Abstract
(1) Background: This systematic review focuses on identifying the main features of effective music teachers and teaching recently examined in the educational and psychological literature. It aims to identify how recent studies have discussed the promotion of effectiveness in the context of both preservice and in-service music teachers. (2) Methods: A search in the main scientific databases for educational research (Eric, Science Direct, WWS, Web of Science, JSTOR) was conducted using keywords associated with the topics of effective teachers and teaching in the field of music instruction. In the end, thirty-six papers were identified and analyzed. (3) Results: The main themes were related to various dimensions of music teaching and teachers: teachers’ personal characteristics (self-esteem, resilience, etc.) and personality traits; professional skills; cognitive and psychological aspects of teachers’ professional identity (self-efficacy, professional motivation, beliefs regarding teaching and learning music, etc.); training experiences (pre- and in-service); social competence and the interpersonal relationship between the teacher and the students. (4) Conclusions: These dimensions seem interrelated and contribute to simultaneously define the effective music teacher and effective teaching in music. Specific attention should be paid to the impact of learning contexts on teachers’ activities, leading to a contextualized definition of effective music teachers.
1. Introduction
What is necessary to be an effective teacher in music education and instruction today? This question is fundamental not only to determine the main features that characterize the figure of the effective music teacher and the main elements of effective music teaching, but also to develop relevant hints and indications that can allow us to improve music teachers’ initial training and professional development. Exploring the concept of an effective teacher in music is a complex task since this construct involves several interrelated dimensions. In addition, different beliefs regarding the meaning of “effectiveness” in music education, the teacher’s role in music instruction, and the teacher’s impact on students’ learning may make it more difficult to examine the core features that could define the figure of the effective music teacher [1]. To encourage a systematic approach to educational research pertaining to this theme, some main concepts should be clarified. These definitions should also take into account the characteristics of the current sociocultural situation, such as the fact that the world is constantly and rapidly changing, as well as the educational approaches, aims, learning goals and practices associated with music education [2] and with all other disciplines. Accordingly, understanding the core characteristics of effective music teachers is a process that could support the development of training experiences for teachers, with the final goal of allowing them to acquire the competences necessary to enhance and support students’ learning processes in many different learning contexts [3].
Before discussing the main themes of the analysis, it is necessary to make a distinction. In the current survey, the topics of effective music teachers and effective music teaching are viewed as connected topics. More specifically, when considering the multidimensional nature of the figure of the effective teacher, effective teaching can be considered to constitute one of the core components of the profile of the music teacher, which also includes relational, motivational, reflective, and emotional dimensions.
Interest in examining the main characteristics of effective teaching has increased since the end of the 1940s [4]. Being defined as a “good” or “excellent” music teacher is a process that depends on several elements. Depending on the type of learning objectives in question, music educators may adopt different approaches and strategies to effectively reach the planned educational goals. Teachers must also adapt to specific learning contexts, which are characterized by different sociocultural and economic backgrounds. In addition, teachers must adapt to each student, considering their personal characteristics, attitudes, objectives, needs, potentialities, etc. The role of students has gained increasing relevance in the teaching–learning process; therefore, pupils’ learning outcomes and feedback are currently considered to be indicators of teaching effectiveness [5].
Recently, music education has shifted from a pedagogical paradigm based on the transmission of traditional praxis to an approach that is more focused on the overall development and personal growth of pupils. If music is considered a human mode of aesthetic communication that involves creative and emotional dimensions [6], the main educational goals of music education should shift from “learning to play” to “learning to live with music”. The development of a personal and critical aesthetic taste, the enhancement of creative skills, the acquisition of transferable skills, and the empowerment of personal well-being are all aspects that should be considered in the context of music education and instruction. This situation implies the need to rethink learning objectives and restructure teaching methods and strategies. The role of the teacher is evolving from “master” to “tutor” and “learning facilitator” [7], and the need to change and revise some teaching approaches and strategies is becoming urgent. Teachers should support students in becoming autonomous [8] with respect to managing the process of music learning. Accordingly, what are the characteristics of effective teachers in music education at present? What has changed since the past? These questions have a great deal of theoretical and practical relevance since identifying the main construct associated with this theme may offer relevant hints for training music teachers and improving the educational experience for music students.
Considering the current situation and the need to provide hints and suggestions that can empower teachers’ competences in music education, a systematic review of the literature has been conducted. The aim of this review was to examine the research concerning the topic of effective music teachers and teaching, and to define the main features of the figure of the effective music teacher and the effective process of music teaching. Educational implications for both teachers and students are also considered and included in the discussion.
2. Materials and Methods
Three main research questions have guided the current investigation:
- (1)
- What are the main features related to effective music teachers and effective music teaching that have been examined recently in educational research?
- (2)
- How has the research viewed the analysis and promotion of effectiveness in both preservice and in-service music teachers?
- (3)
- What is the role of teacher training (preservice and in-service) in enhancing the characteristics of effective teaching in music education according to the research?
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
Some criteria for selecting papers have been defined:
- (1)
- The articles must present a research study (qualitative or quantitative) pertaining to the theme of effective music teachers and teaching.
- (2)
- The articles must have been published between 2002 and 20221 in a peer-reviewed journal in the field of educational and psychological research.
- (3)
- The articles must be written in English.
- (4)
- The terms “effective/effectiveness” and “music teacher/teaching” must be included in the keywords or the main topics of the articles.
- (5)
- Participants must be pre- or in-service specialist music teachers (not generalist teachers who also teach music in their classes).
2.2. Search Strategies
First, an online search was performed on the main scientific databases in the field of educational and psychological research. The keywords selected to discover possible studies pertaining to the topic of interest were “effective”, “effectiveness”, “teacher”, “teaching”, and “music”, which were combined in the following ways: “effective AND teacher AND music”, “effective AND teaching AND music”, “teacher AND effectiveness AND music”, and “teaching AND effectiveness AND music”.
