Assessment and Learning in Knowledge Spaces (ALEKS) Adaptive System Impact on Students’ Perception and Self-Regulated Learning Skills
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Purpose
- Does the students’ total self-regulated learning skills’ score in eight SRL variables (task strategy, perception, goal setting, persistence, self-evaluation, time management, environmental-structuring, and help seeking) change during a semester when using the ALEKS adaptive learning system?
- What are the students’ perceptions of using ALEKS as their adaptive learning system?
3. Theoretical Framework
3.1. Self-Regulated Learning Skills (SRL)
3.2. Adaptive Learning
3.3. Self-Regulated Learning in Adaptive Learning Environments
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Instruments
4.2.1. ALEKS Adaptive Learning System
4.2.2. Adaptive Self-regulated Learning Questionnaire (ASRQ)
4.2.3. Open-Ended Survey
4.3. Data Analysis
4.3.1. Qualitative Analysis of the ASRQ
4.3.2. Qualitative Analysis of the Survey
5. Results
5.1. Tests of Normality
5.2. Descriptive Statistics of the Variables
5.3. Dependent Test for Paired Samples
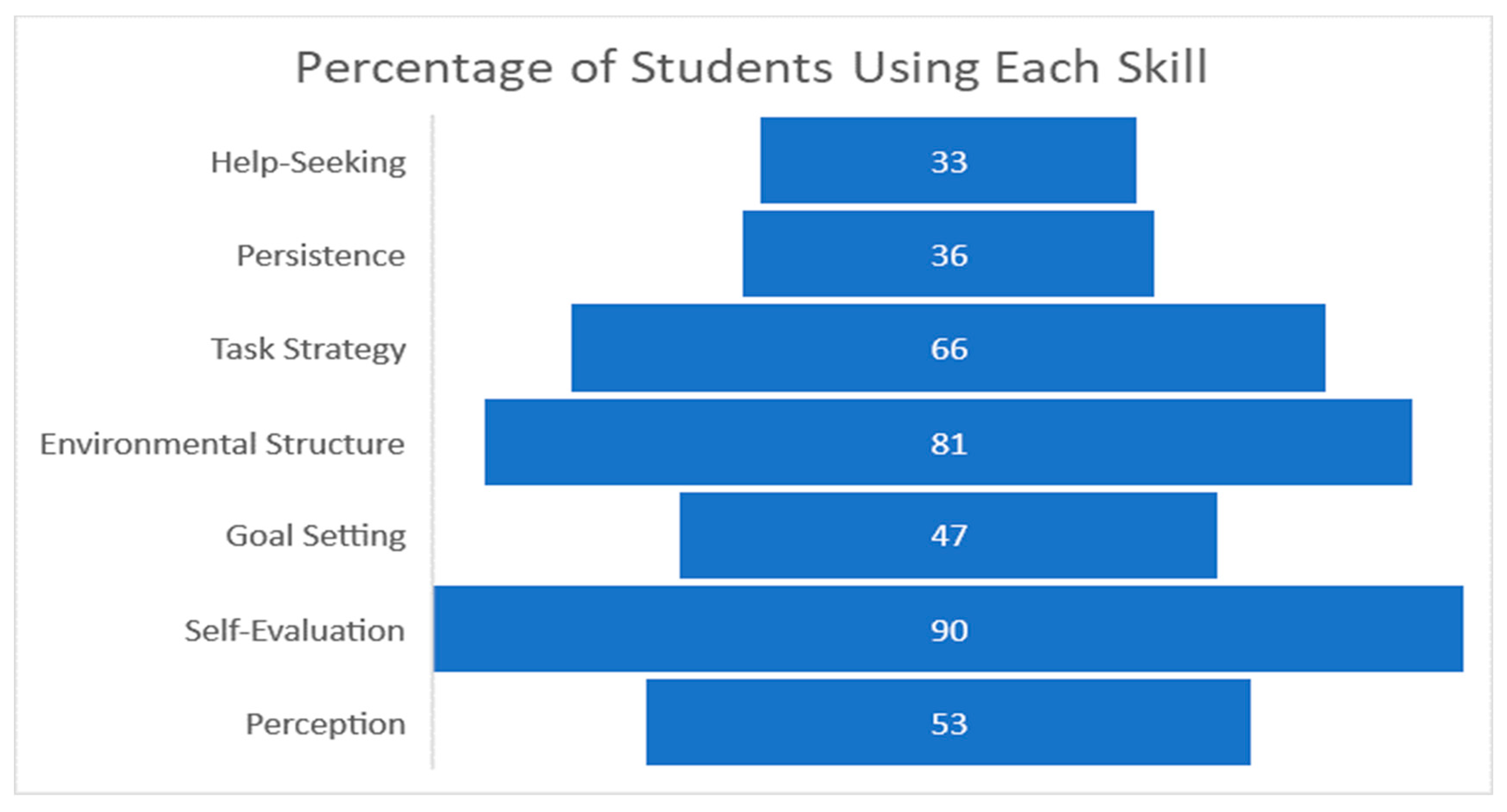
5.4. Survey Qualitative Analysis
6. Discussion
6.1. Influential Factors in the Drop of SRL Skills’ Score from Pretest to Posttest
6.2. The Need for High SRL Skills in Adaptive Students
6.2.1. Help Seeking
6.2.2. Persistence
6.2.3. Task Strategy
6.2.4. Environmental-Structuring
6.2.5. Goal Setting
6.2.6. Self-Evaluation
6.2.7. Perception
6.2.8. Time Management
6.3. Adaptive Learning Systems Benefits and Hurdles
- Embed audiovisual tools for learners with different learning styles.
- Integrate higher-order thinking tasks instead of multiple-choice tests.
- Reduce the number of topics in each course.
- Give a chance to students to make mistakes without losing any points.
- Remove the repetitive procedures, tests, or tasks.
- Add more help options.
- Scaffold students to improve their SRL skills.
- Provide virtual tours of different features of the system and benefits of each.
