A Survey of Robots in Healthcare
Abstract
1. Introduction
- What research has been performed towards developing robotics for healthcare?
- How commercially available robots are used in healthcare?
- What are the challenges the robots are facing in the -world environments?
2. Methodology
3. Care Robots
4. Hospital Robots
5. Assistive Robots
6. Rehabilitation Robots
6.1. Upper Limb Rehabilitation
6.2. Lower Limb Rehabilitation
7. Walking Assisting Robots
8. Open Challenges for Robots in Healthcare and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sander, M.; Oxlund, B.; Jespersen, A.; Krasnik, A.; Mortensen, E.L.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; Rasmussen, L.J. The challenges of human population ageing. Age Ageing 2015, 44, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.M. Caregiver Shortage Reaches Critical Stage. Provider (Wash. DC) 2017, 43, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Poghosyan, L.; Clarke, S.P.; Finlayson, M.; Aiken, L.H. Nurse burnout and quality of care: Cross-national investigation in six countries. Res. Nurs. Health 2010, 33, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.H.; Johnson, J.; Watt, I.; Tsipa, A.; O’Connor, D.B. Healthcare staff wellbeing, burnout, and patient safety: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J. Interviewing Roomba: A posthuman study of humans and robot vacuum cleaners. Explor. Media Ecol. 2020, 19, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudwell, C.; Lacey, C. What do home robots want? The ambivalent power of cuteness in robotic relationships. Convergence 2020, 26, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smids, J.; Nyholm, S.; Berkers, H. Robots in the Workplace: A Threat to—Or Opportunity for—Meaningful Work? Philos. Technol. 2020, 33, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evjemo, L.D.; Gjerstad, T.; Grøtli, E.I.; Sziebig, G. Trends in Smart Manufacturing: Role of Humans and Industrial Robots in Smart Factories. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2020, 1, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoste, J.; Heidmets, M. The impact of educational robots as learning tools on mathematics learning outcomes in basic education. In Digital Turn in Schools—Research, Policy, Practice; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 203–217. [Google Scholar]
- Kwoh, Y.S.; Hou, J.; Jonckheere, E.A.; Hayati, S. A robot with improved absolute positioning accuracy for CT guided stereotactic brain surgery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1988, 35, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic. Acta Bio Medica Atenei Parm. 2020, 91, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.H.; Siddique, A.; Lee, C.W. Robotics Utilization for Healthcare Digitization in Global COVID-19 Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynsberghe, A. Designing Robots for Care: Care Centered Value-Sensitive Design. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2013, 19, 407–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson-Pajala, R.M.; Thommes, K.; Hoppe, J.; Tuisku, O.; Hennala, L.; Pekkarinen, S.; Melkas, H.; Gustafsson, C. Care Robot Orientation: What, Who and How? Potential Users’ Perceptions. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandemeulebroucke, T.; Dierckx de Casterlé, B.; Gastmans, C. The use of care robots in aged care: A systematic review of argument-based ethics literature. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2018, 74, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordoch, E.; Osterreicher, A.; Guse, L.; Roger, K.; Thompson, G. Use of social commitment robots in the care of elderly people with dementia: A literature review. Maturitas 2012, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, R.; Yussof, H. Feasibility of care robots for children with special needs: A review. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors (IRIS), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 5–7 October 2017; pp. 379–382. [Google Scholar]
- Dawe, J.; Sutherland, C.; Barco, A.; Broadbent, E. Can social robots help children in healthcare contexts? A scoping review. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2019, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, D.E.; Breazeal, C.; Goodwin, M.S.; Jeong, S.; O’Connell, B.; Smith-Freedman, D.; Heathers, J.; Weinstock, P. Social Robots for Hospitalized Children. Pediatrics 2019, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Allaban, A.; Wang, M.; Padır, T. A Systematic Review of Robotics Research in Support of In-Home Care for Older Adults. Information 2020, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Martin, E.; Escalona, F.; Cazorla, M. Socially Assistive Robots for Older Adults and People with Autism: An Overview. Electronics 2020, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Gelin, R. A Mass-Produced Sociable Humanoid Robot: Pepper: The First Machine of Its Kind. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2018, 25, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper in Healthcare. Available online: https://www.softbankrobotics.com/emea/en/pepper-healthcare-ga (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Tanaka, F.; Isshiki, K.; Takahashi, F.; Uekusa, M.; Sei, R.; Hayashi, K. Pepper learns together with children: Development of an educational application. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE-RAS 15th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Seoul, Korea, 3–5 November 2015; pp. 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Lu, M.; Tseng, S.; Fu, L. A companion robot for daily care of elders based on homeostasis. In Proceedings of the 2017 56th Annual Conference of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers of Japan (SICE), Kanazawa, Japan, 19–22 September 2017; pp. 1401–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Yasuhara, Y.; Osaka, K.; Ito, H.; Dino, M.J.S.; Ong, I.L.; Zhao, Y.; Tanioka, T. Rehabilitation care with Pepper humanoid robot: A qualitative case study of older patients with schizophrenia and/or dementia in Japan. Enferm. Clín. 2020, 30, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carros, F.; Meurer, J.; Löffler, D.; Unbehaun, D.; Matthies, S.; Koch, I.; Wieching, R.; Randall, D.; Hassenzahl, M.; Wulf, V. Exploring Human-Robot Interaction with the Elderly: Results from a Ten-Week Case Study in a Care Home. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI ’20), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IIT NCSR Demokritos Presentation at Thessaloniki International Fair. Available online: https://www.iit.demokritos.gr/ (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Costa, A.; Martinez-Martin, E.; Cazorla, M.; Julian, V. PHAROS—PHysical assistant RObot system. Sensors 2018, 18, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Martin, E.; Costa, A.; Cazorla, M. PHAROS 2.0—A PHysical Assistant RObot System Improved. Sensors 2019, 19, 4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousif, J.; Yousif, M. Humanoid Robot as Assistant Tutor for Autistic Children. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Sci. 2020, 8, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari, P.T.V.; Vignesh, S.; Papitha, S.; Dharmarajan, R.S. Humanoid robot based physiotherapeutic assistive trainer for elderly health care. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Recent Trends in Information Technology (ICRTIT), Chennai, India, 25–27 July 2013; pp. 