Mass Spectrometry as an Analytical Tool for Detection of Microplastics in the Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Application of Mass Spectrometry for the Detection of Microplastics
2.1. Detection of MPs in Marine and Freshwater Organisms
2.2. Detection of MPs in Various Water Sources
2.2.1. In Seawater and Artificial Sea Water
2.2.2. Detection of MPs in Freshwater
2.2.3. Detection of MPs in Wastewater
2.3. Detection of MPs in Sediments
2.4. Detection of MPs in Other Environmental Samples
3. LC-MS-Based Analysis of the Effects of MPs
3.1. LC-MS-Based Analysis on the Effects of MPs on Aquatic Creatures and in Water Sources
3.2. Detection of MPs in Miscellaneous Sources
4. Other MS-Based Microplastic Sensors
5. Challenges and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, K.P.; Sharma, D.; Saha, S.; Satapathy, B.K. From outbreak of COVID-19 to launching of vaccination drive: Invigorating single-use plastics, mitigation strategies, and way forward. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 55811–55845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaverková, M.D. Landfill Impacts on the Environment—Review. Geosciences 2019, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, B.; Laitala, K.; Klepp, I.G. Microfibres from apparel and home textiles: Prospects for including microplastics in environmental sustainability assessment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 652, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöpel, B.; Stamminger, R. A Comprehensive Literature Study on Microfibres from Washing Machines. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2019, 56, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschoor, A.; De Poorter, L.; Dröge, R.; Kuenen, J.; de Valk, E. Emission of Microplastics and Potential Mitigation Measures: Abrasive Cleaning Agents, Paints and Tyre Wear; National Institute for Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, C.Q.Y.; Valiyaveettil, S.; Tang, B.L. Toxicity of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Mammalian Systems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kik, K.; Bukowska, B.; Krokosz, A.; Sicińska, P. Oxidative Properties of Polystyrene Nanoparticles with Different Diameters in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (In Vitro Study). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Pan, J.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Bartlam, M.; Wang, Y. Selective enrichment of bacterial pathogens by microplastic biofilm. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. An assessment of the toxicity of polypropylene microplastics in human derived cells. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 684, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primpke, S.; Christiansen, S.H.; Cowger, C.W.; De Frond, H.; Deshpande, A.; Fischer, M.; Holland, E.B.; Meyns, M.; O’Donnell, B.A.; Ossmann, B.E.; et al. Critical Assessment of Analytical Methods for the Harmonized and Cost-Efficient Analysis of Microplastics. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 1012–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Takehana, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Yamaji, H.; Maeda, Y.; Toyohara, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate). Science 2016, 351, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.P.D.C.; de Melo, N.F.S.; Junior, A.G.D.O.; Rodrigues, F.P.; Fernandes, T.; Vieira, J.E.D.A.; Rocha, T.L.; Malafaia, G. How much are microplastics harmful to the health of amphibians? A study with pristine polyethylene microplastics and Physalaemus cuvieri. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, O.; Kang, B.; Cho, S.K.; Park, J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, W.-I.; Marunga, J.; Hwang, I.; Kim, J. Identification of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae causing bacterial leaf blight of Miscanthus sinensis. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2017, 124, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, M.; Hua, P.-Y.; Wu, H.-F. Rapid endophytic bacterial detection by enzyme incorporated MALDI MS. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 50233–50240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, L.; Mahaffy, P.; Trainer, M.; Eigenbrode, J.; Arevalo, R.; Brinckerhoff, W.; Getty, S.; Grefenstette, N.; Da Poian, V.; Fricke, G.M.; et al. Planetary Mass Spectrometry for Agnostic Life Detection in the Solar System. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2021, 8, 755100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.A.; Hendrickson, E.; Minor, E.C.; Schreiner, K.; Halbur, J.; Bratton, S.P. Pyr-GC/MS analysis of microplastics extracted from the stomach content of benthivore fish from the Texas Gulf Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanslik, L.; Sommer, C.; Huppertsberg, S.; Dittmar, S.; Knepper, T.P.; Braunbeck, T. Microplastic-associated trophic transfer of benzo(k)fluoranthene in a limnic food web: Effects in two freshwater invertebrates (Daphnia magna, Chironomus riparius) and zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 237, 108849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanslik, L.; Seiwert, B.; Huppertsberg, S.; Knepper, T.P.; Reemtsma, T.; Braunbeck, T. Biomarker responses in zebrafish (Danio rerio) following long-term exposure to microplastic-associated chlorpyrifos and benzo(k)fluoranthene. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 245, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrank, I.; Trotter, B.; Dummert, J.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M.; Löder, M.G.; Laforsch, C. Effects of microplastic particles and leaching additive on the life history and morphology of Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas; Hadibarata, T.; Sathishkumar, P.; Prasetia, H.; Hikmat; Pusfitasari, E.D.; Tasfiyati, A.N.; Muzdalifah, D.; Waluyo, J.; Randy, A.; et al. Microplastic contamination in the Skipjack Tuna (Euthynnus affinis) collected from Southern Coast of Java, Indonesia. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, R.; Gürses, R.K.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Kimoto, T.; Kitagawa, S.; Iiguni, Y.; Ohtani, H. Pyrolysis-GC–MS analysis of ingested polystyrene microsphere content in individual Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Echeverría, T.; Beiras, R. Acute toxicity of bioplastic leachates to Paracentrotus lividus sea urchin larvae. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 176, 105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saliu, F.; Biale, G.; Raguso, C.; La Nasa, J.; Degano, I.; Seveso, D.; Galli, P.; Lasagni, M.; Modugno, F. Detection of plastic particles in marine sponges by a combined infrared micro-spectroscopy and pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry approach. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 819, 152965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brutto, S.L.; Iaciofano, D.; Turco, V.L.; Potortì, A.; Rando, R.; Arizza, V.; Di Stefano, V. First Assessment of Plasticizers in Marine Coastal Litter-Feeder Fauna in the Mediterranean Sea. Toxics 2021, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbach, M.; Vogel, M.; Tammen, J.K.; Rüdel, H.; Koschorreck, J.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M. 30 years trends of microplastic pollution: Mass-quantitative analysis of archived mussel samples from the North and Baltic Seas. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pojar, I.; Stănică, A.; Stock, F.; Kochleus, C.; Schultz, M.; Bradley, C. Sedimentary microplastic concentrations from the Romanian Danube River to the Black Sea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, P.; Shi, H.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Shi, Y.; Gao, S. Photo aging and fragmentation of polypropylene food packaging materials in artificial seawater. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biale, G.; La Nasa, J.; Mattonai, M.; Corti, A.; Castelvetro, V.; Modugno, F. Seeping plastics: Potentially harmful molecular fragments leaching out from microplastics during accelerated ageing in seawater. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Peng, Q.; Yuan, H.; Li, N.; Duan, L.; Ma, J. Concentrations and distribution of phthalate esters in the seamount area of the Tropical Western Pacific Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyen, P.; Hermabessiere, L.; Dehaut, A.; Himber, C.; Decodts, M.; Degraeve, T.; Delord, L.; Gaboriaud, M.; Moné, P.; Sacco, J.; et al. Occurrence and identification of microplastics in beach sediments from the Hauts-de-France region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 28010–28021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermabessiere, L.; Rochman, C.M. Microwave-Assisted Extraction for Quantification of Microplastics Using Pyrolysis–Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 2733–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermabessiere, L.; Himber, C.; Boricaud, B.; Kazour, M.; Amara, R.; Cassone, A.-L.; Laurentie, M.; Paul-Pont, I.; Soudant, P.; Dehaut, A.; et al. Optimization, performance, and application of a pyrolysis-GC/MS method for the identification of microplastics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6663–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.-C.; Lai, Y.-J.; Yu, S.-J.; Li, P.; Zhou, X.-X.; Dong, L.-J.; Liu, X.; Yao, Z.-W.; Liu, J.-F. Sequential Isolation of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Environmental Waters by Membrane Filtration, Followed by Cloud-Point Extraction. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4559–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, E.; Minor, E.C.; Schreiner, K. Microplastic Abundance and Composition in Western Lake Superior As Determined via Microscopy, Pyr-GC/MS, and FTIR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscher, L.; Halbach, M.; Nguyen, M.T.; Hebeler, M.; Luschtinetz, F.