Electronic Nose and Tongue for Assessing Human Microbiota
Abstract
:1. Introduction
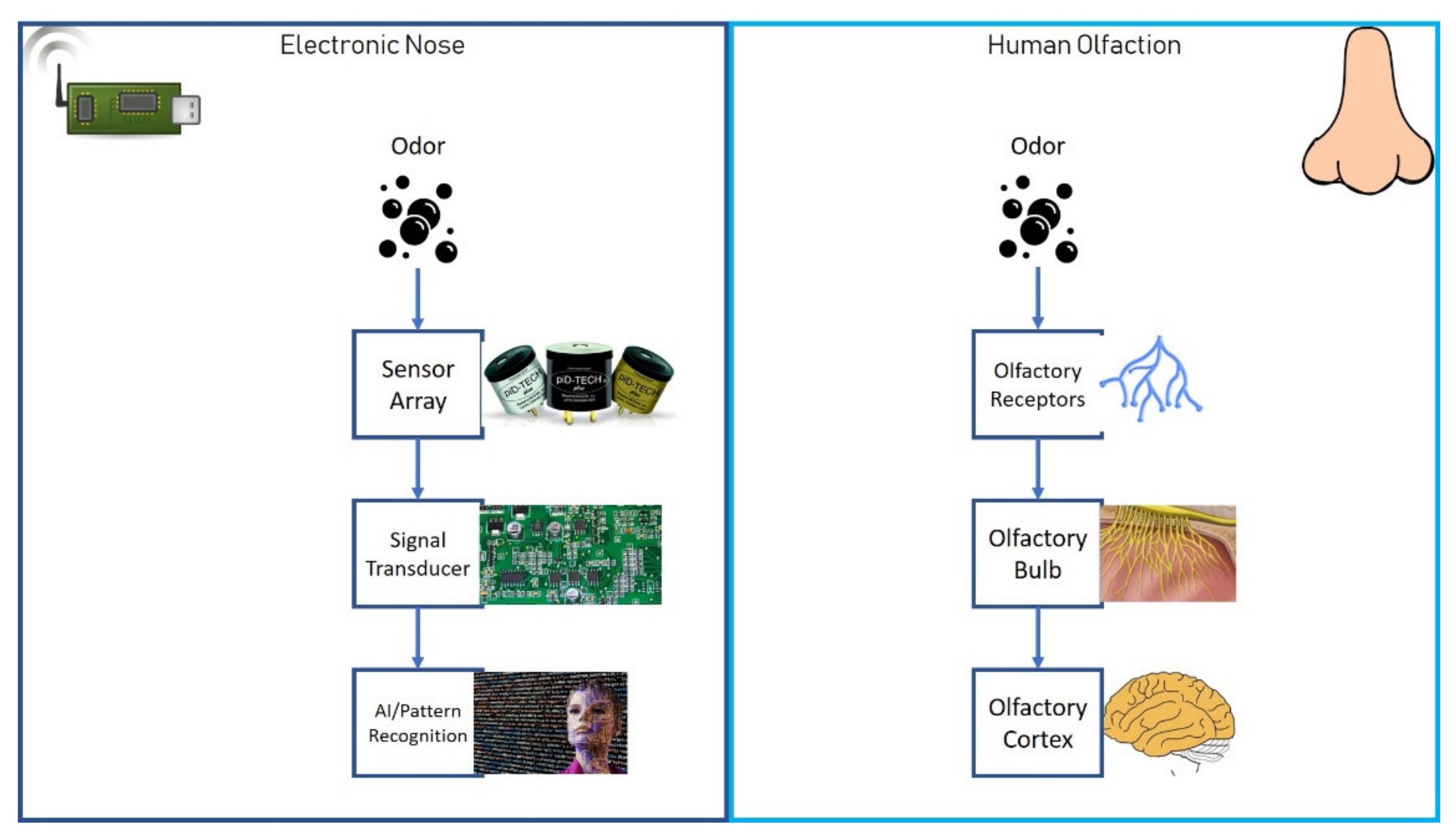
2. How Does an E-Nose Work?
3. E-Nose Use in the Analysis of the Composition of Human Microbiota
4. Principles of Functioning of the E-Tongue
- E is the measured voltage between the sensor and the reference electrode;
- E° is the standard potential of the membrane-based electrode;
- R is the constant of ideal gases;
- T is the absolute temperature;
- Zi and Zj are the valences, respectively, of the species the concentration of whom has to be calculated and of another ion present in the solution and interfering with the species;
- F is the Faraday constant;
- ai and aj are the activities, respectively, of the primary ion and the interfering one;
- Kij is the selectivity constant.