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiakas, K.; Abujelala, M.; Makedon, F. Task engagement as personalization feedback for socially-assistive robots and cognitive training. Technologies 2018, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, J.P.M.; Couceiro, M.S.; Rodrigues, N.M.M.; Figueiredo, C.M.; Ferreira, N.M.F. Fostering the NAO platform as an elderly care robot. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Serious Games and Applications for Health (SeGAH), Vilamoura, Portugal, 2–3 May 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Qidwai, U.; Kashem, S.B.A.; Conor, O. Humanoid Robot as a Teacher’s Assistant: Helping Children with Autism to Learn Social and Academic Skills. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2019, 98, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Softbank Robotics Europe/CC BY-SA. Available online: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0 (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Zora Robots. Available online: https://www.zorarobotics.be (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Van den Heuvel, R.; Lexis, M.; Witte, L. Robot ZORA in rehabilitation and special education for children with severe physical disabilities: A pilot study. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2017, 40, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, C.; Kort, H.S.M. Two-Year Use of Care Robot Zora in Dutch Nursing Homes: An Evaluation Study. Healthcare 2019, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robots.nu. Available online: https://robots.nu/en/robot/james-robot (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Kittmann, R.; Fröhlich, T.; Schäfer, J.; Reiser, U.; Weisshardt, F.; Haug, A. Let me Introduce Myself: I am Care-O-bot 4, a Gentleman Robot. In Mensch und Computer 2015—Proceedings; Diefenbach, S., Henze, N., Pielot, M., Eds.; De Gruyter Oldenbourg: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Kort, H.; Huisman, C. Care Robot ZORA in Dutch Nursing Homes; An Evaluation Study. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2017, 242, 527–534. [Google Scholar]
- Lüdtke, M. Mathias (Fraunhofer IPA): Service robots with CAN-driven devices. CAN Newsletters 2017, 1, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Care-O-bot 3. Available online: https://www.care-o-bot.de/en/care-o-bot-3.html (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Jacobs, T.; Graf, B. Practical evaluation of service robots for support and routine tasks in an elderly care facility. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Workshop on Advanced Robotics and its Social Impacts (ARSO), Munich, Germany, 21–23 May 2012; pp. 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Care-O-Bot. Available online: https://www.care-o-bot.de/en/care-o-bot-4/download/images.html (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Miseikis, J.; Caroni, P.; Duchamp, P.; Gasser, A.; Marko, R.; Miseikiene, N.; Zwilling, F.; Castelbajac, C.; Eicher, L.; Frueh, M.; et al. Lio—A Personal Robot Assistant for Human-Robot Interaction and Care Applications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 5339–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P-Rob. Available online: https://www.fp-robotics.com/en/p-rob/ (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- F&P Robotics. Available online: https://www.fp-robotics.com/ (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Fischinger, D.; Einramhof, P.; Papoutsakis, K.; Wohlkinger, W.; Mayer, P.; Panek, P.; Hofmann, S.; Koertner, T.; Weiss, A.; Argyros, A.; et al. Hobbit, a care robot supporting independent living at home: First prototype and lessons learned. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 75, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostavelis, I.; Giakoumis, D.; Malasiotis, S.; Tzovaras, D. Ramcip: Towards a robotic assistant to support elderly with mild cognitive impairments at home. In International Symposium on Pervasive Computing Paradigms for Mental Health; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 186–195. [Google Scholar]
- RAMCIP—Robotic Assistant for MCI Patients at home. Available online: https://ramcip-project.eu/ (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Koceski, S.; Koceska, N. Evaluation of an assistive telepresence robot for elderly healthcare. J. Med. Syst. 2016, 40, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranney, M.L.; Griffeth, V.; Jha, A.K. Critical supply shortages—The need for ventilators and personal protective equipment during the Covid-19 pandemic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxi Helps Hospitals and Clinical Staff. Available online: https://diligentrobots.com/moxi (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- Ackerman, E. How Diligent’s Robots Are Making a Difference in Texas Hospitals. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/automaton/robotics/medical-robots/how-diligents-robots-are-making-a-difference-in-texas-hospitals (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- ABB Demonstrates Concept of Mobile Laboratory Robot for Hospital of the Future. Available online: https://new.abb.com/news/detail/37279/hospital-of-the-future (accessed on 31 March 2020).
- Tug. Change Healthcare. Mobile Robots Improve Patient Care, Employee Satisfaction, Safety, Productivity and More. Available online: https://aethon.com/mobile-robots-for-healthcare/ (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- Relay Autonomous Service Robot for Hospitals. Available online: https://www.swisslog-healthcare.com/en-us/products-and-services/transport-automation/relay-autonomous-service-robot/ (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- The Strong Robot with the Gentle Touch. Available online: https://www.riken.jp/en/news_pubs/research_news/pr/2015/20150223_2/ (accessed on 23 February 2015).
- Perry, T.S. Profile: Veebot. Making a Robot That Can Draw Blood Faster and More Safely Than a Human Can. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/robotics/medical-robots/profile-veebot (accessed on 26 July 2013).
- Healthcare. Embrace Robotics in e-Healthcare and Create Digital Patient-Enablement Journey. Available online: https://www.softbankrobotics.com/emea/en/industries/healthcare (accessed on 17 September 2020).
- Das, S.K.; Sahu, A.; Popa, D.O. Mobile app for human-interaction with sitter robots. In Smart Biomedical and Physiological Sensor Technology XIV; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Anaheim, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 10216, p. 102160D. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.K. Adaptive Physical Human-Robot Interaction (PHRI) with a Robotic Nursing Assistant. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Louisville, Louisville, Kentucky, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abubakar, S.; Das, S.K.; Robinson, C.; Saadatzi, M.N.; Logsdon, M.C.; Mitchell, H.; Chlebowy, D.; Popa, D.O. ARNA, a Service robot for Nursing Assistance: System Overview and User Acceptability. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 16th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Hong Kong, China, 20–21 August 2020; pp. 1408–1414. [Google Scholar]
- DeKonBot—Mobile Robot for Disinfecting Potentially Contaminated Surfaces. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lBj6P9lfXDM&feature=emb_title&ab_channel=FraunhoferIPA (accessed on 26 September 2020).
