Abstract
The large temporal and spatial variability of rainwater quality, as well as the relatively small number of tests, makes the preliminary assessment of its economic exploitation difficult. Determining the relationship between the conditions and location of rainwater collection and rainwater quality would help indicate the range of options for rainwater use, as well as the parameters that require improvement. The aim of the presented article is to establish the physical, chemical, and microbiological parameters of different rainwater sources and, from the results obtained, determine the possibilities for its safe use in households. The research was carried out for two years. Samples of rainfall were collected from spring to fall from the following roofing materials: Concrete roof tiles, ceramic roof tiles, galvanized steel sheet, and epoxy-coated terrace. The physical, chemical, and microbiological quality were assessed on the basis of the pH, turbidity, electrical conductivity, the concentration of biogenic compounds, the concentration of chosen elements, the number of Escherichia coli, and the number of fecal streptococci. Significant bacterial contamination, decreased pH, and increased turbidity were identified in the water, depending on the parameters of the roofing washed by the rainfall and the intensity and frequency of precipitation.
1. Introduction
Currently, approximately 36% of the world’s population faces a water crisis. In many areas, satisfying the increasing demand for this resource is not possible as a result of restricted access to a fresh water supply. It is believed that countries with water resources below 2000 m3 per capita per year may face difficulties addressing the needs of their population, while countries with resources below 1000 m3 per capita per year are considered to be areas with a severe water deficit [1].
In Poland, apart from the high variability of precipitation, the biggest problems in water management are lowered groundwater tables, changes in the natural hydrological regime of surface water, water pollution, and changes in natural morphological conditions related to river channel regulation, water damming, and solutions for small and large retention [2].
Analysis of the domestic water consumption structure shows that approximately 50% of potable water can be substituted by rainwater, and in public buildings, this value is almost 65% [3]. Rainwater harvesting and storage systems have been implemented in several countries. Water collected in this way is a valuable source of freshwater that can reduce the demand for tap water and be used during periods of drought [4]. Rainwater harvesting technologies are used worldwide to support drinking water supplies [5,6], rainwater management, and flood risk mitigation by reducing the volume of water that flows into storm drainage systems [7,8]. These technologies also constitute one of the elements of an efficient and environmentally sound functioning of buildings [9]. In areas with dispersed housing and high costs of building classic water supply systems, the RWHS (rainwater harvested system) has been found to be an affordable and sustainable alternative [10,11,12] for supplying drinking water.
Rainwater can be used for a variety of household purposes, including sanitary facility flushing, laundry, cleaning, lawn and crop watering, as well as car washing. In areas exposed to a particularly high risk of water deficit, such as Kenya and Bangladesh, rainwater is also considered as water intended for consumption [13]. Thus, knowing the quality of harvested water is crucial for the protection of public health.
While it is generally believed that rainwater is relatively clean, test results prove that it is physically, chemically, and microbiologically polluted [14,15]. The quality of harvested rainwater is characterized by significant variability in both time and space. The composition of rainwater is dependent on many factors, such as atmospheric pollution (including the presence of dust, pollen, and bioaerosols), the type of catchment, land use (industrial areas and roads and highways), the local microclimate, and the type of the runoff surface (various roof pitches and various roofing materials). Rainwater contamination reaches the highest levels in urban areas, which is mainly linked to the emissions of power plants, local boiler plants, and industry [16,17]. The source of rainwater pollution is, to a large extent, substances that are washed out of the atmosphere, but the greatest pollution occurs in rainwater that flows down the surface of terrains, roofs, gutters, or pipeline networks. However, the greatest contamination is caused by the entry of microbial pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and protozoa [18]. Indicators of microbial contamination of rainwater are E. coli or thermotolerant strains of coliforms. Pathogenic microorganisms are also detected, such as Cryptosporidium, Giardia, Campylobacter, Vibrio, Salmonella, Shigella, and Pseudomonas [19].
The quality of water is a very important factor with regards to the possible options for its economic utilization, although the highest quality (that is, the quality that meets the standards for consumption and hygienic applications) is not always required for such utilization. Rainwater can be a carrier of pollution that gets into surface water and soil. The impact of rainfall may be partly explained by researching the quality of these resources, such as the condition of water in water reservoirs [20].
In Poland, rainwater quality is monitored on a national scale by testing many parameters to determine the spatial and temporal distribution of pollutant loads that are introduced through the penetration of wet precipitation into the ground. However, these studies only apply to water taken directly from precipitation and its physicochemical quality. Detailed data on the microbiological quality of rainwater, including water collected from roof surfaces, are lacking.
This article pays special attention to the bacteriological quality of rainwater because of its possible use for drinking in crisis conditions. A wide range of measurements was studied because many factors influence the multiplication of microorganisms. In addition to typical parameters such as temperature and pH, biogenic substances such as organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus have a special impact that stimulates the growth of microorganisms. It is also important to determine the presence of substances that can inhibit the growth of microorganisms. These inhibitors include metal ions.
The presented results may be the beginning of a larger body of research on the quality of rainwater in this part of Europe and facilitate the development of treatment technologies and the determination of possible new applications for such water.
This article indicates the impact of various factors (the type of roofing material and the content of nutrients and metal ions) on the microbiological quality of rainwater in the context of its possible use for drinking in crisis conditions and for hygienic purposes (e.g., washing fruits and vegetables that are consumed raw).
2. Materials and Methods
The research was carried out from 2015 to 2016 in a nonindustrialized area located in the immediate vicinity of the city of Rzeszów, which is located in the southeastern part of Poland (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Location of Rzeszów in the context of Europe.
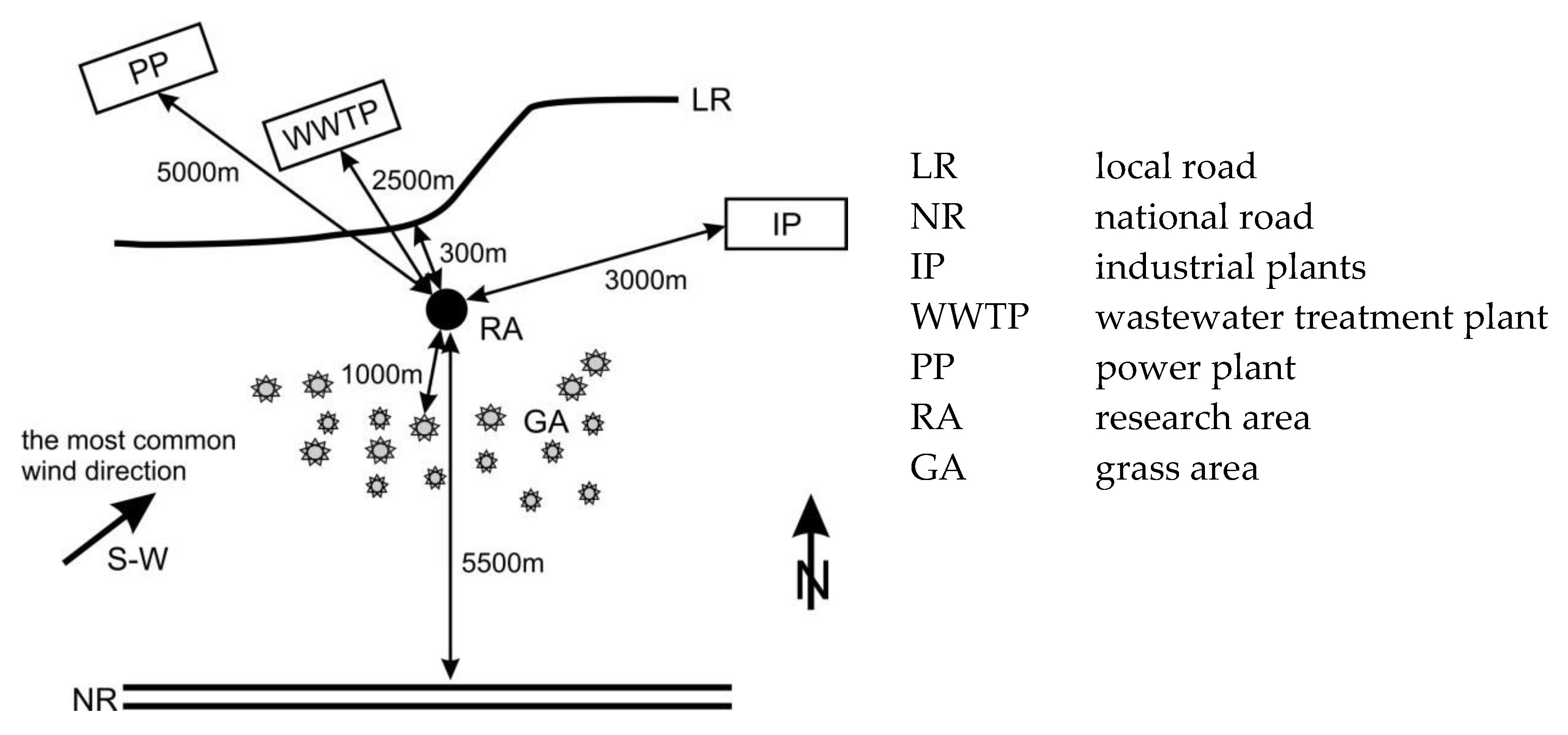
The area within a 3 km radius of the sampling site is characterized by low emission of dust pollution due to the lack of industrial and organic plants; an exception occurs in the summer period, during which dust formation is associated with mowing grass. The nearest transport route is a county road with limited traffic intensity (0.3 km from the sampling site) and a national road (5.5 km away in the southerly direction). The area in which sampling was conducted is overgrown with low shrubs and grasses, and the nearest trees and agricultural fields are located approximately 1 km to the west of the housing. A water treatment plant (2.5 km) and the power plant Załęże (approx. 5 km) are located to the northwest of the sampling site. Westerly and southwesterly winds prevailed during the study period (Figure 2).
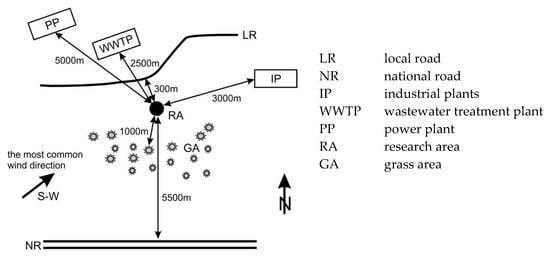
Figure 2.
Characteristics of the research area.
