Bone Mineral Density, C-Terminal Telopeptide of Type I Collagen, and Osteocalcin as Monitoring Parameters of Bone Remodeling in CML Patients Undergoing Imatinib Therapy: A Basic Science and Clinical Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physiology of Bone Turnover
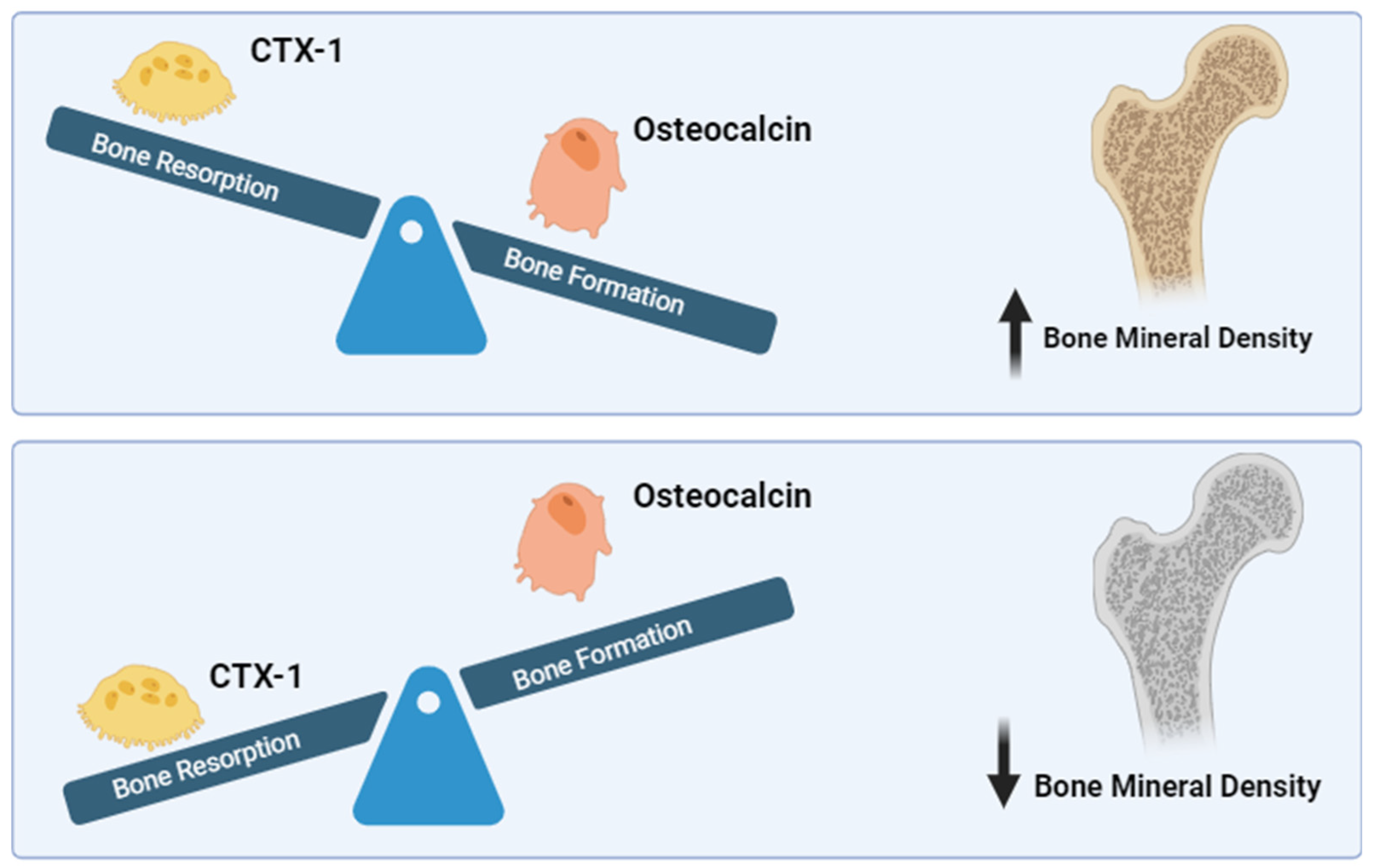
3. Interaction of Bone Mineral Density, CTX-1, and Osteocalcin
3.1. Bone Mineral Density
3.2. The C-Terminal Telopeptide of Type I Collagen
3.3. Osteocalcin
3.4. Interplay of BMD, CTX-1, and OCN
4. Role of Tyrosine Kinase in Bone Metabolism
5. Impact of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Bone Turnover
6. Impact of Imatinib to BMD, CTX-1, and Osteocalcin
7. Rationale for Combination of BMD, Osteocalcin, and CTX-1 to Monitor Bone Remodeling
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pandey, N.; Yadav, G.; Kushwaha, R.; Verma, S.P.; Singh, U.S.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, P. Effect of Imatinib on Bone Marrow Morphology and Angiogenesis in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Adv. Hematol. 2019, 2019, 1835091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, N.; Iqbal, N. Imatinib: A Breakthrough of Targeted Therapy in Cancer. Chemother. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 357027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, E.; Girotra, M.; Cheng, C.; Chanel, S.; Maki, R.; Shelat, M.; Strauss, H.W.; Fleisher, M.; Heller, G.; Farooki, A. Effect of long-term imatinib on bone in adults with chronic myelogenous leukemia and gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.; Kapoor, N.; Bondu, J.; Thomas, N.; Paul, T. Bone turnover markers: An emerging tool in the management of osteoporosis. Indian. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 20, 846. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.P.; Don-Wauchope, A.; Douville, P.; Albert, C.; Vasikaran, S.D. Current use of bone turnover markers in the management of osteoporosis. Clin. Biochem. 2022, 109–110, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiraju, D.; Ahmed, I. Human skeletal physiology and factors affecting its modeling and remodeling. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 112, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, B. Normal bone anatomy and physiology. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3 (Suppl. S3), 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Chi, G.; Xu, J.; Tan, Y.; Xu, J.; Lv, S.; Xu, Z.; Xia, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Y. Extracellular matrix stiffness controls the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells mediated by integrin α5. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, C.; Ferretti, M. The Osteocyte: From “Prisoner” to “Orchestrator”. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2021, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veis, D.J.; O’Brien, C.A. Osteoclasts, Master Sculptors of Bone. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2023, 18, 257–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.J.; Seeman, E. Bone Remodeling and Modeling: Cellular Targets for Antiresorptive and Anabolic Treatments, Including Approaches Through the Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)/PTH-Related Protein Pathway. Neurospine 2023, 20, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orvalho, J.M.; Fernandes, J.C.H.; Moraes Castilho, R.; Fernandes, G.V.O. The Macrophage’s Role on Bone Remodeling and Osteogenesis: A Systematic Review. Clin. Rev. Bone Min. Metab. 2023, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.V.O.; Cavagis, A.D.M.; Ferreira, C.V.; Olej, B.; de Souza Leão, M.; Yano, C.L.; Zambuzzi, W.F. Osteoblast Adhesion Dynamics: A Possible Role for ROS and LMW-PTP. J. Cell Biochem. 