A Role for Acyclic Retinoid in the Chemoprevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Therapeutic Strategy Targeting Phosphorylated Retinoid X Receptor-?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Retinoids and Their Receptors
2.2. RXRα and Lipid Metabolism in the Liver
2.3. RXRα Phosphorylation and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
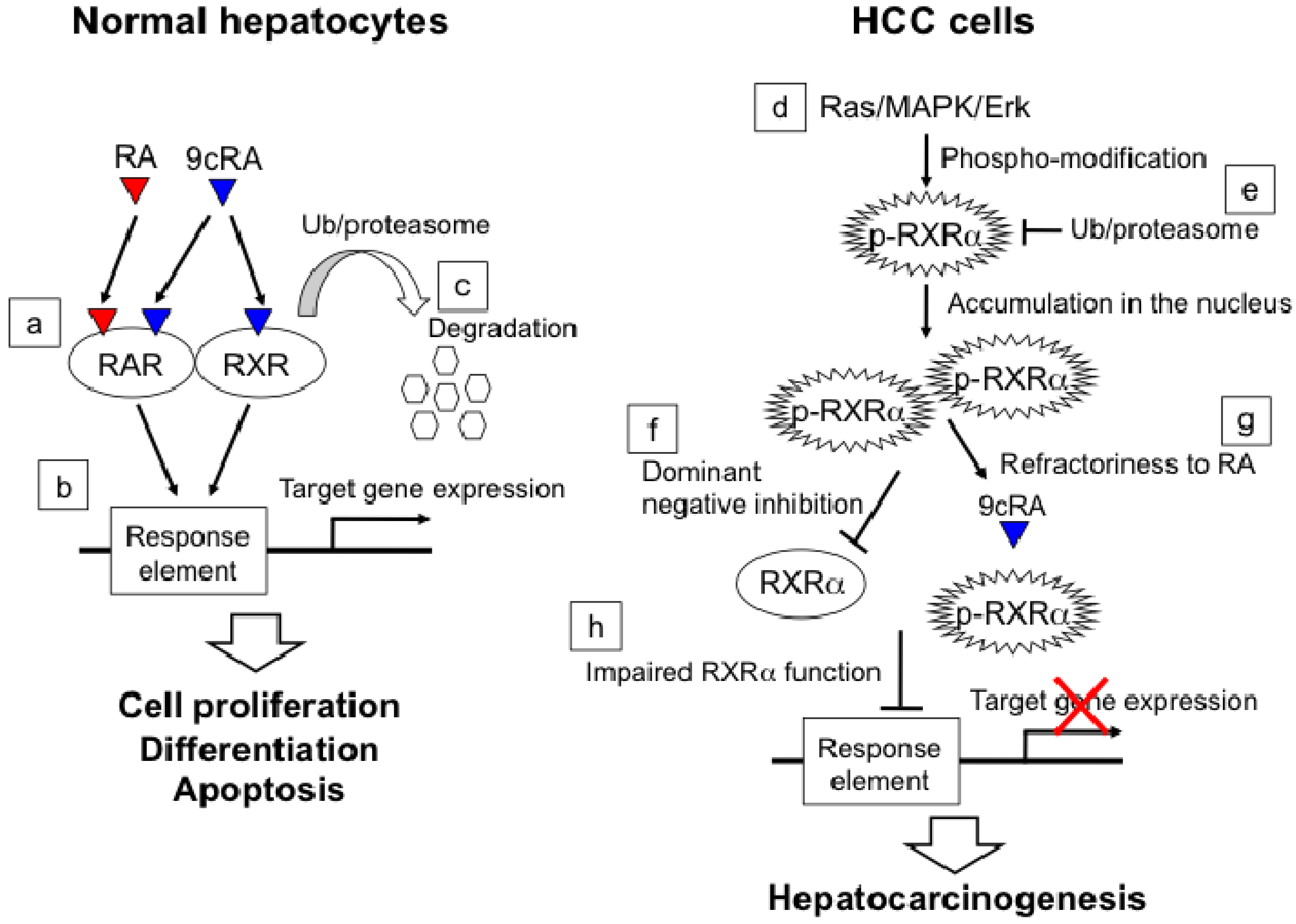
2.4. Molecular Mechanism of ACR in Chemoprevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma

2.5. Chemoprevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using ACR
2.6. “Clonal Deletion” in Chemoprevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma

2.7. Combination Chemoprevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using ACR
3. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Ducreux, M.; Lencioni, R.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Galle, P.R.; Dufour, J.F.; Greten, T.F.; Raymond, E.; Roskams, T.; De Baere, T.; et al. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 908–943. [Google Scholar]
- El-Serag, H.B. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, F.X.; Ribes, J.; Diaz, M.; Cleries, R. Primary liver cancer: Worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology 2004, 127 (Suppl. 1), S5–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, M.Y.; Rhim, H.; Han, J.K. Systematic review of randomized trials for hepatocellular carcinoma treated with percutaneous ablation therapies. Hepatology 2009, 49, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Fuster, J.; Bruix, J. Intention-to-treat analysis of surgical treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma: resection versus transplantation. Hepatology 1999, 30, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Schwartz, M.; Mazzaferro, V. Resection and liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2005, 25, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 2003, 37, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Roberts, L.R. Hepatocellular carcinoma: A global view. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.H.; You, S.L.; Chen, C.J.; Liu, C.J.; Lee, C.M.; Lin, S.M.; Chu, H.C.; Wu, T.C.; Yang, S.S.; Kuo, H.S.; et al. Decreased incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B vaccinees: A 20-year follow-up study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, A.R.; Van Damme, P.; Shouval, D. The global impact of vaccination against hepatitis B: A historical overview. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6266–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.S.; Wong, G.L.; Tsoi, K.K.; Wong, V.W.; Cheung, S.Y.; Chong, C.N.; Wong, J.; Lee, K.F.; Lai, P.B.; Chan, H.L. Meta-analysis: The efficacy of anti-viral therapy in prevention of recurrence after curative treatment of chronic hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.C.; Hsu, C.; Chen, L.T.; Cheng, C.C.; Hu, F.C.; Cheng, A.L. Adjuvant interferon therapy after curative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): A meta-regression approach. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Takaki, A.; Iwasaki, Y.; Yamamoto, K. Meta-analysis: Interferon-alpha prevents the recurrence after curative treatment of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Volk, M.L.; Jensen, D.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Schoenfeld, P.S. A sustained viral response is associated with reduced liver-related morbidity and mortality in patients with hepatitis C virus. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 280–288, 288 e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, Y.; Moriwaki, H.; Ninomiya, M.; Adachi, S.; Saito, A.; Takasaki, K.T.; Tanaka, T.; Tsurumi, K.; Okuno, M.; Tomita, E.; et al. Prevention of second primary tumors by an acyclic retinoid, polyprenoic acid, in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatoma Prevention Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1561–1567. [Google Scholar]
- Muto, Y.; Moriwaki, H.; Saito, A. Prevention of second primary tumors by an acyclic retinoid in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1046–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, K.; Okuno, M.; Yasuda, I.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Uematsu, T.; Tsurumi, H.; Shiratori, Y.; Muto, Y.; Moriwaki, H. Prevention of second primary tumors by an acyclic retinoid in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Updated analysis of the long-term follow-up data. Intervirology 2005, 48, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporn, M.B.; Newton, D.L. Chemoprevention of cancer with retinoids. Fed. Proc. 1979, 38, 2528–2534. [Google Scholar]
