The COVID-19 Pandemic Impact and Responses in Emerging Economies: Evidence from Vietnamese Firms
Abstract
1. Introduction
- °
- (1) Non-adoption (i.e., adopting no coping strategy).
- °
- (2) Promoting e-commerce.
- °
- (3) Transforming key products/services.
- °
- (4) Training employees to improve professional qualifications/skills.
- °
- (5) Finding new markets for input materials.
- °
- (6) Finding markets for products outside of the traditional market.
- °
- (7) Producing/providing new products/services according to market demand during the epidemic period.
- °
- (8) Other strategies.
- °
- (1) Micro enterprises, <9 Laborers.
- °
- (2) Small enterprises, 10–49 Laborers.
- °
- (3) Medium enterprises, 50–249 Laborers.
- °
- (4) Large enterprises, >250 Laborers.
- °
- (5) State-owned enterprises.
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Data
3.2. Data Analysis and Empirical Model
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Assessment of the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Firm Performance
4.1.1. Impact of Pandemic by Firm Size
4.1.2. Impact of Pandemic on Firm Operating Status
4.2. Assessment of the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Firm Revenue
4.3. Assessment of Firm Responses to the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
4.4. Factors Affecting Firm Choices of Response Strategies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ajmal, Mian M., Mehmood Khan, and Muhammad Kashif Shad. 2021. The global economic cost of coronavirus pandemic: Current and future implications. Public Administration and Policy: An Asia-Pacific Journal 24: 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuwailem, Alhanouf Abdulrahman, Emad Salem, Abdul Khader Jilani Saudagar, Abdullah AlTameem, Mohammed AlKhathami, Muhammad Badruddin Khan, and Mozaherul Hoque Abul Hasanat. 2021. Impacts of COVID-19 on the Food Supply Chain: A Case Study on Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 14: 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, Dao Le Trang, and Christopher Gan. 2020. The impact of the COVID-19 lockdown on stock market performance: Evidence from Vietnam. Journal of Economic Studies 2: 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartik, Alexander W., Marianne Bertrand, Zoe Cullen, Edward L. Glaeser, Michael Luca, and Christopher Stanton. 2020. The impact of COVID-19 on small business outcomes and expectations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 117: 17656–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucal, Arlan, Arti Grover, and Santiago Reyes Ortega. 2021. Damaged by the Disaster—The Impact of COVID-19 on Firms in South Asia. Policy Research Working Paper No. 9604. Washington, DC: World Bank. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, Dzung, Lena Dräger, Bernd Hayo, and Giang Nghiem. 2022. The effects of fiscal policy on households during the COVID-19 pandemic: Evidence from Thailand and Vietnam. World Development 153: 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, Erdal, and Sayed H. Saghaian. 2022. The COVID-19 Pandemic and Dynamics of Price Adjustment in the US Beef Sector. Sustainability 14: 4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganda, Fortune. 2021. The impact of health expenditure on environmental quality: The case of BRICS. Development Studies Research 8: 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Statistics Office. 2020. Report on the Impact of the COVID-19 Epidemic on Labor and Employment in the Fourth Quarter and 2020. Hanoi: General Statistics Office. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Shiwei, and Yuyao Zhang. 2021. COVID-19 pandemic and firm performance: Cross-country evidence. International Review of Economics & Finance 74: 365–72. [Google Scholar]
- ILO. 2020. Monitor: COVID-19 and the World of Work. Seventh Edition. Available online: https://www.ilo.org/global/topics/coronavirus/impacts-and-responses/WCMS_767028/lang--en/index.htm (accessed on 16 May 2020).
