Interference Alignment for Cognitive Radio Communications and Networks: A Survey
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Notation
2. Interference Alignment
2.1. Principles
2.2. General IA Techniques
2.3. Applications
3. Interference Alignment in Cognitive Radio: First Paradigm
3.1. System Model For Paradigm 1
3.2. Techniques For IA in CR Networks
3.2.1. Propagation Delay IA
3.2.2. Leakage of Interference Signals/Distributed Algorithm IA
3.2.3. Symbol Extensions IA
3.2.4. OFDMA IA
3.2.5. Other Endeavours
3.3. Applications
4. Interference Alignment in Cognitive Radio: Second Paradigm
4.1. System Model for Paradigm II
- The PU and SUs operate in the same frequency band and all channels are Rayleigh flat-fading.
- The PU link is a single user MIMO channel, which is represented as a matrix, with channel gains .
- CSI is perfectly known at both the transmitter and receiver, thus is also perfectly known.
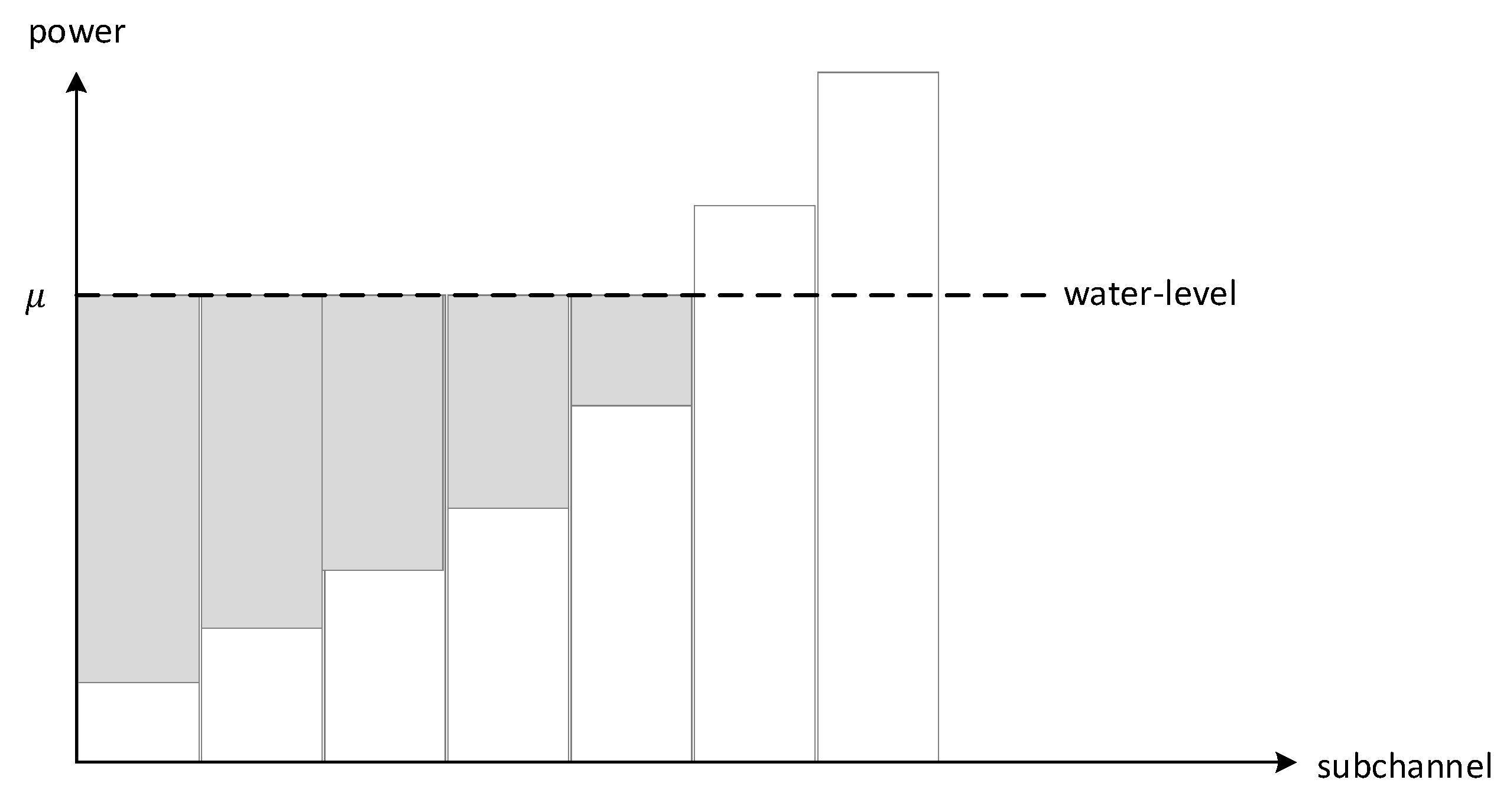
4.2. Water-Filling Techniques For IA in CR Networks
4.2.1. Spatial Water Filling (SWF)
Single User MIMO SU Link
Multi User MIMO SU Link
Leakage Interference
Interference Cancellation
4.2.2. Space–Time Water-Filling (ST-WF)
4.3. Other Endeavours
5. Comparison of Research Literature and Analysis
6. Open Research Challenges
6.1. Channel State Information Knowledge and Feedback
6.2. CR Network Synchronization and Organization
6.3. IA in Relay Based CR Networks
6.4. Algorithms Optimization of IA in CR Networks
6.5. Practical Implementation of IA in CR Networks
6.6. IA in CR Networks with Reinforcement Learning
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chuah, M.C.; Zhang, Q. Design and Performance of 3G Wireless Networks and Wireless LANs; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rehmani, M.H.; Faheem, Y. Cognitive Radio Sensor Networks: Applications, Architectures, and Challenges; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Medeisis, A.; Holland, O. Cognitive Radio Policy and Regulation Techno-Economic Studies to Facilitate Dynamic Spectrum Access; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, W.A.; Jo, H.S.; Ikki, S.; Nekovee, M. Spectrum-Sharing Method for Co-Existence Between 5G OFDM-Based System and Fixed Service. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 77460–77475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitola, J.; Maguire, G.Q. Cognitive radio: Making software radios more personal. IEEE Pers. Commun. 1999, 6, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Long, Y.; Wang, J.; Errapotu, S.M.; Li, H.; Pan, M.; Han, Z. D-FROST: Distributed Frequency Reuse-Based Opportunistic Spectrum Trading via Matching With Evolving Preferences. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 3794–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, H.-H.; Meng, W. Cooperative Communications for Cognitive Radio Networks—From Theory to Applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.C.; Chen, K.C.; Li, G.Y.; Mahonen, P. Cognitive radio networking and communications: An overview. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 3386–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, S.; Abolhassani, B. A new practical interference mitigation scheme for interference cognitive radio networks. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2012, 26, 1617–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S. Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered wireless communications. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2005, 23, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.B.H.; Werbach, K.; Sicker, D.C.; Bastidas, C.E.C. On the Application of Blockchains to Spectrum Management. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2019, 5, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, T.; Zhao, N.; Yin, H.; Yu, F.R. Interference alignment for overlay cognitive radio based on game theory. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 14th International Conference on Communication Technology, Chengdu, China, 9–11 November 2012; pp. 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Jafar, S.A. Interference Alignment—A New Look at Signal Dimensions in a Communication Network (no. 1); Now Publishers: Delft, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1–134. [Google Scholar]