- Muto, Y.; Moriwaki, H. Antitumor activity of vitamin A and its derivatives. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1984, 73, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Moriwaki, H.; Shimizu, M.; Okuno, M.; Nishiwaki-Matsushima, R. Chemoprevention of liver carcinogenesis with retinoids: Basic and clinical aspects. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37 (Suppl. 2), S299–S302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Takai, K.; Moriwaki, H. Strategy and mechanism for the prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma: phosphorylated retinoid X receptor alpha is a critical target for hepatocellular carcinoma chemoprevention. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Sakai, H.; Moriwaki, H. Chemoprevention of hepatocellular carcinoma by acyclic retinoid. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2011, 16, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambon, P. A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 940–954. [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Thummel, C.; Beato, M.; Herrlich, P.; Schutz, G.; Umesono, K.; Blumberg, B.; Kastner, P.; Mark, M.; Chambon, P.; et al. The nuclear receptor superfamily: The second decade. Cell 1995, 83, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, P.; Chambon, P.; Eichele, G.; Evans, R.M.; Lazar, M.A.; Leid, M.; De Lera, A.R.; Lotan, R.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Gronemeyer, H. International Union of Pharmacology. LX. Retinoic acid receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolle, P.; Fraulob, V.; Kastner, P.; Chambon, P. Developmental expression of murine retinoid X receptor (RXR) genes. Mech. Dev. 1994, 45, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Ong, E.S.; Dyck, J.A.; Evans, R.M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature 1990, 345, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Borgmeyer, U.; Heyman, R.A.; Zhou, J.Y.; Ong, E.S.; Oro, A.E.; Kakizuka, A.; Evans, R.M. Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1992, 6, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, K.; Gleason, S.L.; Levi, B.Z.; Hirschfeld, S.; Appella, E.; Ozato, K. H-2RIIBP, a member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that binds to both the regulatory element of major histocompatibility class I genes and the estrogen response element. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 8289–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, V.C.; Delsert, C.; Andersen, B.; Holloway, J.M.; Devary, O.V.; Naar, A.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Boutin, J.M.; Glass, C.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. RXR beta: A coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell 1991, 67, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.Y.; Misner, D.; Kempermann, G.; Schikorski, T.; Giguere, V.; Sucov, H.M.; Gage, F.H.; Stevens, C.F.; Evans, R.M. An essential role for retinoid receptors RARbeta and RXRgamma in long-term potentiation and depression. Neuron 1998, 21, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, B.R.; Brown, N.S.; Wood, W.M.; Gordon, D.F.; Ridgway, E.C. The thyrotrope-restricted isoform of the retinoid-X receptor-gamma1 mediates 9-cis-retinoic acid suppression of thyrotropin-beta promoter activity. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 481–489. [Google Scholar]
