Learning Forecast-Efficient Yield Curve Factor Decompositions with Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dynamic Nelson and Siegel Model and Extensions
2.1. The Dynamic Nelson and Siegel Model
2.2. The Dynamic Nelson, Siegel, and Svensson Model
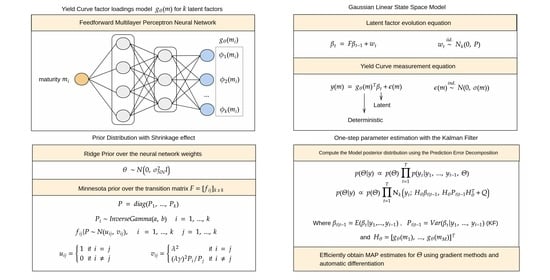
3. Neural Network Augmented State-Space Model
3.1. Model Definition
3.2. Specification of Prior Distribution
4. Empirical Evaluation
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Forecast Evaluation
- Obtain the forecast of the yield curve factors from t using the filtered factors and the estimated transition matrix ;
- Convert the forecasted factors using the estimated measurement matrix to obtain the prediction of the complete yield curve from t to :
- Update the Kalman filter recurrence equations using the next observation to obtain .
4.3. Results
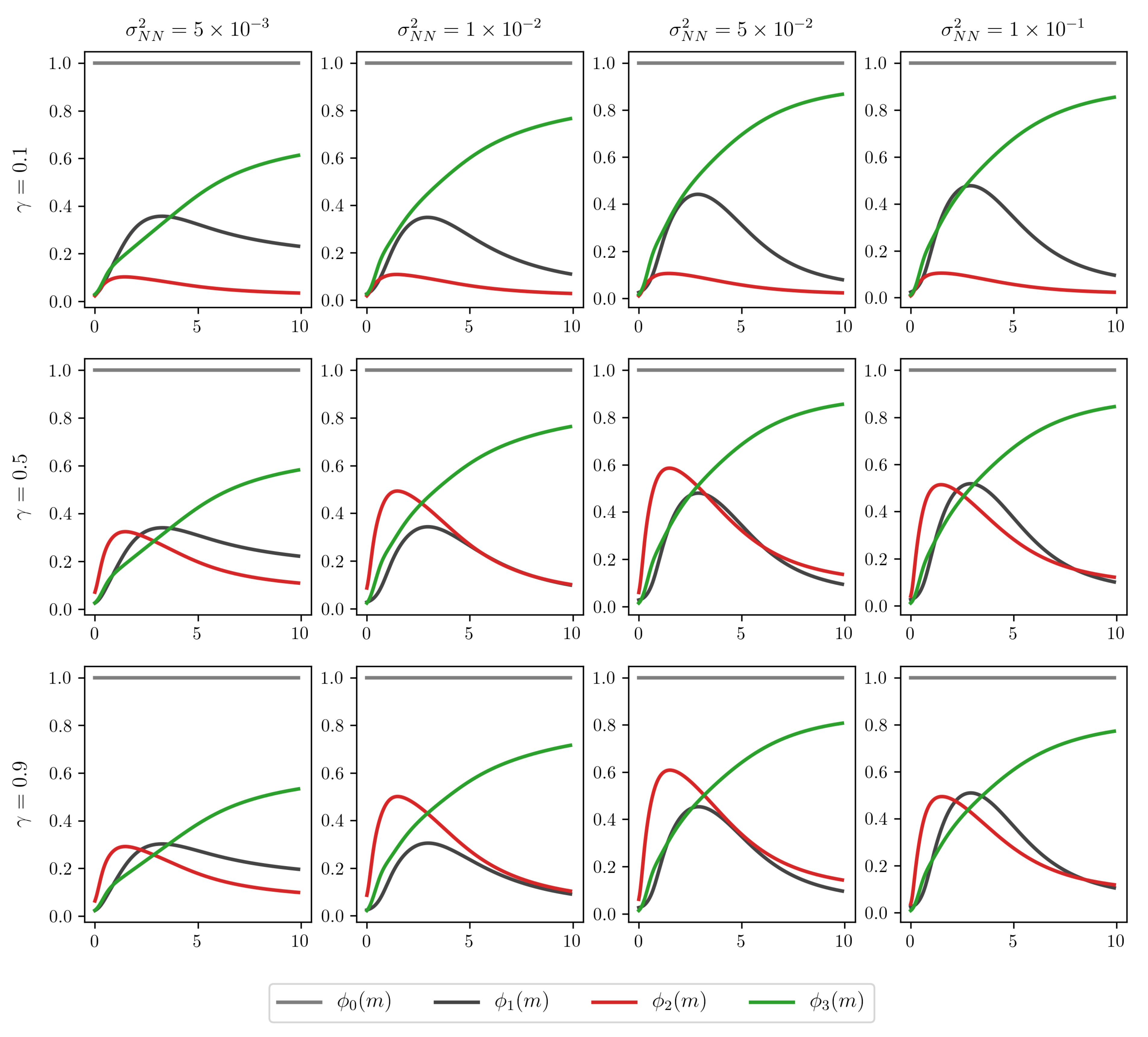
4.4. Impact Analysis of the Prior Distribution Hyperparameters
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Ang, Andrew, and Monika Piazzesi. 2003. A no-arbitrage vector autoregression of term structure dynamics with macroeconomic and latent variables. Journal of Monetary Economics 50: 745–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, Andrew R. 1991. Complexity regularization with application to artificial neural networks. In Nonparametric Functional Estimation and Related Topics. Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 561–76. [Google Scholar]
- Bingham, Eli, Jonathan P. Chen, Martin Jankowiak, Fritz Obermeyer, Neeraj Pradhan, Theofanis Karaletsos, Rohit Singh, Paul Szerlip, Paul Horsfall, and Noah D. Goodman. 2019. Pyro: Deep universal probabilistic programming. The Journal of Machine Learning Research 20: 973–78. [Google Scholar]
- Bowsher, Clive G., and Roland Meeks. 2008. The dynamics of economic functions: Modeling and forecasting the yield curve. Journal of the American Statistical Association 103: 1419–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cajueiro, Daniel O., Jose A. Divino, and Benjamin M. Tabak. 2009. Forecasting the yield curve for Brazil. Central Bank of Brazil Working Paper Series 197: 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Caldeira, Joao, Guilherme V. Moura, and Marcelo Savino Portugal. 2010. Efficient yield curve estimation and forecasting in Brazil. Revista Economia 11: 27–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, John C., Jonathan E. Ingersoll Jr., and Stephen A. Ross. 2005. A theory of the term structure of interest rates. In Theory of Valuation. Singapore: World Scientific, pp. 129–64. [Google Scholar]