- Embed collaborative group activities and interactive social tools (like a chatbot, social media, etc.).
- Create a more flexible setting with a more straightforward language.
- Provide some audiovisual adaptive learning materials (instead of adaptive tests) based on the knowledge level of students.
7. Implications
8. Limitations
9. Suggestions for Further Research
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. ASRQ Questionnaire
- I set academic goals for my adaptive courses.
- I create a study plan for my adaptive courses.
- I track my progress in my adaptive courses.
- 4.
- I choose a certain amount of time to study for my adaptive courses.
- 5.
- I choose a special place to study for my adaptive courses.
- 6.
- I avoid any distractions when I am studying for my adaptive courses.
- 7.
- I have a specific schedule to study for my adaptive courses.
- 8.
- I allocate specific studying time for my adaptive courses.
- 9.
- I use my time efficiently to finish my exercises in my adaptive courses.
- 10.
- I contact the ‘Help Center’ to solve my technical problems in my adaptive courses.
- 11.
- I use ‘Tutorials’ and/or ‘Help Page’ to solve my technical problems in my adaptive courses.
- 12.
- I contact the instructor and/or knowledgeable peers to help me solve problems with content in my adaptive courses.
- 13.
- I make an extra effort to complete difficult exercises in my adaptive courses.
- 14.
- I am Persistent in working on topics that I have not learned in my adaptive courses (Note: ALEKS indicates your mastery level in each topic).
- 15.
- I do not give up until I finish all the exercises in my adaptive courses.
- 16.
- I evaluate the usefulness of the learning strategies that I use in my adaptive courses.
- 17.
- I evaluate my performance in my adaptive courses every time I login into the system.
- 18.
- I study the materials more than once to figure out my problems in my adaptive courses.
- 19.
- I use a variety of learning strategies in my adaptive courses.
