Abstract
Korea’s small- and medium-sized enterprises are desperate to improve their performance through engaging in technological innovation, due to the fierce competition prevalent in a low growth economic environment. However, most small- and medium-sized enterprises are having difficulty responding to changes in the economic environment due to the challenge of developing their own technologies and their limited resources. The aim of this study is to assess whether government financial support for R&D aimed at small- and medium-sized enterprises has contributed to improvements in their business management performance. The sample of this study was comprised of 105 KOSDAQ-listed small- and medium-sized enterprises with experience in technology development. The empirical analysis was conducted on the basis of the mediating effect measurement method of Baron and Kenny (1986). It was found that company technological innovation capabilities have a positive effect on management performance, and in particular, that the majority of companies that received government financial support for R&D have improved their management performance. Therefore, it is recommended that small- and medium-sized companies take an active part in various government R&D financial support programs and make efforts to strengthen their technological innovation in areas such as their product service and process innovation capabilities.
1. Introduction
The proportion of small- and medium-sized companies is a significant factor in the domestic industry of Korea, considering the large number of businesses and the number of people they employ. Therefore, the government has been supporting the development of small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and sustainable ecosystems in terms of funding, sales, manpower and R&D. In particular, successive governments have promoted innovative growth policies for SMEs through R&D investment since 1998. As a result, in 2018, approximately KRW 2 trillion of the total R&D spending of the Korean government went to support small and medium enterprises [1]. In particular, companies have been trying to improve their business management performance and international competitiveness through various types of innovation activities. However, one constraint is that continuing technological innovation, which can add value in a fierce competitive environment, may be difficult to achieve in the short term due to costs and lack of resources. However, it can be achieved through a focus on the strategic and managerial capabilities of the organization, as well as its overall capabilities [2]. From a business perspective, technology innovation can lead the improvement of a firm’s technology activities and support a strategy of securing competitive advantage [3]. In the highly innovative situation that normally arises in the initial stage of a firm’s existence, an “open-and-closed” strategy that secures a firm’s core area of strength while being open to collaboration with external entities in relation to its weaker operations, can be very effective [4,5,6]. The purpose of our research is to verify the kind of effect and efficiency of government R&D funding on the business performance of SMEs, and to assess the mediating effect of technological innovation. In Section 2 this study will look at the theoretical understanding of and the prior research on technological innovation, management and government R&D financial support programs. In Section 3, our study model and variables are set out, while empirical analysis is conducted in Section 4, and finally Section 5 presents the conclusions of our study and its research limitations.
2. Literature Reviews
2.1. Technology Innovation and Business Performance
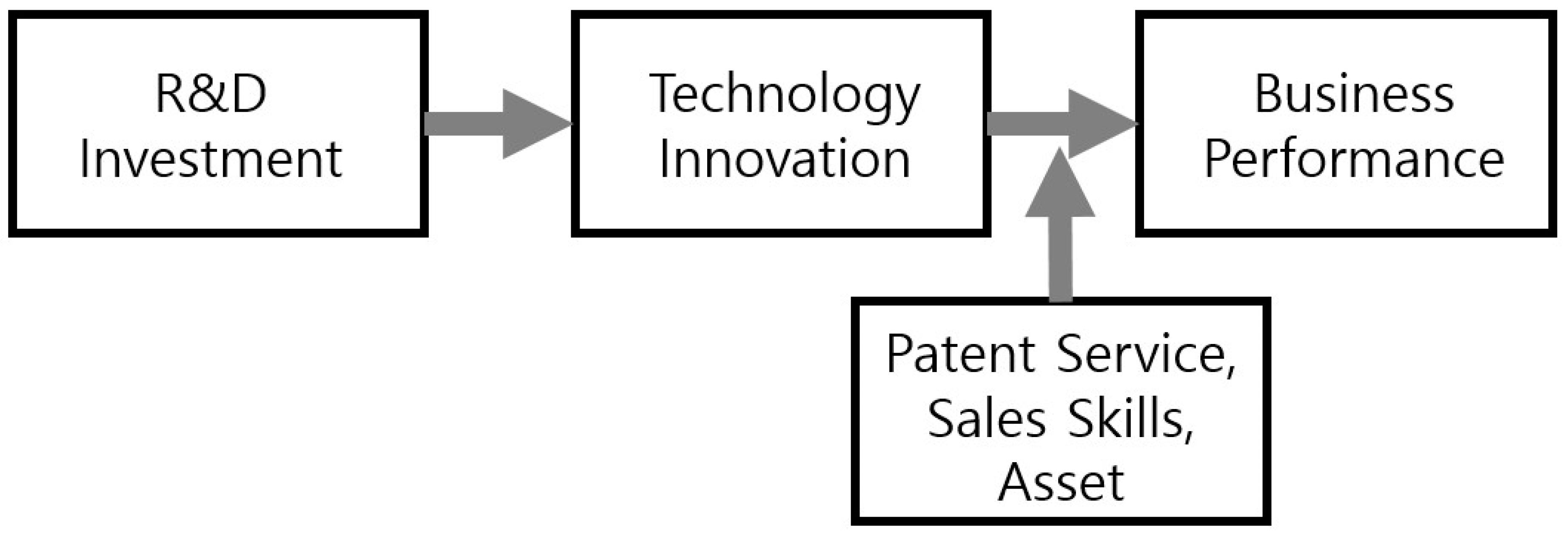