- Diebold, Francis X., and Canlin Li. 2006. Forecasting the term structure of government bond yields. Journal of Econometrics 130: 337–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diebold, Francis X., Glenn D. Rudebusch, and S. Boragan Aruoba. 2006. The macroeconomy and the yield curve: A dynamic latent factor approach. Journal of Econometrics 131: 309–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diebold, Francis X., Canlin Li, and Vivian Z. Yue. 2008. Global yield curve dynamics and interactions: A dynamic Nelson–Siegel approach. Journal of Econometrics 146: 351–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duffie, Darrell, and Rui Kan. 1996. A yield-factor model of interest rates. Mathematical Finance 6: 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faria, Adriano, and Caio Almeida. 2018. A hybrid spline-based parametric model for the yield curve. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control 86: 72–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filos, Angelos, Sebastian Farquhar, Aidan N. Gomez, Tim G. J. Rudner, Zachary Kenton, Lewis Smith, Milad Alizadeh, Arnoud de Kroon, and Yarin Gal. 2019. A Systematic Comparison of Bayesian Deep Learning Robustness in Diabetic Retinopathy Tasks. arXiv arXiv:1912.10481. [Google Scholar]
- Hays, Spencer, Haipeng Shen, and Jianhua Z. Huang. 2012. Functional dynamic factor models with application to yield curve forecasting. The Annals of Applied Statistics 6: 870–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, David, Robert Jarrow, and Andrew Morton. 1992. Bond pricing and the term structure of interest rates: A new methodology for contingent claims valuation. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society 60: 77–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerl, Arthur E., and Robert W. Kennard. 1970. Ridge regression: Applications to nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics 12: 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, John, and Alan White. 1990. Pricing interest-rate-derivative securities. The Review of Financial Studies 3: 573–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, Rudolph Emil. 1960. A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. Transactions of the ASME–Journal of Basic Engineering 82: 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeCun, Yann A., Léon Bottou, Genevieve B. Orr, and Klaus-Robert Müller. 2012. Efficient backprop. In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 9–48. [Google Scholar]
- Litterman, Robert B. 1986. Forecasting with Bayesian vector autoregressions—Five years of experience. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics 4: 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- MacKay, David J. C. 1992. A practical Bayesian framework for backpropagation networks. Neural Computation 4: 448–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltz, Allan. 