A Population Based Study of Liver Function amongst Adults with Hyperuricemia and Gout in the United States
Abstract
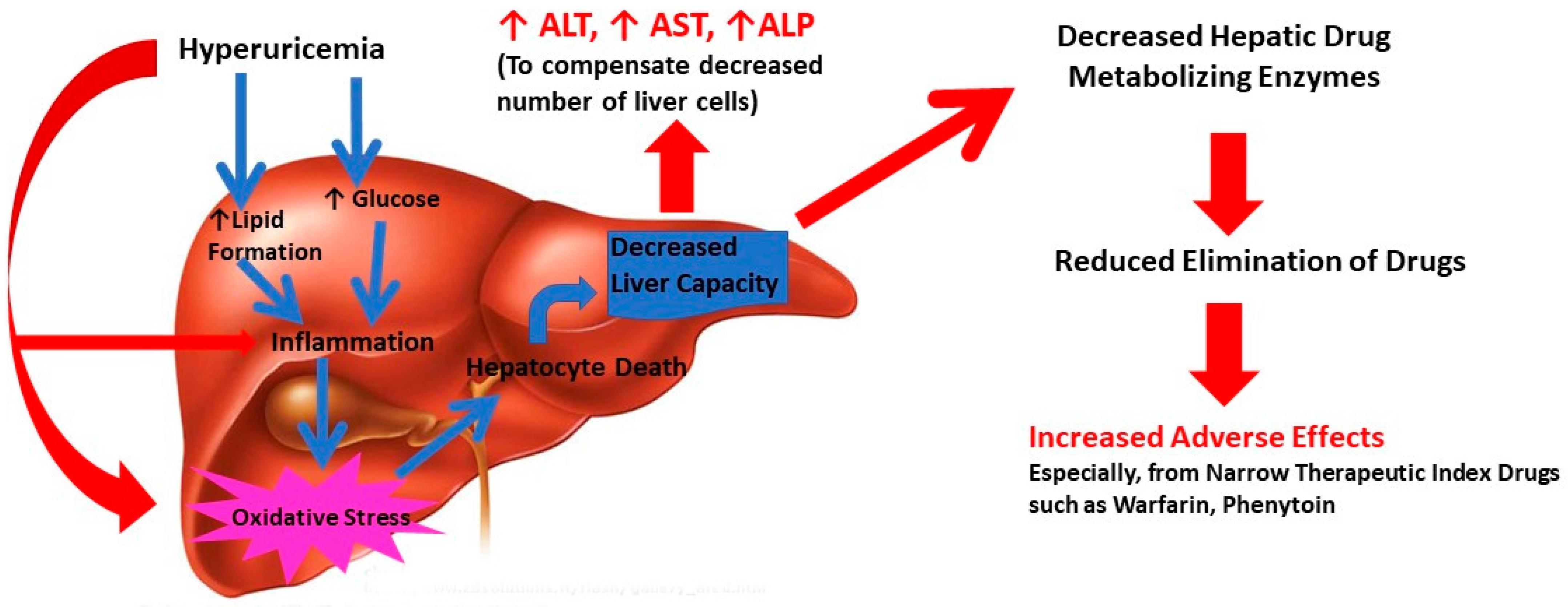
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Covariates
2.3. Assessment of Gout and Hyperuricemia
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants
3.2. Association of Participants Characteristics and Uric Acid Levels
3.3. Association of Uric Acid Levels with Abnormal Liver Enzymes
3.4. Association of Gender-Based Target Values of Uric Acid with Abnormal Liver Enzymes
3.5. Predictors of High Liver Enzymes Levels on Regression Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen-Xu, M.; Yokose, C.; Rai, S.K.; Pillinger, M.H.; Choi, H.K. Contemporary Prevalence of Gout and Hyperuricemia in the United States and Decadal Trends: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2016. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FitzGerald, J.D.; Dalbeth, N.; Mikuls, T.; Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Guyatt, G.; Abeles, A.M.; Gelber, A.C.; Harrold, L.R.; Khanna, D.; King, C.; et al. 2020 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of Gout. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 744–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehlin, M.; Jacobsson, L.; Roddy, E. Global epidemiology of gout: Prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Lu, J.M.; Yao, Q. Hyperuricemia-Related Diseases and Xanthine Oxidoreductase (XOR) Inhibitors: An Overview. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 2501–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Contreras-Zentella, M.L.; Hernandez-Munoz, R. Is Liver Enzyme Release Really Associated with Cell Necrosis Induced by Oxidant Stress? Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 3529149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharaf El Din, U.A.A.; Salem, M.M.; Abdulazim, D.O. Uric acid in the pathogenesis of metabolic, renal, and cardiovascular diseases: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanaspa, M.A.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Choi, Y.J.; Cicerchi, C.; Kanbay, M.; Roncal-Jimenez, C.A.; Ishimoto, T.; Li, N.; Marek, G.; Duranay, M.; et al. Uric acid induces hepatic steatosis by generation of mitochondrial oxidative stress: Potential role in fructose-dependent and -independent fatty liver. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40732–40744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), National Center for Health Statistics. 2017. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/analyticguidelines.aspx (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- The Practical Guide Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. NHLBI Obesity Education Initiative, National Institute of Health. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/files/docs/guidelines/prctgdc.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) Guidelines At-a-Glance Quick Desk Reference. National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP). Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/files/docs/guidelines/atglance.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Stata Statistical Software: Release 13; Software; StataCorp, LP.: College Station, TX, USA, 2013.
