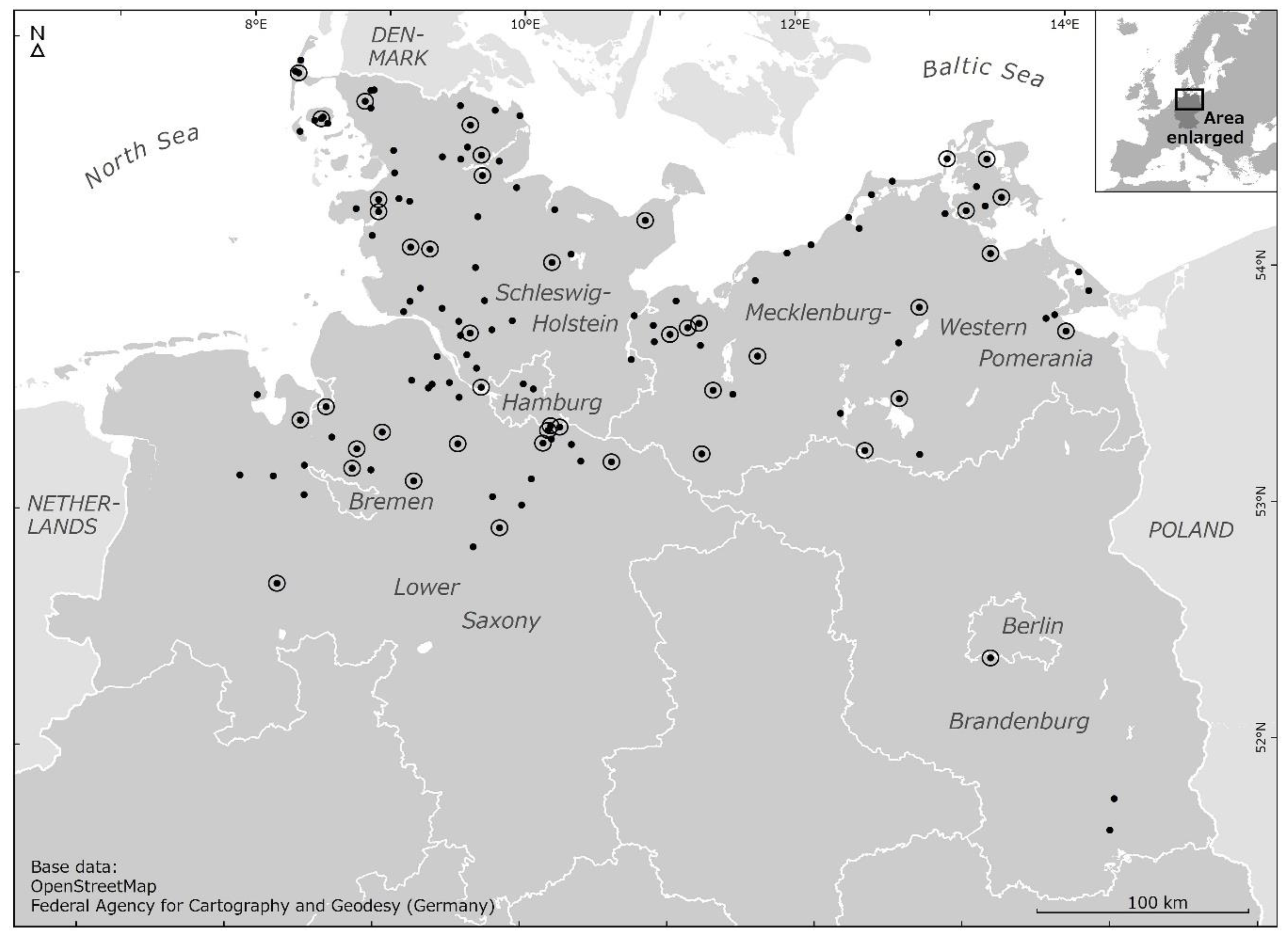
Most of the responding thatching companies are specialized on thatching. About two thirds of the companies (62%, n = 29) work with reed as the only roofing material, while 38% (n = 18) also use other materials. Some specialized thatchers are also trading reed (n = 2), harvesting reed (n = 4), or cultivating reed (n = 1). In terms of employment, all thatching companies can be classified as small and medium scale enterprises (SME) ranging from pure self-employment to a maximum of 28 full-time employees. On average, the companies employ almost six full-time employees (SD = 5.53). Part-time employment (n = 15) and seasonal employment (n = 4) are not very common. While 26% (n = 12) of the companies provided thatching services only in their local district, 11% (n = 5) covered all categories reaching from local district over other districts of their federal state to other federal states and even other countries. Services were provided for instance in the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxemburg, France, Great Britain, Ireland, Poland, Sweden, and Iran. In summary, the responding thatching companies in Northern Germany can be characterized as small and medium scale enterprises with a high level of specialization and a permanent labor force. The market orientation ranges between a very local market and a European market dominated by a regional and national market orientation.