The research on technological innovation and economic performance proposed by Schumpeter (1935) [7] gained new impetus in 1960. Schumpeter argued that monopoly profits that large oligopolies temporarily enjoy are an important factor in creating technological innovation. Since the late 1980s, many innovation researchers have been debating the size and market structure of large companies as well as small- and medium-sized enterprises, and the relationship between technological innovation and company size [8,9,10,11]. Pavitt (1984) [12] categorized types of technological innovation according to industry and suggests that large- and small-scale innovation differ depending on the size of industry. Technological innovation is a main key factor in securing competitiveness, as science and technology performance is commercialized through technological innovation and can result in productivity improvements [13,14]. Technology innovation performance can vary depending on the strategic management capacity, operational performance and management capability of the organization [15,16]. Small and medium venture companies are able to establish their own technology support systems through continuous focus on technological innovation activities and can solve problems related to internal technical support in areas such as technology, manpower and equipment [17]. Therefore, when companies have the capacity to systematically operate and manage the process of technological innovation, performance improvements can take place [18,19]. On the other hand, much research has focused on the ways in which a company’s technological innovation capabilities affect its business performance, on the basis of the determinants of such technological innovation. Figure 1 illustrates the process of R&D investment that leads to the creation of technological innovation and the generation of management performance improvements [20,21]. In this regard, Koellinger (2008) argues that it is difficult to define innovation activities and to analyze management performance on the basis of technology development, innovation, management practices and the optimal path to take in order to ensure the development of innovation activities. Economic theory suggests that innovation can be divided into technological superiority, process innovation and product service innovation, and process innovation and product service innovation can lead to business competitiveness by increasing productivity and efficiency.
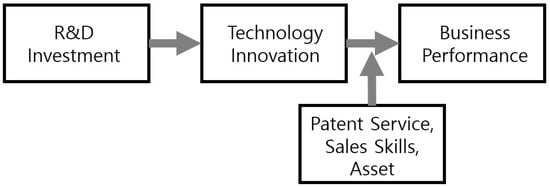
Figure 1.
Process of Technology Innovation and Business Performance.
Prior research on technological innovation and business management suggests that, first of all, innovation is a process both of creating and inventing new things and of reinventing them, in other words of transforming them from existing forms into new forms [22]. It is a series of processes that take into account new factors in a given environment and develop and utilize them. Meanwhile, the sales of technological innovations and business management-related indicators have long been recognized as important signs of business performance by many scholars [23,24]. One study showed that patented inventions had a positive effect on the sales growth of 365 U.S. companies, and while R&D did not increase their marginal profits overall, it increased profits through specific marginal profit increases. It has also been argued that sales can be increased based on a company’s innovative performance [9]. A survey of activities in the steel and petrochemical industries over the course of 40 years showed that innovative companies grow faster than others [25]. In particular, technological research and development can have a similar effect on sales growth [26]. In addition, a study on the performance of 539 British companies over the course of nine years from 1972 to 1983 showed that those that produced at least one innovation had better results in terms of sales and profit growth compared to those that did not generate any innovations at all. However, the effect of certain innovation activities on sales is seen as short-term, because the innovation effect on growth leads to an increase in sales [27,28]. Unlike the existing theory [9] of Scherer (1965), this is a different claim from that made by previous research, because it recognizes that innovation activities can have more impact on marginal profit growth than on sales growth. On the other hand, the profitability performance index of management can be seen as the operating profit rate when analyzing the relationship between technological innovation and management performance, when available data is limited in areas such as the assessment of management performance achieved through innovation [29,30]. Prior research has compared factors that influence management performance such as Technology innovation vs. Revenue, Innovation product Vs. Revenue, Innovation company Vs. Non-Innovation company, and R&D Activity Vs. Revenue [31,32,33,34].
