A Foreign Object Detection Method for Belt Conveyors Based on an Improved YOLOX Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Foreign Object Detection Methods Based on Image Processing
2.2. Foreign Object Detection Method Based on Deep Learning
2.3. Discussion
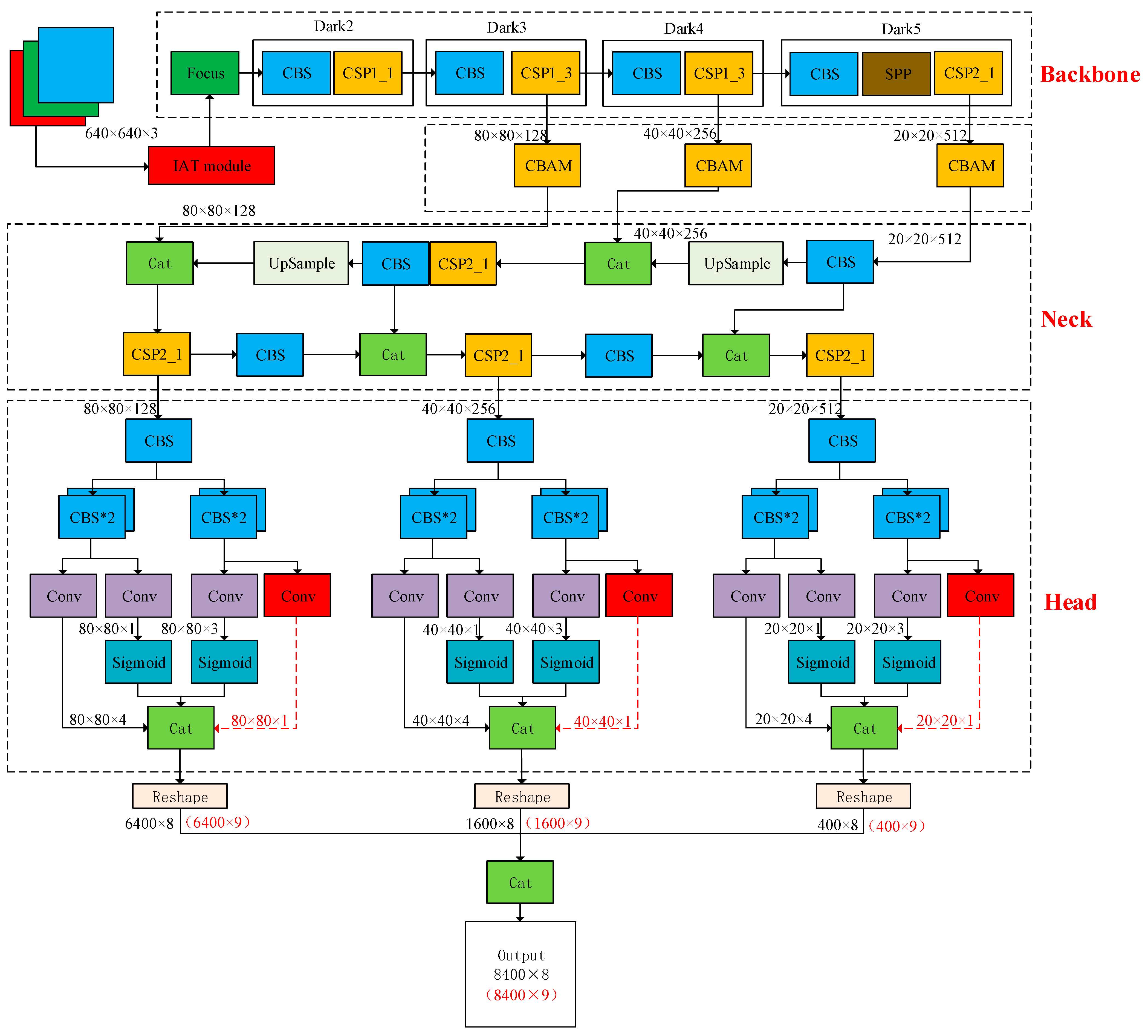
3. The Proposed Foreign Object Detection Method
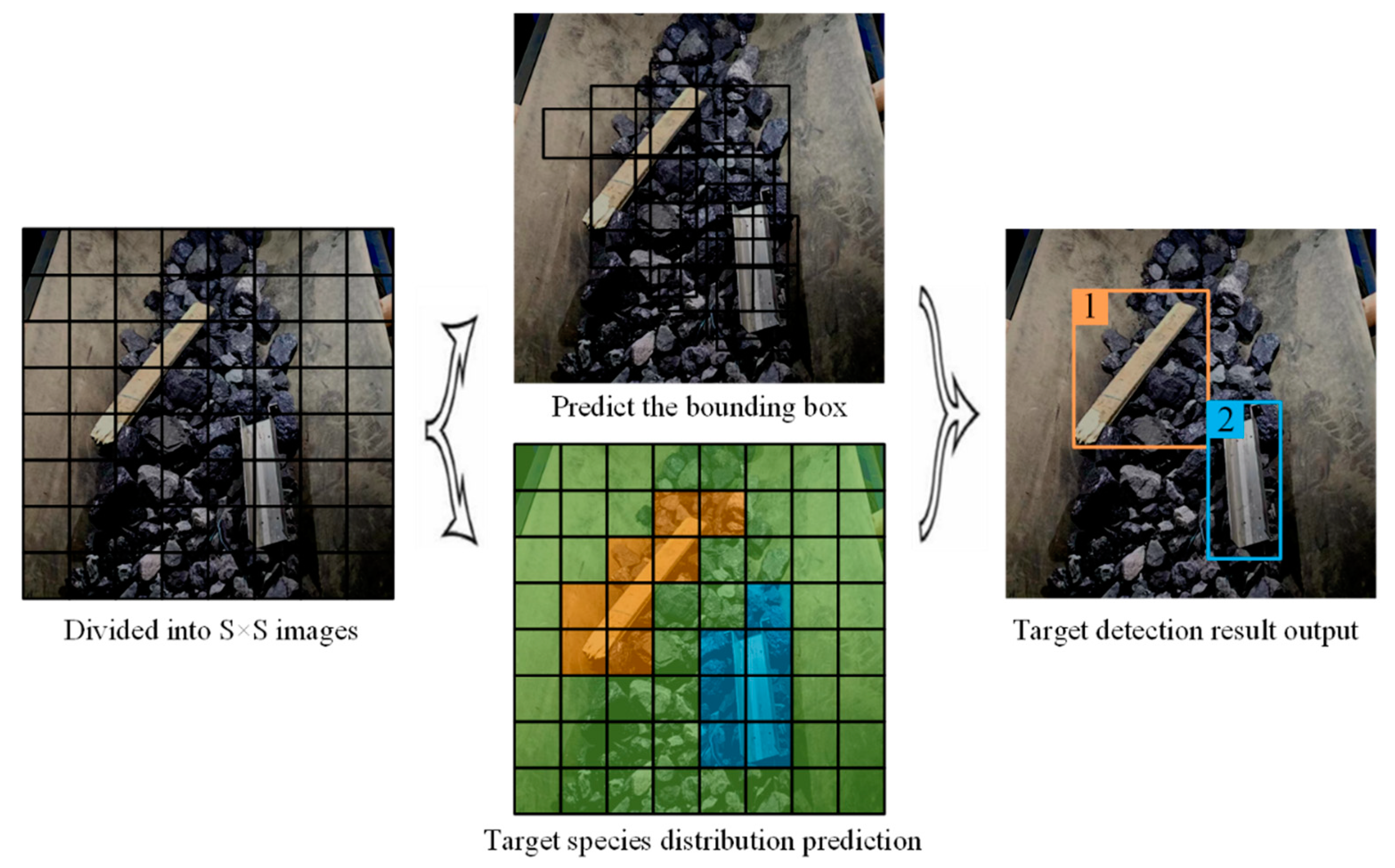
3.1. Target Detection of YOLO Model
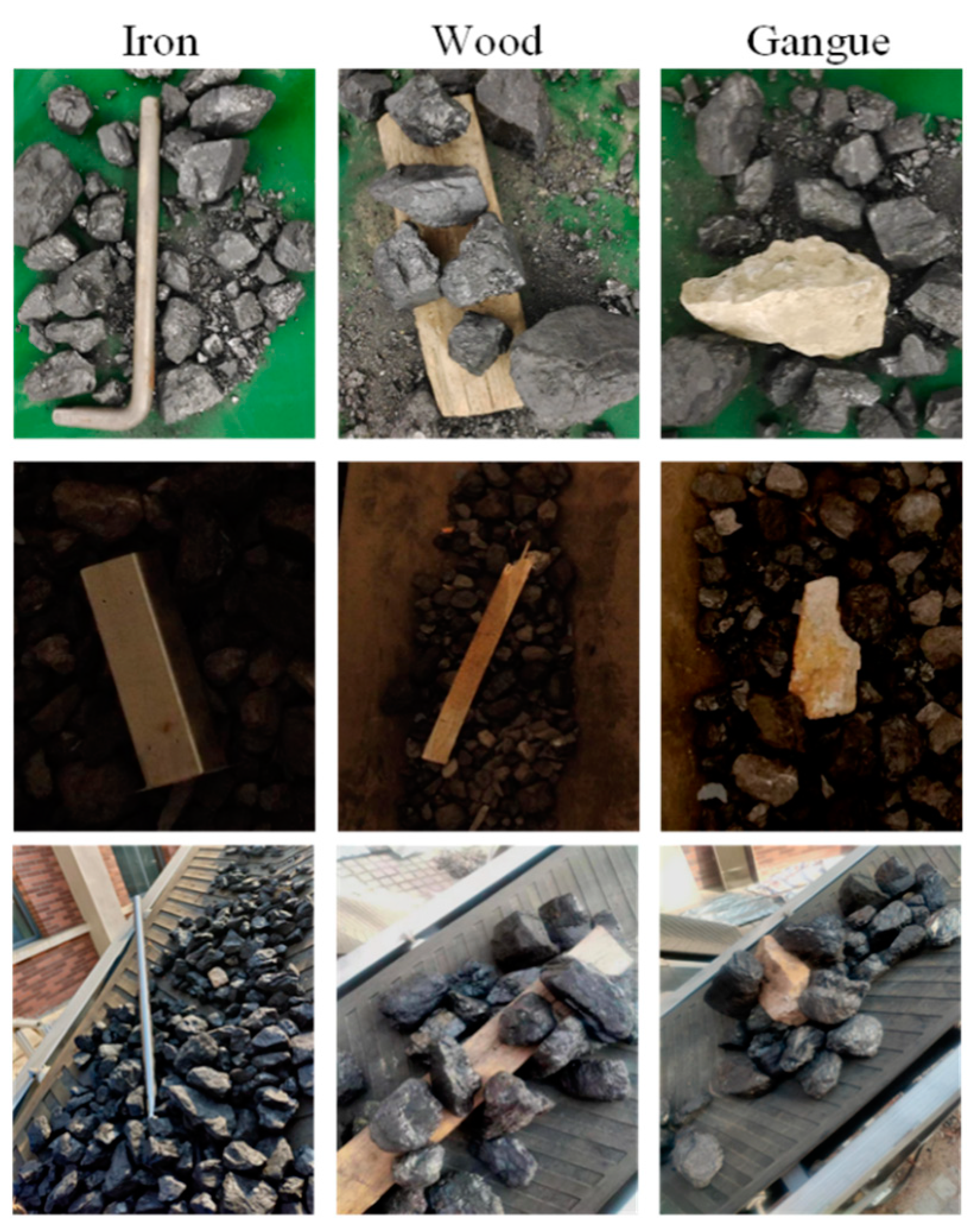
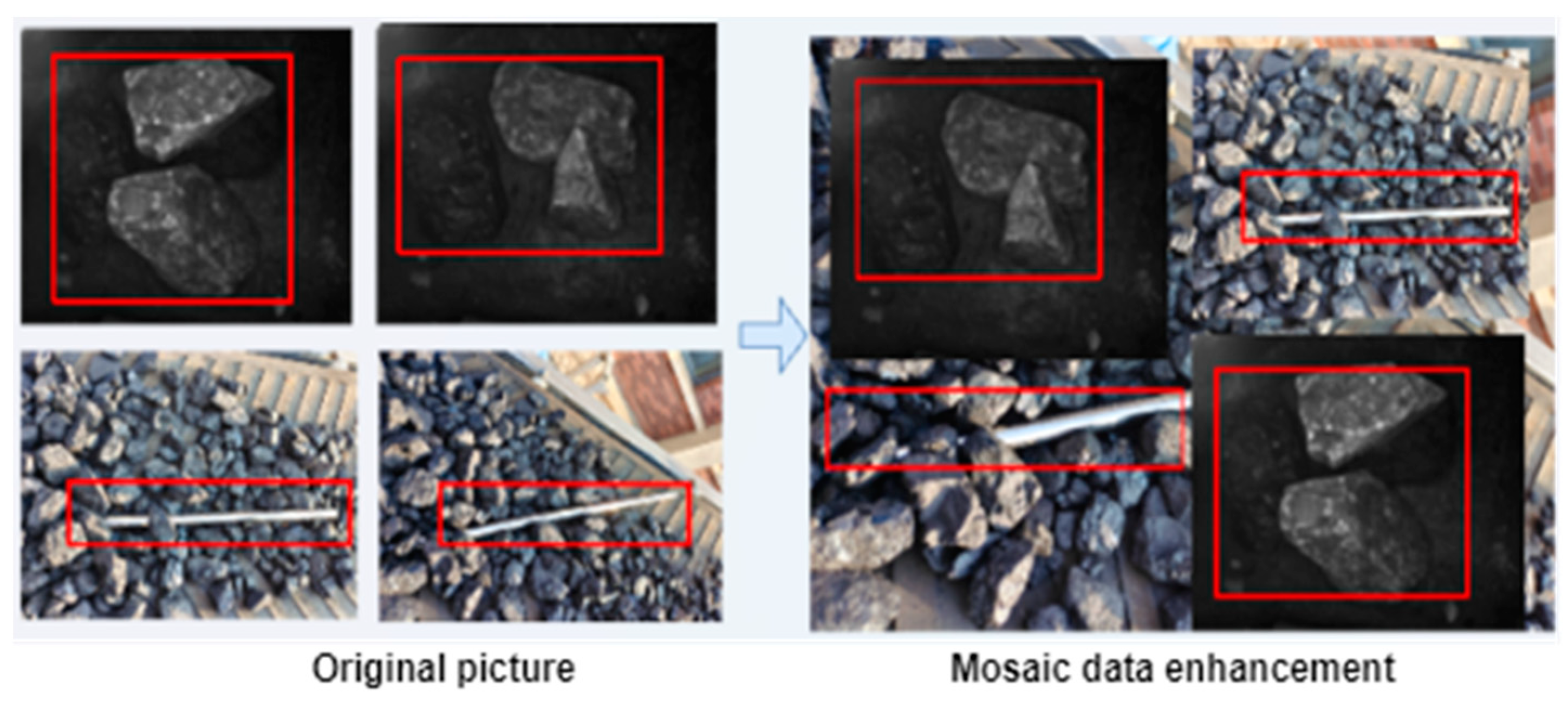
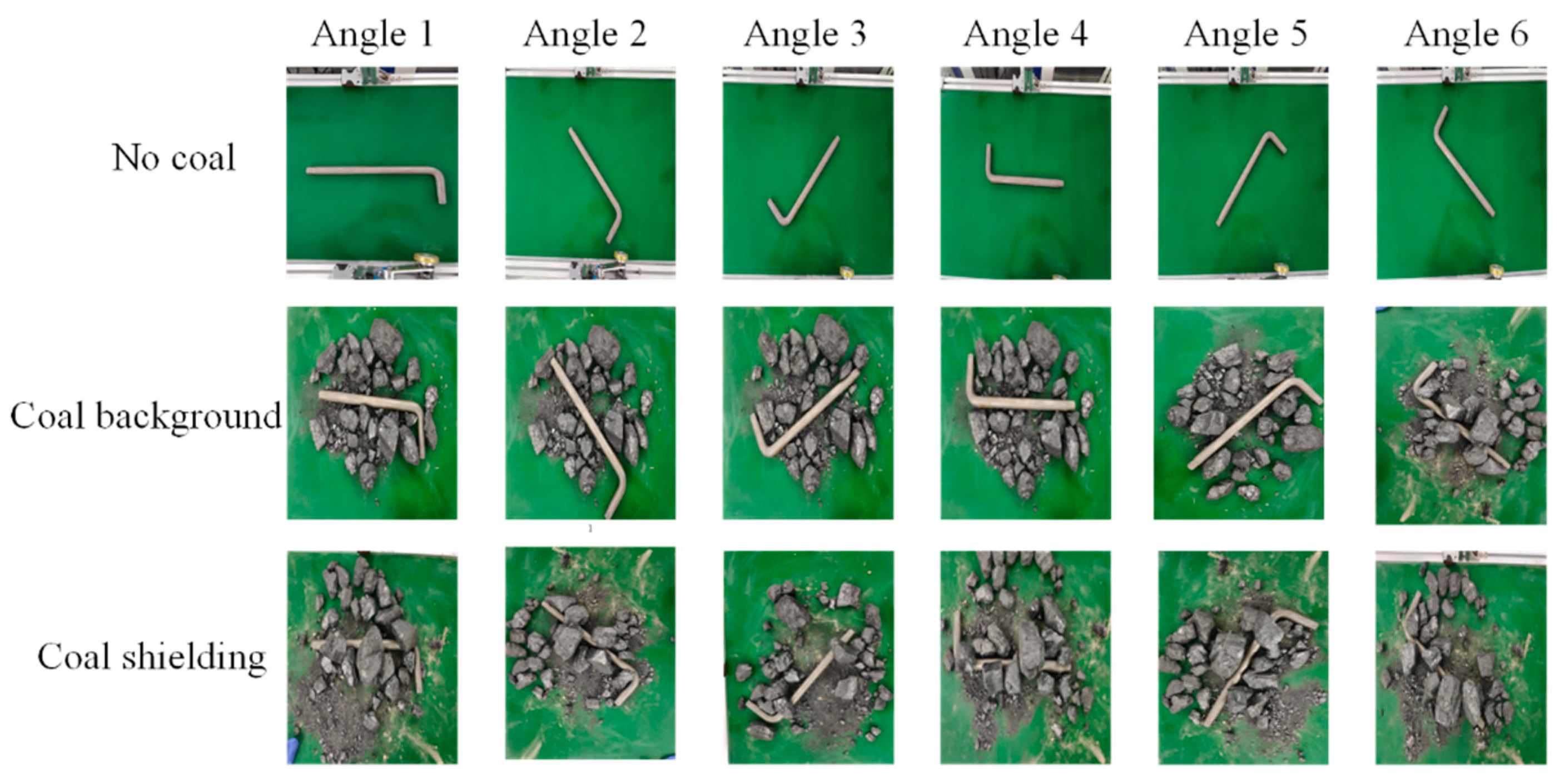
3.2. Established Foreign Object Image Dataset
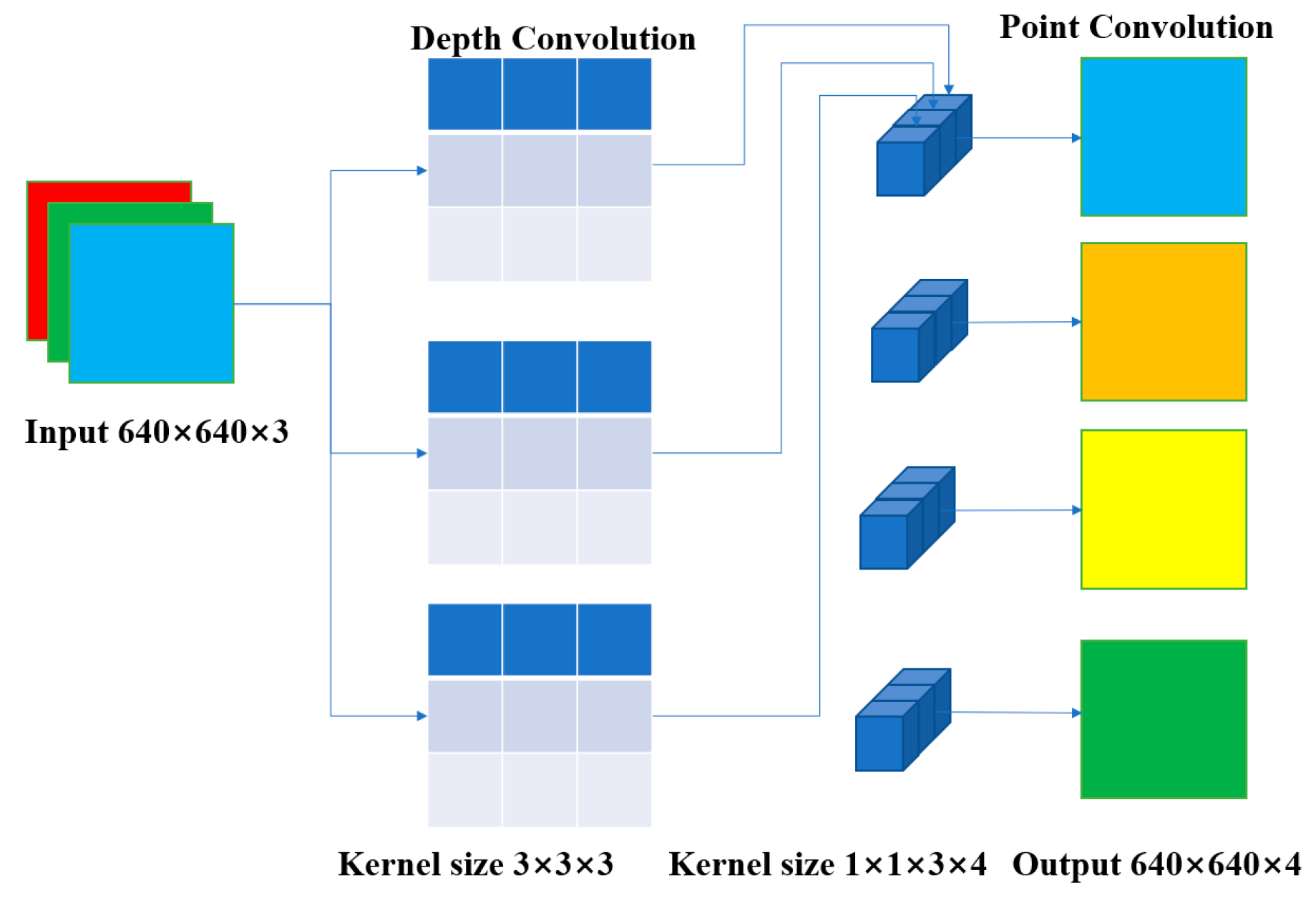
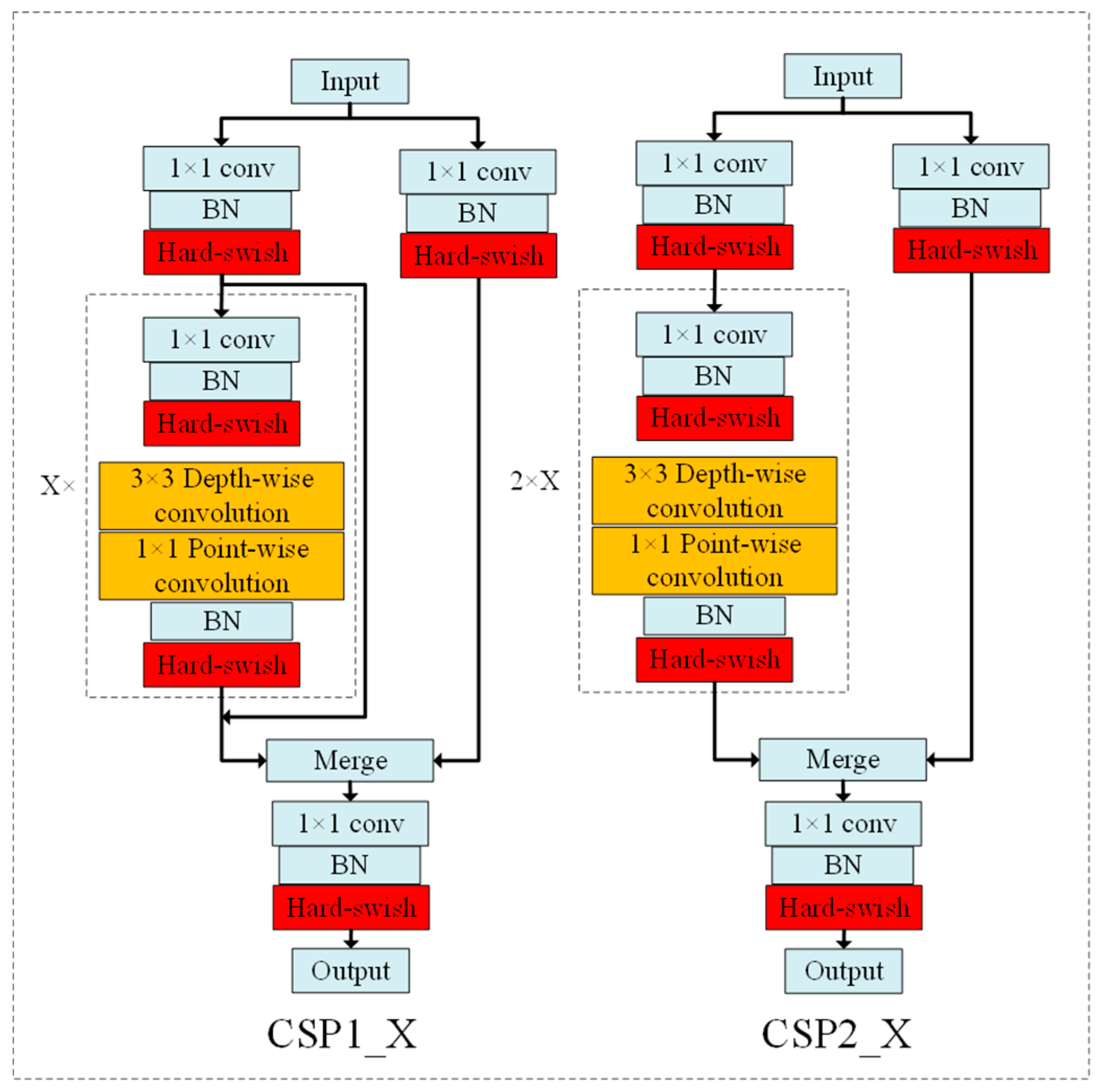
3.3. Improved Depthwise Separable Convolution Block
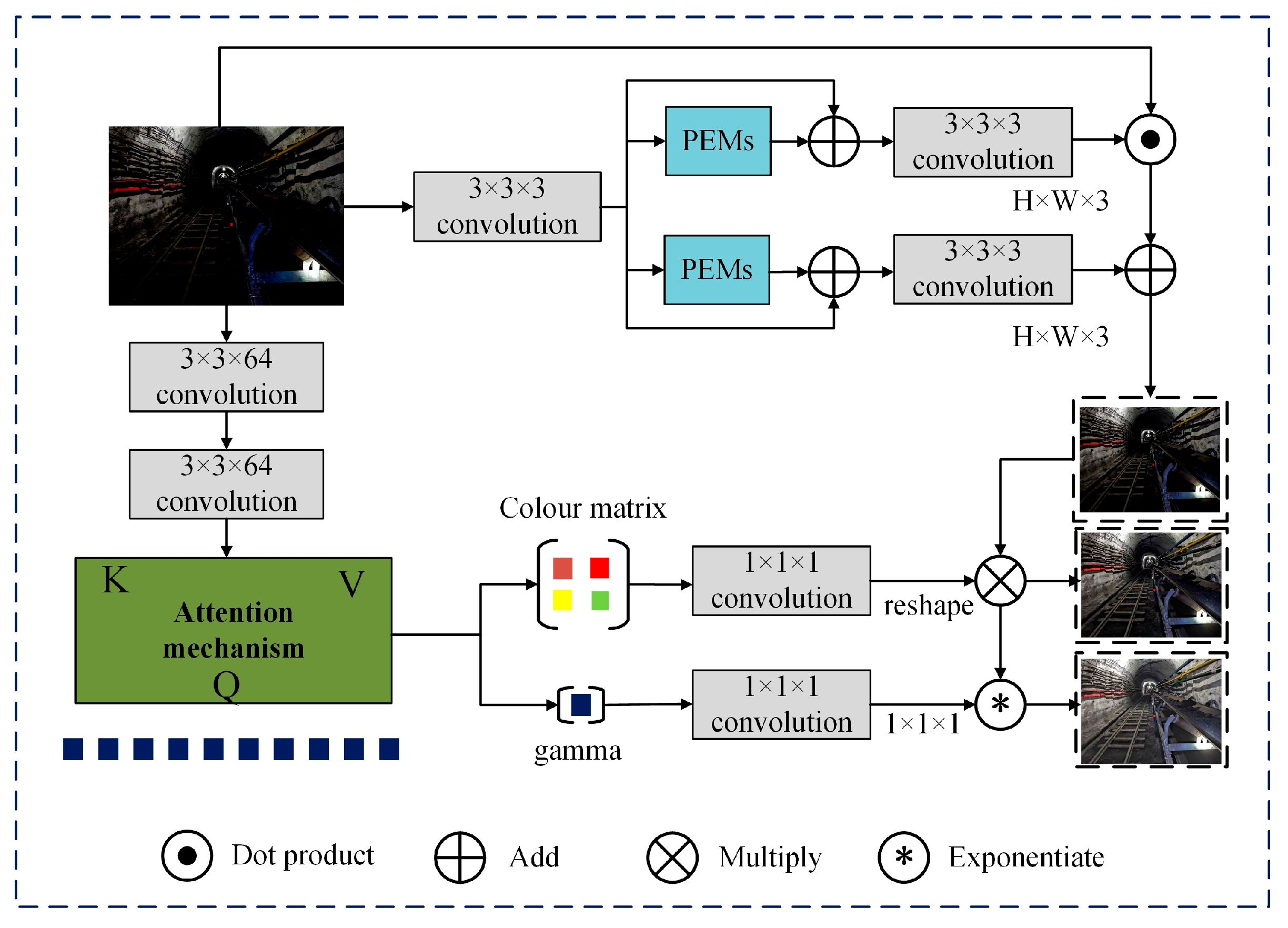
3.4. IAT Image Enhancement Module
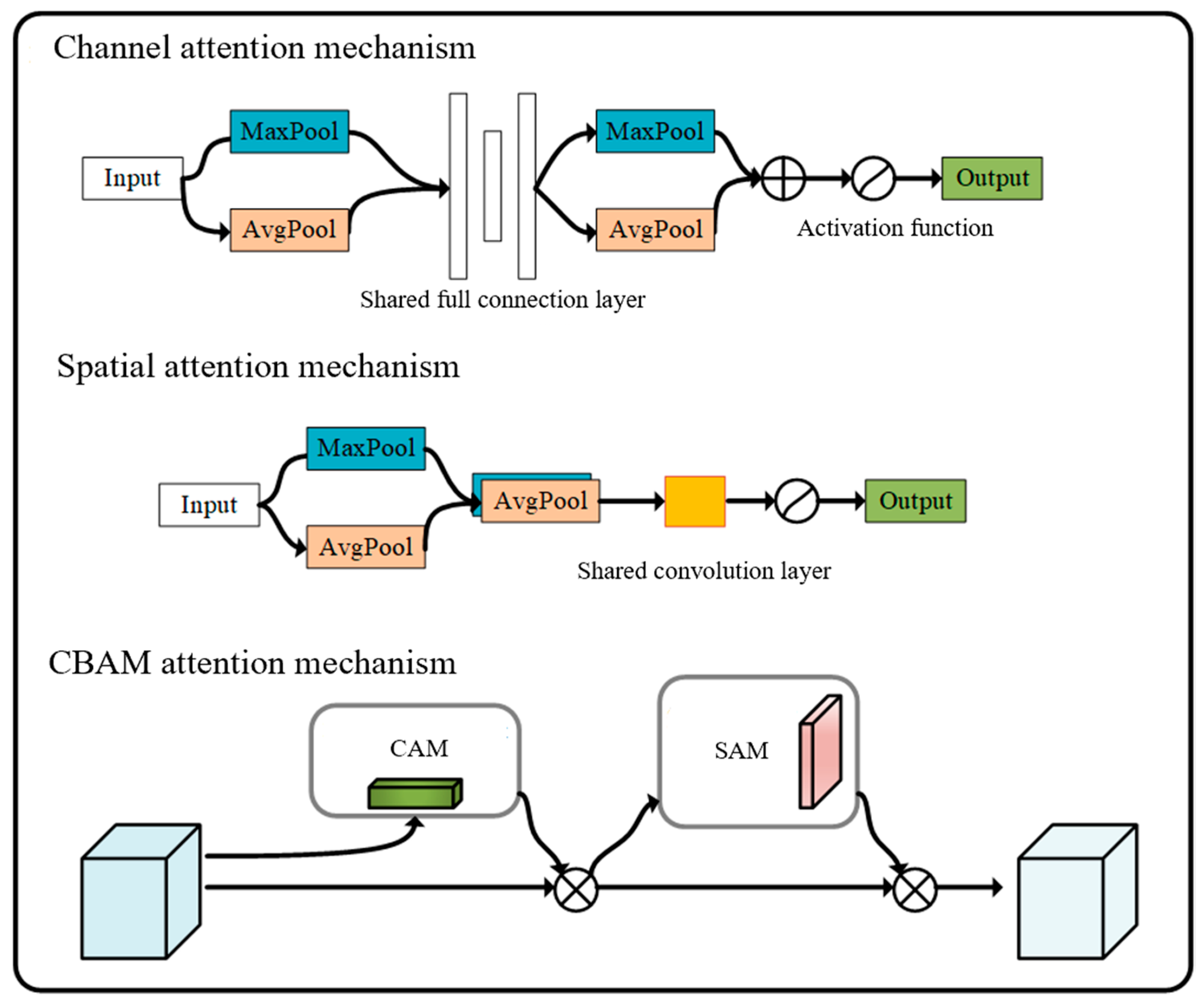
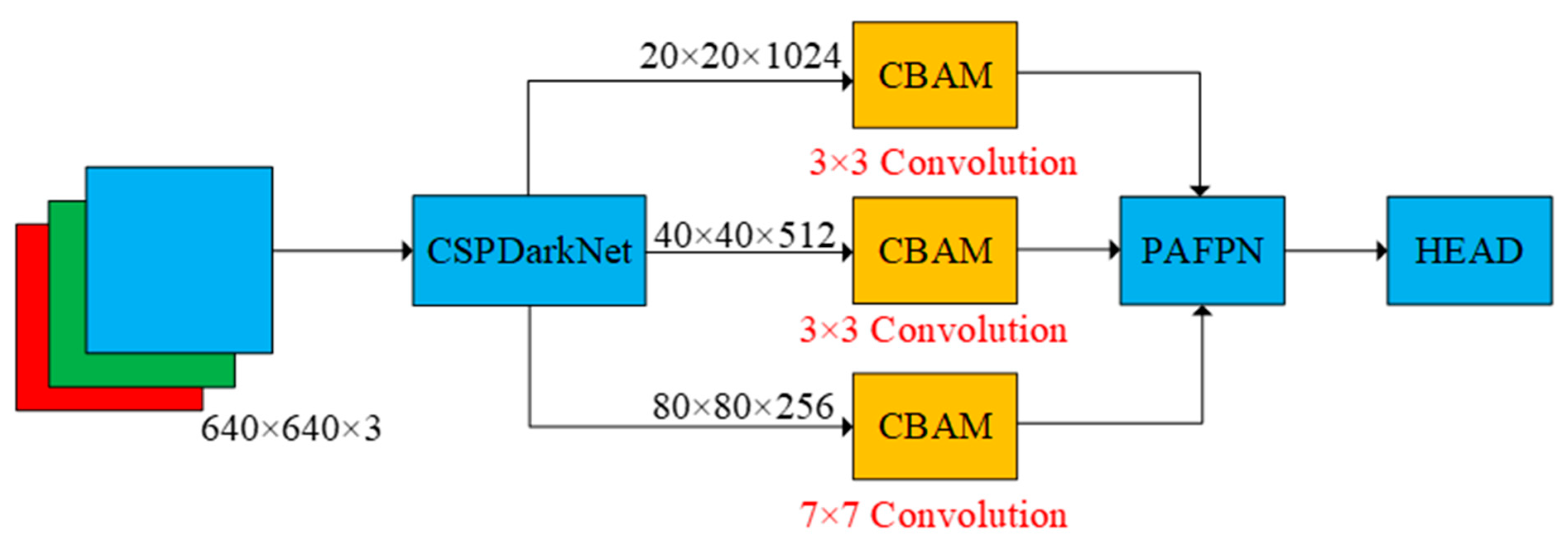
3.5. Improved CBAM Attention Block
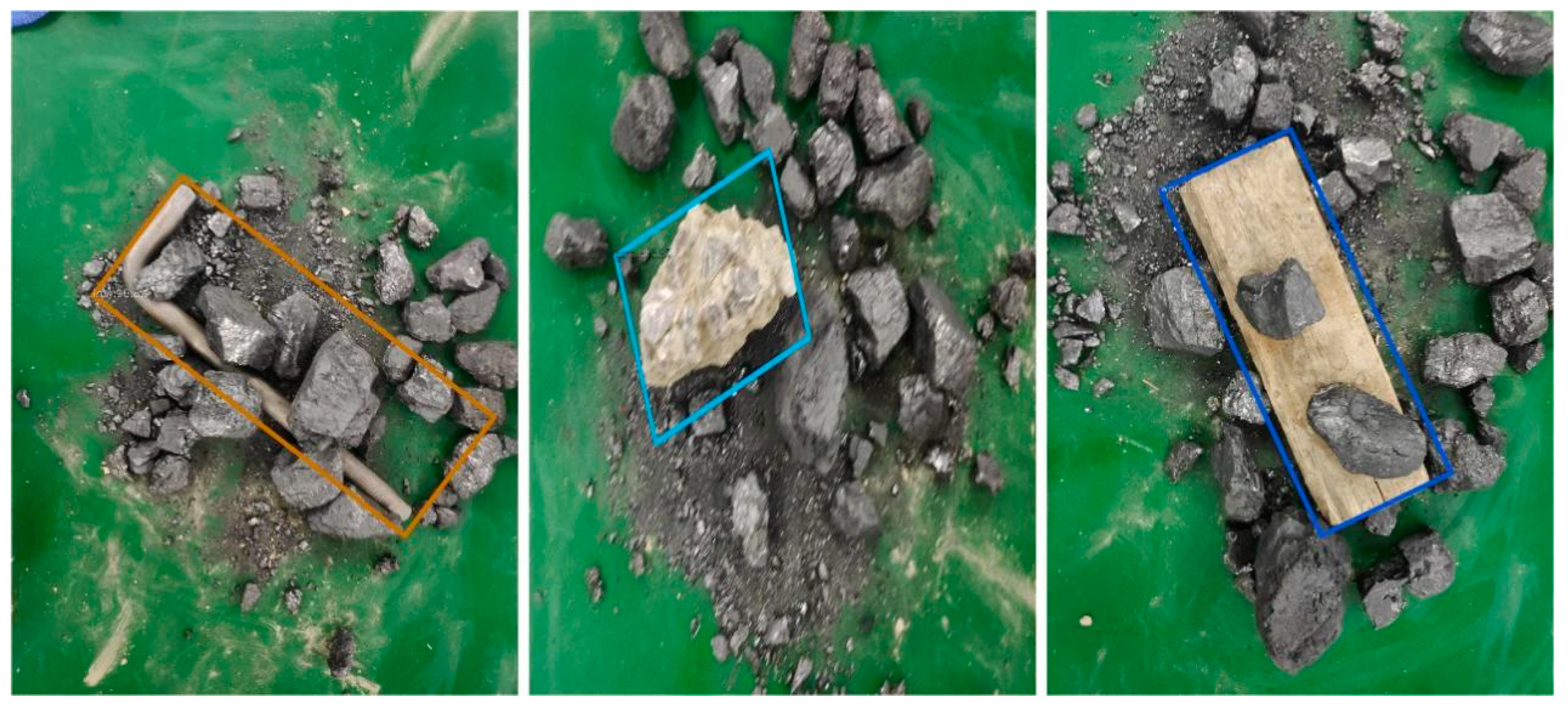
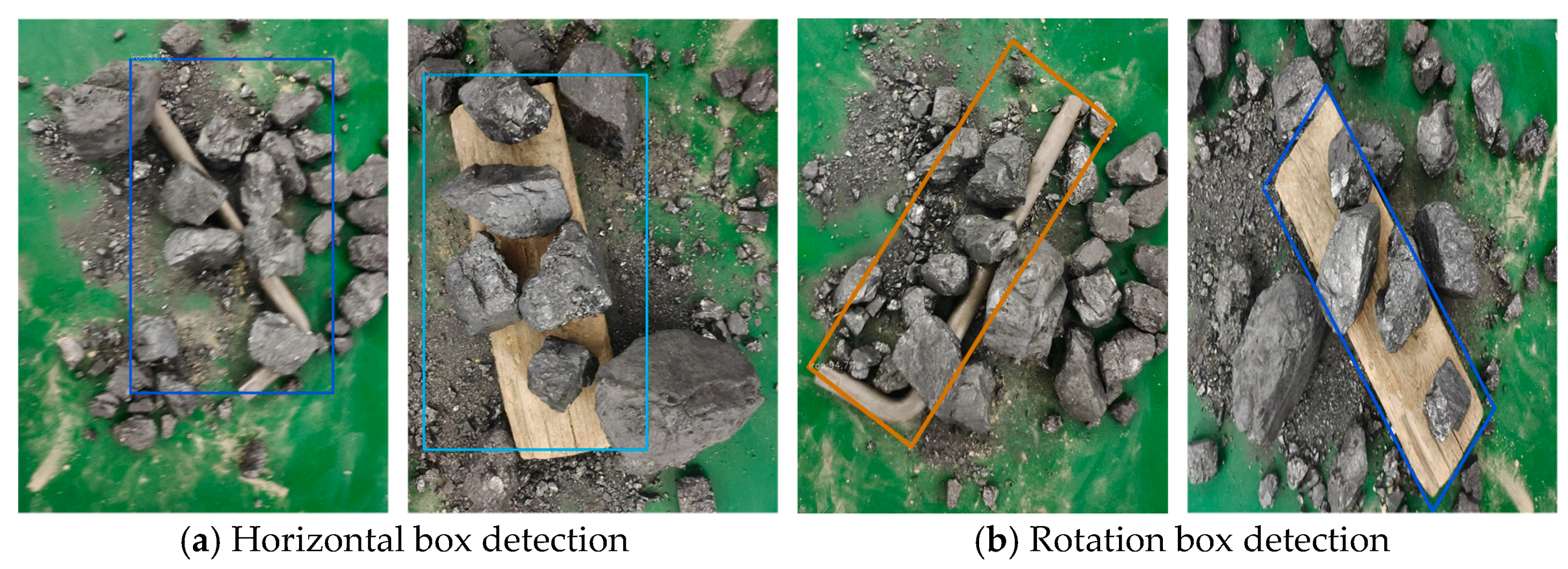
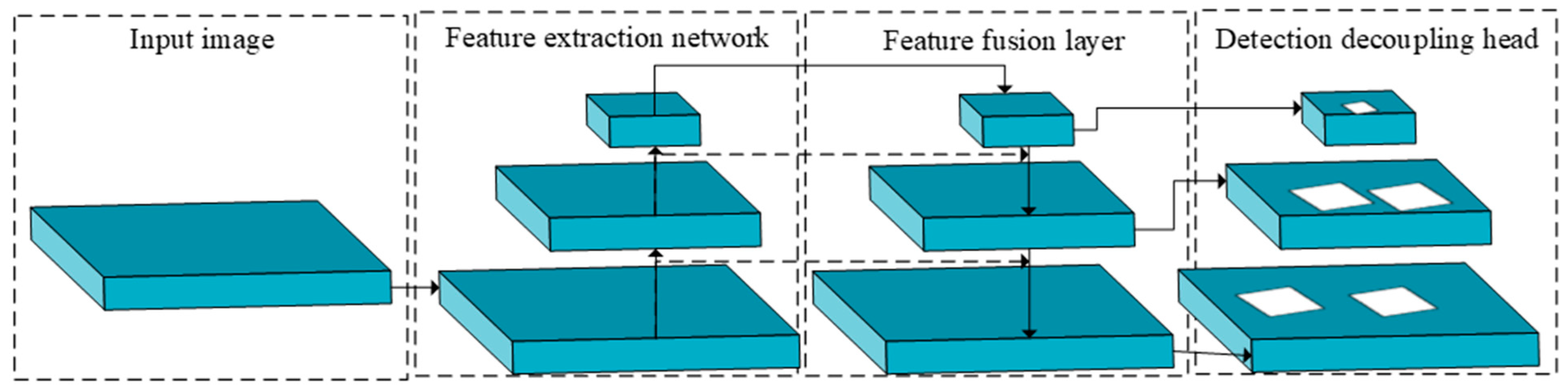
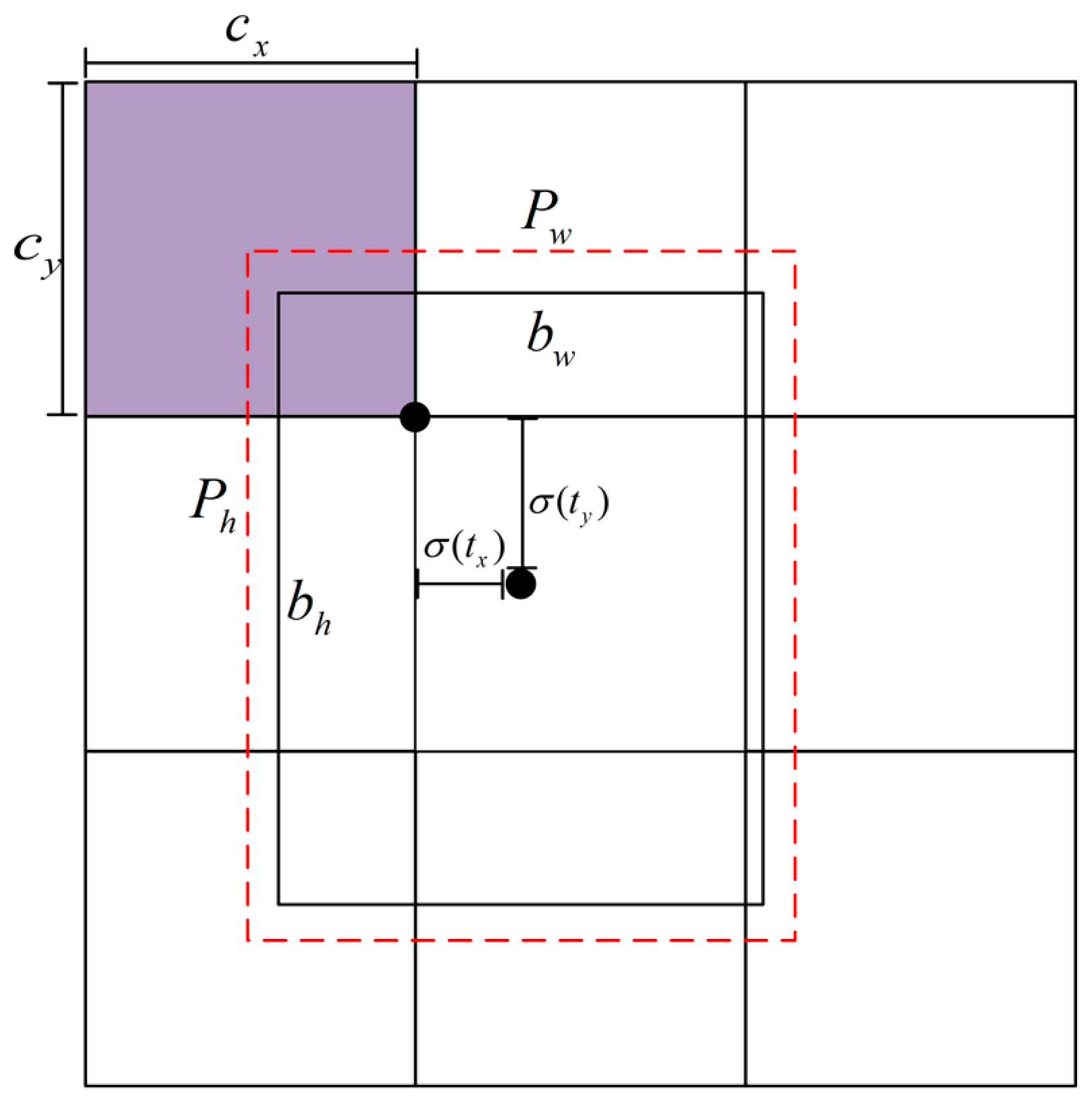
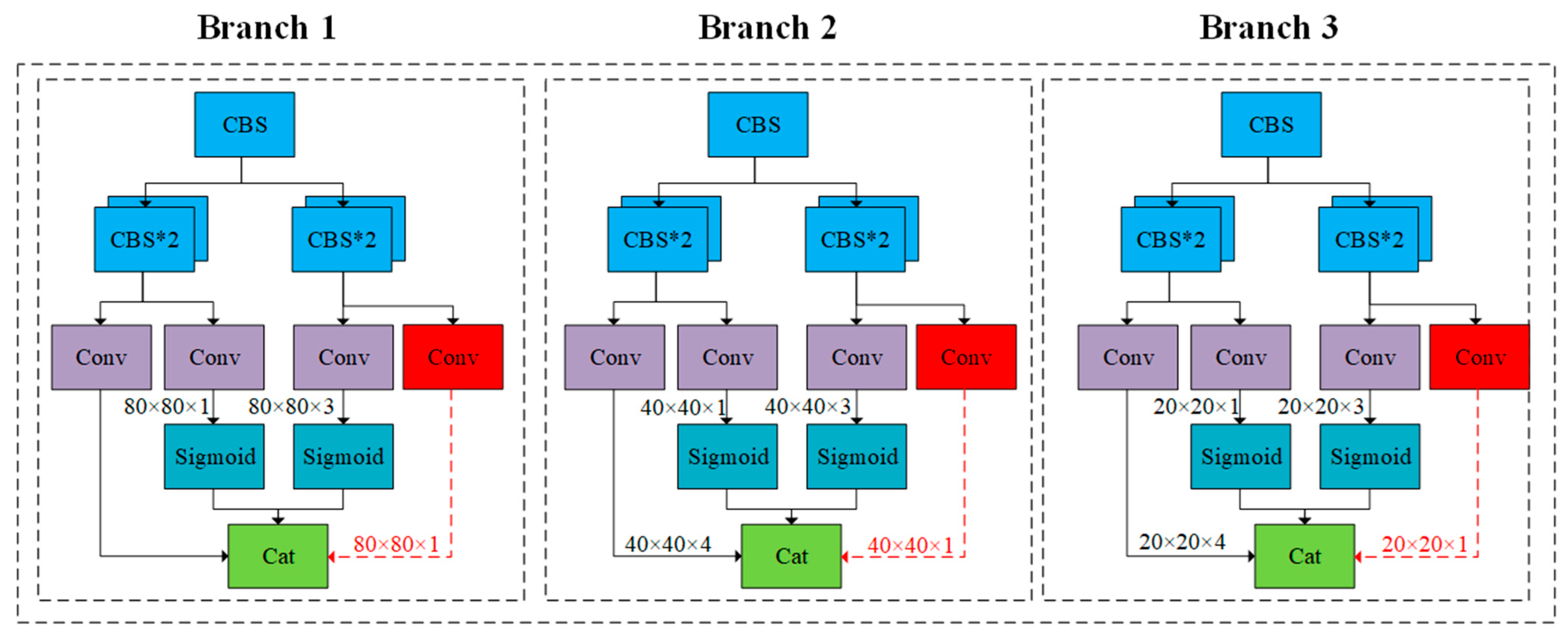
3.6. Designed Rotating Decoupling Head and MO-YOLOX Network
4. Experimental Example and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Platform
4.2. Experimental Comparisons
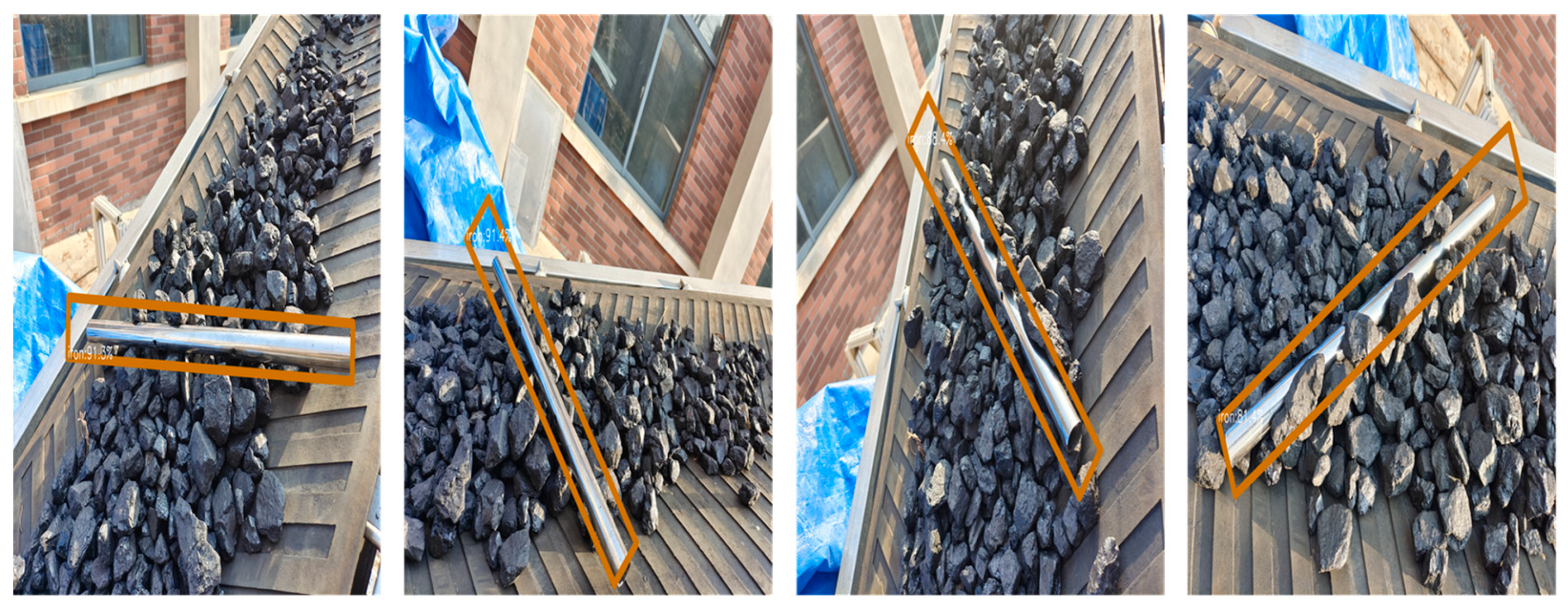
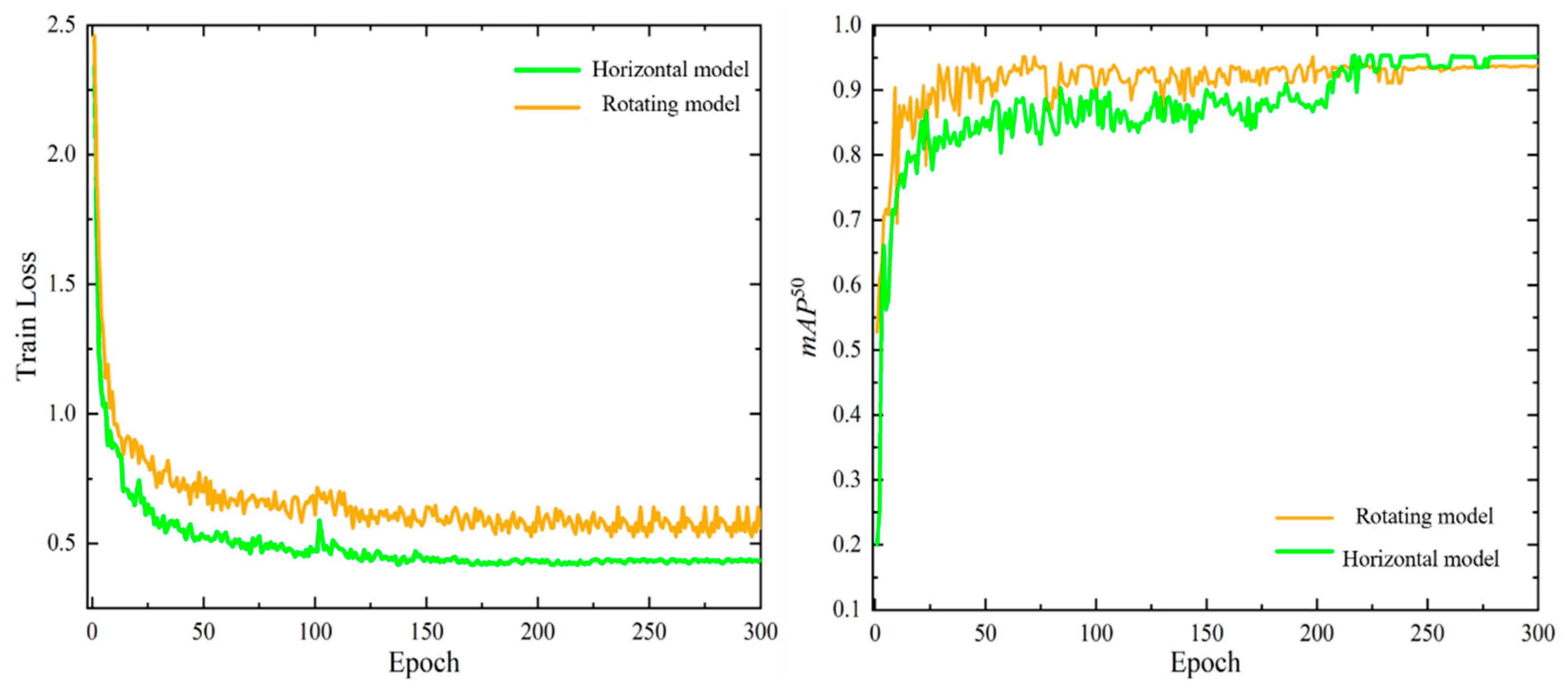
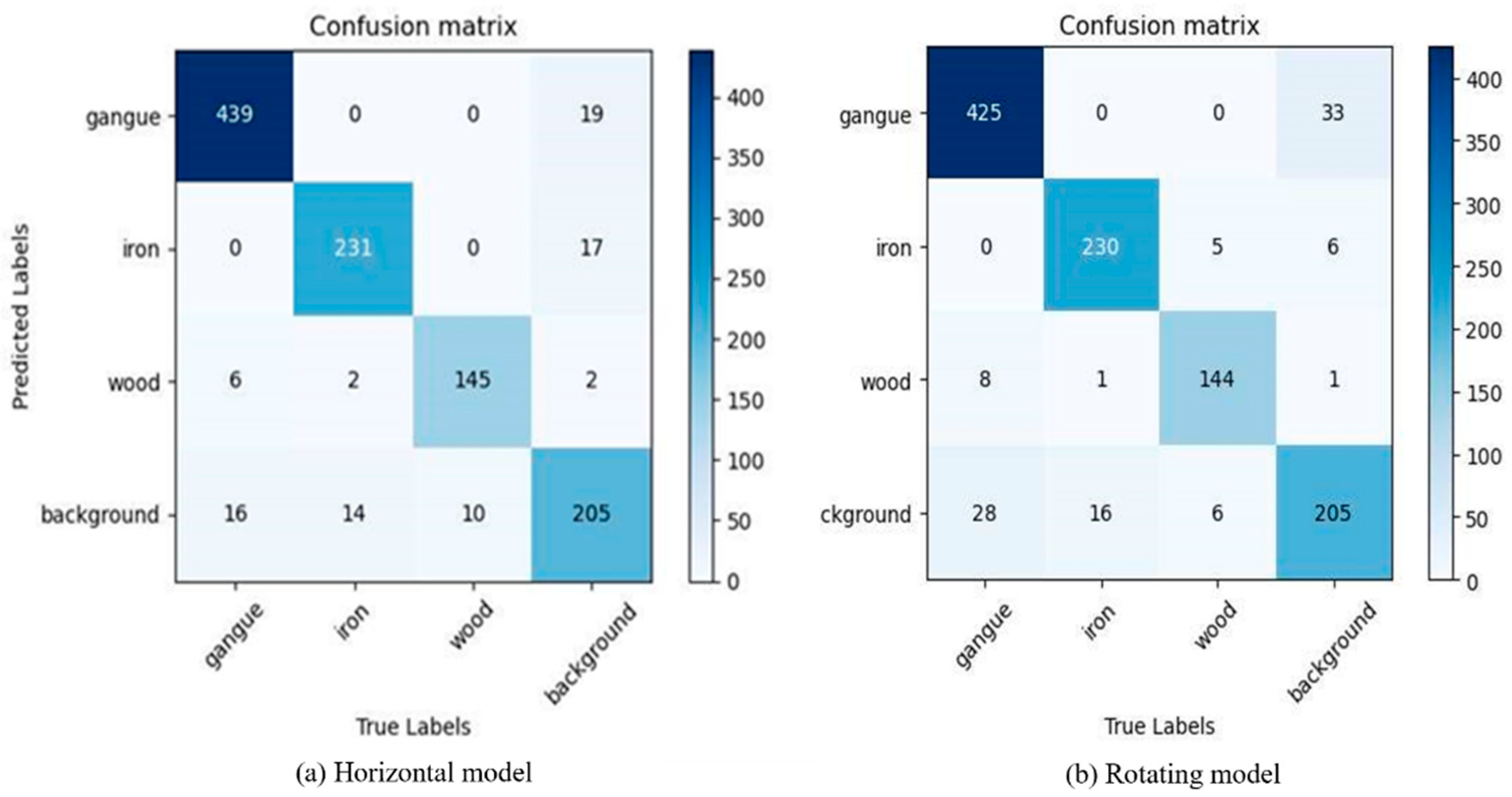