2002. Estimation of zero coupon curves in Datametrics. RiskMetrics Journal 3: 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mineo, Eduardo, Airlane Pereira Alencar, Marcelo Moura, and Antonio Elias Fabris. 2020. Forecasting the Term Structure of Interest Rates with Dynamic Constrained Smoothing B-Splines. Journal of Risk and Financial Management 13: 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neal, Radford M. 1992. Bayesian Training of Backpropagation Networks by the Hybrid Monte Carlo Method. Technical Report, Citeseer. Toronto: Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, Charles R., and Andrew F. Siegel. 1987. Parsimonious modeling of yield curves. Journal of Business 60: 473–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, Adam, Sam Gross, Francisco Massa, Adam Lerer, James Bradbury, Gregory Chanan, Trevor Killeen, Zeming Lin, Natalia Gimelshein, Luca Antiga, and et al. 2019. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32: 8026–37. [Google Scholar]
- Rall, Louis B. 1986. The Arithmetic of Differentiation. Mathematics Magazine 59: 275–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Särkkä, Simo, and Ángel F. García-Fernández. 2019. Temporal parallelization of bayesian filters and smoothers. arXiv arXiv:1905.13002. [Google Scholar]
- Svensson, Lars E. O. 1994. Estimating and Interpreting forward Interest Rates: Sweden 1992–1994. Technical Report. Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, Hellinton H., and Julio M. Stern. 2015. Non-negative matrix factorization and term structure of interest rates. AIP Conference Proceedings American Institute of Physics 1641: 369–77. [Google Scholar]
- Vasicek, Oldrich. 1977. An equilibrium characterization of the term structure. Journal of Financial Economics 5: 177–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, José, and Benjamin M. Tabak. 2008. Forecasting bond yields in the Brazilian fixed income market. International Journal of Forecasting 24: 490–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, Mark W., and Robert F. Engle. 1983. Alternative algorithms for the estimation of dynamic factor, mimic and varying coefficient regression models. Journal of Econometrics 23: 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wengert, Robert Edwin. 1964. A Simple Automatic Derivative Evaluation Program. Communications of the ACM 7: 463–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model | Maturity (Business Months) | Avg. | Std. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | |||
| RW | 0.95 | 0.95 | 1.07 | 1.47 | 1.99 | 2.66 | 2.90 | 2.98 | 3.02 | 3.03 | 3.03 | 2.19 | 0.87 |
| 2-step DNS | 1.02 | 0.79 | 1.14 | 2.15 | 2.54 | 2.66 | 2.99 | 3.03 | 3.00 | 3.15 | 3.34 | 2.34 | 0.89 |
| 1-step DNS | 1.10 | 0.81 | 1.17 | 2.20 | 2.53 | 2.80 | 2.95 | 2.94 | 2.95 | 3.05 | 3.20 | 2.34 | 0.84 |