- 20.
- I manage the content and technology challenges in my adaptive courses.
- 21.
- I fill-in my knowledge gaps in the subject matter by using the adaptive learning system (Note: the ALEKS system).
- 22.
- I try to take more notes because they are more important for learning in the adaptive course than in a regular classroom.
- 23.
- I feel my adaptive courses are engaging.
- 24.
- I am confident in the level of my knowledge in my adaptive courses.
- 25.
- I have a positive learning experience in my adaptive courses.
- 26.
- The system feedback meets my expectations.
Appendix B. Survey
References
- Li, H.; Liu, S.-M.; Yu, X.-H.; Tang, S.-L.; Tang, C.-K. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Current status and future perspectives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Román-Cañizares, M.; Palacios-Pacheco, X. Improvement of an Online Education Model with the Integration of Machine Learning and Data Analysis in an LMS. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Educause Horizon Report (2020). Teaching and Learning Edition. Available online: https://www.educause.edu/horizon-report-2020 (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Drissi, S.; Amirat, A. An adaptive E-learning system based on student’s learning styles: An empirical study. Int. J. Distance Edu. Technol. 2016, 14, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Roman-Cañizares, M.; Jaramillo-Alcázar, A.; Palacios-Pacheco, X. Data Analysis as a Tool for the Application of Adaptive Learning in a University Environment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard-Brak, L.; Lan, W.Y.; Paton, V.O. Profiles in Self-Regulated Learning in the Online Learning Environment. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distance Learn. 2010, 11. Available online: http://www.irrodl.org/index.php/irrodl/article/view/769/1480 (accessed on 12 February 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quince, R.B. The Effects of Self-Regulated Learning Strategy Instruction and Structured-Diary Use on Students’ Self-Regulated Learning Conduct and Academic Success in Online Community-College General Education Courses. Ph.D. Thesis, University of San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013. Unpublished. Available online: https://repository.usfca.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1063&context=diss (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Heo, H.; Joung, S.; Self-Regulated Strategies and Technologies for Adaptive Learning Management Systems for Web-Based Instruction. Association for Educational Communications and Technology. 2004. Available online: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED485141 (accessed on 19 July 2021).
- Bail, F.T.; Zhang, S.; Tachiyama, G.T. Effects of a self-regulated learning course on the academic performance and graduation rate of college students in an academic support program. J. Coll. Read. Learn. 2008, 39, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, F.; Staley, R.K.; DuBois, N.F. A Self-regulated learning approach to teaching educational psychology. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2007, 9, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harati, H.; Yen, C.J.; Tu, C.T.; Cruickshank, B.; Armfield, S.W. Online adaptive learning: A study of score validity of the adaptive self-regulated learning model. Int. J. Web-Based Learn. Teach. Technol. 2020, 15, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Attainment of Self-regulated: A social cognitive perspective. In Handbook of Self-Regulated; Boekaerts, M., Pintrich, P.R., Zeidner, M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pintrich, R.R. The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In Handbook of Self-Regulation; Boekaerts, M., Pintrich, P.R., Zeidner, M., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Panadero, E. A Review of Self-Regulated Learning: Six Models and Four Directions for Research. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabbagh, N.; Kitsantas, A. Personal Learning Environments, social media, and Self-regulated learning: A natural formula for connecting formal and informal learning. Internet High. Educ. 2011, 15, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghatala, E.S. Strategy-monitoring training enables young learners to select effective strategies. Educational Psychol. 1986, 21, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Self-regulated learning and academic achievement. Educational Psychol. 1990, 25, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social Foundations of Thought and Action: A Social Cognitive Theory; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bandura, A. Self-Efficacy: The Exercise of Control; Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Models of Self-regulated learning and academic achievement. In Self-Regulated Learning and Academic Achievement: Theory, Research, and Practice; Zimmerman, B.J., Schunk, D.H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ethink. Three Benefits of Adaptive Learning in Your LMS. March 2018. Available online: https://ethinkeducation.com/blog/3-benefits-utilizing-adaptive-learning-lms/ (accessed on 7 August 2021).
