Abstract
Recently many enterprises have been in need of design outsourcing services through which they can form creative ideas and innovations. In this respect, the innovation competency of design consulting firms is unprecedentedly regarded as a deciding competitive edge. This study examines the effects of design innovation competencies as personal innovation competency, organizational innovation competency, and technological innovation competency on the competitiveness of the design outsourcing service in meditating design innovativeness. Data were collected through a survey conducted among 392 design consulting enterprises by way of random sampling over seven regions in Korea. As a result of hypothesis verification, it turned out that the personal innovation competency of designers at design consulting enterprises and technological innovation competency, which represents their design methods and skills, had significant effects on design innovativeness. In contrast, organizational innovation competency showed no significant effects on design innovativeness. For a design consulting enterprise to become an innovative one with better outsourcing service competitiveness, it needs to pursue a strategic direction of strengthening designers’ personal innovation and technological design innovation.
1. Introduction
On viewing corporate environments today, much more emphasis is being put on developing marketing-centered business strategies in the area of production. Particularly, consumer choices are expanding in the context of customized production. In line with the 4th Industrial Revolution new production systems have been introduced to manufacturer customized items at mass-production unit prices, and the new process customized for individual consumers is expanding on the basis of small quantity batch production in order to meet the instant needs of consumers [1,2]. As consumers pursue unique lifestyles and appreciate the emotional values of products, demands in the market have become more segmented [3]. In the changed market, enterprises tend to seek ways of improving competitiveness through design innovativeness to customer-focused innovation strategies [4].
As the role of design is emphasized further in such a market-based customized production system, design strategies and specialty in design outsourcing are viewed as crucial for corporate competitiveness based on innovative design [5]. In 2017, the scale of the design industry was as large as 17 trillion and 545 billion won, which indicates a 3.7% increase compared to 16 trillion and 913.7 billion won in 2016. In the same year, the number of design-utilizing enterprises reached 125,278, which also indicates a 6.2% increase compared to 117,934 in 2016. This clearly shows that the demands for design in the industry sectors are increasing [6]. Such utilization of design goes beyond the level of mere support for design development in the past and often leads to the creation of innovative products and services. Global design consulting enterprises such as the ‘Ideo’, ‘Flog’, and ‘Engine’ have been widely recognized as innovative consulting enterprises rather than design outsourcing businesses [7,8].
Today, design outsourcing is recognized as a core innovative strategy of business management, and not merely as a design production service. Phillips realizes sustainable business management strategies on the basis of design R&D for products aiming at third-world regions such as Africa and India. P&G has established its corporate education system in cooperation with IDEA to improve creativity, not only among executives but also among all employees. Virgin, along with ’Engine, has developed its ‘Upper Service’ based on a new service innovation process. As such, design outsourcing is pursued increasingly for the purpose of creating original and innovative products and services, as well as new markets, as a new motivational power of innovation that enterprises need [9].
In this regard, the connection between design outsourcing and business innovation has been discussed continually [10]. However, there has been little empirical research on the clear definition of design innovativeness or direct effects of design innovativeness on business performance. In addition, there have been limitations in previous research on the operation strategies and effectiveness of design outsourcing, which many enterprises seek for innovative products or services.
Thus, this study aims to identify the design innovation competencies of design consulting enterprises involved in design service outsourcing and research on the empirical results of the effects of design innovation competencies on design innovativeness and competitiveness of the design outsourcing service. With such competency and design innovativeness of design consulting enterprises examined, this study discusses the specific direction for and significance of promotion of design utilization among enterprises, as well as the growth of the design outsourcing industry.
2. Theoretical Background and Hypothesis Development
2.1. Innovation Competency and Design Innovativeness
Innovation means to “combine production elements in a way of producing new goods, introducing new production methods, opening up a new market, acquiring and using new resources, and establishing a new organization in line with changes in the existing economic structure, with technical advancement and innovation being introduced into the economy” [11]. The economist who first used the term “innovation” in the context of economic principles was Joseph Alois Schumpeter. He stated: "The economic development of capitalism means inner reform as a result of a new combination of production elements. As such, a process of creative demolition and reorganization is repeated, and capitalism and enterprises pursuing it survive and advance. In this context, such reorganization is innovation.” Rogers [12] defined innovation as the application of new ideas for other creative perspectives on products, process, and business activities. Stock and Watson [13] defined it as a comprehensive activity of introducing and applying new ideas and technology, converting and internalizing them into products, production processes, and corporate activities, and thus creating values from them.
