Real-Time Deployment of Ultrasound Image Interpretation AI Models for Emergency Medicine Triage Using a Swine Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Procedures and Manual Ultrasound Image Capture
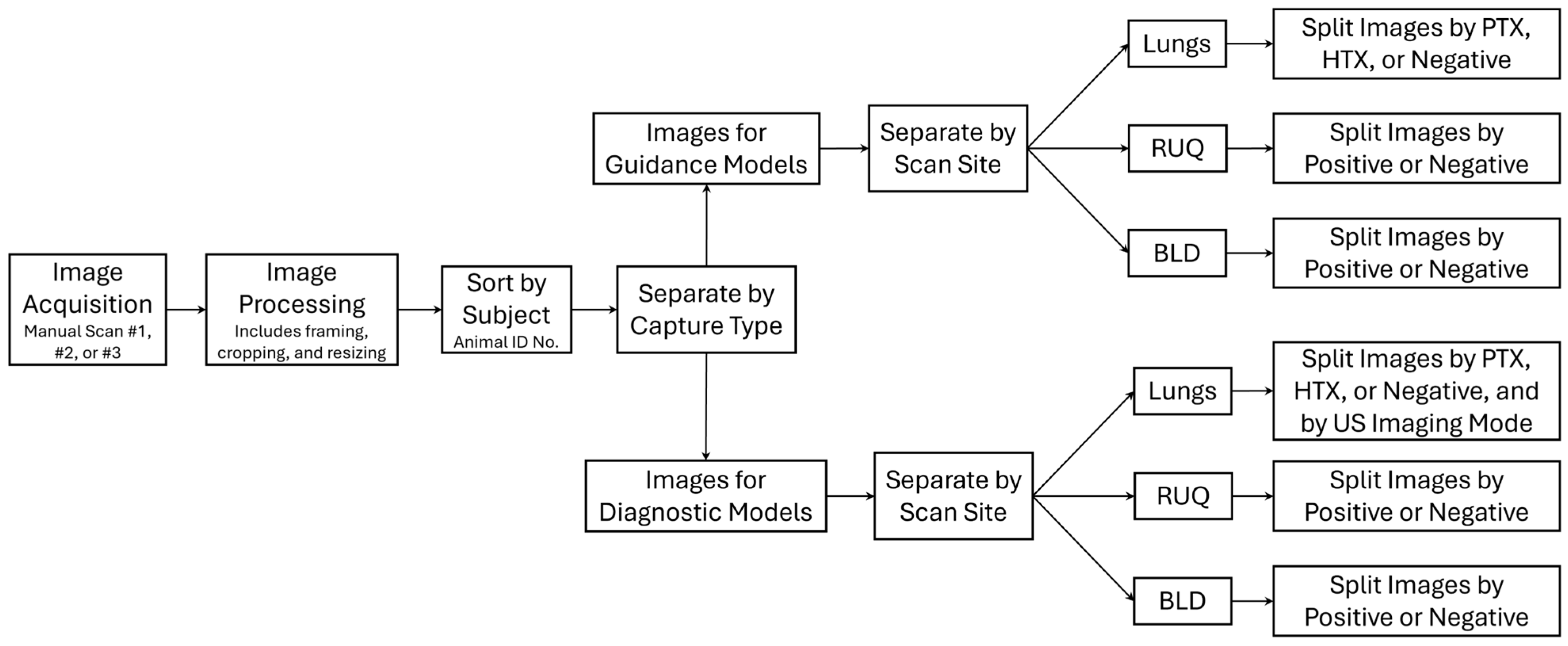
2.2. Data Processing
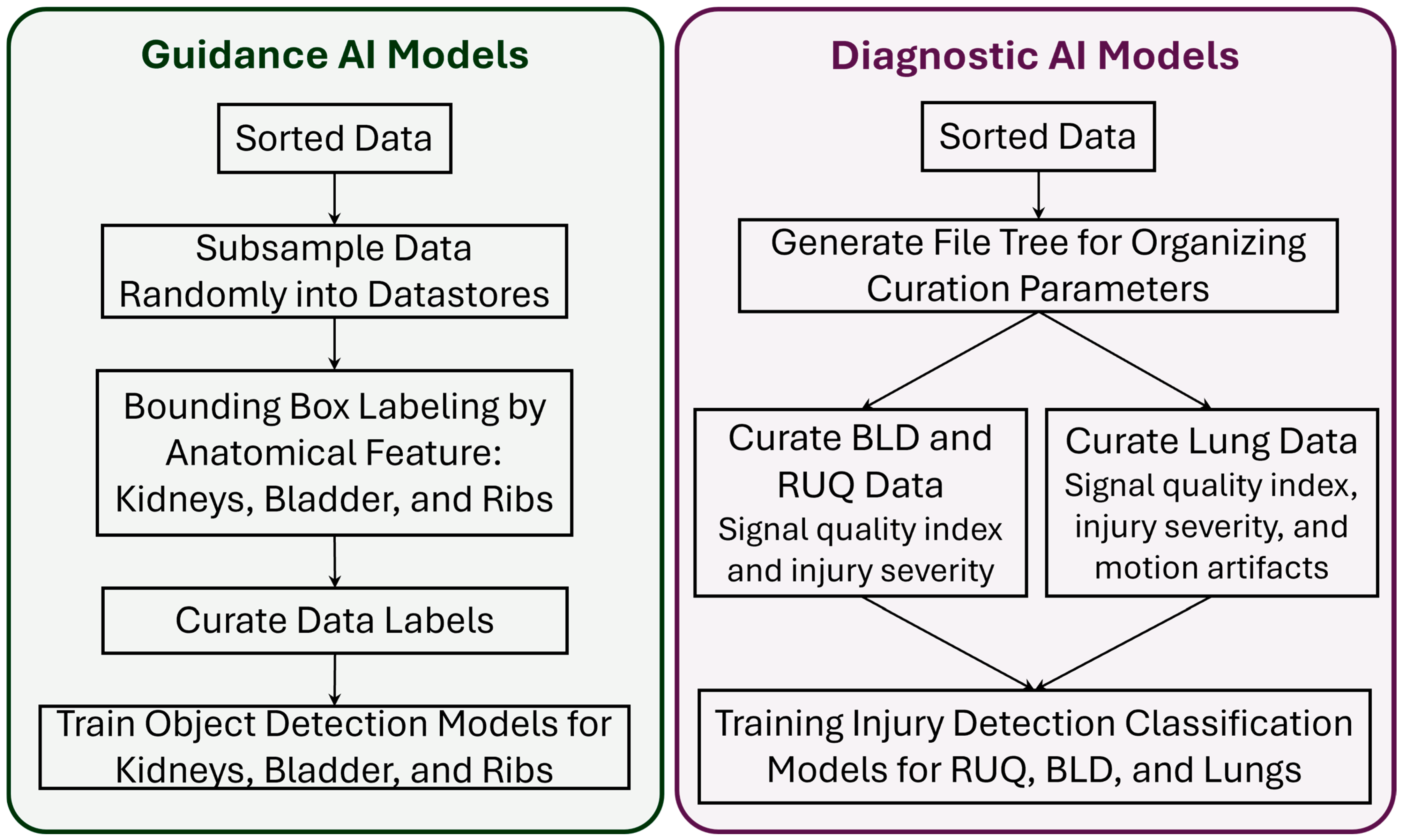
2.3. Guidance AI Models
2.4. Diagnostic AI Models
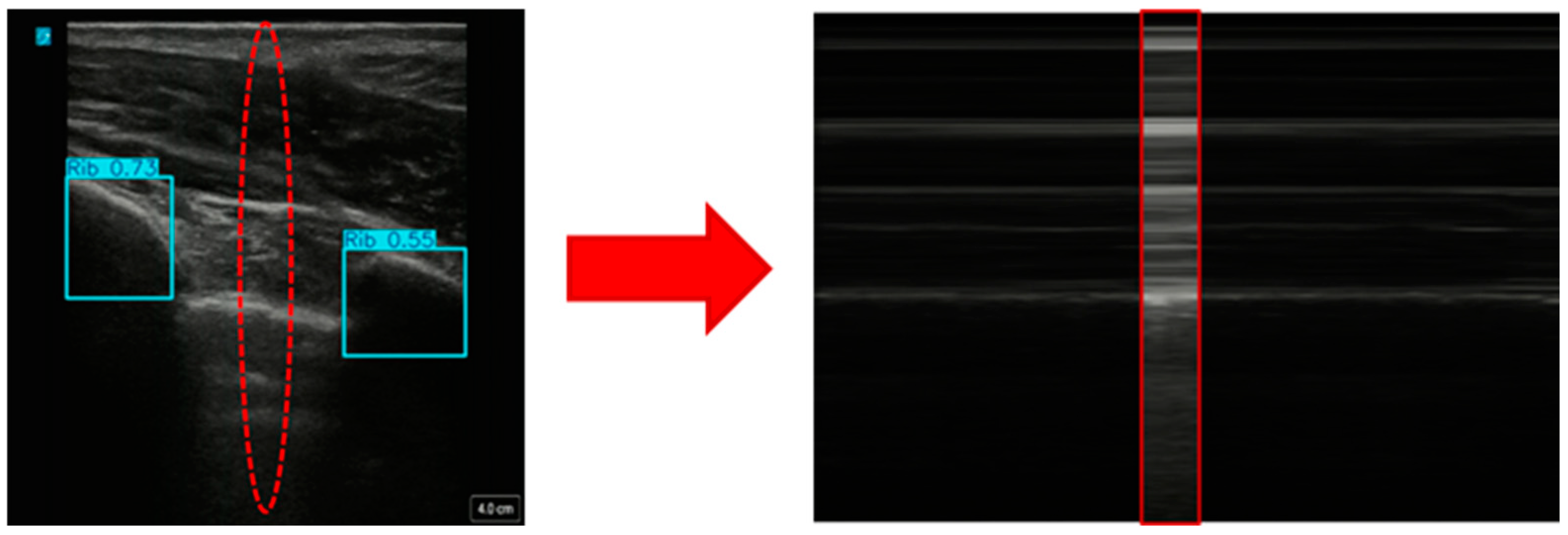
2.4.1. Creating Custom Motion Mode Images from US Scans
2.4.2. Training AI Models for Injury Identification
2.5. Real-Time Validation of AI Models
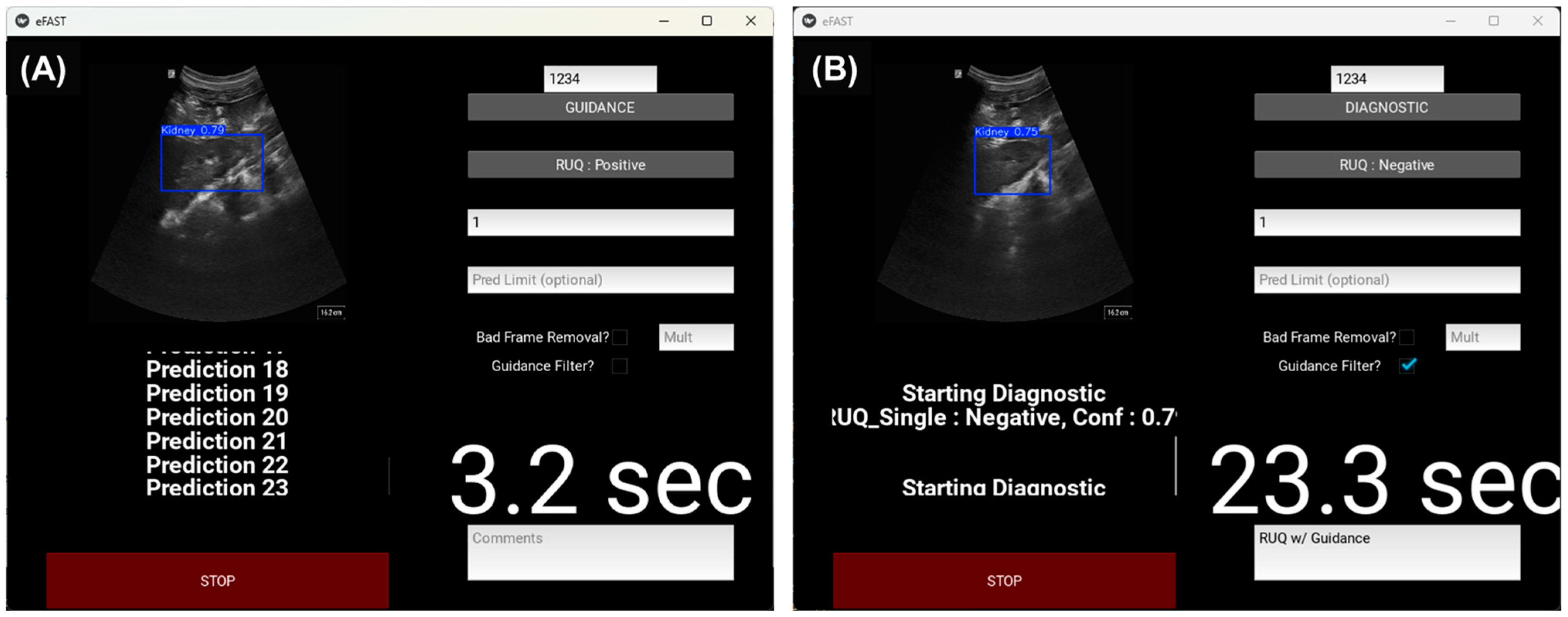
2.5.1. Real-Time eFAST Application
Ultrasound Image Filtering Features
2.5.2. Manual eFAST Exam with AI Model Guidance
2.5.3. Automated Robotic US eFAST Exam
Robotic Platform Configuration
Robotic eFAST (RoboFAST) Exam with AI Model Guidance
3. Results
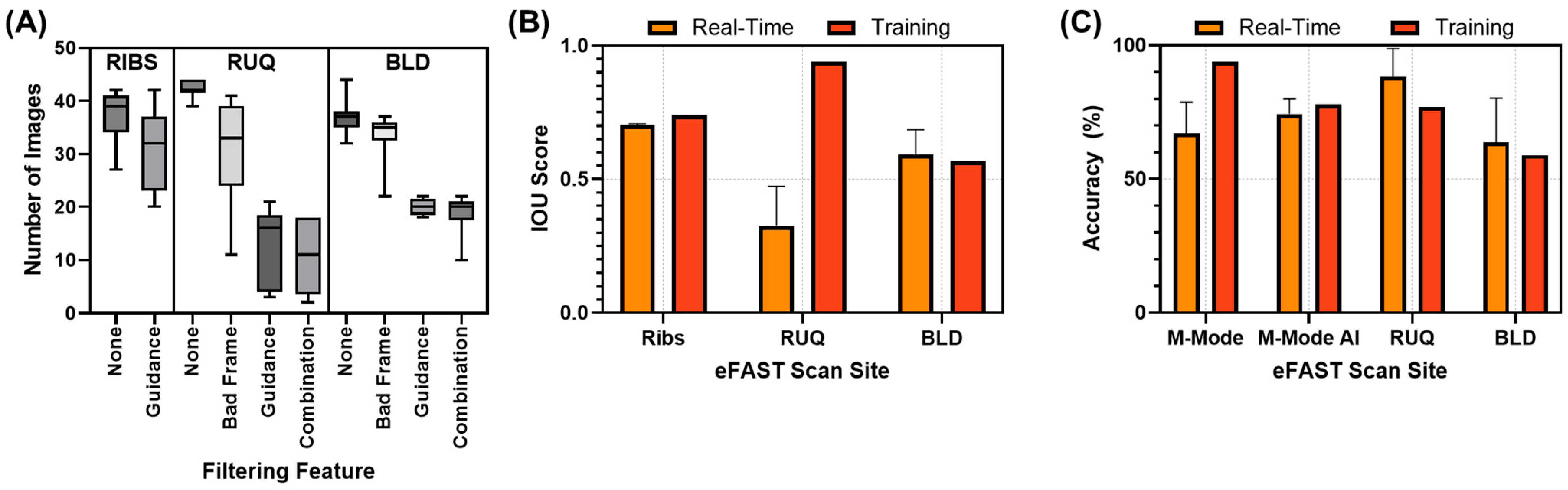
3.1. Guidance AI Performance
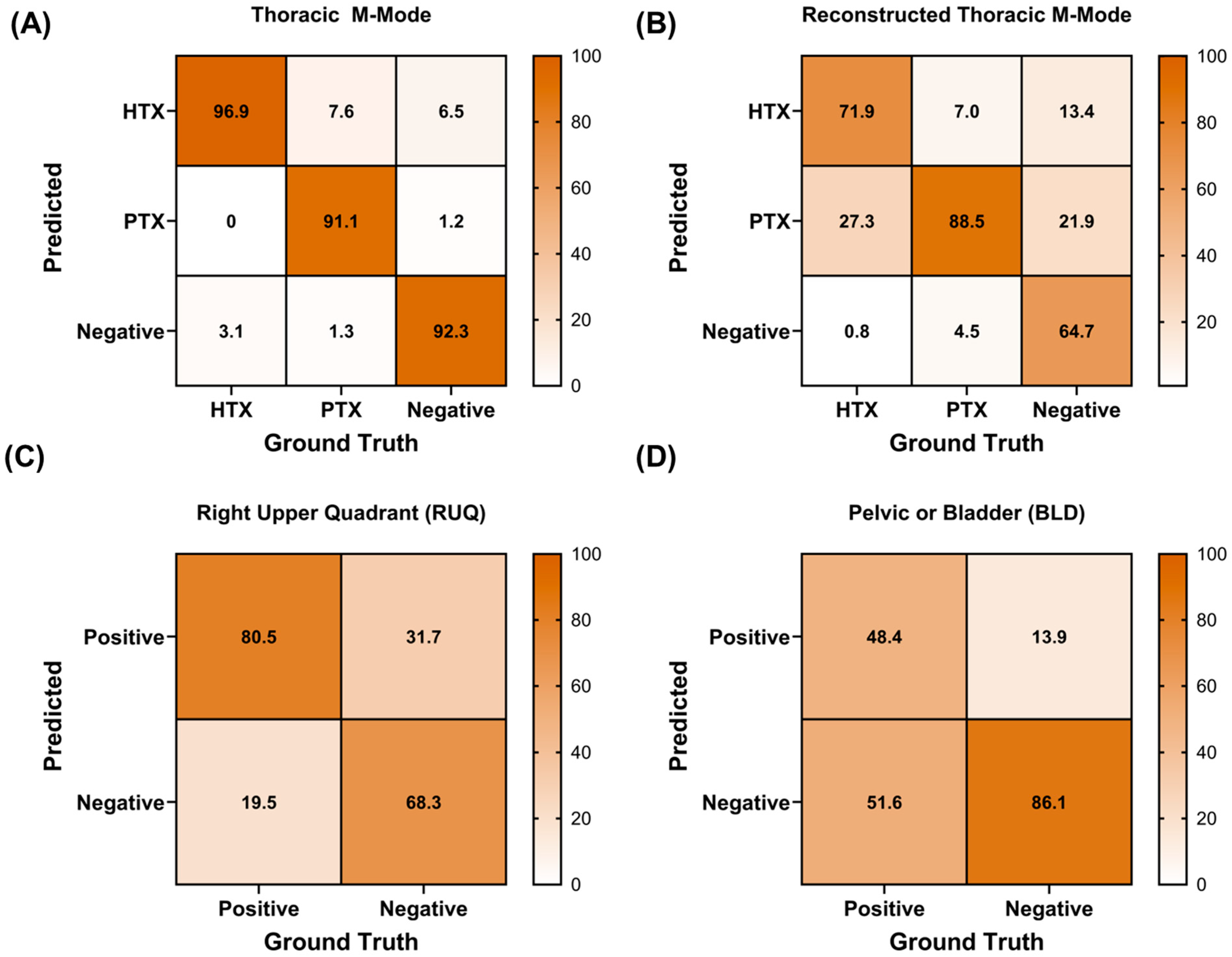
3.2. Diagnostic AI Performance
3.3. Real-Time Model Performance
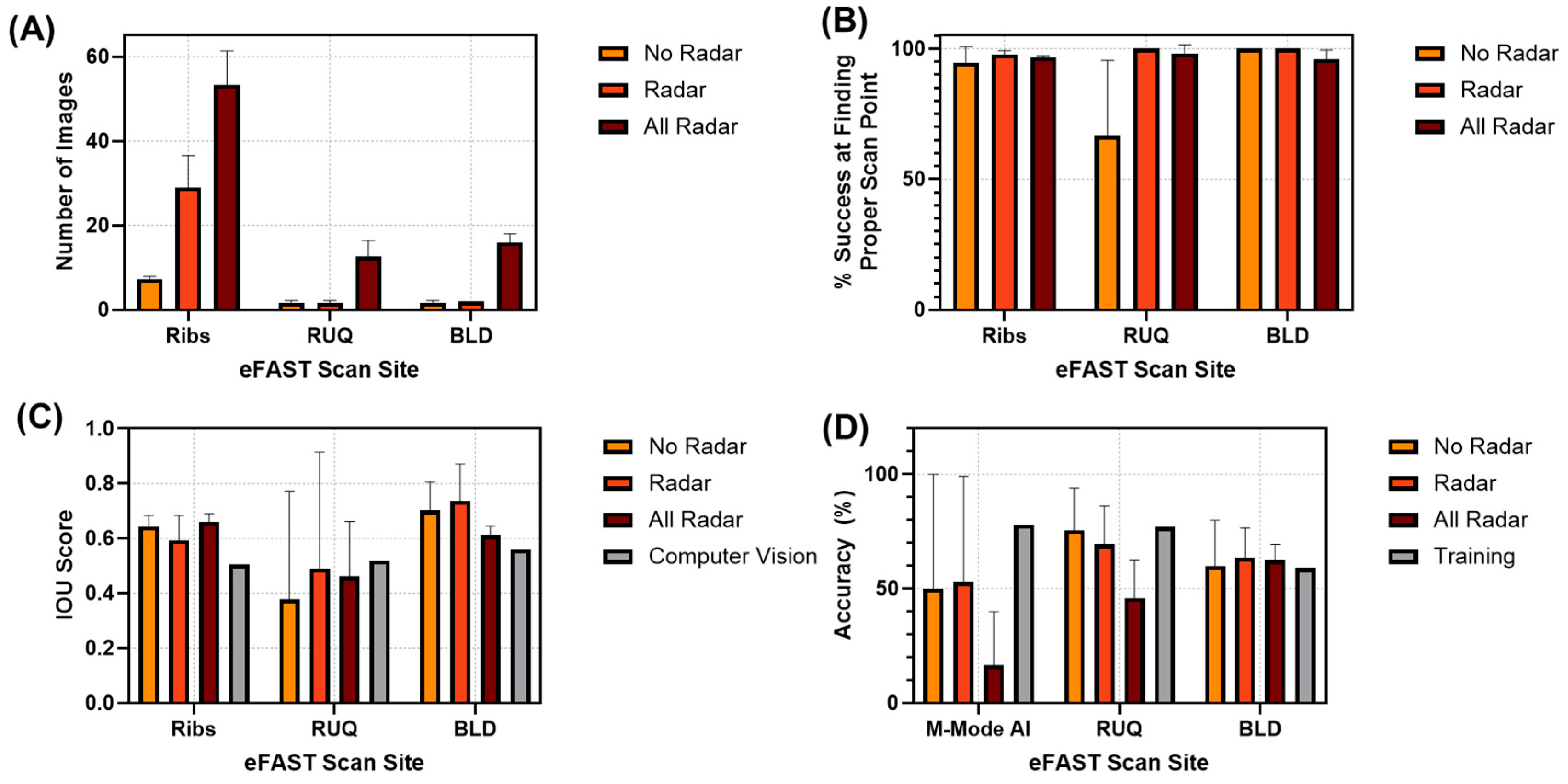
3.3.1. Evaluation of the Real-Time eFAST Application
3.3.2. RoboFAST Evaluation
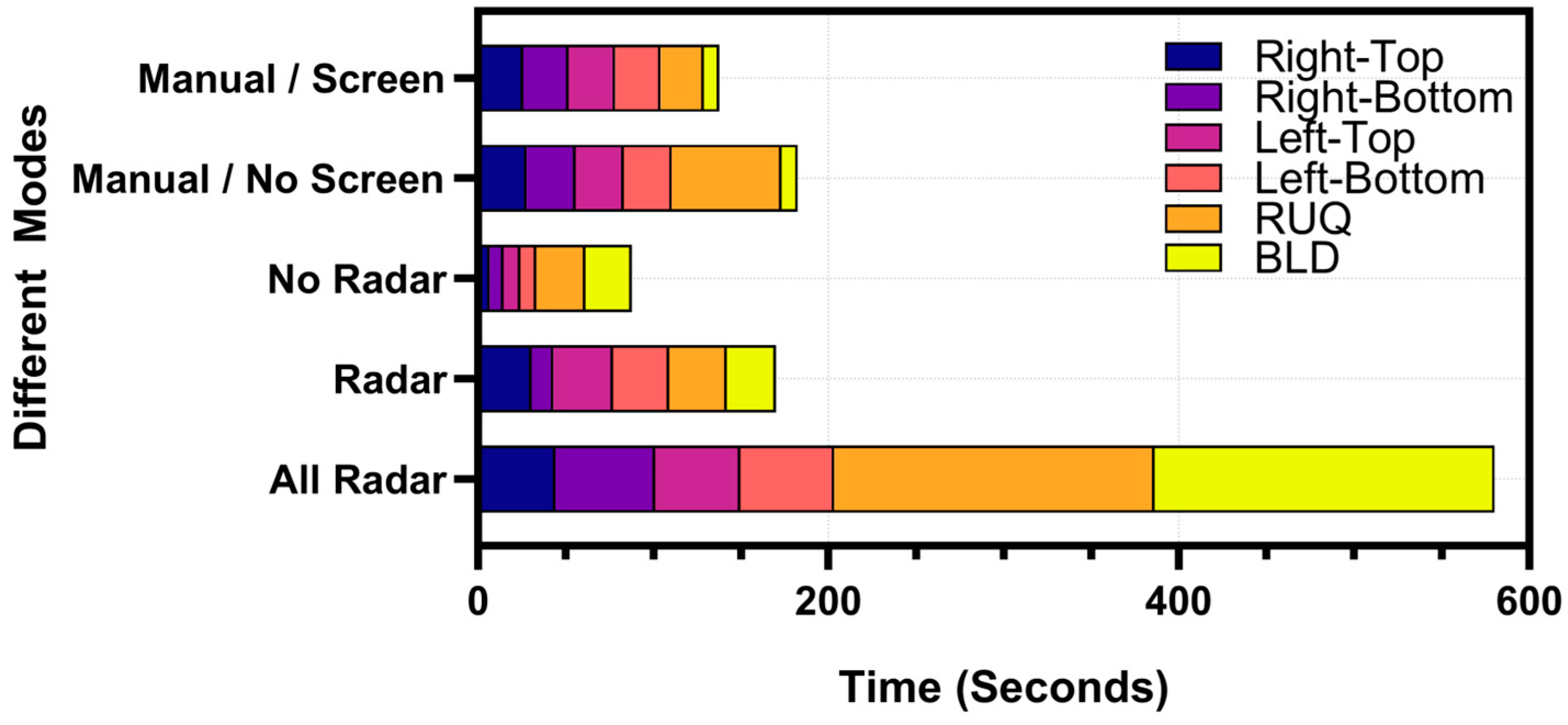
