Unraveling Pneumomediastinum in COVID-19 Patients: Insights from a High-Volume-Center Case–Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
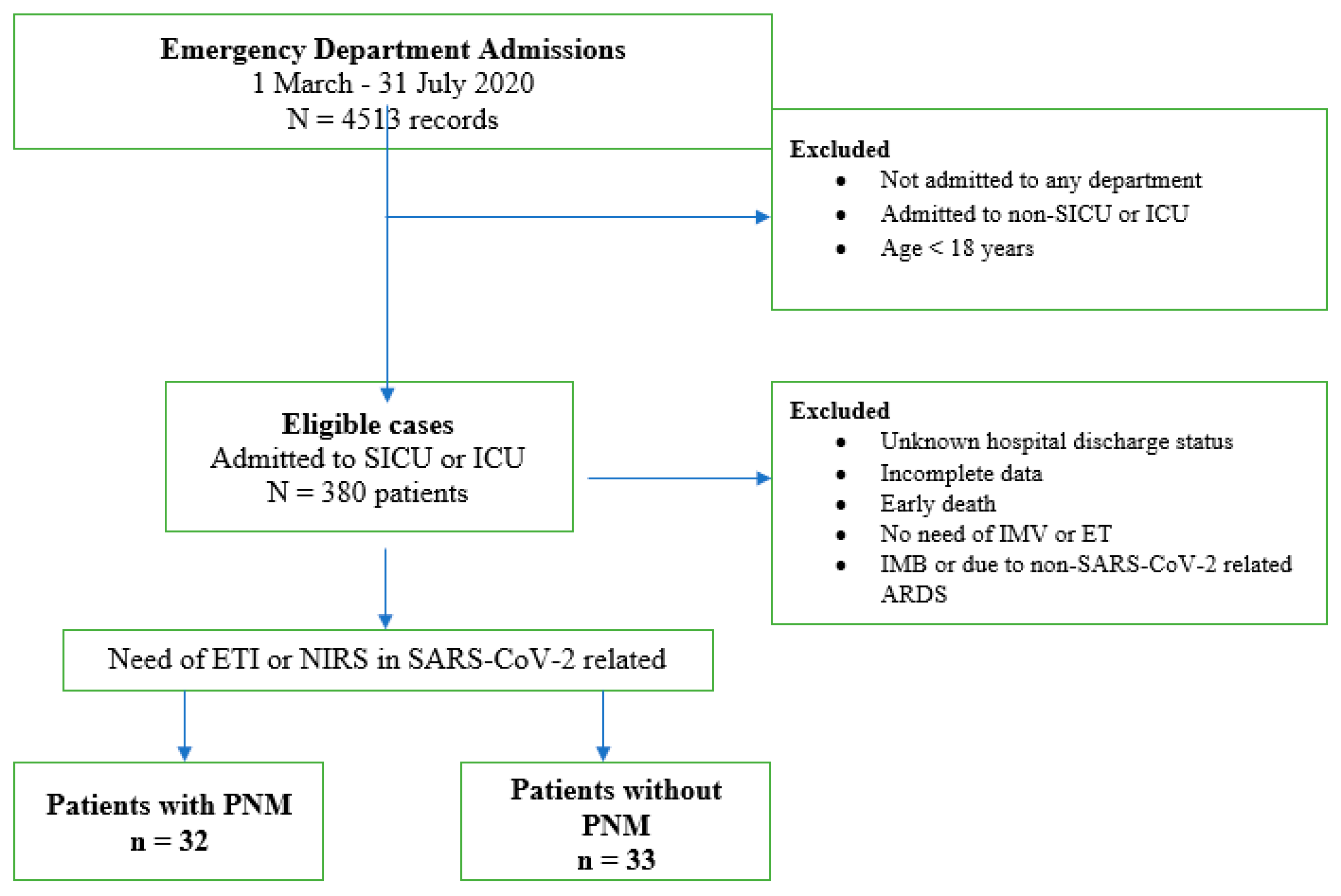
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tetaj, N.; Garotto, G.; Albarello, F.; Mastrobattista, A.; Maritti, M.; Stazi, G.V.; Marini, M.C.; Caravella, I.; Macchione, M.; De Angelis, G.; et al. Incidence of Pneumothorax and Pneumomediastinum in 497 COVID-19 Patients with Moderate–Severe ARDS over a Year of the Pandemic: An Observational Study in an Italian Third Level COVID-19 Hospital. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belletti, A.; Palumbo, D.; Zangrillo, A.; Fominskiy, E.V.; Franchini, S.; Dell’Acqua, A.; Marinosci, A.; Monti, G.; Vitali, G.; Colombo, S.; et al. Predictors of Pneumothorax/Pneumomediastinum in Mechanically Ventilated COVID-19 Patients. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2021, 35, 3642–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, J.A.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, B.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Jeong, S.J.; et al. Risk factors of pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum in COVID-19: A matched case–control study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, W.H.; Saha, B.K.; Hu, K.; Chopra, A. The incidence, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of pneumothorax in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A systematic review. Hear. Lung 2021, 50, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piroth, L.; Cottenet, J.; Mariet, A.-S.; Bonniaud, P.; Blot, M.; Tubert-Bitter, P.; Quantin, C. Comparison of the characteristics, morbidity, and mortality of COVID-19 and seasonal influenza: A nationwide, population-based retrospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, M.J.; Fard, F.B.; Samimi, K.; Rasti, H.; Pressacco, J. Spontaneous pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum as a rare complication of COVID-19 pneumonia: Report of 6 cases. Radiol. Case Rep. 2021, 16, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.K.; Charles, W.N.; Sklavounos, A.; Dutt, A.; Seed, P.T.; Khajuria, A. The effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 93, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanduzzi, A.; Ciasullo, E.; Capitelli, L.; Zamparelli, S.S.; Bocchino, M. Alpha-1-Antitrypsin Deficiency and Bronchiectasis: A Concomitance or a Real Association? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, H.C.; Sussman, J.B.; Wiersinga, W.J. Postcritical illness vulnerability. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2020, 26, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.M.; Bai, P.; He, W.; Wu, F.; Liu, X.F.; Han, D.M.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.K. Gender Differences in Patients With COVID-19: Focus on Severity and Mortality. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Lloclla, J.P.; León-Jiménez, F.; Urquiaga-Calderón, J.; Temoche-Nizama, H.; Bryce-Alberti, M.; Portmann-Baracco, A.; Bryce-Moncloa, A. Spontaneous Pneumopericardium and Pneumomediastinum in Twelve COVID-19 Patients. Arch. De Bronconeumol. 2020, 57, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.F.S.; Seposo, X.T.; Moi, M.L.; Tajudin, M.A.B.A.; Madaniyazi, L.; Sahani, M. Characteristics of COVID-19 epidemic and control measures to curb transmission in Malaysia. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Kojima, S.; Kawamoto, A.; Fukushima, M. COVID-19 pathogenesis, prognostic factors, and treatment strategy: Urgent recommendations. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 93, 2694–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.-H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartier, P. Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis-Associated Chronic Uveitis: Recent Therapeutic Approaches. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhoen, S.; Heidenreich, J.F.; Metz, C.; Petritsch, B.; Benkert, T.; Hebestreit, H.U.; Bley, T.A.; Köstler, H.; Weng, A.M. Three-dimensional Ultrashort Echotime Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Combined Morphologic and Ventilation Imaging in Pediatric Patients With Pulmonary Disease. J. Thorac. Imaging 2020, 36, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaire, N.; Deshmukh, S.; Agarwal, E.; Mahale, N.; Khaladkar, S.; Desai, S.; Kulkarni, A. Pneumomediastinum: A marker of severity in COVID-19 disease. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Yin, G.; Chen, Y.; Song, J.; Ye, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Song, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y. Corticosteroid, oseltamivir and delayed admission are independent risk factors for prolonged viral shedding in patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Respir. J. 2020, 14, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Han, X.; Jiang, N.; Cao, Y.; Alwalid, O.; Gu, J.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, C. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, D.; Zerunian, M.; Polici, M.; Pucciarelli, F.; Polidori, T.; Rucci, C.; Guido, G.; Bracci, B.; De Dominicis, C.; Laghi, A. Chest CT Features of COVID-19 in Rome, Italy. Radiology 2020, 296, E79–E85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaskani, N.; Khandashpoor, M.; Livani, S. Pneumothorax, Pneumomediastinum, and Subcutaneous Emphysema as Complications of COVID-19 Infection: A Case Series. Tanaffos 2021, 20, 368–372. [Google Scholar]
