Models of Instructional Design in Gamification: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Phase 1: Research questions (RQ). They are organized around three areas: (a) conceptual framework, to analyze the relationships between the keywords identified in the literature (RQ1); (b) documentary characteristics, to identify geographical location and research methodologies used (RQ2,RQ3); and (c) pedagogical dimension (RQ4,RQ5), to recognize the methodological strategies for the inclusion of gamified practices in the field of teacher training and their relationship with other active methodologies, as well as instructional design models applied in the studies analyzed (Table 1).
- Phase 2: Eligibility criteria and sources of information. Articles published in scientific journals without time delimitation were included, containing in their titles, abstracts, or keywords the terms “gamification,” “teacher training,” “teacher education,” or “teacher professional development”, in English, Portuguese, or Spanish. Empirical studies with quantitative or qualitative methods were included. The exclusion criteria applied were for articles that did not develop educational research related to gamification. Articles that presented, in isolation, the use of applications such as Kahoot!, Socrative, or Quizizz were also excluded.
- Phase 3: Search strategies. The databases Web of Science (Wos), Scopus, and Dialnet were used for the selection of articles. In each of the databases, the keywords “gamification,” “teacher training,” “teacher education,” and “teacher professional development” were used, with no time limitation. The search includes results published up to August 2021. The search syntaxes are included in the coding sheet in Supplementary Material (https://bit.ly/3q9whrL).
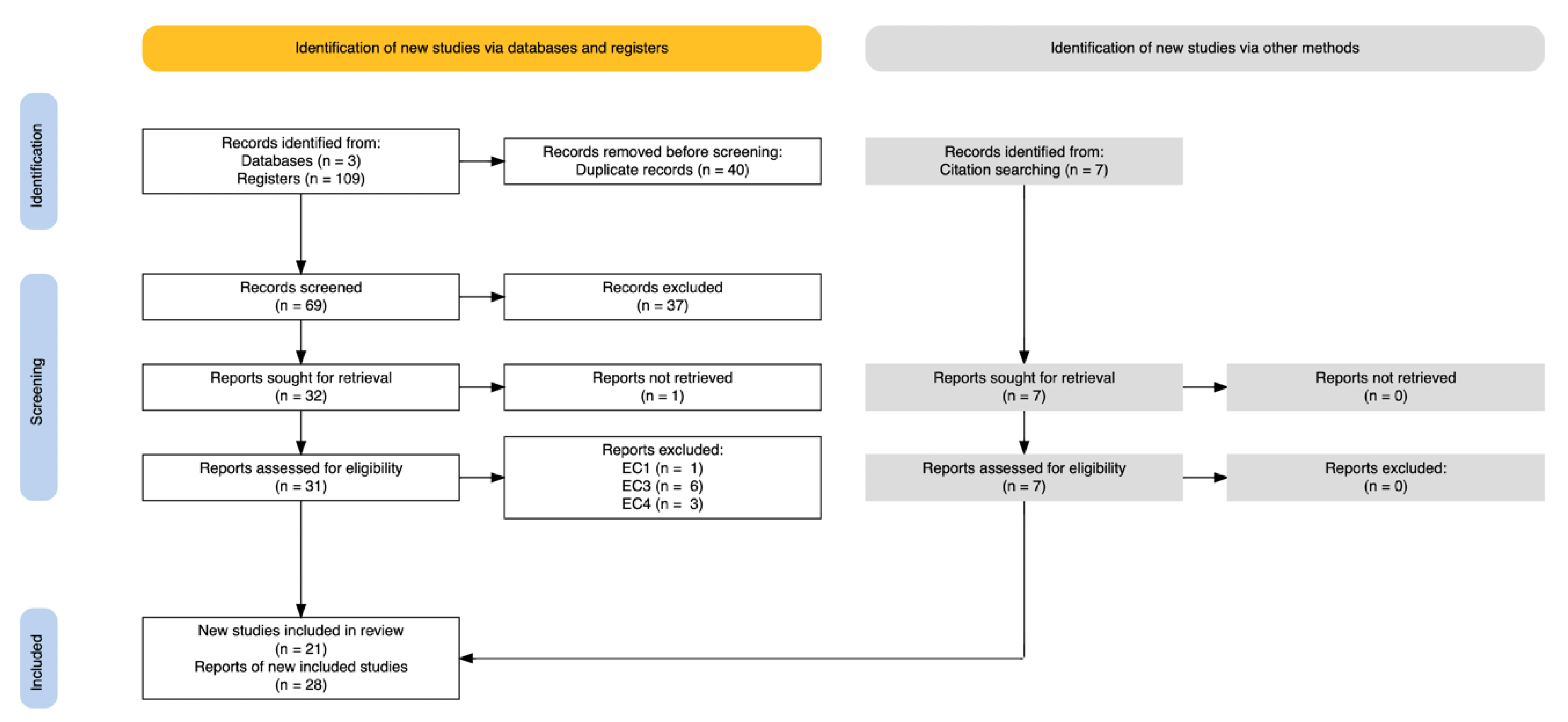
- Phase 4: Study selection process. The initial search resulted in 109 articles, of which 40 were duplicates. All the authors analyzed the 69 articles on the basis of the title and abstract, according to the inclusion–exclusion criteria. After agreeing on the results, 37 articles were excluded. The remaining 32 were analyzed in full text in a second selection process independently by the investigators, resulting in the exclusion, by agreement, of 11 articles. The “snowball” method [22] was applied to the citations included in the 21 selected articles, and 7 articles were added to complete the final sample of documents for the systematic review (n = 28), as can be seen in Figure 1.
