The Role of Nano-Sensors in Breath Analysis for Early and Non-Invasive Disease Diagnosis
Abstract
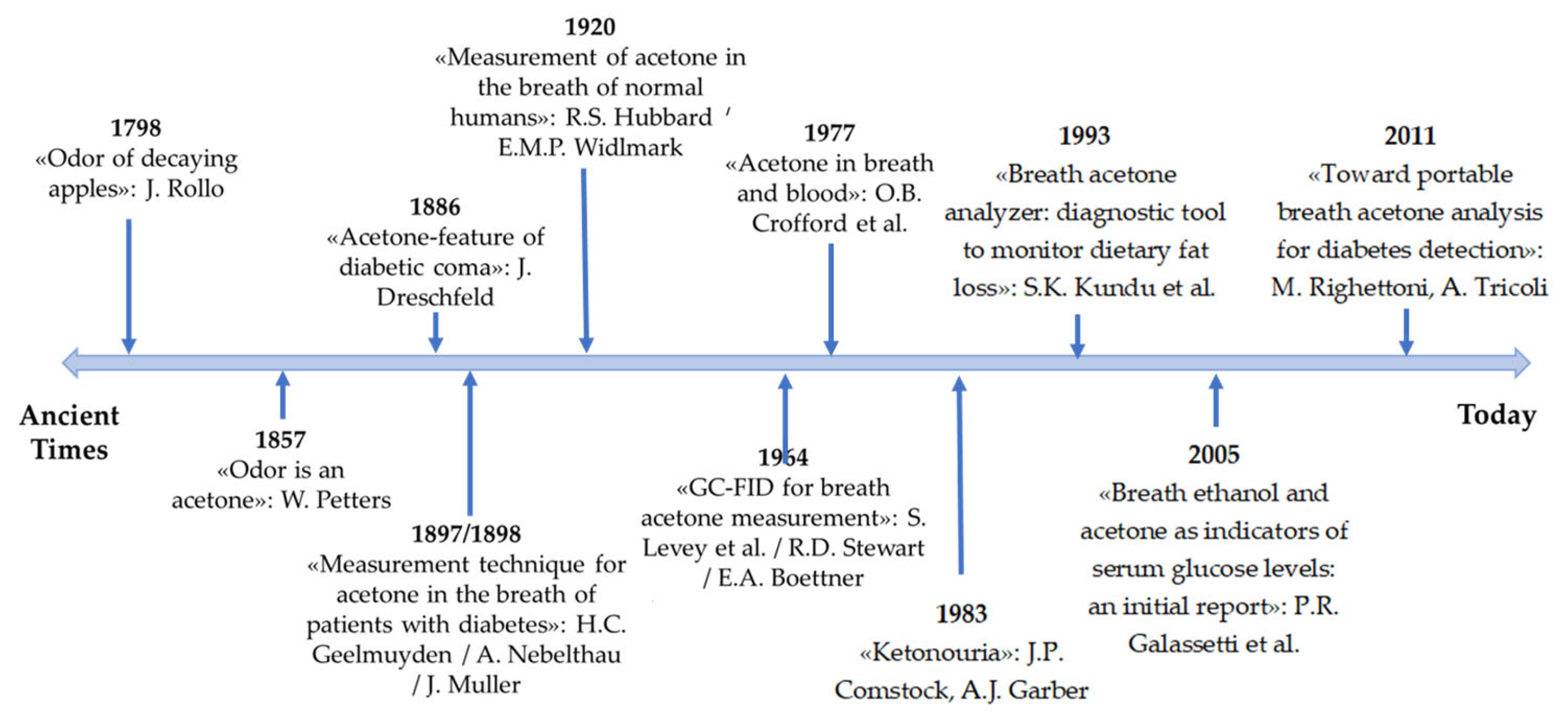
1. Introduction
2. Nanomaterials and Gas-Based Nanosensors
2.1. Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering
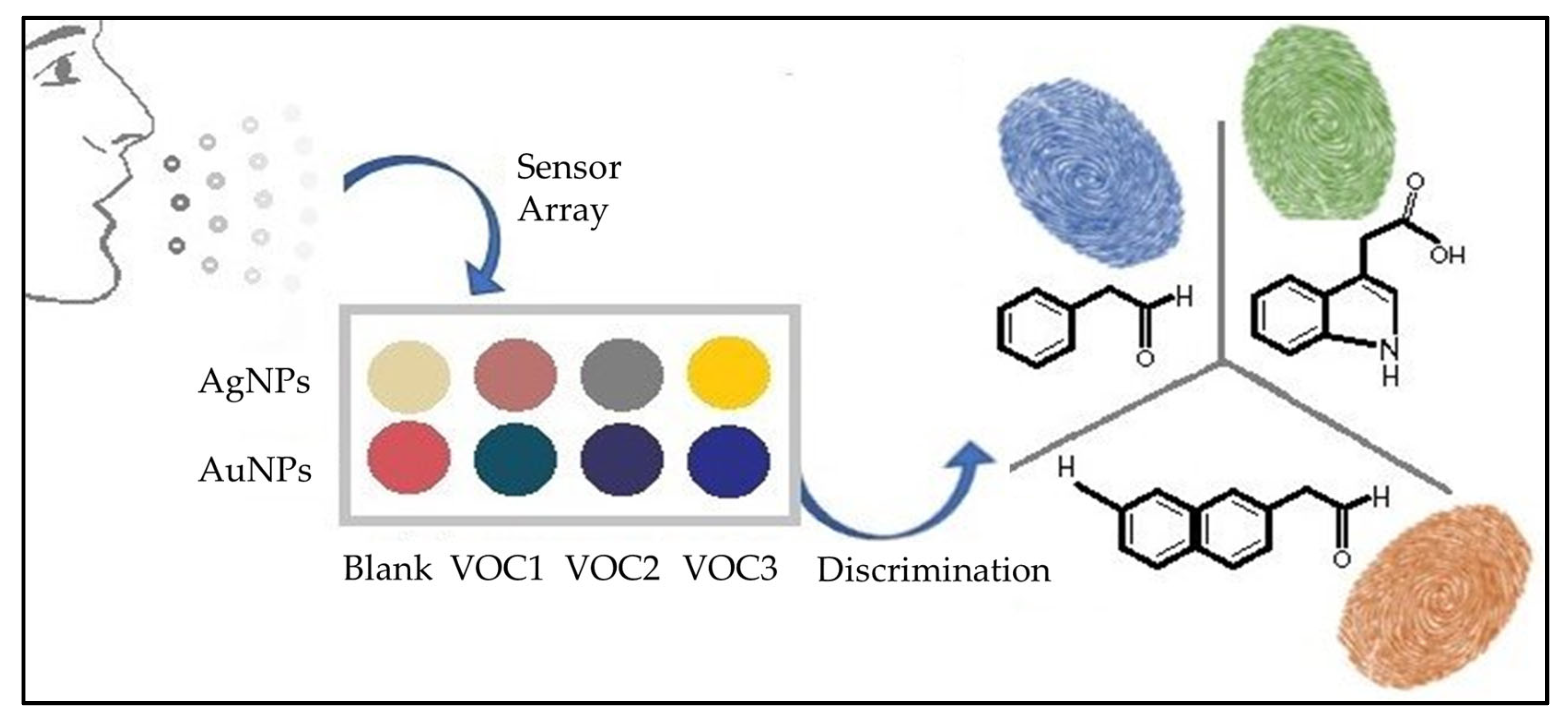
2.2. Colorimetric Sensors
2.3. Electrochemical Sensors
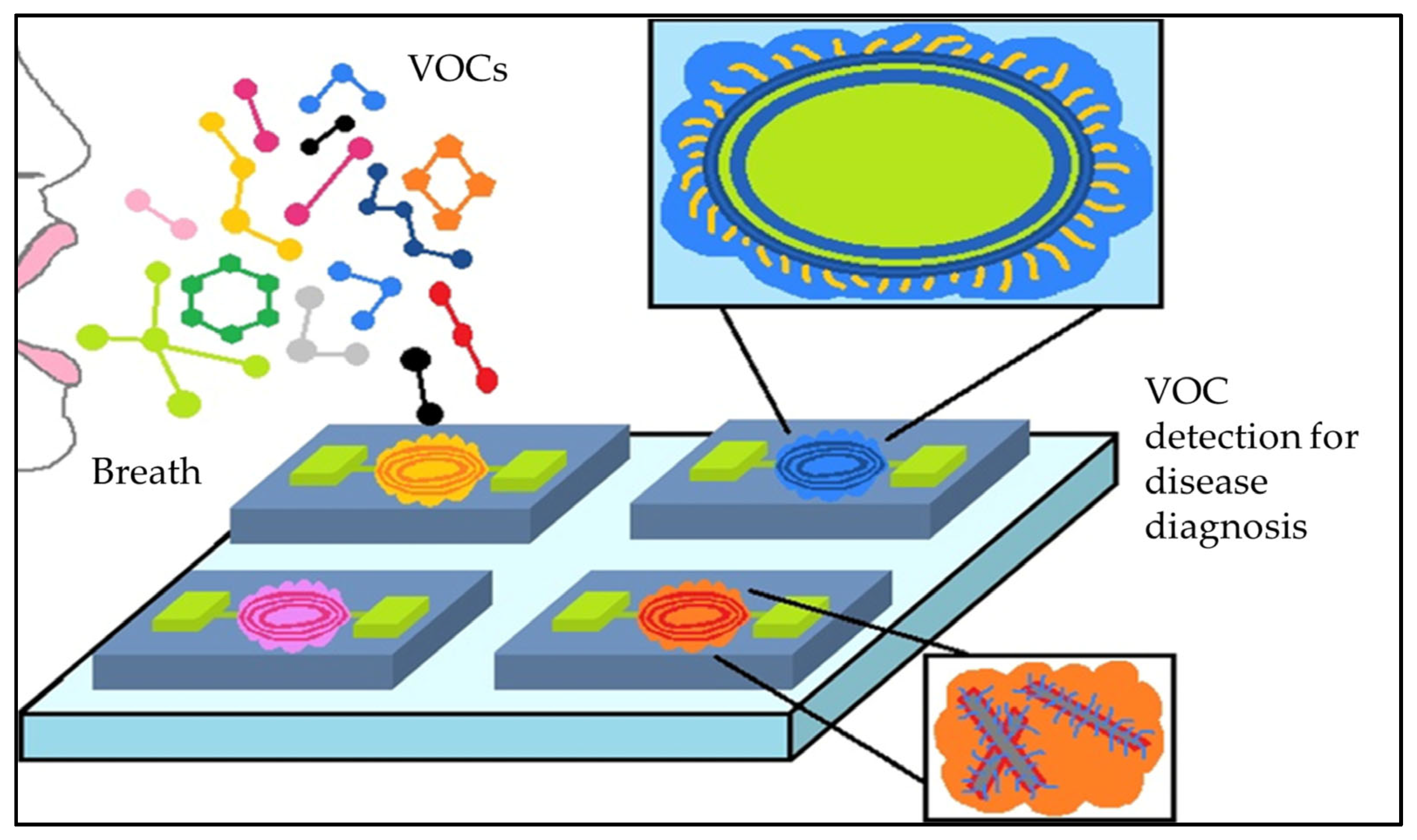
2.4. Chemiresistors
2.4.1. MOS-Based Chemiresistors
2.4.2. Carbon-Based Chemiresistors
2.5. Piezoelectric Sensors
Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensors
2.6. Electronic Noses
2.7. Surface Modification of Sensors
3. Nanosensors for Disease Diagnosis through Exhaled Breath Monitoring
3.1. Diabetes and Diagnosis Using Nanosensors
Nanotechnology and Nanobiosensors for Diabetes Diagnosis
3.2. Nanobiosensors for Cancer Diagnosis
3.2.1. Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
3.2.2. Nanobiosensors for Lung Cancer Diagnosis
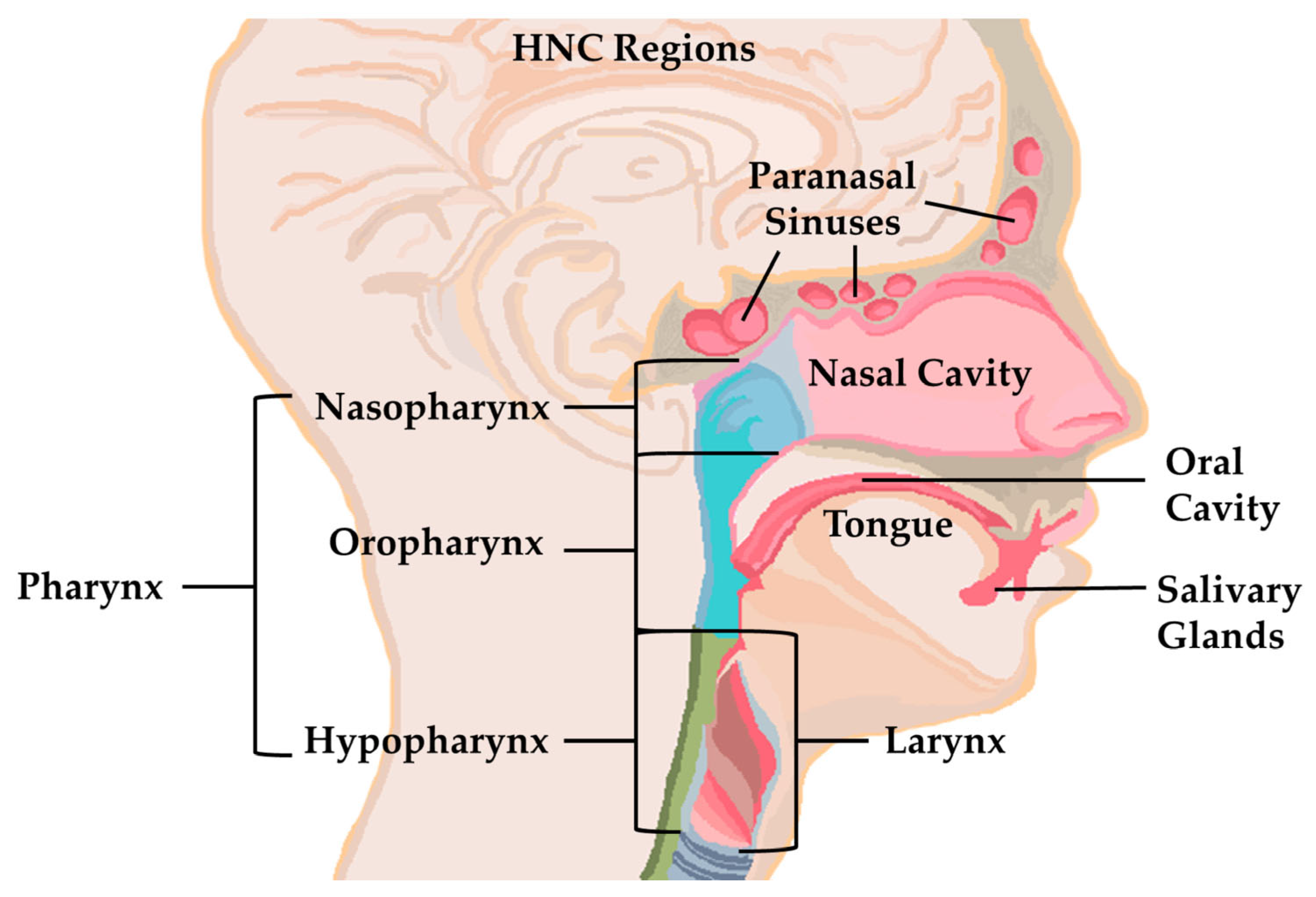
3.2.3. Nanobiosensors for Use in Head and Neck Cancer Diagnosis
3.3. Nanobiosensors for the Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Diseases
3.3.1. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease
3.3.2. Multiple Sclerosis Diagnosis
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maxim, L.D.; Niebo, R.; Utell, M.J. Screening tests: A review with examples. Inhal. Toxicol. 2014, 26, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtar, B.; Kandas, I.; Gamal, M.; Omran, N.; Hassanin, A.H.; Shehata, N. Nano-Enriched Self-Powered Wireless Body Area Network for Sustainable Health Monitoring Services. Sensors 2023, 23, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselbeck, A.H.; Im, J.; Prifti, K.; Marks, F.; Holm, M.; Zellweger, R.M. Serology as a Tool to Assess Infectious Disease Landscapes and Guide Public Health Policy. Pathogens 2022, 11, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmawardana, N.; Goddard, T.; Woods, C.; Watson, D.I.; Ooi, E.H.; Yazbeck, R. Development of a non-invasive exhaled breath test for the diagnosis of head and neck cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, M.P.; Veliks, V.; Stonāns, I.; Padilla, M.; Šuba, O.; Svare, A.; Krupnova, I.; Ivanovs, N.; Bēma, D.; Mitrovics, J.; et al. Breath Sensor Technology for the Use in Mechanical Lung Ventilation Equipment for Monitoring Critically Ill Patients. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Pal, S.; Mitra, M. Significance of Exhaled Breath Test in Clinical Diagnosis: A Special Focus on the Detection of Diabetes Mellitus. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2016, 36, 605–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belizário, J.E.; Faintuch, J.; Malpartida, M.G. Breath Biopsy and Discovery of Exclusive Volatile Organic Compounds for Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 564194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soodaeva, S.; Kubysheva, N.; Klimanov, I.; Nikitina, L.; Batyrshin, I. Features of Oxidative and Nitrosative Metabolism in Lung Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1689861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, T.L.; Pownraj, P.; Abdulla, S.; Pullithadathil, B. Technologies for Clinical Diagnosis Using Expired Human Breath Analysis. Diagnostics 2015, 5, 27–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, G.; Szurszewski, J.H. Carbon Monoxide, Hydrogen Sulfide, and Nitric Oxide as Signaling Molecules in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broza, Y.Y.; Haick, H. Nanomaterial-based sensors for detection of disease by volatile organic compounds. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 785–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiele, A.; Wicaksono, A.; Daulton, E.; Ifeachor, E.; Eyre, V.; Clarke, S.; Timings, L.; Pearson, S.; Covington, J.A.; Li, X. Breath-based non-invasive diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A pilot study. J. Breath Res. 2020, 14, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettema, A.R.; Lenders, M.W.P.M.; Vliegen, J.; Slettenaar, A.; Tjepkema-Cloostermans, M.C.; de Vos, C. Detecting multiple sclerosis via breath analysis using an eNose, a pilot study. J. Breath Res. 2021, 15, 027101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondanelli, M.; Perdoni, F.; Infantino, V.; Faliva, M.A.; Peroni, G.; Iannello, G.; Nichetti, M.; Alalwan, T.; Perna, S.; Cocuzza, C. Volatile Organic Compounds as Biomarkers of Gastrointestinal Diseases and Nutritional Status. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 7247802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, K.; Dantanarayana, A.; Minteer, S.D. Materials Approaches for Improving Electrochemical Sensor Performance. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 11820–11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevanandam, J.; Barhoum, A.; Chan, Y.S.; Dufresne, A.; Danquah, M.K. Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: History, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1050–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, N.; Clarke, C. Nanostructured Gas Sensors for Medical and Health Applications: Low to High Dimensional Materials. Biosensors 2019, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagopati, N.; Evangelou, K.; Falaras, P.; Tsilibary, E.-P.C.; Vasileiou, P.V.S.; Havaki, S.; Angelopoulou, A.; Pavlatou, E.A.; Gorgoulis, V.G. Nanomedicine: Photo-activated nanostructured titanium dioxide, as a promising anticancer agent. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 222, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremi, I.; Havaki, S.; Georgitsopoulou, S.; Lagopati, N.; Georgakilas, V.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Georgakilas, A.G. A Guide for Using Transmission Electron Microscopy for Studying the Radiosensitizing Effects of Gold Nanoparticles In Vitro. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagopati, N.; Kotsinas, A.; Veroutis, D.; Evangelou, K.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Arfanis, M.; Falaras, P.; Kitsiou, P.V.; Pateras, I.; Bergonzini, A.; et al. Biological Effect of Silver-Modified Nanostructured Titanium Dioxide in Cancer. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2021, 18 (Suppl. 