- Germain, P.; Chambon, P.; Eichele, G.; Evans, R.M.; Lazar, M.A.; Leid, M.; De Lera, A.R.; Lotan, R.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Gronemeyer, H. International Union of Pharmacology. LXIII. Retinoid X receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfahl, M. Signal transduction by retinoid receptors. Skin Pharmacol. 1993, 6 (Suppl. 1), 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.J.; An, D.; Cai, Y.; Repa, J.J.; Hung-Po Chen, T.; Flores, M.; Postic, C.; Magnuson, M.A.; Chen, J.; Chien, K.R.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific mutation establishes retinoid X receptor alpha as a heterodimeric integrator of multiple physiological processes in the liver. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 4436–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontonoz, P.; Graves, R.A.; Budavari, A.I.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Lui, M.; Hu, E.; Tempst, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipocyte-specific transcription factor ARF6 is a heterodimeric complex of two nuclear hormone receptors, PPAR gamma and RXR alpha. Nucl. Acids Res. 1994, 22, 5628–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repa, J.J.; Turley, S.D.; Lobaccaro, J.A.; Medina, J.; Li, L.; Lustig, K.; Shan, B.; Heyman, R.A.; Dietschy, J.M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Regulation of absorption and ABC1-mediated efflux of cholesterol by RXR heterodimers. Science 2000, 289, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.J.; Cai, Y.; Lungo, W.; Fu, P.; Locker, J.; French, S.; Sucov, H.M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha-mediated pathways are altered in hepatocyte-specific retinoid X receptor alpha-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28285–28290. [Google Scholar]
- Gyamfi, M.A.; Tanaka, Y.; He, L.; Klaassen, C.D.; Wan, Y.J. Hepatic effects of a methionine-choline-deficient diet in hepatocyte RXRalpha-null mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 234, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.A.; Sigman, C.C.; Andreola, F.; Ross, S.A.; Kelloff, G.J.; De Luca, L.M. Retinoids in chemoprevention and differentiation therapy. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, Y.; Omori, M.; Sugawara, K. Demonstration of a novel cellular retinol-binding protein, F-type, in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gann 1979, 70, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Muto, Y.; Omori, M. A novel cellular retinoid-binding protein, F-type, in hepatocellular carcinom. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1981, 359, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, N.; Shimizu, M.; Okuno, M.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Tsurumi, H.; Tanaka, T.; Moriwaki, H. Expression of retinoid X receptor alpha is decreased in 3'-methyl-4-dimethylaminoazobenzene-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Shirakami, Y.; Gottesman, M.E.; Blaner, W.S. Diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis is suppressed in lecithin:retinol acyltransferase-deficient mice primarily through retinoid actions immediately after carcinogen administration. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Shidoji, Y.; Nishiwaki, S.; Yamada, T.; Moriwaki, H.; Muto, Y. Aberrant metabolism of retinoid X receptor proteins in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1996, 121, 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Okuno, M.; Adachi, S.; Sano, T.; Akita, K.; Moriwaki, H.; Friedman, S.L.; Kojima, S. Phosphorylation of retinoid X receptor alpha at serine 260 impairs its metabolism and function in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 7675–7682. [Google Scholar]
- Rochette-Egly, C. Nuclear receptors: Integration of multiple signalling pathways through phosphorylation. Cell Signal. 2003, 15, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastien, J.; Adam-Stitah, S.; Plassat, J.L.; Chambon, P.; Rochette-Egly, C. The phosphorylation site located in the A region of retinoic X receptor alpha is required for the antiproliferative effect of retinoic acid (RA) and the activation of RA target genes in F9 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 28683–28689. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Suh, Y.A.; Robinson, M.J.; Clifford, J.L.; Hong, W.K.; Woodgett, J.R.; Cobb, M.H.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Kurie, J.M. Stress pathway activation induces phosphorylation of retinoid X receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 32193–32199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, C.; White, J.H.; Kremer, R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibits 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-dependent signal transduction by phosphorylating human retinoid X receptor alpha. J. Clin. Invest. 1999, 103, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, S.; Okuno, M.