2.2. Government R&D Support and Performance
Korea is a country with world-class levels of R&D investment and with a high level of GDP, and it supports large R&D budgets for small- and medium-sized companies. Korea’s R&D development costs in 2016 were approximately KRW 69 trillion, accounting for 4.2 percent of GDP, the second highest rate in the world, and the government R&D budget for small- and medium-sized enterprises was about 15.7 percent of the total R&D budget in the same year. In the five years 2012–2016, the average amount of R&D financial support for small- and medium-sized enterprises increased steadily to KRW 8.4 trillion (a 35% annual increase), and the number of R&D projects supported by the government was 28,542, which represents an increase of about 51% year-on-year during the period. In particular, the Small and Medium Venture Business Ministry invested KRW 4.27 trillion in 30,302 R&D projects over these five years. Analysis has shown that most of the SMEs which received government R&D support had positive outcomes in terms of sales and increased assets, as well as an increased number of employees. In particular, companies that received R&D support from the mid-term government displayed a high level of growth in terms of sales and employee numbers. According to Ministry of Science, Technology and Technology data (2018), the ratio of SMEs with less than 250 employees who received government R&D support was 56.8%, which is a higher level than the equivalent number in advanced countries such as the United States (11.4%), France (24.8%) and Germany (45.0%). As these numbers show, Korea seems to focus on national R&D support and efficiency maximization policies in order to improve the innovation capacity of companies. In the meantime, the net profit growth rate of small- and medium-sized enterprises who receive government funds and other financial support is higher than that of other companies [35], and the government’s funding has a positive effect on various business operations such as sales, which is a profitability indicator of small- and medium-sized enterprises [36]. In addition, government funding can produce improvements in all aspects of management performance [37]. In this regard, government funding provides short-term liquidity to small- and medium-sized enterprises and plays an important role in maintaining employment in these companies [38]. In particular, when comparing the management performance of small- and medium-sized enterprises which receive R&D funding with that of other sample companies, the former have higher net profit growth rates in the following year [35]. In addition, it has been demonstrated that companies that received government R&D support enjoy positive results in terms of increasing sales and operating profits, which can improve their profitability [39]. In terms of a wider range of performance indicators, government R&D funds also improve stability indicators such as flow ratio and debt ratio [40]. It also has the effect of improving the financial performance of small- and medium-sized companies in the short term [36]. Other research has shown the impact of government financial support on the growth of employment [41,42], the effect of R&D financial support on the productivity and employment rate of small- and medium-sized enterprises [43], and the outcome of innovative R&D activities and technology development [44]. In addition, various studies on the indicators and variables used to measure management performance have also been carried out [45,46]. Financial indicators such as sales, revenue, market share, productivity, debt ratio, and value have been measured as indices of business performance [47]. Based on this research, performance measurement has been conducted that distinguishes between financial and non-financial factors [48]. This work focuses mainly on economic performance, technology development and level of employment. In addition, it has also been shown that government R&D support in relation to patents, which are a knowledge generation indicator, can increase the number of patents generated by small and medium enterprises [49]. Because of information asymmetry, it is difficult for government or external investors to invest in company R&D with confidence, so in the initial stages of their R&D development, SMEs generally use internal funds [50]. In addition, government support for small and medium enterprises has mainly been limited to the provision of funding, and there have not been many areas of R&D support that can be said to be very important factors in securing the sustainability and survival of small and medium enterprises. This is simply because the effect of government R&D funding has been assessed only through a financial comparison of the differences in performance of supported and non-supported companies [51].
3. Design and Methodology
3.1. Research Model and Hypothesis
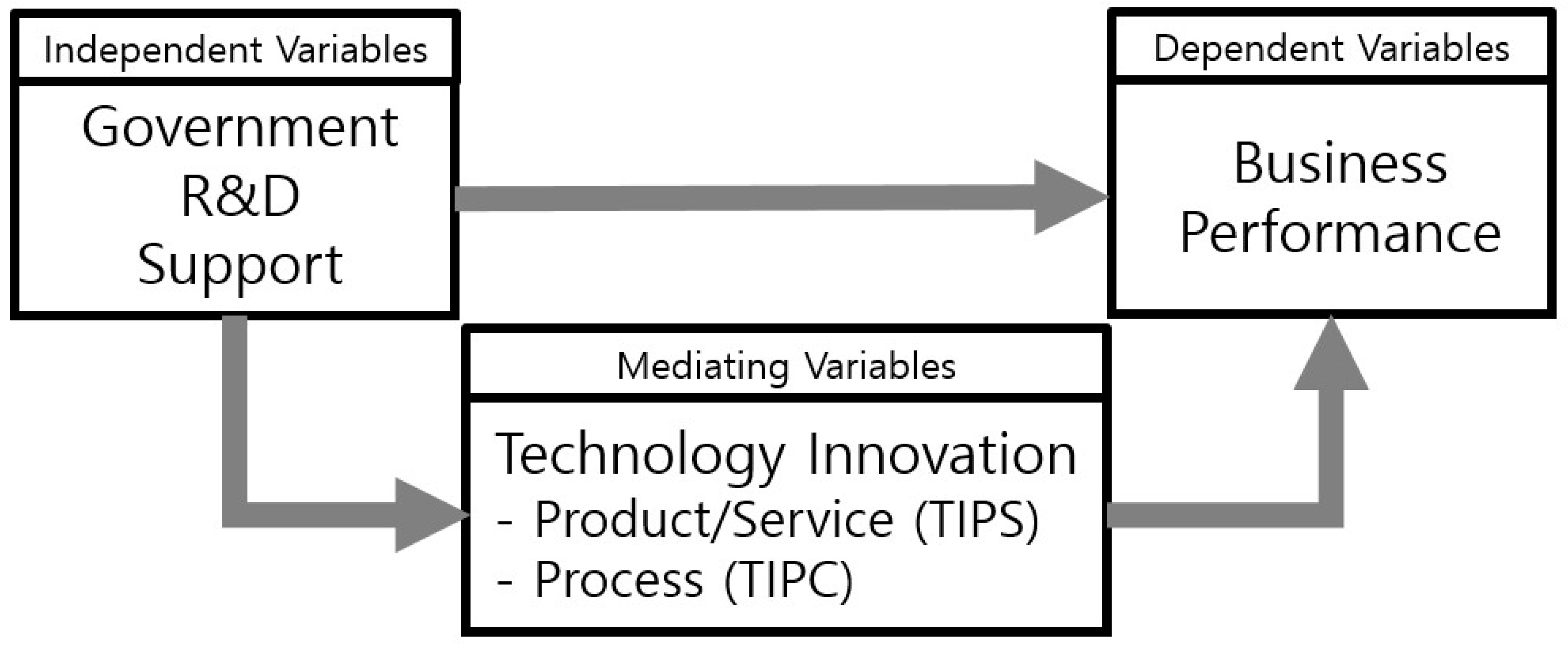
Based on the results of prior research, this study established a research model (Figure 2) and verified its research hypotheses by measuring the mediating effect of a company’s technological innovation capability on the impact of government R&D financial support, in terms of management performance.