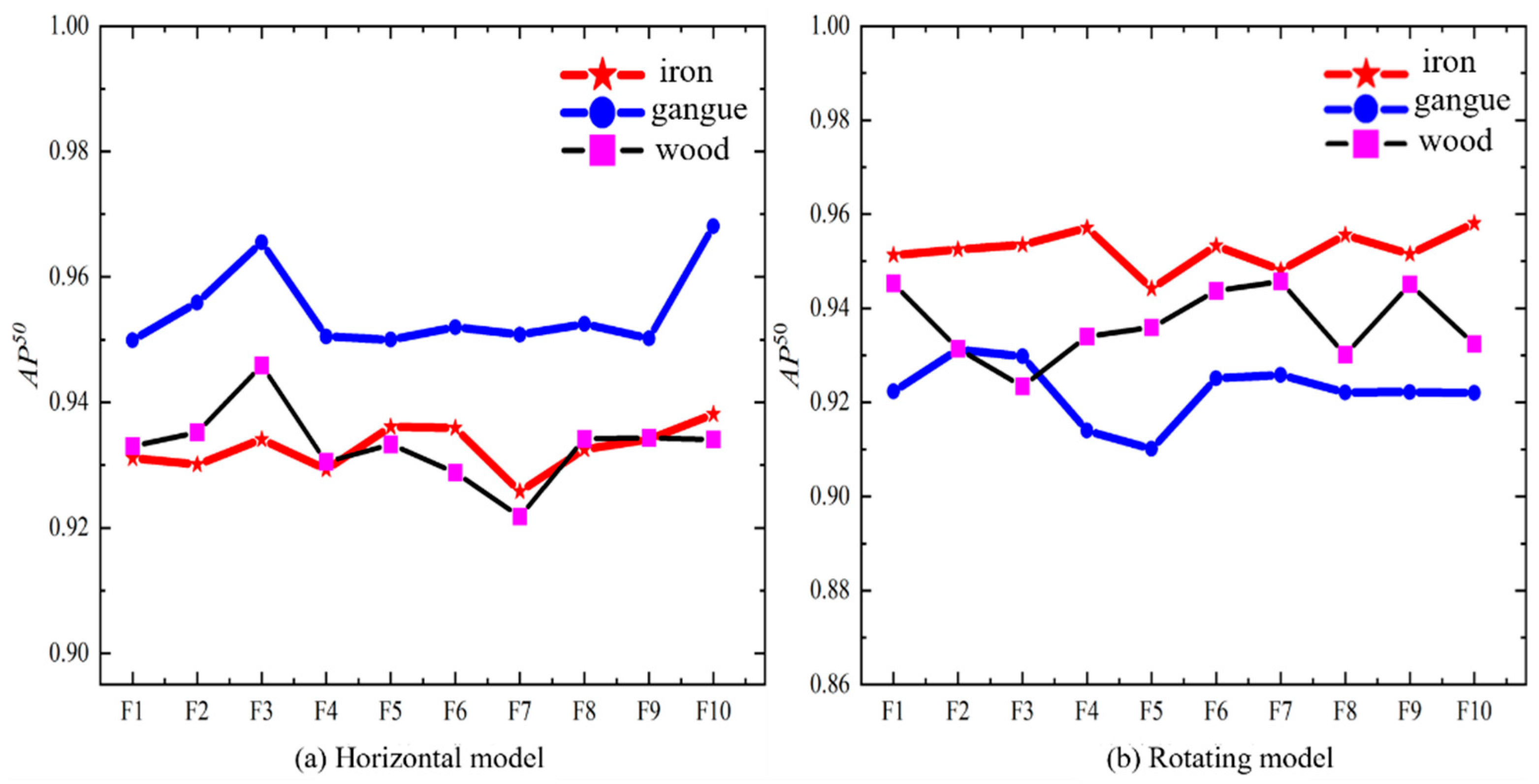
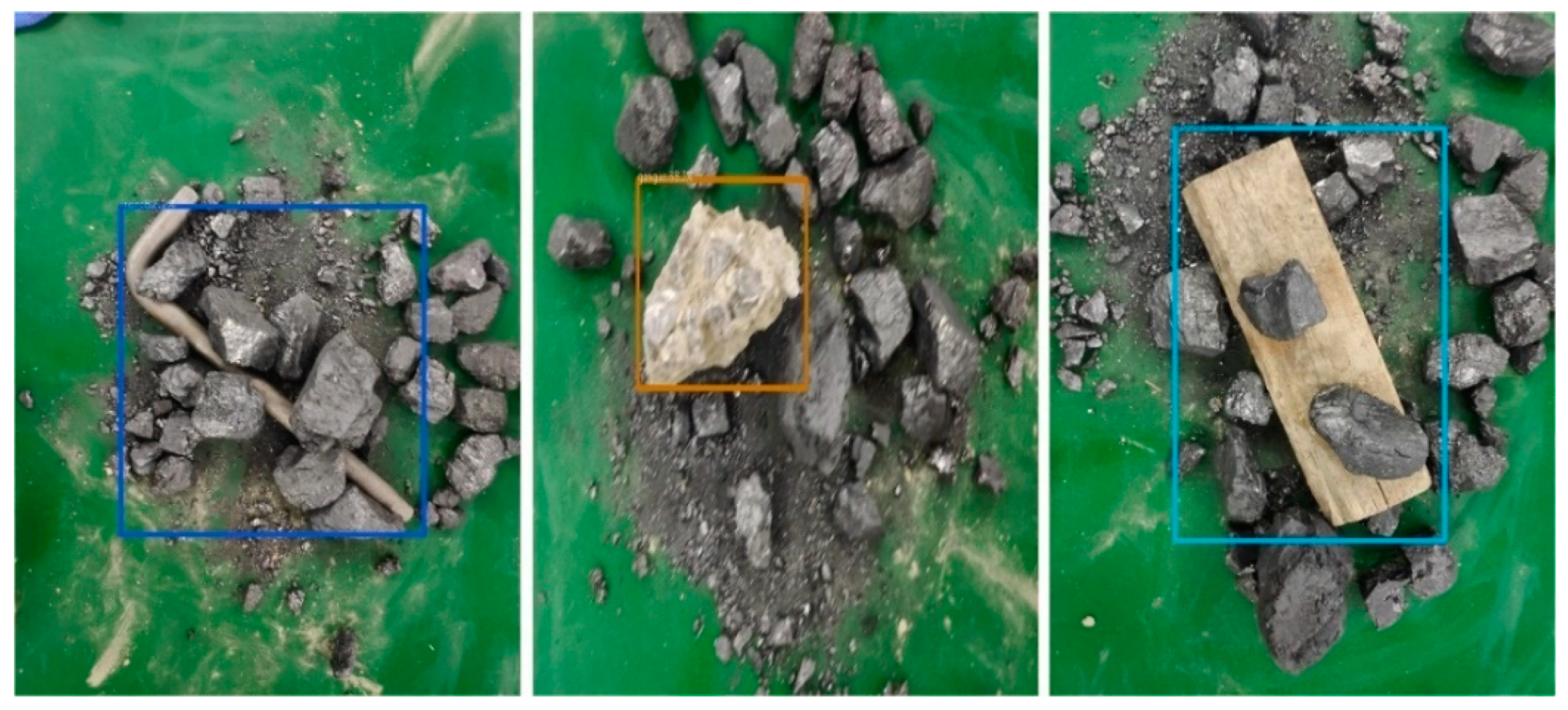
4.3. Experimental Testing and Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petrikova, I.; Marvalova, B.; Samal, S.; Cadek, M. Digital image correlation as a measurement tool for large deformations of a Conveyor Belt. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 732, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimroz, R.; Stefaniak, P.K.; Bartelmus, W.; Hardygora, M. Novel techniques of diagnostic data processing for belt conveyor maintenance. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium Continuous Surface Mining—Aachen 2014; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.Q. Study and analysis on tear belt and break belt of belt conveyor in coal mine. Coal Sci. Technol. 2015, S2, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.J. Recognition method of non-coal foreign matter in belt conveyor based on deep learning. J. Mine Autom. 2021, 47, 106653. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Wang, X. Coal mine safety intelligent monitoring based on wireless sensor network. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 25465–25471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Li, W.; Dai, K. Design of coal mine intelligent monitoring system based on ZigBee wireless sensor network. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Mechanics, Materials and Structural Engineering (ICMMSE 2016), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 18–20 March 2016; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Saydirasulovich, S.N.; Abdusalomov, A.; Jamil, M.K.; Nasimov, R.; Kozhamzharova, D.; Cho, Y.I. A YOLOv6-based improved fire detection approach for smart city environments. Sensors 2023, 23, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhou, Z.; Geng, Z. Safety monitoring method of moving target in underground coal mine based on computer vision processing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Qi, P.; Lu, H.; Liu, X.; Hua, D.; Guo, X. Image enhancement method in underground coal mines based on an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Li, L.; Shi, W.; Liu, J.P. Ultrasonic imaging recognition of coal-rock interface based on the improved variational mode decomposition. Measurement 2021, 170, 108728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wu, Y. Improved YOLO-V3 with DenseNet for multi-scale remote sensing target detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Li, K.; Gu, L.; Su, S.; Gao, P.; Jiang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Harada, T. You Only Need 90K Parameters to Adapt Light: A Light Weight Transformer for Image Enhancement and Exposure Correction. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.14871. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Cheng, M.; Huang, S.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H. A deep learning approach incorporating YOLO v5 and attention mechanisms for field real-time detection of the invasive weed Solanum rostra-tum Dunal seedlings. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 199, 107194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Peng, G.; Xu, B.; Lu, Y.; Wang, W. Foreign object recognition technology for port transportation channel based on automatic image recognition. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2018, 2018, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Su, X.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y. Multi-scale image segmentation of coal piles on a belt based on the Hessian matrix. Particuology 2013, 11, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, G.; Ganguly, A.; Tripathi, V.; Kumar, A.A.; Gigie, A.; Bhaumik, C.; Chakravarty, T. Multi-modal imaging-based foreign particle detection system on coal conveyor belt. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2022, 75, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.; Zhong, S.; Peng, Q. Moving object detection method based on complementary multi resolution background models. J. Cent. South Univ. 2014, 21, 2306–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, R.G.; Givigi, S.N. Automatic crack detection and measurement based on image analysis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, Y.; Jeong, H.; Choi, S.H.; Park, K.B.; Lee, J.Y. Deep