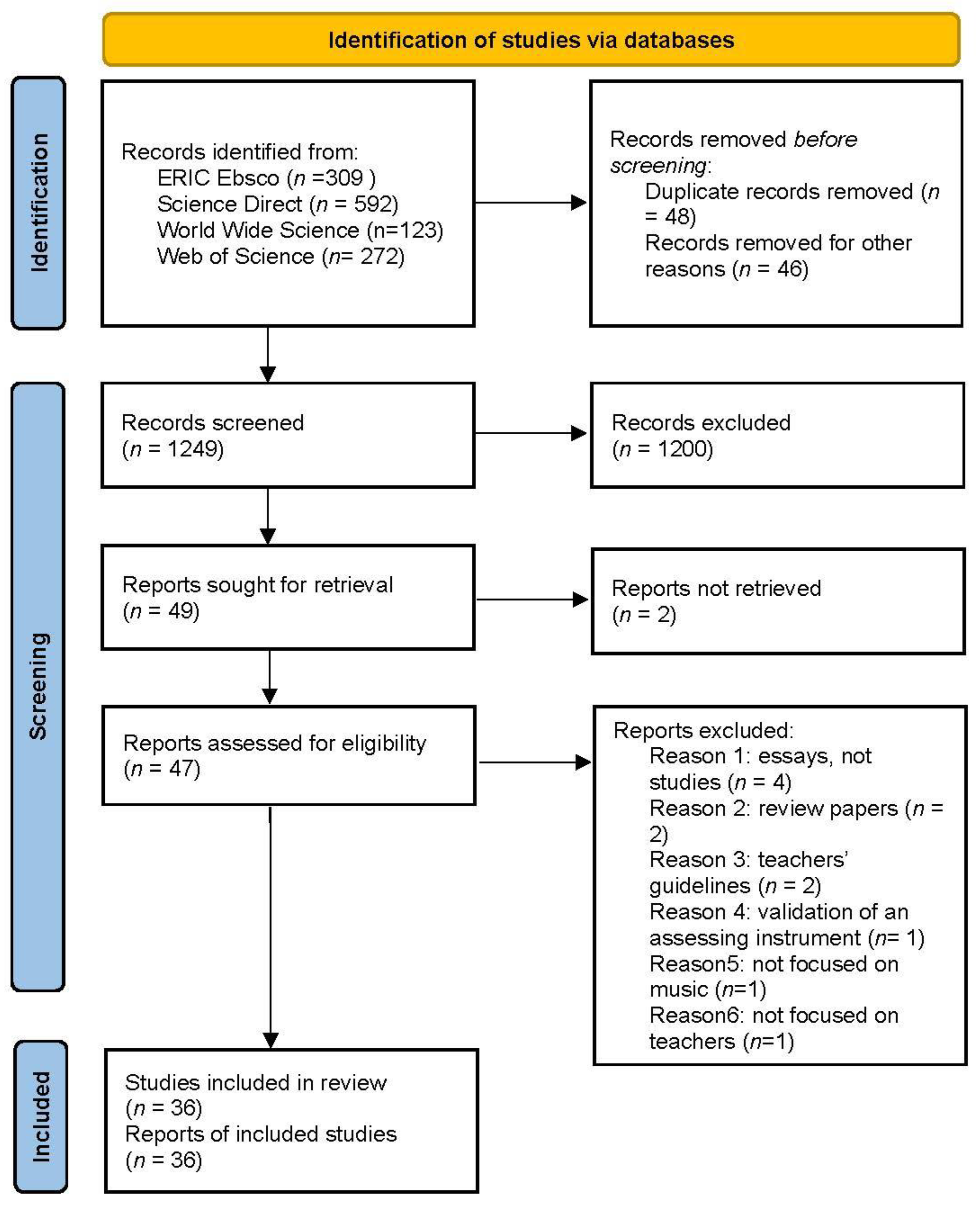
Second, online scientific databases were selected, specifically those that included research articles dealing with educational sciences, psychology of education, and pedagogy. The database search returned 1338 results overall. From these initial results, 94 articles were excluded due to duplicated records or for other reasons, for example, some documents were not considered for the current analysis since they were not specifically articles from peer-reviewed scientific journals (but, instead, conference papers, book chapters, etc.). The remaining articles were screened, examining their main focus, topics, and research aims; only the articles which considered the topics of effective music teacher and teaching as main research theme were taken into account. Papers which dealt partially which these topics or mentioned them as secondary theme were excluded, and as a final result, 3025 papers were identified from ERIC, 65 from Science Direct, 8 from WorldWideScience, 4 from Web Of Science, and 1 from JSTOR, for a total number of 4932 articles, among which forty-seven were available in full-text version and downloaded in full-text version.
Third, the full-text version of each paper was reviewed, and articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria were discarded. This process led to the rejection of 11 papers for the following reasons:
- -
- Some articles were essays explicating and discussing a specific theoretical claim (n = 4).
- -
- Other articles were reviews of the literature (rather than empirical studies; n = 2).
- -
- Others were articles offering practical suggestions for music teachers (n = 2).
- -
- One article was a research study that addressed effective teaching from a general perspective (thus lacking a specific focus on music education).
- -
- One article was the report of a validation process for an assessing instrument.
- -
- One article was mainly focused on the effectiveness of a training course for preservice music teachers.
Figure 1 summarizes the search procedure in accordance with the PRISMA statement [9].
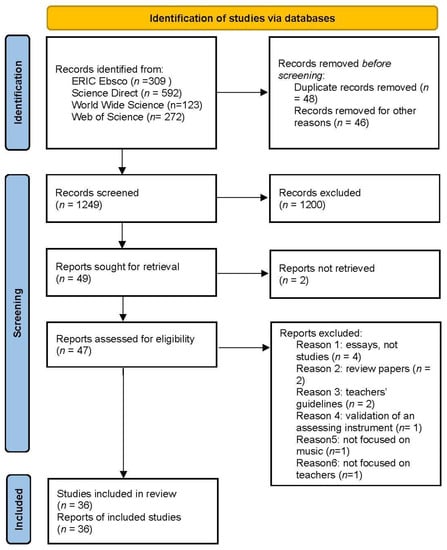
Figure 1.
Flow diagram (based on PRISMA statement) summarizing the search procedure.
2.3. Analysis of the Articles
The remaining 36 articles were reviewed with respect to some specific features, which were entered into a table on an Excel sheet. For each included study, certain specific aspects were examined, i.e., year of publication, participant characteristics (nationality, professional profile, number of participants), type of research methodology adopted, main variables/factors considered in the research, and main findings. The results of this analysis are reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Systematic analysis of the documents considering authors, years of publication, nationality of the research, type of document, main topic and main findings for each document.
3. Results
Two types of analyses were performed on the collected articles. First, the frequencies of some features (year of publication, nationality of the study and the participants, and research methodology) were identified to highlight the main trends in the current educational research concerning the topic of effective teachers and effective teaching in music education. Second, considering the main variables or factors examined with respect to each study, a categorization of the main dimension emphasized by the research concerning effective music teachers and teaching was made.