Water samples were collected during spring (March–May), summer (June–August), and autumn (September–November); sampling was not conducted in winter because temperatures fell below 0 °C, and therefore, no technical opportunities for rainwater collection occurred. Rainwater quality tests were carried out for samples taken from the outlet pipes of roofs. The impact of roofing materials on water quality was analyzed. The following materials were analyzed in the study: (I) Concrete roof tiles (Co), (II) ceramic roof tiles (Ce), (III) galvanized steel sheet (Gs), and (IV) epoxide-coated material (E). The control was a rainwater sample that did not come into contact with any roof surfaces and was collected directly from atmospheric precipitation. Test samples of atmospheric precipitation were taken using a series of flat, disinfected plastic vessels covering an area of 1 m2. The vessels were placed on a rack that was 1.5 m high above the ground level in a place consistent with the guidelines of ISO 5667-8: 1993, Water quality—Sampling—Part 8: Guidance on the sampling of wet deposition [21].
Samples were collected during selected rain episodes according to rainfall intensity and after rejecting the first runoff. The first runoff time was established for intensive and moderate rainfall and for heavy or moderate torrential rain. A determining factor was the ability to measure rainfall intensity with available tools. Sampling was carried out at particular points of time after the start of the rainfall, and quality control marks were made (Table 1).

Table 1.
Changes in the quality of rainwater during precipitation: Determining the time of the first runoff.
On this basis, the time necessary for the first runoff of roof surfaces and the moment for sampling during rainfall were set. Measurements were taken from rainwater collected directly from atmospheric precipitation and from concrete tile roofing. The time of sampling was established to improve the measured quality of rainwater. Up to about 10 min, the quality of rainwater collected directly from precipitation and from the roof surface improved. For the next 10 min, no significant improvement in the microbiological quality or turbidity of the rainwater samples was observed. On the basis of these results, it was determined that samples would be taken 10 min after the onset of rain at a specified intensity. Rainwater collected during moderate and intense rainfall that lasted for at least 1 h with an intensity exceeding 4 mm/h was analyzed. The intensity of rainfall was qualified using the rainfall classification scale according to Chomicz [22].
The selected physical, chemical, and microbiological rainwater parameters were determined according to applicable surface water and groundwater research procedures and standards (Table 2).

Table 2.
Scope and methodology for the determination of physicochemical and microbiological properties of the examined rainwater.
3. Results
3.1. Test Cycle Characteristics
Tests were carried out on rainwater harvested in 2015 and 2016. Each test cycle was described by the number of rain episodes, total monthly rainfall, duration of intervals between rainfalls, and average air temperatures (Table 3).

Table 3.
Characteristics of research cycles.
In 2015, there were significantly fewer rain events, longer rainless periods, and higher air temperatures than in 2016.
Annual rainfall in 2016 was nearly twice that in 2015. The characteristics of the test seasons refer to the area in which rainwater samples were taken. In 2016, the monthly precipitation exceeded 40 mm in April, May, July, September, October, and November; in 2015, rainfall exceeded 40 mm in March only.
3.2. Physical and Chemical Rainwater Quality
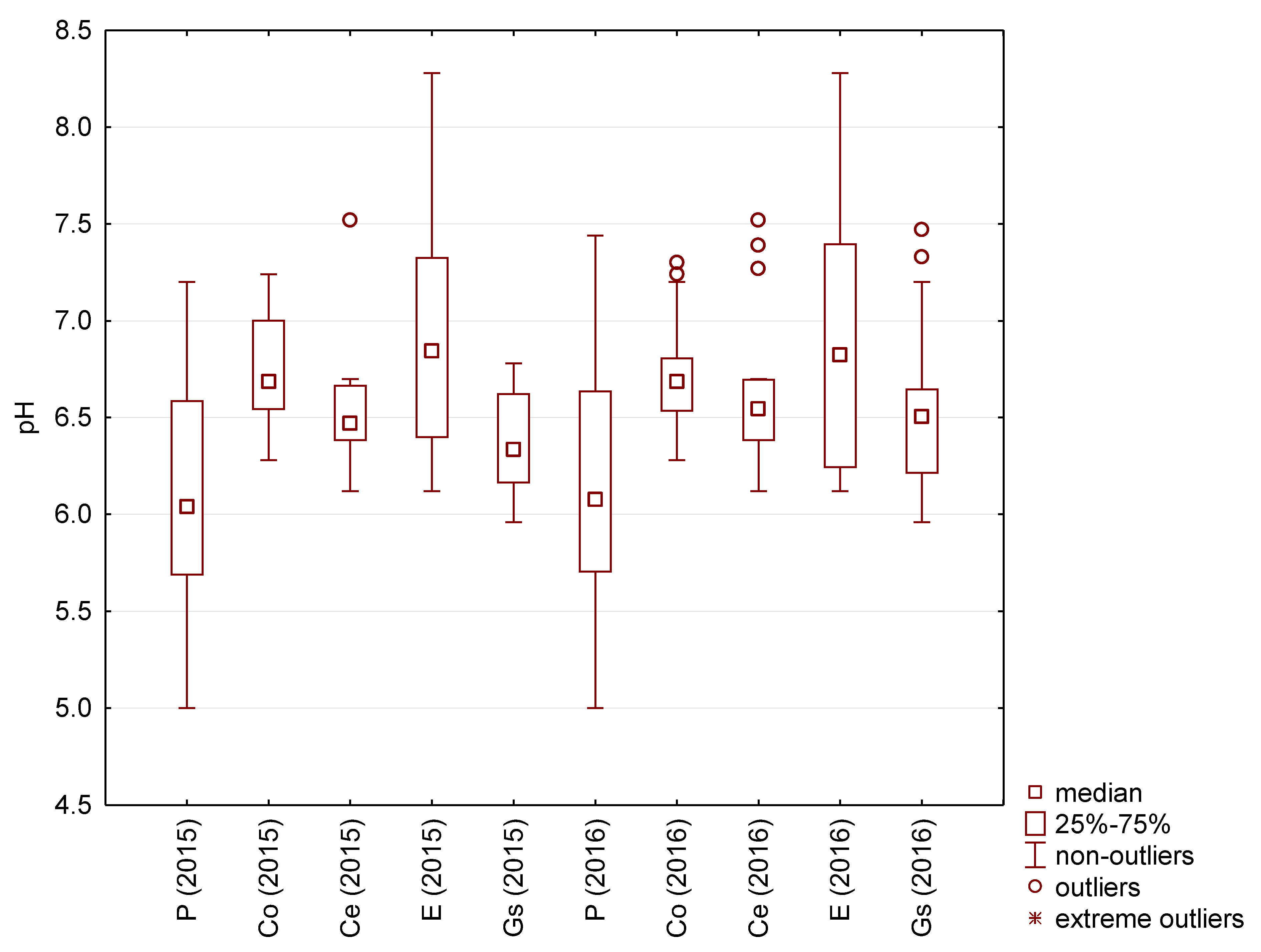
The most commonly used parameters to describe rainwater quality are the pH and turbidity. The lowest pH values were recorded for rainwater taken directly from the air, both in relation to extreme values (pH 5.0) and median values (pH 6.0) (Figure 3).
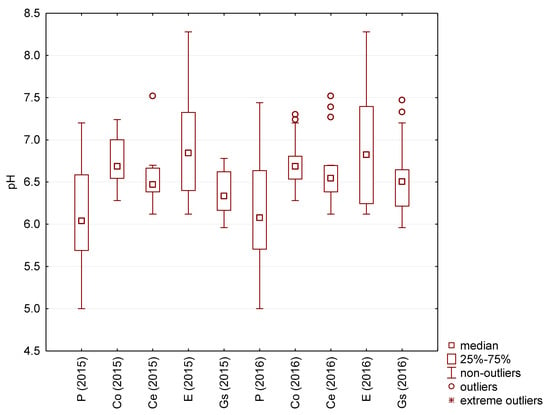
Figure 3.
pH of the tested rainwater.
Among rainwater collected from different roofing materials, rainwater collected from the galvanized steel sheet had the lowest pH.
Rainwater collected directly from atmospheric precipitation had lower pH values than roof-harvested rainwater. Sulfur compounds and NOx had an acidic character in rainwater deposited as a result of air pollution. However, after flowing over the roof surfaces, the water was gradually neutralized to varying degrees.
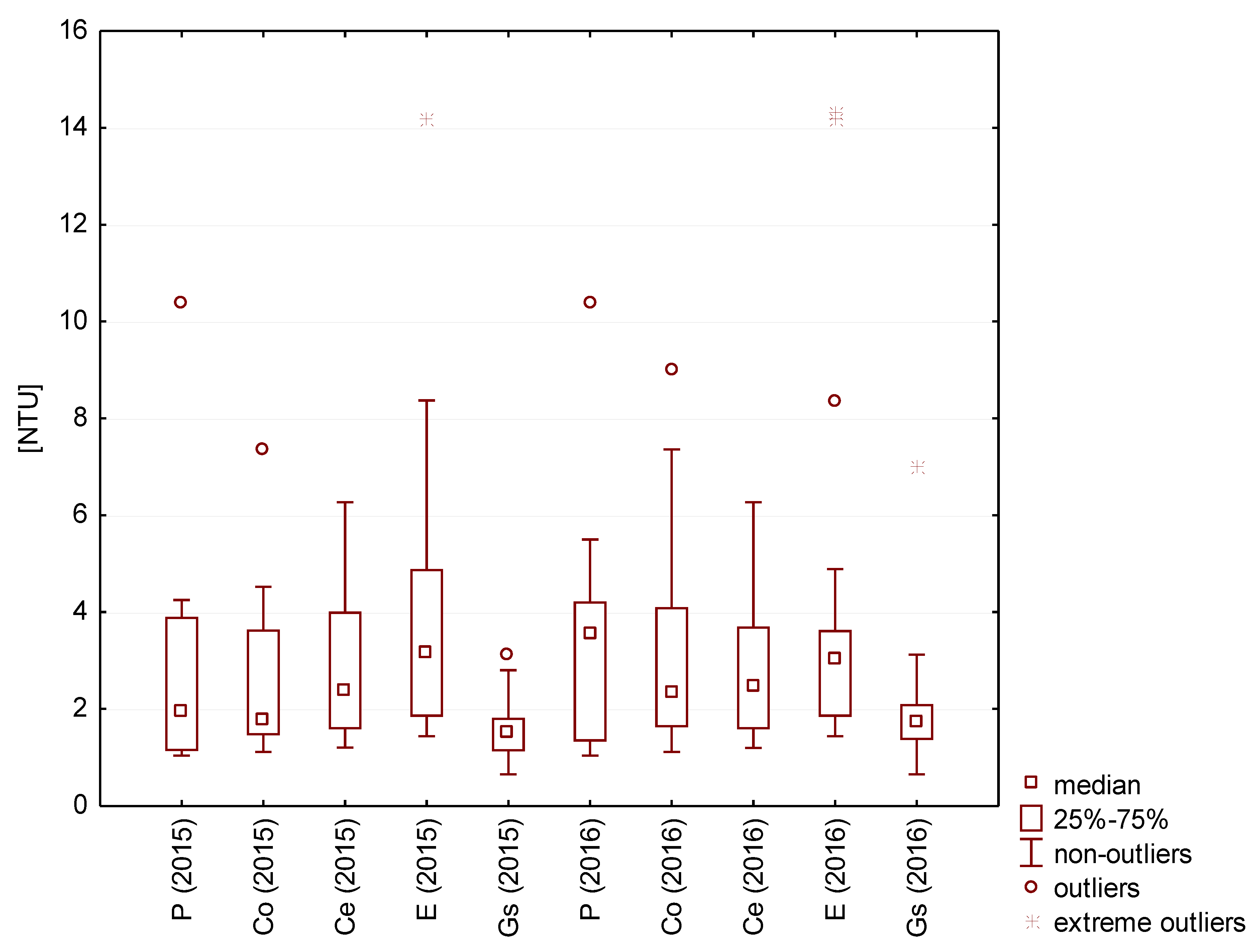
In turn, water that was characterized by the highest turbidity (max. 14 NTU) was collected from the surface coated with epoxy resin, and the lowest turbidity was found in rainwater collected from the zinc-coated metal sheet (medians of 1.5 and 2.0 NTU in 2015 and 2016) (Figure 4).