- El Ayach, O.; Peters, S.; Heath, R.W. The practical challenges of interference alignment. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2013, 20, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, N.; Yu, F.R.; Jin, M.; Yan, Q.; Leung, V.C.M. Interference Alignment and Its Applications: A Survey, Research Issues, and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1779–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafar, S.A.; Fakhereddin, M.J. Degrees of Freedom for the MIMO Interference Channel. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 53, 2637–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cadambe, V.R.; Jafar, S.A. Interference Alignment and Degrees of Freedom of the K User Interference Channel. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2008, 54, 3425–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; No, J. Achievable Degrees of Freedom of Relay-Aided MIMO Cellular Networks Using Opposite Directional Interference Alignment. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 67, 4750–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddah-ali, M.; Motahari, A.; Khandani, A. Signaling over MIMO Multi-Base Systems: Combination of Multi-Access and Broadcast Schemes. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Seattle, WA, USA, 9–14 July 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafar, S.A. Degrees of Freedom on the MIMO X Channel-Optimality of the MMK scheme. CoRR 2006, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jafar, S.A.; Shamai, S. Degrees of Freedom Region of the MIMO X Channel. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2008, 54, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grokop, L.H.; Tse, D.N.C.; Yates, R.D. Interference Alignment for Line-of-Sight Channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 5820–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torbatian, M.; Najafi, H.; Damen, M.O. Asynchronous Interference Alignment. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 11, 3148–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perlaza, S.M.; Fawaz, N.; Lasaulce, S.; Debbah, M. From Spectrum Pooling to Space Pooling: Opportunistic Interference Alignment in MIMO Cognitive Networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 3728–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zorzi, M.; Khamesi, A.R.; Lahouti, F. Exact Assessment of the Delay-Rate Tradeoff in Ergodic Interference Alignment. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Clerckx, B.; Chun, J.; Jeong, B.J. Lattice Reduction-Aided Successive Interference Cancelation for MIMO Interference Channels. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 4131–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Shin, W.-Y.; Jung, B.C.; Suh, C.; Paulraj, A. Opportunistic Downlink Interference Alignment for Multi-Cell MIMO Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 1533–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cadambe, V.R.; Jafar, S.A.; Maleki, H.; Ramchandran, K.; Suh, C. Asymptotic Interference Alignment for Optimal Repair of MDS Codes in Distributed Storage. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2013, 59, 2974–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shin, W.; Lee, J. Linear Degrees of Freedom for $K$ -user MISO Interference Channels With Blind Interference Alignment. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 1921–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Mo, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C. Linear Space-Time Interference Alignment for $K$ -User MIMO Interference Channels. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilina, P.; Ratnarajah, T. Linear Interference Alignment in Full-Duplex MIMO Networks With Imperfect CSI. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2017, 65, 5226–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sridharan, G.; Yu, W. Linear Beamformer Design for Interference Alignment via Rank Minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 5910–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Tandon, R.; Heath, R.W. Distributed Space–Time Interference Alignment With Moderately Delayed CSIT. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2015, 14, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ratnarajah, T.; Xue, J.; Khan, F.A. Interference Alignment in Two-Tier Randomly Distributed Heterogeneous Wireless Networks Using Stochastic Geometry Approach. IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 12, 2238–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zeng, S.; Wang, C.; Pan, D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. A Distributed Interference Alignment Approach Based on Grouping in Heterogeneous Network. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 2484–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, D.; Silva, A.; Gameiro, A. Retrospective Interference Alignment: Degrees of Freedom Scaling With Distributed Transmitters. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2017, 63, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gou, T.; Jafar, S.A. Subspace Alignment Chains and the Degrees of Freedom of the Three-User MIMO Interference Channel. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2014, 60, 2432–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Liang, Q. Partial Interference Alignment for Heterogeneous Cellular Networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 22592–22601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeldin, Y.H.; Seddik, K.G. Pseudo-Lattice Treatment for Subspace Aligned Interference Signals. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 4729–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhen, L.; Cui, S.; Shin, K.G.; Liu, J. Coordinated Multi-Point Transmissions Based on Interference Alignment and Neutralization. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 18, 3347–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaa, A.M.; Ismail, M.H. Achievable Degrees of Freedom of the$K$-User SISO Interference Channel With Blind Interference Alignment Using Staggered Antenna Switching. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 2825–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.F.; Huang, A.; Peng, M.; Qu, F.; Fan, L. On the Mode Switching of Reconfigurable-Antenna-Based Blind Interference Alignment. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 6958–6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahn, S.; Chae, S.H. Blind Integer-Forcing Interference Alignment for Downlink Cellular Networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 23, 306–309. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, B.; Wang, W.-Q.; Liu, C.C. Ergodic Interference Alignment for Spectrum Sharing Radar-Communication Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yuen, C. On Interference Alignment With Imperfect CSI: Characterizations of Outage Probability, Ergodic Rate and SER. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Lee, J. Retrospective Interference Alignment for the Two-Cell MIMO Interfering Multiple Access Channel. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2015, 14, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, D.; Silva, A.; Gameiro, A. Retrospective Interference Alignment for the K-User M × N MIMO Interference Channel. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2016, 15, 8368–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauryzbayev, G.; Alsusa, E. Interference Alignment Cancellation in Compounded MIMO Broadcast Channels With General Message Sets. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 3702–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauryzbayev, G.; Alsusa, E. Enhanced Multiplexing Gain Using Interference Alignment Cancellation in Multi-Cell MIMO Networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2016, 62, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Lee, N.; Yang, H.; Lee, J. Relay-Aided Successive Aligned Interference Cancellation for Wireless$X$Networks With Full-Duplex Relays. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Jiao, W.; Li, J. Interference Alignment and Cancelation for the Uplink of Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, L.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Davidson, T.N. Achievable Sum Rate and Degrees of Freedom of Opportunistic Interference Alignment in MIMO Interfering Broadcast Channel. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 67, 4062–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, F.R.; Zhao, N.; Yin, H.; Leung, V.C.M.; Zhang, Y. Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Based Optimization for Cache-Enabled Opportunistic Interference Alignment Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 10433–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzi, S.; Dietl, G.; Utschick, W. Large System Analysis of Interference Alignment Achievable Rates for the MIMO Interference Channel. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jie, F.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z. Interference alignment performance in gaussian interference channel. IET Commun. 2014, 8, 2619–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Tadaion, A. Sum-Rate Improvement in Cognitive Radio Through Interference Alignment. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sboui, L.; Ghazzai, H.; Rezki, Z.; Alouini, M. Achievable Rates of UAV-Relayed Cooperative Cognitive Radio MIMO Systems. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 5190–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, T.; Li, Z.; Yao, Y.