3.1. Year of Publication (Frequencies)
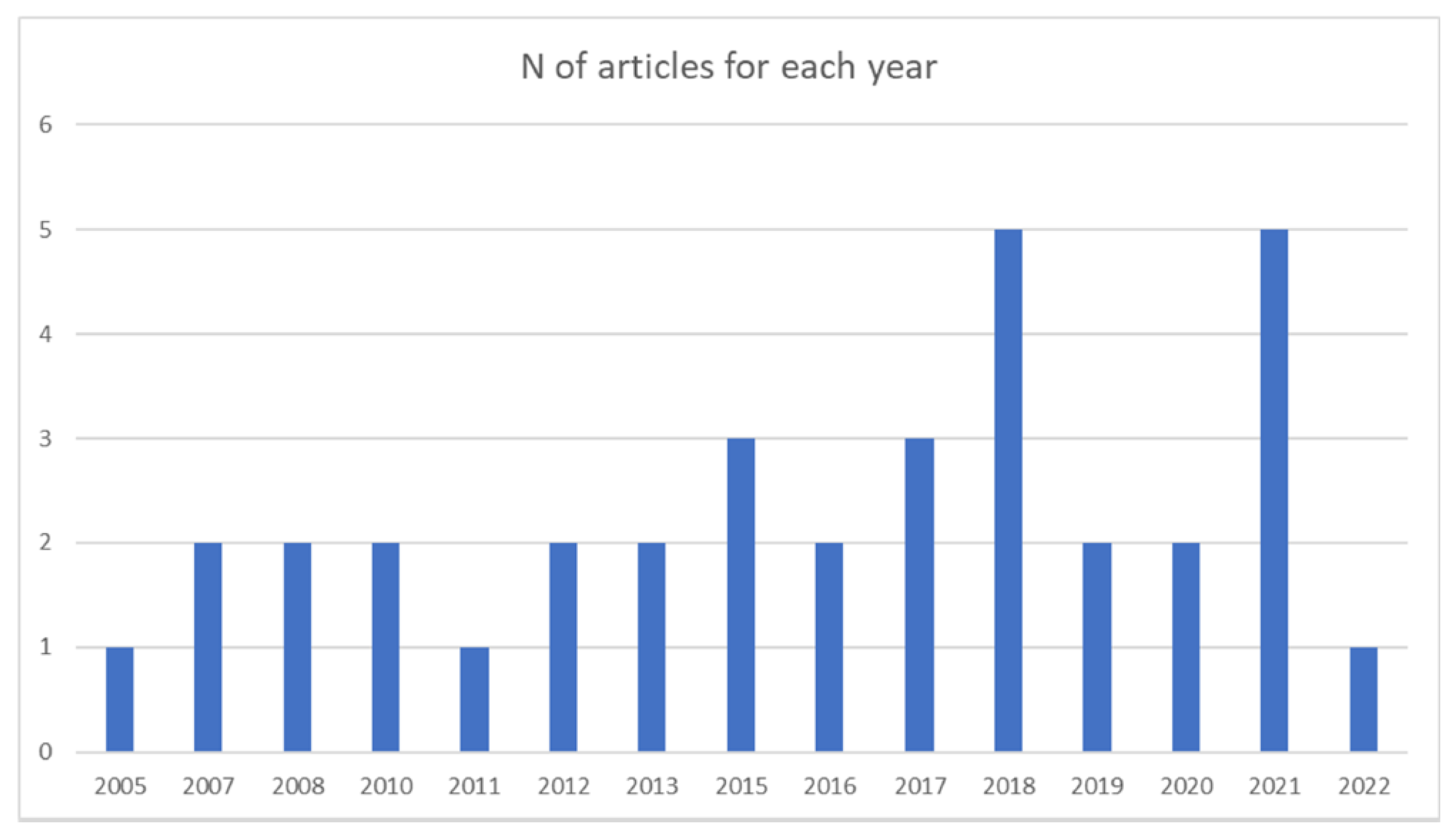
The main aspect that was considered in the analysis was the year of publication. The number of articles published each year seems to have increased over the past two decades (there was only a decrease in 2020, perhaps due to the general interruption of activities resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic). This finding highlights the increasing interest in the topic of effective teaching and teachers in music education. The results are reported in Figure 2.
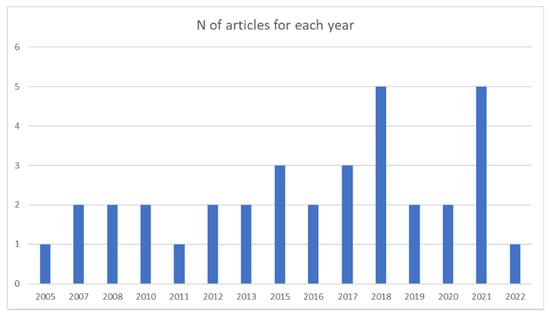
Figure 2.
Documents published for each year (frequencies).
3.2. Nationality of the Study and Participants (Frequencies)
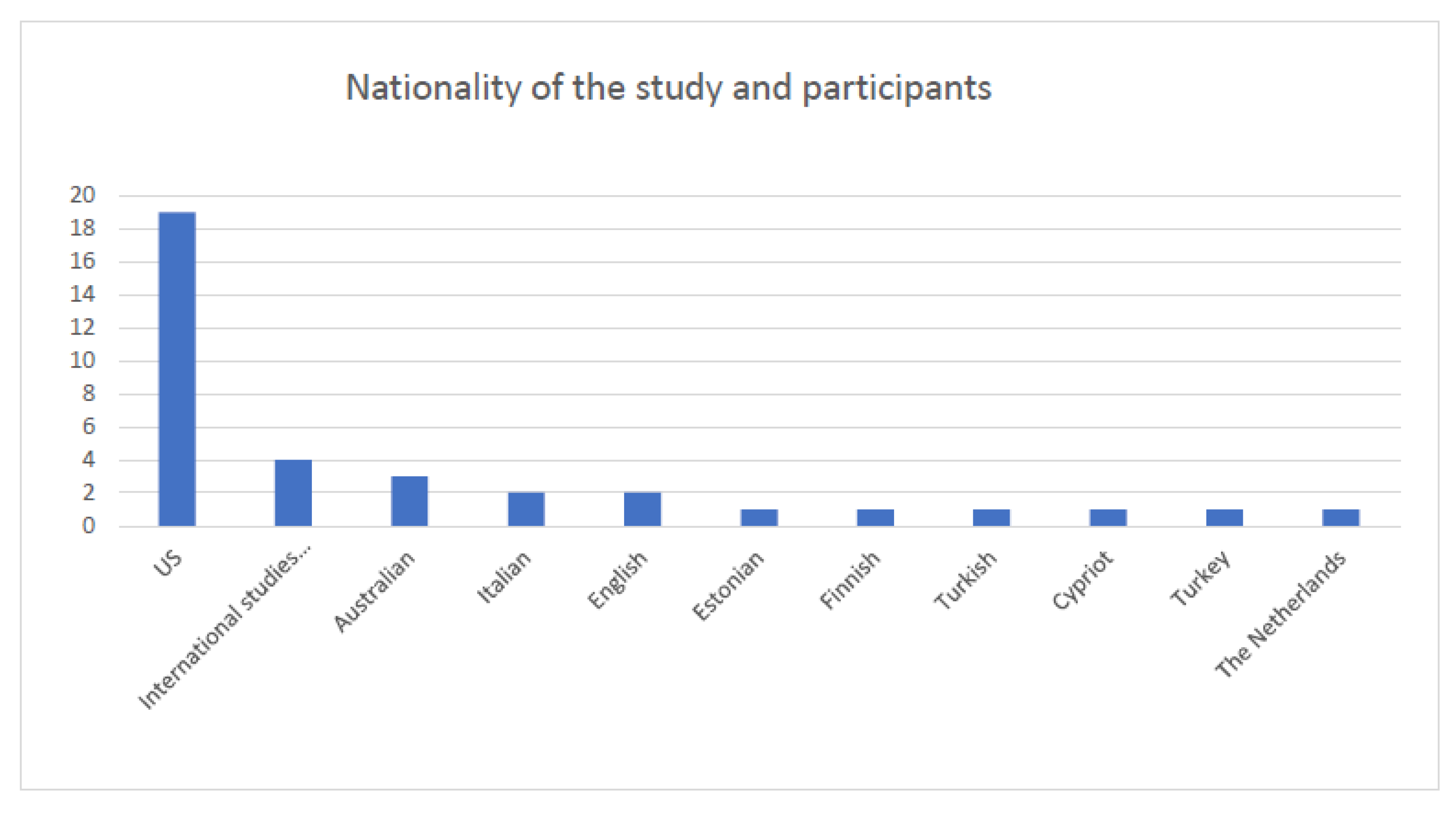
The nationalities of the study and those of the participants included different countries worldwide. Most of the research studies included (N = 17, more than half) were conducted in the US, while several research projects involved international research teams and participants to facilitate comparison of the data across different cultural backgrounds (n = 4). Other nationalities mainly included participants from European countries, while a few studies involved countries outside the EU. The prevalence of American and European countries is mainly linked to the fact that the studies were focused on music education in the Western tradition. The results are reported in Figure 3.