5. E-Tongue in the Analysis of the Human Microbiota: Possibilities and Open Challenges
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaillard, I.; Rouquier, S.; Giorgi, D. Olfactory receptors. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roper, S.D.; Chaudhari, N. Taste buds: Cells, signals and synapses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persaud, K.C. Engineering aspects of olfaction. In Neuromorphic Olfaction; Persaud, K.C., Marco, S., Gutiérrez-Gálvez, A., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kodogiannis, V.S.; Lygouras, J.N.; Tarczynski, A.; Chowdrey, H.S. Artificial odor discrimination system using electronic nose and neural networks for the identification of urinary tract infection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2008, 12, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tonacci, A.; Corda, D.; Tartarisco, G.; Pioggia, G.; Domenici, C. A smart sensor system for detecting hydrocarbon Volatile Organic Compounds in sea water. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2015, 43, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, D.; Pieri, G.; Salvetti, O.; Tampucci, M.; Domenici, C.; Tonacci, A. Sensorized Buoy for Oil Spill Early Detection. Methods Oceanogr. 2016, 17, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesti, M.; Taglieri, I.; Bianchi, A.; Tonacci, A.; Sansone, F.; Bellincontro, A.; Venturi, F.; Sanmartin, C. E-Nose and Olfactory Assessment: Teamwork or a Challenge to the Last Data? The Case of Virgin Olive Oil Stability and Shelf Life. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonacci, A.; Lacava, G.; Lippa, M.A.; Lupi, L.; Cocco, M.; Domenici, C. Electronic Nose and AUV: A Novel Perspective in Marine Pollution Monitoring. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2015, 49, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Hernandez Bennetts, V.; Schaffernicht, E.; Lilienthal, A.J. Towards Gas Discrimination and Mapping in Emergency Response Scenarios Using a Mobile Robot with an Electronic Nose. Sensors 2019, 19, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzatenta, A.; Di Giulio, C.; Pokorski, M. Pathologies currently identified by exhaled biomarkers. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 187, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binson, V.A.; Subramoniam, M.; Mathew, L. Discrimination of COPD and lung cancer from controls through breath analysis using a self-developed e-nose. J. Breath Res. 2021, 15, 046003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, A.; Witt, K.; Fischer, C.; Reulecke, S.; Poitz, W.; Kechagias, V.; Surber, R.; Figulla, H.R. Smelling heart failure from human skin odor with an electronic nose. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2012, 2012, 4034–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, J.P.; Gold, M.; Mengel, D.; Hattesohl, A.; Lubbe, D.; Schmid, S.; Tackenberg, B.; Rieke, J.; Maddula, S.; Baumbach, J.I.; et al. Measuring Compounds in Exhaled Air to Detect Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baldini, C.; Billeci, L.; Sansone, F.; Conte, R.; Domenici, C.; Tonacci, A. Electronic Nose as a Novel Method for Diagnosing Cancer: A Systematic Review. Biosensors 2020, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitrescu, L.; Popescu-Olaru, I.; Cozma, L.; Tulbă, D.; Hinescu, M.E.; Ceafalan, L.C.; Gherghiceanu, M.; Popescu, B.O. Oxidative Stress and the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2406594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, C.; et al. The role of microbiota in the development of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 2032–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiola, F.; Nicoletti, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ponziani, F.R. Gut microbiota and aging. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7404–7413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandwitz, P. Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota. Brain Res. 2018, 1693, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konjevod, M.; Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Sáiz, J.; Svob Strac, D.; Barbas, C.; Rojo, D. Metabolomics analysis of microbiota-gut-brain axis in neurodegenerative and psychiatric diseases. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 194, 113681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, S.K.; Zarei, K.; Guseva, N.V.; Mangalam, A.K. Microbiota Analysis Using Two-step PCR and Next-generation 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 152, e59980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.S.; Spakowicz, D.J.; Hong, B.Y.; Petersen, L.M.; Demkowicz, P.; Chen, L.; Leopold, S.R.; Hanson, B.M.; Agresta, H.O.; Gerstein, M.; et al. Evaluation of 16S rRNA gene sequencing for species and strain-level microbiome analysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hood, L.; Friend, S.H. Predictive, personalized, preventive, participatory (P4) cancer medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeker, P. On ‘Electronic Nose’ methodology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q. Recent Progress in Smart Electronic Nose Technologies Enabled with Machine Learning Methods. Sensors 2021, 21, 7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ache, B.W. Position Review: Functional Selectivity in Mammalian Olfactory Receptors. Chem. Senses 2020, 45, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Park, T.H. The bioelectronic nose and tongue using olfactory and taste receptors: Analytical tools for food quality and safety assessment. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, F.B. Electronic nose: Current status and future trends. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.R.; Edwards, P.M.; Evans, M.J.; Lee, J.D.; Shaw, M.D.; Squires, F.; Wilde, S.; Lewis, A.C. Clustering approaches to improve the performance of low cost air pollution sensors. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 200, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Yan, W.; Zhuang, X.; Ng, K.W.; Cheng, X. Sensitive and Low-Power Metal Oxide Gas Sensors with a Low-Cost Microelectromechanical Heater. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzoni, A.; Baratto, C.; Cattabiani, N.; Falasconi, M.; Galstyan, V.; Nunez-Carmona, E.; Rigoni, F.; Sberveglieri, V.; Zambotti, G.; Zappa, D. Metal Oxide Gas Sensors, a Survey of Selectivity Issues Addressed at the SENSOR Lab, Brescia (Italy). Sensors 2017, 17, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Li, N.; Yu, H.; Wei, Z.; Liao, M.; Chen, P.; Wang, S.; Shi, D.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, G. Highly Sensitive MoS2 Humidity Sensors Array for Noncontact Sensation. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, X.; Tolbert, L.; Wang, F.; Liang, Z.; Costinett, D.; Blalock, B.J. A high temperature silicon carbide mosfet power module with integrated silicon-on-insulator-based gate drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 1432–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D.; Scott, S.M.; Ali, Z.; O’Hare, W.T. Chemical Sensors for Electronic Nose Systems. Microchim. Acta 2005, 149, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonacci, A.; Sansone, F.; Conte, R.; Domenici, C. Use of Electronic Noses in Seawater Quality Monitoring: A Systematic Review. Biosensors 2018, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sierra-Padilla, A.; García-Guzmán, J.J.; López-Iglesias, D.; Palacios-Santander, J.M.; Cubillana-Aguilera, L. E-Tongues/Noses Based on Conducting Polymers and Composite Materials: Expanding the Possibilities in Complex Analytical Sensing. Sensors 2021, 21, 4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Yang, G.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, M.; Kuo, C.C.; Wang, S.D. Conducting polymer-inorganic nanocomposite-based gas sensors: A review. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2021, 21, 768–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, S.; Tiele, A.; Agbroko, S.O.; Covington, J.A. Development of a Tuneable NDIR Optical Electronic Nose. Sensors 2020, 20, 6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, S.; Covington, J.A. Low Cost Optical Electronic Nose for Biomedical Applications. Proceedings 2017, 1, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khatoon, Z.; Fouad, H.; Alothman, O.Y.; Hashem, M.; Ansari, Z.A.; Ansari, S.A. Doped SnO2 Nanomaterials for E-Nose Based Electrochemical Sensing of Biomarkers of Lung Cancer. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 27645–27654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Brady, J.; Al-Badani, F.; Yu, S.; Hart, J.; Jung, S.; Tran, T.T.; Myung, N.V. Nanoengineering Approaches Toward Artificial Nose. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 629329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayasaka, T.; Lin, A.; Copa, V.C.; Lopez, L.P., Jr.; Loberternos, R.A.; Ballesteros, L.I.M.; Kubota, Y.; Liu, Y.; Salvador, A.A.; Lin, L. An electronic nose using a single graphene FET and machine learning for water, methanol, and ethanol. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasaradnam, R.P.; Ouaret, N.; Thomas, M.G.; Quraishi, N.; Heatherington, E.; Nwokolo, C.U.; Bardhan, K.D.; Covington, J.A. A novel tool for noninvasive diagnosis and tracking of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, R.B.; Wu, G.D. Roles for Intestinal Bacteria, Viruses, and Fungi in Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Therapeutic Approaches. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 327–339.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.F.; Liu, S.B.; Meng, F.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Jin, Z.; Kong, L.T.; Liu, J.H. Metal oxide nanostructures and their gas sensing properties: A review. Sensors 2012, 12, 2610–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Meij, T.G.; van der Schee, M.P.; Berkhout, D.J.; van de Velde, M.E.; Jansen, A.E.; Kramer, B.W.; van Weissenbruch, M.M.; van Kaam, A.H.; Andriessen, P.; van Goudoever, J.B.; et al. Early Detection of Necrotizing Enterocolitis by Fecal Volatile Organic Compounds Analysis. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 562–567.e1, Erratum in: J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhout, D.J.C.; Niemarkt, H.J.; Buijck, M.; van Weissenbruch, M.M.; Brinkman, P.; Benninga, M.A.; van Kaam, A.H.; Kramer, B.W.; Andriessen, P.; de Boer, N.K.H.; et al. Detection of Sepsis in Preterm Infants by Fecal Volatile Organic Compounds Analysis: A Proof of Principle Study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, e47–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, D.J.C.; Niemarkt, H.J.; Andriessen, P.; Vijlbrief, D.C.; Bomers, M.K.; Cossey, V.; Hulzebos, C.V.; van Kaam, A.H.; Kramer, B.W.; van Lingen, R.A.; et al. Preclinical Detection of Non-catheter Related Late-onset Sepsis in Preterm Infants by Fecal Volatile Compounds Analysis: A Prospective, Multi-center Cohort Study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, E.H.; Berkhout, D.J.C.; Singh, J.; Vermeulen, A.; Ashtiani, N.; de Boer, N.K.; van Wijk, J.A.E.; de Meij, T.G.; Bökenkamp, A. Smell—Adding a New Dimension to Urinalysis. Biosensors 2020, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dospinescu, V.-M.; Tiele, A.; Covington, J.A. Sniffing Out Urinary Tract Infection—Diagnosis Based on Volatile Organic Compounds and Smell Profile. Biosensors 2020, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, D.J.C.; van Keulen, B.J.; Niemarkt, H.J.; Bessem, J.R.; de Boode, W.P.; Cossey, V.; Hoogenes, N.; Hulzebos, C.V.; Klaver, E.; Andriessen, P.; et al. Late-onset Sepsis in Preterm Infants Can Be Detected Preclinically by Fecal Volatile Organic Compound Analysis: A Prospective, Multicenter Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, D.; Niemarkt, H.; Benninga, M.; Budding, A.E.; van Kaam, A.H.; Kramer, B.W.; Pantophlet, C.M.; van Weissenbruch, M.M.; de Boer, N.K.H.; de Meij, T.G.J. Development of severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia is associated with alterations in fecal volatile organic compounds. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Meij, T.G.; Larbi, I.B.; van der Schee, M.P.; Lentferink, Y.E.; Paff, T.; Terhaar Sive Droste, J.S.; Mulder, C.J.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; de Boer, N.K. Electronic nose can discriminate colorectal carcinoma and advanced adenomas by fecal volatile biomarker analysis: Proof of principle study. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westenbrink, E.; Arasaradnam, R.P.; O’Connell, N.; Bailey, C.; Nwokolo, C.; Bardhan, K.D.; Covington, J.A. Development and application of a new electronic nose instrument for the detection of colorectal cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonta, G.; Anania, G.; Fabbri, B.; Gaiardo, A.; Gherardi, S.; Giberti, A.; Landini, N.; Malagù, C.; Scagliarini, L.; Guidi, V. Preventive screening of colorectal cancer with a device based on chemoresistive sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, G.; Malagù, C.; Gherardi, S.; Giberti, A.; Pezzoli, A.; de Togni, A.; Palmonari, C. Clinical Validation Results of an Innovative Non-Invasive Device for Colorectal Cancer Preventive Screening through Fecal Exhalation Analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, H.; Daulton, E.; Bannaga, A.S.; Arasaradnam, R.P.; Covington, J.A. Non-Invasive Detection and Staging of Colorectal Cancer Using a Portable Electronic Nose. Sensors 2021, 21, 5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.K.; Leggett, C.L.; Wang, K.K. Diagnosing gastrointestinal illnesses using fecal headspace volatile organic compounds. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, S.F.; McGuire, N.D.; de Lacy Costello, B.P.; Ewen, R.J.; Jayasena, D.H.; Vaughan, K.; Ahmed, I.; Probert, C.S.; Ratcliffe, N.M. The use of a gas chromatograph coupled to a metal oxide sensor for rapid assessment of stool samples from irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease patients. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 026001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arasaradnam, R.P.; Ouaret, N.; Thomas, M.G.; Gold, P.; Quraishi, M.N.; Nwokolo, C.U.; Bardhan, K.D.; Covington, J.A. Evaluation of gut bacterial populations using an electronic e-nose and field asymmetric ion mobility spectrometry: Further insights into ‘fermentonomics’. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2012, 36, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosfield, B.D.; Pecoraro, A.R.; Baxter, N.T.; Hawkins, T.B.; Markel, T.A. The Assessment of Fecal Volatile Organic Compounds in Healthy Infants: Electronic Nose Device Predicts Patient Demographics and Microbial Enterotype. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 254, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martignon, L.; Vitouch, O.; Takezawa, M.; Forster, M.R. Naive and yet enlightened: From natural frequencies to fast and frugal decision trees. In Thinking: Psychological Perspectives on Reasoning, Judgment and Decision Making; Hardman, D., Macchi, L., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Chapter 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.P.; Magan, N. Electronic noses and disease diagnostics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlou, A.K.; Magan, N.; Jones, J.M.; Brown, J.; Klatser, P.; Turner, A.P. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) in vitro and in situ using an electronic nose in combination with a neural network system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Heer, K.; Kok, M.G.; Fens, N.; Weersink, E.J.; Zwinderman, A.H.; van der Schee, M.P.; Visser, C.E.; van Oers, M.H.; Sterk, P.J. Detection of Airway Colonization by Aspergillus fumigatus by Use of Electronic Nose Technology in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bordugo, A.; Salvetti, E.; Rodella, G.; Piazza, M.; Dianin, A.; Amoruso, A.; Piacentini, G.; Pane, M.; Torriani, S.; Vitulo, N.; et al. Assessing Gut Microbiota in an Infant with Congenital Propionic Acidemia before and after Probiotic Supplementation. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Manouni el Hassani, S.; Niemarkt, H.J.; Said, H.; Berkhout, D.J.C.; van Kaam, A.H.; van Lingen, R.A.; Benninga, M.A.; de Boer, N.K.H.; de Meij, T.G.J. Fecal Volatile Organic Compounds in Preterm Infants Are Influenced by Enteral Feeding Composition. Sensors 2018, 18, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deianova, N.; el Manouni el Hassani, S.; Niemarkt, H.J.; Cossey, V.; van Kaam, A.H.; Jenken, F.; van Weissenbruch, M.M.; Doedes, E.M.; Baelde, K.; Menezes, R.; et al. Fecal Volatile Organic Compound Profiles are Not Influenced by Gestational Age and Mode of Delivery: A Longitudinal Multicenter Cohort Study. Biosensors 2020, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, S.; Lemmen, J.P.; Menezes, R.; van der Hulst, R.; Kuijvenhoven, J.; Stokkers, P.C.; de Meij, T.G.; de Boer, N.K. The influence of lifestyle factors on fecal volatile organic compound composition as measured by an electronic nose. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, 046001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, R.L. Treatments for smell and taste disorders: A critical review. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 164, 455–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, E.T. Taste and smell processing in the brain. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 164, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J.; Fenniri, H. Cutting Edge Methods for Non-Invasive Disease Diagnosis Using E-Tongue and E-Nose Devices. Biosensors 2017, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwata, S.; Yoshida, R.; Ninomiya, Y. Taste transductions in taste receptor cells: Basic tastes and moreover. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2684–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, C. Multisensory flavor perception. Cell 2015, 161, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Mahmut, M.K.; Oaten, M.J. The role of attention in the localization of odors to the mouth. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2011, 73, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Citterio, D.; Suzuki, K. Smart taste sensors. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3965–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lvova, L.; Jahatspanian, I.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Correa, D.S.; Oleneva, E.; Legin, A.; di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R. Potentiometric E-Tongue System for Geosmin/Isoborneol Presence Monitoring in Drinkable Water. Sensors 2020, 20, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Łabańska, M.; Ciosek-Skibińska, P.; Wróblewski, W. Critical Evaluation of Laboratory Potentiometric Electronic Tongues for Pharmaceutical Analysis-An Overview. Sensors 2019, 19, 5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Tahara, Y.; Yatabe, R.; Toko, K. Taste Sensor: Electronic Tongue with Lipid Membranes. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciosek, P.; Wróblewski, W. Sensor arrays for liquid sensing—Electronic tongue systems. Analyst 2007, 132, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Qi, L.; Hou, C.; Fang, S.; Qin, W. Self-Sterilizing Polymeric Membrane Sensors Based on 6-Chloroindole Release for Prevention of Marine Biofouling. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 12132–12136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fah, M.K.; Reynolds, K.A.; Sexton, J.D.; Riley, M.R.; Anne, M.L.; Bureau, B.; Lucas, P. Opto-electrophoretic detection of bio-molecules using conducting chalcogenide glass sensors. Opt. Express. 2010, 18, 26754–26759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.; Sheng, G.; Li, W.; Yu, H.; Raichlin, Y.; Katzir, A.; Mizaikoff, B. IR-ATR chemical sensors based on planar silver halide waveguides coated with an ethylene/propylene copolymer for detection of multiple organic contaminants in water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 2265–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiardo, A.; Fabbri, B.; Guidi, V.; Bellutti, P.; Giberti, A.; Gherardi, S.; Vanzetti, L.; Malagù, C.; Zonta, G. Metal Sulfides as Sensing Materials for Chemoresistive Gas Sensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, M. Ion-sensitive field-effect transistor for biological sensing. Sensors 2009, 9, 7111–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apetrei, C.; Apetrei, I.M.; Villanueva, S.; de Saja, J.A.; Gutierrez-Rosales, F.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L. Combination of an E-Nose, an e-Tongue and an e-Eye for the Characterisation of Olive Oils with Different Degree of Bitterness. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 663, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, A.H.; Alam, F.; Roychoudhury, S.; Umasankar, Y.; Pala, N.; Bhansali, S. Prospects and Challenges of Volatile Organic Compound Sensors in Human Healthcare. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1246–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaim, O.; Diouf, A.; El Bari, N.; Lagdali, N.; Benelbarhdadi, I.; Ajana, F.Z.; Llobet, E.; Bouchikhi, B. Comparative analysis of volatile organic compounds of breath and urine for distinguishing patients with liver cirrhosis from healthy controls by using electronic nose and voltammetric electronic tongue. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1184, 339028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, L.; Taverna, G.; Bellini, A.; Eusebio, L.; Buffi, N.; Lazzeri, M.; Guazzoni, G.; Bozzini, G.; Seveso, M.; Mandressi, A.; et al. Application and Uses of Electronic Noses for Clinical Diagnosis on Urine Samples: A Review. Sensors 2016, 16, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falk, M.; Nilsson, E.J.; Cirovic, S.; Tudosoiu, B.; Shleev, S. Wearable Electronic Tongue for Non-Invasive Assessment of Human Sweat. Sensors 2021, 21, 7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.K.; Panchariya, P.C.; Kundu, M. Classification and authentication of unknown water samples using machine learning algorithms. ISA Trans. 