-D.; Qi, P. Random, Persistent, and Adaptive Spectrum Sensing Strategies for Multiband Spectrum Sensing in Cognitive Radio Networks With Secondary User Hardware Limitation. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 14854–14866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Zhao, N.; Jin, M.; Kim, J.M. Optimal Transceiver Design for Interference Alignment Based Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2015, 19, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkadir, Y.; Simpson, O.; Nwanekezie, N.; Sun, Y. Space-time opportunistic interference alignment in cognitive radio networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Doha, Qatar, 3–6 April 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, A.; Bahrami, H.R.; Maleki, M.; Sastry, S. Spatial Sensing and Cognitive Radio Communication in the Presence of a$K$-User Interference Primary Network. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qin, C.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. Low Complexity Interference Alignment for mmWave MIMO Channels in Three-Cell Mobile Network. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Yang, C.; Anpalagan, A.; Ni, Q.; Guizani, M. Joint Interference Management in Ultra-Dense Small-Cell Networks: A Multi-Domain Coordination Perspective. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2018, 66, 5470–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Nguyen, D.H.N.; Do-Hong, T.; Ngo-Van, S. Achievable Rates With Cooperative Spectrum Sharing in the Modulation-Based Dimension. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 654–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Wen, J.; Cao, J. Interference-Aware Cooperative Communication in Multi-Radio Multi-Channel Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2016, 65, 1528–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Qin, X.; Yuan, X.; Shi, Y.; Hou, Y.T.; Lou, W. Cooperative Interference Neutralization in Multi-Hop Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2018, 66, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvandi, M.; Mehmet-Ali, M.; Hayes, J.F. Delay Optimization and Cross-Layer Design in Multihop Wireless Networks With Network Coding and Successive Interference Cancelation. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sboui, L.; Ghazzai, H.; Rezki, Z.; Alouini, M. Achievable Rate of Spectrum Sharing Cognitive Radio Multiple-Antenna Channels. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2015, 14, 4847–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasani-Baferani, M.; Zeinalpour-Yazdi, Z.; Abouei, J. Interference alignment in overlay cognitive radio femtocell networks. IET Commun. 2016, 10, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubail, D.; El-Absi, M.; Ikki, S.S.; Mesbah, W.; Kaiser, T. Artificial Noise-Based Physical-Layer Security in Interference Alignment Multipair Two-Way Relaying Networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 19073–19085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Yu, F.R.; Li, M.; Yan, Q.; Leung, V.C.M. Physical layer security issues in interference- alignment-based wireless networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, F.L.; Rossetto, F.; Bauch, G. Time Interference Alignment via Delay Offset for Long Delay Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2014, 62, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosleh, S.; Abouei, J.; Aghabozorgi, M.R. Distributed Opportunistic Interference Alignment Using Threshold-Based Beamforming in MIMO Overlay Cognitive Radi. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 3783–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q. SERS: Social-Aware Energy-Efficient Relay Selection in D2D Communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 5331–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, P.; Gerstacker, W.H. Sensing Algorithms and Protocol for Simultaneous Sensing and Reception-Based Cognitive D2D Communications in LTE-A Systems. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2018, 4, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Wang, R.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Li, P.; Dou, J. Degrees of Freedom of the Circular Multirelay MIMO Interference Channel in IoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadambe, V.R.; Jafar, S.A. Degrees of Freedom of Wireless Networks—What a Difference Delay Makes. In Proceedings of the 2007 Conference Record of the Forty-First Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 4–7 November 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ratnarajah, T. A Novel Interference Draining Scheme for Cognitive Radio Based on Interference Alignment. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Symposium on New Frontiers in Dynamic Spectrum (DySPAN), Singapore, 6–9 April 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gomadam, K.; Cadambe, V.R.; Jafar, S.A. A Distributed Numerical Approach to Interference Alignment and Applications to Wireless Interference Networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 3309–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Ratnarajah, T.; Zhou, H.; Liang, Y.C. Interference alignment for peer-to-peer underlay MIMO cognitive radio network. In Proceedings of the 2011 Conference Record of the Forty Fifth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR), Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 6–9 November 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Palomar, D.P.; Ottersten, B. Statistically Robust Design of Linear MIMO Transceivers. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 3678–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Ratnarajah, T. Robust joint signal and interference alignment for MIMO cognitive radio network. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Shanghai, China, 1–4 April 2012; pp. 448–452. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Dong, L.; Ratnarajah, T.; Du, H. Robust joint signal and interference alignment in cognitive radio networks with ellipsoidal channel state information uncertainties. IET Commun. 2013, 7, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.R.; Xue, F. An iterative algorithm for joint signal and interference alignment. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Austin, TX, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2293–2297. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.; El Ghaoui, L.; Féron, É.; Balakrishnan, V. Linear Matrix Inequalities in System and Control Theory; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-J.; Giannakis, G.B. Optimal Resource Allocation for MIMO Ad Hoc Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 3117–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Park, S. Performance analysis of multiple-input multiple-output interference alignment with user selection. IET Commun. 2015, 9, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, H.; Wang, C.; Skoglund, M. Ergodic Interference Alignment With Limited Feedback: Power Control and Rate Adaptation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2015, 14, 6679–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddah-Ali, M.A.; Motahari, A.S.; Khandani, A.K. Communication Over MIMO X Channels: Interference Alignment, Decomposition, and Performance Analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2008, 54, 3457–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoli, J.; Ghasemi, A.; Khandani, A.K. Interference and X Networks With Noisy Cooperation and Feedback. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2015, 61, 4367–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ratnarajah, T.; Liang, Y. On secondary network interference alignment in cognitive radio. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN), Aachen, Germany, 3–6 May 2011; pp. 637–641. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaojuan, B. Space alignment for cognitive transmission with multiple primary users. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 1619–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, H.; Chou, C.; Wu, J.; Chang, R.Y. On the Achievable Degrees of Freedom of Two-Cell Multiuser MIMO Interference Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2014, 62, 2880–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Lee, N.; Lim, J.; Shin, C.; Jang, K. On the Design of Interference Alignment Scheme for Two-Cell MIMO Interfering Broadcast Channels. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2011, 10, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, I. Degrees of Freedom for Mutually Interfering Broadcast Channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2012, 58, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, R.; Liu, Q. On Feasibility of Interference Alignment for L-Cell Constant Cellular Interfering Networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2012, 16, 714–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maso, M.; Lakshminarayana, S.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Poor, H.V. The Price of Self-Sustainability for Block Transmission Systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maso, M.; Lakshminarayana, S.