learning-based object detection in augmented reality: A systematic review. Comput. Ind. 2022, 139, 103661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Singh, W. Tools, techniques, datasets and application areas for object detection in an image: A review. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 38297–38351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Apel, D.B.; Szmigiel, A.; Chen, J. Image recognition of coal and coal gangue using a convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Energies 2019, 12, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dang, L. Video detection of foreign objects on the surface of belt conveyor underground coal mine based on improved SSD. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 14, 5507–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Niu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X. Intelligent detection of foreign matter in coal mine transportation belt based on convolution neural network. Sci. Program. 2022, 2022, 9740622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Kang, Z.; Yu, H.; Wan, L. Research on belt foreign body detection method based on deep learning. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2022, 44, 2919–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2017.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Li, K.; Gu, L.; Su, S.; Gao, P.; Jiang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Harada, T. Illumination adaptive transformer. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.14871. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, G.; Yang, X.; Tang, J.; He, T.; Yan, J. Detecting rotated objects as gaussian distributions and its 3-d generalization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 4335–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer International Publishing: Cham, The Netherlands; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Xia, G.S. Align deep features for oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5602511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, J.; Ji, X.; Ye, Q. Beyond Bounding-Box: Convex-hull Feature Adaptation for Oriented and Densely Packed Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8792–8801. [Google Scholar]

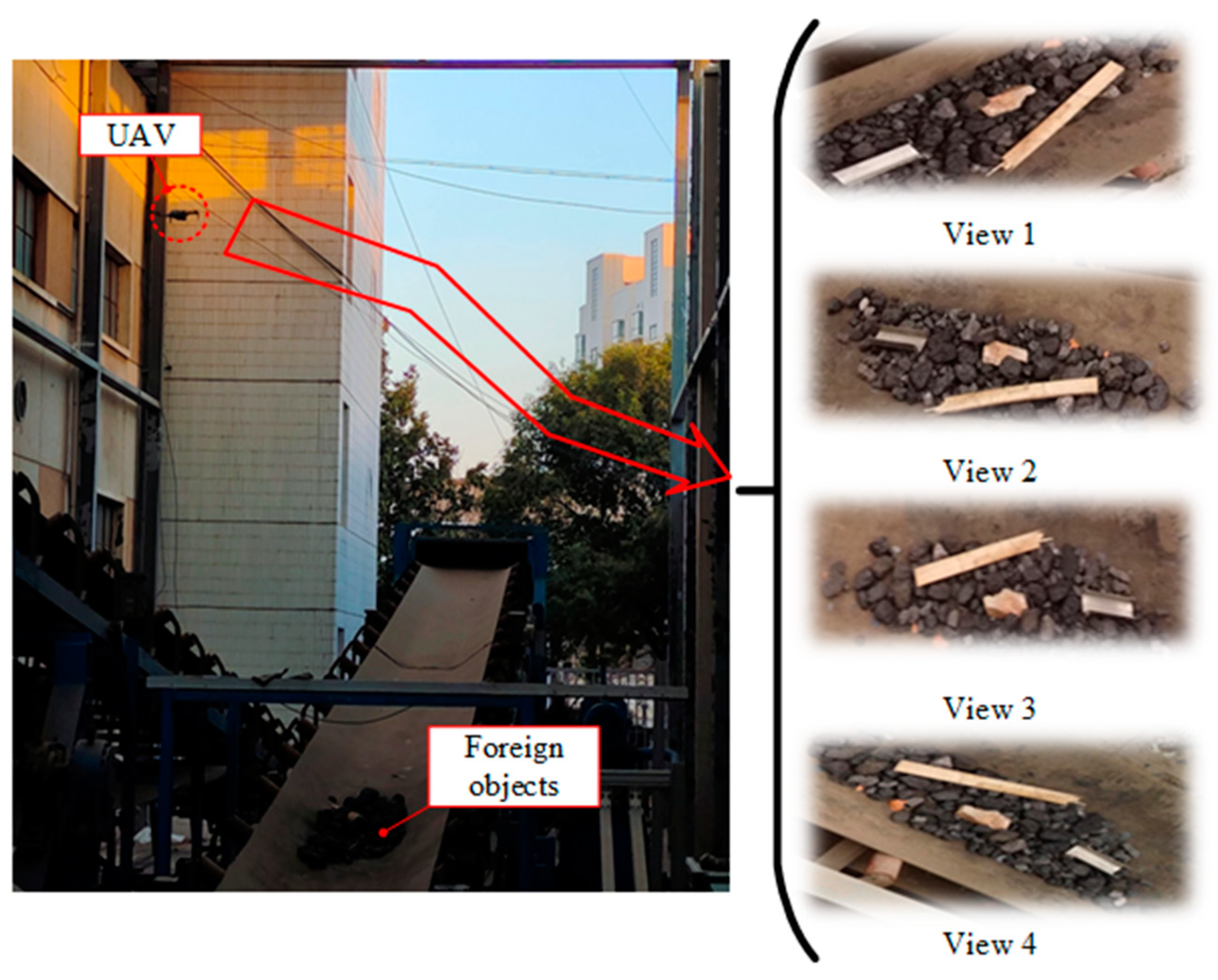

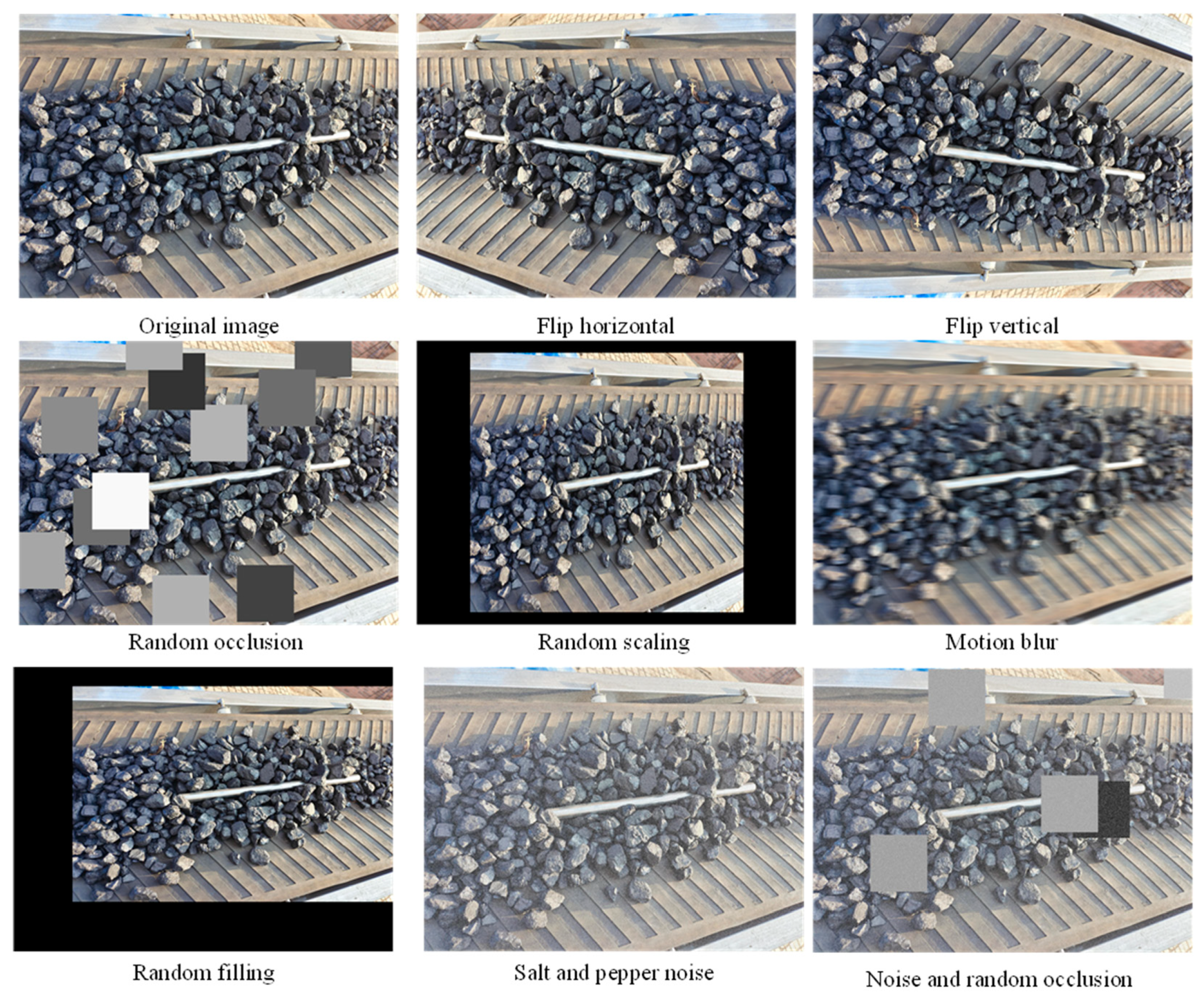



| Name | Parameter |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Core i9-10980XE |
| Hard disk | 2 T |
| GPU | NVIDIA RTX A4000 |
| Memory | 16 G |
| Deep learning framework | Pytorch1.8.0 |
| OS | Window10 |
| Programming Language | Python3.8 |
| CUDA | 11.2 |
| Model | MO-YOLOX | YOLOX-Small | SSD300 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | ||||
| mAP50 | 71.9% | 70.6% | 68.7% | |
| Bird AP50 | 74.2% | 74.2% | 71.2% | |