Corporate innovation is classified into managerial innovation, technological innovation, product innovation, and process innovation [14]. Such innovation may result from competency either in or out of an enterprise. Innovation competency is defined as a knowledge-intensive ability for an enterprise to harmoniously utilize resources necessary for business management, which makes it possible to develop innovative products and processes successfully in given circumstances [15]. Spencer and Spencer [16] stated that such innovative competency is an instrument for an enterprise to cope with uncertain circumstances properly and to secure competitive advantages continually. They also added that an enterprise can multi-dimensionally utilize various capabilities, including technology and knowledge, in order to create new technology, products, and services.
Previous studies introduced various approaches to components of innovative competency. For example, Yam, et al. [17] stated that key elements of innovation competency include learning competency, R&D competency, resource distribution competency, production competency, marketing competency, organizing competency, and strategic planning competency. Romijn and Albaladejo [18] distinguished internal resources of innovation competency from external resources: External resources include network intensity, proximity, and institutional sponsoring while internal resources include professionalism of the CEO, professional competency of the labor force, and internal effort put forth into technical development according to them.
When it comes to internal factors, innovative competency is divided into three types: personal competency, organizational competency, and technical competency. As to personal competency, a person’s professionalism or personal work performance affects innovation critically. Thus, innovation is of utmost importance in relation to individuals’ work performance in a relevant organization [19]. In addition, organizational competency such as the CEO’s talents, organization, workforce, and resource procurement may be affected [20] and such factors as new product development, research capability enhancement, and market competitiveness, as part of technical competency, can induce corporate innovation [21,22].
Rampino [23] classifies design innovation into aesthetic innovation, use innovation, semantic innovation, and typological innovation. This means to try to make new things with design elements. Design innovativeness may be defined differently depending on the scope of design access approaches. In the scope centering on the aesthetic activities of design, it may be defined as creation of a new design [24,25]. In terms of design use and semantic approaches, it may be identified as development of a new process that focuses on usability and receptivity [26]. In addition, it may be explained in connection with an enterprise’s creation of new images, new technology, and new products [27,28,29].
Since such design innovativeness is embodied in pursuit of the innovative design service activities of a design-consulting enterprise, it is likely to be affected by the internal innovation competency of that enterprise [30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. Accordingly, this study developed the following hypotheses on the basis of previous studies;
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
A design consulting enterprise’s design personal innovation competency will have a positive (+) impact on the enhancement of outsourcing service design innovativeness.
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
A consulting enterprise’s design organization innovation competency will have a positive (+) impact on the enhancement of outsourcing service design innovativeness.
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
A design consulting enterprise’s design technique innovation competency will have a positive (+) impact on the enhancement of outsourcing service design innovativeness.
2.2. Design Innovativeness and Outsourcing Service Competitiveness
Outsourcing means for an enterprise to entrust a task to a third party or be supplied by it with part of its various functions [37,38]. In this context, design service outsourcing is defined as “a strategic act of an enterprise to entrust an external design consulting enterprise with development and production for design services to be presented to its consumers.” As managerial circumstances of businesses became unstable and uncertain in the late 1980s, the trend of business downsizing to reduce the risks of business management expanded. Instead, various business activities were implemented by way of outsourcing [39,40]. Against this background, the rate of outsourcing increased in the area of design instead of in-house design. As a result, the scale of the outsourcing industry has increased continually among design consulting enterprises [41].
Since the 1990s, the outsourcing service of design consulting enterprises has increased drastically and even has expanded its area to consulting on product design. Accordingly, client businesses tend to pay keen attention to consumers’ desires and needs that have yet to be clarified and to induce product development in terms of aesthetics. In the final part of the design consulting process, they provide design outputs. Today, however, such a design outsourcing service is advancing into professional and multidisciplinary consulting services that cover various areas such as marketing, strategy, and engineering, as well as design, by contributing to corporate growth strategies and providing new business models through corporate innovations, without staying in the range of mere product or service development [42].