| 2-step DSV | 0.77 | 0.79 | 1.05 | 1.46 | 2.16 | 2.68 | 2.90 | 3.01 | 2.98 | 3.04 | 3.15 | 2.18 | 0.93 |
| 1-step DSV | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.98 | 1.35 | 2.18 | 2.81 | 2.81 | 2.90 | 2.95 | 3.01 | 3.12 | 2.15 | 0.93 |
| 4-GLSS | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.97 | 1.51 | 2.16 | 2.79 | 2.81 | 2.89 | 2.96 | 3.01 | 3.08 | 2.15 | 0.93 |
| 5-GLSS | 0.69 | 0.89 | 1.28 | 1.89 | 2.10 | 2.60 | 2.87 | 3.06 | 3.10 | 3.02 | 3.01 | 2.23 | 0.87 |
| 4-NNSS | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.89 | 1.36 | 2.08 | 2.80 | 2.81 | 2.90 | 2.96 | 3.00 | 3.05 | 2.12 | 0.94 |
| 5-NNSS | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.89 | 1.37 | 2.07 | 2.65 | 2.85 | 2.96 | 3.00 | 2.98 | 2.96 | 2.10 | 0.95 |
| Model | Maturity (Business Months) | Avg. | Std. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | |||
| RW | 3.27 | 3.24 | 3.34 | 3.75 | 4.40 | 5.34 | 5.76 | 5.91 | 5.98 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 4.82 | 1.16 |
| 2-step DNS | 1.57 | 1.98 | 2.57 | 3.86 | 4.72 | 5.09 | 5.60 | 5.92 | 6.02 | 6.25 | 6.47 | 4.55 | 1.70 |
| 1-step DNS | 1.58 | 1.94 | 2.51 | 3.75 | 4.65 | 5.19 | 5.36 | 5.56 | 5.73 | 5.88 | 6.04 | 4.38 | 1.58 |
| 2-step DSV | 1.31 | 1.69 | 2.11 | 2.93 | 4.00 | 4.98 | 5.48 | 5.77 | 5.85 | 6.03 | 6.25 | 4.22 | 1.80 |
| 1-step DSV | 1.61 | 1.79 | 2.02 | 2.72 | 4.18 | 5.41 | 5.49 | 5.62 | 5.76 | 5.87 | 6.02 | 4.23 | 1.74 |
| 4-GLSS | 1.75 | 2.00 | 2.32 | 3.06 | 4.23 | 5.40 | 5.48 | 5.61 | 5.74 | 5.80 | 5.88 | 4.30 | 1.61 |
| 5-GLSS | 2.24 | 2.70 | 3.12 | 3.76 | 4.24 | 5.19 | 5.71 | 6.06 | 6.09 | 5.92 | 5.86 | 4.63 | 1.40 |
| 4-NNSS | 1.63 | 1.75 | 2.00 | 2.72 | 4.03 | 5.32 | 5.42 | 5.56 | 5.70 | 5.78 | 5.85 | 4.16 | 1.70 |
| 5-NNSS | 1.77 | 1.98 | 2.24 | 2.94 | 4.07 | 5.16 | 5.49 | 5.65 | 5.67 | 5.59 | 5.53 | 4.19 | 1.56 |
| Model | Maturity (Business Months) | Avg. | Std. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | |||
| RW | 9.35 | 9.33 | 9.34 | 9.46 | 9.87 | 11.09 | 11.89 | 12.05 | 12.00 | 11.99 | 11.96 | 10.76 | 1.21 |
| 2-step DNS | 4.51 | 5.20 | 5.90 | 7.52 | 9.05 | 10.27 | 11.27 | 11.77 | 11.92 | 12.20 | 12.45 | 9.28 | 2.87 |
| 1-step DNS | 4.42 | 5.03 | 5.63 | 7.14 | 8.93 | 10.37 | 10.80 | 11.03 | 11.17 | 11.27 | 11.37 | 8.83 | 2.63 |
| 2-step DSV | 3.64 | 4.24 | 4.80 | 6.05 | 7.50 | 9.24 | 10.42 | 11.08 | 11.36 | 11.76 | 12.11 | 8.38 | 3.09 |
| 1-step DSV | 4.20 | 4.42 | 4.68 | 5.77 | 8.14 | 10.46 | 10.87 | 11.01 | 11.10 | 11.15 | 11.24 | 8.46 | 2.93 |
| 4-GLSS | 4.98 | 5.29 | 5.57 | 6.32 | 8.12 | 10.32 | 10.69 | 10.83 | 10.90 | 10.89 | 10.93 | 8.62 | 2.47 |
| 5-GLSS | 6.49 | 6.80 | 7.01 | 7.21 | 7.91 | 9.92 | 10.83 | 11.26 | 11.27 | 11.08 | 10.99 | 9.16 | 1.95 |
| 4-NNSS | 4.14 | 4.40 | 4.67 | 5.60 | 7.70 | 10.09 | 10.58 | 10.79 | 10.91 | 10.96 | 11.02 | 8.26 | 2.85 |