3.2. Thatching Services and Market Development
The final market for thatching services can be divided into three market segments (1) thatching new roofs, (2) renewal of roofs, and (3) repair of roofs.
Table 2 shows the number of orders carried out by responding thatchers in 2018. A total of 83 roofs were newly built and 231 roofs were completely renewed. There were also 1778 orders to repair a thatched roof. On average, one company carried out around 2 orders to cover newly built thatched roof houses, 6 orders for complete renovation, and 47 repairs. The SD indicates that there is a large variation for orders across companies, especially for repairs.
Thatchers were asked how they rate the development of the market for newly constructed roofs in the ten years before 2018 on a scale of 1–7, where 1 indicated greatly reduced and 7 greatly increased. Overall, the frequency of newly thatched houses in the past 10 years was assessed as slightly increasing (n = 41, M = 4.4, SD = 1.7). Thatchers were also asked how they assess the development of general roofing market relative to the thatching market on a Likert-Scale from 1—much worse to 7—much better. On average, the general market for roofing was considered to have developed slightly better (n = 46, M = 5, SD = 1.6).
3.3. Reed Bundles Per Company and for Thatching Services
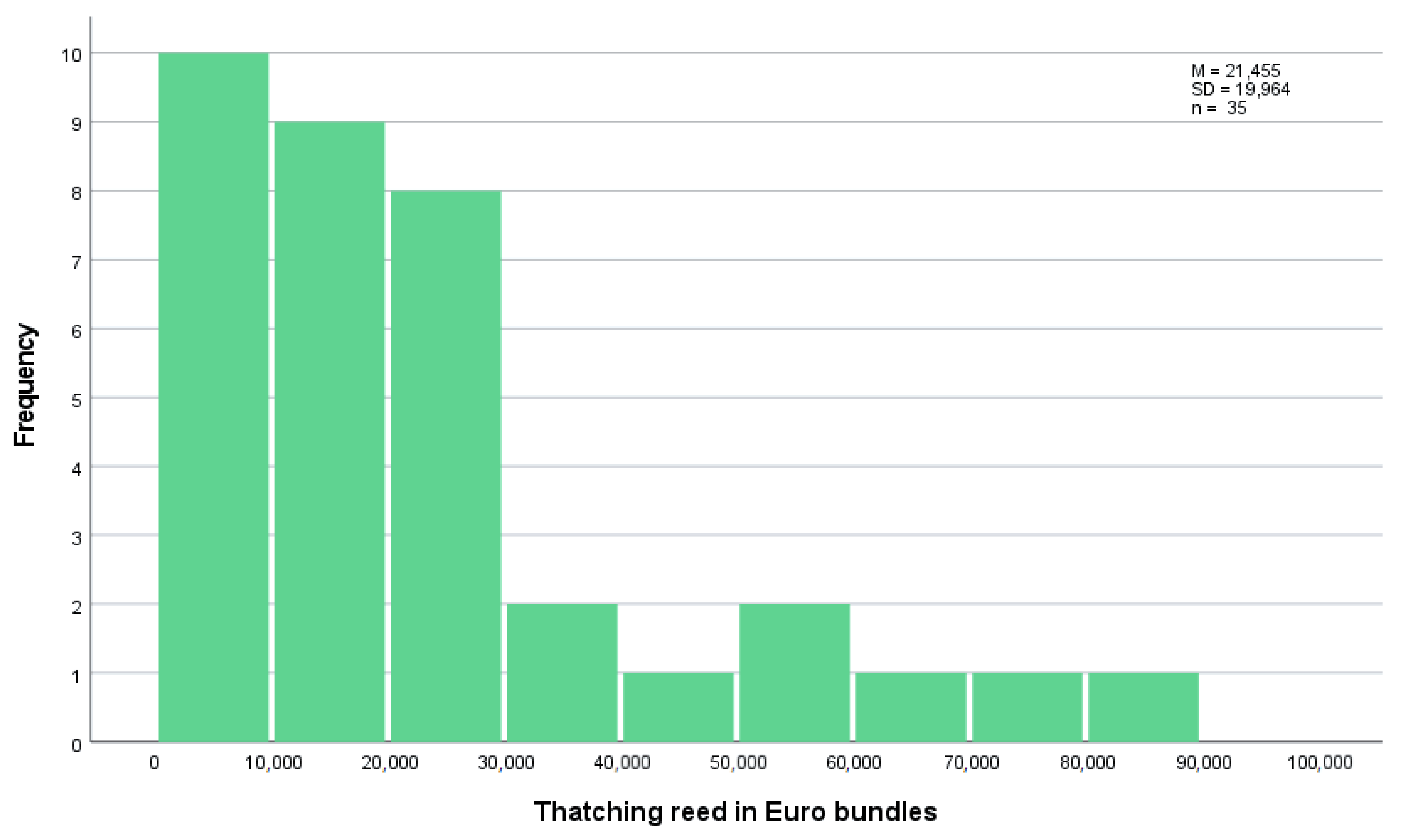
The thatchers were asked how many Euro bundles of reed they installed in 2018. The distribution is depicted in
Figure 3. Most of them installed less than 10,000 bundles with a minimum of 200 and a maximum of 80,000 bundles. For the sample of 35 respondents, a total of 750,575 bundles of reed were installed (M = 21,445, SD = 19,964).