3), 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalidoss, R.; Kothalam, R.; Manikandan, A.; Jaganathan, S.K.; Khan, A.; Asiri, A.M. Socio-economic demands and challenges for non-invasive disease diagnosis through a portable breathalyzer by the incorporation of 2D nanosheets and SMO nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 21216–21234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munawar, A.; Ong, Y.; Schirhagl, R.; Tahir, M.A.; Khan, W.S.; Bajwa, S.Z. Nanosensors for diagnosis with optical, electric and mechanical transducers. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6793–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, D.; Xu, K. Recent Progress in Gas Sensor Based on Nanomaterials. Micromachines 2022, 13, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.; Su, B.; Liu, C.; Song, Q.; Luo, D.; Mo, G.; Wang, T. Selective Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering for Quantitative Detection of Lung Cancer Biomarkers in Superparticle@MOF Structure. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1702275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Dai, X.; Stogin, B.B.; Wong, T.-S. Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection in common fluids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 113, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilot, R.; Signorini, R.; Durante, C.; Orian, L.; Bhamidipati, M.; Fabris, L. A Review on Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Biosensors 2019, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, P.; Loeseken, C.; Schubert, J.K.; Miekisch, W. Breath gas aldehydes as biomarkers of lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 2663–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, W.; Wang, J.; Luo, D.; Qiao, X.; Qin, X.; Wang, T. Ultrasensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Sensor of Gaseous Aldehydes as Biomarkers of Lung Cancer on Dendritic Ag Nanocrystals. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakouz, T.; Vaskevich, A.; Rubinstein, I. Polymer-Coated Gold Island Films as Localized Plasmon Transducers for Gas Sensing. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 14530–14538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-M.; Li, X.; Liu, W.-H.; Han, C.-Y.; Wang, X.-L. Gas Sensor Based on Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering. Materials 2021, 14, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, Y.; He, L.; Pang, J.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y. Colorimetric sensor array based on gold nanoparticles: Design principles and recent advances. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Xu, Y.; Hou, C.; Yang, M.; Fa, H. A novel optical chemical sensor based AuNR-MTPP and dyes for lung cancer biomarkers in exhaled breath identification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 199, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Li, D.; Du, W.; Yan, M.; Wang, Y.; Huo, D.; Hou, C. Rapid recognition of volatile organic compounds with colorimetric sensor arrays for lung cancer screening. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3671–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, G.; Liu, H.; Fu, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhi, X.; et al. Identification of Volatile Biomarkers of Gastric Cancer Cells and Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Detection based on Sensing Interface of Au-Ag Alloy coated MWCNTs. Theranostics 2014, 4, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermeier, J.; Trefz, P.; Wex, K.; Sabel, B.; Schubert, J.; Miekisch, W. Electrochemical sensor system for breath analysis of aldehydes, CO and NO. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 016008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayoonnia, S.; Zeinali, S. Design and fabrication of capacitive nanosensor based on MOF nanoparticles as sensing layer for VOCs detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chi, H.; Tian, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Y. Research Progress of Graphene and Its Derivatives towards Exhaled Breath Analysis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, A.; Lee, N.-E. Recent Advancements in Development of Wearable Gas Sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2000883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yin, W.; Gao, S.; Sun, Y.; Xu, P.; Wu, S.; Kong, H.; Yang, G.; Wei, G. The Combination of Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials with Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Gas Sensors: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ji, H.; Yuan, Z.; Meng, F. Novel combined waveform temperature modulation method of NiO-In2O3 based gas sensor for measuring and identifying VOC gases. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 918, 165510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broza, Y.Y.; Vishinkin, R.; Barash, O.; Nakhleh, M.K.; Haick, H. Synergy between nanomaterials and volatile organic compounds for non-invasive medical evaluation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4781–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekha, S.; Suchetha, M. Recent Advancements and Future Prospects on E-Nose Sensors Technology and Machine Learning Approaches for Non-Invasive Diabetes Diagnosis: A Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 14, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Lou, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; Jiang, K.; Fu, Z.; Han, W.; Shen, G. Fiber gas sensor-integrated smart face mask for room-temperature distinguishing of target gases. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panes-Ruiz, L.A.; Riemenschneider, L.; Al Chawa, M.M.; Löffler, M.; Rellinghaus, B.; Tetzlaff, R.; Bezugly, V.; Ibarlucea, B.; Cuniberti, G. Selective and self-validating breath-level detection of hydrogen sulfide in humid air by gold nanoparticle-functionalized nanotube arrays. Nano Res. 2021, 15, 2512–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haick, H. Chemical sensors based on molecularly modified metallic nanoparticles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 7173–7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, E.; Raza, N.; Kumar, V.; Singh, J.; Tsang, Y.F.; Lim, D.K.; Szulejko, J.E.; Kim, K.