Most traditional design consulting companies for products have been converted into corporate innovation consulting companies, providing outsourcing services in various areas such as product, service, process, human resource management, and marketing. Furthermore, many enterprises find it difficult to catch up as the global market grows rapidly and reflects customer needs promptly in the technical advancement area. Accordingly, design consulting based on innovation strategies for competitiveness has become an important outsourcing service for enterprises in almost every industry sector in order to satisfy the needs of consumers and markets properly [43].
As technical environments such as AI and big data are changing rapidly in this 4th Industrial Revolution recently, creating new business models and digital innovation strategies has been strengthened among businesses [44,45,46]. The activity of design outsourcing service provision has become crucial in creating values through innovative corporate activity and goes beyond the level of mere profit hunt through design development. Thus, active value creation is essential now, and the trend of the design outsourcing service is changing into providing outsourcing services on the basis of design thinking or design innovation. Kim et al. [47] pointed out that outsourcing may be categorized into cost-saving outsourcing, spin-off type outsourcing, network type outsourcing, and core competency outsourcing. Today, corporate outsourcing management is expected to provide services that can support aggressive innovation strategies, as well as defensive innovation strategies. As to design outsourcing, the approach aims to strengthen corporate competitiveness in pursuit of aggressive innovation competency rather than cost-saving or spin-off [21,48].
As business competition becomes fiercer than before, the level of innovation has increased. As Terwiesch and Ulrich [49] stated, providing a proper level of innovation expected by enterprises today requires not only upgrades in technology and capital operation but also innovative business management in line with internal and external circumstances. Such basic considerations are reflected in design outsourcing services accordingly [50]. Thus, this study assumes on the basis of such previous studies that improving a design consulting enterprise’s design innovativeness will satisfy the needs of innovation among client companies and contribute positively to enhancing their outsourcing service competitiveness.
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
A design consulting enterprise’s design innovation competency will have positive (+) impact on the competitiveness of design outsourcing service.
3. Methods
3.1. Research Model
This study classifies the innovation competency of design consulting enterprises into personal innovation competency, organizational innovation competency, and technological innovation competency. As part of its empirical analysis, effects of such innovative competency factors on design outsourcing service competitiveness, with design innovativeness as a medium, are examined in this study. In general, it has been discussed that when it comes to design outsourcing service, a designer’s personal innovation competency affects the level of service satisfaction or achievement significantly unlike other outsourcing services in business management [51].
As the environments change depending on the times, however, design service projects based on teamwork and technology are strengthened. Accordingly, organizational and technological innovation competency factors of design consulting enterprises can contribute to improving design innovativeness [52]. This study aims to verify the direct effects of such innovation competency on design innovativeness improvement and outsourcing service performance. Additionally, it is sought to derive competency factors necessary for design consulting enterprises to improve their outsourcing service competitiveness.
Based on relevant previous studies, hypotheses have been derived regarding the relations. Finally, the research model in Figure 1 was developed. Independent variables are the design consulting enterprises’ three innovation competency factors: personal competency, organization competency, and technical competency. The applied parameter is design innovativeness, which is a major design service result. The dependent variable is competitiveness of a design outsourcing service. The developed model was verified through confirmatory factory analysis and path analysis based on structural equations.
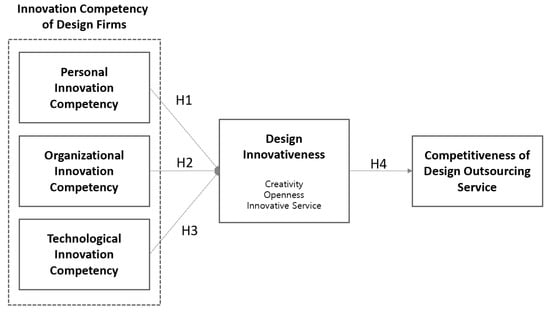
Figure 1.