In order to link the number of orders for thatching with the amount of reed, a linear regression through the origin was carried out (n = 30). The regression estimated that 2132 bundles (p < 0.000) were installed for each newly built house, 1923 bundles for each completely renewed roof (p < 0.000), and 24 bundles for each repair (p = 0.521). Overall, the number of orders significantly influenced how many bundles of reed were installed in 2018 (F = 40.2, p < 0.000). The regression explains 82% of the variance in the installed bundles. It should be noted that the repairs were not statistically significant, obviously, since the area size per order can vary greatly.
Thus, in terms of reed bundles used, the market for completely renewed roofs is estimated to be the largest (59% of the annually installed reed), followed by newly constructed roofs (24%), and finally roof repairs (17%), if the latter includes the residuals.
The results of the linear regression of the orders and installed bundles can be compared with the size of a roof and thus validated. The roof area of a single-family house in Germany is approximately 150 m
2 [
40]. At least 12 bundles of thatch are required to cover one square meter of roof [
7,
41,
42]. If the roof area is now calculated using the number of bundles installed per order, this amounts to an average of 178 m
2 for newly built houses and an average of 161 m
2 for renovated houses. Because these are realistic sizes, it can be assumed that the data given are consistent.
3.4. Market Shares by Origins of Thatching Reed
Thatchers were asked where the thatch came from in 2018. As can be seen in
Table 3, the respondents indicated that 12.8% came from their respective federal state and a further 4.1% from other parts of Germany. A total of 4.3% came from the Polish part of Pomerania, i.e., the neighboring region of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, and the main part came from the remaining European market with 62.7%. In addition, 16.1% of the reed was imported from China.
For validation, the information on the origin of reed for thatched roofs in Northern Germany can be compared with EU import statistics from 2018. Of the 6367 tons of reed imported to Germany, 80% came from the European domestic market (EU28 intra, Belarus, Turkey, and Ukraine) and 20% from China. The imports make up 100% of the reed used. For comparing these figures with the information from the questionnaire, the share of nonimported reed (17%) must be included. Considering an import rate of 83%, EU trade statistics reveal 66% of the reed coming from the European market and 17% from China. In comparison to the information provided by thatchers (67% from the European market, including the Polish part of Pomerania, and 16% from China), the percentage figures hardly differ.
3.5. Thatching Reed Sales Prices and Origins
Thatchers were asked for the price at which a Euro bundle is sold to the customer (
Table 4). The thatchers stated that a Euro bundle of reed imported to Germany was sold to their customers for an average price of €3.90, while a Euro bundle of reed from Germany cost on average €3.57.
For companies selling reed from Germany as well as from other origins (n = 24), a Wilcoxon matched pair signed rank-Test indicated that thatching reed from Germany is offered at a significant slightly lower price (p = 0.037).
3.6. Purchasing Criteria of Thatchers
When purchasing reed, the origin of reed is a relevant criterion for 54% of the thatchers (
Table 5). However, other criteria are more important. All thatchers stated that quality is an important purchasing criterion for them. Quality requirements for thatch according to the “Product data sheet for thatch” published by the “German roofing association” include: cleanliness, culm length, and breaking strength [
25]. These criteria were considered as relevant by 91%, 87%, and 70% of the thatchers, respectively. In a question, where the thatchers should rank the three most important criteria, quality was the most important criterion for 56% and the second most important criterion for another 10% (n = 43). Origin was the most important criteria only for one thatcher (2%), and the second most important for three (7%).
Interestingly, price was a relevant criterion only for about one third of the responding thatchers. No thatcher mentioned price as the most important criterion; however, four thatchers mentioned price as the second and another three as the third most important criterion. Color of reed was least important.
3.7. Regional Origin of Thatching Reed and Quality
Regional origin is a fussy concept. Therefore, the thatchers were asked at first how do they understand the term “regional” in relation to reed. For the responding thatchers, “regional” primarily means reed from Germany (33%), from their own federal state (28%), and from their own district (26%) (n = 47). For only 5%, “regional” means from the entire European Single Market. As we had anticipated those diverse concepts of regionality, all further questions on regional reed applied a uniform definition: “Regional reed include all reed from a radius of up to 150 km”.
