Grain-Size Specific Characterisation and Resource Potentials of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Bottom Ash: A German Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Resource Potential of MSWI Bottom Ash
2.1. Metal Recovery Potential
2.2. Utilisation of Processed Bottom Ash
2.3. MSWI Bottom Ash Characterisation and Sampling
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. MSWI Plant
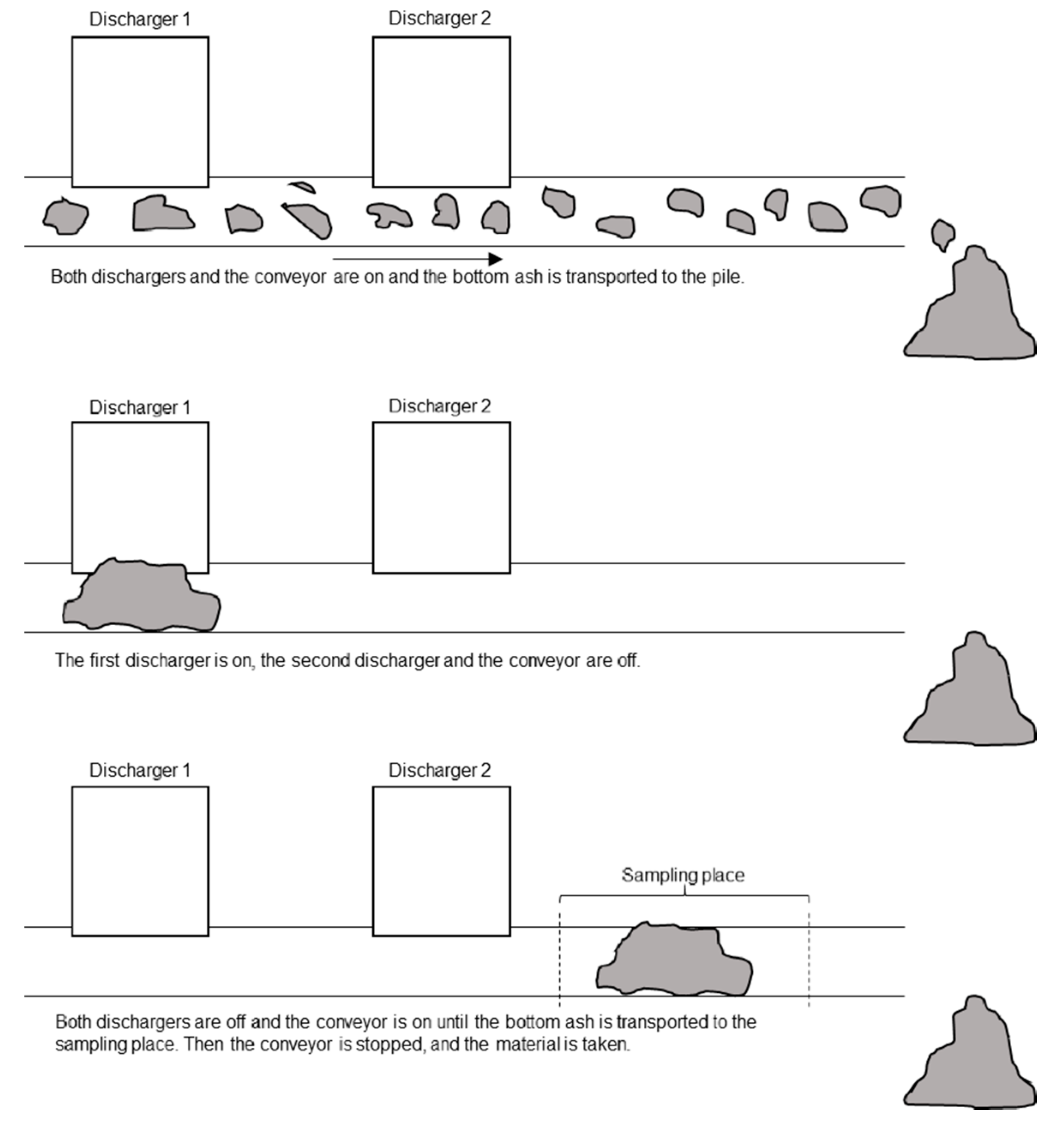
3.2. Sampling
3.3. Sample Preparation and Analysis
3.4. Chemical Analyses
3.5. Determination of Resource Potentials
3.6. Statistical Measures
4. Results
4.1. MSWI Bottom Ash Characterisation
4.1.1. Particle Size Distribution
4.1.2. Material Composition
4.1.3. Total Contents
4.1.4. Leaching Concentrations
4.2. Resource Potentials
4.2.1. Metal Recovery
4.2.2. Minerals Utilisation
5. Discussion
5.1. Sampling and Processing
5.2. Characterisation
5.3. Resource Potentials
5.3.1. Metals
5.3.2. Mineral Fraction
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eurostat. Waste Treatment 2016. Available online: https://appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/nui/show.do?dataset=env_wastrt&lang=en (accessed on 13 February 2020).