Research model.
3.2. Measurement Variable
A survey was conducted to collect data necessary to analyze this type of model. For the questionnaire, questions presented in Table 1 below were developed based on previous studies. Manipulative variables of questionnaire factors were also defined. For the survey, the following manipulative definitions of used variables were applied: Among innovation competency factors of design consulting enterprises, “personal innovation competency” is defined as innovation competency that is shown by individual designers at a design consulting enterprise. “Organizational innovation competency” is an innovation competency that is manifested organizationally. “Technological innovation competency" is defined as innovation competency related to technology required in the process of design service. “design innovativeness,” which is applied in this study as a parameter, is the innovation competency factor of a design consulting enterprise in its activity of design outsourcing service. The dependent variable “competitiveness of design outsourcing service” represents the evaluation of design service quality and satisfaction of outsourcers, which indicates the design consulting enterprise’s performance.

Table 1.
Variable definitions.
Such variables defined as above are included in the questionnaire as items in the 5-point Likert- type Scale. As to “personal innovation competency,” the three qualities; “creativity”, “organizing ability”, and “expressive ability” of designers at the enterprise were designed based on the previous study of Kim and Jeon [3]. As to “organizational innovation competency,” “organizational policy,” “system and process,” and “organizational culture”, they were designed on the basis of the previous studies of Aubert et al. [53] and Damanpour [54]. As to “technological innovation competency,” “technology utilization,” “technical environment,” “and “new technique”, they were designed based on the previous studies of Yam, et al. [17], Adler and Shenbar [55]. As to the parameter “design innovativeness,” “creativity”, “openness”, and “service innovation” reflected in the process of the design development process of a design consulting enterprise, they were applied on the basis of the previous studies of Talke, et al. [56], Townsend and Shu [57]. Finally, as to the dependent variable “competitiveness of design outsourcing service,” “service quality”, “customer satisfaction”, and “continued relationship”, they were selected based on the previous studies of Voss [58] and Covin et al. [59]. Among these, however, “new technique,” which is a technical competency factor, was excluded from this study since it turned out to be insignificant according to the analysis of model and convergent validity.
As part of this study, a survey was conducted among design consulting enterprises that conducted the businesses of the design outsourcing service in Korea. The survey was conducted mainly in seven regions which are Seoul, Gyeonggi, Chungcheong, Gyeongsang, Jeolla, Gangwon, and Jeju in South Korea. The survey was conducted for 36 days from August 16 to September 20, 2019. A total number of 405 questionnaires was collected, 392 of them were analyzed, and 13 with incomplete answers were excluded. SPSS 24.0 was utilized to analyze demographic characteristics, technical statistics, and exploratory factors with the aim to verify the basic reliability and validity of the data. For confirmatory analysis, model verification, and path analysis based on the structural equation model, AMOS 25.0, were utilized.
4. Results
4.1. Demographic Information of the Data
A survey was conducted among designers working at a design consulting enterprise. After the demographic data of the respondents had been analyzed, it turned out that male and female respondents accounted for 54.8% and 45.2%, respectively, and that the largest portion (42.6%) was those in their 30s, 28.8% those in their 40s, and 16.1% aged less than 30. This result shows that most workers were in their 20s to 40s. The career of 30.9% was less than 5 years, and that of 27.6% was between 5–10 years. As to specific areas of design, 32.7% were specializing in product design, 27% in visual design, and 15.6% in service design. As to academic background, 64.8% were college graduates and 25% were with a master’s degree (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Demographics of survey participants.