2014, 115, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ruan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Tu, X. The Osteocyte Stimulated by Wnt Agonist SKL2001 Is a Safe Osteogenic Niche Improving Bioactivities in a Polycaprolactone and Cell Integrated 3D Module. Cells 2022, 11, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, E.; Lara-Castillo, N.; Akhter, M.P.; Dallas, M.; Scott, J.M.; Ganesh, T.; Johnson, M.L. Osteocyte Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation upon mechanical loading is altered in ovariectomized mice. Bone Rep. 2021, 15, 101129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuoti, E.; Lehenkari, P.; Tuukkanen, J.; Glumoff, V.; Kylmäoja, E. Osteoclastogenesis of human peripheral blood, bone marrow, and cord blood monocytes. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leon-Oliva, D.; Barrena-Blázquez, S.; Jiménez-Álvarez, L.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; García-Montero, C.; López-González, L.; Ortega, M.A. The RANK–RANKL–OPG System: A Multifaceted Regulator of Homeostasis, Immunity, and Cancer. Medicina 2023, 59, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.J.; Phillipov, G. Bone mineral density—Frequently asked questions. Aust. Fam. Physician 2006, 35, 341–344. [Google Scholar]
- Kranioti, E.F.; Bonicelli, A.; García-Donas, J.G. Bone-mineral density: Clinical significance, methods of quantification and forensic applications. Res. Rep. Forensic Med. Sci. 2019, 9, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, I.; Nunes, C.; Pereira, F.; Travassos, R.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Marques, F.; McEvoy, M.; Santos, M.; Oliveira, C.; Marto, C.M.; et al. Bone Mineral Density through DEXA and CBCT: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Chan, W.P.; Zhang, H.W.; Tsai, Z.R.; Peng, H.C.; Huang, S.W.; Jang, Y.-C.; Kuo, Y.-J. Automated osteoporosis classification and T -score prediction using hip radiographs via deep learning algorithm. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demeuse, J.; Determe, W.; Grifnée, E.; Massonnet, P.; Schoumacher, M.; Huyghebaert, L.; Dubrowski, T.; Peeters, S.; Le Goff, C.; Cavalier, E. Characterization of c-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (ctx) species in human plasma and serum using high resolution mass spectrometry. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2024, 32, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemare, M.; Senay, A.; Delisle, J.; Banica, A.; Beaumont, P.; Giroux, M.; Jodoin, A.; Laflamme, Y.; Leduc, S.; MacThiong, J.; et al. Assessment of CTX-1 Bone Biomarker as An Indicator of Antiresorptive Therapy Efficacy and of Persistence In A Fracture Liaison Service. Value Health 2016, 19, A531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerre-Bastos, J.J.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; Karsdal, M.A.; Byrjalsen, I.; Andersen, J.R.; Riis, B.J.; Christiansen, C.; Bihlet, A. Biomarkers of bone and cartilage turnover CTX-I and CTX-II predict total joint replacements in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, S31–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Kushida, K.; Nagano, A.; Inoue, T. Comparison of the analytical and clinical performance characteristics of an N-MID versus an intact osteocalcin immunoradiometric assay. Clin. Chim. Acta 2000, 294, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.; Gennari, L.; Merlotti, D.; Dotta, F.; Nuti, R. Endocrine Actions of Osteocalcin. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 846480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.R.; Chen, C.H. Bone biomarker for the clinical assessment of osteoporosis: Recent developments and future perspectives. Biomark. Res. 2017, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan-Speranza, T.C.; Conigrave, A.D. Osteocalcin: An Osteoblast-Derived Polypeptide Hormone that Modulates Whole Body Energy Metabolism. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 96, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, M.B.; Tsai, J.N.; Wein, M.N. Bone Turnover Markers in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Metabolic Bone Disease. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; You, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zou, W. Mechanical regulation of bone remodeling. Bone Res. 2022, 10, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, H.N.; Moses, A.C.; Garber, J.; Iloputaife, I.D.; Ross, D.S.; Lee, S.L.; Greenspan, S.L. Serum CTX: A New Marker of Bone Resorption That Shows Treatment Effect More Often Than Other Markers Because of Low Coefficient of Variability and Large Changes with Bisphosphonate Therapy. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2000, 66, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Dai, Z. An overview of osteocalcin progress. J. Bone Min. Metab. 2016, 34, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferron, M.; McKee, M.D.; Levine, R.L.; Ducy, P.; Karsenty, G. Intermittent injections of osteocalcin improve glucose metabolism and prevent type 2 diabetes in mice. Bone 2012, 50, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferron, M.; Hinoi, E.; Karsenty, G.; Ducy, P. Osteocalcin differentially regulates β cell and adipocyte gene expression and affects the development of metabolic diseases in wild-type mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5266–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Zang, W.; Wu, S.; Sun, H. Intermittent injections of osteocalcin reverse autophagic dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress resulting from diet-induced obesity in the vascular tissue via the NFκB-p65-dependent mechanism. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodish, M.B.; Stratakis, C.A. Endocrine side effects of broad-acting kinase inhibitors. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemán, J.O.; Farooki, A.; Girotra, M. Effects of tyrosine kinase inhibition on bone metabolism: Untargeted consequences of targeted therapies. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, R247–R259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T.; Yasuda, K.; Mizuta, K.; Kawaue, H.; Kokabu, S. Tyrosine Kinase Src Is a Regulatory Factor of Bone Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.-Y.; Pokhrel, N.K.; Jung, H.-J.; Kim, H.J.; Seok, J.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-G.; et al. Mer tyrosine kinase regulates bone metabolism, and its deficiency partially ameliorates periodontitis- and ovariectomy-induced bone loss in mice. JBMR Plus. 2024, 8, ziad014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, I.; Seong, S.; Kim, N. c-Src–Dependent and –Independent Functions of Matk in Osteoclasts and Osteoblasts. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandyke, K.; Fitter, S.; Drew, J.; Fukumoto, S.; Schultz, C.G.; Sims, N.A.; Yeung, D.T.; Hughes, T.P.; Zannettino, A.C.W. Prospective Histomorphometric and DXA Evaluation of Bone Remodeling in Imatinib-Treated CML Patients: Evidence for Site-Specific Skeletal Effects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Id Boufker, H.; Lagneaux, L.; Najar, M.; Piccart, M.; Ghanem, G.; Body, J.J.; Journé, F. The Src inhibitor dasatinib accelerates the differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells into osteoblasts. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 298. [Google Scholar]
- Grüllich, C. Cabozantinib: Multi-kinase Inhibitor of MET, AXL, RET, and VEGFR2. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018, 211, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brassard, M.; Neraud, B.; Trabado, S.; Salenave, S.; Brailly-Tabard, S.; Borget, I.; Baudin, E.; Leboulleux, S.; Chanson, P.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. Endocrine Effects of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Vandetanib in Patients Treated for Thyroid Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 2741–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Piemontese, M.; Onal, M.; Campbell, J.; Goellner, J.J.; Dusevich, V.; Bonewald, L.; Manolagas, S.C.; O’brien, C.A. Osteocytes, not Osteoblasts or Lining Cells, are the Main Source of the RANKL Required for Osteoclast Formation in Remodeling Bone. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodish, M.B. Kinase Inhibitors: Adverse Effects Related to the Endocrine System. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.L. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced hypothyroidism: Incidence, etiology, and management. Target. Oncol. 