-H. Recent Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Human Breath Analytical Technology for Clinical Diagnosis and the Way Forward. Chem 2019, 5, 3020–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.; Joshi, R.; Vishnu, G.K.A.; Bhalerao, S.; Pandya, H.J. Electronic nose: A non-invasive technology for breath analysis of diabetes and lung cancer patients. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloumenou, M.; Skotadis, E.; Lagopati, N.; Efstathopoulos, E.; Tsoukalas, D. Breath Analysis: A Promising Tool for Disease Diagnosis—The Role of Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-D.; Choi, S.-J.; Kim, S.-J.; Jang, J.-S. Exhaled Breath Sensors. In Smart Sensors for Health and Environment Monitoring; Kyung, C.M., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 19–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.M.; Steenwelle, R.J.A.; Knobel, H.H.; Davie, A.; Steijvers, R.; Verhoeckx, F.; Goodacre, R.; Fowler, S.J.; Rijnders, A.J.H.M.; Nijsen, T.M.; et al. Development of a sensor device with polymer-coated piezoelectric micro-cantilevers for detection of volatile organic compounds. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 31, 035103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, G.; Pennazza, G.; Santonico, M.; Longo, F.; Rocco, R.; Crucitti, P.; Incalzi, R.A. Breathprinting and Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konvalina, G.; Haick, H. Sensors for Breath Testing: From Nanomaterials to Comprehensive Disease Detection. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, T.; Hidayat, S.N.; Rianjanu, A.; Dharmawan, A.B.; Wasisto, H.S.; Triyana, K. Intelligent mobile electronic nose system comprising a hybrid polymer-functionalized quartz crystal microbalance sensor array. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 29492–29503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rianjanu, A.; Fauzi, F.; Triyana, K.; Wasisto, H.S. Electrospun nanofibers for quartz crystal microbalance gas sensors: A review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 9957–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisch, U.; Schlesinger, I.; Ionescu, R.; Nassar, M.; Axelrod, N.; Robertman, D.; Tessler, Y.; Azar, F.; Marmur, A.; Aharon-Peretz, J.; et al. Detection of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease from exhaled breath using nanomaterial-based sensors. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dai, X.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, K.; Li, W. Recent advances in development of nanomedicines for multiple sclerosis diagnosis. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 024101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, R.; Brinkman, P.; Van Der Schee, M.P.; Fens, N.; Dijkers, E.; Bootsma, S.; De Jongh, F.H.C.; Sterk, P.J. Integration of electronic nose technology with spirometry: Validation of a new approach for exhaled breath analysis. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 046001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, E.; Haberer, J.; Barreto, G.; Degen, M.; Seeger, W.; Guenther, A. Recognition of breathprints of lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease using the Aeonose® electronic nose. J. Breath Res. 2020, 14, 046004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Lizier, J.T.; Berna, A.Z.; Bravo, F.G.; Trowell, S.C. Human breath-print identification by E-nose, using information-theoretic feature selection prior to classification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 217, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konvalina, G.; Haick, H. Effect of Humidity on Nanoparticle-Based Chemiresistors: A Comparison between Synthetic and Real-World Samples. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velumani, M.; Prasanth, A.; Narasimman, S.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Sampson, A.; Meher, S.R.; Rajalingam, S.; Rufus, E.; Alex, Z.C. Nanomaterial-Based Sensors for Exhaled Breath Analysis: A Review. Coatings 2022, 12, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhleh, M.K.; Broza, Y.Y.; Haick, H. Monolayer-capped gold nanoparticles for disease detection from breath. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emam, S.; Nasrollahpour, M.; Colarusso, B.; Cai, X.; Grant, S.; Kulkarni, P.; Ekenseair, A.; Gharagouzloo, C.; Ferris, C.F.; Sun, N. Detection of presymptomatic Alzheimer’s disease through breath biomarkers. Alzheimers Dement 2020, 12, e12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care 2018, 41 (Suppl. 1), S13–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szunerits, S.; Melinte, S.; Barras, A.; Pagneux, Q.; Voronova, A.; Abderrahmani, A.; Boukherroub, R. The impact of chemical engineering and technological advances on managing diabetes: Present and future concepts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 2102–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debele, T.A.; Park, Y. Application of Nanoparticles: Diagnosis, Therapeutics, and Delivery of Insulin/Anti-Diabetic Drugs to Enhance the Therapeutic Efficacy of Diabetes Mellitus. Life 2022, 12, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repaske, D.R. Medication-induced diabetes mellitus. Pediatr. Diabetes 2016, 17, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, S62–S67. [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43 (Suppl. S1), S14–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Zhang, W. Risk Factors Contributing to Type 2 Diabetes and Recent Advances in the Treatment and Prevention. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 1185–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Peñalver, J.J.; Martín-Timón, I.; Sevillano-Collantes, C.; Del Cañizo-Gómez, F.J. Update on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 354–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, A.F.; Klein, H.H. The Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2014, 111, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, K.; Fardindoost, S.; Ravishankara, A.; Tasnim, N.; Hoorfar, M. Exhaled Breath Analysis for Diabetes Diagnosis and Monitoring: Relevance, Challenges and Possibilities. Biosensors 2021, 11, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Morera, J.L.; Rodriguez-Rodero, S.; Menéndez-Torre, E.; Fraga, M.F. The Possible Role of Epigenetics in Gestational Diabetes: Cause, Consequence, or Both. Obstet. Gynecol. Int. 2010, 2010, 605163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmerman, L.R.; Das, D.; Higuita-Castro, N.; Mirmira, R.G.; Gallego-Perez, D. Nanomedicine-Based Strategies for Diabetes: Diagnostics, Monitoring, and Treatment. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2021, 31, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagopati, N.; Pavlatou, E.A. Nanotechnology in Diabetes Management. Interv. Obes. Diabetes 2021, 5, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Chang, S.J.; Chen, C.-J.; Liu, J.-T. Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Monitoring Technology: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydosz, A. Chapter 28—Nanosensors for exhaled breath monitoring as a possible tool for noninvasive diabetes detection. In Nanosensors for Smart Cities; Kumar Singh, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saasa, V.; Malwela, T.; Beukes, M.; Mokgotho, M.; Liu, C.-P.; Mwakikunga, B. Sensing Technologies for Detection of Acetone in Human Breath for Diabetes Diagnosis and Monitoring. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Hossain, K.S.; Das, S.; Kundu, S.; Adegoke, E.O.; Rahman, A.; Hannan, A.; Uddin, J.; Pang, M.-G. Role of Insulin in Health and Disease: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.J.; Siraki, A.G.; Shangari, N. Aldehyde sources, metabolism, molecular toxicity mechanisms, and possible effects on human health. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2005, 35, 609–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Jagt, D.L. Methylglyoxal, diabetes mellitus and diabetic complications. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2008, 23, 93–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trefz, P.; Schmidt, S.C.; Sukul, P.; Schubert, J.K.; Miekisch, W.; Fischer, D.-C. Non-Invasive Assessment of Metabolic Adaptation in Paediatric Patients Suffering from Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, R.; Varadwaj, P. Smelling the Disease: Diagnostic Potential of Breath Analysis. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2023, 27, 321–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.G.; Jung, Y.; Jun, D.; Park, J.H.; Chang, Y.W.; Park, H.-H.; Kang, C.-Y.; Kim, C.; Kaner, R.B. Hollow Pt-Functionalized SnO2 Hemipill Network Formation Using a Bacterial Skeleton for the Noninvasive Diagnosis of Diabetes. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Yin, M.; Wang, C. Facile synthesis of Ca2+/Au co-doped SnO2 nanofibers and their application in acetone sensor. Mater. Lett. 2017, 194, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, F.I.; Chikhale, L.P.; Mulla, I.S.; Suryavanshi. S.S. Synthesis, characterization and enhanced acetone sensing performance of Pd loaded Sm doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 10307–10315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Nikan, E.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Mortazavi, Y. Highly sensitive carbon nanotubes–SnO2 nanocomposite sensor for acetone detection in diabetes mellitus breath. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 205, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-J.; Jang, B.-H.; Lee, S.-J.; Min, B.K.; Rothschild, A.; Kim, I.-D. Selective detection of acetone and hydrogen sulfide for the diagnosis of diabetes and halitosis using SnO(2) nanofibers functionalized with reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Xue, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, P.; Lian, K.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Shi, J.; et al. Synthesis and gas sensing properties of NiO/SnO2 hierarchical structures toward ppb-level acetone detection. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 102, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cheng, Z.; Xiang, Q.; Yan, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, J. Bimetal PdAu decorated SnO2 nanosheets based gas sensor with temperature-dependent dual selectivity for detecting formaldehyde and acetone. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, A.; Marani, P.; Morandi, S.; Lettieri, S.; Mazzocchi, M.; Sacerdoti, M.; Carotta, M.C. Growth Mechanisms of ZnO Micro-Nanomorphologies and Their Role in Enhancing Gas Sensing Properties. Sensors 2021, 21, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenezi, M.R.; Henley, S.J.; Emersona, N.G.; Silva, S.R.P. From 1D and 2D ZnO nanostructures to 3D hierarchical structures with enhanced gas sensing properties. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Hou, N.; Jin, Z.; Sun, B.; Li, W.; Xiao, X.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Liu, J. Sub-ppb detection of acetone using Au-modified flower-like hierarchical ZnO structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 219, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xing, R.; Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Song, H. Three-dimensional ordered ZnO–CuO inverse opals toward low concentration acetone detection for exhaled breath sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 211, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, K.; Vanaraja, M.; Boomadevi, S.; Kumar Karn, R.; Singh, V.; Singh, P.K.; Pandiyan, K. Studies on acetone sensing characteristics of ZnO thin film prepared by sol–gel dip coating. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 673, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Hao, P.; Tian, J.; Cui, H.; Wang, X. Soft-templated formation of double-shelled ZnO hollow microspheres for acetone gas sensing at low concentration/near room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, A.; Yoo, R.; Woo, S.P.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, W. Enhanced acetone-sensing properties of pt-decorated al-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 280, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.; Park, Y.; Jung, H.; Rim, H.J.; Cho, S.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, W. Acetone-sensing properties of doped ZnO nanoparticles for breath-analyzer applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 803, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Pysanenko, A.; Dryahina, K.; Španěl, P.; Smith, D. Analysis of breath, exhaled via the mouth and nose, and the air in the oral cavity. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 037013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Wang, X.-Y.