4.2. Analysis Results of Reliability and Validity
To analyze the reliability and validity of the structural equation model, the composite reliability index was measured. As shown Table 3, the proper level of internal consistency reliability was secured when the index was 0.7 or higher [60]. The convergent validity was evaluated based on the factor load, Cronbach α, and composite reliability index. Since the factor load was at least 0.4, the Cronbach α was at least 0.6, the values were statistically significant, and the proper level of convergent validity was secured [5]. In consideration of these criteria, the factor loads were all between 0.645 and 0.851 (0.6 or higher), which was sufficient. As to the internal reliability, the composite reliability level was between 0.759 and 0.855, which was significant. Since the values of t were all at least 6.0, it was statistically significant. The average sampling variance (AVE) value was between 0.616 and 0.720, and Cronbach α was between 0.713 and 0.789. Hence, the proper level of composite validity was secured. As the fitness of the measurement model was analyzed, χ2(p) was 76.066, and χ2 /degree of freedom was 1.729. The value of Goodness-of-Fit-Index (GFI) was 0.968, and the value of Adjusted Goodness-of-Fit-Index (AGFI) was 0.944. Normal Fit Index (NFI) was 0.961 and Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) was 0.043. Thus, the fitness values of the measurement model proved to be satisfactory.

Table 3.
Analysis of the measurement model’s reliability and composite validity.
The analysis of correlation was conducted based on the criteria suggested by Nam et al. [61]. It was shown that the discriminant validity of each latent variable was secured as the AVE square root value of each latent variable was larger than the correlation coefficient of each latent variable. Since the correlation coefficient between each latent variable and the AVE value was analyzed as in Table 3, it turned out that the AVE square root value of each latent variable was larger than the correlation coefficient of latent variables, and the correlation coefficient values as well were at least 0.7, which was significant. Hence, it was verified that the discriminant validity was secured (see Table 4).

Table 4.
Discriminant validity.
4.3. Analysis Results of the Structural Model
In the structural equation fitness analysis, χ2(p) was 89.718 and χ2/degree of freedom was 1.909. The value of GFI was 0.961 (larger than 0.9) and that of AGFI was 0.954. The value of NFI was 0.968, and that of RMSEA was 0.048. The model fitness was viewed significant since the fitness component values were satisfactory. The value of CFI (Comparative Fit Index), which was not affected by the sample but represented the explanatory power of the model, was 0.977. The value of TLI, which indicates the explanatory power of the structural model, was 0.968. Since both of them were larger than 0.9, it was shown that the basic model was quite appropriate [62,63].
As shown in Table 5, a path analysis was conducted based on the structural equation modeling result, and 1 out of the 4 hypotheses was rejected. Among innovation competency factors of a design consulting enterprise, the value of t, which represented design competency of individual designers, was 3.322 (p < 0.001), turning out to affect design innovativeness positively (+). The value of design technology competency was as large as 5.281(p < 0.001), which turned out to affect design innovativeness positively (+). As to design organization competency, however, the value was 0.124 and the hypothesis was rejected. It turned out that design organization competency did not affect design innovativeness. Finally, design innovativeness showed positive (+) impact on the dependent variable—outsourcing competitiveness—which was 11.545 (p < 0.001). Hence, this hypothesis was accepted.

Table 5.
Hypothesis verification.
To verify the mediation effect of design innovativeness, the indirect effect was analyzed. It was found that personal design competency (0.185, p < 0.05) and technology competency (0.454, p < 0.01) had a positive impact on the outsourcing competitiveness of the design consulting enterprise, with design innovativeness as a medium. In contrast, organizational innovation competency had no impact on outsourcing competitiveness, with design innovativeness as a medium (See Table 6).

Table 6.
Discriminant validity.
5. Conclusions
5.1. Discussion: Open Innovation in Design
This study analyzed the effects of the personal, organizational, and technology design innovation competency factors of a design consulting enterprise on its competitiveness of design outsourcing service, with design innovativeness as a mediating factor. The analysis result shows that personal innovation competency and technological innovation competency manifested by designers at a design consulting enterprise contributed to improving the innovativeness of the design consulting enterprise as they improved the creativity and openness in the process of design development.
However, the organizational innovation competency of a design consulting enterprise turned out to have no significant effect on design innovativeness, which is indicated in the activity of design work [64]. It means that the cultural and environmental factors of the organization had no significant effect on the process of innovation. We also can consider that the results are related with the status that the design consulting enterprises in Korea, operate in a minor scale design outsourcing project and involve little organizational activity. However, even if design consulting enterprises provide outsourcing services as a minor project, the innovation in the segment of design development needs to service design outsourcing. Then the personal innovation competency based on individual designers’ ideas and creativity rather than organizational innovation competency is more significant in this regard [65].
