Successful Treatment of Pulmonary and Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Associated with Pneumocystis Pneumonia in an HIV Patient
Abstract
:1. Introduction
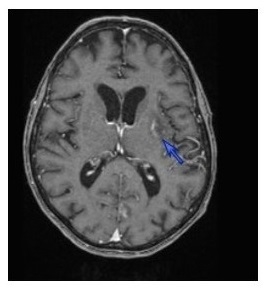
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catherinot, E.; Lanternier, F.; Bougnoux, M.E.; Lecuit, M.; Couderc, L.J.; Lortholary, O. Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 24, 107–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbier, F.; Coquet, I.; Legriel, S.; Pavie, J.; Darmon, M.; Mayaux, J.; Molina, J.M.; Schlemmer, B.; Azoulay, E. Etiologies and outcome of acute respiratory failure in HIV-infected patients. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaud, C.; May, T.; Lucet, J.C.; Leport, C.; Ambroise-Thomas, P.; Canton, P. Pulmonary toxoplasmosis in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus: A French National Survey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 23, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Iguacel, R.; Ahlström, M.G.; Touma, M.; Engsig, F.N.; Stærke, N.B.; Stærkind, M.; Obel, N.; Rasmussen, L.D. Incidence, presentation and outcome of toxoplasmosis in HIV infected in the combination antiretroviral therapy era. J. Infect. 2017, 75, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pupaibool, J.; Limper, A.H. Other HIV-associated pneumonias. Clin. Chest. Med. 2013, 34, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, J.E.; Benson, C.; Holmes, K.H.; Brooks, J.T.; Pau, A.; Masur, H. Guidelines for prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in HIV-infected adults and adolescents: Recommendations from CDC, the National Institutes of Health, and the HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2009, 58, 1–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wakefield, A.E.; Pixley, F.J.; Banerji, S.; Sinclair, K.; Miller, R.F.; Moxon, E.R.; Hopkin, J.M. Amplification of mitochondrial ribosomal RNA sequences from Pneumocystis carinii DNA of rat and human origin. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1990, 43, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reischl, U.; Bretagne, S.; Krüger, D.; Ernault, P.; Costa, J.M. Comparaison of two DNA targets for the diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis by real-time PCR using fluorescence resonance energy transfer hybridation probes. BMC Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarcz, L.; Chen, M.J.; Vittinghoff, E.; Hsu, L.; Schwarcz, S. Declining incidence of AIDS-defining opportunistic illnesses. AIDS 2013, 27, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Arminio Monforte, A.; Cinque, P.; Mocroft, A.; Goebel, F.D.; Antunes, F.; Katlama, C.; Justesen, U.S.; Vella, S.; Kirk, O.; Lundgren, J.; et al. Changing incidence of central nervous system diseases in the EuroSIDA cohort. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 320–328. [Google Scholar]
- Kovari, H.; Ebnöther, C.; Schweiger, A.; Berther, N.; Kuster, H.; Günthard, H.F. Pulmonary toxoplasmosis, a rare but severe manifestation of a common opportunistic infection in late HIV presenters: Report of two cases. Infection 2010, 38, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruck, P.E.; Das, S.; Allan, P.S. Evidence-based practice: Management of combined toxoplasma meningo-encephalitis and Pneumocystis pneumonia in HIV. Virulence 2010, 1, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, H.H.; Hung, C.C.; Lee, C.M.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, M.Y.; Sheng, W.H.; Hsieh, S.M.; Sun, H.Y.; Ho, C.C.; Yu, C.J. Admissions to intensive care unit of HIV-infected patients in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy: Etiology and prognostic factors. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomeroy, C.; Filice, G.A. Pulmonary toxoplasmosis: A review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 14, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugin, J.; Vanhems, P.; Hirschel, B.; Chave, J.P.; Flepp, M. Extreme elevations of serum lactic dehydrogenase differentiating pulmonary toxoplasmosis from Pneumocystis pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 1226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.; Dockrell, D.; Edwards, S.; BHIVA Guidelines Subcommittee; Angus, B.; Barton, S.; Beeching, N.; Bergin, C.; Boffito, M.; Breen, R.; et al. British HIV Association and British Infection Association Guidelines for the Treatment of Opportunistic Infection in HIV-seropositive Individuals 2011. HIV Med. 2011, 12 (Suppl. 2), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abgrall, S.; Rabaud, C.; Costagliola, D. Clinical Epidemiology Group of the French Hospital Database on HIV. Incidence and risk factors for toxoplasmic encephalitis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients before and during the highly active antiretroviral therapy era. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contini, C. Clinical and diagnostic management of toxoplasmosis in the immunocompromised patient. Parassitologia 2008, 50, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1993 revised classification system for HIV infection and expanded surveillance case definition for AIDS among adolescents and adults. JAMA 1993, 269, 729–730. [Google Scholar]
- Torre, D.; Casari, S.; Speranza, F.; Donisi, A.; Gregis, G.; Poggio, A.; Ranieri, S.; Orani, A.; Angarano, G.; Chiodo, F.; et al. Randomized trial of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole versus pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine for therapy of toxoplasmic encephalitis in patients with AIDS. Italian Collaborative Study Group. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 1346–1349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crabtree-Ramírez, B.; Caro-Vega, Y.; Shepherd, B.E.; Grinsztejn, B.; Wolff, M.; Cortes, C.P.; Padgett, D.; Carriquiry, G.; Fink, V.; Jayathilake, K.; et al. Time to HAART Initiation after Diagnosis and Treatment of Opportunistic Infections in Patients with AIDS in Latin America. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdoch, D.M.; Venter, W.D.; Van Rie, A.; Feldman, C. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS): A review of common infectious manifestations and treatment options. AIDS Res. Ther. 2007, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rey, M.-F.; Mary, C.; Sanguinetti, D.; Ranque, S.; Bartoli, C.; L’Ollivier, C. Successful Treatment of Pulmonary and Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Associated with Pneumocystis Pneumonia in an HIV Patient. Diseases 2017, 5, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases5040035
Rey M-F, Mary C, Sanguinetti D, Ranque S, Bartoli C, L’Ollivier C. Successful Treatment of Pulmonary and Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Associated with Pneumocystis Pneumonia in an HIV Patient. Diseases. 2017; 5(4):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases5040035
Chicago/Turabian StyleRey, Marie-Françoise, Charles Mary, Diane Sanguinetti, Stéphane Ranque, Christophe Bartoli, and Coralie L’Ollivier. 2017. "Successful Treatment of Pulmonary and Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Associated with Pneumocystis Pneumonia in an HIV Patient" Diseases 5, no. 4: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases5040035
APA StyleRey, M.-F., Mary, C., Sanguinetti, D., Ranque, S., Bartoli, C., & L’Ollivier, C. (2017). Successful Treatment of Pulmonary and Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Associated with Pneumocystis Pneumonia in an HIV Patient. Diseases, 5(4), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases5040035