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Poor, H.V. A Composite Approach to Self-Sustainable Transmissions: Rethinking OFDM. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2014, 62, 3904–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Absi, M.; Shaat, M.; Bader, F.; Kaiser, T. Interference Alignment With Frequency-Clustering for Efficient Resource Allocation in Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2015, 14, 7070–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Absi, M.; Shaat, M.; Bader, F.; Kaiser, T. Interference alignment with frequency-clustering for efficient resource allocation in cognitive radio networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 8–12 December 2014; pp. 979–985. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Swindlehurst, A.; Wei, J. Rank minimization designs for underlay MIMO cognitive radio networks with completely unknown primary CSI. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Anaheim, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazel, M.; Hindi, H.; Boyd, S.P. Log-det heuristic for matrix rank minimization with applications to Hankel and Euclidean distance matrices. In Proceedings of the 2003 American Control Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 4–6 June 2003; pp. 2156–2162. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ali, A.K.; Sun, Y.; Felice, M.D.; Paavola, J.; Chowdhury, K.R. Accessing Spectrum Databases Using Interference Alignment in Vehicular Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Yu, F.R.; Sun, H.; Li, M. Adaptive Power Allocation Schemes for Spectrum Sharing in Interference-Alignment-Based Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 3700–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, N.; Sun, Y.; Yu, F.R. Interference Alignment Based on Antenna Selection With Imperfect Channel State Information in Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 5497–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Du, X. Aligning Guard Zones of Massive MIMO in Cognitive Femtocell Networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2014, 18, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.N.R.S.V.; Hossain, E.; Bhargava, V.K. Energy Efficiency in Massive MIMO-Based 5G Networks: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, B.; Yener, A. Selective Interference Alignment for MIMO Cognitive Femtocell Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Cespedes, M.; Plata-Chaves, J.; Toumpakaris, D.; Jafar, S.A.; Armada, A.G. Cognitive Blind Interference Alignment for Macro-Femto Networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 5121–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbetli, S.; Yener, A. Transceiver optimization for multiuser MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2004, 52, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, A.; Jafar, S.A.; Jindal, N.; Vishwanath, S. Capacity limits of MIMO channels. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2003, 21, 684–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Z.; Heath, R.W.; Andrews, J.G.; Evans, B.L. Space-Time Water-Filling for Composite MIMO Fading Channels. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2006, 2006, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Heath, R.W.; Andrews, J.G.; Evans, B.L. Comparison of space-time water-filling and spatial water-filling for MIMO fading channels. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, 2004. GLOBECOM ’04, Dallas, TX, USA, 29 November–3 December 2004; pp. 431–435. [Google Scholar]
- Krikidis, I. A SVD-Based Location Coding for Cognitive Radio in MIMO Uplink Channels. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2010, 14, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Lambotharan, S.; Pomeroy, S. Interference cancellation and alignment techniques for multiple-input and multiple-output cognitive relay networks. IET Signal Process. 2013, 7, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Fitz, M.P. Opportunistic Spatial Orthogonalization and Its Application in Fading Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2011, 5, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liang, Y. Exploiting Multi-Antennas for Opportunistic Spectrum Sharing in Cognitive Radio Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2008, 2, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X. Space alignment based on primary transmission-outage for cognitive transmission. Electron. Lett. 2012, 48, 1213–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, M.; El-Keyi, A.; Nafie, M. Constrained Interference Alignment and the Spatial Degrees of Freedom of MIMO Cognitive Networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 2994–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.; Park, D. Interference Alignment with Cooperative Primary Receiver in Cognitive Networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2012, 16, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetis, C.M.; Gou, T.; Jafar, S.A.; Kayran, A.H. On Feasibility of Interference Alignment in MIMO Interference Networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 4771–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.J.; Shin, W.