- Aragon, G.; Younossi, Z.M. When and how to evaluate mildly elevated liver enzymes in apparently healthy patients. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2010, 77, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.; Puthanveetil, P.; Sakharkar, P. A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study of the Association between Liver Enzymes and Lipid Levels. Int. J. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 1286170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakharkar, P.; Deb, S. Examining Liver Function in Adults with Diabetes in the United States. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 24, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Liang, J.; Yang, L.; An, S.; Gao, C.; Liao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, B. Reversing cytotoxicity of uric acid by supramolecular encapsulation with acyclic cucurbit[n]uril. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 16, 035025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzali, A.; Weiss, N.S.; Boyko, E.J.; Ioannou, G.N. Association between serum uric acid level and chronic liver disease in the United States. Hepatology 2010, 52, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirota, J.C.; McFann, K.; Targher, G.; Johnson, R.J.; Chonchol, M.; Jalal, D.I. Elevated serum uric acid levels are associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease independently of metabolic syndrome features in the United States: Liver ultrasound data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Metabolism 2013, 62, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.; Yang, N.; Xing, X.; Chang, D.; Li, J.; Deng, J.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhang, R.; Lu, X.; et al. Obesity interacts with hyperuricemia on the severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, M.H.; Lazo, M.; Liu, S.H.; Bonekamp, S.; Hernaez, R.; Clark, J.M. Association between serum uric acid and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the US population. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2015, 114, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vos, M.B.; Colvin, R.; Belt, P.; Molleston, J.P.; Murray, K.F.; Rosenthal, P.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Tonascia, J.; Unalp, A.; Lavine, J.E.; et al. Correlation of vitamin E, uric acid, and diet composition with histologic features of pediatric NAFLD. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catanzaro, R.; Sciuto, M.; He, F.; Singh, B.; Marotta, F. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Correlation with hyperuricemia in a European Mediterranean population. Acta Clin. Belg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Ying, Z.; Gong, L.; Du, J.; Ji, G.; Li, Z.; Gao, W.; Jiang, X.; Yang, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. Association between Serum Uric Acid and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Nonobese Postmenopausal Women: A Cross-sectional Study. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 10072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yu, C.; Xu, L.; Miao, M.; Li, Y. High serum uric acid increases the risk for nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease: A prospective observational study. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, T.; Niwa, K.; Hisatome, I.; Kanbay, M.; Andres-Hernando, A.; Roncal-Jimenez, C.A.; Sato, Y.; Garcia, G.; Ohno, M.; Lanaspa, M.A.; et al. Increased Serum Uric Acid over five years is a Risk Factor for Developing Fatty Liver. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evangelopoulos, A.A.; Vallianou, N.G.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Georgiou, A.T.; Zacharias, G.A.; Vogiatzakis, E.D.; Avgerinos, P.C. The Association Between Uric Acid and Hepatic Function Markers With the Metabolic Syndrome in Middle-aged, Overweight, and Obese People. Endocrinologist 2010, 20, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.R.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, Y.H.; Shim, J.Y. Association between serum uric acid and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2010, 48, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oral, A.; Sahin, T.; Turker, F.; Kocak, E. Relationship Between Serum Uric Acid Levels and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Non-Obese Patients. Medicina 2019, 55, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Ben-Assuli, O.; Rabinowich, L.; Goldstein, A.; Magid, A.; Shalev, V.; Shibolet, O.; Chodick, G. The association between the serum levels of uric acid and alanine aminotransferase in a population-based cohort. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 2408–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, P.; Clare, K.; George, J.; Dillon, J.F. Determining the role for uric acid in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis development and the utility of urate metabolites in diagnosis: An opinion review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, M.; Rezen, T.; Rozman, D. Regulation of hepatic cytochromes p450 by lipids and cholesterol. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, C.; Cherubini, A.; Ble, A.; Bos, A.J.; Maggio, M.; Dixit, V.D.; Lauretani, F.; Bandinelli, S.; Senin, U.; Ferrucci, L. Uric acid and inflammatory markers. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballestri, S.; Nascimbeni, F.; Romagnoli, D.; Lonardo, A. The independent predictors of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and its individual histological features.: Insulin resistance, serum uric acid, metabolic syndrome, alanine aminotransferase and serum total cholesterol are a clue to pathogenesis and candidate targets for treatment. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Ballestri, S.; Marchesini, G.; Angulo, P.; Loria, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A precursor of the metabolic syndrome. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mantovani, A. NAFLD and risk of cardiac arrhythmias: Is hyperuricemia a neglected pathogenic mechanism? Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 518–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, S.; Matsuo, R.; Imatake, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Yagi, T.; Matsumoto, N.; Okumura, Y. The serum uric acid level in females may be a better indicator of metabolic syndrome and its components than in males in a Japanese population. J. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Uric Acid | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Sample N = 14,946 | Normal n = 12,714 (85.0) | Elevated n = 2232 (15.0) | p-Value | |
| Age (yrs.) (Mean ± SE) | 49.3 (0.15) | 48.2 (0.16) | 51.4 (0.40) | <0.001 ** |
| Age (yrs.) | ||||
| 20–44 | 6447 (51.9) | 5712 (52.9) | 735 (45.5) | <0.001 ** |
| 45–64 | 4771 (29.2) | 4080 (29.3) | 691 (28.3) | |
| ≥65 | 3728 (18.9) | 2922 (17.8) | 806 (26.2) | |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 7037 (45.8) | 5539 (44.1) | 1678 (76.2) | <0.001 ** |
| Female | 7909 (54.2) | 7355 (58.9) | 554 (23.8) | |
| Marital Status | ||||
| Single | 2820 (21.5) | 2447 (21.5) | 373 (21.2) | 0.960 |