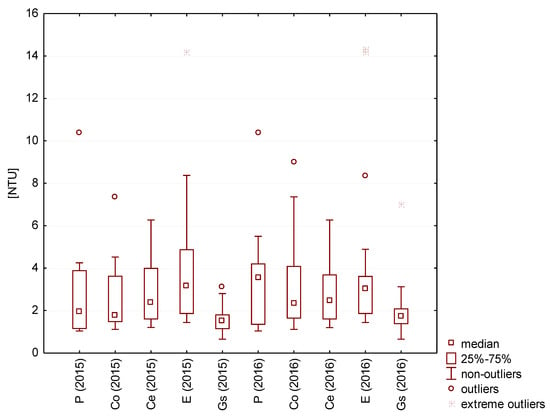
Figure 4.
Turbidity of rainwater tested.
In the case of water harvested directly from the air, the turbidity reached 4 NTU in 2015 and 2 NTU in 2016.
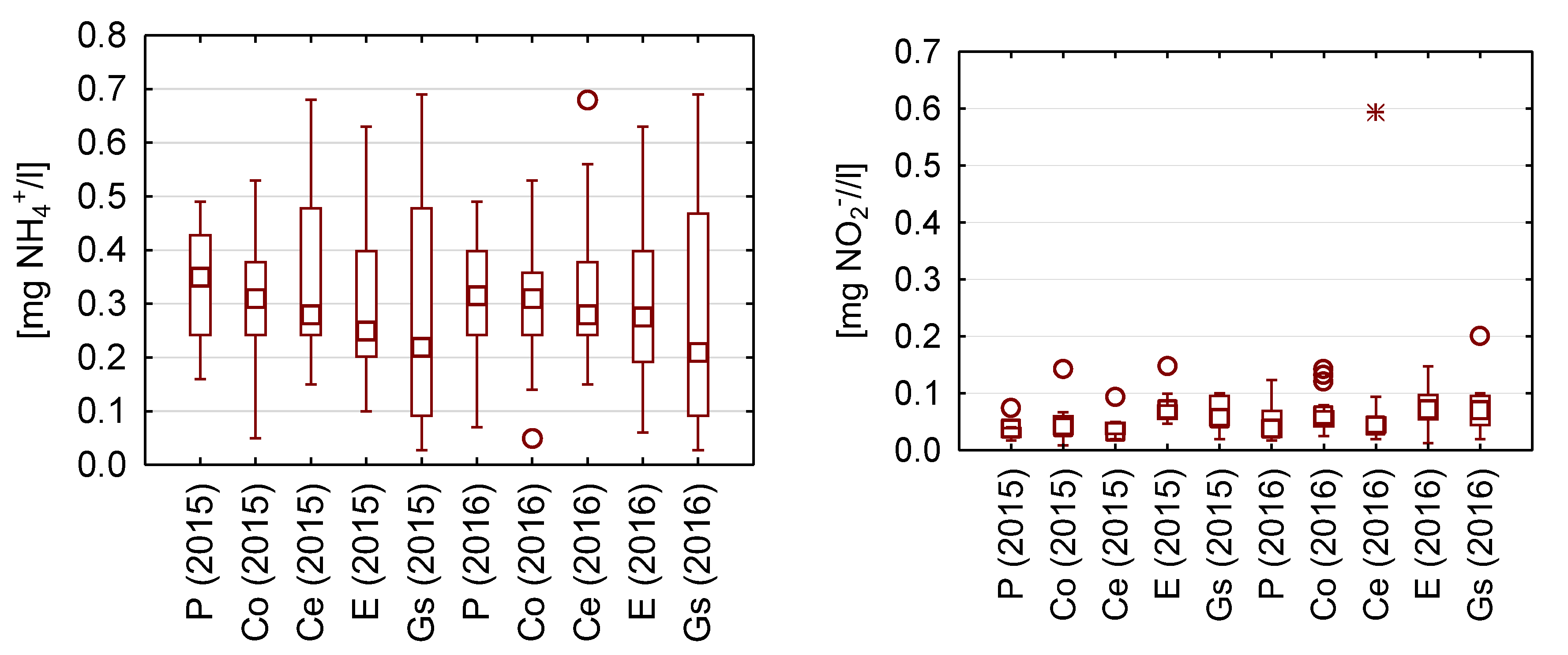
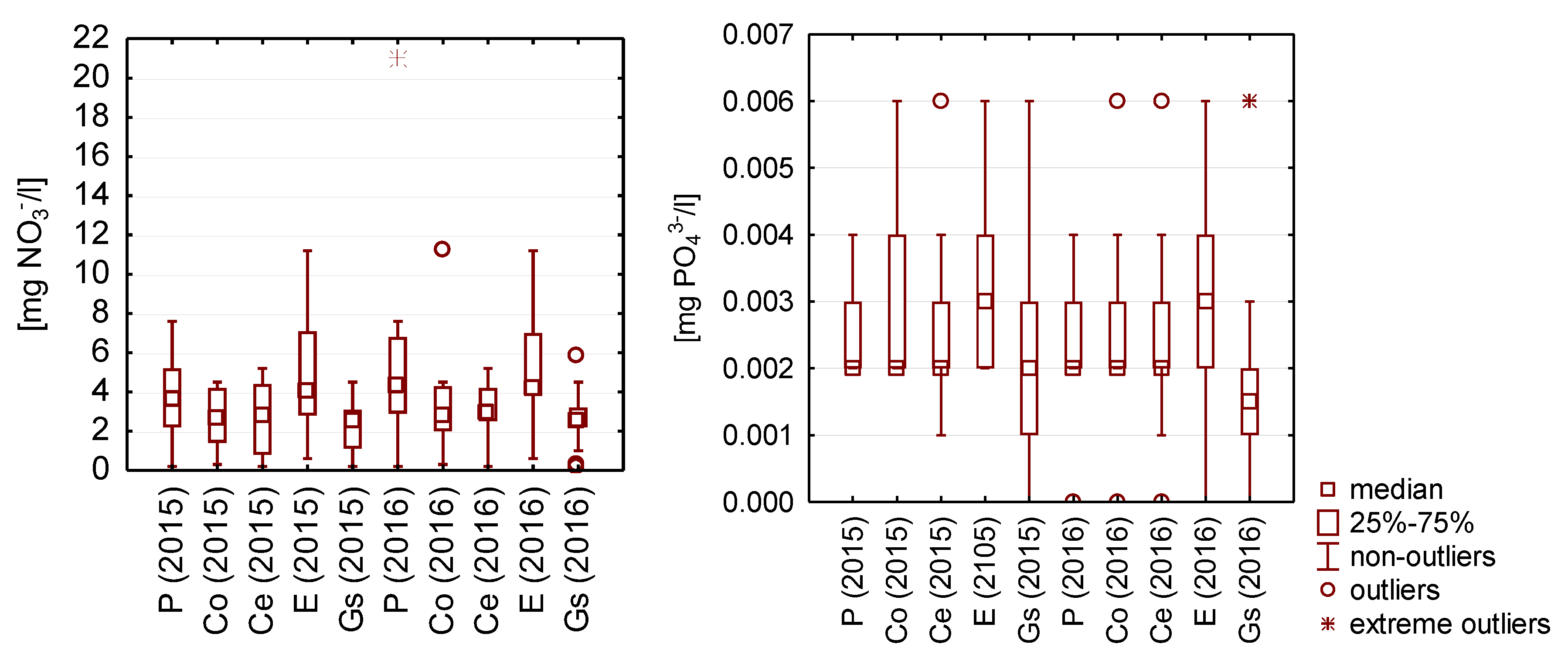
The concentrations of nitrogen compounds were similar in all examined rainwater samples (Figure 5).
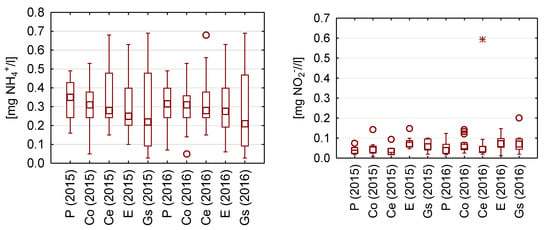
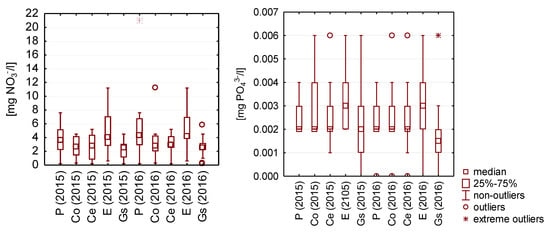
Figure 5.
Statistical data for the content of nutrients in the analyzed rainwater.
The median values of ammoniacal nitrogen concentrations were found to range from 0.20 to 0.35 mg NH4+/L (0.16–0.27 mg N/L). Extreme values were obtained for rainwater collected from the galvanized steel sheet roof and the rainwater collected directly from precipitation.
The highest concentrations of nitrite ions (III) were measured in rainwater taken from the surface covered with epoxy resin and amounted to 4 mg NO2−/L (1.22 mg N/L), and the lowest concentration was found in rainwater flowing from ceramic, concrete, and galvanized steel sheet, for which it reached a value of 2 mg NO2−/L (0.6 mg N/L).
The lowest concentrations of phosphates were found in rainwater collected from the zinc-coated metal sheet, and the highest concentrations were in rainwater from the surface covered with epoxide coating.
