FTSMAC: A Multi-Channel Hybrid Reader Collision Avoidance Protocol for RFID Network
Abstract
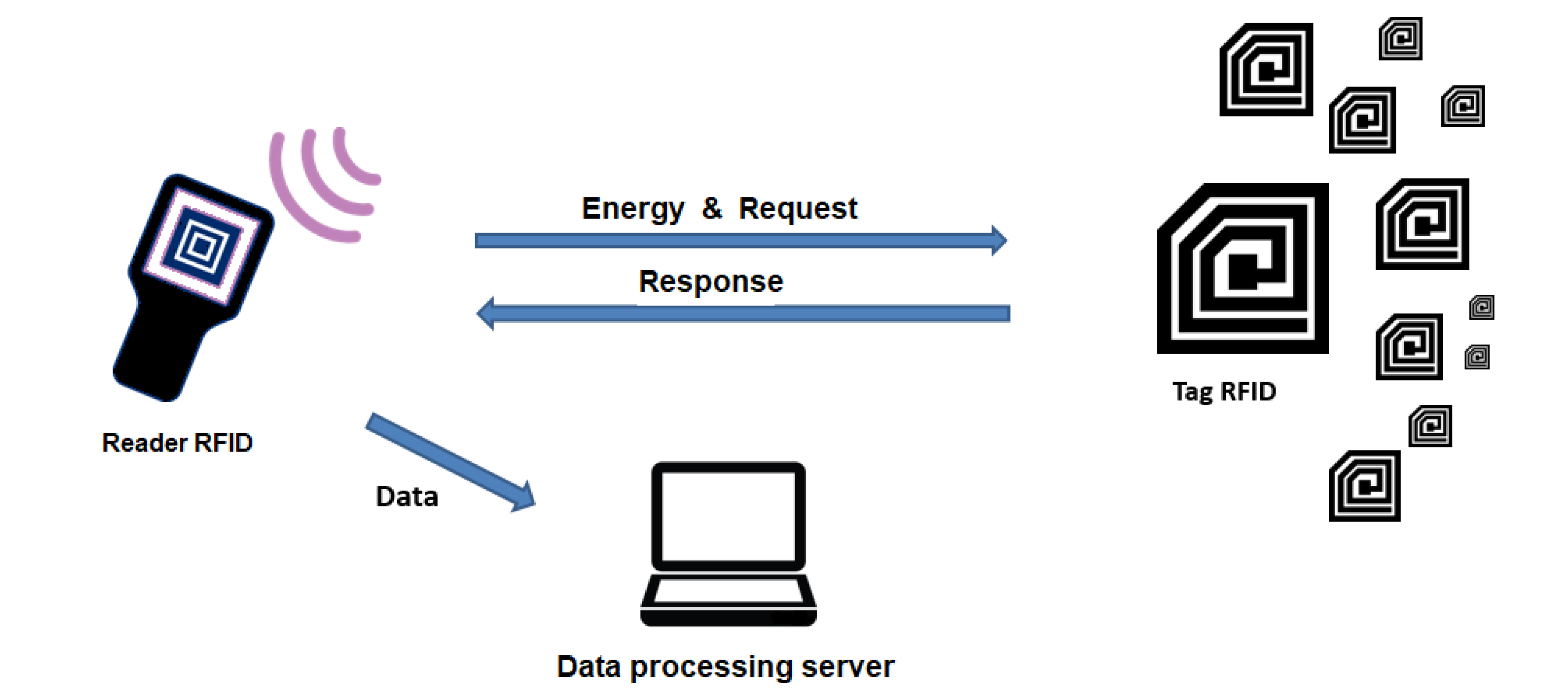
:1. Introduction
2. Background and Related Work
2.1. Background
2.1.1. RRI—Reader-to-Reader Interference
2.1.2. RTI—Reader-to-Tag Interference
2.2. Related Work
3. Proposed Algorithm
3.1. Basic Principle
- USED_PROTOCOL: The channel access methods used, FTDMA or CSMA.
- READER_IN_CHAIN: The readers constitute the FTDMA_Scheme to which this reader belongs.
- AFFECT_FREQ: The frequency to reuse.
- AFFECT_TS: The time slot to reuse.
- TYPE: The type of message (REQUEST1, REQUEST2, RESPONSE, ADD_TO_CHAIN or NEW_CHAIN) according to the use case.