| Married | 7664 (52.6) | 6490 (52.5) | 1174 (52.9) | |
| Other | 4456 (25.9) | 3771 (26.0) | 685 (25.9) | |
| Race/Ethnicity | ||||
| Mexican American | 3300 (14.2) | 2916 (14.5) | 384 (12.2) | <0.001 ** |
| Other Hispanic | 2105 (8.7) | 1856 (8.8) | 249 (7.3) | |
| Non-Hispanic White | 4324 (55.3) | 3637 (53.2) | 687 (54.4) | |
| Non-Hispanic black | 3020 (12.3) | 2428 (11.9) | 592 (15.1) | |
| Other | 2197 (11.5) | 1877 (11.6) | 320 (11.0) | |
| Education | ||||
| <9th Grade | 2087 (9.6) | 2087 (9.6) | 384 (11.2) | <0.001 ** |
| 9–11th Grade | 1935 (12.0) | 1935 (12.0) | 364 (12.8) | |
| High School/GED | 2565 (19.0) | 2565 (19.0) | 515 (24.3) | |
| Some College or AA degree | 3305 (29.9) | 3305 (29.9) | 556 (28.8) | |
| College Graduate or above | 2808 (29.5) | 2808 (29.5) | 409 (22.9) | |
| Family Income | ||||
| <USD 25,000 | 5078 (28.4) | 4270 (28.2) | 808 (29.9) | 0.020 * |
| USD 25,000–USD 54,999 | 4690 (31.6) | 3997 (31.4) | 693 (32.8) | |
| USD 55,000–USD 99,999 | 2445 (20.1) | 2074 (19.9) | 371 (20.9) | |
| >USD 100,000 | 1882 (19.9) | 1652 (20.4) | 230 (16.4) | |
| Ratio of Family Income to Poverty | ||||
| <1.35 | 5108 (28.6) | 4357 (28.6) | 751 (28.4) | 0.027 * |
| 1.35–1.84 | 1717 (10.8) | 1440 (10.7) | 277 (11.6) | |
| 1.85–2.99 | 2401 (17.9) | 2021 (17.5) | 380 (20.3) | |
| ≥3.00 | 4219 (42.7) | 3626 (43.2) | 593 (39.7) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||
| Underweight | 240 (1.8) | 229 (2.0) | 11 (0.5) | <0.001 ** |
| Normal | 4301 (31.5) | 3972 (34.2) | 329 (14.3) | |
| Overweight | 5021 (33.1) | 4306 (33.2) | 715 (32.6) | |
| Obese | 5210 (33.6) | 4073 (30.6) | 1137 (52.6) | |
| SBP | ||||
| <135 mmHg | 9903 (75.1) | 8642 (76.7) | 1261 (65.2) | <0.001 ** |
| ≥135 mmHg | 4474 (24.9) | 3577(25.3) | 897 (34.8) | |
| DBP | ||||
| <85 mmHg | 13,186 (92.7) | 11,303 (93.6) | 1883 (87.1) | <0.001 ** |
| ≥85 mmHg | 1191 (7.3) | 916 (6.4) | 275 (12.9) | |
| Hypertension (135/85 mmHg) | ||||
| Yes | 9633 (73.2) | 8834 (75.0) | 1199 (61.9) | <0.001 ** |
| No | 4744 (26.8) | 3785 (25.0) | 959 (38.1) | |
| Taking prescription for hypertension | ||||
| Yes | 4447 (84.1) | 3388 (83.6) | 1059 (85.9) | 0.208 |
| No | 622 (15.9) | 511 (16.4) | 111 (14.1) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) (Mean ± SE) | 28.6 (0.05) | 28.1 (0.06) | 31.1 (0.14) | <0.001 ** |
| Waist Circumference (cm) (Mean ±SE) | 97.5 (0.13) | 96 (0.14) | 106.1 (0.34) | <0.001 ** |
| SBP (mmHg) (Mean ± SE) | 123.8 (0.2) | 122.9 (0.17) | 129.0 (0.42) | <0.001 ** |
| DBP (mmHg) (Mean ± SE) | 69.1 (0.11) | 68.9 (0.11) | 70.1 (0.32) | <0.001 ** |
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) (Mean ± SE) | 5.4 (0.01) | 5.0 (0.01) | 7.8 (0.02) | <0.001 ** |
| ALT (U/L) | AST/ALT Ratio | Total Bilrubin (μmol/L) | |||||||||
| Uric Acid | <20 | ≥20–29 | ≥30–39 | ≥40 | p-Value | <1 | ≥1 | p-Value | <17 | ≥17 | p-Value |
| Normal | 6056 (48.4) | 4203 (32.4) a | 1305 (10.5) | 1150 (8.7) | <0.001 ** | 4035 (35.6) | 8679 (68.4) | <0.001 ** | 11,078 (86.7) | 1636 (13.3) | <0.001 ** |
| Elevated | 702 (25.4) | 789 (35.2) a | 368 (19.2) | 373 (20.2) | 939 (48.7) | 1293 (51.3) | 1800 (77.5) | 432 (22.5) | |||
| AST (U/L) | ALP (U/L) | ||||||||||
| <20 | ≥20–29 | ≥30–39 | ≥40 | <120 | ≥120 | ||||||
| Normal | 3332 (26.0) | 7225 (56.7) a | 12,362 (98.0) | 352 (2.0) | <0.001 ** | 12,362 (98.0) | 352 (2.0) | 0.541 | |||
| Elevated | 332 (11.8) | 1268 (57.5) a | 2164 (97.8) | 68 (2.2) | 2164 (97.8) | 68 (2.2) | |||||
| ALT (U/L) | |||
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) | Normal | Elevated | p-Value |
| Normal | 11,562 (92.5) | 1152 (7.5) | <0.001 ** |