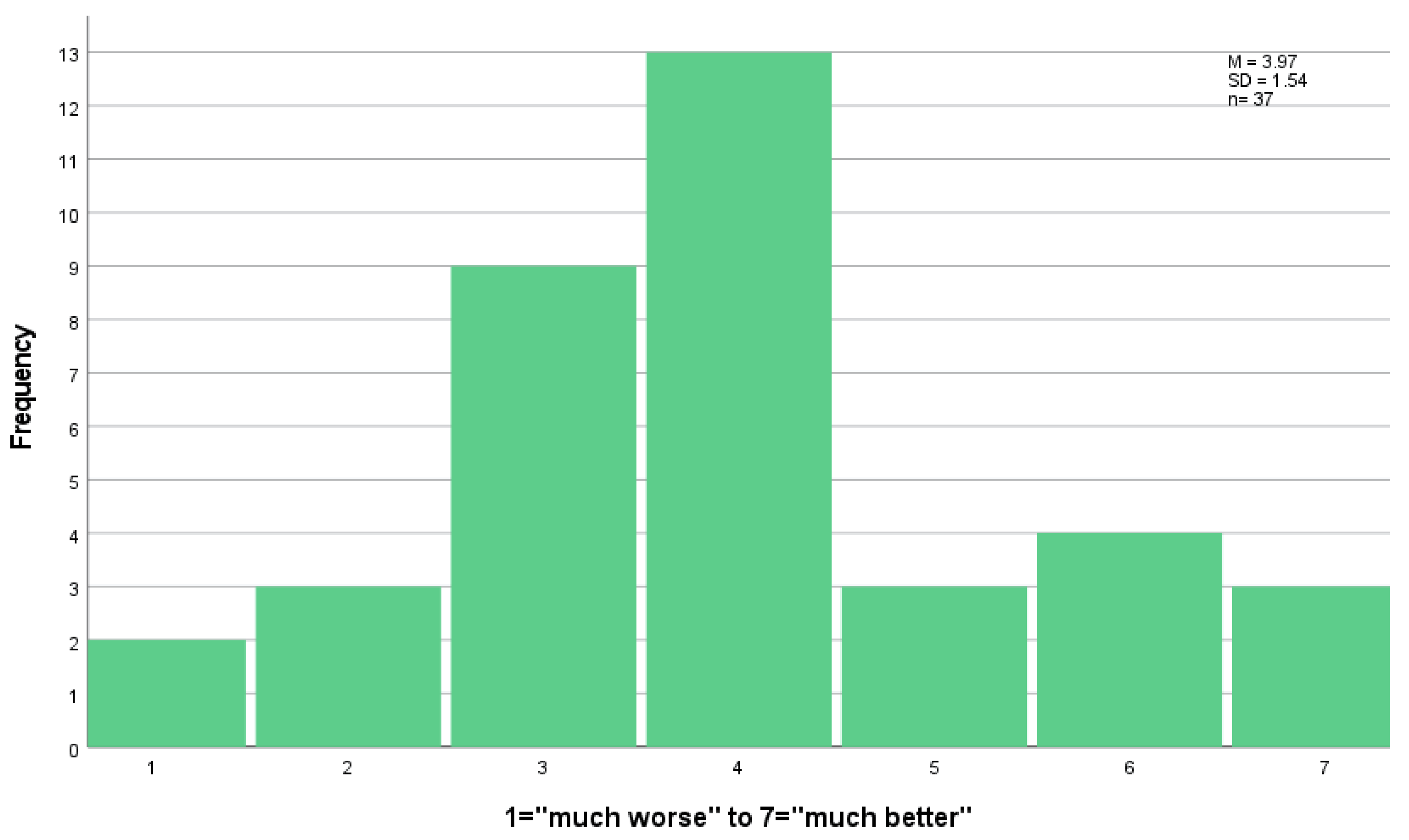
Thatchers were asked how they assess the quality of regional reed as compared to other sources (
Figure 4). On average the quality was assessed as equal. Of the respondents (n = 37), 10 thatchers considered the quality as superior and 14 as inferior. All thatching companies that were engaged in harvesting reed (n = 4) considered regional reed of superior quality.