- READER_SENDER: The reader source identification.
- READER_RECEIVER: The reader destination identification.
- READER_IN_CHAIN: The set of readers’ IDs using the same frequency.
- AFFECT_FREQ: The frequency to reuse by the destination reader.
- AFFECT_TS: The time slot to reuse by the destination reader.
3.2. The Description of the Proposed Algorithm FTSMAC
3.2.1. Interrogation Phase
3.2.2. Sending Phase
3.2.3. Reception Phase
3.3. Illustrative Example
4. Simulations and Results
- −
- A notification mechanism is used to exchange the frequency and temporary resource allocation packets through the control channel in a distributed mode by the readers to create the different FTDMA_Schemes.
- −
- FTDMA_Scheme can include and activate a maximum number of readers to obtain available resources and interrogate the tags without collision.
- −
- Use of a hybrid solution based on the MAC layer shared channel access methods: FDMA, TDMA, and CSMA.
- −
- FDMA is used for permanent data channel allocation to readers to solve the RRI collision problem.
- −
- TDMA is used for temporary allocation of the data channels to readers to solve the RRI collision problem. The number of TDMA periods is equal to the number of generated FTDMA_Schemes.
- −
- CSMA is used by readers that do not belong to any FTDMA_Scheme to manage concurrent access to the backup data channel.
- −
- Use of a backoff adapts the time of creation of the FTDMA_Scheme according to the number of readers to avoid control channel access collisions.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A






References
- Juels, A. RFID security and privacy: A research survey. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2006, 24, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahson, S.A.; Ilyas, M. RFID Handbook: Applications, Technology, Security, and Privacy; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Zhu, M.; Xiao, B.; Yang, X.; Gong, C.; Wu, J. Joint RFID and UWB Technologies in Intelligent Warehousing Management System. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 72, 11640–11655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelkhail, A.; Baroudi, U.; Raad, M.; Sheltami, T. Internet of things for healthcare monitoring applications based on RFID clustering scheme. Wirel. Netw. 2021, 27, 747–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, B.; Pei, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J. An indoor localization method based on AOA and PDOA using virtual stations in multipath and NLOS environments for passive UHF RFID. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 31772–31782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, A.; Dabo, A.A.A. A review of RFID in supply chain management: 2000–2015. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2016, 17, 189–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ajrawi, S.; Bialek, H.; Sarkar, M.; Rao, R.; Ahmed, S.H. Bi-directional channel modeling for implantable UHF–RFID transceivers in brain–computer interface applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 88, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, P.M.S.; Nandan, D. Utilization of the Internet of Things in Agriculture: Possibilities and Challenges. In Soft Computing: Theories and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 837–848. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; Kant, K. Internet of perishable logistics: Building smart fresh food supply chain networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 17675–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shousong, C.; Xiaoguang, W.; Yuanjun, Z. Revenue model of supply chain by internet of things technology. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 4091–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorov, M.; Ong, M.T.; Sridharan, R.V.; Nakamura, J.; Ohmura, R.; Khor, J.H. Ultralightweight mutual authentication RFID protocol for blockchain enabled supply chains. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 7273–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Gu, C.; Wang, Z.; Rocchio, J.; Hu, W.; Yu, X. Big data driven agricultural products supply chain management: A trustworthy scheduling optimization approach. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 49990–50002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W. An intelligent supply chain information collaboration model based on Internet of Things and Big Data. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 58324–58335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mo, L.; Zhang, D. Review on UHF RFID Localization methods. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2019, 3, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, S.A.; Ismail, W.; Zulkifli, C.Z.; Abdullah, S. Dual Band RFID-Based Blood Glucose Monitoring System in Wireless Sensor Network Platform. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2018, 103, 2229–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, R. Evaluation of Throughput of TDMA Anti-Collision Protocols in Static and Mobile RFID Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies, Split, Croatia, 18–21 June 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Golsorkhtabaramiri, M.; Issazadehkojidi, N.; Pouresfehani, N.; Mohammadialamoti, M.; Hosseinzadehsadati, S.M. Comparison of energy consumption for reader anti-collision protocols in dense RFID networks. Wirel. Netw. 2019, 25, 2393–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaluce, H.; Arjona, L.; Perallos, A.; Falcone, F.; Angulo, I.; Muralter, F. A review of iot sensing applications and challenges using RFID and wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Li, L.; Zhou, W. Design and implementation of a RFID reader/router in RFID-WSN hybrid system. Future Internet 2018, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobral, J.V.; Rodrigues, J.J.; Rabelo, R.A.; Lima Filho, J.C.; Sousa, N.; Araujo, H.S.; Holanda Filho, R. A framework for enhancing the performance of Internet of Things applications based on RFID and WSNs. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 107, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adame, T.; Bel, A.; Carreras, A.; Melia-Segui, J.; Oliver, M.; Pous, R. CUIDATS: An RFID–WSN hybrid monitoring system for smart health care environments. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 78, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfian, G.; Rhee, J.; Ahn, H.; Lee, J.; Farooq, U.; Ijaz, M.F.; Syaekhoni, M.A. Integration of RFID, wireless sensor networks, and data mining in an e-pedigree food traceability system. J. Food Eng. 2017, 212, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; He, S.; Cheng, P.; Sun, Y. Towards balanced energy charging and transmission collision in wireless rechargeable sensor networks. J. Commun. Netw. 2017, 19, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Jing, C.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, X. A new underdetermined NMF based anti-collision algorithm for RFID systems. ISA Trans. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, G.; Xu, D.; Wang, S. Evaluation of Centralized Reader Anti-Collision Protocols for Mobile RFID System Based on Maximum Independent Set: A Simulation Study. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 123381–123397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, X.; Li, K. Efficient Anti-collision Algorithm for RFID EPC Generation-2 Protocol Based on Continuous Detection. Int. J. Wirel. Inf. Netw. 2020, 27, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Gu, Y.; Lv, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. RFID Reader Anti-Collision Based on Distributed Parallel Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Aggarwal, A.; Gopal, K. A novel and efficient reader-to-reader and tag-to-tag anti-collision protocol. IETE J. Res. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Li, Z.; Xia, Y.; Wang, K.; Pei, W. A widely linear MMSE anti-collision method for multi-antenna RFID readers. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 23, 644–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, H.; Golsorkhtabaramiri, M. A fair reader collision avoidance protocol for RFID dense reader environments. Wirel. Netw. 2018, 24, 1953–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, P.J.; Tsai, W.T. SwitchTable: An efficient anti-collision algorithm for RFID networks. Iet Commun. 2017, 11, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Sheng, Z.; Xie, L. A collision-tolerant-based anti-collision algorithm for large scale RFID system. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.T.; Li, H.; Lin, M.; Han, J.; Apduhan, B.O. NQA: A nested anti-collision algorithm for RFID systems. ACM Trans. Embed. Comput. Syst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbasian, A.; Safkhani, M. CNCAA: A new anti-collision algorithm using both collided and non-collided parts of information. Comput. Netw. 2020, 172, 107159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Jiang, N. Research on hybrid of ALOHA and multi-fork tree Anti-collision algorithm for RFID. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 183, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saia, R.; Carta, S.; Recupero, D.R.; Fenu, G. Internet of Entities (IoE): A Blockchain-based Distributed Paradigm for Data Exchange between Wireless-based Devices. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Sensor Networks, Prague, Czech Republic, 26–27 February 2019; pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Su, X. An anti-collision algorithm for rfid based on an array and encoding scheme. Information 2018, 9, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Safa, H.; El-Hajj, W.; Meguerditchian, C.; Safa, H.; El-Hajj, W.; Meguerditchian, C. A distributed multi-channel reader anti-collision algorithm for RFID environments. Comput. Commun. 2015, 64, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbacke, A.A.; Mitton, N.; Rivano, H. A survey of RFID readers anticollision protocols. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2018, 2, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birari, S.M.; Iyer, S. PULSE: A MAC protocol for RFID networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, M.A.; Mitton, N.; Rivano, H. Rfid reader anticollision protocols for dense and mobile deployments. Electronics 2016, 5, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Olaleye, O.G.; Ali, A.; Perkins, D.; Bayoumi, M. Modeling and performance simulation of PULSE and MCMAC protocols in RFID-based IoT network using OMNeT++. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on RFID, Orlando, FL, USA, 10–12 April 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Golsorkhtabaramiri, M.; Issazadehkojidi, N. A distance based RFID reader collision avoidance protocol for dense reader environments. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 95, 1781–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno-Delgado, M.V.; Ferrero, R.; Gandino, F.; Pavon-Marino, P.; Rebaudengo, M. A geometric distribution reader anti-collision protocol for RFID dense reader environments. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2012, 10, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assarian, A.; Khademzadeh, A.; HosseinZadeh, M.; Setayeshi, S. A beacon analysis-based RFID reader anti-collision protocol for dense reader environments. Comput. Commun. 2018, 128, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, G.; Wang, S. NFRA-AIC: A RFID reader anti-collision protocol with adaptive interrogation capacity. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 86493–86509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, J.B.; Yim, S.B.; Lee, T.J. An efcient reader anticollision algorithm in dense RFID networks with mobile RFID readers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 23262336. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.H.; Nguyen, N.T.; Pham, V.T.; Yeh, Y.H. A maximum-weight-independent-set-based algorithm for reader-coverage collision avoidance arrangement in RFID networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 16, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddeb, A.; Jaballah, A. Algorithm for readers arrangement without collision in RFID networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 18th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Computing, Applications and Technologies (PDCAT), Taipei, Taiwan, 18–20 December 2017; pp. 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.; Choudhury, S.; Wei, R. A machine learning auxiliary approach for the distributed dense RFID readers arrangement algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 42270–42284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golsorkhtabaramiri, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Reshadi, M.; Rahmani, A.M. A reader anti-collision protocol for RFID-enhanced wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2015, 81, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkenzeller, K. RFID Handbook: Fundamentals and Applications in Contactless Smart Cards, Radio Frequency Identification and Near-Field Communication; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]










| Attributes | PULSE | CORA | MCMAC | DIMAC | NFRA-AIC | BACP | DRCA | MWISBA | MWISBAII | Distributed-MWISBAII | FTSMAC (Proposed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRI | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RTI | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Distributed | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| Centralized | - | - | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | - |
| Multi data channel | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ |
| CSMA | ✓ | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ |
| FDMA | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | ✓ |
| TDMA | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ |
| Message Type | READER_SENDER | READER_RECEIVER | READER_IN_CHAIN | AFFECT_FREQ | AFFECT_TS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REQUEST1 | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - |
| REQUEST2 | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| RESPONSE | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - |
| ADD_TO_CHAIN | - | ✓ | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| NEW_CHAIN | - | ✓ | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| USED_PROTOCOLUSED_PROTOCOL | READER_IN_CHAIN | AFFECT_FREQ | AFFECT_TS |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Simulation range | 300 × 300 m |
| Number of readers (case 1) | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 |
| Number of readers (case 2) | 50 |
| Simulation time (case 1) | 300 |
| Simulation time (case 2) | 0, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300 |
| Number of tags (case 2) | 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 |
| Reader and Tag position | Random |
| Type of antenna | Omni-directional |
| Read range of data channel (rr) | 3.5 m |
| Collision range of data channel (cr) | 8 m |
| Read range of control channel (crr) | 2 × cr |
| Collision range of control channel (crc) | 30 m |
| Number of Data Channel (case 1) | 3 |
| Number of Data Channel (case 2) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
| Number of Time Slot (case 1) | 3 |
| Number of Time Slot (case 2) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
| Number of control channel | 1 |
| Number of samples for evaluation | 10 |
| protocols compared | PULSE, MCMAC |
| Backoff | (ReaderID-1) × CW |
| CW | Convergence time of all readers |
| Tmin | 5 ms (Standard EPC) |
| T | Neighboring readers response time |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mafamane, R.; Ait Mansour, A.; Ouadou, M.; Minaoui, K. FTSMAC: A Multi-Channel Hybrid Reader Collision Avoidance Protocol for RFID Network. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2021, 10, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan10030046
Mafamane R, Ait Mansour A, Ouadou M, Minaoui K. FTSMAC: A Multi-Channel Hybrid Reader Collision Avoidance Protocol for RFID Network. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks. 2021; 10(3):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan10030046
Chicago/Turabian StyleMafamane, Rachid, Asmae Ait Mansour, Mourad Ouadou, and Khalid Minaoui. 2021. "FTSMAC: A Multi-Channel Hybrid Reader Collision Avoidance Protocol for RFID Network" Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks 10, no. 3: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan10030046
APA StyleMafamane, R., Ait Mansour, A., Ouadou, M., & Minaoui, K. (2021). FTSMAC: A Multi-Channel Hybrid Reader Collision Avoidance Protocol for RFID Network. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, 10(3), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan10030046