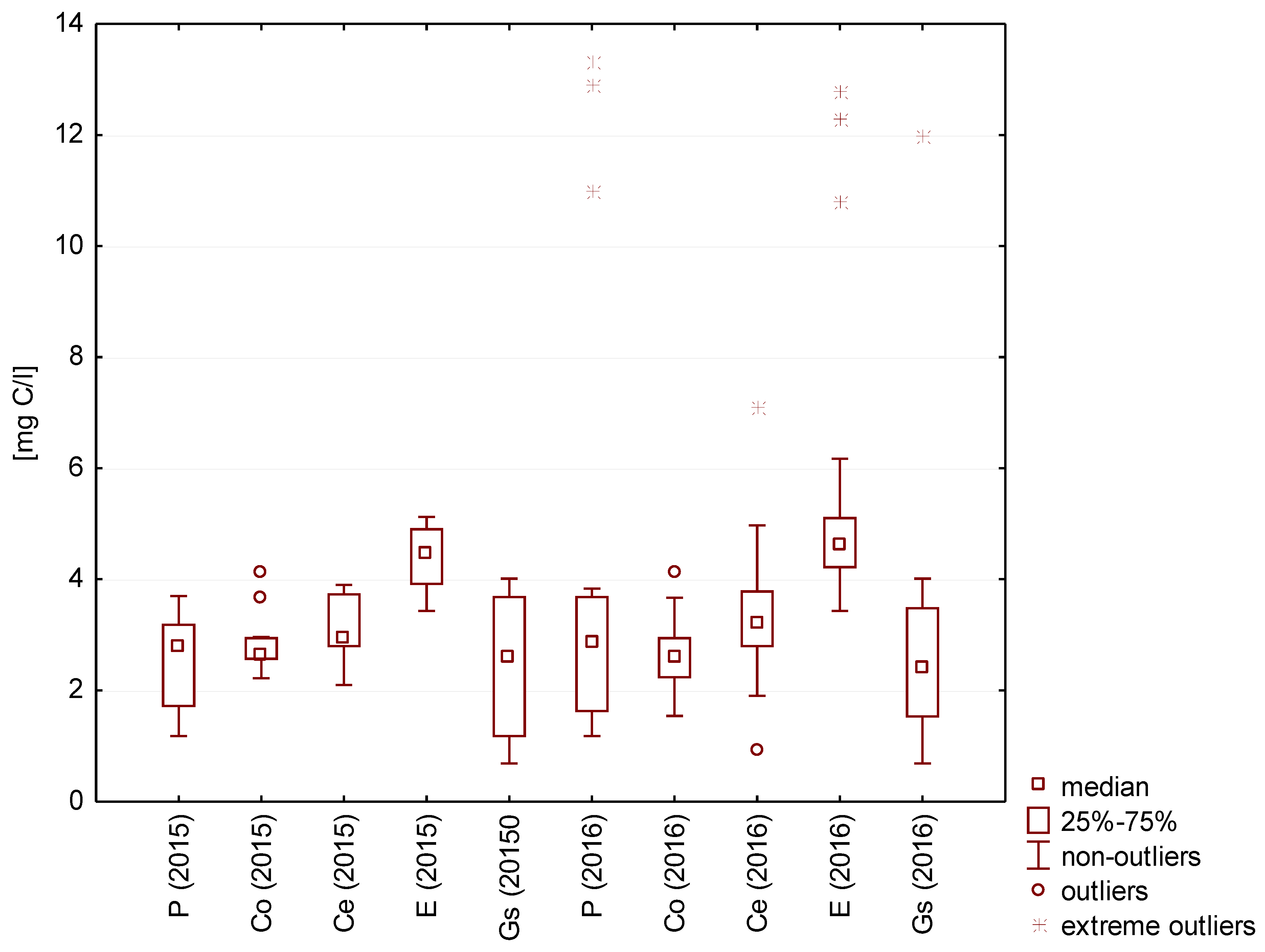
Total organic carbon (TOC) is a parameter that describes the level of water pollution by organic matter. The highest median TOC values were identified for rainwater from the surface covered with epoxide coating (5 mg C/L) (Figure 6).
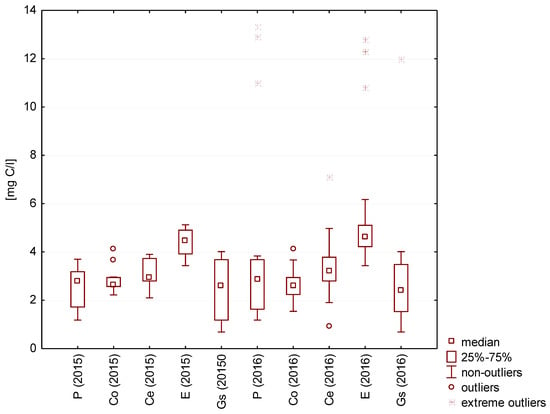
Figure 6.
Statistical data for total organic carbon content in the analyzed rainwater.
3.3. Heavy Metals in Rainwater
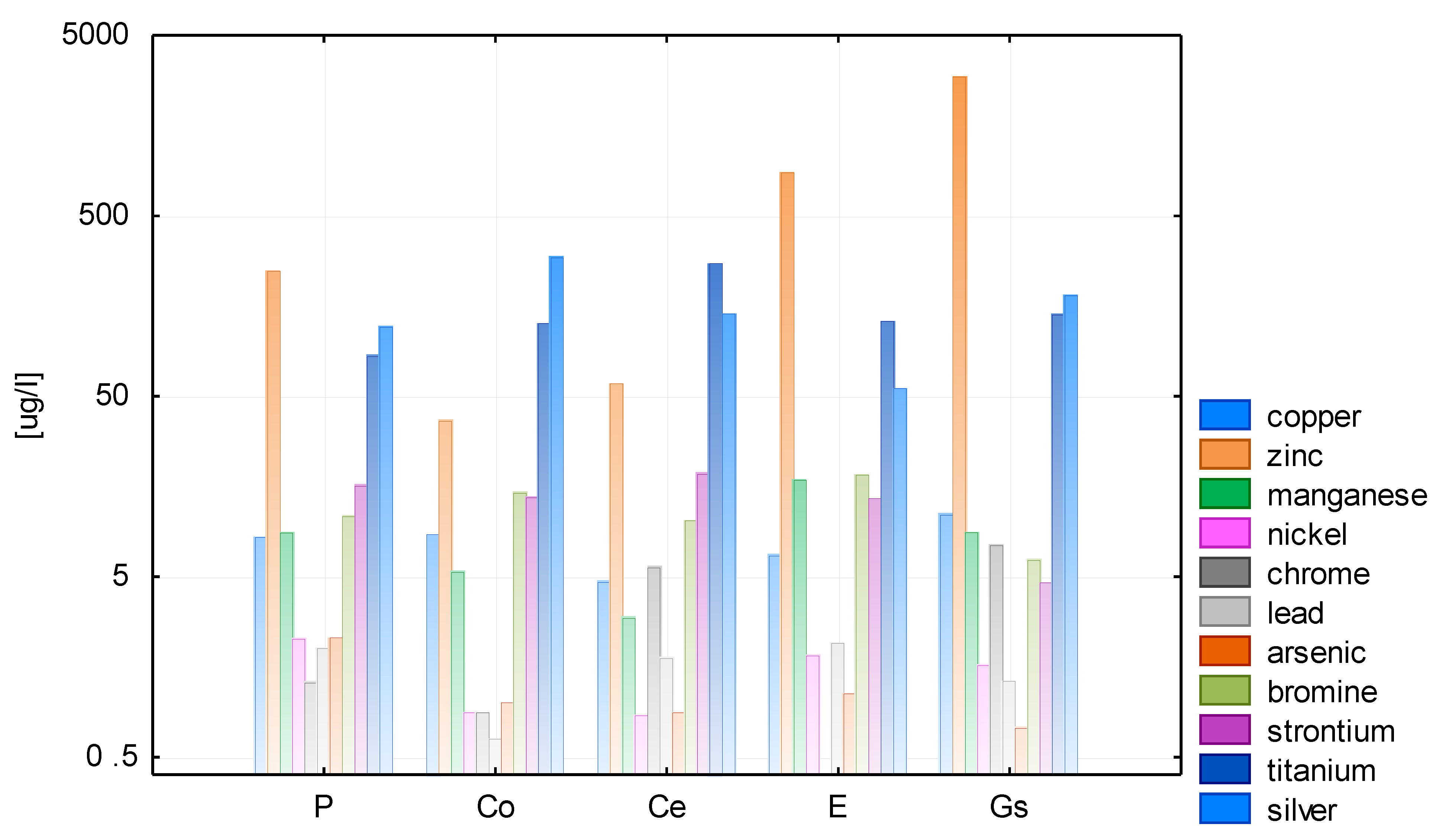
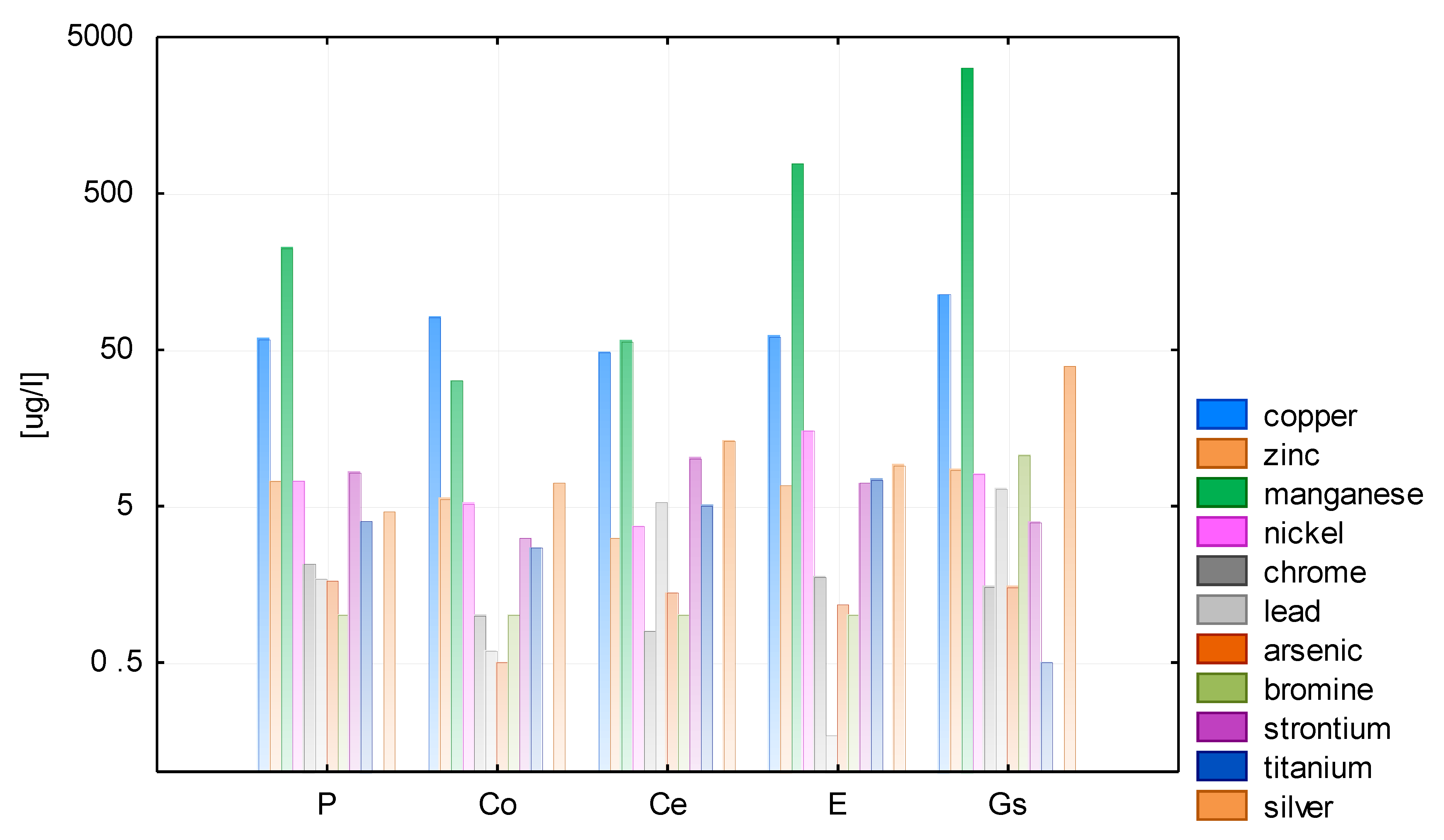
The results of the analysis of heavy metal ions in both test cycles are displayed in Figure 5 and Figure 6. Each tested water sample appeared to contain trace amounts of nickel, chromium, lead, and arsenic at concentrations slightly above 1 µg/L; ions of copper, manganese, bromine, and strontium were measured at levels of around 10 µg/L, and the concentrations of iron, zinc, titanium, and silver often exceeded 100 µg/L.