| Elevated | 1942 (87.2) | 290 (12.8) | |
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) | AST (U/L) | ||
| Normal | Elevated | ||
| Normal | 11,276 (89.4) | 1438 (10.6) | <0.001 ** |
| Elevated | 1785 (78.1) | 447 (21.9) | |
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) | GGT (U/L) | ||
| Normal | Elevated | ||
| Normal | 9579 (75.8) | 3135 (24.2) | <0.001 ** |
| Elevated | 1437 (58.5) | 795 (41.5) | |
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) | ALT (U/L) | AST (U/L) | AST/ALT Ratio | |||
| OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | |
| Universal | 2.22 (1.94, 2.54) | <0.001 ** | 2.36 (2.02, 2.77) | <0.001** | 0.49 (0.42, 0.56) | <0.001 ** |
| Gender-based | 1.90 (1.70, 2.11) | <0.001 ** | 1.84 (1.59, 2.13) | <0.001** | 0.64 (0.58, 0.72) | <0.001 ** |
| ALP (U/L) | GGT (U/L) | Total Bilirubin (μmol/L) | ||||
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value |
| Universal | 1.11 (0.80, 1.53) | 0.542 | 2.20 (1.88, 2.57) | <0.001 ** | 1.89 (1.64, 2.18) | <0.001 ** |
| Gender-based | 1.09 (0.82, 1.47) | 0.539 | 2.26 (1.90, 2.69) | <0.001 ** | 1.29 (1.13, 1.47) | <0.001 ** |
| ALT (U/L) | AST (U/L) | AST/ALT Ratio | ||||
| OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | |
| Age | 0.99 (0.98, 0.99) | <0.001 ** | 0.99 (0.99, 1.00) | 0.365 | 1.02 (1.01, 1.02) | <0.001 ** |
| Gender | 0.50 (0.45, 0.56) | <0.001 ** | 0.45 (0.40, 0.50) | <0.001 ** | 3.58 (3.20, 4.00) | <0.001 ** |
| Race | 0.86 (0.81, 0.90) | <0.001 ** | 0.92 (0.87, 0.96) | <0.001 ** | 1.18 (1.13, 1.23) | <0.001 ** |
| BMI | 1.06 (1.05, 1.07) | <0.001 ** | 1.02 (1.01, 1.03) | <0.001 * | 0.92 (0.91, 0.93) | <0.001 ** |
| HTN | 1.19 (1.03, 1.36) | 0.015 * | 1.27 (1.08, 1.50) | 0.005 * | 0.95 (0.84, 1.06) | 0.348 |
| Uric Acid | 1.57 (1.36, 1.80) | <0.001 ** | 1.68 (1.42, 2.00) | <0.001 ** | 0.84 (0.71, 0.98) | 0.029 * |
| ALP (U/L) | GGT (U/L) | Total Bilirubin (μmol/L) | ||||
| OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | |
| Age | 1.02 (1.00, 1.03) | <0.001 ** | 1.01 (1.00, 1.01) | <0.001 ** | 0.99 (0.99, 1.02) | 0.382 |
| Gender | 1.34 (0.96, 1.88) | 0.082 | 1.89 (1.56, 2.29) | <0.001 ** | 0.37 (0.32, 0.43) | <0.001 ** |
| Race | 0.80 (0.72, 0.89) | <0.001 ** | 0.96 (0.89, 1.03) | 0.264 | 0.99 (0.93, 1.05) | 0.650 |
| BMI | 1.04 (1.02, 1.05) | <0.001 ** | 1.04 (1.03, 1.05) | <0.001 ** | 0.93 (0.92, 0.94) | <0.001 ** |
| HTN | 1.38 (1.04, 1.84) | 0.028 * | 1.43 (1.18, 1.72) | <0.001 ** | 0.96 (0.81, 1.13) | 0.608 |
| Uric Acid | 1.00 (0.66, 1.53) | 0.967 | 1.86 (1.47, 2.34) | <0.001 ** | 1.79 (1.51, 2.12) | <0.001 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deb, S.; Sakharkar, P. A Population Based Study of Liver Function amongst Adults with Hyperuricemia and Gout in the United States. Diseases 2021, 9, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases9030061
Deb S, Sakharkar P. A Population Based Study of Liver Function amongst Adults with Hyperuricemia and Gout in the United States. Diseases. 2021; 9(3):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases9030061
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeb, Subrata, and Prashant Sakharkar. 2021. "A Population Based Study of Liver Function amongst Adults with Hyperuricemia and Gout in the United States" Diseases 9, no. 3: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases9030061
APA StyleDeb, S., & Sakharkar, P. (2021). A Population Based Study of Liver Function amongst Adults with Hyperuricemia and Gout in the United States. Diseases, 9(3), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases9030061