Based on the results above, the following implications of this study are considered; First, in order to enhance the innovativeness of design service outsourcing successfully, a design-consulting enterprise needs to induce individual designers’ creativity and design development in the design consulting enterprise rather than provide services based on quantitative growth or organizational activity. Second, it is necessary to seek business development strategies that focus on developing technology elements, as well as design styles and concepts featuring innovation originality rather than on design products or aesthetic production activities merely wanted by client companies.
As shown in previous studies, the needs for an outsourcing service from design consulting enterprises have changed [50,66]. A design consulting enterprise, which had provided attractive styling elements has become a common and basic innovative project service like new business model development and new market sensing. Efforts need to be put forth into developing advanced outsourcing services that can contribute to product and service innovation among enterprises based on original and innovative ideas and design technology. Accordingly, this study empirically examines the design innovativeness and design innovation competency of design consulting enterprises and deepens understanding of the relation between design and innovation, which is of academic significance [67,68,69]. In addition, this study is of practical significance in that it presents a direction for design consulting enterprises to improve their design innovativeness [70,71], as well as innovation competency in this fiercely competitive global market.
5.2. Research Limtation and Future Researchs
However, this study has the following limitations: First, this study was conducted among design consulting enterprises in Korea. It has limitations in the aspect of generalizing the findings regarding design outsourcing service competitiveness to the global market. Hence, a future study needs to comparatively analyze major design consulting enterprises in the U.S. and Europe, as well as the differences between large and small enterprises. Second, this study is based on previous studies that defined the variables of innovative design competency and design innovativeness. However, it fails to take into consideration the characteristics of design development activity. Based on qualitative research, a future study needs to derive innovation competency factors that are required in design development activity and to clarify the factors of design innovativeness that are different from those of other innovation types.
Third, this study has limitations in that it takes little consideration of the control variables concerning the scale and organizational environments of design consulting enterprises regarding the theoretical conceptualization. A future study needs to consider the overall research design to analyze differences in design outsourcing service activities in terms of design service provision types and development processes. Finally, in this research, competitiveness of the firm defined the design service superiority or excellence in the design outsourcing business environment. To analysis the final design service excellence we used the service satisfaction and service quality valuation of the outsourcers. However, the external validity of measuring competitiveness and design innovativeness based on perceptions of employees appears to be highly questionable. In the future, the survey design underlying the study should consider all measures including partner companies or measurement data of competitiveness.
Author Contributions
Funding acquisition, K.H.; methodology, B.Y.; resources, K.H.; supervision, B.K.; writing—original draft, B.K. and K.H.; writing—review and editing, B.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by aSSIST (Seoul School of Integrated Sciences and Technologies).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kim, M.R.; Jeon, J.E. The effects of technology innovation and aesthetic design on product adoption: Focusing on consumers sensation seeking. J. Korea Serv. Manag. Soc. 2018, 19, 243–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiuma, G. Arts catalyst of creative organisations for the fourth industrial revolution. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex 2017, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MSIP. Report of Future Strategy; Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning: Seoul, Korea, 2017.