- Huynh, Da Van, Thuy Thi Kim Truong, Long Hai Duong, Nhan Trong Nguyen, Giang Vu Huong Dao, and Canh Ngoc Dao. 2021. The COVID-19 Pandemic and Its Impacts on Tourism Business in a Developing City: Insight from Vietnam. Economies 9: 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephson, Anna, Talip Kilic, and Jeffrey D. Michler. 2021. Socioeconomic impacts of COVID-19 in low-income countries. Nature Human Behavior 5: 557–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ţigănaşu, Ramona, Loredana Simionov, and Dan Lupu. 2022. European Governments’ Responses to the COVID-19 Pandemic during the First Wave: Resetting Governance Systems to Cope More Effectively with Future Shocks. Applied Spatial Analysis and Policy. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinski, Martin, and Naomi Altman. 2014. Nonparametric tests. Nature Methods 11: 467–68. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nmeth.2937 (accessed on 10 May 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Jongkwan, and Hee-Seung Yang. 2022. Pandemic and employment: Evidence from COVID-19 in South Korea. Journal of Asian Economics 78: 101432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliszewska, Maryla, Aaditya Mattoo, and Dominique Van Der Mensbrugghe. 2020. The Potential Impact of COVID-19 on GDP and Trade: A Preliminary Assessment. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper, No. 9211. Washington, DC: World Bank Group, East Asia and the Pacific Region. [Google Scholar]
- Matějka, Filip, and Alisdair McKay. 2015. Rational Inattention to Discrete Choices: A New Foundation for the Multinomial Logit Model. American Economic Review 105: 272–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, Daniel. 1974. Conditional logit analysis of qualitative choice behavior. In Frontiers in Econometrics. Edited by P. Zarembka. New York: Academic Press, pp. 105–42. [Google Scholar]
- McFadden, Daniel. 1984. Econometric analysis of qualitative response models. In Handbook of Econometrics. Edited by Z. Griliches and M. D. Intriligator. Amsterdam: North-Holland, vol. 2, pp. 1385–457. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, Brent H., Brian Prescott, and Xuguang Simon Sheng. 2022. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on business expectations. International Journal of Forecasting 38: 529–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health’s Portal (MOH). 