3.8. Demand for and Promotion of Reed of Regional Origin
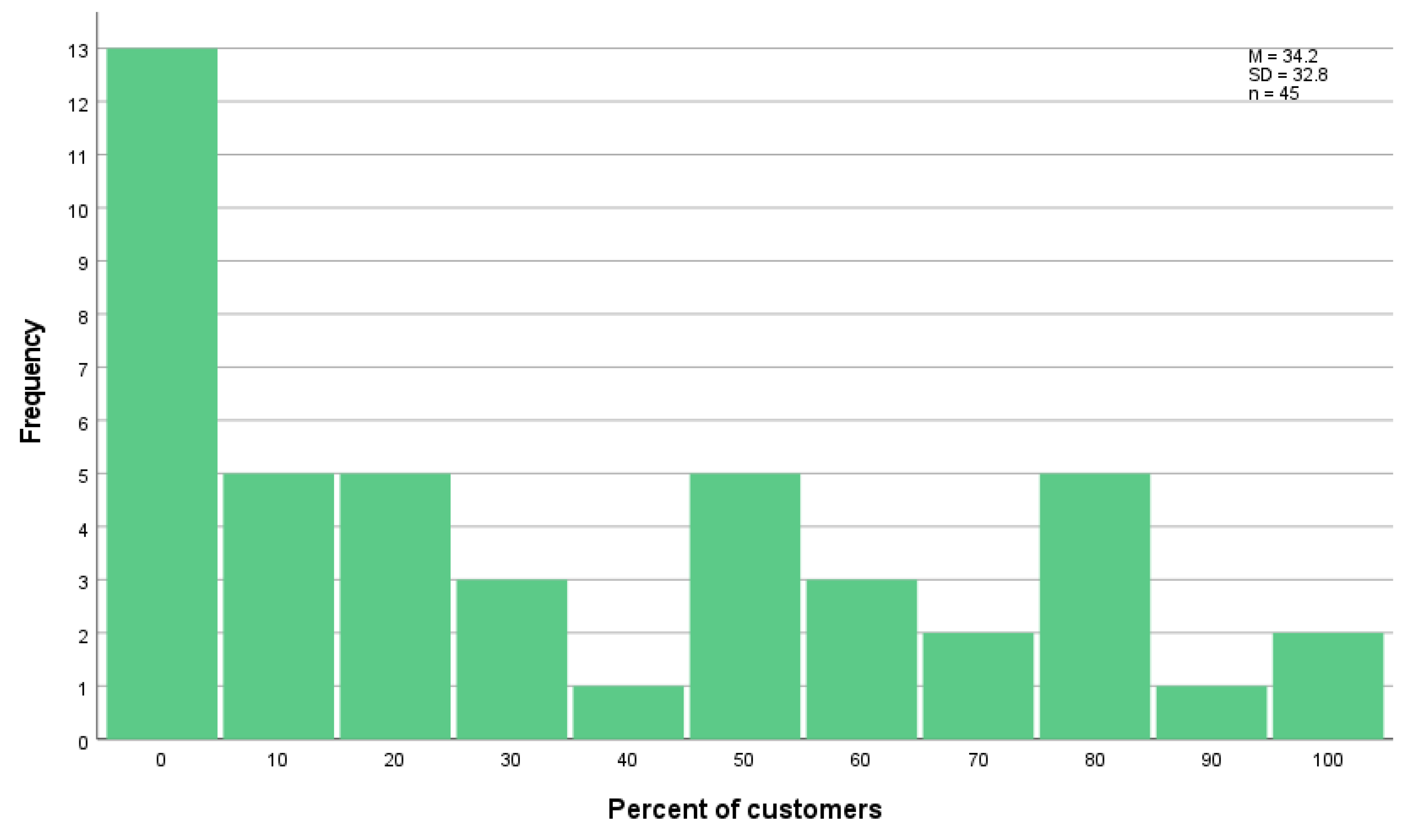
Next to the importance thatching companies assigned to the origin of reed, we also asked for the demand on the part of building owners. The thatchers stated that on average 34% of their customers asked for reed of regional origin on their own (n = 45). Thatching companies with own reed harvest (n = 4) indicated a much higher demand shown by on average 75% of their customers. In the case of 29% of all thatching companies, no customer asked for thatching reed of regional origin (
Figure 5).
Assuming that the share of customers demanding regional reed approximates the share of demanded reed bundles, the before mentioned information can be used to calculate the market potential for reed of regional origin. For the sample of 35 respondents, the latent demand is estimated at 256,846 bundles. Compared to the number of bundles of German origin used for thatching in 2018 (126,594 bundles), this indicates an excess demand and a supply gap for reed of regional origin.
When asked whether thatchers or their employees promote reed of regional origin to their customers only 30% responded that they did (n = 46). For the thatchers denying the promotion of regional reed, the most common reason was an insufficient supply (50%) and the second one the poor quality of reed of regional origin (31%) (n = 31). The quality deficiencies specified consider too short and/or too soft reed (n = 4). All reasons given by thatchers for not promoting reed of regional origin are listed in the original wording in
Appendix Table A1.