3.3.3. Timing Comparison Between Handheld eFAST Application and RoboFAST
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
DOD Disclaimer
References
- Nabrawi, E.; Alanazi, A.T. Imaging in Healthcare: A Glance at the Present and a Glimpse Into the Future. Cureus 2023, 15, e36111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigal, S.; Pons, F. Triage of Mass Casualties in War Conditions: Realities and Lessons Learned. Int. Orthop. 2013, 37, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubecq, C.; Dubourg, O.; Morand, G.; Montagnon, R.; Travers, S.; Mahe, P. Point-of-Care Ultrasound for Treatment and Triage in Austere Military Environments. J. Trauma. Acute Care Surg. 2021, 91, S124–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamilio, D.M.; McReynolds, T.; Endrizzi, J.; Lyons, R.C. Diagnosis and Treatment of a Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy in a Combat Support Hospital during Operation Iraqi Freedom: Case Report and Critique of a Field-Ready Sonographic Device. Mil. Med. 2004, 169, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondelli, M.H.; Remick, K.N.; Shackelford, S.A.; Gurney, J.M.; Pamplin, J.C.; Polk, T.M.; Potter, B.K.; Holt, D.B. Casualty Care Implications of Large-Scale Combat Operations. J. Trauma. Acute Care Surg. 2023, 95, S180–S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, B.A.; Gibbons, R.C. Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Letter from the President: A Shortage of Preventive Medicine Physicians in the Military and Across the Country. Available online: https://www.acpm.org/news/2024/letter-from-the-president-a-shortage-of-preventive (accessed on 29 November 2024).
- Pinto-Coelho, L. How Artificial Intelligence Is Shaping Medical Imaging Technology: A Survey of Innovations and Applications. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Faes, L.; Kale, A.U.; Wagner, S.K.; Fu, D.J.; Bruynseels, A.; Mahendiran, T.; Moraes, G.; Shamdas, M.; Kern, C.; et al. A Comparison of Deep Learning Performance against Health-Care Professionals in Detecting Diseases from Medical Imaging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Digit. Health 2019, 1, e271–e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotter, W.; Diab, A.R.; Haslam, B.; Kim, J.G.; Grisot, G.; Wu, E.; Wu, K.; Onieva, J.O.; Boyer, Y.; Boxerman, J.L.; et al. Robust Breast Cancer Detection in Mammography and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Using an Annotation-Efficient Deep Learning Approach. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P. Telemedicine for the Battlefield: Present and Future Technologies. In Surgical Robotics: Systems Applications and Visions; Rosen, J., Hannaford, B., Satava, R.M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 33–68. ISBN 978-1-4419-1126-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rinehart, J.; Lilot, M.; Lee, C.; Joosten, A.; Huynh, T.; Canales, C.; Imagawa, D.; Demirjian, A.; Cannesson, M. Closed-Loop Assisted versus Manual Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy during High-Risk Abdominal Surgery: A Case-Control Study with Propensity Matching. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, G.C.; Kinsky, M.P.; Prough, D.S.; Salinas, J.; Sondeen, J.L.; Hazel-Scerbo, M.L.; Mitchell, C.E. Closed-Loop Control of Fluid Therapy for Treatment of Hypovolemia. J. Trauma 2008, 64, S333–S341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, S.J.; Berard, D.; Avital, G.; Ross, E.; Snider, E.J. Adaptive Closed-Loop Resuscitation Controllers for Hemorrhagic Shock Resuscitation. Transfusion 2023, 63, S230–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Wara, U.U.; Arshad Shaikh, M.T.; Rahman, R.M.; Zaidi, Z.A. Telesurgery and Robotics: An Improved and Efficient Era. Cureus 2021, 13, e14124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, B.E.; Castle, J.T.; Virodov, A.; Wilt, W.S.; Bumgardner, C.; Brim, T.; McAtee, E.; Schellenberg, M.; Inaba, K.; Warriner, Z.D. Artificial Intelligence Evaluation of Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023, 95, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Lin, Y.; Cao, P.; Zou, X.; Qin, Q.; Lin, Z.; Liang, F.; Li, Z. Automated Detection and Segmentation of Pleural Effusion on Ultrasound Images Using an Attention U-Net. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2024, 25, e14231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Lv, Q.; Hou, S. Progress in the Application of Portable Ultrasound Combined with Artificial Intelligence in Pre-Hospital Emergency and Disaster Sites. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez Torres, S.I.; Ruiz, A.; Holland, L.; Ortiz, R.; Snider, E.J. Evaluation of Deep Learning Model Architectures for Point-of-Care Ultrasound Diagnostics. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amezcua, K.-L.; Collier, J.; Lopez, M.; Hernandez Torres, S.I.; Ruiz, A.; Gathright, R.; Snider, E.J. Design and Testing of Ultrasound Probe Adapters for a Robotic Imaging Platform. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boysen, S.R.; Caulkett, N.A.; Brookfield, C.E.; Warren, A.; Pang, J.M. Splenectomy Versus Sham Splenectomy in a Swine Model of Controlled Hemorrhagic Shock. Shock 2016, 46, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, S.; Nordmann, G.; Brohi, K.; Midwinter, M.; Woolley, T.; Gwyther, R.; Wilson, C.; Poon, H.; Kirkman, E. Evaluation of Prehospital Blood Products to Attenuate Acute Coagulopathy of Trauma in a Model of Severe Injury and Shock in Anesthetized Pigs. Shock 2015, 44, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, E.J.; Hernandez-Torres, S.I.; Boice, E.N. An Image Classification Deep-Learning Algorithm for Shrapnel Detection from Ultrasound Images. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaseen, M. What Is YOLOv8: An In-Depth Exploration of the Internal Features of the Next-Generation Object Detector 2024. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.15857. [Google Scholar]
- Bilous, N.; Malko, V.; Frohme, M.; Nechyporenko, A. Comparison of CNN-Based Architectures for Detection of Different Object Classes. AI 2024, 5, 2300–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.-H.; Pham, T.-L. Ovarian Tumors Detection and Classification on Ultrasound Images Using One-Stage Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Robot. Control. (JRC) 2024, 5, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. YOLO by Ultralytics. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-Cnn: Delving into High Quality Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; IEEE: New York City, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, A.; Lim, R.; Johannigman, J.; Fox, C.J.; Inaba, K.; Vercruysse, G.A.; Thomas, R.W.; Martin, M.J.; Konstantyn, G.; Schwaitzberg, S.D.; et al. Putting Medical Boots on the Ground: Lessons from the War in Ukraine and Applications for Future Conflict with Near-Peer Adversaries. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2023, 237, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernandez Torres, S.I.; Holland, L.; Winter, T.; Ortiz, R.; Amezcua, K.-L.; Ruiz, A.; Thorpe, C.R.; Snider, E.J. Real-Time Deployment of Ultrasound Image Interpretation AI Models for Emergency Medicine Triage Using a Swine Model. Technologies 2025, 13, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13010029
Hernandez Torres SI, Holland L, Winter T, Ortiz R, Amezcua K-L, Ruiz A, Thorpe CR, Snider EJ. Real-Time Deployment of Ultrasound Image Interpretation AI Models for Emergency Medicine Triage Using a Swine Model. Technologies. 2025; 13(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernandez Torres, Sofia I., Lawrence Holland, Theodore Winter, Ryan Ortiz, Krysta-Lynn Amezcua, Austin Ruiz, Catherine R. Thorpe, and Eric J. Snider. 2025. "Real-Time Deployment of Ultrasound Image Interpretation AI Models for Emergency Medicine Triage Using a Swine Model" Technologies 13, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13010029
APA StyleHernandez Torres, S. I., Holland, L., Winter, T., Ortiz, R., Amezcua, K.-L., Ruiz, A., Thorpe, C. R., & Snider, E. J. (2025). Real-Time Deployment of Ultrasound Image Interpretation AI Models for Emergency Medicine Triage Using a Swine Model. Technologies, 13(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13010029