- Eperjesiova, B.; Hart, E.; Shokr, M.; Sinha, P.; Ferguson, G.T. Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum/Pneumothorax in Patients with COVID-19. Cureus 2020, 12, e8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconi, F.; Rogliani, P.; Leonardis, F.; Sarmati, L.; Fabbi, E.; De Carolis, G.; La Rocca, E.; Vanni, G.; Ambrogi, V. Incidence of pneumomediastinum in COVID-19: A single-center comparison between 1st and 2nd wave. Respir. Investig. 2021, 59, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, G.; Zhan, C.; Rosenberg, N.; Azour, L.; Wickstrom, M.; Mason, D.M.; Thomas, K.M.; Moore, W.H. Increased Incidence of Barotrauma in Patients with COVID-19 on Invasive Mechanical Ventilation. Radiology 2020, 297, E252–E262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzueto, A.; Frutos–Vivar, F.; Esteban, A.; Alía, I.; Brochard, L.; Stewart, T.; Benito, S.; Tobin, M.J.; Elizalde, J.; Palizas, F.; et al. Incidence, risk factors and outcome of barotrauma in mechanically ventilated patients. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Aquila, I.; Sacco, M.A.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Procopio, A.C.; Boccuto, L.; Scarpellini, E.; Greco, M.; Foti, D.P.; Ricci, P.; et al. Liver Damage and Impaired Coagulation in COVID-19 Patients: A Case Series. Diseases 2023, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, S.; Mazzuca, E.; Lococo, F.; Mondoni, M.; Covino, M.; Kuzmych, K.; Agati, S.; Amata, M.; Giuseppe, A.; Gabbrielli, L.; et al. Pneumomediastinum in COVID-19: Risk Factors and Outcomes from a Multicentre Case-control Study. Respir. Med. 2024, 230, 107684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, N.G.; Loo, L.; Hee, D.K.H.; Lim, T.P.; Ng, T.M.; Hoo, G.S.R.; Soong, J.L.; Ong, J.C.L.; Tang, S.S.L.; Zhou, Y.P.; et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring of meropenem and piperacillin-tazobactam in the Singapore critically ill population—A prospective, multi-center, observational study (BLAST 1). J. Crit. Care 2022, 68, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, Y.X.; Geetha, H.S.; Mishra, A.K.; Lal, A. Pneumomediastinum in COVID-19: Incidence, Pathogenesis, and Management. Respiratory Care. Mediastinum 2023, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No PNM (n = 33) | PNM (n = 32) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Men | 21 (63%) | 23 (72%) | 0.5977 |
| Age (years) * | 65.4 ± 14.3 | 54.9 ± 18.5 | 0.0214 |
| Smoking exposure | |||
| Never a smoker | 11 (33.3%) | 9 (28.1%) | 0.7893 |
| Former smoker | 14 (42.4%) | 10 (31.3%) | 0.4431 |
| Current smoker | 8 (24.3%) | 13 (40.6%) | 0.1912 |
| Nutritional status | |||
| BMI * | 27.7 ± 6.5 | 26.5 ± 4.9 | 0.5727 |
| Underweight (BMI < 18.5) | 0 | 2 (6.3%) | 0.2385 |
| Overweight (BMI 25–29.9) | 17 (51.5%) | 18 (56.3%) | 0.8050 |
| Obese (BMI > 30) | 10 (30.3%) | 4 (12.5%) | 0.0131 |
| Blood parameters | |||
| CRP at admission (mg/L) * | 73.6 ± 108.7 | 108.1 ± 87.6 | 0.0187 |
| Maximum CRP (mg/L) * | 126.3 ± 123.6 | 139.4 ± 85.9 | 0.3584 |
| D-dimer at admission (ng/mL) * | 7467 ± 12,243 | 5497 ± 10,060 | 0.7195 |
| Maximum D-dimer (ng/mL) * | 10,412 ± 13,075 | 8354 ± 10,150 | 0.9958 |