- Phase 5: Data coding and synthesis. The Zotero bibliographic manager was used to collect data from potentially valid studies. The synthesis of the information was performed using a coding sheet with 26 fields. VOSViewer and NVivo 12 were used for the conceptual network analysis. The three investigators, first independently and then by consensus, acted in the different phases of selection according to criteria for prior inclusion and definitive inclusion in the revision.
3. Results
3.1. What Is the Conceptual Relationship Surrounding the Term Gamification?
3.2. What Is the Geographical Distribution of the Publications?
3.3. What Research Methodologies Are Used in the Selected Studies and What Is the Sample Size?
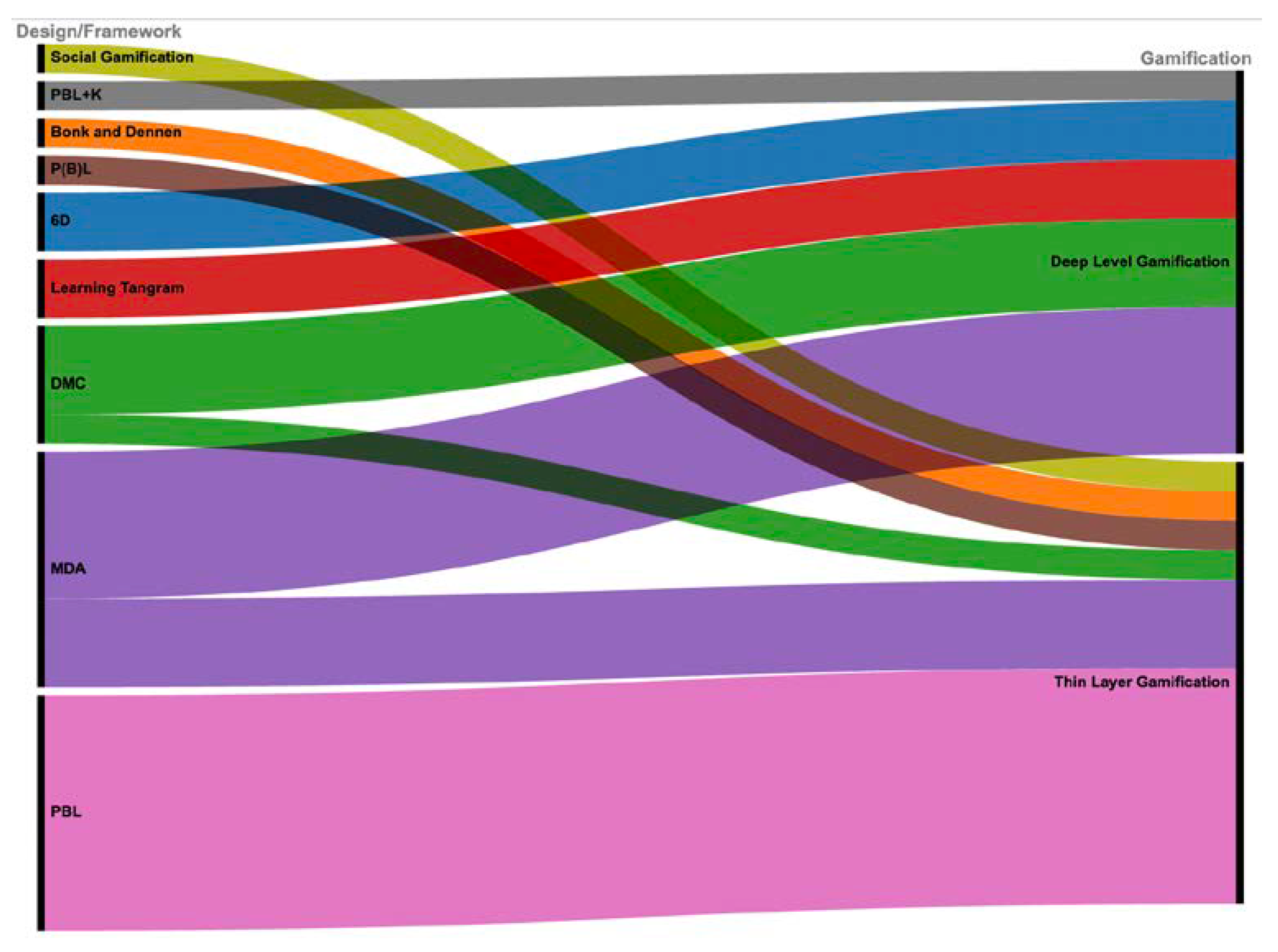
3.4. What Instructional Design Models Applied to Gamification Systems?
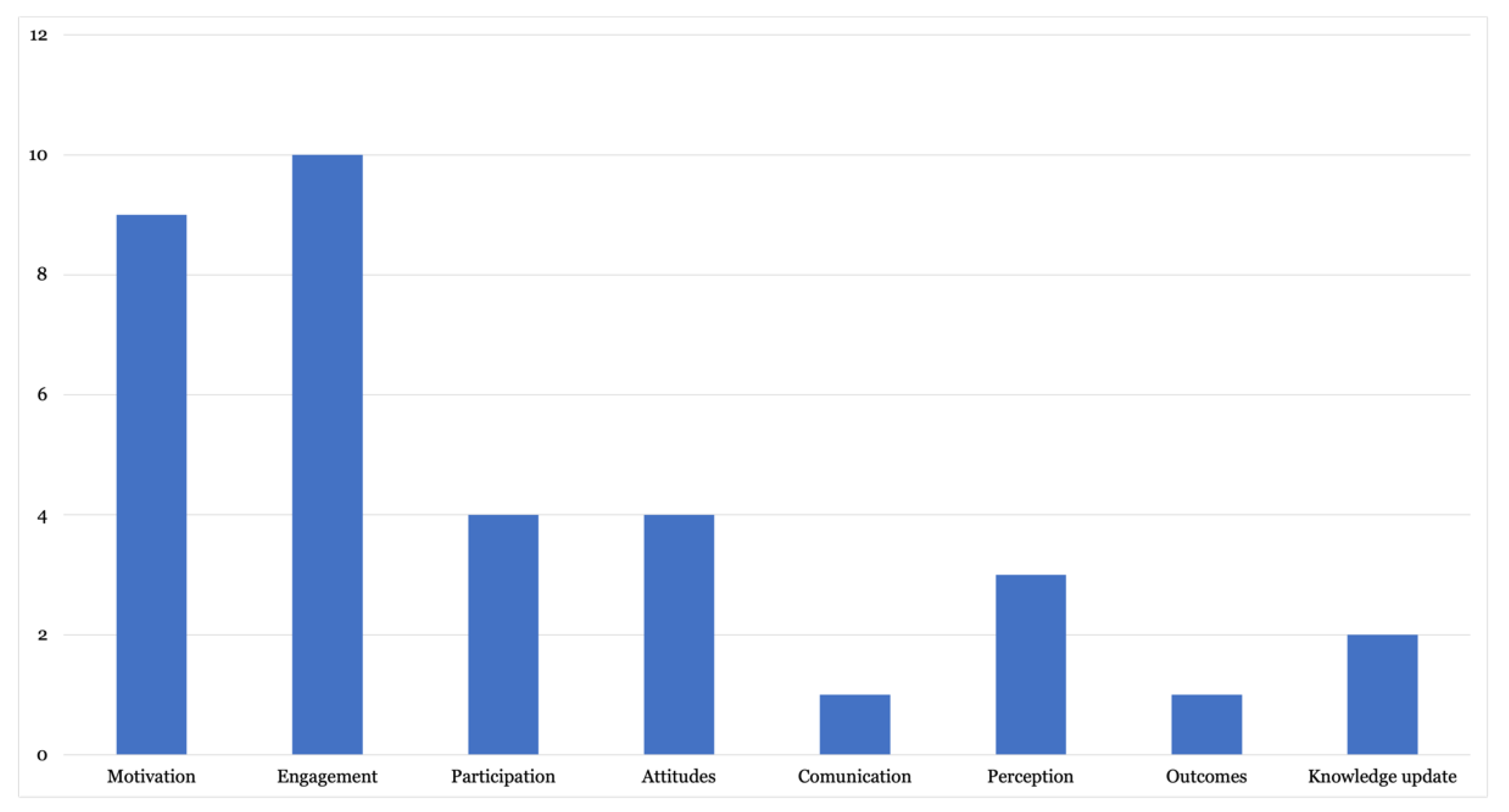
3.5. What Are the Effects of Gamified Practices in the Teaching–learning Process?
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alomari, I.; Al-Samarraie, H.; Yousef, R. The Role of Gamification Techniques in Promoting Student Learning: A Review and Synthesis. J. Inf. Technol. Educ. Res. 2019, 18, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rauschenberger, M.; Willems, A.; Ternieden, M.; Thomaschewski, J. Towards the Use of Gamification Frameworks in Learning Environments. J. Interact. Learn. Res. 2019, 30, 147–165. [Google Scholar]
- Bozkurt, A.; Durak, G. A Systematic Review of Gamification Research: In Pursuit of Homo Ludens. Int. J. Game-Based Learn. 2018, 8, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuddin, Z.; Chu, S.K.W.; Shujahat, M.; Perera, C.J. The impact of gamification on learning and instruction: A systematic review of empirical evidence. Educ. Res. Rev. 2020, 30, 100326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Brito, S.; Mena, J. Gamification and Its Application in the Social Environment: A Tool for Shaping Behaviour. J. Inf. Technol. Res. 2020, 13, 58–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Riera, D.; Gonzalez, C.; Arnedo-Moreno, J. Gamification: A systematic review of design frameworks. J. Comput. High. Educ. 2017, 29, 516–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanzadeh, H.; Fardanesh, H.; Hatami, J.; Talaee, E.; Noroozi, O. Using gamification to support learning English as a second language: A systematic review. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2019, 34, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangsrinoon, S.; Boonbrahm, P. Game elements from literature review of gamification in healthcare context. J. Technol. Sci. Educ. 2019, 9, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gaalen, A.E.J.; Brouwer, J.; Schonrock-Adema, J.; Bouwkamp-Timmer, T.; Jaarsma, A.D.C.; Georgiadis, J.R. Gamification of health professions education: A systematic review. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. 2021, 26, 683–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogiannakis, M.; Papadakis, S.; Zourmpakis, A.-I. Gamification in science education. A systematic review of the literature. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, A.N.; Noori, N.M.; Ozdamli, F. Gamification applications in e-learning: A literature review. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, M. A systematic review of the use of gamification in flipped learning. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2021, 26, 3327–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indriasari, T.D.; Luxton-Reilly, A.; Denny, P. Gamification of student peer review in education: A systematic literature review. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 5205–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadhli, M.; Brick, B.; Setyosari, P.; Ulfa, S.; Kuswandi, D. A meta-analysis of selected studies on the effectiveness of gamification method for children. Int. J. Instr. 2020, 13, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegalajar Palomino, M.C. Implicaciones de la gamificación en Educación Superior: Una revisión sistemática sobre la percepción del estudiante. Rev. Investig. Educ. RIE 2021, 39, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhash, S.; Cudney, E.A. Gamified learning in higher education: A systematic review of the literature. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 87, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Mateos, C.; Pérez-López, I.J.; Marzo, P.F. Gamification in the spanish educational field: A systematic review. Retos 2021, 42, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manterola, C.; Astudillo, P.; Arias, E.; Claros, N. Revisiones sistemáticas de la literatura. Qué se debe saber acerca de ellas. Cir. Esp. 2013, 91, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira González, I.; Urrútia, G.; Alonso-Coello, P. Revisiones sistemáticas y metaanálisis: Bases conceptuales e interpretación. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2011, 64, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawacki-Richter, O.; Kerres, M.; Bedenlier, S.; Bond, M.; Buntins, K. (Eds.) Systematic Reviews in Educational Research: Methodology, Perspectives and Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biernacki, P.; Waldorf, D. Snowball Sampling: Problems and Techniques of Chain Referral Sampling. Sociol. Methods Res. 1981, 10, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalustre Martínez, L.; Del Moral Pérez, M.E. Gamitication: Strategies to optimize learning process and the acquisition of skills in university contexts [Gamificación: Estrategia para optimizar el proceso de aprendizaje y la adquisición de competencias en contextos universitarios]. Digit. Educ. Rev. 2015, 27, 13–31. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda Vázquez, C.; Espejo Garcés, T.; Zurita Ortega, F.; Fernández Revelles, A.B. La formación de los futuros docentes a través de la gamificación, TIC y evaluación continua. Sport TK Rev. Euroam. Cienc. Deporte 2019, 8, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopcha, T.J.; Ding, L.; Neumann, K.L.; Choi, I. Teaching Technology Integration to K-12 Educators: A ‘Gamified’ Approach. TechTrends 2016, 60, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcó Boudet, J.M.; Huertas Talón, J.L. Superpoderes contra el Dr. Discriminador. La mejora de la evaluación continua mediante la ludificación en el Máster en profesorado. Rev. Interuniv. Investig. En Tecnol. Educ. 2018, 4, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Hammer, J. Gamification in Education: What, How, Why Bother? Acad. Exch. Q. 2011, 15, 146. [Google Scholar]
- McGonigal, J. Reality is Broken: Why Games Make us Better and How They Can Change the World; Penguin Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 388. [Google Scholar]
- Zichermann, G.; Cunningham, C. Gamification by Design: Implementing Game Mechanics in Web and Mobile Apps; O’Reilly: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kapp, K.M. The Gamification of Learning and Instruction: Game-Based Methods and Strategies for Training and Education; Pfeiffer: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Werbach, K.; Hunter, D. For the Win: How Game Thinking Can Revolutionize Your Business; Wharton School Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hanus, M.D.; Fox, J. Assessing the effects of gamification in the classroom: A longitudinal study on intrinsic motivation, social comparison, satisfaction, effort, and academic performance. Comput. Educ. 2015, 80, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldemir, T.; Celik, B.; Kaplan, G. A qualitative investigation of student perceptions of game elements in a gamified course. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 78, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, I.; Rivera-García, E. Formar docentes, formar personas: Análisis de los aprendizajes logrados por estudiantes universitarios desde una experiencia de gamificación. Signo Pensam. 2017, 36, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez López, I.J.; Rivera García, E.; Trigueros Cervantes, C. “La profecía de los elegidos”: Un ejemplo de gamificación aplicado a la docencia universitaria. Rev. Int. Med. Cienc. Act. Física Deporte 2017, 17, 243–260. [Google Scholar]
- Barrére, E.; Coelho, J.; Camponez, L. Aspectos metodológicos e de gamificação em um MOOC sobre tecnologias digitais para o ensino de Matemática. Educ. Matemática Debate 2017, 1, 173–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle Rodríguez, J.; Vilagran, M.D.M.S. Secuencias didácticas gamificadas por docentes de LE en formación continua: Puntos, insignias y tablas de clasificación. E-Aesla 2019, 5, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Alsina i Tarrés, M.; Farrés Cullell, I. ¿Jugar o aprender? El aprendizaje lúdico en la formación musical del maestro. Rev. Electrónica Complut. Investig. En Educ. Music. 2021, 18, 83–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornellà Canals, P.; Estebanell Minguell, M. GaMoodlification: Moodle al servicio de la gamificación del aprendizaje. Campus Virtuales 2018, 7, 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez López, I.; Rivera García, E.; Trigueros Cervantes, C. 12 +1. Feelings of physical education college students towards a gamification proposal: “Game of Thrones: The Anger of the Dragons”. Movimento 2019, 25, e25038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega Ruipérez, B.; Alvarado, A.; Chorro, E.; Cuartero, N. Percepción del alumnado sobre la adquisición de la competencia en creación de contenidos digitales con gamificación. Rev. Educ. Tecnol. 2021, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Levitt, R.; Piro, J. Game-changer: Operationalizing the common core using webquests and “gamification” in teacher education. Int. J. Web-Based Learn. Teach. Technol. 