- KEIT. Design, Preparing the 4th Industrial Innovation; PD Issue Report; Korea Institute of Design Promotion: Seoul, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.R.; You, S.C.; Rim, H.S. Comparison of effects on operation of multi-disciplinary organizational structuring of design consultants. Arch. Des. Res. 2010, 23, 226–237. [Google Scholar]
- KIDP. Korea Design Statistical Data; Korea Institute of Design Promotion: Seoul, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.Y.; Kim, H.J. Sustainable innovation of design industry by startup business: Cases and issues in the Korean design industry. Arch. Des. Res. 2018, 31, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Čirjevskis, A. Designing dynamically “signature business model” that support durable competitive advantage. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex 2016, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, P. From design thinking to art thinking with an open innovation perspective: A case study of how art thinking rescued a cultural institution in Dublin. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex 2018, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, J.L. Research, design, and business strategy. Design Manag. Rev. 1997, 8, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Lippman, S.A.; Rumelt, R.P. Uncertain imitability: An analysis of interfirm differences in efficiency under competition. Bell J. Econ. 1982, 10, 418–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M. The definition and measurement of innovation. Parkville VIC Melb. Inst. Appl. Econ. Soc. Res. 1998, 11, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, J.H.; Watson, M.W. Forecasting using principal components from a large number of predictors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2002, 97, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, G.E. Managing design, designing management: Two ideas of the same idea. Design Manag. Rev. 2007, 18, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegg, J.; Alba, J.W.; Dahl, D.W. The good, the bad, and the ugly: Influence of aesthetics on product feature judgements. J. Consum. Psychol. 2010, 20, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, L.M.; Spencer, S.M. Competence at Work: Models for Superior Performance; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Yam, R.C.; Guan, J.C.; Pun, K.F.; Tang, E.P. An audit of technological innovation capabilities in Chinese firms: Some empirical findings in Beijing China. Res. Policy 2004, 33, 1123–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romijn, H.; Albaladejo, M. Determinants of innovation capability in small electronics and software firms in southeast England. Res. Policy 2002, 31, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, S.R. The quest for competencies. Training 1996, 33, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S. Design Management 10 Points That CEO Should Know; Korea Institute of Design Promotion: Seoul, Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bloch, P.H. Seeking the ideal form: Product design and consumer response. J. Mark. 1995, 59, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charters, S. Aesthetic products and aesthetic consumption: A. review. Consum. Mark. Cult. 2006, 9, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampino, L. The innovation pyramid: A categorization of the innovation phenomenon in the product-design field. Int. J. Design 2011, 5, 36–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Choi, S.W. A convergence study on the effect of design corporate employees entrepreneurship and design competency on corporate performance. Korean Soc. Sci. Art 2016, 24, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiuma, G.; Lerro, A. The business model prism: Managing and innovating business models of arts and cultural organisations. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex 2017, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Muiña, F.E.; Navas-López, J.E. Explaining and measuring success in new business: The effect of technological capabilities on firm results. Technovation 2007, 27, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lado, A.A.; Wilson, M.C. Human resource systems and sustained competitive advantage: Acompetency-based perspective. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1994, 19, 699–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Garg, N. Aesthetic principles and cognitive emotion appraisals: How much of the beauty lies in the eye of the beholder? J. Consum. Psychol. 2010, 20, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Yun, J.S.; Kim, N.S.; Han, D.K. The relationship between design organization competency and design performance. Korea Des. Knowl. Soc. 2011, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Acha, V. Open by design: The role of design in open innovation. Acad. Manag. Annu. Meet. Proc. 2008, 1, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savatore, B.; Judy, M. Design-led innovation: Exploring the synthesis of needs, technologies and business models. Particip. Innov. Conf. Proc. 2011, 1, 351–354. [Google Scholar]
- Filippetti, A. Innovation modes and design as a source of innovation: A firm-level analysis. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2011, 14, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.P.; Fisher, T.R.; Trowbridge, M.J.; Bent, C. A design thinking framework for healthcare management and innovation. Healthcare 2016, 4, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, M.S. Using agency theory to design successful outsourcing relationships. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2000, 11, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, D.; Barua, A.; Whinston, A. An empirical analysis of the impact of information capabilities design on business process outsourcing performance. Mis Q. 2010, 34, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathianathan, M.; Panchal, J.H. Incorporating design outsourcing decisions within the design of collaborative design processes. Comput. Ind. 2009, 60, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, T. Outsourcing wisdom: Emerging profiles in design consulting. Design Manag. Rev. 1996, 7, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.O. Problem-solving design platform model based on the methodological distinctiveness of service design. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex 2019, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrar, P.; Gervais, R. Global Outsourcing Strategies: An International Reference on Effective Outsourcing Relationships; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Somjai, S. Advantages and disadvantages of outsourcing. Bus. Manag. Rev. 2017, 9, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Cellini, R.J.; Faust, W.H. Beyond work for hire: Results based compensation in the client-consultant relationship. Des. Manag. Rev. 1996, 7, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiwulu, S.U.; Yunus, E.M.; Ibrahim, F.; Zuruzi, A.S. Sustaining innovation: Creativity among employees of small and medium-sized enterprises and students in higher education institution in Brunei Darussalam. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex 2019, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, R.; Rodriguez, D. Innovation, growth, and getting to where you want to go. Des. Manag. Rev. 2007, 18, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dospinescu, O.; Anastasiei, B.; Dospinescu, N. Key factors determining the expected benefit of customers when using bank cards: An analysis on millennials and generation Z in Romania. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dospinescu, O.; Dospinescu, N. The use of information technology toward the ethics of food safety. Ecoforum 2018, 7, 70–81. [Google Scholar]
- Dospinescu, N.; Florea, D.B. Smartphone brands design and buying decision. Ecoforum 2016, 5, 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.P.; Lee, J.R. Concept and realization direction of design business for paradigm shift to design business. Arch. Design Res. 2005, 5, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.J.; Jeon, Y.O.; Park, H.R.; Nah, K. Collaborative workshop between client and agency for open innovation. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex 2018, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwiesch, C.; Ulrich, K. Innovation Tournaments: Creating and Selecting Exceptional Opportunities; Harvard Business Review Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.H. The effect of design innovation attributes on product and brand attitudes and purchase intention: Focusing on smart watches. J. Korean Soc. Des. Cult. 2019, 25, 403–414. [Google Scholar]
- Crilly, N.J.; Clarkson, J.P. Seeing things: Consumer response to the visual domain. Des. Stud. 2004, 25, 547–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.G. Product innovation and technology strategy. Res. Technol. Manag. 2000, 43, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, B.A.; Rivard, S.; Patry, M. A transaction cost model of IT outsourcing. Inf. Manag. 2004, 41, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanpour, F. Organizational innovation; a meta-analysis of effects of determinants and moderators. Acad. Manag. J. 1991, 34, 555–590. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, P.S.; Shenbar, A. Adapting your technological base: The organizational challenge. Sloan Manag. Rev. 1990, 25, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Talke, K.; Salomo, S.; Wieringa, J.E.; Lutz, A. What about design newness? Investigating the relevance of a neglected dimension of product innovativeness. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2009, 26, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, C.; Shu, S.B. When and how aesthetics influences financial decisions. J. Consum. Psychol. 2010, 20, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, C.A. Measurement of innovation and design performance in services. Design Manag. J. 1992, 3, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Covin, J.G.; Slevin, D.P.; Heeley, M.B. Strategic decision making in an intuitive vs. technocratic mode: Structural and environmental considerations. J. Bus. Res. 2001, 52, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.H.; Kim, B.Y.; Eom, J.G. The effects of job crafting on career success of multinational corporations’ employee. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2019, 6, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.W.; Kim, B.Y.; Carine, B.W. Service open innovation: Design elements for the food and beverage service business. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex 2018, 4, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.A. Confirmatory Factor Analysis for Applied Research; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.T.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. A Multidiscip. J. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulos, S.; Kitsios, F.; Babulac, E. From e to u: Towards an innovative digital era. In Ubiquitous and Pervasive Computing: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications; Symonds, J., Ed.; IGI Global Publishing: Hershey, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kitsios, F.; Kamariotou, M. Mapping new service development: A review and synthesis of literature. Serv. Ind. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsios, F.; Kamariotou, M. Service innovation process digitization: Areas for exploitation and exploration. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.H. Business Model Design Compass: Open Innovation Funnel to Schumpeterian New Compbnation Business Model Developing Circle; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tushman, M.; Lakhani, K.R.; Lifshitz-Assaf, H. Open innovation and organization design. J. Organ. Des. 2012, 1, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Saebi, T.; Foss, N.J. Business models for open innovation: Matching heterogeneous open innovation strategies with business model dimensions. Eur. Manag. J. 2015, 33, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, A.; Bascavusoglu-Moreau, E.; Hughes, A. Open service innovation and the firms search for external knowledge. Res. Policy 2014, 43, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, B. Open innovation, networking, and business model dynamics: The two sides. J. Innov. Entrep. 2014, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).