2022. Available online: https://moh.gov.vn/web/ministry-of-health/statistics (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Nordhagen, Stella, Uduak Igbeka, Hannah Rowlands, Ritta Sabbas Shine, Emily Heneghan, and Jonathan Tench. 2021. COVID-19 and small enterprises in the food supply chain: Early impacts and implications for longer-term food system resilience in low-and middle-income countries. World Development 141: 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapir, André. 2020. Why has COVID-19 hit different European Union economies so differently? Policy Contribution 2020/18. Brussels: Bruegel. [Google Scholar]
- Olczyk, Magdalena, and Marta Ewa Kuc-Czarnecka. 2021. Determinants of COVID-19 Impact on the Private Sector: A Multi-Country Analysis Based on Survey Data. Energies 14: 4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, Anton, Vered Blass, and Gal Raz. 2014. Economic and Environmental Assessment of Remanufacturing Strategies for Product + Service Firms. Production Operation Management 23: 744–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, Rakesh, and K. P. Prabheesh. 2021. The economics of COVID-19 pandemic: A survey. Economic Analysis and Policy 70: 220–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S. Shanmuga, Erdem Cuce, and K. Sudhakar. 2021. A perspective of COVID 19 impact on global economy, energy and environment. International Journal of Sustainable Engineering 14: 1290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Yunfeng, Haiwei Li, and Ren Zhang. 2021. Effects of Pandemic Outbreak on Economies: Evidence From Business History Context. Frontiers in Public Health 9: 632043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Huayu, Mengyao Fu, Hongyu Pan, Zhongfu Yu, and Yongquan Chen. 2020. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on firm performance. Emerging Markets Finance and Trade 56: 2213–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škare, Marinko, Domingo Riberio Soriano, and Małgorzata Porada-Rochoń. 2021. Impact of COVID-19 on the travel and tourism industry. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 163: 120469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thukral, Esha. 2021. COVID-19: Small and medium enterprises challenges and responses with creativity, innovation, and entrepreneurship. Strategic Change 30: 153–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Bach Xuan, Hien Thi Nguyen, Huong Thi Le, Carl A. Latkin, Hai Quang