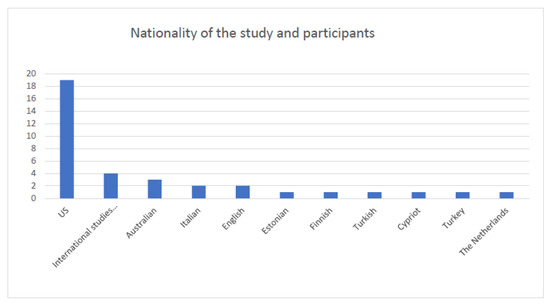
Figure 3.
Nationality of the research (frequencies).
3.3. Research Methodology (Frequencies)
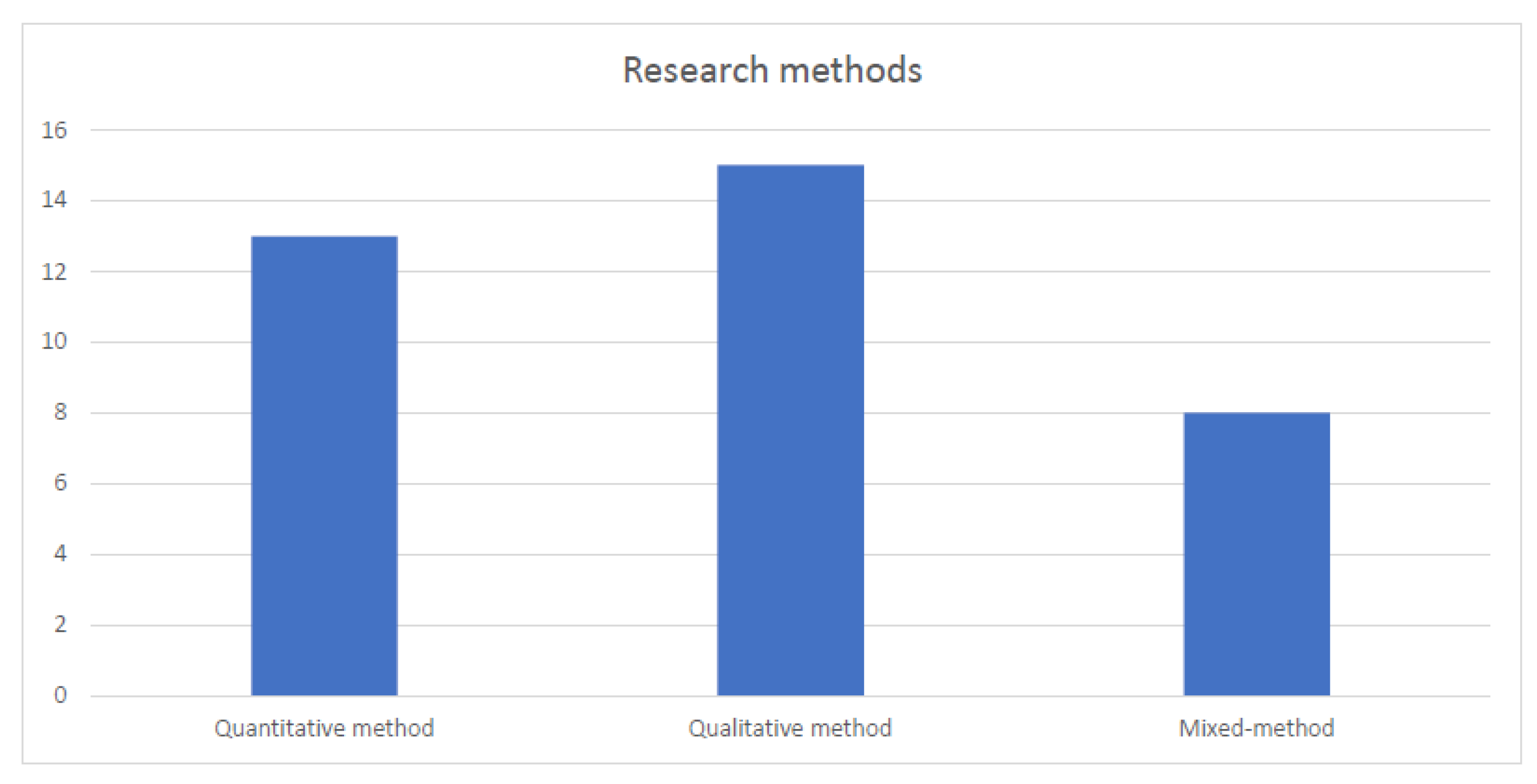
Considering the research method adopted in the study, the articles examined employed quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods in nearly equal numbers. This fact highlights the different aims (exploratory or confirmative) that characterized the studies examined. The frequencies of the different kinds of research methods are reported in Figure 4.