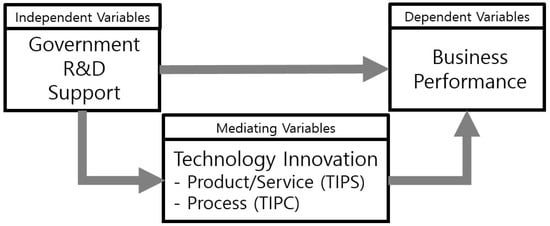
Figure 2.
Research Model. Note: Mediating effects of Technology innovation on product and service (TIPS) and process (TIPC).
First of all, our research hypotheses pose the question as to whether government R&D financial support affects management performance. If this support affects companies’ technological innovation capability, this capability will affect management performance. Three research hypotheses were proposed, and verification of them was then carried out. Technology innovation capability denotes the level of product service innovation and process innovation present in small and medium enterprises. The level of technological innovation capability is also used as a factor which can confirm the second stage of the three-step analysis method proposed by Baron and Kenny (1986). A company’s management performance can be gauged on the basis of sales and the employment increased, which are representative company growth indicators. In this light, and based on prior research related to government R&D financial support, < hypothesis 1 >, composed of two parts, was formulated as follows:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Government R&D financial support positively affects management performance (+). (1-1) Ministry of SMEs and Startups (MSS) R&D financial support positively affects management performance (+). (1-2) KOBIR R&D financial support positively affects management performance (+).
Government R&D financial support affects technological innovation capabilities. The results of this study’s preliminary research confirmed that the government’s R&D financial support program contributed to the improvement of the innovation activity index of affected companies [43,44]. This preliminary work was applied to the formulation of both < hypothesis 2 > and < hypothesis 3 >. The technical innovation capability of a company related to < hypothesis 3 >, which stipulates that this capability has a median impact on the relationship between government R&D financial support and management performance. As a result of the potential benefits, the R&D financial support (3-1) of the mid-sized government and the Korean Small Business Innovation Research Program (KOSBIR) (3-2) were established.
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Government R&D financial support has a positive effect on company technological innovation capabilities (+). (2-1) MSS R&D financial support positively affects company product and service innovation capability (+). (2-2) KOSBIR R&D financial support positively affects company process innovation capability (+).
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
The technological innovation capability of a company mediates the impact of the government’s R&D financial support on management performance. (3-1) Product and service innovation capability mediates the impact of MSS R&D financial support on management performance. (3-2) Process innovation capability mediates the impact of KOSBIR R&D financial support on management performance.
3.2. Research Model and Hypothesis
The sample of the experimental analysis consisted of 105 small and medium-sized enterprises for whom financial performance and other data was available, from among KOSDAQ-listed companies which were included in the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Policy Research Study from 2012 to 2017, which is based on the variables included in previous research [52]. KOSDAQ (Korea Securities Dealers Automated Quotations) is a trading board of Korea Exchange (KRX) in South Korea established in 1996. It is operated as SME market division of KRX (Korea Exchange), As of 19 February 2017. In total, 1,029 companies are listed on KOSDAQ for trading. The data show the type of R&D financial and operational support the government provided to small and medium enterprises, including KOSBIR R&D support (provided by 14 central administrative agencies, including 7 government investment institutions) and the support provided by 21 government investment institutions of more than KRW 30 billion per year. In total, 28,075 of SME were supported by these government R&D funds. SME should submit a proper R&D planning proposal to be eligible to these funding plan which government announced. Government select the SMEs to be supported twice a year. The overall growth of the firm is usually measured by tangible/fixed assets or total assets and their growth. Activity and productivity authors usually operationalize by the indicators of assets turnover, labor productivity (value-added per labor cost) and total factor productivity (TFP). Profitability and rentability are usually measured by the indicators of sales (or turnover), value added or profit [53]. The important lesson that was taken from the previous studies is that the trend is now shifting towards using multiple indicators [54,55,56], instead of using one or two measures, providing a structured overview on the overall effect of the grants on firm financial performance and productivity [53]. Business outcome variables, which are dependent variables, included two indicators, revenue and employment growth. In addition, the parameter was established of dividing companies’ technological innovation capacity into product service innovation and process innovation. Process innovation focuses on the number of new or greatly improved production methods and logistics arrangements as variables. Finally, the control variable was selected, and was comprised of the age of the company (how long the company is sustained from the establishment) and company location (whether or not a company is located in a metropolitan area), (which reflects the real world conditions of the domestic business environment, in terms of differences in size, economic environment and competitiveness of companies). In this study, a “metropolitan area” denotes the Seoul and Gyeonggi areas, while other areas are non-metropolitan areas < Table 1 >.

Table 1.
Key variables and data source.