- CEWEP. Bottom Ash Factsheet. Available online: https://www.cewep.eu/bottom-ash-factsheet/ (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- ITAD. Reststoffe (Residues). Available online: https://www.itad.de/wissen/reststoffe (accessed on 5 April 2020).
- Böni, D.; Morf, L.S. Thermo-Recycling: Efficient Recovery of Valuable Materials from Dry Bottom Ash; ZAR: Hinwil, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bunge, R. Aufbereitung von Abfallverbrennungsaschen—Eine Übersicht (Processing of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash—An overview). In Mineralische Nebenprodukte und Abfälle (Mineral by-Products and Waste); Thomé-Kozmiensky, K.J., Ed.; TK: Neuruppin, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783944310282. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchta, K.; Enzner, V. Metallrückgewinnung aus Rostaschen aus Abfallverbrennungsanlagen: Bewertung der Ressourceneffizienz (Metal Recovery from Bottom Ash From Waste Incineration Plants: Assessment of Resource Efficiency). Available online: https://entsorgergemeinschaft.de/tileviewer.html?d=17&pc=54 (accessed on 7 December 2018).
- Bunge, R. Recovery of Metals from Waste Incinerator Bottom Ash. 2019. Available online: https://www.umtec.ch/fileadmin/user_upload/umtec.hsr.ch/Dokumente/Metals_from_MWIBA_6_2019.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Astrup, T. Pretreatment and utilization of waste incineration bottom ashes: Danish experiences. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meima, J.A.; Comans, R.N.J. Geochemical modeling of weathering reactions in municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasenbauer, D.; Huber, F.; Lederer, J.; Quina, M.J.; Blanc-Biscarat, D.; Bogush, A.; Bontempi, E.; Blondeau, J.; Chimenos, J.M.; Dahlbo, H.; et al. Legal situation and current practice of waste incineration bottom ash utilisation in Europe. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 868–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjelmar, O.; Johnson, A.; Comans, R.N.J. Incineration: Solid residues. In Solid Waste Technology & Management; Christensen, T.H., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2011; pp. 430–462. ISBN 9781405175173. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, A.J.; Eighmy, T.T.; Hjelmar, O.; Kosson, D.S.; Sawell, S.E.; Vehlow, J.; Van der Sloot, H.A.; Hartlén, J. Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator Residues; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; ISBN 9780080537184. [Google Scholar]
- Knorr, W. Rückstände aus der Müllverbrennung (Residues from Waste Incineration); Erich Schmidt: Berlin, Germany, 1999; ISBN 3503048588. [Google Scholar]
- Caviglia, C.; Confalonieri, G.; Corazzari, I.; Destefanis, E.; Mandrone, G.; Pastero, L.; Boero, R.; Pavese, A. Effects of particle size on properties and thermal inertization of bottom ashes (MSW of Turin’s incinerator). Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle-Zermeño, R.; Gómez-Manrique, J.; Giro-Paloma, J.; Formosa, J.; Chimenos, J.M. Material characterization of the MSWI bottom ash as a function of particle size. Effects of glass recycling over time. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šyc, M.; Krausová, A.; Kameníková, P.; Šomplák, R.; Pavlas, M.; Zach, B.; Pohořelý, M.; Svoboda, K.; Punčochář, M. Material analysis of Bottom ash from waste-to-energy plants. Waste Manag. 2018, 73, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loginova, E.; Volkov, D.S.; Van de Wouw, P.M.F.; Florea, M.V.A.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Detailed characterization of particle size fractions of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimenos, J.M.; Segarra, M.; Fernández, M.A.; Espiell, F. Characterization of the bottom ash in municipal solid waste incinerator. J. Hazard. Mater. 