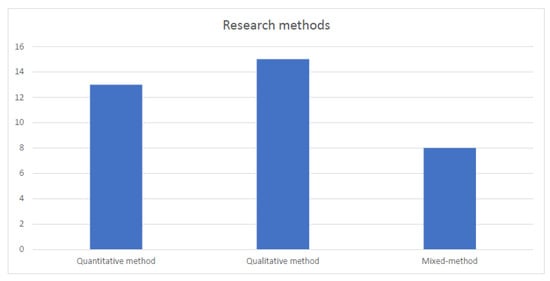
Figure 4.
Type of research methodology (frequencies).
3.4. Dimensions of Effective Teaching and Teachers (Categories)
Considering the main factors and variables examined in the research included in the review, some categories emerged. The number of studies that focused on each category is reported (considering the fact that some articles involved more than one factor/variable). Factors that are mentioned only once have been reported for two general categories, one in the category of teaching and musical competences and another in the category of personal cognitive, motivational and emotional aspects.
- Pedagogical approach to teaching and teaching strategies (n = 9);
- Role of training experiences (preservice and in-service, n = 7);
- Interpersonal relations and teacher’s social competence (n = 5);
- Personality traits (n = 5);
- Professional self-efficacy (n = 4);
- Communication and communicative style (n = 4);
- Professional expertise and motivation (n = 3);
- Instructional cycle (n = 2);
- Performing skills (n = 2);
- Other aspects related to teachers’ personal, cognitive and emotional aspects (n = 7);
- Other aspects related to teachers’ professional competences (n = 4).
Each category is described in further detail below.
3.4.1. Pedagogical Approach to Teaching and Teaching Strategies
In music teaching, the pedagogical approach may influence the way in which the lesson is structured, as well as the meaning that is attributed to the teacher–student relationship. Music teachers may adopt different kinds of teaching strategies with respect to the main focus of the teaching approach (the student, the subject, the evaluation, or the management of the lessons, [19]). The most effective teaching approach seems to be the student-centered approach [20,28,29,32,42]; in this approach, the teacher is focused on meeting students’ needs and developing innovative strategies for personalizing the teaching process [32]. In the student-centered approach, the basic assumption is that each student has unique characteristics; it is the teaching process that must adapt to the student rather than the opposite. Although this teaching approach is considered to be the most effective approach in general, it is possible, in some cases, to introduce additional teacher-centered learning tasks, especially in the context of younger students, who are less self-regulated and must be guided during the initial phases of the music-learning process [29]. Scaffolding is a teaching strategy useful with high performing students, who may also already have self-regulated skills [25] and who may benefit from the mediation of the teacher as a learning facilitator. Another strategy frequently used with music students is represented by side coaching [17], where the teacher offers relevant indications while the student is performing. In side coaching, to avoid frequent and useless interruptions of a student’s performance, the instructor has to select the most urgent and relevant issues to direct the pupil’s attention to them. The general pedagogical framework of the most effective teaching strategies seems to be similar both for instrumental and vocal music instruction [33], underlining that overall learning objectives may be very similar: presenting students with performing models, and supporting them in understanding, achieving, re-elaborating and consolidating these patterns.
3.4.2. Role of Training Experiences (Preservice and In-Service)
One feature that is frequently identified as a predictor of effective teaching is the impact of training experiences, both in terms of preservice courses in academic contexts [12,18,27,32] and in-service proposals for professional development [16,21,40]. With respect to preservice training, most relevant experiences occur in university contexts, where courses for teacher training are offered. The aspects that emerged as the most significant for supporting the development of effectiveness in teaching are related to the integration of theory and practice and the connection between the academic world and the professional contexts in which the prospective teachers are to conduct their professional activity [12]. These courses may be the proper contexts in which to train teachers in general pedagogical knowledge and competences, as well as to allow them to develop a student-centered approach in music education [27] and the specific social and communicative skills that are necessary to manage the teacher–student relationship effectively [32]. In addition, in preservice experiences, student teachers may share ideas, proposals, and feedback with their colleagues and work collaboratively to accomplish learning tasks [18], thus laying the foundations for the creation of a professional community of practice that could support teachers in their future work. After music teachers have started their professional careers, they may benefit from a lifelong learning process of professional development. These opportunities may help participants develop effective teaching strategies and an awareness of the importance of adapting the educational process to suit students’ needs [16] from the perspective of a student-centered pedagogical approach. For preservice training, in-service professional development experiences may enhance social competences to improve teacher–student relationships, which are considered to constitute a core component of effective music teaching [21]. Additionally, the importance of creating a community of practice for music teachers is particularly evident during the first phases of their professional careers, when they may benefit from advice and tutoring from more expert colleagues [40].
3.4.3. Interpersonal Relations and Teachers’ Social Competences
As previously noted, when discussing the role of training, the social dimension plays a key role in music teaching [13,20,23,32,35]. This dimension not only refers to the interpersonal relationship between teacher and student, but also, from a broader perspective, takes into account all the social interactions that the music teacher has with his or her colleagues, institutional figures, and families [13]. An effective music teacher has a good level of social competence [23], which is necessary to develop positive relationships with students that are based on mutual respect and attention to others’ needs and requests [32]. This requirement is particularly relevant since one of the most frequent teaching strategies is based on one-on-one instruction [20], which features a direct interaction between teacher and student without the mediating role of classmates.
3.4.4. Personality Traits
Becoming an effective music teacher may be easier if certain personality traits are present [42]. These traits may facilitate the process of developing a good level of professional competence, particularly by influencing interactions with the students and the levels of effort that they invest in their educational activity. For example, effective music teachers seem to be more resilient [11,15] charismatic and emphatic [20], particularly in the social interactions with students. In addition, they often exhibit positive attitudes toward people, music and teaching [43], a characteristic that may sustain the motivation to work as music teachers.
3.4.5. Professional Self-Efficacy
A personal sense of efficacy related to professional competence seems to be positively associated with teaching effectiveness in music education [46]. The development of a good level of professional self-efficacy may depend on certain aspects. First, it may be influenced by social skills, since positive interpersonal relationships in class may enhance teachers’ perceptions of effectiveness [14]. Second, personal aspects such as coping strategies and resilience [15] can positively affect the development of self-efficacy among music teachers as well as their professional expertise [14]. Third, in accordance with Bandura’s theory [47], previous experiences in terms of both mastery experience and vicarious experience may contribute to increasing teachers’ sense of being effective in their educational activities [37]. In general, music teachers exhibit a higher level of self-efficacy than other teachers [39], which is probably because teaching music requires specific musical skills and knowledge, which music teachers achieve by means of a lengthy and demanding training process.