-Y.; Jung, B.C.; Paulraj, A. Opportunistic Interference Alignment for MIMO Interfering Multiple-Access Channels. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 2180–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Tadaion, A. Interference alignment in cognitive radio networks. IET Commun. 2014, 8, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmohammadi, M.; Koyluoglu, O.O.; Khattab, T.M.S.; El Gamal, H. Joint interference cancellation and dirty paper coding for cognitive cellular networks. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Cancun, Mexico, 28–31 March 2011; pp. 1972–1976. [Google Scholar]
- Moussa, M.; Foukalas, F.; Khattab, T. Interference cancellation through interference alignment for downlink of cognitive cellular networks. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sboui, L.; Ghazzai, H.; Rezki, Z.; Alouini, M. Achievable Rate of a Cognitive MIMO Multiple Access Channel With Multi-Secondary Users. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2015, 19, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsinos, C.G.; Berberidis, K. Blind Opportunistic Interference Alignment in MIMO Cognitive Radio Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2013, 3, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, W.; Hattab, G.; Cherif, N.; Ibnkahla, M.; Abdelkefi, F.; Siala, M. Cooperative Spectrum Sensing With Heterogeneous Devices: Hard Combining Versus Soft Combining. IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 12, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z.; Cui, S.; Poor, H.V.; Sayed, A.H. Collaborative wideband sensing for cognitive radios. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Li, G.Y.; Maaref, A. Spatial-Frequency Signal Alignment for Opportunistic Transmission. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 1561–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, R. Rayleigh quotient based interference alignment spectrum sharing in MIMO cognitive radio networks. China Commun. 2015, 12, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Tugnait, J.K. Secure Degrees of Freedom in Cooperative MIMO Cognitive Radio Systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 4377–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Gerstlauer, A.; Heath, R.W. Distributed Real-Time Implementation of Interference Alignment with Analog Feedback. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 3513–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Zhao, N.; Leung, V.C.M. Interference-Alignment and Soft-Space-Reuse Based Cooperative Transmission for Multi-cell Massive MIMO Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 1907–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Acronym | Definition | Acronym | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | antenna selection | OFDM | orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing |
| BER | bit error rate | OIA | opportunistic interference alignment |
| BS | base stations | OSO | opportunistic spatial orthogonalisation |
| CP | cyclic-prefix | OTD | optimal transceiver design |
| CR | cognitive radios | PA | power allocation |
| CSI | channel state information | PU | primary users |
| CSS | cooperative spectrum sensing | Rx | receiver |
| DoF | degrees of freedom | SA | space-alignment |
| DOIA | distributed OIA | SD | spatial directions |
| DPC | dirty paper coding | SIA | selective IA |
| DSA | dynamic spectrum access | SIC | successive IC |
| EE | energy efficiency | SIMO | single-input multiple-output |
| FAP | femtocell access points | SINR | signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio |
| FBS | femtocell base stations | SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
| FC | fusion centre | SR | spatial reuse |
| FSA | fixed spectrum access | SS | spectrum sensing |
| GA | grouping algorithm | ST-WF | space–time water-filling |
| GLRT | generalized likelihood ratio test | SU | secondary users |
| IA | interference alignment | SVD | singular value decomposition |
| IC | interference channel | SWF | spatial water-filling |