Baron and Kenny (1986) proposed a three-step mediated effect analysis as a method of hypothesis verification, which our study adopts. Parametric effect analysis entails assessing the relationship between the independent variables and the dependent variables on the basis of the set parameter [57]. However, in order to execute a mediated effect analysis, the following conditions must be met. First, in the initial analytical step, there should be a significant effect on the regression between the independent variables and the dependent variables. In the second stage, there should be a statistically significant relationship between the independent variables and the parameter regression analysis. In the last three stages, independent variables and parameters should be assessed in tandem with dependent variables and regression analysis, and parameters should be proved to be statistically significant for dependent variables [57,58,59]. “Completely mediated” denotes the situation in which the independent variable has no significant effect on the dependent variable during the three-step analysis, and “partially mediated” denotes the situation in which the statistical significance of the result and the regression coefficient absolute value are reduced. In addition, the three-step mediated effect verification of the results employed a point estimation verification method, but to compensate for the limitations of this method, the verification method of Sobel (1982) [60], based on interval estimation, was used to secure the reliability of the research results [61,62].
4. Results and Findings
In our study, the technology statistics for the six years from 2012 to 2017 of 105 companies whose data are in the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Policy database (which includes a total of 1,473 SMEs) were analyzed, on the basis of data for 105 corporations. The results are shown in Table 2. When multiple regression analysis is applied, as was done in our study, it is generally possible for multiple coherence between variables to occur. In this case, it is determined whether there is a multi-coherent problem through the dispersion expansion index (VIF) value. This study’s multiple regression analysis showed that the variance expansion index (VIF) value was less than 10, and it was determined that the experimental analysis of the study was problem-free in this respect.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics for complete cases (n = 105).
Step 1 in Table 3 displays the result of the testing of Hypothesis 1. The suggested model, which was used to explain the business performance increase through government R&D financial support, had an explanatory power (R2) of 0.61. The effects of MSS R&D financial support (MRD) and KOSBIR R&D financial support (KRD) were found to be significant in improving the business performance, in terms of increases in revenue and employment, of SMB companies in Korea at the 99.9% confidence interval. This result fully described Hypothesis 1, which explores that business performance will increase with both MSS and KOSBIR R&D financial support. From Step 2 of the three-step procedure suggested by Baron and Kenny (1996) in Table 3, MSS R&D financial support (MRD) and KOSBIR R&D financial support (KRD) had a significant influence on the product and service innovation index with a 99.9% confidence interval. The results in Step 3 illustrate the mediating effect of the level of company product and service index, which consequently mediated the relationship between the variables of government R&D financial support (MRD, KRD) and the improvement in business performance (REV, EMP) at the 99.5% confidence interval. More specifically, in relation to government R&D financial support, the mediating effect between MSS R&D financial support and revenue increases was significant at all stages over the 99.5% confidence interval. The unstandardized coefficient for MSS R&D support declined from 0.32 in Step 1 to 0.16 in Step 3, which shows that the product and service innovation index partially mediates the relationship between MSS R&D financial support (MRD) and revenue increases. In addition, the product and service innovation index partially mediates the relationship between MSS R&D financial support (MRD) and increases employment, as the unstandardized coefficient decreased from 1.14 in Step 1 to 0.73 in Step 3. The mediating effect between KOSBIR R&D financial support and revenue increases was significant at all three stages over the 99.5% confidence interval level. The mediating effect of the product and service innovation index between KOSBIR and increases in revenue and employment was also partial, as the unstandardized coefficient decreased from 2.42 to 0.98 and from 0.95 to 0.66, respectively.

Table 3.
Factors affecting increase on business performance and mediating effect of product and service innovation (PSI).
From Step 2 in Table 4, both MSS and KOSBIR R&D financial support (MRD and KRD, respectively) had a significant influence on companies’ process innovation index at the 99.9% confidence interval. The results in Step 3 illustrate the mediating effect for the process innovation index level, which importantly mediated the relationship between the variables of government R&D financial support (MRD, KRD) and improvements in business performance (REV, EMP) at the 99.5% confidence interval. More specifically, in relation to government R&D financial support, the mediating effect between MSS R&D financial support and revenue increases was significant at all three stages above the 99.5% confidence interval. The unstandardized coefficient for MSS R&D support decreased from 0.18 in Step 1 to 0.09 in Step 3, which indicates that a company’s process innovation index partially mediates the relationship between MSS R&D financial support and revenue increases. In addition, companies’ process innovation index partially mediated the relationship between MSS R&D financial support and patent increases, as the unstandardized coefficient decreased from 1.14 in Step 1 to 0.85 in Step 3. The mediating effect between KOSBIR R&D financial support and revenue increases was significant at all three stages above the 99.5% confidence interval. The mediating effect of companies’ process innovation index between KOSBIR and increases in revenue and employment was also related to the partial mediation, as the unstandardized coefficient decreased from 4.31 to 2.18 and from 0.95 to 0.32, respectively.

Table 4.
Factors affecting increase on business performance and mediating effect of PRI.
A summary of the mediating effects of technological innovation, product and service innovation and process innovation are presented in Table 5. Product and service innovation partially mediated the relationship between MSS and KOSBIR financial support, and business performance improved in terms of revenue and increases employment. In addition, process innovation partially mediated the relationship between MSS and KOSBIR financial support and the business performance of the SMBs.