3.4.6. Communication and Communicative Style
Communication is a core dimension of music teaching; effective teaching is characterized by a multidimensional communicative style, including eye contact, nonverbal communication, and modulation of the teacher’s voice [34]. Since communication is also characterized by a musical dimension, nonverbal behaviors and sensitivity are particularly relevant to the task of transmitting indications and feedback to students [26]. Verbal instructions are also relevant in music lessons, but they must be specific and coherent with musical and nonverbal communicative hints [31], such as through the use of figurative language to help students understand complex contents [41].
3.4.7. Instructional Cycle
A dimension of effective teaching that is particularly associated with activity in class includes the structure of the instructional cycle. The instructional cycle refers to the sequence of phases that characterize the process of delivering a lesson [31]. The most effective cycle of instruction seems to include clear learning objectives, a focus on the procedure, quick feedback concerning student performance and potential reinforcement when required standards have been achieved [22].
3.4.8. Professional Expertise and Motivation
Professional experience may be a predictor of teaching effectiveness and self-efficacy [14] since, during their educational career, music teachers may experiment with different approaches and strategies, find solutions to problems, and change and renovate traditional teaching practices to comply with new pedagogical developments. Expert teachers are also more precise and knowledgeable regarding their work and their evaluations of their colleagues’ activity [30]. Moreover, motivation is a relevant factor for effective music teachers [38]: teachers are motivated in their professional activity by the possibility to positively affect students’ personal and artistic growth.
3.4.9. Performing Skills
Music teachers are also good musicians; they must have a thorough knowledge of instrumental or vocal techniques to act as a model for students [11]. Accordingly, playing music with students offers a visual and acoustic model that can be considered and followed. A good level of performing skills is crucial for integrating verbal explanations with practical examples in a process of modeling and scaffolding [35].
3.4.10. Other Aspects Related to Teachers’ Personal, Cognitive and Emotional Aspects
Some aspects linked to psychological, cognitive and emotional constructs seem to be related to effective music teaching. Considering the cognitive dimension, critical-thinking skills may enhance the improvement of teaching practices [10]. In terms of the emotional and motivational aspects, effective music teachers are characterized by a deep personal interest in music and its meaning as a form of human expression [43], which also manifests in their motivation to teach music [35] and the positive emotions that are associated with musical activity [13]. Another relevant aspect that could influence the way in which the teacher manages their educational relationship with the student is orientation toward music skills and learning, which is considered to be incremental and can, thus, be potentially improved via learning experiences [45]. In addition, it has to be mentioned that there may be some aspects related to personal appearance that may influence the evaluation of teacher’s effectiveness, for example, the masculinity of their voice [44]; it is important to be aware of these stereotypical beliefs in order to avoid incorrect judgements about the effectiveness of music teachers.
3.4.11. Other Aspects Related to Teachers’ Professional Competences
In the professional profile of a music teacher, certain other elements may serve as conditions of effective teaching. The studies examined in the current analysis have highlighted the role of classroom management abilities [11], especially for teachers who manage collective music classes (ensembles, choirs, bands, etc.). In addition to musical competences (performing skills), the teacher must also possess a good level of general pedagogical knowledge [42] to be able to adopt the most effective strategies for introducing and presenting musical contents and teaching performing practices. They must also adopt a reflective attitude toward the educational activity, with the aim of monitoring and improving their activity both in and outside the class [45]. From an innovative perspective, the music teacher should become a learning facilitator for her or his students, encouraging them to gradually become autonomous and self-regulated with respect to their learning process [24].
4. Discussion
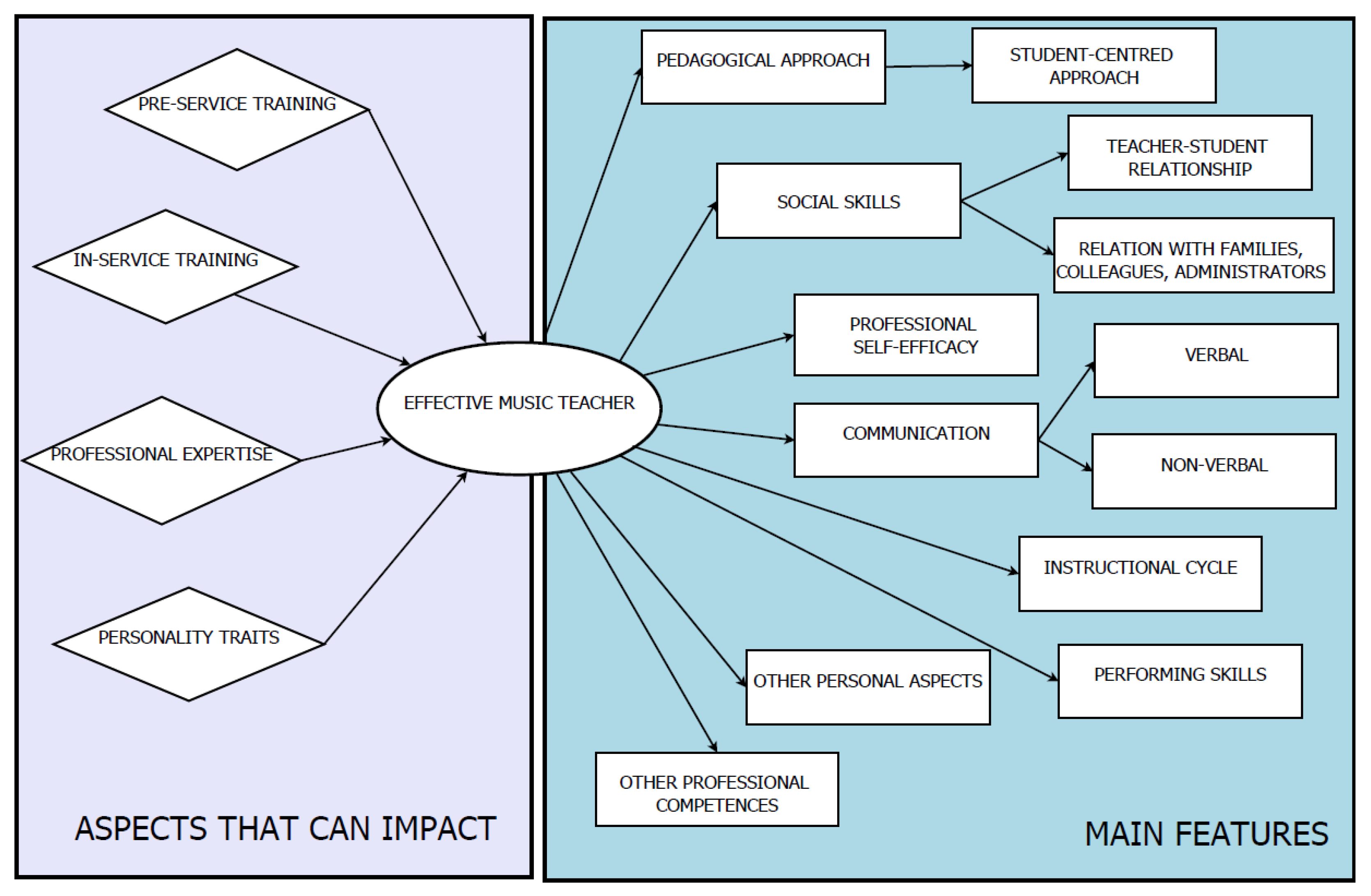
The current survey systematically examined the most significant literature concerning the topics of effective teachers and effective teaching in music instruction. The analysis considered research studies published over the past 20 years. The aspects that emerged during the analysis can be divided into two main groups: features that can impact and enhance the effectiveness of music teachers and music teaching, and the characteristics of effective music teachers. These aspects are summarized in the model proposed in Figure 5.