1999, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, T.; Christensen, T.H. Waste Incineration Bottom Ashes in Denmark: Status and Development Needs by 2003; Affald Danmark & Environment & Resources DTU, Technical University of Denmark: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Allegrini, E.; Maresca, A.; Olsson, M.E.; Holtze, M.S.; Boldrin, A.; Astrup, T.F. Quantification of the resource recovery potential of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ashes. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; He, P.; Shao, L.; Zhang, H. Metal distribution characteristic of MSWI bottom ash in view of metal recovery. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2017, 52, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morf, L.S.; Gloor, R.; Haag, O.; Haupt, M.; Skutan, S.; Di Lorenzo, F.; Böni, D. Precious metals and rare earth elements in municipal solid waste—ources and fate in a Swiss incineration plant. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchova, L.; Bakker, E.; Rem, P. Precious metals in municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2009, 9, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gisbertz, K.; Hilgendorf, S.; Friedrich, B.; Heinrichs, S.; Rüßmann, D.; Pretz, T. Maximising metal recovery from incineration ashes. In Proceedings of the European Metallurgical Conference EMC 2013, Munich, Germany, 23 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Deike, R.; Ebert, D.; Warnecke, R.; Vogell, M. Abschlussbericht zum Projekt Recyclingpotentiale bei Rückständen aus der Müllverbrennung; (Final Report on the Project “Recovery Potentials of Residues from Waste Incineration”). 2012. Available online: https://www.itad.de/wissen/studien/20130110_deike-hmvarecyclingpotentialabschlussbericht.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2020).
- Lynn, C.J.; Dhir OBE, R.K.; Ghataora, G.S. Municipal incinerated bottom ash characteristics and potential for use as aggregate in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Wegen, G.; Hofstra, U.; Speerstra, J. Upgraded MSWI bottom ash as aggregate in concrete. Waste Biomass Valor 2013, 4, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelmar, O.; Holm, J.; Crillesen, K. Utilisation of MSWI bottom ash as sub-base in road construction: First results from a large-scale test site. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keppert, M.; Pavlík, Z.; Cerný, R.; Reiterman, P. Properties of concrete with municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash. In 2012 IACSIT Coimbatore Conferences; IACSIT Press: Singapore, 2012; pp. 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, U.; Rübner, K. The microstructure of concrete made with municipal waste incinerator bottom ash as an aggregate component. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Blasenbauer, D.; Aschenbrenner, P.; Fellner, J. Chemical composition and leachability of differently sized material fractions of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Blasenbauer, D.; Aschenbrenner, P.; Fellner, J. Complete determination of the material composition of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomé-Kozmiensky, E. Abfallverbrennungsanlagen: Deutschland (Waste Incineration Plants: Germany); TK Verlag Karl Thomé-Kozmiensky: Neuruppin, Germany, 2018; ISBN 978-3-944310-38-1. [Google Scholar]
- Quicker, P.; Stockschläder, J.; Zayat-Vogel, B.; Pretz, T.; Garth, A.; Deike, R.; Ebert, D.; Gellermann, C.; Brämer, T.; Ratering, S.; et al. Möglichkeiten Einer Ressourcenschonenden Kreislaufwirtschaft Durch Weitergehende Gewinnung von Rohstoffen Aus Festen Verbrennungsrückständen Aus der Behandlung von Siedlungsabfällen (Possibilities of a Resource-Efficient Recycling Economy by Further Extraction of Raw Materials from Solid Combustion Residues from the Treatment of Municipal Solid Waste); Umweltbundesamt: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Morf, L.; Gloor, R.; Skutan, S. Sampling, Sample Preparation and Analysis of Solid Residues from Thermal Waste Treatment and Its Processing Products; Methods Report; 2018; Available online: https://zar-ch.ch/fileadmin/user_upload/Contentdokumente/Oeffentliche_Dokumente/Sampling_methods_EN.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2019).