Table 6 shows that the perceived quality of reed has an impact on the promotion of regional reed. A Fisher’s Exact test showed a significant correlation between the promotion of regional reed and the assessment of the quality of reed of regional origin compared to reed from other sources (
p = 0.002; n = 36).
Despite the reed of regional origin being perceived as inferior in some cases, 69% of thatchers who have so far not promoted reed of regional origin would generally be willing to offer more of it, 15% would be unwilling to do so, and 15% had no opinion on this question (n = 32). Of the thatchers who already promoted regional reed, 86% would be willing to offer even more and 14% had no opinion on the subject (n = 14).
3.9. Supply of Reed of Regional Origin
In order to check whether the supply of reed of regional origin is large enough to meet the current demand, the thatchers were asked whether sufficient reed of regional origin was available. Of the respondents (n = 45), 36% stated to have sufficient thatch of regional origin available, while 64% stated that the available thatch could not cover their orders. After a qualitative evaluation, the thatchers gave eight reasons why the demand for reed of regional origin could not have been met. The most common reason (23% of the respondents) was “Too little reed beds/declining stocks”, “Nature conservation”, and “No offer” (n = 28). All reasons given by the thatchers are listed as quotes in
Appendix Table A2.
According to the survey, four companies (8.5%) conduct reed harvesting (n = 4) in Northern Germany. Of the other companies, 12 (25.5%) harvested reed in former timers but gave it up in the 60s or 70s (n = 3), 80s or 90s (n = 3), or since 2000 (n = 6). One of the companies currently harvesting reed is located in Lower Saxony, two of the companies in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and one company in Schleswig-Holstein. The company in Lower Saxony also cultivated reed for this purpose, the other three harvested only existing natural reed beds. The companies that conducted own reed harvesting harvested a total of 54,256 bundles (M = 13,564, SD = 21,274) of reed in winter 2017/2018 (harvest period for 2018), of which 45,456 bundles (84%) were harvested by the company in Lower Saxony. Two of the companies did not state how many Euro bundle of reed they installed in total in 2018. In one of the companies the self-harvested bundles accounted for 10% of the total bundles installed, in the other the installed bundles only made up 40% of the self-harvested bundles.
3.10. Extrapolation of the Market Volume and the Markt Potential for Reed of Regional Origin
Based on the survey information, the results were extrapolated to the entire thatching market in Northern Germany. The focus was on the quantity and value of thatching reed and the market share and market potential for regional reed. According to the Kruskal–Wallis test, the hypothesis that distribution of all above reported variables are identical between Schleswig-Holstein, Lower Saxony, and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania could not be rejected, except for three variables. These were the number of orders for renewed roofs and repairs and the price for thatch of non-German origin. Therefore, we consider it as justifiable to perform a simple extrapolation instead of a weighted one, assuming the whole sample distribution to represent the entire population (
Table 7). The extrapolated point estimates are presented together with the 95% confidence intervals. Because the share of reed of German origin of 17% could be verified by external sources (see
Section 3.4), the market share was taken as certain. All other variables were subjected to a calculation of sampling errors, i.e., estimating how far the population mean is likely to be from the sample mean.
Thus, we estimated a market volume of 3 ± 0.8 million bundles of reed in Northern Germany, where the majority of reed is installed by companies located in Schleswig-Holstein, followed by Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, and Lower Saxony. The total market value of reed in sales prices is estimated at €11.6 ± 2.8 million.
The market volume for regional or German reed in Northern Germany is estimated at 511,000 ± 137,000 bundles and at a market value of €1.8 ± 0.5 million. The market potential, however, is much higher as the final demand for regional reed suggests. Thus, we estimated a supply gap for reed of regional or German origin of 523,000 ± 392,000 bundles or €1.9 ± 1.4 million. If supplied at current quality and prices it is estimated that on average more than double the bundles could have been sold. However, these estimates are connected with substantial uncertainty.
4. Discussion
Thatchers are decisive actors in the reed value chain being responsible for both purchasing reed and thatching roofs for the house owners. Our survey among thatchers provides the first in-depth analysis of the market for thatching reed in Northern Germany. We determined the market volume of thatching reed in Northern Germany and assessed the market potential for reed of regional origin in quantitative and qualitative terms.
4.1. Current State and Development of the Reed Market in Northern Germany
For answering the first research question, we estimated the total market volume for thatching reed in Northern Germany and analyzed the market volume for the three different thatching services identified: (1) newly build roofs, (2) renewal, and (3) repair of existing roofs. The total market volume was estimated at around 3 ± 0.8 million bundles of reed with a monetary value at sales prices of €11.6 ± 2.8 million in 2018. These figures are an extrapolation, which is to be viewed under the fact that there were large differences between the surveyed companies. Few literature is available to verify the extrapolation.