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Microplastics in two German wastewater treatment plants: Year-long effluent analysis with FTIR and Py-GC/MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funck, M.; Yildirim, A.; Nickel, C.; Schram, J.; Schmidt, T.C.; Tuerk, J. Identification of microplastics in wastewater after cascade filtration using Pyrolysis-GC–MS. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.S.; Hamzah, S.R.; Khalik, W.M.A.W.M.; Yusof, K.M.K.K.; Anuar, S.T. Spatiotemporal microplastic occurrence study of Setiu Wetland, South China Sea. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 788, 147809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takdastan, A.; Niari, M.H.; Babaei, A.; Dobaradaran, S.; Jorfi, S.; Ahmadi, M. Occurrence and distribution of microplastic particles and the concentration of Di 2-ethyl hexyl phthalate (DEHP) in microplastics and wastewater in the wastewater treatment plant. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, K.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B.; Wu, W.; Gao, J.; et al. Rapid Monitoring Approach for Microplastics Using Portable Pyrolysis-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4656–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelvetro, V.; Corti, A.; Biale, G.; Ceccarini, A.; Degano, I.; La Nasa, J.; Lomonaco, T.; Manariti, A.; Manco, E.; Modugno, F.; et al. New methodologies for the detection, identification, and quantification of microplastics and their environmental degradation by-products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46764–46780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, A.; Øysæd, K.B.; Palmas, L.; Skogerbø, G. Application of GCMS-pyrolysis to estimate the levels of microplastics in a drinking water supply system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M. Simultaneous Trace Identification and Quantification of Common Types of Microplastics in Environmental Samples by Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5052–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, T.K.; Uddin, M.E.; Jamal, M. Detection and removal of microplastics in wastewater: Evolution and impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16925–16947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.; Gago, J.; Otero, V.; Sobral, P. Microplastics in coastal sediments from Southern Portuguese shelf waters. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 114, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, E.; Dekiff, J.H.; Willmeyer, J.; Nuelle, M.-T.; Ebert, M.; Remy, D. Identification of polymer types and additives in marine microplastic particles using pyrolysis-GC/MS and scanning electron microscopy. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dümichen, E.; Eisentraut, P.; Bannick, C.G.; Barthel, A.K.; Senz, R.; Braun, U. Fast identification of microplastics in complex environmental samples by a thermal degradation method. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biale, G.; La Nasa, J.; Mattonai, M.; Corti, A.; Vinciguerra, V.; Castelvetro, V.; Modugno, F. A Systematic Study on the Degradation Products Generated from Artificially Aged Microplastics. Polymers 2021, 13, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goßmann, I.; Halbach, M.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M. Car and truck tire wear particles in complex environmental samples – A quantitative comparison with “traditional” microplastic polymer mass loads. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hayany, B.; El Fels, L.; Quénéa, K.; Dignac, M.F.; Rumpel, C.; Gupta, V.K.; Hafidi, M. Microplastics from lagooning sludge to composts as revealed by fluorescent staining- image analysis, Raman spectroscopy and pyrolysis-GC/MS. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 275, 111249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Nasa, J.; Biale, G.; Mattonai, M.; Modugno, F. Microwave-assisted solvent extraction and double-shot analytical pyrolysis for the quali-quantitation of plasticizers and microplastics in beach sand samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duemichen, E.; Eisentraut, P.; Celina, M.; Braun, U. Automated thermal extraction-desorption gas chromatography mass spectrometry: A multifunctional tool for comprehensive characterization of polymers and their degradation products. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1592, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.L.; Gallardo, J.D.; Jones, E.W.; Hollliman, P.J.; Watson, T.M.; Sarp, S. Detection of trace sub-micron (nano) plastics in water samples using pyrolysis-gas chromatography time of flight mass spectrometry (PY-GCToF). Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Yu, X.; Cai, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, J. Microplastics and associated PAHs in surface water from the Feilaixia Reservoir in the Beijiang River, China. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primpke, S.; Fischer, M.; Lorenz, C.; Gerdts, G.