- Brusilovsky, P. Adaptive educational hypermedia. Summary of an invited talk at the PEG’01 conference. In Proceedings of the Tenth International PEG Conference, Tampere, Finland, 23–26 June 2001; Available online: http://www.pitt.edu/~peterb/papers/PEG01.html (accessed on 23 July 2020).
- Moskal, P.; Carter, D.; Johnson, D. Seven Things You Should Know about Adaptive Learning. July 2017. Available online: https://library.educause.edu/resources/2017/1/7-things-you-should-know-about-adaptive-learning (accessed on 23 July 2020).
- Brusilovsky, P. Methods and techniques of adaptive hypermedia. In Adaptive Hypertext and Hypermedia; Brusilovsky, P., Kobsa, A., Vassileva, J., Eds.; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Project Tomorrow White Paper. Leveraging Intelligent Adaptive Learning to Personalize Education: A Special White Paper Based upon the 2011 National Findings. 2012. Available online: http://www-static.dreambox.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/DreamBox-Leveraging-Intelligent-Adaptive-Learning.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- Murray, M.C.; Pérez, J. Informing and performing: A study comparing adaptive learning to traditional learning. Int.J. Emerg. Trans-Discip. 2015, 18, 111–125. Available online: http://www.inform.nu/Articles/Vol18/ISJv18p111-125Murray1572.pdf (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Kuntz, D. What Is Adaptive Learning? 2010. Available online: https://www.knewton.com/resources/blog/adaptive-learning/what-is-adaptive-learning/ (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Park, D.; Lee, J. Adaptive instructional system. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2003, 25, 651–684. Available online: http://www.aect.org/edtech/ed1/25.pdf (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Hesterman, D. Report on Intensive Mode Delivery in Engineering, Computer Science, and Mathematics. July 2017. Available online: http://www.ecm.uwa.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0009/2700846/Hesterman-2015-UWA-ECM-Report-on-intensive-mode-delivery.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Yen, C.J.; Bozkurt, A.; Tu, C.H.; Sujo-Montes, L.; Rodas, C.; Harati, H.; Lockwood, A.B. A predictive study of students’ self-regulated learning skills and their roles in the social network interaction of online discussion board. J. Educ. Technol. Dev. Exch. 2019, 11, 2. Available online: https://aquila.usm.edu/jetde/vol11/iss1/2 (accessed on 20 May 2021). [CrossRef]
- McGraw Hill. 2021. Available online: https://www.mheducation.com/ (accessed on 7 August 2021).
- Sabourin, J.; Mott, B.; Lester, J. Discovering behavior patterns of self-regulated learners in an inquiry-based learning environment. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science: Artificial Intelligence in Education; Lane, H.C., Yacef, K., Mostow, J., Pavlik, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 209–218. [Google Scholar]
- Dabbagh, N.; Bannan-Ritland, B. Online Learning: Concept, Strategies, and Applications; Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Inan, F.A.; Yildirim, S.; Kiraz, E. A design and development of an online learning support system (OLSS) for preservice teachers: A discussion of attitudes and utilization. J. Interact. Instr. Dev. 2004, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Latham, G.; Seijts, G.; Slocum, J. The Goal-setting and goal orientation labyrinth. Organ.Dyn. 2016, 45, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaumer, A.; Hillemann, E.; Gütl, C.; Albert, D. A Competence-based service for supporting self-regulated learning in virtual environments. J. Learn. Anal. 2015, 2, 101–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Becoming a Self-regulated learner: An overview. Theory Pract. 2002, 41, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araka, E.; Maina, E.; Gitonga, R.; Oboko, R. A conceptual model for measuring and supporting self-regulated learning using educational data mining on learning management systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 IST-Africa Week Conference (IST-Africa), Nairobi, Kenya, 10 August 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergey, B.W.; Ketelhut, D.J.; Liang, S.; Natarajan, U.; Karakus, M. Scientific inquiry self-efficacy and computer game self-efficacy as predictors and outcomes of middle school boys’ and girls’ performance in a science assessment in a virtual environment. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2015, 24, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ally, M. Foundations of educational theory for online learning. In The Theory and Practice of Online Learning; Anderson, T., Ed.; Athabasca University Press: Edmonton, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 15–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hofer, B.; Yu, S.L. Teaching self-regulated learning through a “Learning to Learn” course. Teac. Psychol. 2003, 30, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, D.H.; Zimmerman, B.J. Social origins of self-regulatory competence. Educ. Psychol. 1997, 32, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marca, A.L.; Longo, L. Addressing student motivation, self-regulation, and engagement in a flipped classroom to decrease boredom. Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2017, 7, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu-Sheng, L.; Huang, H.M. Perceived satisfaction, perceived usefulness, and interactivscore. E-learning environments as predictors to self-regulation in e-learning environments. Comput. Educ. 2013, 60, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollar, I.; Fischer, F. Supporting self-regulated learners for a while and what computers can contribute. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2006, 35, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonk, C.J.; Lee, M.M.; Kou, X.; Xu, S.; Sheu, F.R. Understanding the self-directed online learning preferences, goals, achievements, and challenges of MIT open courseware subscribers. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2015, 18, 349–368. [Google Scholar]
- Inan, A.F.; Flores, R.; Grant, M.M. Perspective on the Design and Evaluation of Adaptive Web-Based Learning Environment. 2010. Available online: https://www.cedtech.net/article/perspectives-on-the-design-and-evaluation-of-adaptive-web-based-learning-environments-5971 (accessed on 7 August 2021).
- ALEKS 2021. Available online: www.aleks.com (accessed on 3 July 2021).
- Albelbisi, N.A.; Yusop, F.D. Factors influencing learners’ self-regulated learning skills in a massive open online course (MOOC) environment. Turk. Online J. Distance Educ. 2019, 20, 1–16. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1221477.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2021). [CrossRef]
- Winters, F.I.; Greene, J.A.; Costich, C.M. Self-regulation of Learning within computer-based learning environments: A critical analysis. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2008, 20, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamison, J. Adaptive Learners, Not Adaptive Learning. 2016. Available online: https://www.mycota.ca/pro-d-blog/2016/07/22/adaptive-learners,-not-adaptive-learning/ (accessed on 10 April 2021).
| SRL Skills | Definition |
|---|---|
| Task strategy | The learner strategies to tackle adaptive learning systems’ complexities to complete tasks |
| Perception | The reflection of learners on their emotions and experiences throughout the learning process |
| Goal setting | The self-initiated plan making based on adaptive learning system’s instructions |
| Persistence | The learners’ efforts to accomplish adaptive learning materials |
| Self-evaluation | The tracking of progress, success, failure, topics completed, or topics remaining based on the system evaluation graphs |
| Time management | The learners’ time set aside for tasks based on the system timetable and instructions. |
| Environmental-structuring | An adaptive learning system’s dashboard arrangement to make it more favorable to pursue learning objectives |
| Help seeking | The self-initiated knowledge resource-seeking for better understanding of adaptive learning systems’ objectives |
| Variable | Frequency | % |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Female | 98 | 81.7 |