The EU trade statistics depict general trends and interannual differences in reed trade between countries [
15] but appear unsuitable for cross validation of the total market volume (in bundles) for a specific year. According to the extrapolated survey data about 2.5 ± 0.7 million bundles were imported. Converting the imports of 6367 tons of reed reported in EU trade statistic into bundles (assuming average weights of 4 kg, based on 3.2 kg dry mass per bundle (range: 2.4–5 kg) [
43] and 15–18% water content in traded bundles) resulted in about 1.5 million bundles. The difference amounts to almost 1 million bundles for the point estimate and 0.3 to 1.7 million bundles for the 95% confidence interval. That reed quantities are not completely pictured by EU trade statistics may be linked to observation gaps for goods traded between EU member states, e.g., due to Intrastat reporting exemption thresholds [
44]. Furthermore, bundles have a standard value for the circumference but not for the mass. Long (>1.90 m), medium long (>1.40 m), and short bundles are distinguished [
25]. Extreme droughts experienced in Europe in 2016/2017 [
45] may have affected the reed growth and led to shorter bundles with lower weight traded in 2018. Finally, reed may be stored and the year of purchase and of thatching may differ.
The calculated total market volume of 3 ± 0.8 million reed bundles, however, equals an earlier estimate of 3 million bundles made by the Society for reed quality assurance (QSR), which was based on information provided by reed traders [
11]. Wichmann and Köbbing [
15] identified further similar estimates of 2–3 million bundles for single periods between 1990 and 2013. A considerably higher value of 4.8 million bundles of reed needed per year in Northern Germany was mentioned in 1996 by the chairman of the thatcher guild Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and published in Schäfer [
46]. Fluctuations between the years [
46] are mentioned as well as a decline of the reed market at the beginning of the 21st century due to observed cases of early decay of thatched roofs [
11]. The recovery of the reed market stated by QSR [
11] seems to have continued since the results of our survey suggest a slightly increased demand for thatching newly built houses in Northern Germany in the past 10 years (2008–2018). According to the conducted linear regression, the responding thatchers used only 24% of the reed for newly constructed roofs in 2018, but 59% for completely renewed roofs, and 17% for roof repairs. It is unknown, however, how many thatched roofs exist in Germany [
11]. Furthermore, it cannot be assessed whether the number of thatched roofs increases due to newly built houses or decreases due to thatched houses being demolished or covered with a hard roof at the end of the lifetime of the soft thatched roof.
4.2. Origins of Reed and Development of Market Shares
The second research question addresses the origin of the reed used for thatching in Northern Germany. The survey results clearly show that most of the reed is imported from the European market (67%) and from China (16%). Only 17% of the reed bundles are from Germany. The calculated import shares were confirmed by EU trade statistics reporting 66% of reed imported from the European market and 17% from China. In an overview study of the European reed market, an import rate fluctuating around 80% from 1990 to 2013 was reported for Germany [
15]. The import rate of 83% revealed by the survey fits well to these literature values. Imports continue to be at a high level and even might have increased slightly.
4.3. The Potential of Reed of Regional Origin
The third research question focuses on the market of reed of regional origin and factors influencing the demand and supply. The majority of the responding thatchers relates the term “regional” to their own federal state (28%) or even to their own district (26%). German reed is considered as being “regional” only by 33% of the respondents. Most of the German reed used by thatchers is indeed from their specific federal state (
Table 3). The thatchers also indicated that on average a third of their customers asked about reed of regional origin, but the range was as wide as possible reaching from 0 to 100%. According to the extrapolation, the current market volume of reed from Germany is 511,000 ± 137,000 bundles with a monetary value of €1.8 ± 0.5 million. The market potential, based on the share of costumers asking for regional reed on their own, is about double (1 ± 0.4 million bundles, €3.7 ± 1.4 million), indicating an excess demand of 523,000 ± 392,000 bundles (€1.9± 1.4 million) not met by the current supply. Assuming an average yield of 500 bundles per hectare [
19], this latent demand can be covered by an additional harvest area of 1046 ± 784 ha. Considering that 70% of the responding thatchers do not promote reed of regional origin, the potential market for reed of regional origin can be larger than calculated. The majority of thatchers who have not yet promoted reed of regional origin would generally be willing to do so (69%). The unavailability of regional reed was mentioned by 50% as the reason for not promoting regional reed and insufficient quality by 31%. Surprisingly, thatching reed from Germany is offered at a significant slightly lower price despite of the demand exceeding the supply. This result might indicate that although regional reed is preferred, final consumers are not willing to pay a higher price. Furthermore, lower prices might be connected with lower quality [
47]. Quality issues were repeatedly reported by the surveyed thatchers as reasons for not promoting regional reed or for the inability to supply the demand of customers (see
Table A1 and
Table A2). Nevertheless, thatchers were quite divided in their assessments and some consider regional reed as of superior quality (see
Figure 4). In particular, thatchers who harvest reed were convinced of the superior quality. Although there is some scientific literature on the quality of reed for thatching from different provinces, the results show the huge variability and are overall inconclusive about the quality of reed of different origins [
48,
49].