| LIF | leakage of interference | TBF | threshold-based beamforming |
| MBS | macrocell base station | TDD | time division duplex |
| MEB | maximum eigenmode beamforming | TDMA | time-division multiple-access |
| MIMO | multiple-input multiple-output | TMA | transmission-mode adaptation |
| MU | macrocell | TO | transmit opportunities |
| MUE | macrocell users equipment | Tx | transmitter |
| References | IA Techniques | CSI | Signal Dimensions (Space, Time, Frequency, Time-Frequency) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [29,30,31,32] | Linear IA | Perfect/delayed | Single/Multi |
| [33,34,35,36] | Distributed IA | Local | Single |
| [37,38,39,40] | Subspace IA | Perfect | Multi |
| [29,41,42,43] | Blind IA | Absent | Single |
| [25,44,45] | Ergodic IA | Perfect/delayed | Single |
| [36,46,47] | Retrospective IA | Delayed | Single |
| [26,39,43] | Lattice Alignment | Perfect | Single |
| [40,48,49,50,51] | IA and Cancelation | Perfect | Single/Multi |
| [27,52,53] | Opportunistic IA | Perfect | Single/Multi |
| [28,54,55] | Asymptotic IA | Perfect | Single |
| References | Applications |
|---|---|
| [56,57,58,59,60] | Cognitive Radio Networks |
| [30,41,47,61] | K User Interference Channel |
| [27,30,31,46,47] | K User M × N MIMO Interference Channels |
| [62,63] | 5G Cellular Wireless Networks |
| [64,65,66] | Cooperative Interference Networks |
| [66,67] | Multihop Interference Networks |
| [68,69] | Ad hoc Networks |
| [70,71] | Physical Layer Security |
| [72,73] | Satellite Networks |
| [74,75] | D2D Networks |
| [50,76] | IoT Networks |
| [34,35,38,51] | Heterogeneous Networks |
| Average Sum Rates of the SU Network Based on the IA Techniques (bits/s/Hertz) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| SNR λ (dB) | Leakage of Interference [80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87] | OFDM [99,100,101] | Other Endeavours [103,104,105] |
| 5 | 5.5 | 9.0 | 1.0 |
| 10 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 |
| 15 | 15.0 | 11.0 | 9.5 |
| 20 | 20.0 | 12.0 | 16.0 |
| 25 | 28.0 | 13.0 | 24.0 |
| 30 | 32.5 | 23.0 | 33.0 |
| Average Sum Rates of the SU Network Based on the IA Techniques (bits/s/Hertz) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dB) | OPA/UPA [24] | Relay [115] | Spectrum Sharing [68] | Fast Sensing [61] |
| 5 | 2.5 | 7.5 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| 10 | 2.0 | 13.5 | 6.0 | 7.0 |
| 15 | 1.8 | 19.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| 20 | 1.5 | 25.5 | 14.0 | 13.0 |
| 25 | 0.5 | 32.5 | 14.0 | 16.0 |
| 30 | 0.1 | 38.0 | 13.5 | 20.0 |
| Average Sum Rates of the SU Network Based on the IA Techniques (bits/s/Hertz) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dB) | Symbol Extensions [93,97] | Feasibility [119,120,121,122,123] | LIF Perfect CSI [80,81,82,83] | LIF CSI Estimation [82,83] |
| 5 | 5 | 16 | 4.5 | 7 |
| 10 | 4 | 24 | 6.5 | 14 |
| 15 | 4 | 30 | 8.5 | 20 |
| 20 | 2 | 38 | 10.0 | 30 |
| 25 | 1 | 46 | 11.5 | 38 |
| 30 | 0.5 | 56 | 12.5 | 47 |
| Average Sum Rates of the SU Network Based on the IA Techniques (bits/s/Hertz) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dB) | Blind [127] | DOIA-TBF with MEB [73] | OIA-FAP with MEB [69] | OFDM-VFDM [99] |
| 5 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| 10 | 8.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| 15 | 13.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 8.0 |
| 20 | 17.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 12.0 |
| 25 | 22.0 | 9.0 | 10.0 | 16.0 |
| 30 | 26.0 | 12.0 | 14.0 | 20.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdulkadir, Y.; Simpson, O.; Sun, Y. Interference Alignment for Cognitive Radio Communications and Networks: A Survey. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2019, 8, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan8040050
Abdulkadir Y, Simpson O, Sun Y. Interference Alignment for Cognitive Radio Communications and Networks: A Survey. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks. 2019; 8(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan8040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdulkadir, Yusuf, Oluyomi Simpson, and Yichuang Sun. 2019. "Interference Alignment for Cognitive Radio Communications and Networks: A Survey" Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks 8, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan8040050
APA StyleAbdulkadir, Y., Simpson, O., & Sun, Y. (2019). Interference Alignment for Cognitive Radio Communications and Networks: A Survey. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, 8(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan8040050