| Male | 22 | 18.3 |
| Ethnicity | ||
| White | 81 | 67.5 |
| Hispanic or Latino | 4 | 3.3 |
| Two or more races | 14 | 11.7 |
| Middle Eastern or Asian | 12 | 10 |
| Black or African American | 2 | 1.7 |
| American Indian or Alaska | 5 | 4.2 |
| Native Hawaiian or Pacific Island | 2 | 1.7 |
| Age | ||
| 18–25 | 118 | 98.3 |
| 26–35 | 2 | 1.7 |
| 26–36+ | 0 | 0 |
| Grade | ||
| Freshman | 66 | 55 |
| Sophomore | 38 | 31.7 |
| Junior | 13 | 10.8 |
| Senior | 3 | 2.05 |
| Kolmogorov–Smirnova | Shapiro–Wilk | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Differences | Statistic | df | Sig. | Statistic | df | Sig. |
| 0.054 | 120 | 2000 * | 0.983 | 120 | 0.147 | |
| Variables | Number of Survey Items | M | Range | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goal setting | 3 | 11.01 | 12.0 | 2.47 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Environmental-structuring | 3 | 9.16 | 12.0 | 2.67 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Task strategy | 4 | 13.63 | 16.0 | 3.45 | 4.0 | 20.0 |
| Time management | 3 | 9.93 | 12.0 | 2.75 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Help seeking | 3 | 9.5 | 12.0 | 2.41 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Persistence | 3 | 11.63 | 12.0 | 2.71 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Self-evaluation | 3 | 10.26 | 12.0 | 2.65 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Perception | 4 | 12.94 | 16.0 | 4.36 | 4.0 | 20.0 |
| Variables | # of Survey Items | M | Range | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goal setting | 3 | 11.03 | 12.0 | 0.26 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Environmental-structuring | 3 | 9.27 | 12.0 | 0.26 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Task strategy | 4 | 12.49 | 16.0 | 0.33 | 4.0 | 20.0 |
| Time management | 3 | 9.75 | 12.0 | 0.26 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Help seeking | 3 | 8.94 | 12.0 | 0.23 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Persistence | 3 | 10.49 | 12.0 | 0.28 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Self-evaluation | 3 | 9.66 | 12.0 | 0.26 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Perception | 4 | 11.58 | 6.0 | 0.40 | 4.0 | 20.0 |
| n | Mean | Std Deviation | Variance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pretest | 120 | 88.07 | 8.07 | 65.1249 |
| Posttest | 120 | 83.22 | 7.22 | 52.1284 |
| Pair1 Pre & Post | Diff. Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | Conf. Lower | Conf. Upper | t | df | Sig. (2-Tailed) |
| 4.86 | 2.83 | 1.141 | 2.54 | 7.18 | 4.178 | 119 | 0.000 |
| Theme | Student Quotes |
|---|---|
| Help seeking |
|
| Persistence |
|
| Task strategy |
|
| Environmental-structuring |
|
| Goal setting |
|
| Self-evaluation |
|
| Perceptions |
|
| Time management |
|
| System Benefits |
|
| System hurdles |
|
| Students’ suggestions |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harati, H.; Sujo-Montes, L.; Tu, C.-H.; Armfield, S.J.W.; Yen, C.-J. Assessment and Learning in Knowledge Spaces (ALEKS) Adaptive System Impact on Students’ Perception and Self-Regulated Learning Skills. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11100603
Harati H, Sujo-Montes L, Tu C-H, Armfield SJW, Yen C-J. Assessment and Learning in Knowledge Spaces (ALEKS) Adaptive System Impact on Students’ Perception and Self-Regulated Learning Skills. Education Sciences. 2021; 11(10):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11100603
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarati, Hoda, Laura Sujo-Montes, Chih-Hsiung Tu, Shadow J. W. Armfield, and Cherng-Jyh Yen. 2021. "Assessment and Learning in Knowledge Spaces (ALEKS) Adaptive System Impact on Students’ Perception and Self-Regulated Learning Skills" Education Sciences 11, no. 10: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11100603
APA StyleHarati, H., Sujo-Montes, L., Tu, C.-H., Armfield, S. J. W., & Yen, C.-J. (2021). Assessment and Learning in Knowledge Spaces (ALEKS) Adaptive System Impact on Students’ Perception and Self-Regulated Learning Skills. Education Sciences, 11(10), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11100603