- Armour, B.S.; Courtney-Long, E.A.; Fox, M.H.; Fredine, H.; Cahill, A. Prevalence and causes of paralysis—United States, 2013. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 1855–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graser, A.; Heyer, T.; Fotoohi, L.; Lange, U.; Kampe, H.; Enjarini, B.; Heyer, S.; Fragkopoulos, C.; Ristic-Durrant, D. A supportive friend at work: Robotic workplace assistance for the disabled. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2013, 20, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, C.; Prenzel, O.; Gräser, A. The rehabilitation robots FRIEND-I & II: Daily life independency through semi-autonomous task-execution. Rehabil. Robot. 2007, 1, 137–162. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, C.S.; Wang, H.; Cooper, R.A. Functional assessment and performance evaluation for assistive robotic manipulators: Literature review. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2013, 36, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KINOVA JACO Assistive Robotic Arm. Available online: https://www.kinovarobotics.com/en/products/assistive-technologies/kinova-jaco-assistive-robotic-arm (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- Gordon, E.K.; Meng, X.; Barnes, M.; Bhattacharjee, T.; Srinivasa, S.S. Adaptive Robot-Assisted Feeding: An Online Learning Framework for Acquiring Previously-Unseen Food Items. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.07088. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, T.; Gordon, E.K.; Scalise, R.; Cabrera, M.E.; Caspi, A.; Cakmak, M.; Srinivasa, S.S. Is More Autonomy Always Better? Exploring Preferences of Users with Mobility Impairments in Robot-assisted Feeding. In Proceedings of the 2020 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, Cambridge, UK, 23–26 March 2020; pp. 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Goldau, F.F.; Shastha, T.K.; Kyrarini, M.; Gräser, A. Autonomous multi-sensory robotic assistant for a drinking task. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar Shastha, T.; Kyrarini, M.; Gräser, A. Application of Reinforcement Learning to a Robotic Drinking Assistant. Robotics 2020, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, M.A.; Kyrarini, M.; Jiang, S.; Ristic-Durrant, D.; Gräser, A. Head gesture-based control for assistive robots. In Proceedings of the 11th PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference, Corfu, Greece, 26–29 June 2018; pp. 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Rudigkeit, N.; Gebhard, M. AMiCUS 2.0—System Presentation and Demonstration of Adaptability to Personal Needs by the Example of an Individual with Progressed Multiple Sclerosis. Sensors 2020, 20, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsharif, S.; Kuzmicheva, O.; Gräser, A. Gaze gesture-based human robot interface. In Technische Unterstützungssysteme, Die Die Menschen Wirklich Wollen; Helmut-Schmidt-Universität: Hamburg, Germany, 2016; p. 339. [Google Scholar]
- Mindermann, B. Untersuchung Eines Hybriden Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) zur Optimalen Auslegung als Mensch-Maschine-Schnittstelle. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Bremen, Bremen, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kyrarini, M.; Zheng, Q.; Haseeb, M.A.; Gräser, A. Robot Learning of Assistive Manipulation Tasks by Demonstration via Head Gesture-based Interface. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 1139–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Rethink Robotics. Available online: https://www.rethinkrobotics.com/ (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- Zhang, F.; Cully, A.; Demiris, Y. Probabilistic real-time user posture tracking for personalized robot-assisted dressing. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2019, 35, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevtić, A.; Valle, A.F.; Alenyà, G.; Chance, G.; Caleb-Solly, P.; Dogramadzi, S.; Torras, C. Personalized robot assistant for support in dressing. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2018, 11, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett Advanced Robotics—The WAM Arm. Available online: https://advanced.barrett.com/wam-arm-1 (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Oladayo, A.S.; Assal, F.S.; El-Hussieny, H. Towards Development of an Autonomous Robotic System for Beard Shaving Assistance for Disabled People. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Bari, Italy, 6–9 October 2019; pp. 3435–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, J. Hair-Brushing Robot Shows How Artificial Intelligence May Help the Disabled. Available online: https://fortune.com/2019/12/11/robot-hair-brushing-elderly/ (accessed on 11 December 2019).