| Dog AP50 | 78.7% | 75.2% | 72.8% | |
| Cat AP50 | 78.5% | 80.3% | 73.9% | |
| Person AP50 | 72.8% | 72.5% | 69.8% | |
| Sofa AP50 | 71.1% | 71.8% | 71.9% | |
| Car AP50 | 79.1% | 70.2% | 70.8% | |
| Bottle AP50 | 49.2% | 50.9% | 49.9% | |
| Average inference time | 21 ms | 28 ms | 27 ms | |
| Model | MO-YOLOX | S2ANet | CFA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | ||||
| mAP50 | 79.44% | 79.26% | 79.57% | |
| PL AP50 | 85.61% | 86.12% | 85.21% | |
| SH AP50 | 83.23% | 82.23% | 83.82% | |
| LV AP50 | 75.22% | 76.32% | 80.91% | |
| HA AP50 | 76.51% | 75.41% | 73.21% | |
| SV AP50 | 78.29% | 75.23% | 76.25% | |
| BD AP50 | 77.78% | 79.25% | 78.00% | |
| Average inference time | 27 ms | 65 ms | 66 ms | |
| Training Parameters | Setting Values |
|---|---|
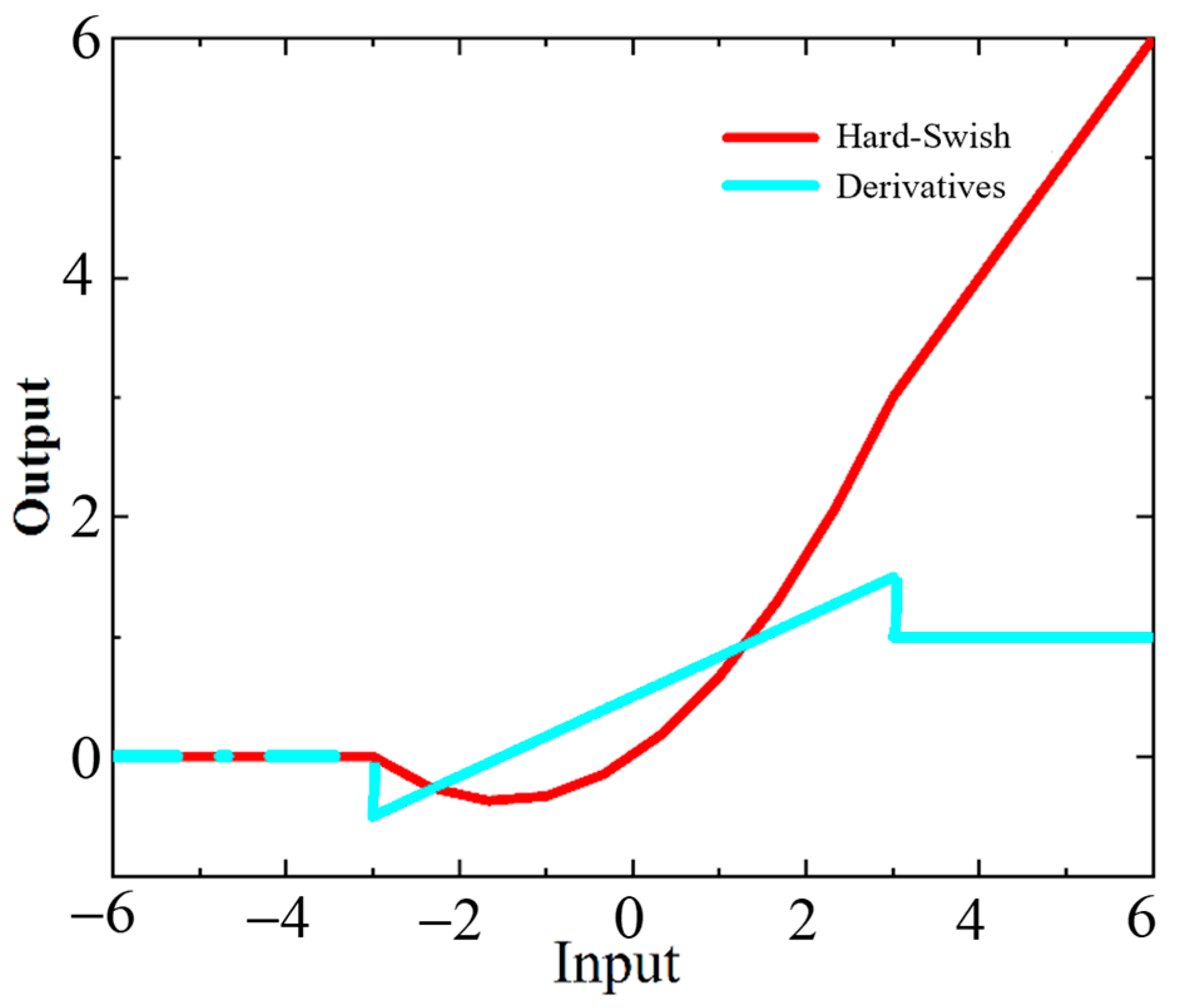
| Activation function | Hard-Swish |
| Pooling method | Max-Pooling |
| Optimization algorithm | Adams, Batch-size = 8, |
| Loss function | Cross-entropy Loss function, KLD |
| Epoch | 300 |
| Data enhancement | Mosaic |
| Learning rate | , Nature Index attenuation |
| Dataset partitioning ratio | Training set:Verification set:Test set = 0.6:0.3:0.1 |
| Precision | Recall | AP50 | F2-Score | Inference Time/ms | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iron | 93.71% | 93.20% | 93.27% | 93.30% | 21 |
| wood | 93.12% | 93.62% | 93.30% | 95.80% | 23 |
| large gangue | 95.32% | 95.92% | 95.45% | 93.52% | 22 |