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Yao, H.-C.; Wang, J.-S.; Li, Z.-J. Highly sensitive and selective acetone sensor based on C-doped WO3 for potential diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 199, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Anand, K.; Kaur, A.; Singh, R.C. Sensitive and selective acetone sensor based on Gd doped WO3/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xu, C.; Cheng, L.; Jia, N.; Huang, J.; Li, C. Acetone sensor based on WO3 nanocrystallines with oxygen defects for low concentration detection. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 101, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Bao, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, X. Highly sensitive acetone gas sensor based on ultra-low content bimetallic PtCu modified WO3·H2O hollow sphere. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2041–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, B.; Liu, W.; Zhou, X.; Liu, M.; Sun, X.; Lv, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Bai, X.; et al. Highly sensitive and selective acetone sensor based on three-dimensional ordered WO3/Au nanocomposite with enhanced performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Xiong, X.; Guan, W.; Long, H. Designed construction of PdO@WO3 core–shell architecture as a high-performance acetone sensor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Luo, Y.; An, B.; Pan, X.; Xie, E. Ex-situ XPS analysis of yolk-shell Sb2O3/WO3 for ultra-fast acetone resistive sensor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Chung, J.-H.; Yoon, J.-W.; Lee, J.-H. Highly selective, sensitive, and rapidly responding acetone sensor using ferroelectric ε-WO3 spheres doped with Nb for monitoring ketogenic diet efficiency. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 338, 129823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Xu, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, N.; Sun, S.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Ola, O.; Zhu, Y. Highly sensitive acetone sensor based on WO3 nanosheets derived from WS2 nanoparticles with inorganic fullerene-like structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 343, 130135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhise, G.D.; Karpe, S.B.; More, P.; Adhyapak, P.V. Optical fibre based acetone sensor using Pd modified WO3 nanostructures. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 156, 108566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.-P.; Shang, Y.-R.; Shi, R.-X.; Che, Q.-D.; Wang, J.-P. Pt-decorated NiWO4/WO3 heterostructure nanotubes for highly selective sensing of acetone. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 1981–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodam, P.M.; Ghadage, P.A.; Nadargi, D.Y.; Shinde, K.; Mulla, I.S.; Park, J.; Suryavanshi, S.S. Ru, Pd doped WO3 nanomaterials: A synergistic effect of noble metals to enhance the acetone response properties. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 17923–17933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Maity, S.; Kundu, S. Fabrication of Fe doped reduced graphene oxide (rGO) decorated WO3 based low temperature ppm level acetone sensor: Unveiling sensing mechanism by impedance spectroscopy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 361, 131706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Su, Q.; Li, J.; An, B.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xie, E. Sea urchins-like WO3 as a material for resistive acetone gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 355, 131262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, T.; Dong, J.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, R.; Gao, J.; Li, L.; Jia, Y.; et al. Construction of mesoporous WO3 nanofibers functionalized with nanoscale PtO catalysts for enhanced acetone sensing properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 933, 167703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shar, A.H.; Lakhan, M.N.; Alali, K.T.; Liu, J.; Ahmed, M.; Shah, A.H.; Wang, J. Facile synthesis of reduced graphene oxide encapsulated selenium nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal method for acetone gas sensors. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 755, 137797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinavel, S.; Balaji, G.; Vadivel, S. High performance ethanol and acetone gas sensing behavior of FeCo2O4/graphene hybrid sensors prepared by facile hydrothermal route. Optik 2020, 223, 165571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ghosh, R. Selective determination of ammonia, ethanol and acetone by reduced graphene oxide based gas sensors at room temperature. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 28, 100336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, A.-R.; Lim, J.E.; Jang, S.; Kang, M.H.; Lee, G.; Chang, H.; Kim, E.; Park, J.K.; Lee, J.-O. Ag2S nanoparticles decorated graphene as a selective chemical sensor for acetone working at room temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 562, 150201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Yu, S.; Cheng, C.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Song, H. Ag nanoparticles modified Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide and their acetone sensing properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 276, 125378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geramilla, M.; Muthukumaravel, C.; Karunakaran, U.; Sairam, T. Gold nanoparticle decorated vertical graphene nanosheets composite/hybrid for acetone sensing at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 288, 116211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, S.; Sun, G.-J.; Hyun, S.K.; Kim, K.-K.; Lee, C. Enhanced acetone gas sensing performance of the multiple-networked Fe2O3-functionalized In2O3 nanowire sensor. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2015, 15, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaoui, M.; Leonardi, S.G.; Latino, M.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Donato, N.; Pullar, R.C.