- Zlatintsi, A.; Dometios, A.; Kardaris, N.; Rodomagoulakis, I.; Koutras, P.; Papageorgiou, X.; Maragos, P.; Tzafestas, C.S.; Vartholomeos, P.; Hauer, K.; et al. I-Support: A robotic platform of an assistive bathing robot for the elderly population. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 126, 103451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajavenkatanarayanan, A.; Kanal, V.; Tsiakas, K.; Calderon, D.; Papakostas, M.; Abujelala, M.; Galib, M.; Ford, J.; Wylie, G.; Makedon, F. A Survey of Assistive Technologies for Assessment and Rehabilitation of Motor Impairments in Multiple Sclerosis. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2019, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ármannsdóttir, A.L.; Beckerle, P.; Moreno, J.C.; van Asseldonk, E.H.; Manrique-Sancho, M.T.; Del-Ama, A.J.; Veneman, J.F.; Briem, K. Assessing the Involvement of Users During Development of Lower Limb Wearable Robotic Exoskeletons: A Survey Study. Hum. Factors 2020, 62, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, J.; Song, R.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. The design and control of a 3DOF lower limb rehabilitation robot. Mechatronics 2016, 33, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiammanussakul, T.; Sangveraphunsiri, V. A lower limb rehabilitation robot in sitting position with a review of training activities. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, J.K.; Mohan, S.; Deepasundar, P.; Kiruba-Shankar, R. Development and control of a new sitting-type lower limb rehabilitation robot. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 67, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikri, M.A.; Abdullah, S.C.; Ramli, M.H.M. Arm exoskeleton for rehabilitation following stroke by learning algorithm prediction. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 42, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Yu, S. Developing Conceptual PSS Models of Upper Limb Exoskeleton based Post-stroke Rehabilitation in China. Procedia CIRP 2019, 80, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamaddan, S.; Jamali, A.; Abidin, A.S.Z.; Jamaludin, M.S.; Abd Majid, N.A.; Ashari, M.F.; Hazmi, H. Development of upper limb rehabilitation robot device for home setting. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 76, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Ji, L.; Bi, S.; Zhang, X.; Huo, J.; Ji, R. Development and implementation of an end-effector upper limb rehabilitation robot for hemiplegic patients with line and circle tracking training. J. Healthc. Eng. 2017, 2017, 4931217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejasz, P.; Eschweiler, J.; Gerlach-Hahn, K.; Jansen-Toy, A.; Leonhardt, S. A survey on robotic devices for upper limb rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Tay, E.H. An Interactive Training System for Upper Limb Rehabilitation Using Visual and Auditory Feedback. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on Robotics and Artificial Intelligence, Singapore, 22–24 November 2019; pp. 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Rijanto, E.; Adiwiguna, E.; Rozaqi, L.; Sadono, A.P.; Nugraha, M.H. Experimental Performance Evaluation of Computer Vision for an Upper Limbs Rehabilitation Robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computer, Control, Informatics and its Applications (IC3INA), Tangerang, Indonesia, 23–24 October 2019; pp. 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Xie, Q.; Yu, H. Upper-Limb Rehabilitation Robot: State of the Art and Existing Problems. In Proceedings of the 12th International Convention on Rehabilitation Engineering and Assistive Technology, Białystok, Poland, 28–30 June 2018; pp. 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, F.; Tang, H.; Wang, J.; Wen, W. System framework of robotics in upper limb rehabilitation on poststroke motor recovery. Behav. Neurol. 