| average value | 94.05% | 94.25% | 94.01% | 94.20% | 22 |
| Precision | Recall | AP50 | F2-Score | Inference Time/ms | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iron | 95.11% | 95.32% | 95.25% | 95.28% | 28 |
| wood | 92.17% | 92.51% | 92.23% | 92.44% | 26 |
| large gangue | 94.32% | 93.25% | 93.56% | 93.46% | 29 |
| average value | 93.87% | 93.69% | 93.68% | 93.73% | 27.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, R.; Qi, P.; Hua, D.; Zhang, X.; Lu, H.; Liu, X. A Foreign Object Detection Method for Belt Conveyors Based on an Improved YOLOX Model. Technologies 2023, 11, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11050114
Yao R, Qi P, Hua D, Zhang X, Lu H, Liu X. A Foreign Object Detection Method for Belt Conveyors Based on an Improved YOLOX Model. Technologies. 2023; 11(5):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11050114
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Rongbin, Peng Qi, Dezheng Hua, Xu Zhang, He Lu, and Xinhua Liu. 2023. "A Foreign Object Detection Method for Belt Conveyors Based on an Improved YOLOX Model" Technologies 11, no. 5: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11050114
APA StyleYao, R., Qi, P., Hua, D., Zhang, X., Lu, H., & Liu, X. (2023). A Foreign Object Detection Method for Belt Conveyors Based on an Improved YOLOX Model. Technologies, 11(5), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11050114