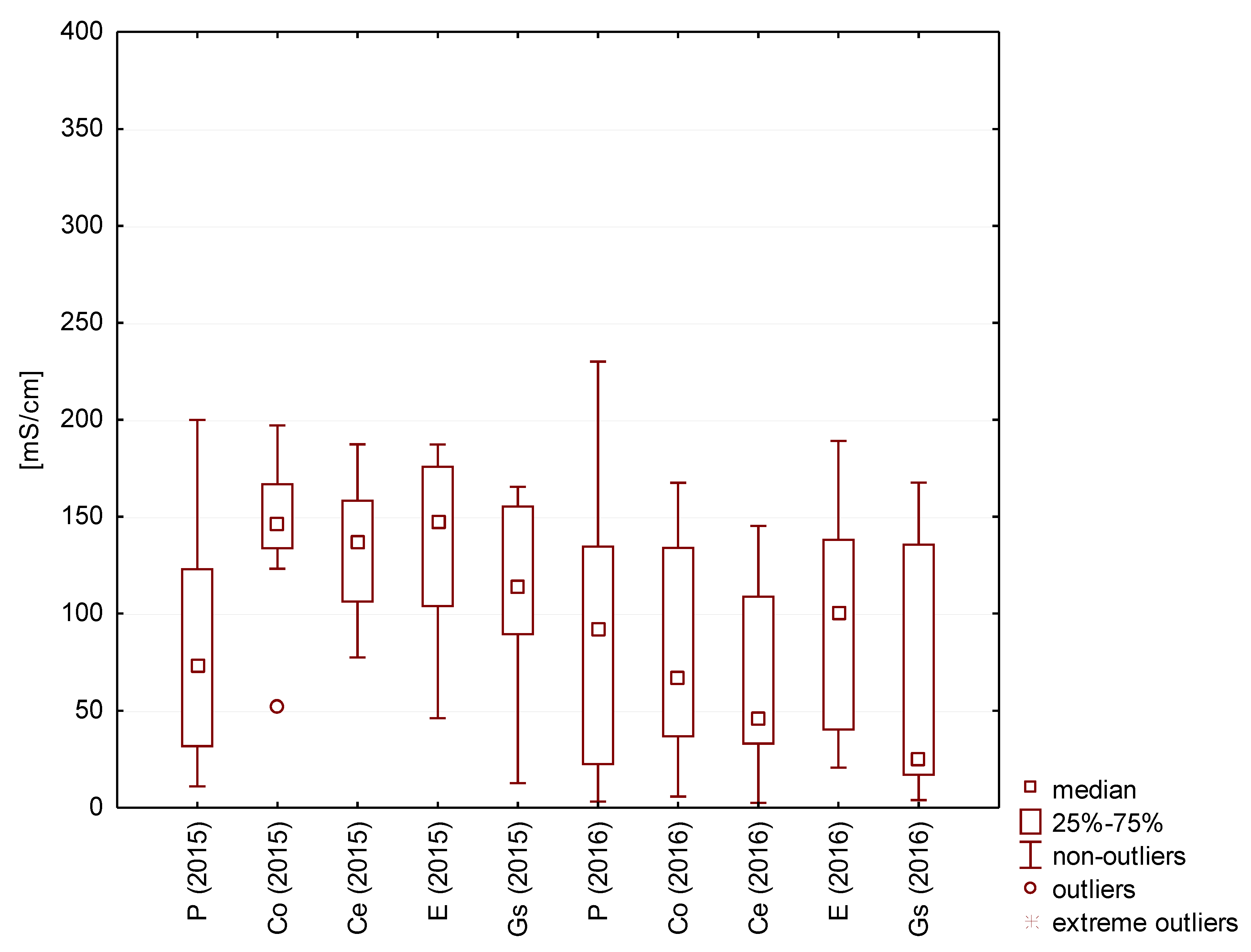
The electrical conductivity of rainwater collected from different roofing materials and directly from the air fluctuated between 1 and 26 µS/cm, and the median values ranged from 1 to 4 µS/cm (Figure 7 and Figure 8).
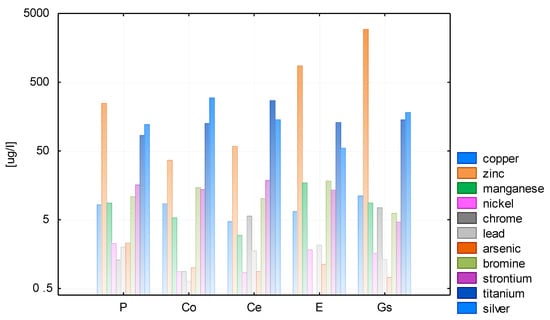
Figure 7.
Median concentration of ions in rainwater in 2015.
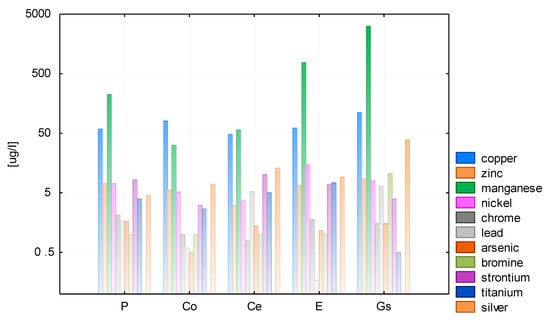
Figure 8.
Median concentration of ions in rainwater in 2016.
The lowest electrical conductivity values were recorded for water collected from the guttering of a roof covered with the galvanized steel sheet (comparable to the values for control samples collected directly from atmospheric precipitation). The type of rainwater with the highest electrical conductivity was not clearly indicated (Figure 9).
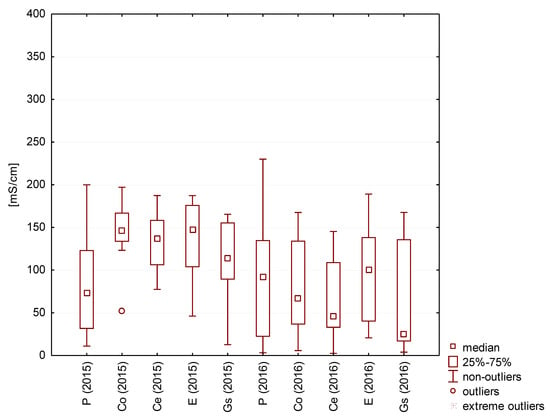
Figure 9.
Statistical data for the specific conductivity in the analyzed rainwater.
3.4. Microbiological Quality of Rainwater
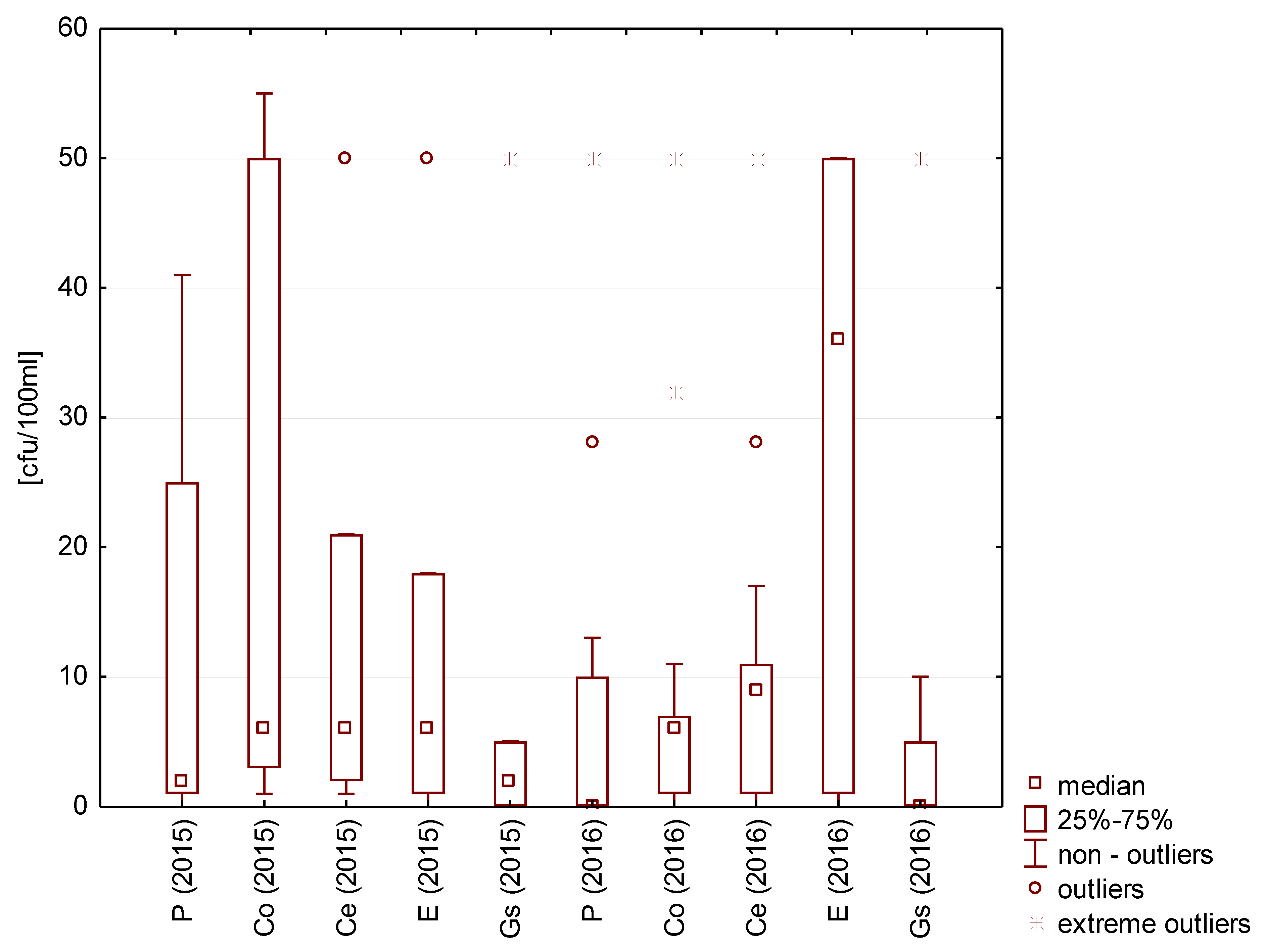
Sanitary quality aspects of water are normally defined by two factors: The number of Escherichia coli and the number of Enterococcus. The counts of both species were measured in each tested rainwater sample (Figure 10).