2018, 2018, 6737056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, G.; Cho, D.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Park, S.B.; Shin, J.H. Comparisons between end-effector and exoskeleton rehabilitation robots regarding upper extremity function among chronic stroke patients with moderate-to-severe upper limb impairment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmat, N.; Zuo, J.; Meng, W.; Liu, Q.; Xie, S.Q.; Liang, H. Upper limb rehabilitation using robotic exoskeleton systems: A systematic review. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2018, 2, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouteraa, Y.; Abdallah, I.B. Exoskeleton robots for upper-limb rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD), Leipzig, Germany, 21–24 March 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, S. Design and Analysis of a Wearable Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot with Characteristics of Tension Mechanism. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, Y.; Aubakir, B.; Hussain, S.; Shintemirov, A. An end-effector based upper-limb rehabilitation robot: Preliminary mechanism design. In Proceedings of the 2014 10th France-Japan/8th Europe-Asia Congress on Mecatronics (MECATRONICS2014-Tokyo), Tokyo, Japan, 27–29 November 2014; pp. 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Burt—The User-Friendly Robot. Available online: https://medical.barrett.com/home (accessed on 18 October 2020).
- The WAM® Arm. Available online: https://advanced.barrett.com/wam-arm-1#:~:text=The%20WAM%C2%AE%20Arm%20is,mechanical%20force%20or%20torque%20sensors (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Lioulemes, A.; Theofanidis, M.; Kanal, V.; Tsiakas, K.; Abujelala, M.; Collander, C.; Townsend, W.B.; Boisselle, A.; Makedon, F. MAGNI Dynamics: A vision-based kinematic and dynamic upper-limb model for intelligent robotic rehabilitation. Int. J. Biomed. Biol. Eng. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 11, 158–167. [Google Scholar]
- Rajavenkatanarayanan, A.; Kanal, V.; Tsiakas, K.; Brady, J.; Calderon, D.; Wylie, G.; Makedon, F. Towards a robot-based multimodal framework to assess the impact of fatigue on user behavior and performance: A pilot study. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, Rhodes, Greece, 5–7 June 2019; pp. 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Kanal, V.; Brady, J.; Nambiappan, H.; Kyrarini, M.; Wylie, G.; Makedon, F. Towards a serious game based human-robot framework for fatigue assessment. In Proceedings of the 13th ACM International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, Corfu, Greece, 30 June–3 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, B.; Artemiadis, P. A Review of Robot-Assisted Lower-Limb Stroke Therapy: Unexplored Paths and Future Directions in Gait Rehabilitation. Front. Neurorobot. 2020, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeilig, G.; Weingarden, H.; Zwecker, M.; Dudkiewicz, I.; Bloch, A.; Esquenazi, A. Safety and tolerance of the ReWalk™ exoskeleton suit for ambulation by people with complete spinal cord injury: A pilot study. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2012, 35, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ReWalk More Than Walking. Available online: https://rewalk.com/ (accessed on 8 December 2020).
- Lokomat. Available online: https://www.hocoma.com/ (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Kuzmicheva, O.; Focke Martinez, S.; Krebs, U.; Spranger, M.; Moosburner, S.; Wagner, B.; Graser, A. Overground robot based gait rehabilitation system MOPASS—Overview and first results from usability testing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3756–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Machine Learning for Gait Classification. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Bremen, Bremen, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Matjačić, Z.; Zadravec, M.; Olenšek, A. Feasibility of robot-based perturbed-balance training during treadmill walking in a high-functioning chronic stroke subject: A case-control study. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadravec, M.; Olenšek, A.; Rudolf, M.; Bizovičar, N.; Goljar, N.; Matjacic, Z. Assessment of dynamic balancing responses following perturbations during slow walking in relation to clinical outcome measures for high-functioning post-stroke subjects. Rev. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straudi, S.; Benedetti, M.G.; Venturini, E.; Manca, M.; Foti, C.; Basaglia, N. Does robot-assisted gait training ameliorate gait abnormalities in multiple sclerosis? A pilot randomized-control trial. NeuroRehabilitation 2013, 33, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.X.; Ge, L.; Wang, C.C.; Ma, Q.S.; Liao, Y.T.; Huang, P.P.; Wang, G.D.; Xie, Q.L.; Rask, M. Robot-assisted therapy for balance function rehabilitation after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2019, 95, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, P.; Zambalde, E.P.; Foley, G.; Graham, J.L.; Wang, R.H.; Adhikari, B.; Mackworth, A.K.; Mihailidis, A.; Miller, W.C.; Mitchell, I.M. Intelligent wheelchair control strategies for older adults with cognitive impairment: User attitudes, needs, and preferences. Auton. Robot. 2017, 41, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, I.; Lee, M.; Ryu, J.; Mun, M. Intelligent robotic wheelchair with EMG-, gesture-, and voice-based interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2003) (Cat. No. 03CH37453), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–31 October 2003; Volume 4, pp. 3453–3458. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, W.; Mohammed, S.; Moreno, J.C.; Amirat, Y. Lower limb wearable robots for assistance and rehabilitation: A state of the art. IEEE Syst. J. 2014, 10, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, H.A.; Sup, F.; Goldfarb, M. Multiclass real-time intent recognition of a powered lower limb prosthesis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 57, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, J.; Tao, C.; Chen, X.; Xu, W. Intelligent mobile walking-aids: Perception, control and safety. Adv. Robot. 2020, 34, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, P.; Hasegawa, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Sekiyama, K.; Fukuda, T.; Huang, J.; Huang, Q. Fall Detection and Prevention Control Using Walking-Aid Cane Robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, J.; Luo, Z. Human-robot coordination stability for fall detection and prevention using cane robot. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Micro-NanoMechatronics and Human Science (MHS), Nagoya, Japan, 28–30 November 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Van Lam, P.; Fujimoto, Y. A Robotic Cane for Balance Maintenance Assistance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 3998–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, J.; Cheng, L. A novel coordinated motion fusion-based walking-aid robot system. Sensors 2018, 18, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cifuentes, C.A.; Rodriguez, C.; Frizera-Neto, A.; Bastos-Filho, T.F.; Carelli, R. Multimodal Human–Robot Interaction for Walker-Assisted Gait. IEEE Syst. J. 2016, 10, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Lin, C.; Huang, K.; Song, K. Shared Control Design of a Walking-Assistant Robot. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2017, 25, 2143–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalvatzaki, G.; Koutras, P.; Hadfield, J.; Papageorgiou, X.S.; Tzafestas, C.S.; Maragos, P. Lstm-based network for human gait stability prediction in an intelligent robotic rollator. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 4225–4232. [Google Scholar]
- Chalvatzaki, G.; Papageorgiou, X.S.; Tzafestas, C.S. Towards a user-adaptive context-aware robotic walker with a pathological gait assessment system: First experimental study. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 5037–5042. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.T.; Jiang, S.Y.; Wu, S.Y. Safe guidance for a walking-assistant robot using gait estimation and obstacle avoidance. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 2070–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokomat Therapy—Robotic Treadmill May Enable Some Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries or Stroke to Learn to Walk Again. Available online: https://www.umms.org/rehab/health-services/therapeutic-technology/lokomat-therapy (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Leading German Private Health Insurer Enters Contract to Provide ReWalk Exoskeletons to Individuals with Spinal Cord Injuries. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2020/12/10/2142922/0/en/Leading-German-Private-Health-Insurer-Enters-Contract-to-Provide-ReWalk-Exoskeletons-to-Individuals-with-Spinal-Cord-Injuries.html (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Korus, S. Industrial Robot Cost Declines Should Trigger Tipping Points in Demand. Available online: https://ark-invest.com/articles/analyst-research/industrial-robot-cost-declines/ (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Wan, S.; Gu, Z.; Ni, Q. Cognitive computing and wireless communications on the edge for healthcare service robots. Comput. Commun. 2020, 149, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13482:2014 Robots and robotic devices—Safety requirements for personal care robots. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/53820.html (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Villaronga, E.F. ISO 13482: 2014 and its confusing categories. Building a bridge between law and robotics. In New Trends in Medical and Service Robots; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Fosch-Villaronga, E. Robots, Healthcare, and the Law: Regulating Automation in Personal Care; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Grasso, C. Challenges and advantages of robotic nursing care: A social and ethical analysis. Available online: https://corporatesocialresponsibilityblog.com/2018/06/26/robotic-nursing-care/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Wachsmuth, I. Robots like me: Challenges and ethical issues in aged care. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.; Lee, H.R.; Kubota, A.; Riek, L.D. Coordinating clinical teams: Using robots to empower nurses to stop the line. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2019, 3, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, B.; Ramachandran, A.; Spaulding, S.; Glas, D.F.; Leite, I.; Koay, K.L. Personalization in long-term human-robot interaction. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), Daegu, Korea, 11–14 March 2019; pp. 685–686. [Google Scholar]
- Rajavenkatanarayanan, A.; Nambiappan, H.R.; Kyrarini, M.; Makedon, F. Towards a Real-Time Cognitive Load Assessment System for Industrial Human-Robot Cooperation. In Proceedings of the 2020 29th IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Naples, Italy, 31 August–4 September 2020; pp. 698–705. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, W. Ruthless Quotas at Amazon Are Maiming Employees. Atlantic 2019. Available online: https://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2019/11/amazon-warehouse-reports-show-worker-injuries/602530/ (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Del Rey, J. How robots are transforming Amazon warehouse jobs—For better and worse. Available online: https://www.vox.com/recode/2019/12/11/20982652/robots-amazon-warehouse-jobs-automation (accessed on 6 January 2021).
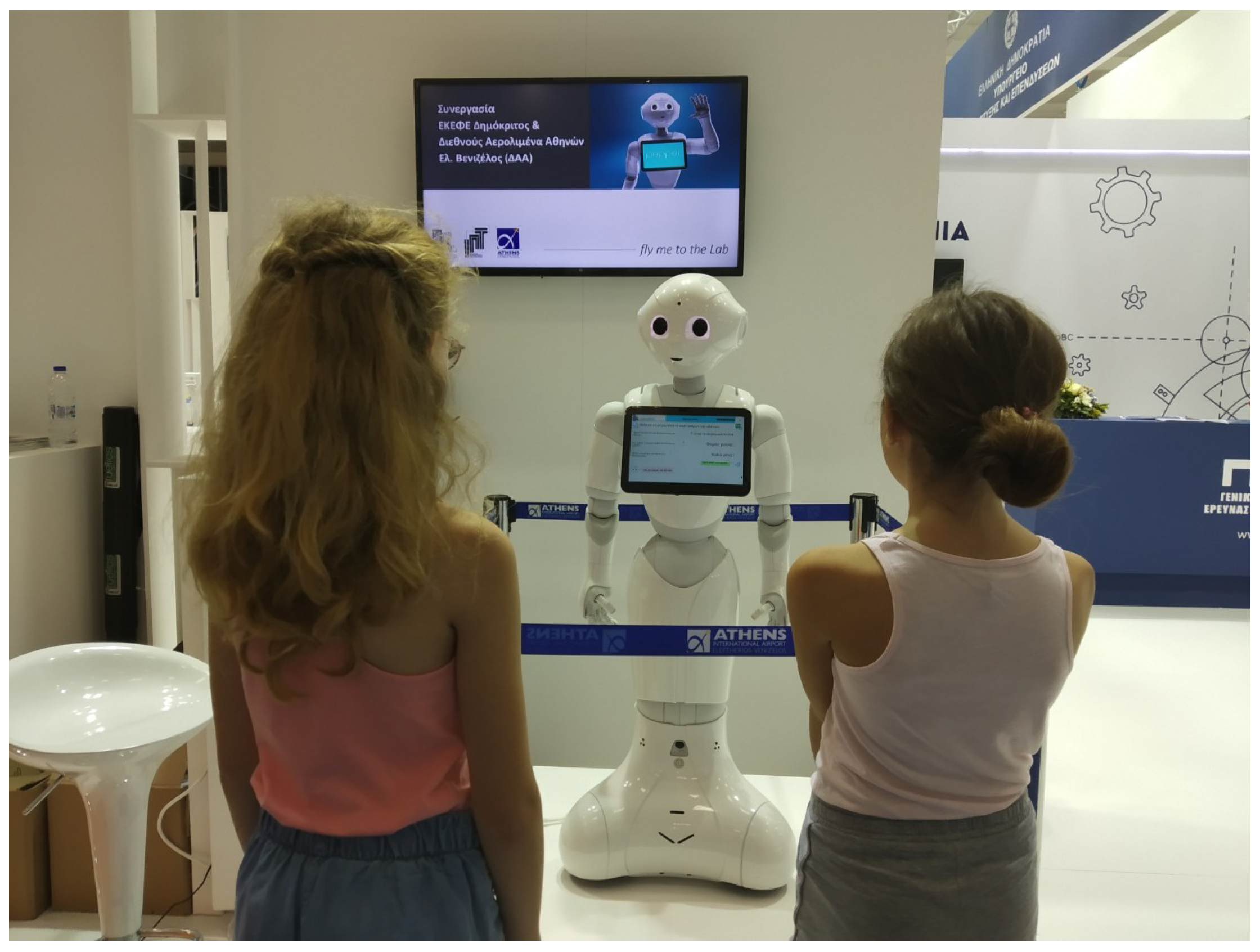
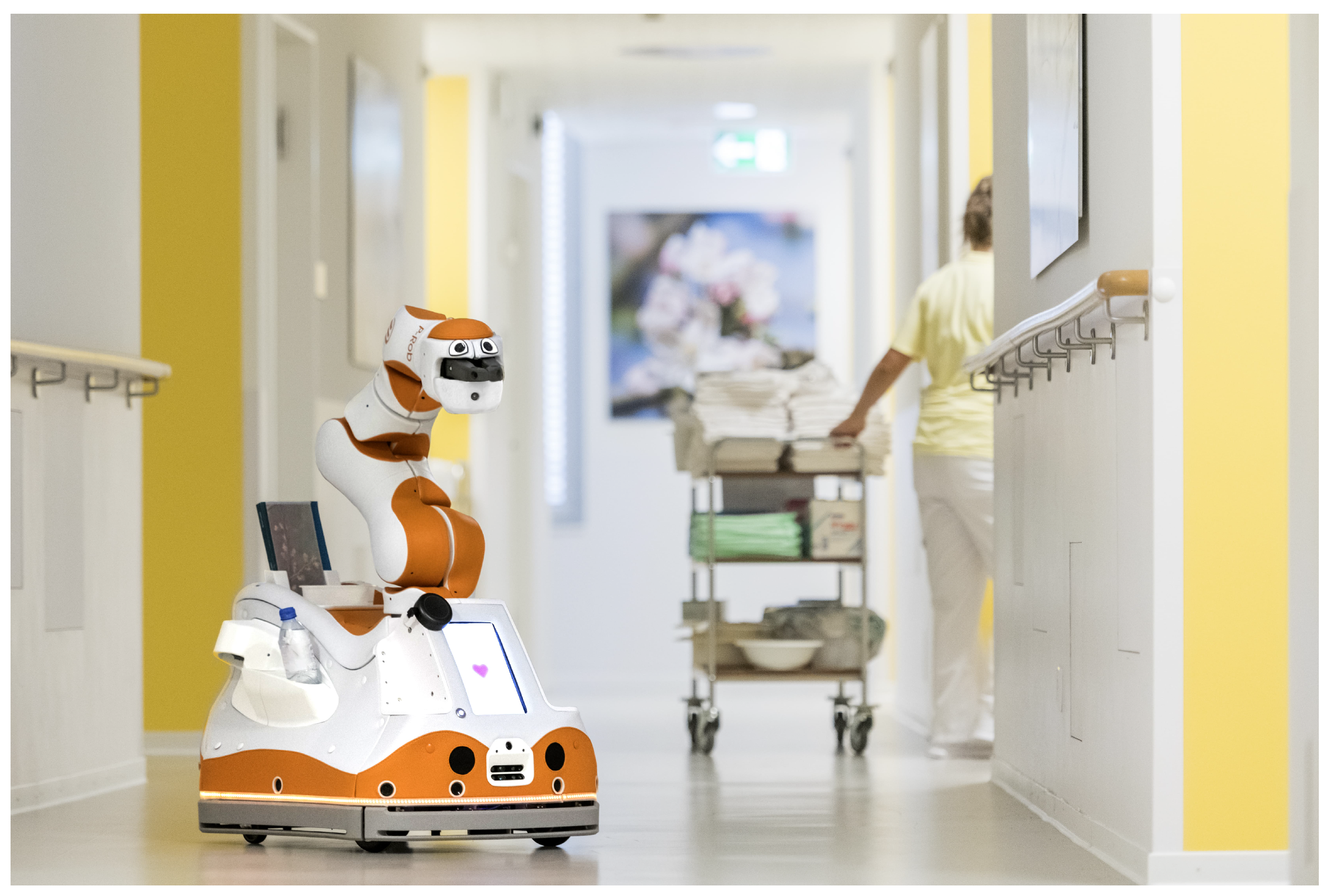










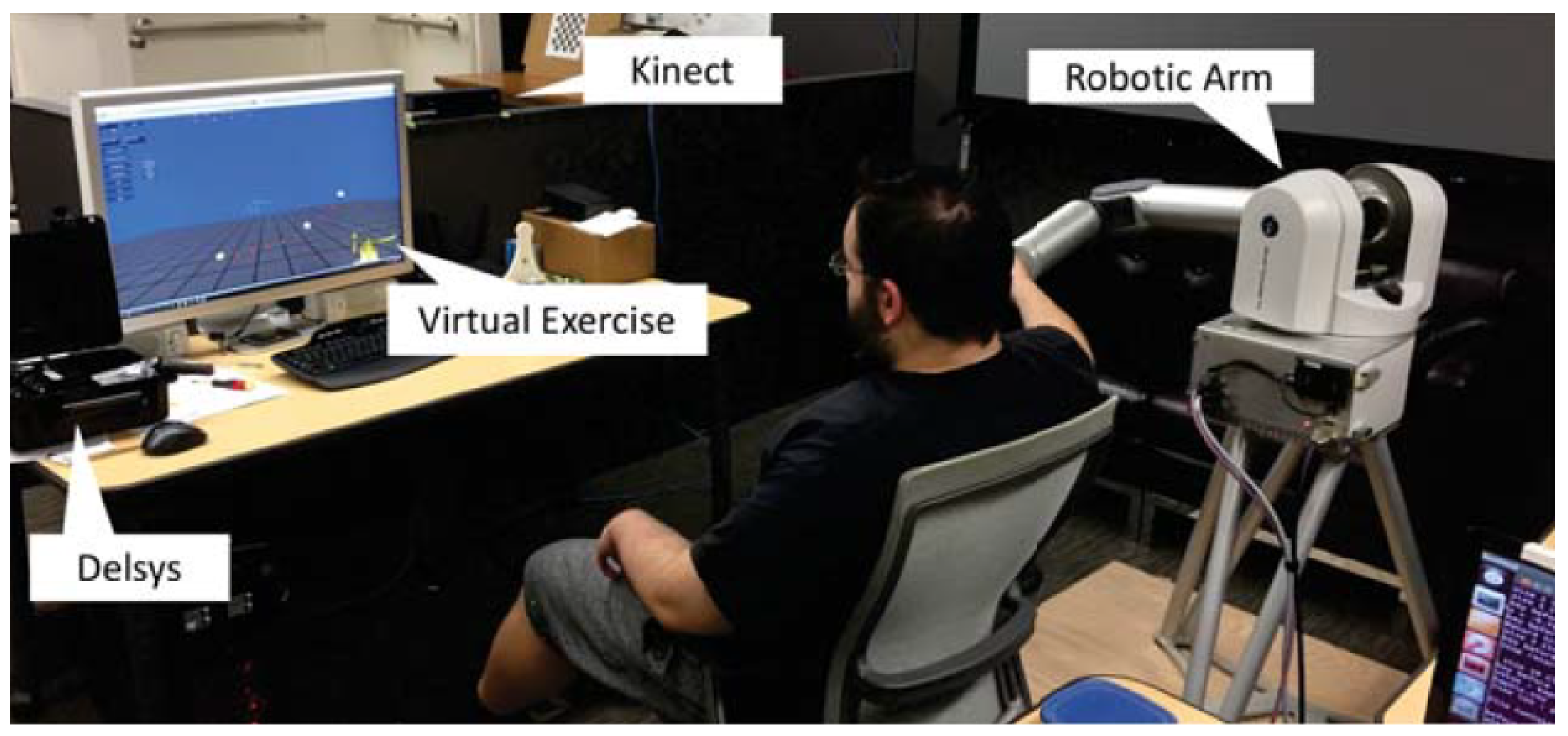
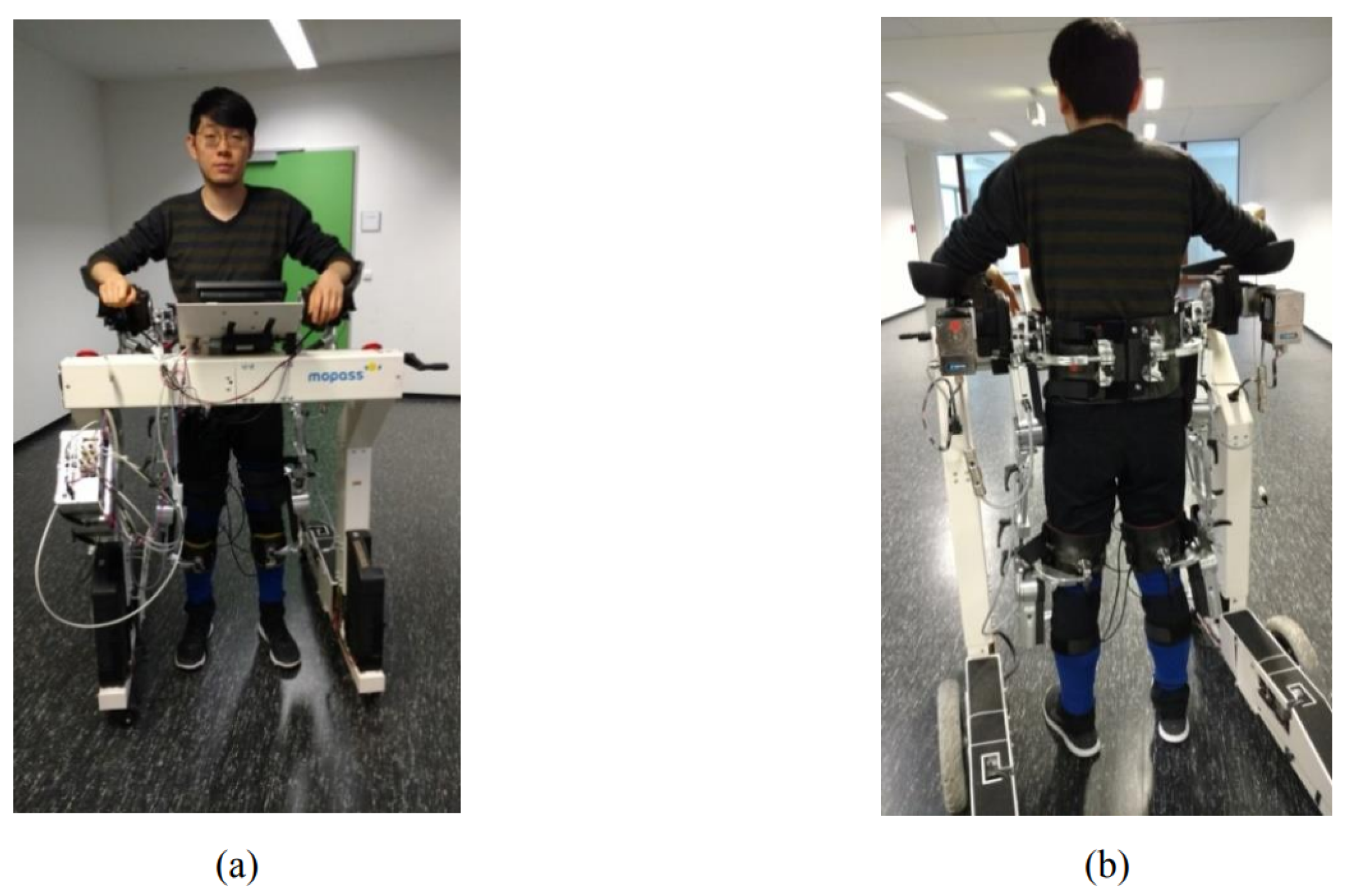

| Robotic Platform | Platform Status | Robot Category | Tasks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pepper | Commercial Product | Care/Hospital | Therapy, Cognitive and Physical Training, Providing Information, Human Activity and Health Monitoring, Conducting Surveys | [21,23,24,25,26,27,29,30] |
| Nao | Commercial Product | Care | Therapy, Cognitive and Physical Training | [31,32,33,34,35,39] |
| Care-O-Bot4 | Research | Care | Collection and Delivery Services, Serving Drinks, Providing Information | [41] |
| Lio | Commercial Product | Care | Collection and Delivery Services, Entertainment and Motivation, Automatically Entering Rooms and Reminding Important Tasks | [47] |
| Hobbit | Research | Care | Collection and Delivery Services, Recognition of a User’s Instability | [50] |
| RAMCIP | Research | Care | Collection and Delivery Services, Recognition of Potential Emergencies | [51] |
| Kosecki et al., 2016 | Research | Care | Collection and Delivery Services, Medication Reminder | [53] |