2011, 6, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lossdörfer, S.; Götz, W.; Jäger, A. PTH(1-34)-induced changes in RANKL and OPG expression by human PDL cells modify osteoclast biology in a co-culture model with RAW 264.7 cells. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2011, 15, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Tanaka, S.; Sanjay, A.; Baron, R. The role of c-Src kinase in the regulation of osteoclast function. Mod. Rheumatol. 2006, 16, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maita, S.; Yuasa, T.; Tsuchiya, N.; Mitobe, Y.; Narita, S.; Horikawa, Y.; Hatake, K.; Fukui, I.; Kimura, S.; Maekawa, T.; et al. Antitumor effect of sunitinib against skeletal metastatic renal cell carcinoma through inhibition of osteoclast function. Int. J. Cancer. 2012, 130, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj Dib, I.; Gallet, M.; Mentaverri, R.; Sévenet, N.; Brazier, M.; Kamel, S. Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec®) enhances mature osteoclast apoptosis and suppresses osteoclast bone resorbing activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 551, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitter, S.; Dewar, A.L.; Kostakis, P.; To, L.B.; Hughes, T.P.; Roberts, M.M.; Lynch, K.; Vernon-Roberts, B.; Zannettino, A.C.W. Long-term imatinib therapy promotes bone formation in CML patients. Blood 2008, 111, 2538–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, E.; Nicolaides, M.; Maki, R.G.; Fleisher, M.; Chanel, S.; Scheu, K.; Sauter, N.P. Altered Bone and Mineral Metabolism in Patients Receiving Imatinib Mesylate. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2006–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jönsson, S.; Standal, T.; Olsson, B.; Mellström, D.; Wadenvik, H. Secondary hyperparathyroidism but stable bone-mineral density in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with imatinib. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, 550–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewar, A.L.; Farrugia, A.N.; Condina, M.R.; To, L.B.; Hughes, T.P.; Vernon-Roberts, B.; Zannettino, A.C. Imatinib as a potential antiresorptive therapy for bone disease. Blood 2006, 107, 4334–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, S.; Horne, A.; Wattie, D.; Porteous, F.; Gamble, G.; Browett, P.; Grey, A. Bone metabolism during long-term treatment with imatinib. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 1783–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpos, E.; Apperley, J.; Milojkovic, D. Imatinib and chronic myeloid leukemia: Close to the bone. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 1581–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choeyprasert, W.; Yansomdet, T.; Natesirinilkul, R.; Wejaphikul, K.; Charoenkwan, P. Adverse effects of imatinib in children with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Pediatr. Int. 2017, 59, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, B.A.S.; Tauer, J.T.; Ulmer, A.; Kuhlisch, E.; Roth, H.J.; Suttorp, M. Changes in bone metabolic parameters in children with chronic myeloid leukemia on imatinib treatment. Med. Sci. Monit. 2012, 18, CR721–CR728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauer, J.T.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Jung, R.; Gerdes, S.; Glauche, I.; Erben, R.G.; Suttorp, M. Impact of Long-Term Exposure to the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Imatinib on the Skeleton of Growing Rats. Eaves CJ, editor. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Chang, Y.F.; Chen, C.H.; Lewiecki, E.M.; Wüster, C.; Reid, I.; Tsai, K.S.; Matsumoto, T.; Mercado-Asis, L.B.; Chan, D.C.; et al. Consensus Statement on the Use of Bone Turnover Markers for Short-Term Monitoring of Osteoporosis Treatment in the Asia-Pacific Region. J. Clin. Densitom. 2021, 24, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.; Liu, D.; Wu, F.; Wang, M.; Cen, Y.; Ma, L. Correlation between bone turnover markers and bone mineral density in patients undergoing long-term anti-osteoporosis treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitepu, E. BioRender [Internet]. BioRender; 21 October 2024. Available online: https://biorender.com/j80q330 (accessed on 17 September 2024).