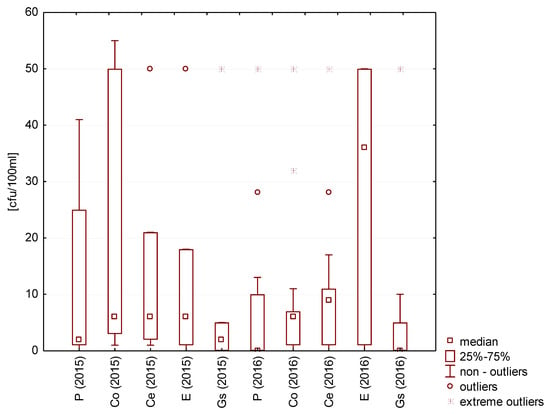
Figure 10.
Statistical data for the number of Escherichia coli bacteria present in rainwater.
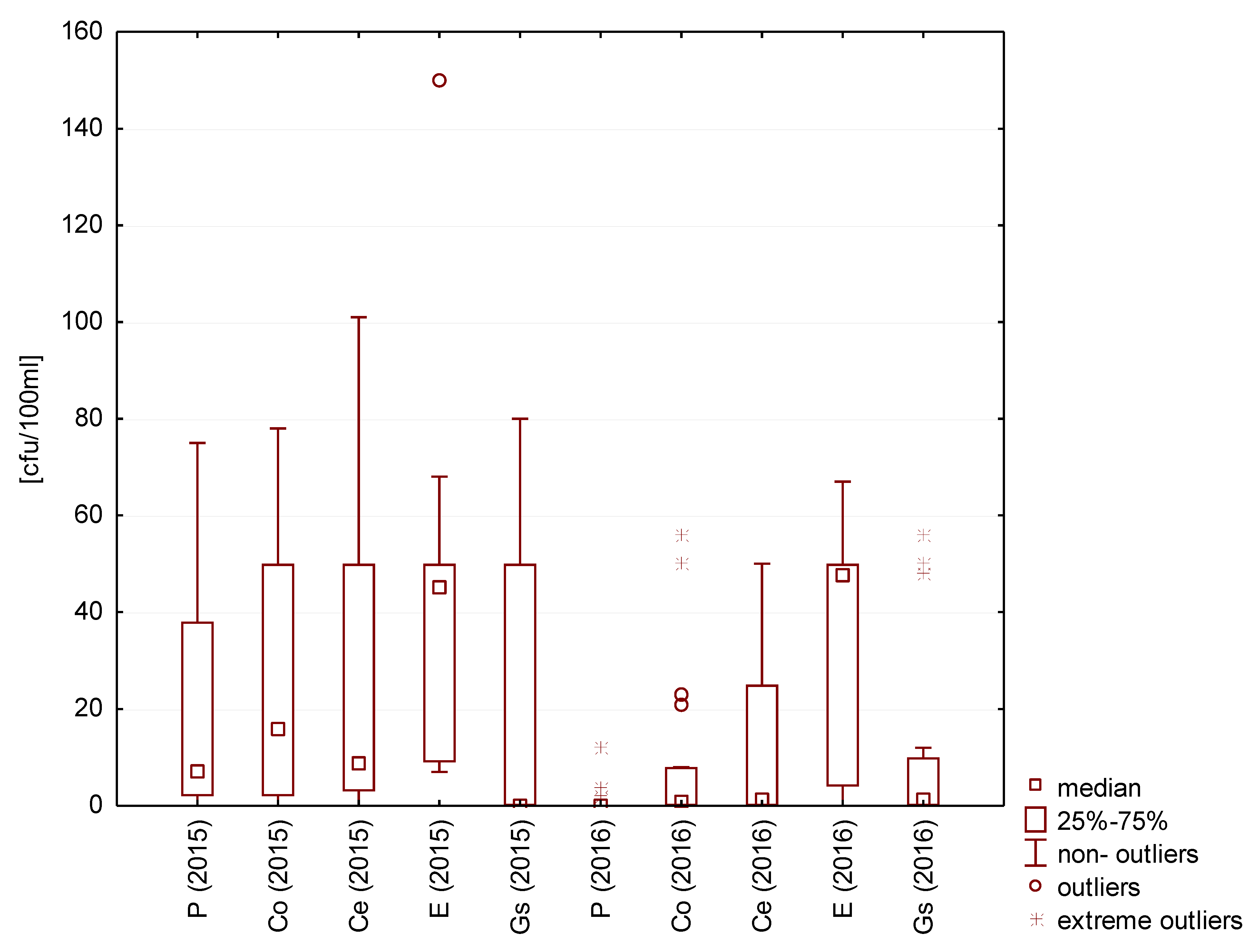
E. coli were the most numerous in rainwater collected from concrete tile roofing during the test seasons in 2015 and in terrace-collected rainwater in 2016. The lowest number of E. coli (excluding the lowest and highest outliers) was measured in the rainwater collected from galvanized steel sheet roofing (less than 5 cfu/100 mL). In this rainwater, the number of bacteria was similar in both test cycles. However, the number of Enterococcus in rainwater collected directly from atmospheric precipitation and from roofs with concrete and ceramic tiles and the galvanized steel sheet was lower in 2016 than in 2015. The values were similar in both test cycles only for the rainwater from the surface covered with epoxide coating (Figure 11).
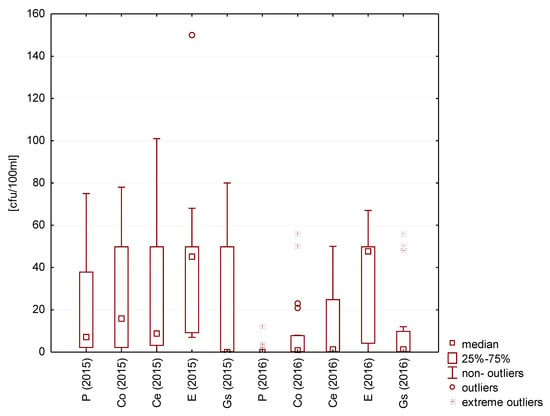
Figure 11.
Statistical data for the number of Enterococci present in rainwater.
The highest median values of Enterococcus were established for rainwater collected from the epoxide-coated terrace surface (approx. 50 cfu/100 mL).
4. Discussion
All the obtained results that describe the quality of rainwater collected from roof surfaces and directly from atmospheric precipitation account for the so-called “time of the first runoff”. The literature data indicate that the quality of rainwater collected from the beginning of the rainfall differs from that measured after the designated time of the first runoff. Nosrati [23] measured the concentrations of phosphates, sulfates, and nitrates in water collected from a bituminous roof without taking into account the first runoff, and the values were four times higher than those in the water collected after a certain time from the beginning of the rainfall.
Generally, rainwater that contacts a roof surface deteriorates in physical, chemical, and microbiological quality. Only in the case of pH does a positive effect result from contact with a roof surface especially in the case of ceramic and concrete tiles. The increase in the pH of water collected from concrete tiles compared with rainwater collected directly from the air is the result of the composition of cement. Concrete tiles, called cement tiles, are made of sand, Portland cement, iron oxide pigments, and water. Cement includes carbonates, such as calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and magnesium carbonate (MgCO3), which may, to some extent, be washed away by rainwater and increase the pH value [24]. Studies on rainwater in highly urbanized zones have reported a significantly lower pH (4.4) in these locations [25]. The acidification of rainfall may be caused by the combustion of fuels, which results in the formation of nitrogen oxides, the so-called NOx, and SO2 (sulfur dioxide). This is a characteristic feature of precipitation in large urban agglomerations [26].
The presented rainwater turbidity tests suggest that this parameter is dependent on the roughness of the roof-covering material. The rainwater turbidity increases with the roughness of the roof surface. Leong et al. [24] demonstrated reverse dependencies and attributed their findings to the capacity of rough surfaces to hold the dirt in rainwater. For glass, metal, and ceramic surfaces, the maximum turbidity values were 92.9, 57.1, and 10.1 NTU. Naddeo et al. reported significantly higher turbidity values for rainwater collected directly from air (25.88 NTU) compared with the obtained results of 4 NTU. This might have resulted from a higher number of suspended dust particles, as well as from the fact that the tests were conducted in an urban area [27]. Rainwater turbidity can also be the result of revivable bacteria [28].