- Biganzoli, L.; Ilyas, A.; van Praagh, M.; Persson, K.M.; Grosso, M. Aluminium recovery vs. hydrogen production as resource recovery options for fine MSWI bottom ash fraction. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.M.; Snellings, R.; Van den Heede, P.; Matthys, S.; de Belie, N. The use of municipal solid waste incineration ash in various building materials: A belgian point of view. Materials (Basel) 2018, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Rem, P.; Van de Winckel, T. Fine Heavy Non-Ferrous and Precious Metals Recovery in Bottom Ash Treatment 2008. Available online: https://www.iswa.org/uploads/tx_iswaknowledgebase/paper38.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2019).
- Pfandl, K.; Stockinger, G.; Höllen, D.; Pomberger, R. Rohstoffpotenzial von MVA-Rostaschen für Metallrückgewinnung und Karbonatisierung (Raw material potential of municipal solid waste incineration ashes for metal recovery and mineral carbonation). Österr Wasser Abfallw 2018, 70, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dou, X.; Ren, F.; Nguyen, M.Q.; Ahamed, A.; Yin, K.; Chan, W.P.; Chang, V.W.-C. Review of MSWI bottom ash utilization from perspectives of collective characterization, treatment and existing application. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LAGA. Anforderungen an die Stoffliche Verwertung von Mineralischen Reststoffen/Abfällen (LAGA M 20) (Requirements for the Recycling of Mineral Residues/Waste). 2003. Available online: https://www.laga-online.de/documents/m20_nov2003u1997_2_1517834540.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2020).
- FGSV. Technische Lieferbedingungen für Gesteinskörnungen im Straßenbau (Technical Delivery Conditions for Aggregates in Road Construction); TL Gestein-StB 04, Ausg. 2004; Forschungsgesellschaft für Straßen-und Verkehrswesen (Road and Transportation Research Association (FGSV): Köln, Germany, 2005; ISBN 3937356436. [Google Scholar]
- Referentenentwurf des Bundesministeriums für Umwelt, Naturschutz, Bau und Reaktorsicherheit: Verordnung zur Einführung einer Ersatzbaustoffverordnung, zur Neufassung der Bundes-Bodenschutz-und Altlastenverordnung und zur Änderung der Deponieverordnung und der Gewerbeabfallverordnung (Ordinance on Groundwater Protection, Mineral Waste Utilization and Federal Soil Protection and Contaminated Sites, Draft Mutual Release. MantelV). 2017. Available online: https://www.bmu.de/fileadmin/Daten_BMU/Download_PDF/Gesetze/mantelv_text.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2020).
- Pfrang-Stotz, G.; Reichelt, J. Einfluss geänderter Stoffströme in der Abfallwirtschaft auf die zukünftige Qualität und die Verwertungsmöglichkeiten von Müllverbrennungsschlacken (Influence of Changed Material Flows in Waste Management on the Future Quality and Recycling Possibilities of Waste Incineration Slags). Forsch. Karlsr. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gy, P. Sampling of Heterogeneous and Dynamic Material Systems: Theories of Heterogeneity, Sampling, and Homogenizing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; ISBN 9780080868370. [Google Scholar]
- Aubert, J.E.; Husson, B.; Vaquier, A. Metallic aluminum in MSWI fly ash: Quantification and influence on the properties of cement-based products. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DIN EN 12457-4. Characterization of Waste—Leaching—Compliance Test for Leaching of Granular Waste Materials and Sludges—Part 4: One Stage Batch Test at a Liquid to Solid Ratio of 10 l/kg for Materials with Particle Size Below 10 mm (without or with Size Reduction); Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2003. (In Germany) [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Best Available Techniques (BAT) Reference Document for Waste Incineration; Publications Office of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hyks, J.; Astrup, T. Influence of operational conditions, waste input and ageing on contaminant leaching from waste incinerator bottom ash: A full-scale study. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wriggers, P.; Moftah, S.O. Mesoscale models for concrete: Homogenisation and damage behaviour. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2006, 42, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CUR. AEC-Granulaat als Toeslagmaterial Voor Beton (Processed Municipal Incinerator Bottom Ash as Aggregate for Concrete): CUR-Aanbeveling 116:2012. Available online: https://www.cur-aanbevelingen.nl/cur-aanbeveling-116 (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- Esbensen, K.H.; Wagner, C. Sampling quality assessment: The replication experiment. Spectrosc. Eur. 2016, 28, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Grünbein, M.; Wegkamp, D.; Rüßmann, D. Steigerung der Wertstoffseparation von rostaschen aus der nassentschlackung durch optimierung konventioneller Technik (Increase in recyclables separation of bottom ash from the wet purification by optimizing conventional technology). In Mineralische Nebenprodukte und Abfälle: Aschen, Schlacken, Stäube und Baurestmassen; Thomé-Kozmiensky, K.J., Ed.; TK: Neuruppin, Germany, 2015; ISBN 9783944310213. [Google Scholar]