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A.; Neri, G. Pt-decorated In2O3 nanoparticles and their ability as a highly sensitive (<10 ppb) acetone sensor for biomedical applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, T.; Gao, X.; Wang, R.; Li, B. Coaxial electrospinning heterojunction SnO2/Au-doped In2O3 core-shell nanofibers for acetone gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 252, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Song, P.; Wang, Q. Enhanced acetone sensing performance of an α-Fe2O3-In2O3 heterostructure nanocomposite sensor. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 120, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, K.; Sun, X.; Duan, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X. Electrochemical sensor to environmental pollutant of acetone based on Pd-loaded on mesoporous In2O3 architecture. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 290, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, Y.; Chen, T.; Lu, Q.; Rehman, S.U.; Zhu, L. Rationally designed mesoporous In2O3 nanofibers functionalized Pt catalysts for high-performance acetone gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, N.; Hastir, A.; Kumari, M.; Singh, R.C. Hydrothermally synthesized heterostructures of In2O3/MWCNT as acetone gas sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 314, 112240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Feng, G.; Sun, T.; Xiao, J.; Guo, W.; Song, C. Excellent gas-sensitive properties towards acetone of In2O3 nanowires prepared by electrospinning. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 45, 100508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Che, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Hu, J.; Xiao, J.; Song, C.; Jiang, L. Sensitivity enhancement of In2O3/ZrO2 composite based acetone gas sensor: A promising collaborative approach of ZrO2 as the heterojunction and dopant for in-situ grown octahedron-like particles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 367, 132087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Xiong, X.; Guan, W.; Long, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Self-templated flower-like WO3-In2O3 hollow microspheres for conductometric acetone sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 361, 131705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mahapatra, P.L.; Mondal, P.P.; Das, T.; Pal, M.; Saha, D. A highly sensitive cobalt chromite thick film based trace acetone sensor with fast response and recovery times for the detection of diabetes from exhaled breath. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 262, 124291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lv, S.; Tang, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Guo, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, C.; et al. YSZ-based acetone sensor using a Cd2SnO4 sensing electrode for exhaled breath detection in medical diagnosis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 345, 130321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Yadav, D.; Singh, A.; Gupta, M.; Thapa, K.; Yadav, B. Detection of acetone via exhaling human breath for regular monitoring of diabetes by low-cost sensing device based on perovskite BaSnO3 nanorods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 361, 131708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, S.; Ray, B.; Vishwakarma, S.; Rath, S.; Datar, S. Polymer modified quartz tuning fork (QTF) sensor array for detection of breath as a biomarker for diabetes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, Q.-Q.; Ji, H.-M.; Yu, J.-J. Semiconducting Nano-structured SmFeO3-based Thin Films Prepared by Novel Sol-Gel Method for Acetone Gas Sensors. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2014, 152, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, S.B.; Phil, A.; Crosbie, P.A.; Balata, H.; Chudziak, J.; Hussell, T.; Dive, C. Progress and prospects of early detection in lung cancer. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roointan, A.; Mir, T.A.; Wani, S.I.; Rehman, M.U.; Hussain, K.K.; Ahmed, B.; Abrahim, S.; Savardashtaki, A.; Gandomani, G.; Gandomani, M.; et al. Early detection of lung cancer biomarkers through biosensor technology: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 164, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, P.J.; Wang, X.-F.; Xu, Y.; Mekhail, T.; Beukemann, M.C.; Na, J.; Kemling, J.W.; Suslick, K.; Sasidhar, M. Exhaled Breath Analysis with a Colorimetric Sensor Array for the Identification and Characterization of Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janfaza, S.; Khorsand, B.; Nikkhah, M.; Zahiri, J. Digging deeper into volatile organic compounds associated with cancer. Biol. Methods Protoc. 2019, 4, bpz014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutaria, S.R.; Gori, S.S.; Morris, J.D.; Xie, Z.; Fu, X.-A.; Nantz, M.H. Lipid Peroxidation Produces a Diverse Mixture of Saturated and Unsaturated Aldehydes in Exhaled Breath That Can Serve as Biomarkers of Lung Cancer—A Review. Metabolites 2022, 12, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Peng, P.; Zhan, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Fang, W.; Zhang, L. Cholesterol synthesis disruption combined with a molecule-targeted drug is a promising metabolic therapy for EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, P.J. Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds in the Exhaled Breath for the Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.P.; DeNicola, G.M. Sulfur metabolism and its contribution to malignancy. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 347, 39–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leemans, M.; Bauër, P.; Cuzuel, V.; Audureau, E.; Fromantin, I. Volatile Organic Compounds Analysis as a Potential Novel Screening Tool for Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. Biomark. Insights 2022, 17, 11772719221100709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binson, V.A.; Subramoniam, M.; Mathew, L. Discrimination of COPD and lung cancer from controls through breath analysis using a self-developed e-nose. J. Breath Res. 2021, 15, 046003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehada, N.; Cancilla, J.C.; Torrecilla, J.S.; Pariente, E.S.; Brönstrup, G.; Christiansen, S.; Johnson, D.W.; Leja, M.; Davies, M.P.A.; Liran, O.; et al. Silicon Nanowire Sensors Enable Diagnosis of Patients via Exhaled Breath. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7047–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Lei, J.; Huo, D.; Hou, C.; Luo, X.; Wu, H.; Fa, H.; Yang, M. A colorimetric detector for lung cancer related volatile organic compounds based on cross-response mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Tisch, U.; Adams, O.; Hakim, M.; Shehada, N.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Haick, H. Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberman, Y.; Tisch, U.; Shuster, G.; Pisula, W.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K.; Haick, H. Carbon nanotube/hexa-perihexabenzocoronene bilayers for discrimination between nonpolar volatile organic compounds of cancer and humid atmospheres. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4317–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barash, O.; Peled, N.; Hirsch, F.R.; Haick, H. Sniffing the unique “odor print” of non-small-cell lung cancer with gold nanoparticles. Small 2009, 5, 2618–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Pan, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X. Sensitive detection of lung cancer biomarkers using an aptameric graphene-based nanosensor with enhanced stability. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chung, M.T.; McHugh, W.; Nidetz, R.; Li, Y.; Fu, J.; Cornell, T.T.; Shanley, T.P.; Kurabayashi, K. Multiplex serum cytokine immunoassay using nanoplasmonic biosensor microarrays. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4173–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisch, U.; Haick, H. Nanomaterials for cross-reactive sensor arrays. MRS Bull. 2010, 35, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, H.P.; Loizeau, F.; Hiou-Feige, A.; Rivals, J.-P.; Romero, P.; Akiyama, T.; Gerber, C.; Meyer, E. Piezoresistive Membrane Surface Stress Sensors for Characterization of Breath Samples of Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Sensors 2016, 16, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, M.L.; Tisch, U.; Jeries, R.; Amal, H.; Hakim, M.; Ronen, O.; Marshak, T.; Zimmerman, D.R.; Israel, O.; Amiga, E.; et al. Analysis of exhaled breath for diagnosing head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A feasibility study. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leunis, N.; Boumans, M.; Kremer, B.; Din, S.; Stobberingh, E.; Kessels, A.G.H.; Kross, K.W. Application of an electronic nose in the diagnosis of head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope 2013, 124, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzivino, R.; Sciancalepore, P.I.; Dragonieri, S.; Quaranta, V.N.; Petrone, P.; Petrone, D.; Quaranta, N.; Carpagnano, G.E. The Role of a Polymer-Based E-Nose in the Detection of Head and Neck Cancer from Exhaled Breath. Sensors 2022, 22, 6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Goor, R.M.G.E.; Hardy, J.C.A.; van Hooren, M.R.A.; Kremer, B.; Kross, K.W. Detecting recurrent head and neck cancer using electronic nose technology: A feasibility study. Head Neck 2019, 41, 2983–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.; Billan, S.; Tisch, U.; Peng, G.; Dvrokind, I.; Marom, O.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Haick, H. Diagnosis of head-and-neck cancer from exhaled breath. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hooren, M.R.A.; Leunis, N.; Brandsma, D.S.; Dingemans, A.-M.C.; Kremer, B.; Kross, K.W. Differentiating head and neck carcinoma from lung carcinoma with an electronic nose: A proof of concept study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 3897–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, J.-P.; Gold, M.; Mengel, D.; Hattesohl, A.; Lübbe, D.; Schmid, S.; Tackenberg, B.; Rieke, J.; Maddula, S.; Baumbach, J.I.; et al. Measuring Compounds in Exhaled Air to Detect Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.-C.; Yu, J.-B.; Lee, H.-W.; Huh, J.-S.; Lim, J.-O. Investigation of Exhaled Breath Samples from Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry and an Exhaled Breath Sensor System. Sensors 2017, 17, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhleh, M.; Badarny, S.; Winer, R.; Jeries, R.; Finberg, J.; Haick, H. Distinguishing idiopathic Parkinson’s disease from other parkinsonian syndromes by breath test. Park. Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrak, M.; Talukder, M.A.H.; Gurgenashvili, K.; Noble, M.; Elfar, J.C. Peripheral nerve injury and myelination: Potential therapeutic strategies. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, R.; Broza, Y.; Shaltieli, H.; Sadeh, D.; Zilberman, Y.; Feng, X.; Glass-Marmor, L.; Lejbkowicz, I.; Müllen, K.; Miller, A.; et al. Detection of multiple sclerosis from exhaled breath using bilayers of polycyclic aromatic hydro-carbons and single-wall carbon nanotubes. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Swargiary, K.; Kongsawang, N.; Jitpratak, P.; Ajchareeyasoontorn, N.; Udomkittivorakul, J.; Viphavakit, C. Recent Advances in Sensing Materials Targeting Clinical Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Biomarkers: A Review. Biosensors 2023, 13, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, B.; Vernekar, P.R.; Shetti, N.P.; Chandra, P. Biosensor nanoengineering: Design, operation, and implementation for biomolecular analysis. Sens. Int. 2020, 1, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cui, D.; Haick, H.; Tang, N. Artificial Intelligence-Based Medical Sensors for Healthcare System. Adv. Sens. Res. 2023, Early View, 2300009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wu, W.; Jian, Y.; Haick, H.; Zhang, G.; Qian, Y.; Yuan, M.; Yao, M. Volatolomics in healthcare and its advanced detection technology. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 8185–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material Used for the Development of SnO2-Based Sensors | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Ca2+/Au co-doped SnO2 nanofibers | Enhanced sensing performance against acetone at 180 °C | [86] |
| Thick film sensors consisting of Pd loaded Sm-doped SnO2 | Increased response equal to 81% towards 25 ppm acetone concentration at 200 °C. Fast response/recovery Excellent selectivity, stability, and reproducibility | [87] |
| MWCNTs/SnO2 nanocomposites | Significantly enhanced response towards acetone (0.5–5 ppm) | [88] |
| SnO2 nanofibers/rGO nanosheets | High sensitivity towards acetone Limit of detection: 100 ppb acetone at 350 °C | [89] |