| 5-NNSS | 4.81 | 5.04 | 5.24 | 5.89 | 7.50 | 9.58 | 10.16 | 10.34 | 10.34 | 10.25 | 10.21 | 8.12 | 2.32 |
| Model | Maturity (Business Months) | Avg. | Std. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | |||
| RW | 18.08 | 18.14 | 18.19 | 18.17 | 17.89 | 18.37 | 19.04 | 18.94 | 18.71 | 18.64 | 18.58 | 18.43 | 0.36 |
| 2-step DNS | 8.82 | 9.55 | 10.30 | 12.27 | 14.39 | 16.28 | 17.49 | 17.89 | 17.90 | 18.10 | 18.31 | 14.66 | 3.59 |
| 1-step DNS | 8.47 | 9.04 | 9.64 | 11.59 | 14.39 | 16.64 | 17.07 | 16.98 | 16.87 | 16.78 | 16.77 | 14.02 | 3.42 |
| 2-step DSV | 8.03 | 8.86 | 9.65 | 11.53 | 13.33 | 15.20 | 16.54 | 17.17 | 17.39 | 17.77 | 18.12 | 13.96 | 3.67 |
| 1-step DSV | 8.49 | 8.86 | 9.34 | 11.24 | 14.38 | 16.89 | 17.06 | 16.85 | 16.70 | 16.56 | 16.54 | 13.90 | 3.47 |
| 4-GLSS | 9.75 | 10.15 | 10.51 | 11.77 | 14.23 | 16.52 | 16.60 | 16.39 | 16.23 | 16.06 | 15.99 | 14.02 | 2.73 |
| 5-GLSS | 10.67 | 10.78 | 10.80 | 11.09 | 12.63 | 15.20 | 15.90 | 16.03 | 15.96 | 15.78 | 15.70 | 13.69 | 2.34 |
| 4-NNSS | 8.03 | 8.43 | 8.82 | 10.39 | 13.36 | 16.11 | 16.48 | 16.40 | 16.34 | 16.24 | 16.23 | 13.35 | 3.49 |
| 5-NNSS | 8.45 | 8.69 | 8.87 | 9.91 | 12.38 | 15.00 | 15.48 | 15.43 | 15.34 | 15.23 | 15.21 | 12.73 | 2.97 |
| Horizon (Days) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 2.16 | 2.15 | 2.14 | 2.14 | |
| 5 | 2.12 | 2.12 | 2.12 | 2.13 | |
| 2.13 | 2.13 | 2.15 | 2.12 | ||
| 4.44 | 4.36 | 4.30 | 4.29 | ||
| 20 | 4.09 | 4.10 | 4.13 | 4.12 | |
| 4.14 | 4.16 | 4.19 | 4.16 | ||
| 10.15 | 9.75 | 9.52 | 9.47 | ||
| 60 | 8.12 | 8.13 | 8.16 | 8.15 | |
| 8.20 | 8.24 | 8.28 | 8.27 | ||
| 18.63 | 17.70 | 17.16 | 17.07 | ||
| 120 | 13.11 | 13.11 | 13.18 | 13.17 | |
| 13.18 | 13.27 | 13.35 | 13.37 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kauffmann, P.C.; Takada, H.H.; Terada, A.T.; Stern, J.M. Learning Forecast-Efficient Yield Curve Factor Decompositions with Neural Networks. Econometrics 2022, 10, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics10020015
Kauffmann PC, Takada HH, Terada AT, Stern JM. Learning Forecast-Efficient Yield Curve Factor Decompositions with Neural Networks. Econometrics. 2022; 10(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics10020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleKauffmann, Piero C., Hellinton H. Takada, Ana T. Terada, and Julio M. Stern. 2022. "Learning Forecast-Efficient Yield Curve Factor Decompositions with Neural Networks" Econometrics 10, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics10020015
APA StyleKauffmann, P. C., Takada, H. H., Terada, A. T., & Stern, J. M. (2022). Learning Forecast-Efficient Yield Curve Factor Decompositions with Neural Networks. Econometrics, 10(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/econometrics10020015