| Moxi | Commercial Product | Hospital | Collection and Delivery Services | [55] |
| YuMi | Commercial Product | Hospital | Collection and Delivery Services | [57] |
| TUG | Commercial Product | Hospital | Collection and Delivery Services | [58] |
| Relay | Commercial Product | Hospital | Collection and Delivery Services | [59] |
| ROBEAR | Experimental | Hospital | Patient Lifting | [60] |
| Veebot | Research | Hospital | Drawing Blood, Inserting IV | [61] |
| ARNA | Research | Hospital/Walking Assistance | Collection and Delivery Services, Patient Monitoring and Walking Assistance | [63,64,65] |
| DeKonBot | Research | Hospital | Disinfection | [66] |
| FRIEND | Research | Assistive | Workplace Assistance, Drinking and Eating Assistance | [68] |
| Jaco 2 | Commercial Product | Assistive | Manipulation Tasks, Drinking/Eating Assistance | [71,72,73,74,75,80] |
| Baxter | Commercial Product | Assistive | Dressing | [82] |
| Barrett’s WAM | Commercial Product | Assistive/Rehabilitation | Shoe Fitting/Game-based Upper limb rehabilitation | [83,109,110,111] |
| Rehmat et al., 2018 | Research | Rehabilitation | Upper Limb Rehabilitation | [103] |
| Zhang et al., 2018 | Research | Rehabilitation | Upper Limb Rehabilitation | [101] |
| Bouteraa et al., 2016 | Research | Rehabilitation | Upper Limb Rehabilitation | [104] |
| Pang et al. | Research | Rehabilitation | Upper Limb Rehabilitation | [105] |
| Burt | Commercial Product | Rehabilitation | Game-based Upper Limb Rehabilitation | [107] |
| Mohamaddan et al., 2015 | Research | Rehabilitation | Upper Limb Rehabilitation | [95] |
| Ding et al., 2019 | Research | Rehabilitation | Upper Limb Rehabilitation | [98] |
| ReWalk | Commercial Product | Rehabilitation | Gait Rehabilitation | [113,114] |
| Lokomat | Commercial Product | Rehabilitation | Gait Rehabilitation | [115] |
| MOPASS | Research | Rehabilitation | Gait Rehabilitation | [116] |
| BART | Research | Rehabilitation | Balance Rehabilitation | [118,119] |
| Di et al., 2016 | Research | Cane-based Walking Assistance | Sit-to-Stand Assistance, Walking Assistance, Walking on a Slope, Emergency Aid, Fall Prevention, Guidance, and Obstacle Avoidance | [127] |
| Yan et al., 2016 | Research | Cane-based Walking Assistance | Walking Assistance, Fall Detection and Prevention | [128] |
| Van Lam and Fujimoto, 2019 | Research | Cane-based Walking Assistance | Walking Assistance, Self-balance, and Fall Prevention | [129] |
| Xu et al., 2018 | Research | Frame-based Walking Assistance | Walking Assistance, Fall detection and Prevention | [130] |
| UFES smart walker | Research | Frame-based Walking Assistance | Walking Assistance, Gait Parameter Estimation | [131] |
| Walbot | Research | Frame-based Walking Assistance | Walking Assistance, Walking on a Slope, Obstacle Detection and Avoidance | [132] |
| iWalk | Research | Frame-based Walking Assistance | Walking-Frame Based Walking Assistants, Patient Monitoring, Human Stability Estimation, Mobility Assessment, Exercise Monitoring, and Gesture Recognition | [133,134] |
| Song et al., 2017 | Research | Frame-based Walking Assistance | Walking Assistance, Fall Prevention, Obstacle Detection, and Avoidance | [135] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kyrarini, M.; Lygerakis, F.; Rajavenkatanarayanan, A.; Sevastopoulos, C.; Nambiappan, H.R.; Chaitanya, K.K.; Babu, A.R.; Mathew, J.; Makedon, F. A Survey of Robots in Healthcare. Technologies 2021, 9, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9010008
Kyrarini M, Lygerakis F, Rajavenkatanarayanan A, Sevastopoulos C, Nambiappan HR, Chaitanya KK, Babu AR, Mathew J, Makedon F. A Survey of Robots in Healthcare. Technologies. 2021; 9(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleKyrarini, Maria, Fotios Lygerakis, Akilesh Rajavenkatanarayanan, Christos Sevastopoulos, Harish Ram Nambiappan, Kodur Krishna Chaitanya, Ashwin Ramesh Babu, Joanne Mathew, and Fillia Makedon. 2021. "A Survey of Robots in Healthcare" Technologies 9, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9010008
APA StyleKyrarini, M., Lygerakis, F., Rajavenkatanarayanan, A., Sevastopoulos, C., Nambiappan, H. R., Chaitanya, K. K., Babu, A. R., Mathew, J., & Makedon, F. (2021). A Survey of Robots in Healthcare. Technologies, 9(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9010008