Table 5.
Summary of results for mediating effect analysis.
The result of the Sobel test is shown in Table 6, which shows that product and service innovation acted as a partial mediator between MSS R&D financial support (MRD) and revenue increases at the 99.5% confidence interval, and between KOSBIR R&D financial support (KRD) and revenue increases at the 99% confidence interval. In addition, product and service innovation had significant mediating effects on the relationship between MRD and KRD, and on increases employment, at the 99.5% confidence interval. Process innovation acted as a partial mediator between MSS and KOSBIR R&D financial support (MRD and KRD, respectively) and revenue increases at the 99% confidence interval. In addition, process innovation displayed significant mediating effects on the relationship between MRD and KRD, and on patent increases, at the 99.5% confidence interval.

Table 6.
Summary of Sobel test results.
The final hypothesis verification results are as follows. First, the two components of < hypothesis 1 >, (1-1), and (1-2), were both confirmed. In other words, government R&D financial support had a significant impact on management performance. In the case of < hypothesis 2 >, both elements, (2-1) and (2-2), were confirmed because the government’s R&D financial support (MSS R&D support, KOSBIR R&D support) had a significant effect on company technological innovation capabilities. In terms of < hypothesis 3 >, both elements, (3-1), and (3-2), were found to be significant.
5. Discussion
In the face of market dynamism that SMEs need to confront, financial stability for R&D and technological innovation are the key factors in their sustainability and competitiveness in a severe business situation. Thus, financial stability and technological innovation are the major challenges that need to be addressed by SMEs that tend to lack awareness of what factors they should develop and how they can improve them. In response, this research provides, from a qualitative comparative analysis perspective (i.e., Baron and Kenny), new insights into the understanding of the factors which enhance the business output of SMEs.
Although there are a variety of business activities, both financial support from government and technological innovation stand as cornerstones in the business process, two factors that along with a strong managerial system and the assets of the SMEs support the business performance improvement in SMEs. Our findings suggest that financial support from government are one of the most important sources of R&D activities of SMEs, and that these R&D activities is performed through the collaboration with the various external companies in developing new insights, ideas, and finally new product and service which can enhance the business performance of the SMEs. Government support literature regarding SMEs stresses the fact that SMEs prefer to collaborate with government in the first place [10]. Our findings suggest that SMEs should focus on developing the abilities to meet the requirements of government R&D funding. Furthermore, when support from government is absent, enhancing technological innovation capabilities are presented as core conditions. These factors are the key capabilities for business output, suggesting SMEs incorporate innovation and financial support from governments for business sustainability and competitiveness. These key capabilities are aimed to assure close cooperation between SMEs and governments, in order to innovate and survive. Therefore, a sensing government cooperation program needs to help SMEs to take advantage of competition, moving established SMEs from an unstable to a stable position of their business status.
Regarding the configurational implications of our research, this study proposed that SMEs can achieve business output through government funds (R&D funds for SMEs) and technological innovation (process and service innovation, process innovation). The results explored through Baron and Kenney analysis indicate that the combination of government R&D fund and technological innovation capabilities of SMEs accounted for the business output enhancement for SMEs.
Analyzing these results in detail, by examining core factors for enhancement of business performance, we detected that government support is a core condition the business enhancement of SMEs. Our findings add to previous research focused on measuring the business output of SMEs [53]. Results concerning technological innovation capabilities (i.e., product and service innovation, process innovation), revealed that it is a peripheral condition for SMEs to enhance their business output. Thus, from an SMEs perspective, being up to date with new technological developments and opportunities seems to be a factor that increases the central functions to enhance SME’s business output. We understand that this could be due to the enhancing impact that digital transformation may be having on SMEs. Furthermore, these results reinforce that combing with technological innovation generates value when it is exploited through government funds that creates opportunities to enhance the various R&D activities internally and externally that can create the values for SMEs.
