Fabrication of Functional Super-Hydrophilic TiO2 Thin Film for pH Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
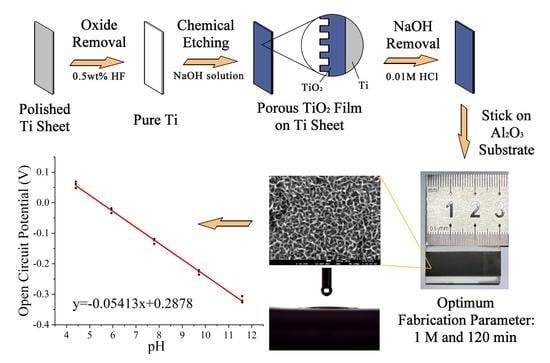
2.1. Fabrication of a Sensitive Electrode with Super-Hydrophilic TiO2 Thin Film
2.2. Characterization of the Porous TiO2 Films and Their pH Sensing Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD and XPS
3.2. Morphology
3.3. Wettability
3.4. pH Response of the Fabricated Electrodes
3.4.1. Sensitivity
3.4.2. Response Time
3.4.3. Potential Deviation
3.4.4. Drift Effect
3.4.5. Hysteresis
3.4.6. Repeatability
3.4.7. Selectivity
3.4.8. Stability of the Super-Hydrophilic TiO2-Sensitive Electrode
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A.; Chikuni, M.; Kojima, E.; Kitamura, A.; Shimohigoshi, M.; Watanabe, T. Light-Induced Amphiphilic Surfaces. Nature 1997, 388, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, E.; Mohammadpour, R. Fabrication of Flexible Self-Powered Humidity Sensor Based on Super-Hydrophilic Titanium Oxide Nanotube Arrays. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Liu, J. A Novel Wearable Sweat Rate Sensor for Both Dominant and Recessive Sweat Rate Measurement. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems & Eurosensors XXXIII (Transducers & Eurosensors XXXIII), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 June 2019; IEEE: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 817–820. [Google Scholar]
- Zamarreño, C.R.; Bravo, J.; Goicoechea, J.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Response Time Enhancement of PH Sensing Films by Means of Hydrophilic Nanostructured Coatings. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 128, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Xu, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, G. A PH Sensor Based on the TiO2 Nanotube Array Modified Ti Electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 5647–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Geng, M.; Xu, K.; Zong, S. Effects of Surface Area on All-Solid-Stated PH Sensor Based on Antimony Electrode. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Szwagierczak, D.; Dahiya, R. Metal Oxides Based Electrochemical PH Sensors: Current Progress and Future Perspectives. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 109, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.C.; Lee, M.C.; Chiang, J.L. Annealing Effect of Sol-Gel TiO2 Thin Film on PH-EGFET Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Computer, Consumer and Control, Taichung, Taiwan, 10–12 June 2014; IEEE: Taichung, Taiwan, 2014; pp. 577–580. [Google Scholar]
- Yusof, K.A.; Abdul Rahman, R.; Zulkefle, M.A.; Herman, S.H.; Abdullah, W.F.H. EGFET PH Sensor Performance Dependence on Sputtered TiO2 Sensing Membrane Deposition Temperature. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Tsai, F.-S.; Wang, S.-J. Preparation of TiO2 Nanowire Arrays through Hydrothermal Growth Method and Their PH Sensing Characteristics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 06JG02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doghmane, H.E.; Touam, T.; Chelouche, A.; Challali, F.; Bordji, B. Investigation of the Influences of Post-Thermal Annealing on Physical Properties of TiO2 Thin Films Deposited by RF Sputtering. Semiconductors 2020, 54, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirghi, L.; Hatanaka, Y. Hydrophilicity of amorphous TiO2 ultra-thin films. Surf. Sci. 2003, 530, L323–L327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N.; Fujishima, A.; Watanabe, T.; Hashimoto, K. Quantitative Evaluation of the Photoinduced Hydrophilic Conversion Properties of TiO2 Thin Film Surfaces by the Reciprocal of Contact Angle. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.-D.; Nakajima, A.; Fujishima, A.; Watanabe, T.; Hashimoto, K. Photoinduced Surface Wettability Conversion of ZnO and TiO2 Thin Films. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppuchamy, S.; Jeong, J.M. Super-Hydrophilic Amorphous Titanium Dioxide Thin Film Deposited by Cathodic Electrodeposition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 93, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, T.; Matsubara, T.; Katagirl, A. Formation of Porous TiO2 by Anodic Oxidation and Chemical Etching of Titanium. Electrochemistry 2000, 68, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, S.; Aonuma, M.; Hirose, N.; Tanaki, T. The Preparation of Porous TiO2 by Immersing Ti in NaOH Solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Hirose, N.; Tanaki, T. Effect of the Temperature and Concentration of NaOH on the Formation of Porous TiO2. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, Y. A Study on Preparation of TiO2 Thin Films by Alkali Treatment of Ti Foils. J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 2013, 6, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarozaman, N.S.; Asiah, M.N.; Aznilinda, Z.; Bakar, R.A.; Abdullah, W.F.H.; Herman, S.H.; Rusop, M. Memristive Behavior of TiO2 Nanostructures Grown at Different Substrate Positioning by Immersion Method. AMR 2013, 795, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Cvejin, K.; Kulawik, J.; Zaraska, K.; Szwagierczak, D.; Socha, R.P. Fabrication of Thick Film Sensitive RuO2-TiO2 and Ag/AgCl/KCl Reference Electrodes and Their Application for PH Measurements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozumi, T.; Mizuno, T.; Kurachi, T. Hydrogen Absorption in Cathodically Polarized Zirconium. Corros. Eng. 1979, 28, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otitoju, T.A.; Ahmad, A.L.; Ooi, B.S. Superhydrophilic (Superwetting) Surfaces: A Review on Fabrication and Application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 47, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extrand, C.W.; Moon, S.I.; Hall, P.; Schmidt, D. Superwetting of Structured Surfaces. Langmuir 2007, 23, 8882–8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.J.; Jiang, L. Design and Creation of Superwetting/Antiwetting Surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3063–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, X.; Akbulut, O.; Hu, J.; Suib, S.L.; Kong, J.; Stellacci, F. Superwetting Nanowire Membranes for Selective Absorption. Nat. Nanotech 2008, 3, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-Y.; Chen, C.-W.; Chou, J.-C. Investigation on the Sensitivity of TiO2:Ru PH Sensor by Taguchi Design of Experiment. Solid-State Electron. 2012, 77, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasatti, S. Physical Electrochemistry of Ceramic Oxides. Electrochim. Acta 1991, 36, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihell, J.A.; Atkinson, J.K. Planar Thick-Film PH Electrodes Based on Ruthenium Dioxide Hydrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1998, 48, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D.E.; Levine, S.; Healy, T.W. Site-Binding Model of the Electrical Double Layer at the Oxide/Water Interface. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 1974, 70, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hilli, S.; Willander, M. The PH Response and Sensing Mechanism of N-Type ZnO/Electrolyte Interfaces. Sensors 2009, 9, 7445–7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.-H.; Chou, J.-C. Preparation and Characterization of the Titanium Dioxide Thin Films Used for PH Electrode and Procaine Drug Sensor by Sol–Gel Method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-D.; Cao, H.; Deb, S.; Chiao, M.; Chiao, J.C. A Flexible PH Sensor Based on the Iridium Oxide Sensing Film. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 169, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Zaraska, K.; Cvejin, K.; Kulawik, J.; Szwagierczak, D. Potentiometric RuO2–Ta2O5 PH Sensors Fabricated Using Thick Film and LTCC Technologies. Talanta 2016, 147, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjakkal, L.; Cvejin, K.; Kulawik, J.; Zaraska, K.; Szwagierczak, D.; Stojanovic, G. Sensing Mechanism of RuO2–SnO2 Thick Film PH Sensors Studied by Potentiometric Method and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 759, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telli, L. Study of a PH Sensor with MnO2 and Montmorillonite-Based Solid-State Internal Reference. Solid State Ion. 2000, 128, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuiykov, S.; Kats, E.; Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Breedon, M.; Miura, N. Influence of Thickness of Sub-Micron Cu2O-Doped RuO2 Electrode on Sensing Performance of Planar Electrochemical PH Sensors. Mater. Lett. 2012, 75, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung-Chuan Chou; Cheng-Wei Chen Fabrication and Application of Ruthenium-Doped Titanium Dioxide Films as Electrode Material for Ion-Sensitive Extended-Gate FETs. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 277–284. [CrossRef]
- Fog, A.; Buck, R.P. Electronic Semiconducting Oxides as PH Sensors. Sens. Actuators 1984, 5, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, W.-D. Modification of Vertically Aligned Carbon Nanotubes with RuO2 for a Solid-State PH Sensor. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 2859–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Neto, J.P.; Crespo, A.; Nunes, D.; Costa, N.; Fonseca, I.M.; Barquinha, P.; Pereira, L.; Silva, J.; Martins, R.; et al. WO3 Nanoparticle-Based Conformable PH Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12226–12234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, Y.; Bühlmann, P.; Umezawa, K.; Tohda, K.; Amemiya, S. Potentiometric Selectivity Coefficients of Ion-Selective Electrodes. Part I. Inorganic Cations (Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1851–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, R.; Matin, A.A.; Jouyban, A. A Membrane Sensor for Selective Determination of Bisacodyl in Tablets. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2006, 53, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Solution Concentration | Reaction Time (min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 60 | 120 | 240 | |
| 1 M | 36.18 mV/h | 15.27 mV/h | 9.29 mV/h | 6.4 mV/h |
| 2 M | 22.53 mV/h | 9.38 mV/h | 7.11 mV/h | 5.16 mV/h |
| Fabrication Parameters | Hysteresis in Loop 1 | Hysteresis in Loop 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 M 60 min | 17.6 mV | 19.3 mV |
| 1 M 120 min | 8.9 mV | 11.4 mV |
| 2 M 60 min | 10 mV | 10.5 mV |
| 2 M 120 min | 7.3 mV | 9.5 mV |
| Sample | Sensitivity | Correlation Coefficient | Response Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrode A1 | 52.63 | 0.996 | 16 s |
| Electrode A2 | 53.79 | 0.989 | 18 s |
| Electrode B1 | 53.47 | 0.998 | 20 s |
| Electrode B2 | 54.58 | 0.987 | 17 s |
| Primary Cation | Interfering Cation | Concentration of Interfering Cation | Kijpot | Log (Kijpot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H+ | Na+ | 0.001 M | 9.54 × 10−4 | −3.02 |
| K+ | 3.61 × 10−4 | –3.44 | ||
| Ca2+ | 3.14 × 10−3 | –2.51 | ||
| Ni2+ | 2.97 × 10−4 | –3.52 | ||
| Fe3+ | 5.11 × 10−4 | –3.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Xu, K.; Zhang, X. Fabrication of Functional Super-Hydrophilic TiO2 Thin Film for pH Detection. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10050182
Chen C, Zhang Y, Gao H, Xu K, Zhang X. Fabrication of Functional Super-Hydrophilic TiO2 Thin Film for pH Detection. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(5):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10050182
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Cheng, Yalei Zhang, Han Gao, Kun Xu, and Xiliang Zhang. 2022. "Fabrication of Functional Super-Hydrophilic TiO2 Thin Film for pH Detection" Chemosensors 10, no. 5: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10050182
APA StyleChen, C., Zhang, Y., Gao, H., Xu, K., & Zhang, X. (2022). Fabrication of Functional Super-Hydrophilic TiO2 Thin Film for pH Detection. Chemosensors, 10(5), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10050182