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Takano, Y.; Kojima, S.; Friedman, S.L.; Moriwaki, H.; Okano, Y. Phosphorylation of retinoid X receptor suppresses its ubiquitination in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2002, 35, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.; Muto, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Okuno, M.; Takano, Y.; Tsurumi, H.; Kojima, S.; Okano, Y.; Moriwaki, H. Phosphorylated retinoid X receptor alpha loses its heterodimeric activity with retinoic acid receptor beta. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippman, S.M.; Lotan, R. Advances in the development of retinoids as chemopreventive agents. J. Nutr. 2000, 130 (Suppl. 2S), 479S–482S. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.Y.; Lotan, R. Retinoids and their receptors in cancer development and chemoprevention. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 41, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altucci, L.; Gronemeyer, H. The promise of retinoids to fight against cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, I.; Shiratori, Y.; Adachi, S.; Obora, A.; Takemura, M.; Okuno, M.; Shidoji, Y.; Seishima, M.; Muto, Y.; Moriwaki, H. Acyclic retinoid induces partial differentiation, down-regulates telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA expression and telomerase activity, and induces apoptosis in human hepatoma-derived cell lines. J. Hepatol. 2002, 36, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, H.; Muto, Y.; Ninomiya, M.; Kawai, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Seto, T. Inhibitory effects of synthetic acidic retinoid and polyprenoic acid on the development of hepatoma in rats induced by 3'-methyl-N,N-dimethyl-4-aminoazobenzene. Gastroenterol. Jpn. 1988, 23, 546–552. [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa, M.; Sano, T.; Ishibashi, N.; Hashimoto, M.; Okuno, M.; Moriwaki, H.; Suzuki, R.; Kohno, H.; Tanaka, T. An acyclic retinoid, NIK-333, inhibits N-diethylnitrosamine-induced rat hepatocarcinogenesis through suppression of TGF-alpha expression and cell proliferation. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Kagawa, M.; Okuno, M.; Ishibashi, N.; Hashimoto, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Suzuki, R.; Kohno, H.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Takano, Y.; et al. Prevention of rat hepatocarcinogenesis by acyclic retinoid is accompanied by reduction in emergence of both TGF-alpha-expressing oval-like cells and activated hepatic stellate cells. Nutr. Cancer 2005, 51, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Sakai, H.; Shirakami, Y.; Iwasa, J.; Yasuda, Y.; Kubota, M.; Takai, K.; Tsurumi, H.; Tanaka, T.; Moriwaki, H. Acyclic retinoid inhibits diethylnitrosamine-induced liver tumorigenesis in obese and diabetic C57BLKS/J- +(db)/+Lepr(db) mice. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2011, 4, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Shidoji, Y.; Fukutomi, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Kaneko, T.; Nakagama, H.; Imawari, M.; Moriwaki, H.; Muto, Y. Positive and negative regulations of albumin gene expression by retinoids in human hepatoma cell lines. Mol. Carcinog. 1994, 10, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, N.; Shidoji, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Moriwaki, H.; Muto, Y. Induction of apoptosis by acyclic retinoid in the human hepatoma-derived cell line, HuH-7. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 207, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutomi, Y.; Omori, M.; Muto, Y.; Ninomiya, M.; Okuno, M.; Moriwaki, H. Inhibitory effects of acyclic retinoid (polyprenoic acid) and its hydroxy derivative on cell growth and on secretion of alpha-fetoprotein in human hepatoma-derived cell line (PLC/PRF/5). Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1990, 81, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzui, M.; Masuda, M.; Lim, J.T.; Albanese, C.; Pestell, R.G.; Weinstein, I.B. Growth inhibition of human hepatoma cells by acyclic retinoid is associated with induction of p21(CIP1) and inhibition of expression of cyclin D1. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 3997–4006. [Google Scholar]