Pham, Linh Gia Vu, Xuan Thi Thanh Le, Thao Thanh Nguyen, Quan Thi Pham, Nhung Thi Kim Ta, and et al. 2020. Impact of COVID-19 on economic well-being and quality of life of the Vietnamese during the national social distancing. Frontiers in Psychology 11: 565153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umaña-Hermosilla, Benito, Hanns de la Fuente-Mella, Claudio Elórtegui-Gómez, and Marisela Fonseca-Fuentes. 2020. Multinomial Logistic Regression to Estimate and Predict the Perceptions of Individuals and Companies in the Face of the COVID-19 Pandemic in the Ñuble Region, Chile. Sustainability 12: 9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinh, N. D. 2021. Socio-economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Vietnam. Proceedings of the 5th Symposium on Information and Communication Technology, Hanoi, Vietnam, 4–5 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. 2020. Impact of COVID-19 on Businesses in Vietnam. Hanoi: World Bank. [Google Scholar]
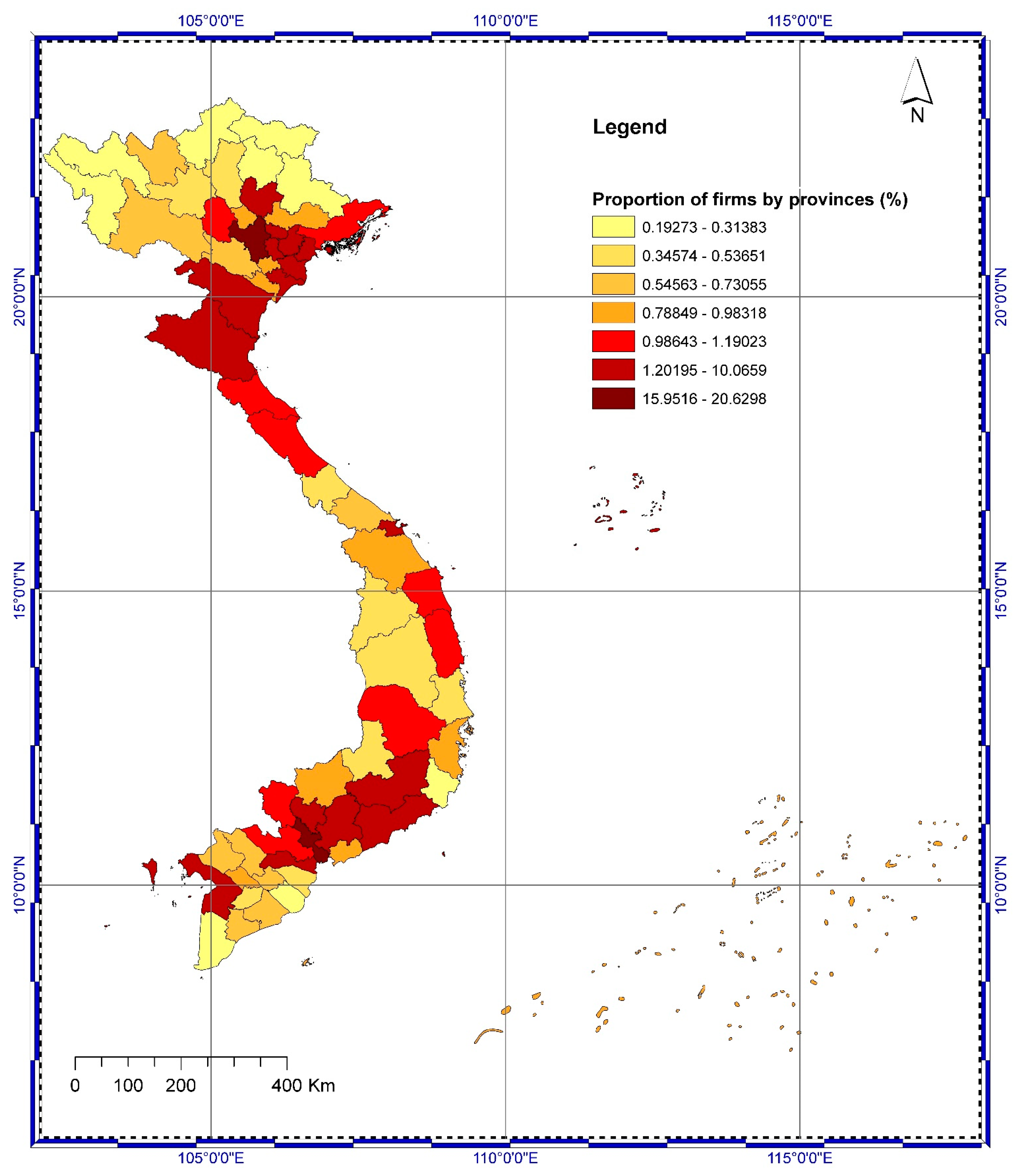




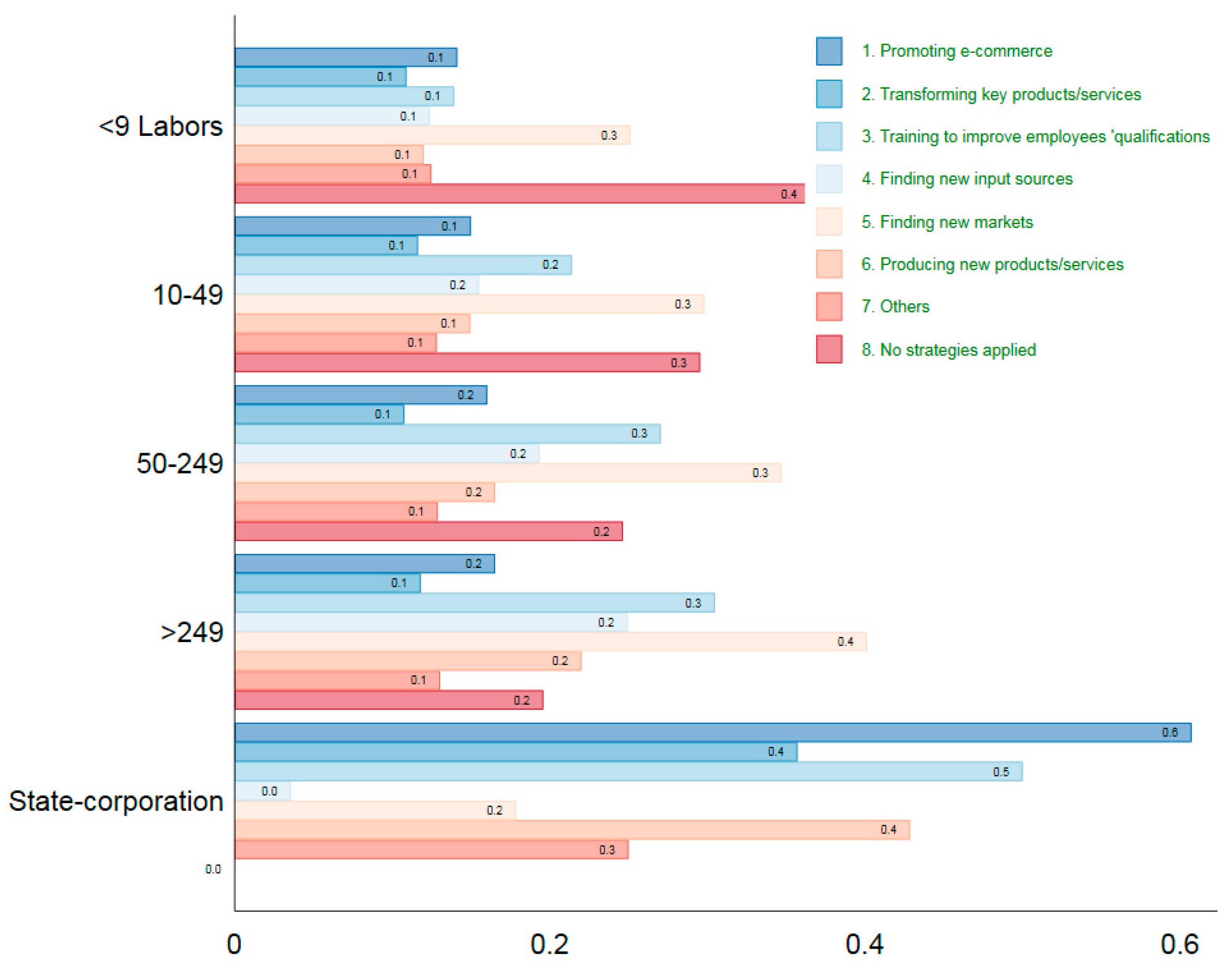
| Strategies | Micro Enterprises | Small Enterprises | Medium Businesses | Large Businesses | State-Owned Enterprises | Full Sample | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freq. | % | Freq. | % | Freq. | % | Freq. | % | Freq. | % | Freq. | % | |
| 0 | 36,274 | 36.54 | 11,827 | 29.54 | 2610 | 24.64 | 9845 | 76.96 | 0 | 0 | 60,556 | 37.21 |
| 1 | 6247 | 6.29 | 2074 | 5.18 | 518 | 4.89 | 144 | 1.13 | 3 | 10.71 | 8986 | 5.52 |
| 2 | 3599 | 3.62 | 1260 | 3.15 | 225 | 2.12 | 59 | 0.46 | 2 | 7.14 | 5145 | 3.16 |
| 3 | 6042 | 6.09 | 3475 | 8.68 | 1051 | 9.92 | 343 | 2.68 | 2 | 7.14 | 10,913 | 6.71 |
| 4 | 4473 | 4.51 | 2005 | 5.01 | 572 | 5.40 | 223 | 1.74 | 0 | 0 | 7273 | 4.47 |
| 5 | 19,172 | 19.31 | 8708 | 21.75 | 2611 | 24.65 | 953 | 7.45 | 2 | 7.14 | 31,446 | 19.32 |
| 6 | 11,078 | 11.16 | 5555 | 13.87 | 1640 | 15.48 | 748 | 5.85 | 12 | 42.86 | 19,033 | 11.70 |
| 7 | 12,399 | 12.49 | 5137 | 12.83 | 1365 | 12.89 | 478 | 3.74 | 7 | 25.00 | 19,386 | 11.91 |
| Total | 99,284 | 100 | 40,041 | 100 | 10,592 | 100 | 12,793 | 100 | 28 | 100 | 162,738 | 100 |
| Numerical Variables | Mean | Std. Dev. |
| Revenue per labor change 2020 vs. 2019 (log) | 5.16 | 1.94 |
| Number of employees temporarily taking unpaid leave (persons) | 1.07 | 18.8 |
| Number of employees on leave/rotational leave (persons) | 2.17 | 84.5 |
| Categorical Variables | Frequency | Percent |
