Current and Emerging Parenteral and Peroral Medications for Weight Loss: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Parenteral Medications for Weight Loss
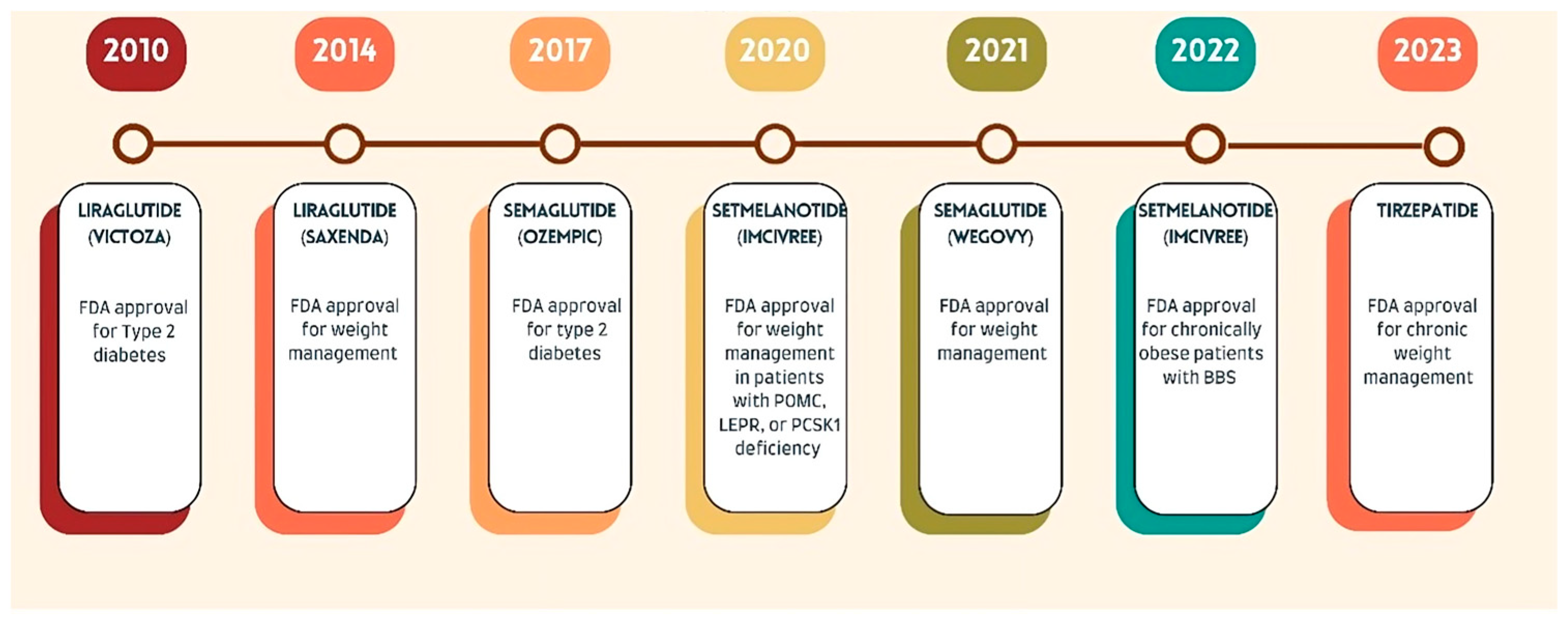
2.1. Liraglutide (Saxenda)
2.2. Semaglutide (Wegovy)
2.3. Setmelanotide (Imcivree)
2.4. Tirzepatide
3. Peroral Medications for Weight Loss
3.1. Phentermine
3.2. Phentermine/Topiramate (Qsymia)
3.3. Bupropion/Naltrexone (Contrave)
3.4. Orlistat (Alli, Xenical)
3.5. Metformin (Off-Label Use)
4. Emerging Medications in Clinical Trials
4.1. Cagrilintide
4.2. Bimagrumab
5. Medications Withdrawn from the Market
Lorcaserin (Belviq)
6. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Weight Loss Treatment
7. Comparison Between Different Weight Loss Management Modalities
8. Safety, Efficacy, and Regulatory Considerations
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5HT2C | 5-hydroxytryptamine 2C receptor |
| AACE | American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists |
| ACC | American College of Cardiology |
| ACE | American College of Endocrinology |
| ADRs | Adverse Drug Reactions |
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AOMs | Anti-Obesity Medications |
| AgRP | Agouti-Related Peptide |
| BBS | Bardet–Biedl Syndrome |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CART | Cocaine- and Amphetamine-Regulated Transcript |
| CVDs | Cardiovascular Diseases |
| DALYs | Disability-Adjusted Life Years |
| DBP | Diastolic Blood Pressure |
| DPP-4 | Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| LEPR | Leptin Receptor |
| MAO | Monoamine Oxidase |
| MC4R | Melanocortin-4 Receptor |
| NPY | Neuropeptide Y |
| PCOS | Polycystic Ovary Syndrome |
| PCSK1 | Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 1 |
| POMC | Proopiomelanocortin |
| QALY | Quality-Adjusted Life Year |
| RCTs | Randomized Control Trials |
| SBP | Systolic Blood Pressure |
| T2D | Type 2 Diabetes |
| TBW | Total Body Weight |
| TOS | The Obesity Society |
| TRG | Triglycerides |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. A Healthy Lifestyle—WHO Recommendations. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/a-healthy-lifestyle---who-recommendations (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.S.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Moreno, I.; Taheem, R.; Woods-Townsend, K.; Chase, D.; Godfrey, K.M.; Modi, N.; Hanson, M. Projected health and economic effects of the increase in childhood obesity during the COVID-19 pandemic in England: The potential cost of inaction. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0296013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Dai, H.; Alsalhe, T.A.; Chalghaf, N.; Riccò, M.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Wu, J. The global burden of disease attributable to high body mass index in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Han, Z.; Xiong, P. The global burden of disease attributable to high body mass index in 204 countries and territories: Findings from 1990 to 2019 and predictions to 2035. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 3998–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aras, M.; Tchang, B.G.; Pape, J. Obesity and diabetes. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 56, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippe, J.M.; Crossley, S.; Ringer, R. Obesity as a chronic disease: Modern medical and lifestyle management. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1998, 98, S9–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.E.; Coakley, E.H.; Must, A.; Spadano, J.L.; Laird, N.; Dietz, W.H.; Rimm, E.; Colditz, G.A. Impact of overweight on the risk of developing common chronic diseases during a 10-year period. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Parise, H.; Levy, D.; D’Agostino, R.B., Sr.; Wolf, P.A.; Vasan, R.S.; Benjamin, E.J. Obesity and the risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation. JAMA 2004, 292, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogers, R.P.; Bemelmans, W.J.; Hoogenveen, R.T.; Boshuizen, H.C.; Woodward, M.; Knekt, P.; van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B.; Visscher, T.L.; Menotti, A.; et al. Association of overweight with increased risk of coronary heart disease partly independent of blood pressure and cholesterol levels: A meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies including more than 300,000 persons. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, P.; Giles, T.D.; Bray, G.A.; Hong, Y.; Stern, J.S.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Hunter, G.; Milani, R.V.; et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss. Circulation 2006, 113, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magkos, F.; Fraterrigo, G.; Yoshino, J.; Luecking, C.; Kirbach, K.; Kelly, S.C.; de las Fuentes, L.; He, S.; Okunade, A.L.; Patterson, B.W.; et al. Effects of moderate and subsequent progressive weight loss on metabolic function and adipose tissue biology in humans with obesity. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bays, H.E.; Toth, P.P.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Abate, N.; Aronne, L.J.; Brown, W.V.; Gonzalez-Campoy, J.M.; Jones, S.R.; Kumar, R.; La Forge, R.; et al. Obesity, adiposity, and dyslipidemia: A consensus statement from the National Lipid Association. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2013, 7, 304–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, R.R.; Lang, W.; Wadden, T.A.; Safford, M.; Knowler, W.C.; Bertoni, A.G.; Hill, J.O.; Brancati, F.L.; Peters, A.; Wagenknecht, L.; et al. Benefits of modest weight loss in improving cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, W.T.; Mechanick, J.I.; Brett, E.M.; Garber, A.J.; Hurley, D.L.; Jastreboff, A.M.; Nadolsky, K.; Pessah-Pollack, R.; Plodkowski, R.; Bays, H.E.; et al. Comprehensive clinical practice guidelines for medical care of patients with obesity. Endocr. Pract. 2016, 22, 842–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.D.; Ryan, D.H.; Apovian, C.M.; Ard, J.D.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Donato, K.A.; Hu, F.B.; Hubbard, V.S.; Jakicic, J.M.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2985–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, S.; Lau, D.C.W.; Vallis, M.; Sharma, A.M.; Biertho, L.; Campbell-Scherer, D.; Adamo, K.; Alberga, A.; Bell, R.; Boulé, N.; et al. Obesity in adults: A clinical practice guideline. CMAJ 2020, 192, E875–E891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, A.J. Long-acting glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: A review of their efficacy and tolerability. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, S279–S284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. Le médicament du mois. Le liraglutide à la dose de 3 mg (Saxenda): Indication dans le traitement de l’obésité. Rev. Med. Liege 2016, 71, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, L.B.; Nielsen, P.F.; Huusfeldt, P.O.; Johansen, N.L.; Madsen, K.; Pedersen, F.Z.; Thøgersen, H.; Wilken, M.; Agersø, H. Potent derivatives of glucagon-like peptide-1 with pharmacokinetic properties suitable for once daily administration. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Egan, J.M. The role of incretins in glucose homeostasis and diabetes treatment. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 470–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Dicker, D.; Mingrone, G.; Pedersen, S.D.; Satylganova, A.; Skovgaard, D.; Sugimoto, D.; Jensen, C.; Mosenzon, O. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide 3.0 mg in individuals with overweight or obesity and type 2 diabetes treated with basal insulin: The SCALE Insulin randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Zambrano-Villacres, R.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Zambrano, A.K. Molecular mechanisms of semaglutide and liraglutide as a therapeutic option for obesity. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1398059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Maeda, N.; Fujishima, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Nagao, H.; Yamaoka, M.; Hirata, A.; Nishizawa, H.; Funahashi, T.; Shimomura, I. Long-term impact of liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue, on body weight and glycemic control in Japanese type 2 diabetes: An observational study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbernon, M.; Saponaro, C.; Helms, H.C.C.; Sanchez-Aguilera, P.; García-Cáceres, C.; Secher, A.; Ferrés-Coy, A.; Díaz-Delfín, J.; Hebert-Chatelain, E.; Tena-Sempere, M.; et al. Tanycytes control hypothalamic liraglutide uptake and its anti-obesity actions. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1054–1063.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secher, A.; Jelsing, J.; Baquero, A.F.; Hecksher-Sørensen, J.; Cowley, M.A.; Dalbøge, L.S.; Hansen, G.; Grove, K.L.; Pyke, C.; Raun, K.; et al. The arcuate nucleus mediates GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide-dependent weight loss. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 4473–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, X.; Astrup, A.; Fujioka, K.; Greenway, F.; Halpern, A.; Krempf, M.; Lau, D.C.; le Roux, C.W.; Violante Ortiz, R.; Jensen, C.B.; et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, A.; Foster, G.D.; Zammit, G.; Rosenberg, R.; Aronne, L.; Wadden, T.; Claudius, B.; Jensen, C.B.; Mignot, E. Effect of liraglutide 3.0 mg in individuals with obesity and moderate or severe obstructive sleep apnea: The SCALE Sleep Apnea randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkind-Hirsch, K.E.; Chappell, N.; Shaler, D.; Storment, J.; Bellanger, D.L. Liraglutide 3 mg on weight, body composition, and hormonal and metabolic parameters in women with obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Fertil. Steril. 2022, 118, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadden, T.A.; Tronieri, J.S.; Sugimoto, D.; Lund, M.T.; Auerbach, P.; Jensen, C.; Rubino, D. Liraglutide 3.0 mg and intensive behavioral therapy (IBT) for obesity in primary care: The SCALE IBT randomized controlled trial. Obesity 2020, 28, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, A.; Rössner, S.; Van Gaal, L.; Rissanen, A.; Niskanen, L.; Al Hakim, M.; Madsen, J.; Rasmussen, M.F.; Lean, M.E.; Wilding, J.P.H.; et al. Effects of liraglutide in the treatment of obesity: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet 2009, 374, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, A.; Carraro, R.; Finer, N.; Harper, A.; Kunesova, M.; Lean, M.E.; Niskanen, L.; Rasmussen, M.F.; Rissanen, A.; Rössner, S.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and sustained weight loss over 2 years with the once-daily human GLP-1 analog, liraglutide. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubino, D.M.; Greenway, F.L.; Khalid, U.; O’Neil, P.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Sørrig, R.; Wadden, T.A.; Wizert, A.; Garvey, W.T.; Davies, M.; et al. Effect of weekly subcutaneous semaglutide vs daily liraglutide on body weight in adults with overweight or obesity without diabetes: The STEP 8 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldhaleei, W.A.; Abegaz, T.M.; Bhagavathula, A.S. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists associated gastrointestinal adverse events: A cross-sectional analysis of the National Institutes of Health All of Us cohort. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franks, A.S.; Lee, P.H.; George, C.M. Pancreatitis: A potential complication of liraglutide? Ann. Pharmacother. 2012, 46, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.M.; Tronieri, J.S.; Amaro, A.; Wadden, T.A. Semaglutide for the treatment of obesity. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 33, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Krauthamer, M.; Bjalme-Evans, M. Wegovy (semaglutide): A new weight loss drug for chronic weight management. J. Investig. Med. 2022, 70, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.; Sugimoto, D.; Wharton, S. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide for weight management: Evidence from the STEP program. Postgrad. Med. 2022, 134 (Suppl. S1), 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, J.; Finlayson, G.; Axelsen, M.; Flint, A.; Gibbons, C.; Kvist, T.; Hjerpsted, J.B. Effects of once-weekly semaglutide on appetite, energy intake, control of eating, food preference, and body weight in subjects with obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. The GLP-1 journey: From discovery science to therapeutic impact. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e175634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrichsen, M.; Breitschaft, A.; Tadayon, S.; Wizert, A.; Skovgaard, D. The effect of semaglutide 2.4 mg once weekly on energy intake, appetite, control of eating, and gastric emptying in adults with obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, N.K.; Hackett, T.A.; Galli, A.; Flynn, C.R. GLP-1: Molecular mechanisms and outcomes of a complex signaling system. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 128, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorli, C.; Harashima, S.I.; Tsoukas, G.M.; Unger, J.; Karsbøl, J.D.; Hansen, T.; Bain, S.C. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide monotherapy versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 1): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multinational, multicentre phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodbard, H.W.; Lingvay, I.; Reed, J.; de la Rosa, R.; Rose, L.; Sugimoto, D.; Araki, E.; Chu, P.L.; Wijayasinghe, N.; Norwood, P. Semaglutide added to basal insulin in type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 5): A randomized, controlled trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 2291–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Bhosekar, V.; Busch, R.; Holst, I.; Ludvik, B.; Thielke, D.; Thrasher, J.; Woo, V.; Philis-Tsimikas, A. Semaglutide once weekly as add-on to SGLT-2 inhibitor therapy in type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 9): A randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratley, R.; Amod, A.; Hoff, S.T.; Kadowaki, T.; Lingvay, I.; Nauck, M.; Pedersen, K.B.; Saugstrup, T.; Meier, J.J.; Bain, S.C.; et al. Oral semaglutide versus subcutaneous liraglutide and placebo in type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 4): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3a trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capehorn, M.S.; Catarig, A.M.; Furberg, J.K.; Janez, A.; Price, H.C.; Tadayon, S.; Vergès, B.; Marre, M. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide 1.0 mg vs once-daily liraglutide 1.2 mg as add-on to 1–3 oral antidiabetic drugs in subjects with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 10). Diabetes Metab. 2020, 46, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weghuber, D.; Barrett, T.; Barrientos-Pérez, M.; Gies, I.; Hesse, D.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Kelly, A.S.; Mastrandrea, L.D.; Sørrig, R.; Arslanian, S.; et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adolescents with obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2245–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagendra, L.; Bg, H.; Sharma, M.; Dutta, D. Semaglutide and cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2023, 17, 102834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clément, K.; van den Akker, E.; Argente, J.; Bahm, A.; Chung, W.K.; Connors, H.; De Waele, K.; Farooqi, I.S.; Gonneau-Lejeune, J.; Gordon, G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of setmelanotide, an MC4R agonist, in individuals with severe obesity due to LEPR or POMC deficiency: Single-arm, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pressley, H.; Cornelio, C.K.; Adams, E.N. Setmelanotide: A Novel Targeted Treatment for Monogenic Obesity. J. Pharm. Technol. 2022, 38, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayers, K.L.; Glicksberg, B.S.; Garfield, A.S.; Longerich, S.; White, J.A.; Yang, P.; Du, L.; Chittenden, T.W.; Gulcher, J.R.; Roy, S.; et al. Melanocortin 4 receptor pathway dysfunction in obesity: Patient stratification aimed at MC4R agonist treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 2601–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markham, A. Setmelanotide: First approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.C.; Rasmussen, M.C.; Forte, A.R.; Schrage, S.B.; Zafar, S.K.; Haqq, A.M. Management of monogenic and syndromic obesity. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 52, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, M.M.; Mohammad, A.; Alam-Eldin, N.; Madhu, D.; Al-Mulla, F.; Abu-Farha, M.; Abubaker, J. Structural analysis of setmelanotide binding to MC4R variants in comparison to wild-type receptor. Life Sci. 2022, 307, 120857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, G.S.H.; Chao, D.H.M.; Siegert, A.M.; Koerperich, Z.M.; Ericson, M.D.; Simonds, S.E.; Larson, C.M.; Luquet, S.; Clarke, I.; Sharma, S.; et al. The melanocortin pathway and energy homeostasis: From discovery to obesity therapy. Mol. Metab. 2021, 48, 101206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakhtoura, M.; Haber, R.; Ghezzawi, M.; Rhayem, C.; Tcheroyan, R.; Mantzoros, C.S. Pharmacotherapy of obesity: An update on the available medications and drugs under investigation. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 58, 101882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haqq, A.M.; Chung, W.K.; Dollfus, H.; Haws, R.M.; Martos-Moreno, G.Á.; Poitou, C.; Yanovski, J.A.; Mittleman, R.S.; Yuan, G.; Forsythe, E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of setmelanotide, a melanocortin-4 receptor agonist, in patients with Bardet-Biedl syndrome and Alström syndrome: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial with an open-label period. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves New Medication for Chronic Weight Management. FDA Press Release. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-medication-chronic-weight-management (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Garvey, W.T.; Frias, J.P.; Jastreboff, A.M.; le Roux, C.W.; Sattar, N.; Aizenberg, D.; Mao, H.; Zhang, S.; Ahmad, N.N.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity in people with type 2 diabetes (SURMOUNT-2): A double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, J.P.; Davies, M.J.; Rosenstock, J.; Pérez Manghi, F.C.; Fernández Landó, L.; Bergman, B.K.; Liu, B.; Cui, X.; Brown, K.; SURPASS-2 Investigators; et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; D’Alessio, D.A. Tirzepatide, a dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor co-agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with unmatched effectiveness regarding glycaemic control and body weight reduction. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; Pan, X.H.; Chew, H.S.J.; Goh, R.S.J.; Lin, C.; Anand, V.V.; Lee, E.C.Z.; Chan, K.E.; Kong, G.; Ong, C.E.Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide for treatment of overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes—State-of-the-art. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myerson, M.; Paparodis, R.D. Pharmacotherapy of weight-loss and obesity with a focus on GLP-1 receptor agonists. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 64, 1204–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi Beshir, S.; Ahmed Elnour, A.; Soorya, A.; Parveen Mohamed, A.; Sir Loon Goh, S.; Hussain, N.; Al Haddad, A.H.I.; Hussain, F.; Yousif Khidir, I.; Abdelnassir, Z. A narrative review of approved and emerging anti-obesity medications. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 101757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, Z.; Cancarevic, I.; Huang, L. FDA-Approved Pharmacotherapy for Weight Loss Over the Last Decade. Cureus 2022, 14, e29262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.H.; Tan, B.; Chin, Y.H.; Lee, E.C.Z.; Kong, G.; Chong, B.; Kueh, M.; Khoo, C.M.; Mehta, A.; Majety, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and other weight loss drugs in overweight and obesity: A network meta-analysis. Obesity 2024, 32, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo Clinic. Phentermine Weight-Loss Drug: Know the Side Effects. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/expert-answers/phentermine/faq-20057940 (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Ulus, I.H.; Maher, T.J.; Wurtman, R.J. Characterization of phentermine and related compounds as monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DrugBank. Phentermine. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00191 (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Hendricks, E.J.; Rothman, R.B.; Greenway, F.L. How physician obesity specialists use drugs to treat obesity. Obesity 2019, 27, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivus. Qsymia (Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release) Capsules, Prescribing Information; Vivus, Inc.: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Munro, J.F.; MacCuish, A.C.; Wilson, E.M.; Duncan, L.J. Comparison of continuous and intermittent anorectic therapy in obesity. BMJ 2018, 1, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apovian, C.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Bessesen, D.H.; McDonnell, M.E.; Murad, M.H.; Pagotto, U.; Ryan, D.H.; Still, C.D.; Endocrine Society Clinical Guidelines Subcommittee; Endocrine Society Obesity Task Force; et al. Pharmacological management of obesity: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 342–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanovski, S.Z.; Yanovski, J.A. Long-term drug treatment for obesity: A systematic and clinical review. JAMA 2014, 311, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeting, A.N.; Tabet, E.; Caterson, I.D.; Markovic, T.P. Management of obesity and cardiometabolic risk—Role of phentermine/extended-release topiramate. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2018, 11, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem. Topiramate. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Topiramate (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Is Topamax Addictive? Medical News Today. Available online: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/drugs-is-topamax-addictive#potential-for-misuse-or-abuse (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Gadde, K.M.; Allison, D.B.; Ryan, D.H.; Peterson, C.A.; Troupin, B.; Schwiers, M.L.; Day, W.W. Effects of low-dose, controlled-release phentermine plus topiramate combination on weight and associated comorbidities in overweight and obese adults (CONQUER): A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, W.T.; Ryan, D.H.; Look, M.; Gadde, K.M.; Allison, D.B.; Peterson, C.A.; Schwiers, M.; Day, W.W.; Bowden, C.H. Two-year sustained weight loss and metabolic benefits with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in obese and overweight adults (SEQUEL): A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 extension study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, D.B.; Gadde, K.M.; Garvey, W.T.; Peterson, C.A.; Schwiers, M.L.; Najarian, T.; Tam, P.Y.; Troupin, B.; Day, W.W. Controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in severely obese adults: A randomized controlled trial (EQUIP). Obesity 2012, 20, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, M.C.; Sanchez, M.; Raether, B.; Weissman, N.J.; Smith, S.R.; Shanahan, W.R.; Anderson, C.M.; for the BLOSSOM Clinical Trial Group. A one-year randomized trial of lorcaserin for weight loss in obese and overweight adults: The BLOSSOM trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 3067–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem. Bupropion. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/bupropion (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Huecker, M.R.; Smiley, A.; Saadabadi, A. Bupropion. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470212/ (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- PubChem. Naltrexone. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Naltrexone (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Singh, D.; Saadabadi, A. Naltrexone. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534811/ (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Greenway, F.L.; Fujioka, K.; Plodkowski, R.A.; Mudaliar, S.; Guttadauria, M.; Erickson, J.; Kim, D.D.; Dunayevich, E.; for the COR-I Study Group. Effect of naltrexone plus bupropion on weight loss in overweight and obese adults (COR-I): A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Foreyt, J.P.; Foster, G.D.; Hill, J.O.; Klein, S.; O’Neil, P.M.; Perri, M.G.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Rock, C.L.; Erickson, J.S.; et al. Weight loss with naltrexone SR/bupropion SR combination therapy as an adjunct to behavior modification: The COR-BMOD trial. Obesity 2011, 19, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K.E.; Prcela, L.; Wadden, T.A.; Buse, J.B.; Bakris, G.; Perez, A.; Smith, S.R. Effect of naltrexone-bupropion on major adverse cardiovascular events in overweight and obese patients with cardiovascular risk factors: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 990–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, M.H.; Hauptman, J.; DiGirolamo, M.; Foreyt, J.P.; Halsted, C.H.; Heber, D.; Heimburger, D.C.; Lucas, C.P.; Robbins, D.C.; Chung, J.; et al. Weight control and risk factor reduction in obese subjects treated for 2 years with orlistat: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1999, 281, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgerson, J.S.; Hauptman, J.; Boldrin, M.N.; Sjöström, L. XENical in the prevention of diabetes in obese subjects (XENDOS) study: A randomized study of orlistat as an adjunct to lifestyle changes for the prevention of type 2 diabetes in obese patients. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, A.B.; Al Khalili, Y. Orlistat. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542202/ (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- PubChem. Orlistat. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Orlistat (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration FDA. Orlistat (Marketed as Alli and Xenical) Information. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/orlistat-marketed-alli-and-xenical-information (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Sjöström, L.; Rissanen, A.; Andersen, T.; Boldrin, M.; Golay, A.; Koppeschaar, H.P.F.; Krempf, M.; for the European Orlistat Obesity Study Group. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss and prevention of weight regain in obese patients. Lancet 1998, 352, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeting, A.N.; Hocking, S.L.; Markovic, T.P. Pharmacotherapy for the treatment of obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 418, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Massey, S.; Story, D.; Li, L. Metformin: An old drug with new applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salpeter, S.R.; Buckley, N.S.; Kahn, J.A.; Salpeter, E.E. Meta-analysis: Metformin treatment in persons at risk for diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Long-term safety, tolerability, and weight loss associated with metformin in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metformin: History and Mechanism of Action. LGC Standards 2020. Available online: https://www.lgcstandards.com/GB/en/Resources/Articles/Pharma-roots-Metformin (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Corcoran, C.; Jacobs, T.F. Metformin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518983/ (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Knowler, W.C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Fowler, S.E.; Hamman, R.F.; Lachin, J.M.; Walker, E.A.; Nathan, D.M.; Bennett, P.H.; Brown, S.A.; Goldberg, R.; et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K.; DeFronzo, R.A. Metformin: A review of its metabolic effects. Diabetes Rev. 1998, 6, 89–131. [Google Scholar]
- Naderpoor, N.; Shorakae, S.; de Courten, B.; Misso, M.L.; Moran, L.J.; Teede, H.J. Metformin and lifestyle modification in polycystic ovary syndrome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2015, 21, 560–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Ortiz, M.; Martinez-Abundis, E.; Robles-Cervantes, J.A.; Ramos-Zavala, M.G.; Barraza-Salas, M. Effect of metformin on insulin sensitivity in obese nondiabetic patients: A double-blind placebo-controlled study. Metabolism 1999, 48, 586–589. [Google Scholar]
- Malin, S.K.; Kashyap, S.R. Effects of metformin on weight loss: Potential mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2014, 21, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.; Deenadayalan, S.; Erichsen, L.; Jodar, E.; Lingvay, I.; Macura, S.; Mathieu, C.; Bajaj, H.S.; Goland, R.S.; Kalra, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of co-administered once-weekly cagrilintide 2.4 mg with once-weekly semaglutide 2.4 mg in type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, L.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, F.; Chen, R.; et al. Cagrilintide: A novel long-acting amylin analog for weight loss therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ascanio, A.M.; Mullally, J.A.; Frishman, W.H. Cagrilintide: A long-acting amylin analog for the treatment of obesity. Cardiol. Rev. 2024, 32, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, A.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, Z.; Wang, F.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists on glycaemic control, body weight, and lipid profile for type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 2024, 384, e076410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enebo, L.B.; Berthelsen, K.K.; Kankam, M.; Lund, M.T.; Rubino, D.M.; Satylganova, A.; Lau, D.C.W. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of concomitant administration of multiple doses of cagrilintide with semaglutide 2.4 mg for weight management: A randomised, controlled, phase 1b trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 1736–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.C.W.; Erichsen, L.; Francisco, A.M.; Satylganova, A.; le Roux, C.W.; McGowan, B.; Pedersen, S.D.; Wharton, S.; Davies, M.J.; Zacho, J.; et al. Once-weekly cagrilintide for weight management in people with overweight and obesity: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled and active-controlled, dose-finding phase 2 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 2160–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walpurgis, K.; Thomas, A.; Dellanna, F.; Schänzer, W.; Thevis, M. Detection of the human anti-ActRII antibody bimagrumab in serum by means of affinity purification, tryptic digestion, and LC-HRMS. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2018, 12, e1700120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Coleman, L.A.; Miller, R.; Rooks, D.S.; Laurent, D.; Petricoul, O.; Praestgaard, J.; Roubenoff, R.; Polidori, D.; MacDougall, D.; et al. Effect of bimagrumab vs placebo on body fat mass among adults with type 2 diabetes and obesity: A phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2033457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monoclonal antibodies. In LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31644151/ (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Nunn, E.; Jaiswal, N.; Gavin, M.; Del Rivero, J.; Gavini, C.K.; Altarejos, J.Y.; Breen, D.M.; Peltekian, K.M.; Heymsfield, S.B.; He, J.; et al. Antibody blockade of activin type II receptors preserves skeletal muscle mass and enhances fat loss during GLP-1 receptor agonism. Mol. Metab. 2024, 80, 101880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooks, D.; Petricoul, O.; Praestgaard, J.; Bartlett, M.; Laurent, D.; Roubenoff, R. Safety and pharmacokinetics of bimagrumab in healthy older and obese adults with body composition changes in the older cohort. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchang, B.G.; Abel, B.; Zecca, C.; Shukla, A.P.; Aronne, L.J. An up-to-date evaluation of lorcaserin hydrochloride for the treatment of obesity. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 21, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamm, S.; Gruber, S.B.; Rabchevsky, A.G.; Emeson, R.B. The activity of the serotonin receptor 2C is regulated by alternative splicing. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. FDA. Safety Clinical Trial Shows Possible Increased Risk of Cancer with Weight-Loss Medicine Belviq, Belviq XR (lorcaserin). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-drug-safety-podcasts/safety-clinical-trial-shows-possible-increased-risk-cancer-weight-loss-medicine-belviq-belviq-xr (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- U.S. FDA. FDA Requests Withdrawal of Weight-Loss Drug Belviq, Belviq XR (lorcaserin) from the Market. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requests-withdrawal-weight-loss-drug-belviq-belviq-xr-lorcaserin-market (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Harvard Medical School. How Artificial Intelligence Is Disrupting Medicine & What It Means for Physicians. Available online: https://postgraduateeducation.hms.harvard.edu/trends-medicine/how-artificial-intelligence-disrupting-medicine-what-means-physicians (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Chew, H.S.J. The use of artificial intelligence-based conversational agents (chatbots) for weight loss: Scoping review and practical recommendations. JMIR Med. Inform. 2022, 10, e32578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Fang, M.L.; Fukuoka, Y. A systematic review of artificial intelligence chatbots for promoting physical activity, healthy diet, and weight loss. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.T.; Huang, R.Y.; Chen, T.T.; Lee, Y.T.; Lee, Y.C.; Kuo, P.H.; Hsu, C.Y. Effect of health literacy and shared decision-making on weight-loss plan choice via an AI robot intervention. Digit. Health 2022, 8, 20552076221136372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.J.; Choi, A.; Schauer, J.M.; Pfammatter, A.F.; Spring, B.J.; Darwiche, A.; Alshurafa, N.I. An explainable artificial intelligence software tool for weight management experts (PRIMO): Mixed methods study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e42047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.D.; Wyatt, H.R.; Hill, J.O.; McGuckin, B.G.; Brill, C.; Mohammed, B.S.; Szapary, P.O.; Rader, D.J.; Edman, J.S.; Klein, S.; et al. Weight and metabolic outcomes after 2 years on a low-carbohydrate versus low-fat diet: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 153, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadden, T.A.; Walsh, O.A.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Leonard, S.M.; Swantek, J.S.; Chao, A.M.; Bakizada, Z.M.; Williams, N.N.; Alamuddin, N.; Dempsey, M.C.; et al. Intensive behavioral therapy for obesity combined with liraglutide 3.0 mg: A randomized controlled trial. Obesity 2019, 27, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditti, E.M.; Wylie-Rosett, J.; Delahanty, L.M.; Mele, L.; Hoskin, M.A.; Edelstein, S.L.; the Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Short and long-term lifestyle coaching approaches used to address diverse participant barriers to weight loss and physical activity adherence. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.W.Y.; Chan, R.S.M.; Sea, M.M.M.; Woo, J. Psychological factors of long-term dietary and physical activity adherence among Chinese adults with overweight and obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yackobovitch-Gavan, M.; Steinberg, D.M.; Endevelt, R.; Benyamini, Y. Factors associated with dropout in a group weight-loss programme: A longitudinal investigation. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 28 (Suppl. S2), 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, O.; Ferretti, V.V.; Ferraris, C.; Trentani, C.; Vinai, P.; Villani, S.; Tagliabue, A. Is drop-out from obesity treatment a predictable and preventable event? Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, W.; Annamaraju, P.; Khan Suheb, M.Z.; Uppaluri, K.R. Ketogenic Diet. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29763005/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Stubbs, B.J.; Cox, P.J.; Evans, R.D.; Cyranka, M.; Clarke, K.; de Wet, H. A ketone ester drink lowers human ghrelin and appetite. Obesity 2018, 26, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumithran, P.; Prendergast, L.A.; Delbridge, E.; Purcell, K.; Shulkes, A.; Kriketos, A.; Proietto, J. Ketosis and appetite-mediating nutrients and hormones after weight loss. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, A.M.; Horgan, G.W.; Murison, S.D.; Bremner, D.M.; Lobley, G.E. Effects of a high-protein ketogenic diet on hunger, appetite, and weight loss in obese men feeding ad libitum. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, H.M.; Mathew, T.C.; Khadada, M.; Al-Mousawi, M.; Talib, H.; Asfar, S.K.; Behbahani, A.I.; Al-Zaid, N.S. Beneficial effects of ketogenic diet in obese diabetic subjects. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 302, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkworth, G.D.; Noakes, M.; Buckley, J.D.; Keogh, J.B.; Clifton, P.M. Long-term effects of a very-low-carbohydrate weight loss diet compared with an isocaloric low-fat diet after 12 months. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, B.; Bellido, D.; Sajoux, I.; Goday, A.; Saavedra, D.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Casanueva, F.F. Comparison of a very low-calorie ketogenic diet with a standard low-calorie diet in the treatment of obesity. Endocrine 2014, 47, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, B.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Bellido, D.; Sajoux, I.; Casanueva, F.F. Obesity treatment by very low-calorie ketogenic diet at two years: Reduction in visceral fat and on the burden of disease. Endocrine 2016, 54, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.C.; Chung, D.E.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, H.D. Early- and late-onset complications of the ketogenic diet for intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia 2004, 45, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, G.; Gonzalez-Izundegui, D.; Shan, K.L.; Campos, A.; Breen-Lyles, M.; Guerrero, A.; Acosta, A.; Nuttall, F.Q.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. Effectiveness of anti-obesity medications approved for long-term use in a multidisciplinary weight management program. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finer, N.; James, W.P.T.; Kopelman, P.G.; Lean, M.E.J.; Williams, G. One-year treatment of obesity: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study of orlistat. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, W.T.; Batterham, R.L.; Bhatta, M.; Busetto, L.; Frias, J.P.; Jódar, E.; Lau, D.C.W.; Halpern, A.; Kyle, T.K.; Yu, A.P.; et al. Two-year effects of semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: The STEP 5 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K.H.; Fischer, H.; Ard, J.; Barton, L.; Bessesen, D.H.; Daley, M.F.; Desai, J.; McDermott, M.; Phimphasone-Brady, P.; Powers, J.D.; et al. Safety and effectiveness of longer-term phentermine use. Obesity 2019, 27, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulton, A.S.; Hibbert, E.J.; Champion, B.L.; Connor, J.P.; Knight, C.; Winstock, A.R.; Nassar, N.; Smith, C.; Shum, D.H.K.; Schofield, P.R.; et al. Piloting a new approach to the treatment of obesity using dexamphetamine. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Blüher, M.; Tschöp, M.H.; DiMarchi, R.D. Anti-obesity drug discovery: Advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifarth, C.; Schehler, B.; Schneider, H.J. Effectiveness of metformin on weight loss in non-diabetic individuals with obesity. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2013, 121, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasoyan, H.; Pfoh, E.R.; Schulte, R.; Dalal, M.R.; Aminian, A.; Arterburn, D.E.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Khandelwal, N.; Lewis, K.H.; Horberg, M.A.; et al. Early- and later-stage persistence with antiobesity medications: A retrospective cohort study. Obesity 2024, 32, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, C.; Thomas, E.; Saxon, D.R. An updated approach to antiobesity pharmacotherapy: Moving beyond the 5% weight loss goal. J. Endocr. Soc. 2023, 7, bvac195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topart, P. Obesity surgery: Which procedure should we choose and why? J. Visc. Surg. 2023, 160, S30–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöström, L. Review of the key results from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) trial—A prospective controlled intervention study of bariatric surgery. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 273, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.E.; Hindle, A.; Brennan, L.; Skinner, S.; Burton, P.; Smith, A.; Crosthwaite, G.; Brown, W. Long-term outcomes after bariatric surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis of weight loss at 10 or more years. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collazo-Clavell, M.L.; Shah, M. Common and rare complications of bariatric surgery. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 49, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.C.; Kim, M.G.; Park, J.K.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, Y.J.; Lim, H.S. Outcomes and adverse events after bariatric surgery: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis, 2013–2023. J. Metab. Bariatr. Surg. 2023, 12, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfeder, L.B.; Ren, C.J.; Gill, J.R. Fatal complications of bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2006, 16, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doble, B.; Wordsworth, S.; Rogers, C.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Blazeby, J.M. What are the real procedural costs of bariatric surgery? Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 2179–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, N.R.; Pearson, S.; Lau, N.S.; Wiggins, B.; Shrestha, R.; Rao, A.; Caterson, I.D. An intragastric balloon in the treatment of obese individuals with metabolic syndrome: A randomized controlled study. Obesity 2013, 21, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Nava, G.; Asokkumar, R.; Bautista-Castaño, I.; Al-Mrabeh, A.; Delhom, E.; Fernández-Corbelle, J.P.; Espinet-Coll, E. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty, laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, and laparoscopic greater curve plication: Do they differ at 2 years? Endoscopy 2021, 53, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, S.; Swain, J.M.; Woodman, G.; Anton, T.; Gonzalez-Campoy, J.M.; Mehta, A.; Al-Amin, A.; Sheikh, E.; Chao, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Randomized sham-controlled trial evaluating efficacy and safety of endoscopic gastric plication for primary obesity: The ESSENTIAL trial. Obesity 2017, 25, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, S.; Stein, R.; Jonnalagadda, S.; Mullady, D.; Kantsevoy, S.; Curvers, W.; Edmundowicz, S.A.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Thompson, C.C.; Shah, R.J.; et al. Aspiration therapy leads to weight loss in obese subjects: A pilot study. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1245–1252.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirapinyo, P.; Hadefi, A.; Thompson, C.C. ASGE-ESGE guideline on primary endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies for adults with obesity. Endoscopy 2024, 56, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Acosta, A.; Camilleri, M.; Mundi, M.S.; Rajan, E.; Thompson, C.C.; Sharma, A.M.; Edmundowicz, S.A.; Ginsberg, G.G.; Rothstein, R.I.; et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty alters gastric physiology and induces loss of body weight in obese individuals. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 37–43.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, J.; Quebbemann, B.B.; Patterson, E.J.; Sharma, A.M.; Jirapinyo, P.; Kim, H.; Yellumahanthi, K.; Barham, H.P.; Clements, R.H.; DeLuca, L.; et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter study evaluating safety and efficacy of intragastric dual-balloon in obesity. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2013, 9, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saumoy, M.; Gandhi, D.; Buller, S.; Silver, E.; Shah, S.; Landau, C.; Khorsandi, P.; Chokshi, R.; Carr-Locke, D.L.; Jirapinyo, P.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of endoscopic, surgical and pharmacological obesity therapies. Gut 2023, 72, 2250–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, R.; Murad, M.H.; Chandar, A.K.; Dulai, P.S.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Loomba, R.; Camilleri, M.; Singh, S.; Mullen, K.D.; et al. Association of pharmacological treatments for obesity with weight loss and adverse events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2016, 315, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.K.; Cho, H.J.; Kang, H.C.; Youn, B.B.; Lee, K.R. Effects on weight reduction and safety of short-term phentermine administration in Korean obese people. Yonsei Med. J. 2006, 47, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwal, R.; Li, S.K.; Lau, D.C. Long-term pharmacotherapy for obesity and overweight. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004, 2003, CD004094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenharo, M. How anti-obesity drugs cause nausea: Finding offers hope for better drugs. Nature 2024, 631, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apovian, C.M.; Aronne, L.; Rubino, D.; Still, C.; Wyatt, H.; Burns, C.; Kim, D.; Dunayevich, E.; Ascher, S.; Hall, G.; et al. A randomized, phase 3 trial of naltrexone SR/bupropion SR on weight and obesity-related risk factors (COR-II). Obesity 2013, 21, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, P.M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; McGowan, B.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; Wharton, S.; Carson, C.G.; Jepsen, C.H.; Kabisch, M.; Wilding, J.P.H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide compared with liraglutide and placebo for weight loss in patients with obesity: A randomised, double-blind, placebo and active controlled, dose-ranging, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubMed. Post-Marketing Safety of Anti-Obesity Medications: Analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS). Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34564826/ (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- PubMed. Safety and Efficacy of Long-Term Phentermine Use in Obesity Management. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27478924/ (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- U.S. FDA Guidance Document. Developing Products for Weight Management. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/developing-products-weight-management-revision-1 (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- EMA. Guideline on Clinical Evaluation of Medicinal Products Used in Weight Management. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-clinical-evaluation-medicinal-products-used-weight-management-revision-1_en.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- ICER. Policy Recommendations for Obesity Management. Available online: https://icer.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/ICER_Obesity_Policy_Recommendations_102022.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- ASOI. Pharmacotherapy in Obesity Management. Available online: https://asoi.info/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/11-IR-Pharmacotherapy-in-Obesity-Management-FINAL.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2025).
| Modality Type | Description | Efficacy and Timeframe | Patient Suitability | Side Effects and Adherence | Cost (Approx.) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle interventions | Low-calorie diet (500–750 kcal/day), aerobic and resistance training, behavior therapy | 6–11% weight loss in 1 year | BMI 25–29.9 (no comorbidities) or BMI ≥ 30 with comorbidities | Non-adherence: 21–60%, barriers include time and motivation | N/A | [77,132,133,134,135,136,137] |
| Dietary readjustment—ketogenic diet | High-fat, low-carbohydrate diet shifts metabolism toward fat oxidation and ketone production; ketones suppress ghrelin, reduce appetite, and promote weight loss. | 14.5–30 kg weight loss over 1 year | No contraindications (e.g., pancreatitis, hepatic failure, fat metabolism or carnitine disorders, porphyrias). Use with caution in diabetics on insulin/oral hypoglycemics due to hypoglycemia risk. | Hypertriglyceridemia, transient hyperuricemia, hypercholesterolemia, renal stones, iron-deficiency anemia | N/A | [138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146] |
| Pharmacotherapy | GLP-1 agonists (Semaglutide, Liraglutide), lipase inhibitors (Orlistat), MC4 agonists, appetite suppressants, insulin sensitizers | 4–18.6% weight loss in 6–12 months | BMI ≥ 30 or BMI ≥ 27 with comorbidities | Adherence: 10–40%, side effects: nausea, headache, constipation | USD 11–USD 1576/month | [77,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155] |
| Bariatric surgery | Gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, gastric banding, duodenal switch | 17–28% weight loss over 1–2 years 12–25% weight loss over 3–10 years 18% weight loss sustained over 20 years | BMI ≥ 40 or BMI ≥ 35 with comorbidities | Side effects: nutritional deficiency, reflux, obstruction, bone loss | USD 7423–USD 33,541 | [77,156,157,158,159,160,161,162] |
| Endoscopic procedures | Intragastric balloons, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG), POSE, AspireAssist | 4.95–21% weight loss in 1 year | BMI ≥ 30 or ≥27 with comorbidities | Side effects: nausea, vomiting, heartburn, pulmonary risks | USD 4105–USD 11,411/QALY | [77,163,164,165,166,167,168,169,170] |
| Combination/Adjunctive Strategy | Simultaneous or sequential use of two or more therapies (e.g., lifestyle + pharmacotherapy, endoscopy + behavioral intervention) to improve long-term outcomes and adherence | 6–13% total weight loss, depending on combination and adherence | Individuals with insufficient response to monotherapy or those at high risk of dropout. BMI ≥ 30 with comorbidities | Adherence improves with behavioral support; side effects depend on pharmacologic or surgical components | Variable depending on treatment mix; often higher than monotherapy alone | [132,133,147,149] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Lawati, A.; Alhabsi, A.; Rahul, R.; Savino, M.-L.; Alwahaibi, H.; Das, S.; Al Lawati, H. Current and Emerging Parenteral and Peroral Medications for Weight Loss: A Narrative Review. Diseases 2025, 13, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13050129
Al Lawati A, Alhabsi A, Rahul R, Savino M-L, Alwahaibi H, Das S, Al Lawati H. Current and Emerging Parenteral and Peroral Medications for Weight Loss: A Narrative Review. Diseases. 2025; 13(5):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13050129
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Lawati, Abdullah, Ayman Alhabsi, Rhieya Rahul, Maria-Luisa Savino, Hamed Alwahaibi, Srijit Das, and Hanan Al Lawati. 2025. "Current and Emerging Parenteral and Peroral Medications for Weight Loss: A Narrative Review" Diseases 13, no. 5: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13050129
APA StyleAl Lawati, A., Alhabsi, A., Rahul, R., Savino, M.-L., Alwahaibi, H., Das, S., & Al Lawati, H. (2025). Current and Emerging Parenteral and Peroral Medications for Weight Loss: A Narrative Review. Diseases, 13(5), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13050129