6. Conclusions and Research Limitations
This research aims to contribute to the improvement of innovation strategies and of management performance by analyzing the mediating effects of SMEs’ technological innovation capabilities on the improvement of management performance. The performance of 102 Korean SMEs that receive government R&D financial support was analyzed in order to assess this mediating effect. This study found that the level of technological innovation of SMEs and their access to government R&D financial support had a positive effect on management performance, and that their technological innovation capabilities played a mediating role. It was also confirmed that the government’s R&D financial support was an important technical innovation capability indicator that directly affects management performance. The significance of this research result is as follows. First, while technological innovation at the corporate level is difficult to sustain on the part of SMEs due to limited resources, it can conversely contribute to improvements in management and in other areas by enhancing internal technology capability through fostering selective technological innovation. Second, by proposing various parameters of management and patent generation, this study proposed indicators for the assessment of government R&D financial support aimed at the establishment of technology innovation strategies for small and medium enterprises, and at the improvement of the business management performance of such companies in the future. In particular, the results of this study suggest that it is necessary for small and medium enterprises without the resources of large companies to make aggressive efforts to utilize government R&D financial support in order to achieve the optimal effect, in light of their level of technological innovation. However, some research limitations are evident in our study. In an era of rapid change, the level of technological innovation displayed by corporations that has been identified in previous research may not be suitable for some small and medium enterprises. This is because the appropriate method of measuring the level of technological innovation activity may vary depending on the size of a company and its technology level, and whether or not it operates in a high-tech sector of the economy. Therefore, additional research will require the development of tools for measuring the scale or level of technological innovation. Furthermore, future research activities could focus on investigating the causal relationships among the management output variables thorough statistical matching approach. Our study did not explore the counterfactual evaluation between the supported companies and not-supported companies from the government because of the data limitation for not-supported companies and also related power analysis. Further study should be considered for the counterfactual evaluation and the power analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.J. and K.L.; methodology, S.J. and K.L.; software, S.J. and K.L.; validation, S.J. and K.L.; formal analysis, S.J.; investigation, S.J. and K.L.; resources, S.J.; data curation, S.J.; writing—original draft preparation, S.J..; writing—review and editing, S.J. and K.L.; visualization, S.J.; supervision, K.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Oh, S.; Kim, S. Performance and Direction of Government R&D Supports. STEPI Insight. Sci. Technol. Policy Inst. 2018, 224, 2–11. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.; Ha, G. A Study of Critical Factors for Technological Innovation of Korean Manufacturing Firms. Korea Ind. Econ. Assoc. 2011, 24, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.S. Technology convergence, open innovation, and dynamic economy. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2017, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.J.; Won, D.; Park, K. Dynamics from open innovation to evolutionary change. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2016, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.J.; Jeong, E.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, K.H. The effect of open innovation on technology value and technology transfer: A comparative analysis of the automotive, robotics, and aviation industries of Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.J.; Lee, M.H.; Park, K.B.; Zhao, X. Open Innovation and Serial Entrepreneurs. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumpeter, J.A. The Analysis of Economic Change. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1935, 17, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamien, M.I.; Schwartz, N.L. Market Structure and Innovation: A Survey. J. Econ. Lit. 1975, 13, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, F.M. Coporate Inventive Output, Profits and Growth. J. Political Econ. 1965, 73, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soete, L.L. Firm Size and Innovative Activity: The Evidence Reconsidered. Eur. Econ. Rev. 1979, 12, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.J. How do we conquer the growth limits of capitalism? Schumpeterian Dynamics of Open Innovation. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2015, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavitt, K. Sectoral Patterns of Technical Change: Towards a Taxonomy and a Theory. Res. Policy 1984, 13, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Jang, D.; Jun, S.; Park, S. A predictive model of technology transfer using patent analysis. Sustainability 2015, 7, 16175–16195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.J.; Jang, H.E. The Relationship Innovativeness with Firm Performance: The Moderating Effects of Miles and Snow’s Strategic Types. J. Creat. Innov. 2015, 8, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, R.; Lee, S. A Comparative Study on the Performance Difference between Strategy Group and Competence Group. J. Mark. Stud. 2001, 10, 51–72. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, H.A.; Mckeen, J.D. How does information technology affect business value? A reassessment and research propositions. Can. J. Adm. Sci. 1993, 10, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, D.; Hwang, K.; Park, H. The impact of open innovation activities on performance of Korean IT SMEs & Venture: Technology Transfer Experiences and Technological Collaborations. Asia-Pac. J. Bus. Ventur. Entrep. 2017, 12, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, W.M.; Levinthal, D.A. Absorptive capacity: A New Perspective on Learning and Innovation. Adm. Sci. Q. 1990, 35, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, T.; Ceylan, C. Factors Impacting the Innovative Capacity in Large-scale Companies. Technovation 2007, 27, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Hong, W. Effect of Firm’s Activities on Their Performances. J. Korea Technol. Innov. Soc. 2011, 14, 373–404. [Google Scholar]
- Koellinger, P. The Relationship between Technology, Innovation, and Firm Performance: Empirical Evidence from e-business in Europe. Res. Policy 2008, 37, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, T.A. Productivity Defined: The Relativity of Efficiency, Effectiveness and Change. In Productivity in Organizations: New Perspectives from Industrial and Organizational Psychology; Campbell, J.P., Campbell, R.J., Eds.; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1988; pp. 230–261. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, I.S. Case Studies on an Improvement of Productivity and Methodologies of Management Innovations in Korean Industries. Product. Rev. 2005, 19, 127–146. [Google Scholar]