The determination of the concentration of nitrogen compounds proves to be particularly important with regard to microbiological tests and the assessment of conditions that promote bacterial survival and growth in water. The source of nutrients in rainwater from atmospheric precipitation can be plant pollen, fungal spores, bacterial cells, and bacterial spores, as well as other substances from origins such as agricultural crops, which pollute roof surfaces by dry deposition. In addition, nutrients may come from natural sources, such as bird droppings, bryophytes, and lichens that pollute roof runoff [29]. In the analyzed rainwater, regardless of the type of roofing material, the concentration of nitrogen compounds oscillated around 0.2–0.4 mg NH4+/L (0.6–1.22 mg N/L). Research on the content of nitrogen compounds in rainwater in urbanized areas showed significantly lower concentrations of NH4+ ions and amounted to an average of 0.02 mg NH4+/dm3 [28]. The highest nitrate concentrations were recorded for rainwater collected from concrete and ceramic tile roofing. Similar nitrate concentrations to those determined for rainwater collected from concrete tile roofing were found in strongly urbanized areas [29]. Lower nitrogen concentrations in rainwater in urbanized areas may result from a lower share of agricultural areas and mowed meadows than in the sampling area in the presented studies. In turn, the concentration of phosphates in the analyzed rainwater samples oscillated around a value of 0.02 mg PO43−/L. Duncan et al. (1995), in their research on rainwater in an urban zone, observed concentrations of 0.01–0.10 mg PO43−/L [29].
The content of biogenic compounds in water is of great importance for the multiplication of microorganisms. Knowledge of the concentration of these compounds allows for the determination of whether the water is microbiologically stable. The content of inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus compounds and organic food substrates, which create conditions for the growth of heterotrophic organisms, including pathogenic microorganisms, determines the microbiological stability [30]. Parameters that limit the secondary development of microorganisms should be lower than 0.25 mg C/L biodegradable dissolved organic carbon (BDOC), 0.2 mg Ninorg/L (sum of nitrogen in the form of ammonium, nitrite, and nitrate ions), and 0.03 mg PO43−/L [31].
Rainwater is microbiologically stable. The method and conditions of collecting rainwater, such as the type of roofing, increase the risk of loss of microbiological stability. In the case of water containing organic compounds and inorganic nitrogen compounds, phosphate ions are of fundamental importance [32,33]. Insufficiency of these ions inhibits the growth of microorganisms to a much greater extent than the lack of other biogenic materials [34]. The data presented in Figure 5 show that the type of roofing has a small effect on the values of parameters that determine the microbiological stability of rainwater. They also demonstrate that the rainwater collected from all roof surfaces contained nitrogen and organic carbon compounds in amounts that indicate a risk of loss of microbial stability. Only the phosphate content met the criterion for stability. To maintain stability and reduce the risk of secondary bacteriological water contamination to a minimum, two of the three biogenic materials that determine the growth of microorganisms should be removed [30]. It should also be noted that phosphorus, as well as other nutrients, can leach from materials that rainwater contacts, resulting in faster microbial growth [35,36]. However, there is a lack of unambiguous and sufficient information on the impact of (i) the materials used to build rainwater collection and distribution systems, (ii) the changes in the quality of water in contact with them, and (iii) the speed of biofilm growth on the materials that build these systems.
Other authors, including those of [37], have emphasized the significant impact of surface roughness on the content of biogenic substances. This observation coincides with the test results obtained in this study. The differences in the levels of phosphates and nitrogen compounds that occurred between water samples collected from different roofs may be primarily due to the structure of these surfaces and the possibility of washing out dry deposition pollutants. It should also be noted that the inclination of the roof surface can have a significant impact on the quality of rainwater. The conducted research indicates that the values of turbidity, nitrates, phosphates, or TOC are the highest in rainwater harvested from the roof with the minimum inclination angle (covered with epoxy resin). This is confirmed by studies carried out much earlier on the quality of rainwater collected from roofs covered with shingles, green roofs, and so-called cold roofs with smooth coatings to prevent overheating, among other roof materials. The results of parameters such as turbidity and total organic carbon content were almost twice as high in water collected from smooth roof surfaces with a small inclination angle compared with water collected from roofs with rough surfaces and a higher slope angle [38].
In 2016, the concentrations of elements detected in rainwater were lower than those found in 2015. This may be the result of the higher total rainfall in 2016. Analyses reported in the literature show that heavy metals can be found in virtually all types rainwater, including water in natural [39], strongly urbanized [25,40], and rural areas [25], as well as in both stored rainwater [17] and the so-called first run-off [41,42]. The sources of heavy metals present in rainwater are the surfaces washed by it since they are points of pollutant accumulation due to dry deposition. The solubility of nonferrous metals, such as lead, may vary according to the rainwater pH [42]. Metals such as Cd, V, Cu, and Zn demonstrate higher solubility than Ni, Cr, and Pb, both in wet and dry deposits [43]. This is confirmed by the concentrations of these elements in the analyzed rainwater types. Water collected from the galvanized steel sheet roof is distinguished by higher zinc content (3164.55 μg Zn/L) than other samples (less than 1000 μg Zn/L). This dependence on roofing material has also been found by other researchers [39,42,44,45,46,47]. However, this concentration is not harmful to human health. In 1982, JECFA proposed a daily zinc requirement of 0.3 mg/kg body weight and a maximum allowable daily intake of 1.0 mg/kg body weight. The daily requirement for adults is therefore 15–22 mg. It was found that determining the value of health guidelines is not currently required. However, at levels above 3 mg/L, water tends to form a greasy film after cooking and has an undesirable astringent taste [48].
Electrical conductivity is an indicator of positive or negative ions present in the water. It may indicate pollution by substances such as heavy metal ions. In the analyzed water samples, the electrical conductivity was around 1–4 μS/cm (median). Zhang et al. obtained similar results for water collected from roofs covered with roof tiles and sheets, and a significantly higher conductivity was determined for runoffs from the green roof [49]. The general mineralization of rainwater in natural conditions may be only several milligrams of the substance dissolved per liter of water; however, in industrialized regions, the mineralization level is increased. The values obtained are relatively low in comparison with those recorded in industrialized zones (614.8 μS/cm) [41].
In each rainwater-type test, including the rainwater collected directly from atmospheric precipitation, fecal contamination indicator bacteria were detected. The presented research results indicate that the microbiological quality of precipitation deteriorates after contact with roof surfaces. Llopart-Mascaró et al. [50] also noted that rainwater collected directly from precipitation had detectable E. coli in only 36% of cases, but 100% of the samples from roof drainage were contaminated. The presence of such bacteria has been demonstrated by almost all analogous studies. Lee et al. determined a lower amount of E. coli in rainwater collected from roofs with concrete tiles (2 cfu/100 mL), ceramic (1 cfu/100 mL), and zinc-coated metal sheets (0 cfu/100 mL). It is interesting to note that in extensive green roof water leachate, an average of only 1 cfu/100 mL was identified. It is believed that the substrate for plant growth may create, in a certain sense, deposits and conditions conducive to the creation of biofilm, which increases the difficulty of washing out microorganisms from roof surfaces [29]. In rainwater samples collected without rejecting the so-called first run-off, the number of E. coli can be significantly higher, with counts of 5500 [41] and even 7670 cfu/100 mL [22]. This is also confirmed by the previously mentioned research by Lee et al., who reported the bacterial counts from the first run-off in water collected from different surfaces: Concrete roof tiles (18 cfu/100 mL), ceramic roof tiles (8 cfu/100 mL), and zinc-coated metal sheets (4 cfu/100 mL) [38].
Escherichia coli and Enterococcus are almost always detected in roof-harvested rainwater. A comparison of the median values of enterococci reveals that their numbers were lower in 2016 than in 2015. The reason may be the different numbers of rain episodes in individual research cycles and thus the different frequencies of leaching microbiological pollutants from roof surfaces. Only for a roof with a minimum inclination are the results comparable in both research cycles. E. coli and Enterococcus are microorganisms present at high levels in the feces of both humans and animals. The presence of these bacteria in roof-harvested rainwater can be explained by the deposition of feces on these roofs by birds and small mammals [51]. Another potential source of contamination by fecal microorganisms is soil particles carried by the wind from agricultural fields fertilized with organic substances or the bioaerosols from free-standing, unsheltered reactors of biological wastewater treatment plants. The sampling points of the tested water are south of the above-mentioned potential sources of microorganisms, and southwest winds were predominant in the study period. Some studies that appear to confirm this hypothesis have shown that the bacteria contained in droplets of water carried by the wind can travel up to 1 km and retain their viability [52,53,54,55,56]. Of the examined water samples, the best microbiological quality was found in the one taken from the roof covered with the galvanized sheet. This is related to the biocidal properties of zinc and the relatively smooth surface of the sheet. Mendez et al. indicated that adequate roofing could be an effective measure to prevent the growth of microorganisms. In the experimental studies, various roof coverings were used, and galvanized steel proved to be the cover with the greatest disinfection properties. This may have resulted from an increase in the temperature of the roof surface [39]. The relationship between the roughness of the roof material and the number of microorganisms has been confirmed by the majority of rainwater researchers [22,40]. At the same time, depending on the rainfall frequency and roofing material, the quality of roof-harvested rainwater can deteriorate or improve compared with rainwater collected directly from atmospheric precipitation.
In Europe, rainwater can be a valuable source of drinking water in crisis situations that are caused by the contamination of water supply systems, large-scale floods, or terrorist threats (biological weapons). This is permitted by Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998, which indicates “all water in its original condition or after treatment intended for drinking, cooking, preparing food or other household purposes, regardless of its origin and whether it is delivered: from a distribution network, tanks or in bottles or containers.” Acceptable values of indicators have also been determined for situations in which it is impossible to obtain and maintain water with the highest microbiological parameters. In natural disaster situations, E. coli in water is permissible at a level of 10 cfu/100 mL. From the results obtained, it can be concluded that only rainwater collected from the roof covered with galvanized steel would be usable as drinking water in crisis conditions [57].
This means that the other water samples would not be suitable as a source of drinking water or for hygienic purposes without prior treatment, which, in certain situations, can be expensive and requires advanced processes. The presence of fecal contamination indicator bacteria precludes this water from being considered safe for watering crops whose fruit can be consumed without being cleaned (such as strawberries or raspberries). This water can only be safely utilized for laundry or dishwashing, provided that appropriate temperature is applied (above 60 °C), as well as for typical cleaning activities in households, such as driveway washing, car washing, or lawn watering.
5. Conclusions
1. The best microbiological quality was measured in the water collected from the roof covered with galvanized steel. The bacterial content meets the requirements set out by the WHO for water used in crisis conditions. Water collected from other roofing materials (concrete tile, ceramic tile, and epoxy resin) contained up to 150 cfu/100 mL, which corresponds to the microbiological quality of surface water and prevents its use without disinfection.
2. The type of material from which the roofing is made determines the bacteriological quality of the water. The porosity of the roofing affects the retention of dust impurities that carry both promoters (C, N, P) and inhibitors (metal ions) of microbial development.
3. Nutrient concentrations in rainwater determine the microbiological stability of the water. This parameter is extremely important in the context of possible uses of stored rainwater. The tested rainwater was biologically stable, but only phosphorus was determined to have stability. Increased deposition of biogenic material on roofs can lead to the loss of microbial stability in rainwater.