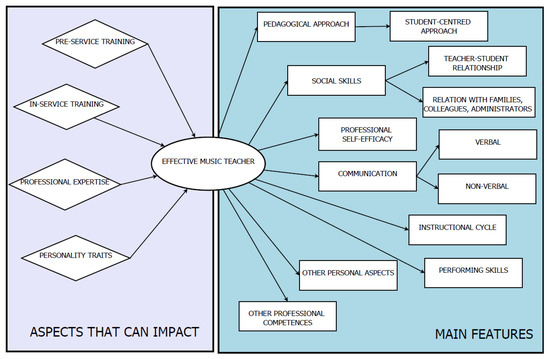
Figure 5.
Model of the effective music teachers.
Considering the aspects that may influence the development of effectiveness in music teaching, teacher training plays a crucial role since, in this context, prospective teachers can discover and employ innovative teaching strategies and relevant pedagogical contents. Particular attention should be given to preservice pedagogical experiences because these experiences may contribute to increasing teachers’ awareness of the role of a student-centered approach in music lessons as well as the importance of personalizing students’ learning experiences. Too frequently, these features are underestimated in music teachers’ preservice courses: according to Allsup [2], in many cases, preservice training remains rooted in a vision of teacher–student relationships that is based on the master–apprentice model. This situation continues to be the case because it represents the most suitable approach if the main goal of learning is the transmission of traditional praxis without a focus on personal re-elaboration and reconstruction. The need to promote the full development of pupils, not only in a musical context but also holistically, implies the need to train music teachers to act as learning facilitators [24] with the aim of gradually supporting students in becoming autonomous learners.
Considering the main characteristics of the profile of effective music teachers, the current model is coherent with the categories identified by the literature review conducted by Brand [1], who identified two main dimensions of effective music teachers: the first such dimension is related to personal features (personality traits, intelligence, attitudes, psychological aspects, etc.), while the second is focused on the professional competences that are needed for activities in class (class management, teaching strategies, etc.). The characteristics associated with the nonverbal component of communication and self-efficacy are reported by Steele [48], who added to these characteristics the notion of servant leadership, a dimension that has not appeared as a relevant research theme in the current analysis. All these aspects are closely connected with interpersonal relationships with students, which can be considered to constitute one of the core dimensions of effective music teachers.
The professional competences of effective music teachers are related to two main areas, i.e., the musical field (e.g., performing skills) and the pedagogical field (pedagogical knowledge, teaching methods, etc.). This component is what Townsend [7] defined as “artistry” in the context of the profile of the effective music teacher. Music teachers are “artists” in the sense of being “masters”, not only with respect to their expertise in musical techniques and performing but also with regard to their pedagogical and educational knowledge.
Comparing the promotion of teaching effectiveness in preservice and in-service music teachers, the main themes investigated are linked to the development of a student-centered approach in music lessons [27] and the achievement of the social and communicative abilities that are needed for an effective interpersonal relationship. For in-service teachers, professional needs are mainly related to promoting teachers’ awareness of the need to personalize music lessons to take into account the specific characteristics of the pupils [16].
In relation to the role of in-service and preservice training experiences for promoting effectiveness in music teaching, there are many aspects that should be addressed in training courses. A topic which should be addressed during the very first years of university is related to the teaching strategies and how to use them effectively in accordance with the educational context and students’ needs and characteristics [17,25]. Training experience should connect the theoretical dimension of music education and instruction and the real world of music instruction [12], preparing prospective music teachers to face the multidimensional contexts of music classes. Theoretical concepts should be supported by the promotion of relational and communicative skills [32], which are fundamental for structuring a positive and fruitful relation with the students. Another transversal aspect which is crucial for music teacher’s professional development is the enhancement of critical-thinking skills [10], as a fundamental competence for reflecting, monitoring and evaluating individual educational activity, in order to improve both teachers’ and students’ educational experience.
The current analysis faces certain limitations. First, all the studies examined focused on music education and instruction in the Western tradition. No information was provided concerning music teaching in cultural backgrounds outside the Western context. It would also be useful to examine the characteristics of effective teachers with reference to music teaching in other cultures in order to identify peculiarities and similarities from an intercultural perspective. Second, according to the search criteria, some potentially relevant papers were excluded; for example, no papers that were related to academic and educational conferences were considered, although many relevant international conferences focus on themes related to music education and instruction. Finally, most of the studies examined refer to instrumental music teachers or do not make a specific distinction in their analysis between vocal and instrumental teachers. This aspect does not allow one to make specifical distinctions between effective features in instrumental and vocal music, highlighting peculiar aspects that are typical of each of these two teaching–learning processes.