| Firm size (smallest to largest, 1–5) | ||
| 1 | 99,284 | 61.01 |
| 2 | 40,041 | 24.60 |
| 3 | 10,592 | 6.51 |
| 4 | 12,793 | 7.86 |
| 5 | 28 | 0.02 |
| Enterprises overall assessment on the impact of Covid-19 (1 = negative, 2 = neutral, 3 = positive) | ||
| 1 | 5073 | 3.12 |
| 2 | 136,962 | 84.16 |
| 3 | 20,703 | 12.72 |
| Impact assessment on source of domestic raw materials (1 = decrease, 2 = unchanged, 3 = increase) | ||
| 1 | 38,516 | 34.53 |
| 2 | 69,946 | 62.71 |
| 3 | 3074 | 2.76 |
| Impact assessment on domestic consumption market (1 = decrease, 2 = unchanged, 3 = increase) | ||
| 1 | 97,247 | 68.56 |
| 2 | 42,546 | 30.00 |
| 3 | 2042 | 1.44 |
| Impact assessment on export market (1 = decrease, 2 = unchanged, 3 = increase) | ||
| 1 | 15,595 | 46.97 |
| 2 | 17,088 | 51.47 |
| 3 | 516 | 1.55 |
| Received support from government (yes = 1) | ||
| 0 | 134,240 | 82.49 |
| 1 | 28,498 | 17.51 |
| Variables | Strategy (2) | Strategy (3) | Strategy (4) | Strategy (5) | Strategy (6) | Strategy (7) | Strategy (8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue per labor change 2020 vs. 2019 (log) | −0.004 *** (0.001) | −0.002 * (0.001) | −0.004 *** (0.002) | −0.001 (0.001) | −0.013 *** (0.003) | −0.004 * (0.002) | −0.002 (0.002) |
| Number of employees temporarily taking unpaid leave (persons) | −0.000 (0.000) | 0.000 *** (0.000) | 0.000 *** (0.000) | 0.000 (0.000) | −0.000 (0.000) | 0.000 * (0.000) | −0.000 (0.000) |
| Number of employees on leave/rotational leave (persons) | −0.000 (0.000) | −0.000 (0.000) | 0.000 *** (0.000) | −0.000 (0.000) | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.000 * (0.000) |
| Firm size | |||||||
| 2 Small | −0.028 *** (0.007) | −0.003 ** (0.004) | 0.011 *** (0.006) | 0.001 * (0.008) | 0.044 *** (0.014) | 0.020 * (0.010) | −0.009 (0.012) |
| 3 Medium | −0.035 *** (0.008) | −0.022 * (0.005) | 0.007 *** (0.008) | −0.009 * (0.007) | 0.108 *** (0.024) | 0.037 * (0.016) | −0.045 *** (0.014) |
| 4 Large | −0.047 *** (0.009) | −0.019 * (0.005) | 0.014 *** (0.008) | 0.006 * (0.013) | 0.087 *** (0.023) | 0.063 * (0.036) | −0.035 ** (0.014) |
| Enterprises overall assessment on the impact of COVID-19 (1 = negative, 2 = neutral, 3 = positive) | |||||||
| 2 Neutral | −0.069 *** (0.016) | −0.007 * (0.013) | 0.017 * (0.01) | −0.026 * (0.012) | 0.035 (0.024) | 0.022 (0.014) | −0.000 (0.013) |
| 3 Positive | −0.082 *** (0.017) | −0.023 * (0.014) | 0.032 ** (0.013) | −0.020 (0.021) | −0.014 (0.033) | 0.011 (0.026) | −0.057 * (0.024) |