- Fichman, R.G. Information technology diffusion: A review of empirical research. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Information Systems, Dallas, TX, USA, 13–16 December 1992; pp. 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield, E. Entry, Gibrat’s Law, Innovation, and the Growth of firms. Am. Econ. Rev. 1962, 52, 1023–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Mowery, D.C. Industrial Research and Firm Size, Survival, and Growth in American Manufacturing, 1921–1946: An Assessment. J. Econ. Hist. 1983, 43, 953–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, P. Complex spaces: Global innovation networks & territorial innovation systems in information & communication technologies. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2017, 3, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Geroski, P.; Machin, S. Do Innovating Firms Outperform Non-Innovators? Bus. Strategy Rev. 1992, 3, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Kim, B. Effects in Response to on the Innovation Activities of SMEs to Dynamic Core Competencies and Business Performance. Asia-Pac. J. Bus. Ventur. Entrep. 2018, 13, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Schiuma, G. Arts catalyst of creative organizations for the fourth industrial revolution. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2017, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Monte, A.; Papagni, E. R&D and the Growth of Firms: Empirical Analysis of a Panel of Italian Firms. Res. Policy 2003, 32, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Freel, M.S. Do Small Innovating Firms Outperform Non-innovators? Small Bus. Econ. 2000, 14, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geroski, P.A.; Toker, S. The Turnover of Market Leaders in UK Manufacturing Industry, 1979–1986. Int. J. Ind. Organ. 1996, 14, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, S. Product Innovation and Small Business Growth: A Comparison of the Strategies of German, UK and Irish Companies. Small Bus. Econ. 1997, 9, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Kim, Y.; Oung, O. The Study on the Effect of SBC Policy Funding Programs on the Improvement of Financial Performance. Korean Small Bus. Rev. 2006, 28, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, Y. The Role and Performance of Policy Loan on the SMEs in Korea: Firm-Level Evidence. Korean Small Bus. Rev. 2010, 32, 153–175. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, H.; Choi, S. A Study on the Financial Performance of SMBA Policy Funding in Small and Medium Sized Firms. J. Financ. Account. Inf. 2009, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, Y.; Joo, M. The Employment Effects of Policy Loan on the SMEs in Korea; Sustainability Analysis. Korean Small Bus. Rev. 2012, 34, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.; Jang, K.; Lee, M. Program Evaluation and Selection Bias: Sequential Selection Model for Government Loan Program for Small Business. Korean Public Adm. Rev. 2008, 42, 197–227. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.J.; Lee, K.Y. The Causal Effects of New Growth Funds on the Financial Performance of SMEs. Korean J. Financ. Assoc. 2013, 26, 183–211. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer, E.; Kleinknecht, A.; Reijnen, J.O. Employment Growth and Innovation at the Firm Level. J. Evol. Econ. 1993, 3, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, H. Public R&D Subsidies and Employment Growth: Microeconomic Evidence from Finnish Firms; Research Institute of the Finnish Economy (ETLA) Discussion Paper 2008, (No. 1143); Research Institute of the Finnish Economy: Helsinki, Finland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Piekkola, H. Public Funding of R&D and Growth: Firm-level Evidence from Finland. Econ. Innov. New Technol. 2007, 16, 195–210. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.J.; Jeong, E.; Yang, J. Open innovation of knowledge cities. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2015, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almus, M.; Czarnitzki, D. The Effects of Public R&D Subsidies on firms’ Innovation Activities: The Case of Eastern Germany. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2003, 21, 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, G. Measuring the Returns of R&D: An Empirical Study of the German Manufacturing Sector over 45 years. Res. Policy 2009, 38, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar]
- March, J.G.; Sutton, R.I. Crossroads-organizational Performance as a Dependent Variable. Organ. Sci. 1997, 8, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittner, C.D.; Larcker, D.F.; Rajan, M.V. The Choice of Performance Measures in Annual Bonus Contracts. Account. Rev. 1997, 72, 231–255. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, N.; Kim, M. Regular Papers: Government R&D Subsidies and the Performance of Small and Medium Enterprises. Korean Small Bus. Rev. 2012, 34, 39–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lipczynski, J.; Wilson, J.; Goddard, J. Industrial Organization: Competition, Strategy, Policy. In Market Structure and Innovation; Kamien, M.I., Schwartz, N.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.J. An Analysis on the Effect of Government Supports for the R&D of SMEs: Focused on Technical, Economic, and Social Outcomes. Korean Soc. Public Adm. 2016, 26, 195–218. [Google Scholar]
- Bogliacino, F.; Pianta, M. Innovation and Employment: A Reinvestigating using Revised Pavitt classes. Res. Policy 2010, 39, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvouletý, O.; Srhoj, S.; Pantea, S. Public SME Grants and Firm Performance in European Union: A Systematic Review of Empirical Evidence. Small Bus. Econ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decramer, S.; Vanormelingen, S. The effectiveness of investment subsidies: Evidence from a regression discontinuity design. Small Bus. Econ. 2016, 47, 1007–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beņkovskis, K.; Tkačevs, O.; Yashiro, N. Importance of EU Regional Support Programs for Firm Performance. Econ. Policy 2019, 34, 267–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srhoj, S.; Lapinski, M.; Walde, J. Size Matters? Impact Evaluation of Business Development Grants on Firm Performance. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2020, 52, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Seo, D.K. Assessing Mediated Moderation and Moderated Mediation: Guidelines and Empirical Illustration. Korean J. Couns. Psychother. 2016, 35, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Lee, N.J. Mediation Effects of BSC Use between the Cultural Traits and Corporate Performance. J. Financ. Account. Inf. 2008, 13, 71–100. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.H. Effects of Psychological Capital on the Learning-Orientation of Local Government-Affiliated Organizations: Mediating Effects of Organizational Commitment. CHUNG-ANG Public Adm. Rev. 2018, 32, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sobel, M.E. Asymptotic Confidence Intervals for Indirect Effects in Structural Equation Models. Sociol. Methodol. 1982, 13, 290–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, O.; Lee, H. Studies of the Mediating Effects of University R&D Funding Factors Shows an affect on University Technology Transfer Performance. Korean Public Adm. Rev. 2016, 25, 57–77. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The Moderator-Mediator Variable Distinction in Social Psychological Research: Conceptual, Strategic, And Statistical Considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).