5. Conclusions
The current systematic review aimed to define the complex profile of effective music teachers. Considering the results that emerged, the figure of the effective music teacher is characterized by several dimensions, which are mainly related to (1) aspects that can support the development of effectiveness in teaching, (2) components of the effective teacher that pertain to personal characteristics, and (3) components of the effective teacher that are related to professional competences (musical and performing skills, general pedagogical contents, and teaching strategies). According to this general model of effective teachers, there is an overarching characteristic that can be identified with flexibility, including cognitive, behavioral, and relational flexibility. This characteristic is the main feature that allows a teacher to adapt successfully to the socio-educational context, to the institutional environment, and, more relevantly, to each pupil’s characteristics and needs. To adapt in a flexible manner, it is necessary to critically reflect on one’s own personal activity in order to adjust and regulate educational and teaching activities to promote a contextualized learning experience. Flexibility and critical thinking are, from this perspective, some of the most relevant transferable skills that should be included in music teachers’ training to help participants become “effective music teachers”.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Brand, M. Music Teacher Effectiveness: Selected Historical and Contemporary Research Approaches. Aust. J. Music Educ. 2009, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsup, R.E. Music teacher quality and the problem of routine expertise. Philos. Music Educ. Rev. 2015, 23, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, J. What music teachers want: The emergence of a unified understanding of an ideal teacher education course. Aust. J. Teach. Educ. 2006, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witty, P. An analysis of the personality traits of effective teachers. J. Educ. Res. 1947, 40, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finefter-Rosenbluh, I.; Ryan, T.; Barnes, M. The impact of student perception surveys on teachers’ practice: Teacher resistance and struggle in student voice-based assessment initiatives of effective teaching. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2021, 106, 103436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.A. A Different Paradigm in Music Education: Re-Examining the Profession; Routledge: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend, A.S. Introduction to Effective Music Teaching: Artistry and Attitude; Rowman & Littlefield: Lanham, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Firrincieli, A. Maieutic: A teaching and learning approach. As applied to western music. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2017, 237, 1520–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayçiçek, B. Integration of critical thinking into curriculum: Perspectives of prospective teachers. Think. Ski. Creat. 2021, 41, 100895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, V.D. Profile of an effective urban music educator. Update Appl. Res. Music Educ. 2012, 31, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, J. Integration, contextualization and continuity: Three themes for the development of effective music teacher education programmes. Int. J. Music Educ. 2007, 25, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, J.; Zhukov, K. A good news story: Early-career music teachers’ accounts of their “flourishing” professional identities. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2017, 68, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasutti, M.; Concina, E. The effective music teacher: The influence of personal, social, and cognitive dimensions on music teacher self-efficacy. Musicae Sci. 2018, 22, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasutti, M.; Concina, E.; Deloughry, C.; Frate, S.; Konkol, G.; Mangiacotti, A.; Rotar Pance, B.; Vidulin, S. The effective music teacher: A model for predicting music teacher’s self-efficacy. Psychol. Music 2021, 49, 1498–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasutti, M.; Frate, S.; Concina, E. Music teachers’ professional development: Assessing a three-year collaborative online course. Music Educ. Res. 2019, 21, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, J. Expertise in applied studio teaching: Teachers working with multiple levels of learners. Int. J. Music Educ. 2020, 38, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.L. Perspective consciousness and cultural relevancy: Partnership considerations for the re-conceptualization of music teacher preparation. Arts Educ. Policy Rev. 2011, 112, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Button, S. Music teachers’ perceptions of effective teaching. Bull. Counc. Res. Music Educ. 2010, 25–38. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/27861470 (accessed on 15 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Daniel, R.; Parkes, K. The Apprentice to Master Journey: Exploring Tertiary Music Instrument Teachers’ Reflections on Their Experiences as Learner. J. Arts Humanit. 2015, 4, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.A.; Seaver, K.J. Music educators’ self-perceptions of interpersonal skills: An exploratory study. Update Appl. Res. Music Educ. 2013, 32, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Williams, L.; Parisi, J.; Brunkan, M. Behavioral characteristics and instructional patterns of expert teaching, and the transfer of those behaviors into a musical setting: Two case studies. Int. J. Music Educ. 2016, 34, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juchniewicz, J. The influence of social intelligence on effective music teaching. J. Res. Music Educ. 2010, 58, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A.E.; Davidson, J.W. Effective educational strategies to promote life-long musical investment: Perceptions of educators. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupers, E.; van Dijk, M.; van Geert, P. Within-teacher differences in one-to-one teacher–student interactions in instrumental music lessons. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2015, 37, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkul, W.W. Nonverbal communication in one-to-one music performance instruction. Psychol. Music 2007, 35, 327–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legette, R.M.; Royo, J. Pre-service music teacher perceptions of peer feedback. Res. Stud. Music Educ. 2021, 43, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijen, Ä.; Linde, R.; Kivestu, T. Perception of professional identity among the violin teachers of Estonian music schools. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 191, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Íñiguez, G.; Pozo, J.I. Analysis of constructive practice in instrumental music education: Case study with an expert cello teacher. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2016, 60, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, K.; Cassidy, J.W. The effect of focus of attention and teaching experience on perceptions of teaching effectiveness and student learning. J. Res. Music Educ. 2005, 53, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, R.B. The perceived effectiveness of nonverbal, co-verbal, and verbal string ensemble instruction: Student, teacher, and observer views. J. Music Teach. Educ. 2018, 27, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millican, J.S.; Forrester, S.H. Music teacher rankings of selected core teaching practices. J. Music Teach. Educ. 2019, 29, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J. Conservatoire students’ perceptions of the characteristics of effective instrumental and vocal tuition. Bull. Counc. Res. Music Educ. 2002, 153–154, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Napoles, J.; MacLeod, R.B. The influences of teacher delivery and student progress on preservice teachers’ perceptions of teaching effectiveness. J. Res. Music Educ. 2013, 61, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.R.; Parker, E.C. Preservice music teachers’ descriptions of successful and unsuccessful teachers. J. Music Teach. Educ. 2017, 26, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.R.; Weaver, M.A.; Henson, R.K. Relationship of preservice music teachers’ primary instrument background and teaching effectiveness in brass and woodwind techniques classes. J. Music Teach. Educ. 2018, 27, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regier, B.J. Examining relationships among concert band directors’ efficacious sources, self-efficacy for teaching strategies, and effective teaching skills. J. Res. Music Educ. 2021, 68, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.A. So many expectations: A study of Australian early-career secondary school music teachers. Res. Stud. Music Educ. 2022, 44, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygi, C.; Kirmizi, F.S. An evaluation of elementary and music teacher candidates’ perceptions of professional self-efficacy: The cases of Pamukkale and Adnan Menderes Universities. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 46, 3655–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M. Mentoring and being mentored: The story of a novice music teacher’s success. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2008, 24, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieker, M.H. The Comparison of Novice and Master Instrumental Music Educators’ Use of Figurative Language and Their Attitudes Concerning It as a Tool for Effective Teaching. Res. Issues Music Educ. 2017, 13, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Stavrou, N.E. Looking at the ideal secondary school music teacher in Cyprus: Teachers’ and students’ perspectives. Music Educ. Res. 2020, 22, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanwick, K. The ‘good-enough’ music teacher. Br. J. Music Educ. 2008, 25, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.M.; Raadt, J.S. Gay-and straight-sounding auditory cues elicit stereotyping about teaching effectiveness. J. Res. Music Educ. 2021, 69, 62–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woody, R.H.; Gilbert, D.; Laird, L.A. Music teacher dispositions: Self-appraisals and values of university music students. J. Res. Music Educ. 2018, 66, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klassen, R.M.; Tze, V.M.C. Teacher’s self-efficacy, personality, and teaching effectiveness: A meta-analysis. Educ. Res. Rev. 2014, 12, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychol. Rev. 1997, 84, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, N.A. Three characteristics of effective teachers. Update Appl. Res. Music Educ. 2010, 28, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).