4. Substances leached from roofing materials may inhibit the growth of microorganisms. High concentrations of zinc in the water collected from the roof covered with galvanized steel could have a beneficial effect on the bacteriological quality of rainwater.
5. It should be remembered that the temperature of the air and surface from which water is collected also determines the microbiological quality. Smooth galvanized steel surfaces that heat easily will likely inhibit the growth of microorganisms in the summer and stimulate growth in early spring and late autumn. However, this should be confirmed in further studies.
6. After it contacts the roof surface, rainwater has higher turbidity compared with water collected directly from atmospheric precipitation. Rough roofing provides favorable conditions for depositing substances such as nutrients that stimulate bacterial growth.
7. Contact with cement and ceramic tiles increases the pH of rainwater to 7.0. This beneficially reduces the water’s acidity but increases its risk of developing bacteria that are hazardous to health since a neutral pH is optimal for their multiplication.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “conceptualization, M.Z., J.Z., D.P.; methodology, M.Z., J.Z., D.P.; validation, M.Z.; investigation, M.Z., J.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z., J.Z., D.P., D.S.; writing—review and editing, M.Z., J.Z.; visualization, M.Z., D.S.; supervision, D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by DS.BO.001.20.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Orlińska-Woźniak, P.; Wilk, P.; Gębala, J. Water availability in reference to water needs in Poland. Meteorol. Hydrol. Water Manag. 2013, 1, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Szalinska, E. Water Quality and Management Changes Over the History of Poland. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 100, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slyś, D. Potential of rainwater utilization in residential housing in Poland. Water Environ. J. 2009, 23, 318–325. [Google Scholar]
- Pochwat, K.; Słyś, D.; Kordana, S. The temporal variability of a rainfall synthetic hyetograph for the dimensioning of storm-water retention tanks in small urban catchments. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Grant, A.; Sharma, A.; Chen, D.; Chen, L. Alternative Water Resources for Rural 5 Residental Development In Western Austarlia. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.P.; Hunt, W.F. Performance of rainwater harvesting systems in the southeastern United States. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Jones, P. In-situ monitoring of energetic and hydrological performance of a semi-intensive green roof and a white roof during a heatwave event in the UK. Indoor Built Environ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stec, A.; Kordana, S.; Slys, D. Analysing the financial efficiency of use of water and energy saving systems in single-family homes. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 151, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basinger, M.; Montalto, F.; Lall, U. A rainwater harvesting system reliability model based on nonparametric stochastic rainfall generator. J. Hydrol. 2010, 392, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stec, A.; Zelenakova, M. An Analysis of the effectiveness of two rainwater harvesting systems located in central eastern Europe. Water 2019, 11, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.T.; Baksh, A.A.; Papon, M.T.I.; Ali, M.A. Rainwater harvesting system: An approach for optimum tank size design and assessment efficiency. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, M.W.; Gitau, N.A.; Ndunge, D. Rainwater Harvesting Technologies in Makueni County, Kenya. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2015, 5, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, C.A.; Harrison, T.; Coombes, P.J.; Dunstan, H.R.; Dunstan, R.H. Identifying the major influences on the microbial composition of roof harvested rainwater and the implications for water quality. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdeb, M.; Zamorska, J.; Papciak, D. Studying microbiology of rain water for of their use in economy. J. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 17, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwezi, W.; Dunjana, N.; Pisa, C.; Taur, O.T.; Nyamadzawo, G. Water quality and public health risks associated with roof rainwater harvesting systems for potable supply: Review and perspectives. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2015, 6, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedler, E.; Gilboa, Y.; Muklada, H. Quality of Roof-Harvested Rainwater as a Function of Environmental and Air Pollution Factors in a Coastal Mediterranean City (Haifa, Israel). Water 2017, 9, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despins, C.; Farahbakhsh, K.; Leidl, C. Assessment of rainwater quality from rainwater harvesting systems in Ontario, Canada. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 2009, 58, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmreich, B.; Horn, H. Opportunities in rainwater harvesting. Desalination 2009, 248, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajni, K.; Rajasekhar, B. Assessment of bacterial pathogens in fresh rainwater and airborne particulate matter using Real-Time PCR. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Koszelnik, P. Atmospheric deposition as a source of nitrogen and phosphorus loads into the Rzeszow 5 reservoir, SE Poland. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2007, 33, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 5667-8: 1993 Water Quality—Sampling—Part 8: Guidance on the Sampling of Wet Deposition; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993.
- Kotowski, A.; Kaźmierczak, B.; Dancewicz, A. Rainfall Modeling for Sewage Sizing, PAN, Warsaw. 2010. Available online: http://www.bartoszkazmierczak.pl/pliki/monografia1.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Nosrati, K. Identification of a water quality indicator for urban roof runoff. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2017, 9–10, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, J.; Oh, K.S.; Poh, P.E.; Chong, M.N. Prospects of hybrid rainwater-greywater decentralized system for water 10 recycling and reuse: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3014–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wang, Z. Anthropogenic influence on rainwater in the Xi’an City, Northwest China: Constrains from sulfur isotope and trace elements analyses. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 137, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.F.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.J.; Liang, C.S.; Ji, J.P.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X. Chemical composition of rainwater and the acid neutralizing effect at Beijing and Chizhou city, China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 164–165, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddeo, V.; Scannapieco, D.; Belgiorno, V. Enhanced drinking water supply through harvested rainwater treatment. J. Hydrol. 2013, 498, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Schweige, R.A.; L’Heureux, M.; Battisti, D.; Po-Chedly, S.; Jonshon, N.; Blanchard Wrigglesworth, E.; Harnos, K.; Zhang, Q.; Estman, R.; et al. Influence of high-latitude atmospheric circulation changes on summertime Arctic sea ice. Nat. Clim. Chang. 1995, 7, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, H.P. A Review of Urban Stormwater Quality Process; Cooperative Research Centre for Catchment Hydrology: Melbourne, Australia, 1995; ISBN 1-876-00606-4. [Google Scholar]
- Papciak, D.; Tchórzewska-Cieslak, B.; Pietrucha-Urbanik, K.; Pietrzyk, A. Analysis of the biological stability of tap water on basis of risk analysis and parameters limiting the secondary growth of microorganisms in water distribution system. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 117, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolska, M. Biological stability of water in water distribution systems. The effect of water treatment trials. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2015, 41, 147–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtola, M.J.; Miettinen, I.T.; Keinanen, M.M.; Kekki, T.K.; Laine, O.; Hirvonen, A.; Vartiainen, T.; Martikainen, P.J. Microbiology, chemistry and biofilm development in a pilot drinking water distribution system with copper and plastic pipes. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3769–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lethola, M.J.; Miettinen, I.T.; Lampola, T.; Hirvonen, A.; Vartiainen, T.; Martikainen, P.J. Pipeline materials modify the effectiveness of disinfectants in drinking water distribution systems. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, T. Microbial diversity in biofilms on water distribution pipes of different materials. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtola, M.J.; Laxander, M.; Miettinen, I.T.; Hirvonen, A.; Vartiainen, T.; Martikainen, P.J. The effects of changing water flow velocity on the formation of biofilms and water quality in pilot distribution system consisting of copper or polyethylene pipes. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2151–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.; Lu, C.; Lee, C. Effects of inorganic nutrients on the regrowth of heterotrophic bacteria in drinking water distribution systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 74, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Tansel, B.; Balbin, M. Influence of residential water use efficiency measures on houshold water dem and: A four year longitudinal study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 56, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Bak, G.; Han, M. Quality of roof–harvested rainwater – Comparison of different roofing 5 materials. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.H.; Ahmad, Y.; Yusoff, I.; Bong, C.W.; Kong, S.Y. Effects of roof pitch gradient and material to harvested rainwater quality. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, C.B.; Klenzendorf, J.B.; Afshar, B.R.; Simmons, M.T.; Barrett, M.E.; Kinney, K.A.; Kirisits, M.J. The effect of roofing material on the quality of harvested Rainwater. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkum, A.; Peke, Y.H.; Tuncel, G. Investigating relationships between aerosol and rainwater compositions at different locations in Turkey. Atmos. Res. 2008, 89, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, G.D.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Assessment of water quality of first-flush roof runoff and harvested rainwater. J. Hydrol. 2012, 466–467, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Han, M.; Choi, J. Comparison of the microbiological anh chemical characterization of harvested rainwater and reservoir water as alternative water resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, R.; Nimmo, M.; Corcoran, P.A. Rain water-aerosol trace metal relationships at cap ferrat: A coastal site in the Western Mediterranean. Mar. Chem. 1997, 58, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardena, J.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Atmospheric deposition as a source of heavy metals in urban stormwater. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaziz, M.I.; Gunting, H.; Sapari, N.; Ghazali, A. Variations in rainwater quality from roof catchments. Water Res. 1989, 23, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialle, C.; Sablayrolles, C.; Lovera, M.; Huau, M.C.; Jacob, S.; Montrejaud-Vignoles, M. Monitoring of water quality from roof runoff: Interpretation using multivariate analysis. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3765–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/17 Zinc in Drinking-Water. Available online: https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/zinc.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hou, P.; Wan, W.; Li, R. Quality and seasonal variation of rainwater harvested from concrete, asphalt, ceramic tile and green roofs in Chongquing, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 132, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopart-Mascaró, A.; Ruiz, R.; Martínez, M.; Malgrat, P.; Rusiñol, M.; Gil, A.; Suárez, J.; Puertas, J.; del Rio, H.; Paraira, M.; et al. Analysis of rainwater quality: Towards sustainable rainwater management in urban environments—Sostaqua Project. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Sustainable Techniques and Strategies in Urban Water Management (NOVATECH 2010), Lyon, France, 27 June–1 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrowsky, P.H.; DeKwaadsteniet, M.; Cloete, T.E.; Khan, W. Distribution of indigenous bacterial pathogens and potential pathogens associated with roof-harvested rainwater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmigielska, M. Zoonoses transmitted by birds, Undomesticated. Ornis Pol. 2010, 51, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Korzeniewska, E.; Filipowska, Z.; Gotkowska–Płachta, A.; Janczukowic, Z.W.; Ritkowski, B. Bacteriological pollution of the atmospheric air at the municipial and dairy Wasterwater Treatment Plant area and in its surroundings. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2008, 34, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ekstrom, S.; Noziere, B.; Hultberg, M.; Alsberg, T.; Magner, J.; Nilsson, E.D.; Artaxo, P. A possible role of ground-based microorganisms on cloud formation in the atmpsphere. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Hwang, C.Y. Prokaryotic abundance and 16S rRNA gene sequences detected in marine aerosols on the East Sea (Korea). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 76, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymenakou, P.N. Atmosphere: A Source of Pathogenic or Beneficial Microbes? Atmosphere 2012, 3, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Manganese in Drinking-Water Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality© World Health Organization 2011; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).