| WBC at admission | 6.5 ± 4.1 | 11.4 ± 5.4 | <0.0001 |
| Maximum WBC | 8.9 ± 5.1 | 16.4 ± 6.1 | <0.0001 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Hypertension | 20 (60.6%) | 16 (50%) | 0.4586 |
| COPD | 5 (15.1%) | 15 (46.9%) | 0.0148 |
| Diabetes mellitus type II | 7 (21.2%) | 3 (9.4%) | 0.3020 |
| CAD | 7 (21.2%) | 6 (18.6%) | >0.0999 |
| Other respiratory diseases (fibrosis and bronchiectasis) | 7 (21.2%) | 5 (15.6%) | 0.7505 |
| No PNM (n = 33) | PNM (n = 32) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extent of lung involvement * | 52.7 ± 27.4 (1–100) | 61.3 ± 20 (1–100) | 0.3278 |
| Number of lobes involved * | 2.6 ± 1.1 (1–5) | 2.6 ± 0.9 (1–5) | 0.8294 |
| Bilateral distribution | 29 (87.9%) | 28 (87.5%) | >0.9999 |
| Ground-glass opacities | 17 (51.5%) | 30 (93.7%) | 0.0002 |
| Consolidations | 14 (42.2%) | 25 (78.1%) | 0.0051 |
| Crazy paving | 6 (18.2%) | 3 (9.4%) | 0.4752 |
| Pleural effusion | 3 (9%) | 9 (28.1%) | 0.0606 |
| Pneumothorax | 1 (3%) | 20 (62.5%) | <0.0001 |
| Emphysema | 0 | 6 (18.6%) | 0.0110 |
| No PNM (n = 33) | PNM (n = 32) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional OT | 13 (39.4%) | 9 (28.1%) | 0.4339 |
| CPAP | 4 (12.1%) | 8 (25%) | 0.3389 |
| BiPAP | 10 (30.3%) | 8 (25%) | 0.1548 |
| HFNC | 6 (18.2%) | 7 (21.9%) | 0.7642 |
| ETI | 10 (30.3%) | 17 (53.1%) | 0.0619 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuzmych, K.; Covino, M.; Paratore, M.; Campanella, A.; Abenavoli, L.; Calabrese, G.; Napolitano, A.G.; Sassorossi, C.; Margaritora, S.; Lococo, F. Unraveling Pneumomediastinum in COVID-19 Patients: Insights from a High-Volume-Center Case–Control Study. Diseases 2024, 12, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12100242
Kuzmych K, Covino M, Paratore M, Campanella A, Abenavoli L, Calabrese G, Napolitano AG, Sassorossi C, Margaritora S, Lococo F. Unraveling Pneumomediastinum in COVID-19 Patients: Insights from a High-Volume-Center Case–Control Study. Diseases. 2024; 12(10):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12100242
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuzmych, Khrystyna, Marcello Covino, Mattia Paratore, Annalisa Campanella, Ludovico Abenavoli, Giuseppe Calabrese, Antonio Giulio Napolitano, Carolina Sassorossi, Stefano Margaritora, and Filippo Lococo. 2024. "Unraveling Pneumomediastinum in COVID-19 Patients: Insights from a High-Volume-Center Case–Control Study" Diseases 12, no. 10: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12100242
APA StyleKuzmych, K., Covino, M., Paratore, M., Campanella, A., Abenavoli, L., Calabrese, G., Napolitano, A. G., Sassorossi, C., Margaritora, S., & Lococo, F. (2024). Unraveling Pneumomediastinum in COVID-19 Patients: Insights from a High-Volume-Center Case–Control Study. Diseases, 12(10), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12100242