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M. Comparison of pyrolysis gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and hyperspectral FTIR imaging spectroscopy for the analysis of microplastics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 8283–8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibke, C.; Fischer, M.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M. Microplastic Mass Concentrations and Distribution in German Bight Waters by Pyrolysis–Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry/Thermochemolysis Reveal Potential Impact of Marine Coatings: Do Ships Leave Skid Marks? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, N.; Anquetil, C.; Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Tassin, B.; Derenne, S. Quantification of Microplastics by Pyrolysis Coupled with Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry in Sediments: Challenges and Implications. Microplastics 2022, 1, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Park, Y.-K.; Kim, H.; Kwon, J.; Moon, H.M.; Lee, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Teramae, N.; Ohtani, H.; Kim, Y.-M. Selective solvent extraction and quantification of synthetic microfibers in textile laundry wastewater using pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimura, T.; Iwai, I.; Matsui, K.; Mattonai, M.; Watanabe, A.; Robberson, W.; Cook, A.-M.; Allen, H.L.; Pipkin, W.; Teramae, N.; et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of mixtures of microplastics in the presence of calcium carbonate by pyrolysis-GC/MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 157, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funck, M.; Al-Azzawi, M.S.; Yildirim, A.; Knoop, O.; Schmidt, T.C.; Drewes, J.E.; Tuerk, J. Release of microplastic particles to the aquatic environment via wastewater treatment plants: The impact of sand filters as tertiary treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.-S.; Kim, Y.-M.; Siddiqui, M.Z.; Watanabe, A.; Han, S.; Jeong, S.; Jung, Y.-W.; Jeon, K.-J. Quantification of tire wear particles in road dust from industrial and residential areas in Seoul, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, H.A.; Chetwynd, A.J.; Kelly, C.A.; Stark, C.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Krause, S.; Lynch, I. An Untargeted Thermogravimetric Analysis-Fourier Transform Infrared-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Approach for Plastic Polymer Identification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8721–8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Yu, J.; Ni, F.; Sheng, Y.; Scircle, A.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Zhou, Y. Separation and identification of microplastics in marine organisms by TGA-FTIR-GC/MS: A case study of mussels from coastal China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, R.; Altmann, K.; Sommerfeld, T.; Braun, U. Quantification of microplastics in a freshwater suspended organic matter using different thermoanalytical methods—Outcome of an interlaboratory comparison. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 148, 104829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravit, B.; Cooper, K.; Moreno, G.; Buckley, B.; Yang, I.; Deshpande, A.; Meola, S.; Jones, D.; Hsieh, A. Microplastics in urban New Jersey freshwaters: Distribution, chemical identification, and biological affects. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2017, 4, 809–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.; Okoffo, E.D.; Rauert, C.; O’Brien, J.W.; Ribeiro, F.; Burrows, S.D.; Toapanta, T.; Wang, X.; Thomas, K.V. Quantification of selected microplastics in Australian urban road dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Liang, S.; Li, H.; Sun, L. Pyr-GC-MS analysis of microplastics extracted from farmland soils. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannick, C.G.; Szewzyk, R.; Ricking, M.; Schniegler, S.; Obermaier, N.; Barthel, A.K.; Altmann, K.; Eisentraut, P.; Braun, U. Development and testing of a fractionated filtration for sampling of microplastics in water. Water Res. 2019, 149, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, U.; Altmann, K.; Herper, D.; Knefel, M.; Bednarz, M.; Bannick, C.G. Smart filters for the analysis of microplastic in beverages filled in plastic bottles. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2021, 38, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekiff, J.H.; Remy, D.; Klasmeier, J.; Fries, E. Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in sediments from Norderney. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuelle, M.-T.; Dekiff, J.H.; Remy, D.; Fries, E. A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, C.; Weber, A.; Stock, F.; Vurusic, S.; Egerci, H.; Kochleus, C.; Arendt, N.; Foeldi, C.; Dierkes, G.; Wagner, M.; et al. Comparative assessment of microplastics in water and sediment of a large European river. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 738, 139866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilakati, B.; Sivasankar, V.; Nyoni, H.; Mamba, B.B.; Omine, K.; Msagati, T.A. The Py-GC-TOF-MS analysis and characterization of microplastics (MPs) in a wastewater treatment plant in Gauteng Province, South Africa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Qin, Z.; Huang, Z.; Bao, Z.; Luo, T.; Jin, Y. Effects of Polyethylene Microplastics on the Microbiome and Metabolism in Larval Zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 282, 117039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolívar-Subirats, G.; Cortina-Puig, M.; Lacorte, S. Multiresidue Method for the Determination of High Production Volume Plastic Additives in River Waters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41314–41325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, T.; Pu, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, L. An Innovative Evaluation Method Based on Polymer Mass Detection to Evaluate the Contribution of Microfibers from Laundry Process to Municipal Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, P.; Wu, X.; Shi, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Gao, S. Insight into Chain Scission and Release Profiles from Photodegradation of Polycarbonate Microplastics. Water Res. 2021, 195, 116980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirinzi, G.F.; Llorca, M.; Seró, R.; Moyano, E.; Barceló, D.; Abad, E.; Farré, M. Trace Analysis of Polystyrene Microplastics in Natural Waters. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Tang, X.; Gong, X.; Dai, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, L. Development and Application of a Mass Spectrometry Method for Quantifying Nylon Microplastics in Environment. Anal Chem. 2020, 92, 13930–13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliu, F.; Montano, S.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Lasagni, M.; Galli, P. A Non-Lethal SPME-LC/MS Method for the Analysis of Plastic-Associated Contaminants in Coral Reef Invertebrates. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliu, F.; Montano, S.; Lasagni, M.; Galli, P. Biocompatible Solid-Phase Microextraction Coupled to Liquid Chromatography Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry Analysis for the Determination of Phthalates in Marine Invertebrate. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1618, 460852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; He, N.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, L. Excretion Characteristics of Nylon Microplastics and Absorption Risk of Nanoplastics in Rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 238, 113586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, Y.; Song, K.; Du, W.; Huang, W.; Gu, Z.; Feng, Z. Microplastics in Different Tissues of Wild Crabs at Three Important Fishing Grounds in China. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, D.; Liu, P.; Ouyang, Z.; Jia, H.; Guo, X. The Characteristics of Dis-solved Organic Matter Release from UV-Aged Microplastics and Its Cytotoxicity on Human Colonic Adenocarcinoma Cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Hou, S.; Sun, H. A Simple Method for Quantifying Polycarbonate and Polyethylene Terephthalate Microplastics in Environmental Samples by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Deng, J.; Gao, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H. Widespread distribution of PET and PC microplastics in dust in urban China and their estimated human exposure. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Peng, C.; Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; He, X.; Wang, L. Comparison of Detection Methods of Microplastics in Landfill Mineralized Refuse and Selection of Degradation Degree Indexes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 13802–13811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Skoczynska, E.; Siddhanti, D.; van Putten, R.-J.; Leslie, H.A.; Gruter, G.-J.M. Quantification of polyethylene terephthalate microplastics and nanoplastics in sands, indoor dust and sludge using a simplified in-matrix depolymerization method. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Peng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Tang, X.; Lu, Y.; Sun, H. Earthworms’ Degradable Bioplastic Diet of Polylactic Acid: Easy to Break Down and Slow to Excrete. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5020–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Yang, J.; Sun, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, L. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in sediments of a man-made lake receiving reclaimed water. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, L.; Duan, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, L. Microplastics in Yellow River Delta wetland: Occurrence, characteristics, human influences, and marker. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panio, A.; Corsarini, S.F.; Bruno, A.; Lasagni, M.; Labra, M.; Saliu, F. Determination of phthalates in fish fillets by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS): A comparison of direct immersion solid phase microextraction (SPME) versus ultrasonic assisted solvent extraction (UASE). Chemosphere 2020, 255, 127034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano, S.; Seveso, D.; Maggioni, D.; Galli, P.; Corsarini, S.; Saliu, F. Spatial variability of phthalates contamination in the reef-building corals Porites lutea, Pocillopora verrucosa and Pavona varians. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 155, 111117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Abrahamsson, D.P.; Song, W.; Yang, C.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J. Non-targeted analysis for organic components of microplastic leachates. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Halden, R.U.; Kannan, K. Polyethylene Terephthalate and Polycarbonate Microplastics in Sewage Sludge Collected from the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Kannan, K. Microplastics in house dust from 12 countries and associated human exposure. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Kannan, K. Polyethylene Terephthalate and Polycarbonate Microplastics in Pet Food and Feces from the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12035–12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, L.; Mascilongo, G.; Berti, M.; Bogdanović, T.; Listeš, E.; Brkljača, M.; Notarstefano, V.; Gioacchini, G.; Giorgini, E.; Olivieri, V.; et al. Potential Impact of Microplastics and Additives on the Health Status of Loggerhead Turtles (Caretta caretta) Stranded along the Central Adriatic Coast. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguso, C.; Saliu, F.; Lasagni, M.; Galli, P.; Clemenza, M.; Montano, S. First detection of microplastics in reef-building corals from a Maldivian atoll. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungnickel, H.; Pund, R.; Tentschert, J.; Reichardt, P.; Laux, P.; Harbach, H.; Luch, A. Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (ToF-SIMS)-Based Analysis and Imaging of Polyethylene Microplastics Formation during Sea Surf Simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.F.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Boegehold, A.G.; Peraino, N.J.; Westrick, J.A.; Kashian, D.R. Microplastic Ingestion by Quagga Mussels, Dreissena Bugensis, and Its Effects on Physiological Processes. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Q.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, G. Thermal Fragmentation Enhanced Identification and Quantification of Polystyrene Micro/Nanoplastics in Complex Me-dia. Talanta 2020, 208, 120478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironti, C.; Ricciardi, M.; Motta, O.; Miele, Y.; Proto, A.; Montano, L. Microplastics in the Environment: Intake through the Food Web, Human Exposure and Toxicological Effects. Toxics 2021, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, M.S.; Xu, L.; Cai, J.; Vedarethinam, V.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Huang, H.; Shen, N.; Di, W.; Ding, H.; et al. Zirconia Hybrid Nanoshells for Nutrient and Toxin Detection. Small 2020, 16, 2003902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinan, T.; Ronci, M.; Vasani, R.; Kobus, H.; Voelcker, N.H. Comparison of the performance of different silicon-based SALDI substrates for illicit drug detection. Talanta 2015, 132, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinan, T.; Della Vedova, C.; Kobus, H.; Voelcker, N.H. Mass spectrometry imaging of fingerprint sweat on nanostructured silicon. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6088–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, A.R.; Stopka, S.A.; Morris, N.; Razunguzwa, T.; Vertes, A. Large-Scale Metabolite Analysis of Standards and Human Serum by Laser Desorption Ionization Mass Spectrometry from Silicon Nanopost Arrays. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8989–8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, Q. Direct detection of the anti-cancer drug 9-phenylacridine in tissues by graphite rod laser desorption vacuum-ultraviolet post-ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 29, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.S.; Gopal, J.; Hua, P.-Y.; Wu, H.-F. Graphene nanosheet mediated MALDI-MS (GN-MALDI-MS) for rapid, in situ detection of intact incipient biofilm on material surfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 66, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

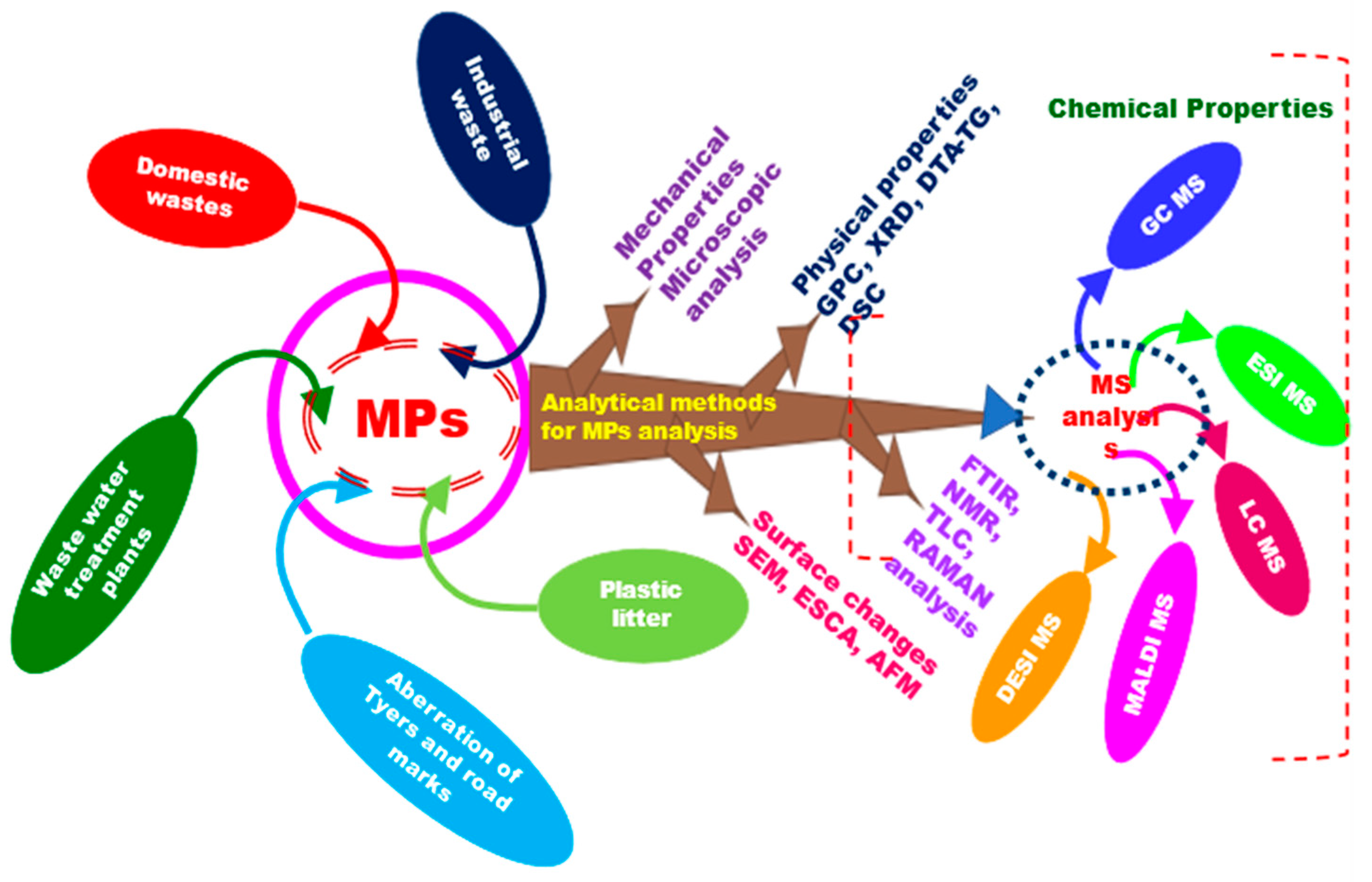
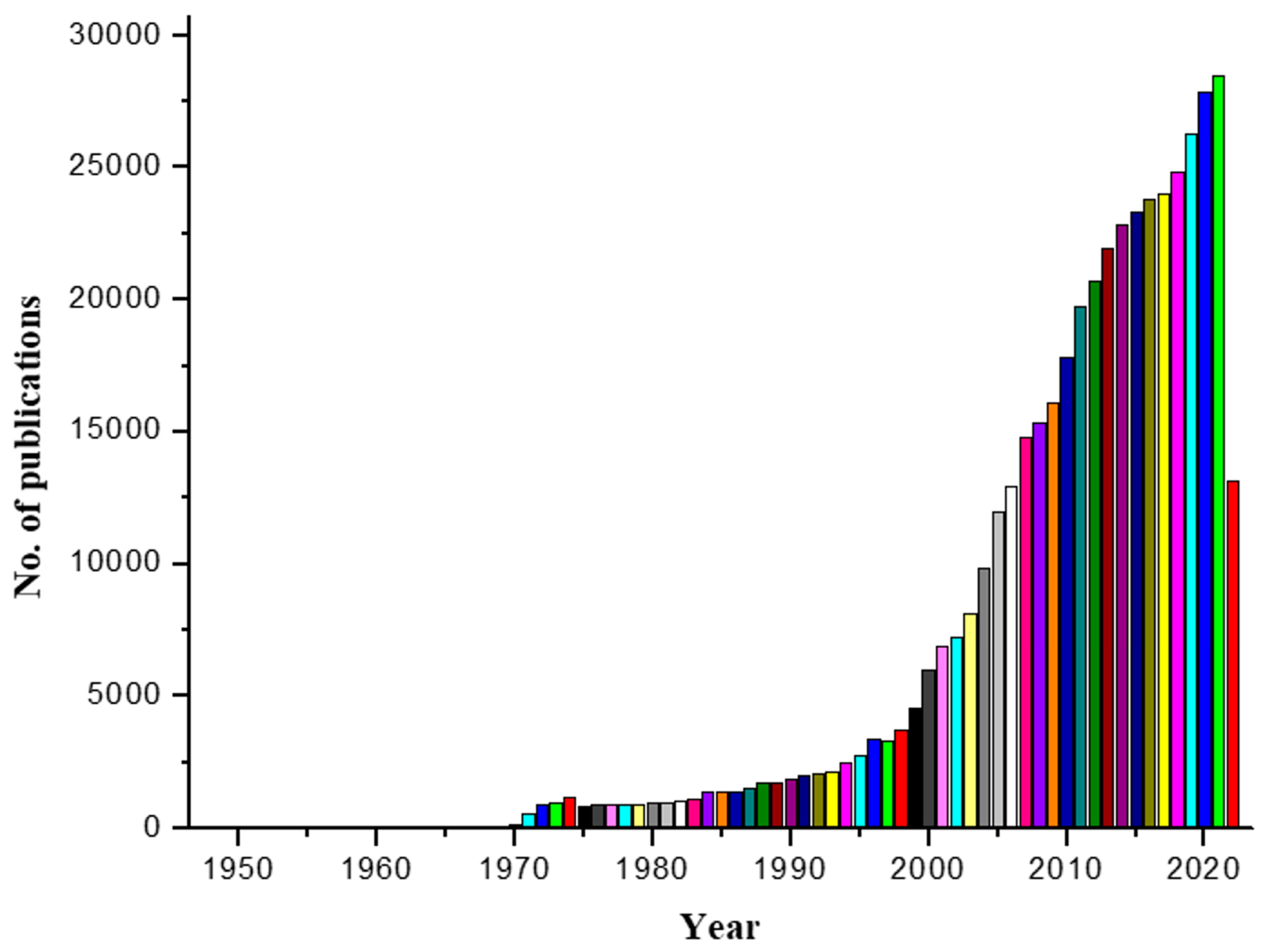
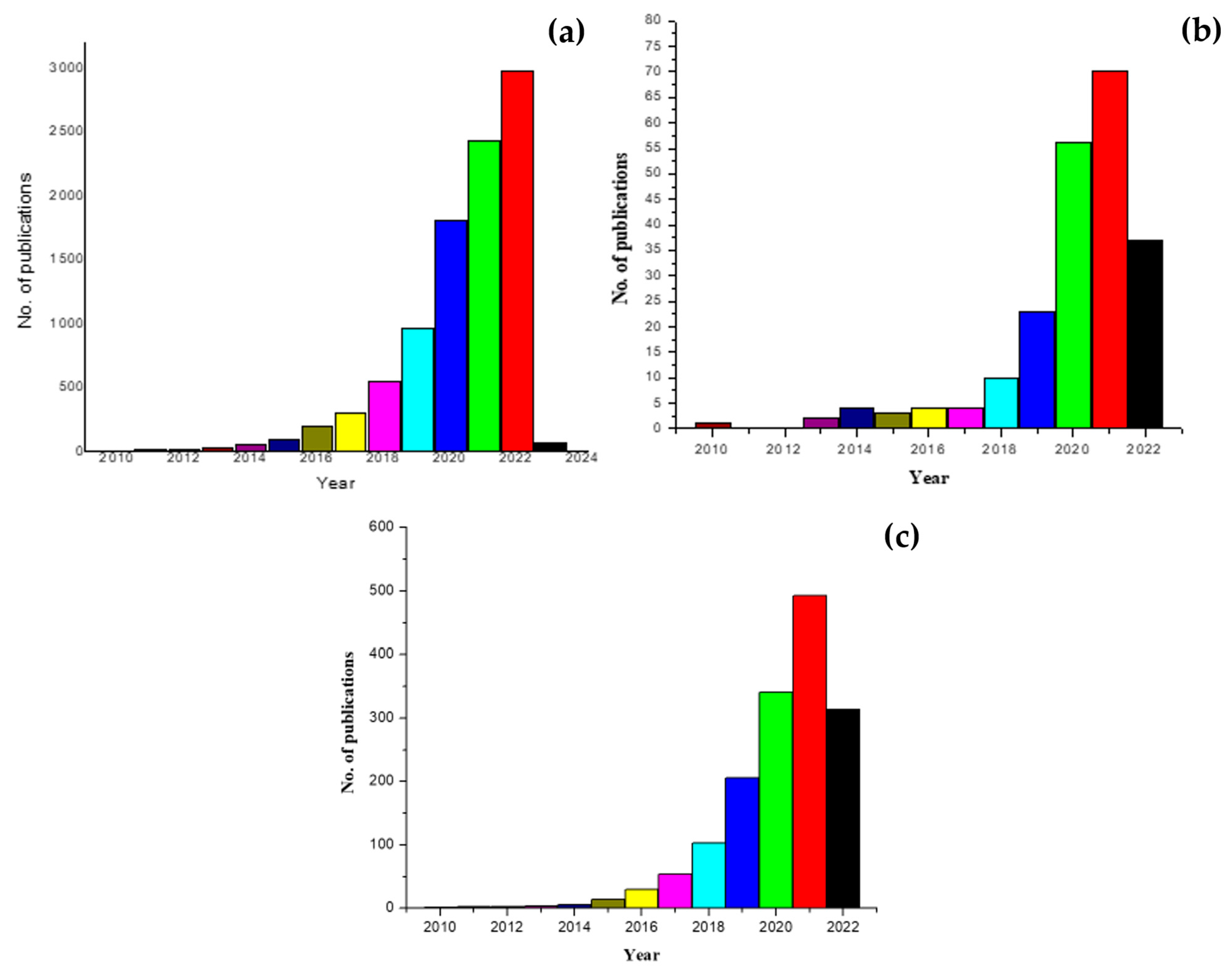
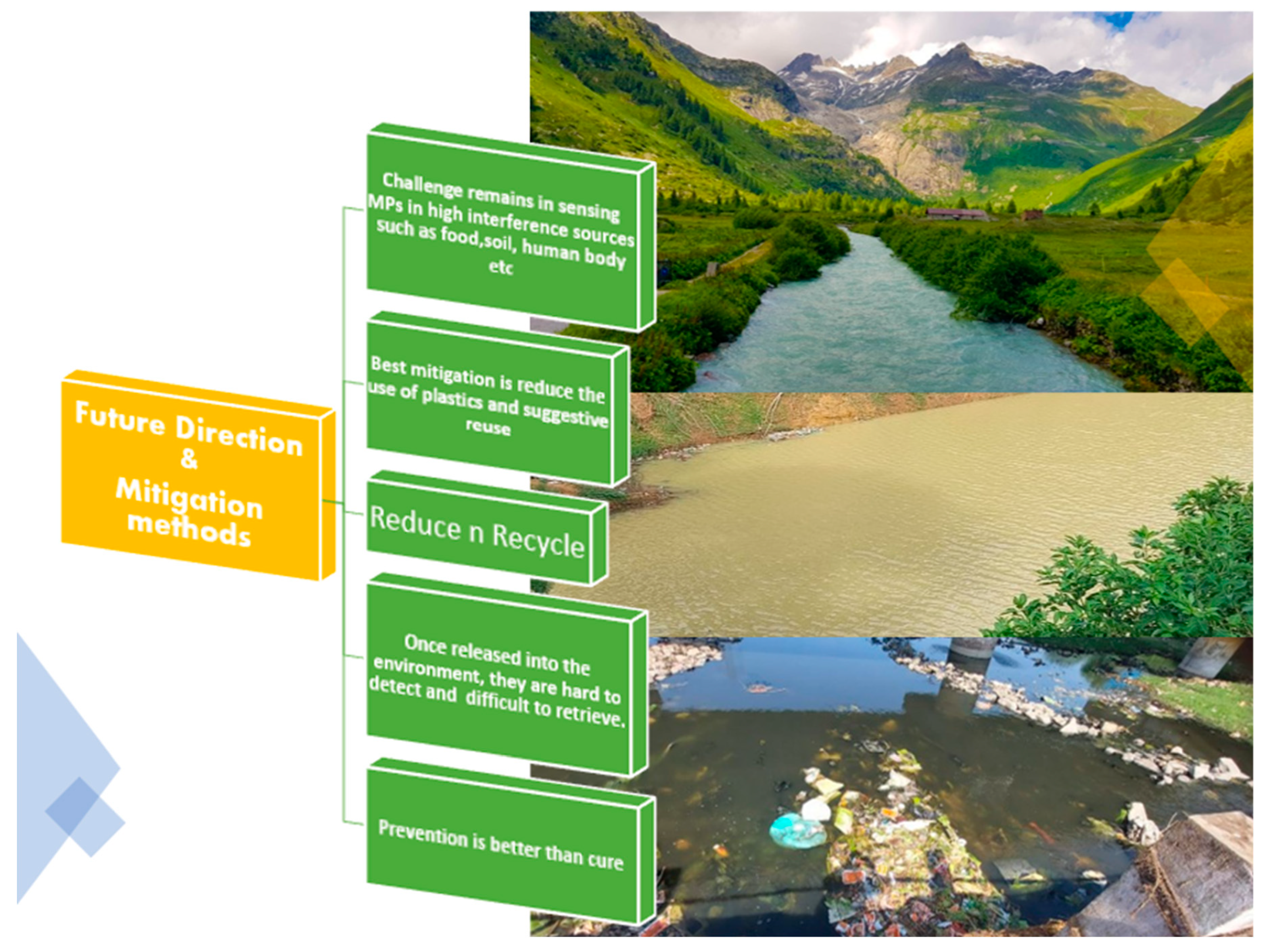
| Technique | Source | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| GC-MS | River surface water | The composition and concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in microplastics were determined. | [53] |
| Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) imaging analysis and Pyr-GC/MS | Sea surface water and sediment | FTIR detects a broad range and even very low numbers of smaller sized particles, Pyrolysis -GC/MS, when exceeding a detection threshold, enables a condensed overview of polymer types represented by a shared chemical backbone expressed by basic polymer clusters. | [54] |
| Pyr-GC/MS | German Bight waters | Polyethylene, polypropylene, poly(ethylene terephthalate), polystyrene, poly-(vinyl chloride), polycarbonate, and poly(methyl methacrylate) were detected. | [55] |
| Pyr-GC/MS | Estuary of the Seine river sediments | Highlighted the challenges associated with the use of Pyr-GC/MS for the quantification of microplastics in sediments. | [56] |
| Pyr-GC/MS | Raw and treated drinking water | The most dominant polymer type in drinking water samples was polyethylene > polyamide > polyethylene terphtalate > polypropylene > polystyrene. | [41] |
| Pyr-GC-MS | Textile laundry wastewater | Polyethylene terephthalate, nylon-6, and polyacrylonitrile were quantified. | [57] |
| Pyr-GC–MS | Daphnia magna (zooplankton) | The content of polystyrene ingested by an individual Daphnia magna was successfully determined. | [21] |
| Pyr-GC–MS | Sea surface water and mixture of twelve types of standard polymers | The microplastic samples twelve polymers were identified and quantified by Pyrolysis-GC/MS with calcium carbonate. | [58] |
| Pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) and Pyr-GC-MS | Sediment, suspended matter, soil, and sewage sludge | Polyethylene and polypropylene were detected in all samples. | [59] |
| Pyr-GC–MS | Road dust samples | Quantified the tire and road wear microplastics in road dust samples. | [60] |
| Pyr-GC-MS | Sandy beach sediments | Identified 68.8% of the analyzed particles. | [30] |
| TGA-FTIR-GC-MS | Reference polymers and mesoplastics from beach and beach sediments. | Provided physical and chemical properties of the analyzed polymers. Identified 11 types of polymers. | [61] |
| TGA-FTIR-GC-MS | Mussels | Quantified polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, and polystyrene microplastics in mussel tissue. | [62] |
| Pyr-GC–MS | Chaetodipterus faber (Atlantic spadefish), Cynoscion arenarius (sand trout), Lagodon rhomboids (pinfish), Menticirrhus americanus (southern kingfish), Micropogonias undulates (Atlantic croaker), and Orthopristis chrysoptera (grunt) | Polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene terephthalate, nylon, silicone, and epoxy resin were identified. | [16] |
| Pyr-GC-MS, TED-GC-MS, and TGA-FTIR | River sediment | Polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and polyethylene terephthalate were identified and quantified. | [63] |
| Pyr-GC-MS and solid phase micro-extraction (SPME) coupled with headspace gas (HS) chromatography/ion trap (IT)-MS | Raritan River surface water | Identified compounds associated with microplastic debris and characterized the major plastic types. | [64] |
| Pyr-GC-MS | Road dust | Microplastics of Polypropylene, polystyrene, polyethylene terephthalate, polyvinyl chloride, poly (methyl methacrylate), and polyethylene were quantified. | [30] |
| Pyrolysis-GC-MS | Sandy beach sediments | Identified 68.8% of the analyzed particles. | [65] |
| Pyr-GC-MS | Farmland soil | Identified and quantified microplastics in soil samples. | [66] |
| TED-GC-MS | Artificial water | Provided information about pyrolysis behavior, as well as the microplastics content. | [67] |
| TED-GC-MS | Bottled water and other beverages | Determined microplastic contents below 0.01 µg/L up to 2 µg/L, depending on beverages bottle type. | [68] |
| Thermal desorption (TD)- Pyr-GC-MS | Coastline sediments | Identified several polymer types. | [69] |
| Pyr-GC-MS | Coastline sediments | Polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride and polyethylene terephthalate were identified. | [70] |
| Pyr-GC-MS | River water and sediment | Polyethylene, polypropylene and polystyrene were quantified. | [71] |
| Pyr-GC-MS | Standard plastics materials | Polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, and polymethyl methacrylate were detected. | [49] |
| Pyr-GC-TOF-MS | Wastewater samples | Polyvinyl chloride, polyamide, polyethylene terephthalate, and polyethylene were quantified. | [72] |
| Microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) combined with Pyr-GC–MS | Reference plastics | Extracted and quantified a wide range of plastic polymers. | [31] |
| Pyr-GC–MS and scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray microanalyser (EDXA) | Coastal sediments | Simultaneously identified polymer types of microplastic particles and associated organic plastic additives using Pyrolysis-GC–MS. SEM-EDXA identified inorganic plastic additives. | [45] |
| μ-Raman and Pyr-GC/MS | Bivalve, beach and sea water surface | The optimized Pyrolysis-GC/MS method identified 100% of the 40 previously identified particles with μ-Raman as plastic and demonstrated that this method is reliable for microplastic identification. | [32] |