| Study/Authors | Study Type | Participants/Subjects | Key Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jönsson et al. [54] | Longitudinal Study | 17 CML patients | A total of 7/17 developed secondary hyperparathyroidism; increased serum parathyroid hormone levels over four years; mean areal and volumetric BMD remained stable; cortical BMD higher than controls. |
| Dib et al. [51] | Clinical/Preclinical | Not specified | Imatinib influences mature osteoclasts through c-fms inhibition; potential clinical value in treating osteoporosis and osteolysis. |
| Dewar et al. [55] | Animal Study | Mice | Imatinib inhibits osteoclast formation and activity in vivo. It is an effective antiosteolytic agent and affects c-fms signaling and RANK expression. |
| O’Sullivan [56] | Animal Study | Healthy mice | Early osteoblast differentiation promoted reduced mineralization at low concentrations. There is no long-term effect on BMD, and it does not alter bone resorption markers. |
| Choeyprasert et al. [58] | Clinical Study | 44 CML children | Correlation with low BMD without affecting bone parameters; high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency; Imatinib linked to low BMD and vitamin D deficiency. |
| Jaeger et al. [59] | Clinical Study | 17 children with CML on prolonged Imatinib | Decrease in N-mid OCN; CTX-I levels high in a majority of patients. |
| Tauer et al. [60] | Animal Study | Mice | Similar findings as Jaeger et al. in terms of N-mid OCN. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Indarwulan, N.; Savitri, M.; Ashariati, A.; Bintoro, S.U.Y.; Diansyah, M.N.; Amrita, P.N.A.; Romadhon, P.Z. Bone Mineral Density, C-Terminal Telopeptide of Type I Collagen, and Osteocalcin as Monitoring Parameters of Bone Remodeling in CML Patients Undergoing Imatinib Therapy: A Basic Science and Clinical Review. Diseases 2024, 12, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12110275
Indarwulan N, Savitri M, Ashariati A, Bintoro SUY, Diansyah MN, Amrita PNA, Romadhon PZ. Bone Mineral Density, C-Terminal Telopeptide of Type I Collagen, and Osteocalcin as Monitoring Parameters of Bone Remodeling in CML Patients Undergoing Imatinib Therapy: A Basic Science and Clinical Review. Diseases. 2024; 12(11):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12110275
Chicago/Turabian StyleIndarwulan, Nurita, Merlyna Savitri, Ami Ashariati, Siprianus Ugroseno Yudho Bintoro, Muhammad Noor Diansyah, Putu Niken Ayu Amrita, and Pradana Zaky Romadhon. 2024. "Bone Mineral Density, C-Terminal Telopeptide of Type I Collagen, and Osteocalcin as Monitoring Parameters of Bone Remodeling in CML Patients Undergoing Imatinib Therapy: A Basic Science and Clinical Review" Diseases 12, no. 11: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12110275
APA StyleIndarwulan, N., Savitri, M., Ashariati, A., Bintoro, S. U. Y., Diansyah, M. N., Amrita, P. N. A., & Romadhon, P. Z. (2024). Bone Mineral Density, C-Terminal Telopeptide of Type I Collagen, and Osteocalcin as Monitoring Parameters of Bone Remodeling in CML Patients Undergoing Imatinib Therapy: A Basic Science and Clinical Review. Diseases, 12(11), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12110275