2014, 9, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klock, A.C.T.; Gasparini, I.; Pimenta, M.S.; Hamari, J. Tailored gamification: A review of literature. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2020, 144, 102495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano-León, A.; Camacho-Lazarraga, P.; Guerrero, M.; Guerrero-Puerta, L.; Aguilar-Parra, J.; Trigueros, R.; Alias, A. Between level up and game over: A systematic literature review of gamification in education. Sustain. Switz. 2021, 13, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Areas | Research Questions | Coding Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Conceptual Framework | RQ1. What is the conceptual relationship surrounding the term gamification? | Word frequency and co-occurrence of keywords. Co-citation |
| Documentary Characteristics | RQ2. What is the geographical distribution of the publications? | Country and language |
| RQ3. What research methodologies are applied in the selected studies and what is the size of their samples? | Approaches, methodologies, and sample size | |
| Pedagogical Dimension | RQ4. What are the instructional design models applied to gamification systems? | Instructional design models |
| RQ5. What are the effects of gamified practices in teaching–learning processes? | Implications or empirical evidence |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Fernández, A.; Revuelta-Domínguez, F.-I.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.R. Models of Instructional Design in Gamification: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12010044
González-Fernández A, Revuelta-Domínguez F-I, Fernández-Sánchez MR. Models of Instructional Design in Gamification: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Education Sciences. 2022; 12(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Fernández, Alberto, Francisco-Ignacio Revuelta-Domínguez, and María Rosa Fernández-Sánchez. 2022. "Models of Instructional Design in Gamification: A Systematic Review of the Literature" Education Sciences 12, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12010044
APA StyleGonzález-Fernández, A., Revuelta-Domínguez, F.-I., & Fernández-Sánchez, M. R. (2022). Models of Instructional Design in Gamification: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Education Sciences, 12(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12010044