| Thermal Extraction/Desorption (TED)-GC/MS | Wastewater | Requires little sample preparation and quantification limits for polystyrene and polyethylene. | [36] |
| Pyr-GC–MS and ATR-FTIR | Western Lake Superior surface water | Polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene, and polyethylene were identified in Lake Superior. | [34] |
| TED-GC-MS | Biogas plant, rivers | Polypropylene, polyethylene and polystyrene were identified. | [51] |
| Curie-point-Pyr-GC-MS | Standard polymers and fish | Simultaneously identified and optionally quantified microplastic in environmental samples on a polymer-specific mass-related trace level. | [35] |
| TED-GC-MS | Wastewater treatment plants effluents | polyethylene was consistently the most prominent polymer in samples. | [66] |
| Double shot Pyr-GC-MS | Shoreline (beach) sand samples | Provided recoveries higher than 96 % for phthalates and polystyrene. | [50] |
| Technique | Source | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC-MS/MS | Landfill sludge, marine sediment, indoor dust, digestive residues mussels and clams, sea salt and rock salt | The amounts of polycarbonate and polyethylene terephthalate were quantified in environmental samples. | [84] |
| LC-MS/MS | Indoor and outdoor dust samples | Mass concentrations of polyethylene terephthalate and polycarbonate microplastics were determined. | [85] |
| LC-MS/MS | Landfill | Polyethylene terephthalate and polycarbonate were quantified. | [86] |
| LC-MS/MS | Laundry wastewater, influents, and effluents of wastewater treatment plants. | Mass of polyethylene terephthalate polymer was quantified. | [75] |
| LC-MS/MS | Polyethylene terephthalate plastic powder (nano-polyethylene terephthalate) | Mass concentrations of polyethylene terephthalate polymers were detected. | [86] |
| LC-MS/MS | Earthworm casts | Submicron (0.1–0.8 μm) and nanocron (20–100 nm) particles of fossil-based poly(ethylene terephthalate) and bio-based poly(lactic acid) were detected in excretion. | [87] |
| LC-MS/MS | Lake sediments | Masses of bisphenol A (BPA) and p-phthalic acid were detected. | [88] |
| LC-MS/MS | Yellow River Delta wetland soil | In all soil samples, polyethylene terephthalate concentrations were much higher than polycarbonate concentrations. | [89] |
| LC-MS/MS | Fish fillets | Determined phthalates in fresh fish fillets. | [90] |
| LC-MS/MS | Coral fragments | Dibutyl-phthalate, benzylbutyl-phthalate, diethyl-phthalate, Bis(2-ethylhexyl)-phthalate, and dimethyl-phthalate were quantified in corals. | [91] |
| LC-ESI-MS | Marine beach sand, indoor dust, and sludge | Quantified polyethylene terephthalate microplastics and nanoplastics. | [92] |
| LC-quadruple-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (QTOF)/MS | Microplastic leachates | Bisphenol A, BPA, 1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one, decanoic acid, octanoic acid, and palmitamide were identified in leachates. | [93] |
| HPLC-ESI-MS/MS | Sewage sludge | Polyethylene terephthalate, polycarbonate, and their monomers of terephthalic acid and bisphenol A were quantified. | [94] |
| HPLC-ESI-MS/MS | Indoor dust | Polyethylene terephthalate and polycarbonate were detected and quantified. | [95] |
| HPLC-electrospray (ESI)-MS/MS | Cat and dog foods | Polyethylene terephthalate and polycarbonate were detected and quantified. Microplastic monomers such as bisphenol A and terephthalic acid were also quantified. | [96] |
| UPLC-MS/MS | Loggerhead sea turtle (liver and fat tissue) | The concentrations of polyethylene terephthalate, polycarbonate, para phthalic acid, and bisphenol A were determined in fat and liver tissues. | [97] |
| Solid phase microextraction (SPME)-LC/MS | Coral reef invertebrates (Danafungia scruposa and Tridacna maxima) | Quantified phthalate esters. | [79] |
| SPME-LC-MS/MS | Coral fragments | Di-methyl phthalate, di-ethyl phthalate, di-butyl phthalate, benzyl butyl phthalate, and bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in coral samples were detected. | [98] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chun, S.; Muthu, M.; Gopal, J. Mass Spectrometry as an Analytical Tool for Detection of Microplastics in the Environment. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10120530
Chun S, Muthu M, Gopal J. Mass Spectrometry as an Analytical Tool for Detection of Microplastics in the Environment. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(12):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10120530
Chicago/Turabian StyleChun, Sechul, Manikandan Muthu, and Judy Gopal. 2022. "Mass Spectrometry as an Analytical Tool for Detection of Microplastics in the Environment" Chemosensors 10, no. 12: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10120530
APA StyleChun, S., Muthu, M., & Gopal, J. (2022). Mass Spectrometry as an Analytical Tool for Detection of Microplastics in the Environment. Chemosensors, 10(12), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10120530