| Impact assessment on source of domestic raw materials (1 = decrease, 2 = unchanged, 3 = increase) | |||||||
| 2 Unchanged | −0.024 *** (0.004) | −0.007 (0.004) | −0.003 (0.005) | −0.072 *** (0.006) | 0.049 *** (0.012) | −0.014 * (0.007) | −0.003 (0.008) |
| 3 Increase | −0.031 * (0.017) | 0.001 (0.015) | −0.037 *** (0.009) | −0.015 (0.013) | 0.065 * (0.028) | 0.034 (0.027) | −0.022 (0.023) |
| Impact assessment on domestic consumption market (1 = decrease, 2 = unchanged, 3 = increase) | |||||||
| 2 Unchanged | −0.001 (0.005) | 0.002 *** (0.005) | 0.023 *** (0.008) | 0.015 * (0.009) | −0.094 *** (0.010) | −0.041 *** (0.011) | 0.013 (0.009) |
| 3 Increase | −0.040 *** (0.015) | 0.012 ** (0.016) | 0.006 (0.025) | 0.078 *** (0.028) | −0.006 (0.037) | 0.046 (0.057) | −0.018 (0.036) |
| Impact assessment on export market (1 = decrease, 2 = unchanged, 3 = increase) | |||||||
| 2 Unchanged | 0.014 *** (0.005) | 0.004 *** (0.004) | 0.029 *** (0.008) | 0.009 (0.006) | −0.028 (0.014) | −0.037 *** (0.010) | −0.012 * (0.009) |
| 3 Increase | 0.097 * (0.05) | 0.014 ** (0.019) | 0.015 (0.027) | 0.026 (0.027) | 0.023 * (0.055) | −0.019 (0.035) | −0.092 (0.023) |
| Received support from government (yes = 1) | −0.010 * (0.006) | −0.006 * (0.004) | −0.001 (0.005) | 0.002 (0.005) | 0.026 ** (0.011) | 0.009 (0.009) | 0.000 (0.009) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kien, N.D.; Hung, P.X.; Quan, T.T.; Hien, N.M. The COVID-19 Pandemic Impact and Responses in Emerging Economies: Evidence from Vietnamese Firms. Economies 2023, 11, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies11010010
Kien ND, Hung PX, Quan TT, Hien NM. The COVID-19 Pandemic Impact and Responses in Emerging Economies: Evidence from Vietnamese Firms. Economies. 2023; 11(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies11010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleKien, Nguyen Duc, Pham Xuan Hung, Truong Tan Quan, and Nguyen Minh Hien. 2023. "The COVID-19 Pandemic Impact and Responses in Emerging Economies: Evidence from Vietnamese Firms" Economies 11, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies11010010
APA StyleKien, N. D., Hung, P. X., Quan, T. T., & Hien, N. M. (2023). The COVID-19 Pandemic Impact and Responses in Emerging Economies: Evidence from Vietnamese Firms. Economies, 11(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies11010010