2011, 50, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Saad, B.; Surif, M.; Ahmad, M.N.; Md Shakaff, A.Y. Disposable E-Tongue for the Assessment of Water Quality in Fish Tanks. Sensors 2008, 8, 3665–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podrażka, M.; Bączyńska, E.; Kundys, M.; Jeleń, P.S.; Witkowska Nery, E. Electronic Tongue-A Tool for All Tastes? Biosensors 2017, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poghossian, A.; Geissler, H.; Schöning, M.J. Rapid methods and sensors for milk quality monitoring and spoilage detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 140, 111272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ramahi, R.; Zaid, A.N.; Abu-Khalaf, N. Evaluating the potential use of electronic tongue in early identification and diagnosis of bacterial infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2445–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lvova, L.; Martinelli, E.; Dini, F.; Bergamini, A.; Paolesse, R.; di Natale, C.; D’Amico, A. Clinical analysis of human urine by means of potentiometric Electronic tongue. Talanta 2009, 77, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belugina, R.; Karpushchenko, E.; Sleptsov, A.; Protoshchak, V.; Legin, A.; Kirsanov, D. Developing non-invasive bladder cancer screening methodology through potentiometric multisensor urine analysis. Talanta 2021, 234, 122696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vincentis, A.; Santonico, M.; del Chierico, F.; Altomare, A.; Marigliano, B.; Laudisio, A.; Reddel, S.; Grasso, S.; Zompanti, A.; Pennazza, G.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Related Electronic Multisensorial System Changes in Subjects with Symptomatic Uncomplicated Diverticular Disease Undergoing Rifaximin Therapy. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 655474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heras, J.Y.; Pallarola, D.; Battaglini, F. Electronic tongue for simultaneous detection of endotoxins and other contaminants of microbiological origin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2470–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderström, C.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Legin, A.; Krantz-Rülcker, C. Differentiation of four Aspergillus species and one Zygosaccharomyces with two electronic tongues based on different measurement techniques. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 119, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, S.; Summerson, V.; Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Tongson, E.; Lipovetzky, N.; Wilkinson, K.L.; Szeto, C.; Unnithan, R.R. Assessment of Smoke Contamination in Grapevine Berries and Taint in Wines Due to Bushfires Using a Low-Cost E-Nose and an Artificial Intelligence Approach. Sensors 2020, 20, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D. Noninvasive Early Disease Diagnosis by Electronic-Nose and Related VOC-Detection Devices. Biosensors 2020, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D. Application of Electronic-Nose Technologies and VOC-Biomarkers for the Noninvasive Early Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Diseases. Sensors 2018, 18, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capelli, L.; Bax, C.; Grizzi, F.; Taverna, G. Optimization of training and measurement protocol for eNose analysis of urine headspace aimed at prostate cancer diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tian, F.; Zhang, D. Electronic Nose: Algorithmic Challenges; Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.: Gateway East, Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekha, S.; Suchetha, M. Recent Advancements and Future Prospects on E-Nose Sensors Technology and Machine Learning Approaches for Non-Invasive Diabetes Diagnosis: A Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 14, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozaki, Y.; Nakamoto, T. An Olfactory Sensor Array for Predicting Chemical Odor Characteristics from Mass Spectra with Deep Learning. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2027, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tonacci, A.; Scafile, A.; Billeci, L.; Sansone, F. Electronic Nose and Tongue for Assessing Human Microbiota. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020085
Tonacci A, Scafile A, Billeci L, Sansone F. Electronic Nose and Tongue for Assessing Human Microbiota. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(2):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020085
Chicago/Turabian StyleTonacci, Alessandro, Alessandro Scafile, Lucia Billeci, and Francesco Sansone. 2022. "Electronic Nose and Tongue for Assessing Human Microbiota" Chemosensors 10, no. 2: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020085
APA StyleTonacci, A., Scafile, A., Billeci, L., & Sansone, F. (2022). Electronic Nose and Tongue for Assessing Human Microbiota. Chemosensors, 10(2), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020085