4.4. Potential and Obstacles of Cultivating Reed
It can be concluded that there is a demand for more and above all more high-quality reed of regional origin. Cultivating reed may improve both quantity and quality of regional reed for thatching. Thus, cultivating thatching reed is one promising and climate-smart alternative to drained agricultural peatlands. Growing reed on rewetted peatlands can generate climate benefits in several ways: (a) minimizing CO
2 emissions from peat oxidation [
50], (b) acting as strong CO
2 sink [
51] due to carbon-capture and long-term storage in belowground biomass and peat formation, (c) using reed for replacing fossil resources, e.g., avoided emissions caused by energy use in roof tile production, and (d) (temporal) carbon-capture and storage if harvested aboveground biomass is used as long-life building material.
In terms of area demand, however, 6000 ± 1600 ha with an average yield of 500 bundles per hectare [
15] would be sufficient to produce even all 3 ± 0.8 million bundles of the current total market. Considering a surplus area, e.g., for buffering for harvest failures, a maximum area of 10,000 ha is needed. Applying national GHG emission factors (including emission of CO
2, CH
4, N
2O) for drained cropland (40.4 t CO
2-eq.), drained grassland (31.7 t CO
2-eq.) and rewetted sites (5.5 t CO
2-eq [
52]), the annual saving due to minimized peat oxidation for 10,000 ha could be 260,000 to 350,000 t CO
2-eq. In relation to total emissions of about 45 Mio t CO
2-eq from agricultural used drained peatlands in Germany [
52], this saving can only be a small component. Other biomass utilization options and further crops need to be investigated to provide economically viable paludiculture options [
19] for about 383,000 ha of arable land and 852,000 ha of grassland on drained organic soils [
53] in Germany.
The cultivation of reed may range from shifting the harvest season from summer to winter, over improved water management, the planting of pre-cultivated seedlings for stand establishment, up to the selection of provenances, genotypes, or even breeding for improved reed quality. So far, winter harvested reed stands in Germany are not eligible for direct payment under the EU Common Agricultural Policy [
54]. Therefore, it is not surprising that reed cutters report wet grassland to be mown by the land manager in summer (and thus impeding a winter harvest for thatching) just for generating EU subsidies despite of a lack of utilization for the biomass. Negotiations on the new CAP post 2020 include proposals for considering paludiculture as eligible for agricultural payments in the future, which would eliminate a major obstacle of reed cultivation. Another factor is the need for special harvesting equipment adapted to the low bearing capacity of reed stands and equipped with a specific mowing (and cleaning) device [
55]. The purchase of such a machine is economically feasible only with a certain minimum size of harvesting area. Our results showed, however, that the current reed harvesting area is limited (
Table A2: not available, too small, very restricted use, nature conservation). Several pilot trials proved the feasibility of planting reed for establishing a reed stand in Great Britain [
56], the Netherlands [
16], and Germany [
57,
58], and practical experience of the commercial harvest of planted reed stands is available. Research on how to achieve and improve thatching qualities of reed cultivated on rewetted peatlands is still in progress.
4.5. Limitations of the Study
When evaluating the results and the extrapolation, it should be kept in mind that with a participation rate of 33%, the situation of 94 thatching companies in Northern Germany remains unknown. It should also be noted that due to individual unanswered questions, the response rate of 33% was not met for all questions. These nonresponses reduced the effective sample size and unavoidably increased the sampling error. Based on the assumption that nonresponses were completely random, confidence intervals for major extrapolated variables could be computed. However, nonsampling errors might have occurred. The participation was determined by the willingness of the thatchers to take part in the survey. It is conceivable that responses were given by larger companies that had the human resources or by thatchers who were already interested in the topic of “regionality”. This was attempted to be reduced by avoiding the topic of regionality at the beginning and in the cover letter of the questionnaire. Overall, it can be concluded that, based on the target group and the survey design, a response rate of 33% represents a satisfactory effective sample size suitable to make valid statements, which was demonstrated by the comparison with trade data and literature values. It can therefore be assumed that despite all uncertainties, overall a good overview of the market for reed in Northern Germany could be given. Limitations concern the concept of “regional reed”, which may be defined differently by thatchers and house owners. In addition, the question on prices paid for a reed bundle by the end consumer lacks a specification on gross and net values so that the stated prices must be viewed with caution. In conclusion, it is pointed out that the present work is limited to the perspective of thatchers. Addressing further actors of the reed value chain such as reed cutters, traders of thatching reed, or the owners of thatched house can provide further insights into the reed market.