- Araki, H.; Shidoji, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Moriwaki, H.; Muto, Y. Retinoid agonist activities of synthetic geranyl geranoic acid derivatives. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 209, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Okuno, M.; Takano, Y.; Kojima, S.; Friedman, S.L.; Moriwaki, H. Molecular mechanism for growth suppression of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by acyclic retinoid. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, T.; Shimizu, M.; Okuno, M.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Tsurumi, H.; Kojima, S.; Moriwaki, H. Synergistic growth inhibition by acyclic retinoid and vitamin K2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obora, A.; Shiratori, Y.; Okuno, M.; Adachi, S.; Takano, Y.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Yasuda, I.; Yamada, Y.; Akita, K.; Sano, T.; et al. Synergistic induction of apoptosis by acyclic retinoid and interferon-beta in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 2002, 36, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Suzui, M.; Deguchi, A.; Lim, J.T.; Xiao, D.; Hayes, J.H.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Weinstein, I.B. Synergistic effects of acyclic retinoid and OSI-461 on growth inhibition and gene expression in human hepatoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6710–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatebe, H.; Shimizu, M.; Shirakami, Y.; Tsurumi, H.; Moriwaki, H. Synergistic growth inhibition by 9-cis-retinoic acid plus trastuzumab in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2806–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzui, M.; Shimizu, M.; Masuda, M.; Lim, J.T.; Yoshimi, N.; Weinstein, I.B. Acyclic retinoid activates retinoic acid receptor beta and induces transcriptional activation of p21(CIP1) in HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Komi, Y.; Sogabe, Y.; Ishibashi, N.; Sato, Y.; Moriwaki, H.; Shimokado, K.; Kojima, S. Acyclic retinoid inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing the MAPK pathway. Lab. Invest. 2010, 90, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, M.; Suzui, M.; Deguchi, A.; Lim, J.T.; Weinstein, I.B. Effects of acyclic retinoid on growth, cell cycle control, epidermal growth factor receptor signaling, and gene expression in human squamous cell carcinoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.X.; Otsuka, M.; Kato, N.; Taniguchi, H.; Hoshida, Y.; Moriyama, M.; Kawabe, T.; Omata, M. Acyclic retinoid inhibits human hepatoma cell growth by suppressing fibroblast growth factor-mediated signaling pathways. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, M.M.; Morrison, D.K. Integrating signals from RTKs to ERK/MAPK. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3113–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimakami, T.; Honda, M.; Shirasaki, T.; Takabatake, R.; Liu, F.; Murai, K.; Shiomoto, T.; Funaki, M.; Yamane, D.; Murakami, S.; et al. The acyclic retinoid Peretinoin inhibits hepatitis C virus replication and infectious virus release in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4688. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, M.; Yamashita, T.; Arai, K.; Sakai, Y.; Sakai, A.; Nakamura, M.; Mizukoshi, E.; Kaneko, S. Peretinoin, an acyclic retinoid, improves the hepatic gene signature of chronic hepatitis C following curative therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.Y.; Wei, F.; Tanokura, M.; Ishibashi, N.; Shimizu, M.; Moriwaki, H.; Kojima, S. The effect of acyclic retinoid on the metabolomic profiles of hepatocytes and hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One 2013, 8, e82860. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Romito, R.; Schiavo, M.; Mariani, L.; Camerini, T.; Bhoori, S.; Capussotti, L.; Calise, F.; Pellicci, R.; Belli, G.; et al. Prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence with alpha-interferon after liver resection in HCV cirrhosis. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okusaka, T.; Ueno, H.; Ikeda, M.; Morizane, C. Phase I and pharmacokinetic clinical trial of oral administration of the acyclic retinoid NIK-333. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, K.; Izumi, N.; Matsui, O.; Tanaka, K.; Kaneko, S.; Moriwaki, H.; Ikeda, K.; Osaki, Y.; Numata, K.; Nakachi, K.; et al. Peretinoin after curative therapy of hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. J. Gastroenterol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaughter, D.P.; Southwick, H.W.; Smejkal, W. Field cancerization in oral stratified squamous epithelium; clinical implications of multicentric origin. Cancer 1953, 6, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, H.; Yasuda, I.; Shiratori, Y.; Uematsu, T.; Okuno, M.; Muto, Y. Deletion of serum lectin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein by acyclic retinoid: a potent biomarker in the chemoprevention of second primary hepatoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 727–731. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.W.; Tsuchida, T.; Shimao, T.; Li, B.; Takebe, T.; Zhang, R.R.; Sakurai, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Sekine, K.; Ishibashi, N.; et al. The CD133+CD44+ Precancerous Subpopulation of Oval Cells is a Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Stem Cells Dev. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Shimizu, M.; Okuno, M.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Kanemura, N.; Araki, H.; Tsurumi, H.; Kojima, S.; Weinstein, I.B.; Moriwaki, H. Synergistic effects of RXR alpha and PPAR gamma ligands to inhibit growth in human colon cancer cells—Phosphorylated RXR alpha is a critical target for colon cancer management. Gut 2007, 56, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Moriwaki, H. Synergistic Effects of PPARgamma Ligands and Retinoids in Cancer Treatment. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 181047. [Google Scholar]
- Tatebe, H.; Shimizu, M.; Shirakami, Y.; Sakai, H.; Yasuda, Y.; Tsurumi, H.; Moriwaki, H. Acyclic retinoid synergises with valproic acid to inhibit growth in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 285, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Shirakami, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Kubota, M.; Sakai, H.; Yasuda, Y.; Kochi, T.; Tsurumi, H.; Moriwaki, H. Synergistic growth inhibition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by acyclic retinoid and GW4064, a farnesoid X receptor ligand. Cancer Lett. 2012, 323, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Shirakami, Y.; Sakai, H.; Iwasa, J.; Shiraki, M.; Takai, K.; Naiki, T.; Moriwaki, H. Combination of acyclic retinoid with branched-chain amino acids inhibits xenograft growth of human hepatoma cells in nude mice. Hepatol. Res. 2012, 42, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.; Shimizu, M.; Ohno, T.; Shirakami, Y.; Kubota, M.; Kochi, T.; Terakura, D.; Tsurumi, H.; Moriwaki, H. Synergistic growth inhibition by acyclic retinoid and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor in human hepatoma cells. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, J.A.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.C.; Shin, E.S.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, B.I.; Bae, S.H.; et al. Genetic predisposition of hand-foot skin reaction after sorafenib therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2013, 119, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakai, H.; Shimizu, M.; Moriwaki, H. A Role for Acyclic Retinoid in the Chemoprevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Therapeutic Strategy Targeting Phosphorylated Retinoid X Receptor-? Diseases 2014, 2, 226-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases2030226
Sakai H, Shimizu M, Moriwaki H. A Role for Acyclic Retinoid in the Chemoprevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Therapeutic Strategy Targeting Phosphorylated Retinoid X Receptor-? Diseases. 2014; 2(3):226-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases2030226
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakai, Hiroyasu, Masahito Shimizu, and Hisataka Moriwaki. 2014. "A Role for Acyclic Retinoid in the Chemoprevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Therapeutic Strategy Targeting Phosphorylated Retinoid X Receptor-?" Diseases 2, no. 3: 226-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases2030226
APA StyleSakai, H., Shimizu, M., & Moriwaki, H. (2014). A Role for Acyclic Retinoid in the Chemoprevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Therapeutic Strategy Targeting Phosphorylated Retinoid X Receptor-? Diseases, 2(3), 226-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases2030226