- Muchova, L. Wet Physical Separation of MSWI Bottom Ash. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Breitenstein, B. Das “RENE-Verfahren” zur Rückgewinnung von NE-Metallen aus feinkörnigen Rostaschen der Thermischen Abfallbehandlung und Energetischen Verwertung (The “RENE process” for Recovery of Non-Ferrous Metals from Fine-Grained Bottom Ashes from the Municipal Solid Waste Incineration). Ph.D. Thesis, Clausthal University of Technology, Clausthal, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Cheng, Y.; He, D.; Yang, E.-H. Review of leaching behavior of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) ash. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyssinet, P.; Piantone, P.; Azaroual, M.; Itard, Y.; Clozel-Leloup, B.; Guyonnet, D.; Baubron, J.C. Chemical changes and leachate mass balance of municipal solid waste bottom ash submitted to weathering. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, O.; Wollik, E.; Johanna Bley, T. Recovery of copper from small grain size fractions of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash by means of density separation. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2017, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, O.; Simon, F.-G. Innovative treatment trains of bottom ash (BA) from municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) in Germany. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Saffarzadeh, A.; Shimaoka, T.; Kawano, T. Existence of Cl in municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash and dechlorination effect of thermal treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 267, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, Q.; Florea, M.V.A.; Schollbach, K.; Brouwers, H.J.H. A two-stage treatment for Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) bottom ash to remove agglomerated fine particles and leachable contaminants. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockinger, G. Nassaufbereitung von Abfallverbrennungsaschen-Betriebsergebnisse einer großtechnischen anlage in Österreich (Wet processing of MSWI bottom ash—Results of a large-scale plant in Austria). In Mineralische Nebenprodukte und Abfälle (Mineral By-Products and Waste); Thomé-Kozmiensky, K.J., Ed.; TK: Neuruppin, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783944310282. [Google Scholar]








| Element | Content (mg/kg) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Al (metallic) | 12,000–17,000 | [20,22,36] |
| Fe (metallic) | 60,000–12,000 | [15,16,20] |
| Cd | 2.6–14 | [22,31,39] |
| Cr | 180–1500 | [22,31,39] |
| Hg | 0.5 | [31] |
| Pb | 540–970 | [22,31,39] |
| Ni | 120–640 | [22,31] |
| Cu | 700–5200 | [20,22] |
| Zn | 1600–3400 | [20,22] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vateva, I.; Laner, D. Grain-Size Specific Characterisation and Resource Potentials of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Bottom Ash: A German Case Study. Resources 2020, 9, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources9060066
Vateva I, Laner D. Grain-Size Specific Characterisation and Resource Potentials of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Bottom Ash: A German Case Study. Resources. 2020; 9(6):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources9060066
Chicago/Turabian StyleVateva, Iveta, and David Laner. 2020. "Grain-Size Specific Characterisation and Resource Potentials of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Bottom Ash: A German Case Study" Resources 9, no. 6: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources9060066
APA StyleVateva, I., & Laner, D. (2020). Grain-Size Specific Characterisation and Resource Potentials of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Bottom Ash: A German Case Study. Resources, 9(6), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources9060066