| Flower-like pristine SnO2 and NiO/SnO2 hierarchical nanostructures | Very good acetone sensing performance at 300 °C | [90] |
| Pd-Au bimetallic nanoparticles decorated SnO2 nanosheets | Temperature-dependent dual selectivity for detecting both formaldehyde (110 °C) and acetone (250 °C). Increased response, recovery time, and great selectivity under their optimum operating temperature. The ability to detect ultra-low concentrations of acetone in high RH (relative humidity) environments (94%). | [91] |
| Material Used for the Development of ZnO-Based Sensors | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Novel hierarchical ZnO nanoparticles | Increased gas sensing performance, sensitivity, and response towards acetone | [93] |
| Au-modified flower-like hierarchical ZnO nanostructures | Significantly increased response to acetone in comparison to bare nano-ZnO or non-modified flower-like hierarchical ZnO nanostructures. Limit of detection: 0.5 ppb | [94] |
| ZnO-CuO hybrid composites | Successful acetone detection at 310 °C. Improved response, good resolution under low concentrations. Limit of detection: 100 ppb | [95] |
| ZnO thin-films | High response and selectivity towards acetone. Limit of detection: 2 ppm at room temperature. | [96] |
| novel double-shelled ZnO hollow microspheres | High-performance sensing materials towards acetone. Increased sensitivity, response/recovery time, stability, and selectivity towards acetone. Limit of detection: 0.5 ppm | [97] |
| Pt decorated Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles | Superior sensing performance under exposure to 10 ppm acetone (450 °C). | [98] |
| Al, Cu and Co doped ZnO nanoparticles | Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles presented the most increased response during the exposure to acetone (1 ppm at 500 °C). Limit of detection: 0.01 ppm at 90% humidity. | [99] |
| Material Used for the Development of WO3-Based Sensors | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| C-doped WO3 poly-crystalline sensor | Enhanced response, rapid recovery at an acetone concentration range 0.2–5 ppm at 300 °C. Adequate long-term stability. Capability of discerning healthy persons (<0.9 ppm) and diabetic patients (>1.8 ppm), at 95% relative humidity. | [101] |
| Gd-doped WO3/RGO nanostructures | Enhanced response (54) towards 50 ppm acetone at 350 °C. | [102] |
| monoclinic WO3 | Limit of detection: 7.5 ppb | [103] |
| PtCu/WO3·H2O hollow spheres | Enhanced sensitivity, efficient selectivity rapid response/recovery speeds, ultra-low detection limit (0.01 ppm), and good stability. | [104] |
| 3D inverse opal (3DIO) WO3/Au | Increased response and selectivity towards acetone. Limit of detection: 100 ppb. | [105] |
| PdO@WO3 core-shell | Enhanced response (equal to 40) towards 50 ppm acetone. | [106] |
| Sb2O3/WO3 yolk-shell | High sensitivity, increased selectivity towards acetone, stability up to 2 months. Enhanced response (equal to 50) towards 100 ppm acetone. | [107] |
| Nb-doped ferroelectric ε-WO₃ spheres | Enhnanced acetone’s surface reaction due to ferroelectricity. Rapid response time. Ultra-low limit of detection: 8.9 ppb | [108] |
| 2D WO3 nanosheets | Increased response (14.7–50 ppm of acetone) Extremely low limit of detection (ppb level). Adequate selectivity towards other VOCs Rapid response/recovery rates (6/9 s to 0.17 ppm of acetone) Good repeatability (100 cycles) Long-term stability (14 days) | [109] |
| Pd@WO3 nanostructures | Low-cost, reliability, repeatability. Remarkable acetone response at 20–1000 ppm, at room temperature. Enhanced selectivity, good stability. | [110] |
| Pt-decorated NiWO4/WO3 nanotubes | Supreme response at 375 °C towards acetone sensing. Excellent stability and selectivity | [111] |
| Ru-Pd/WO3 | Selectivity, increased stability, rapid response/recovery times,. Ultra-high sensitivity (~99.80%) at 10 ppm acetone. | [112] |
| Fe-doped reduced graphene oxide (rGO) decorated WO3 | Excellent selectivity, adequate reproducibility and stability. Limit of detection: 1 ppm | [113] |
| Various morphologies of WO3 (spheres, nanorods, flowers and sea urchins) | The sea urchin morphology was the best choice. Supreme stability and sensitivity. Selective and rapid response to acetone concentrations 2–5000 ppm at 200 °C. | [114] |
| 0.5% PtO-WO3 nanofibers | Excellent sensing performance at 260 °C. Acceptable stability and selectivity towards the acetone biomarker. | [115] |
| Material Used for the Development of Graphene-Based Sensors | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| rGO-Se nanocomposite | Advanced response towards 100 ppm of acetone at 135 °C. Fast response/recovery times and good reproducibility. | [116] |
| ternary FeCo2O4/graphene hybrid nanocomposite | Increased sensitivity towards acetone gas. | [117] |
| reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and rGO-rosebengal (RB) composites | rGO-RB composite indicated the most enhanced response. (1.6% to 3.2% for 1000 and 2000 ppm of acetone, respectively) at room temperature | [118] |
| decorated graphene with Ag2S nanoparticles | Sufficiently enhanced response. Selectivity and sensitivity towards acetone. | [119] |
| Ag nanoparticles modified Fe3O4/rGO composites | Excellent selectivity to acetone. | [120] |
| AuNPs decorated vertical graphene nanosheet composites | Acetone detection at 140 ppm at room temperature. Rapid response time (300 s). Adequate recovery time (152 s). | [121] |
| Material Used for the Development of In2O3-Based Sensors | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Fe2O3-functionalized In2O3 nanowires | Responses ranging from 298 to 960% to acetone concentrations 10–500 ppm at 200 °C. | [122] |
| sub-spherical Pt-In2O3 nanoparticles | Exceptionally low detection limit (10 ppb) | [123] |
| SnO2/Au-doped In2O3 core-shell nanofibers | High response (at 300 °C) Rapid response and acceptable selectivity towards acetone gas. | [124] |
| α-Fe2O3-In2O3 heterostructure nanocomposites | Ideal operating at 300 °C, Enhanced response (37) at acetone concentration 20 ppm compared to bare material (about seven times greater). | [125] |
| Pd sensitized mesoporous In2O3 nanocomposites (1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 mol% Pd-loading amount) | Noticeable sensitivity, selectivity, MS, and response for acetone gas (50 ppm) of the 1.5 mol% Pd-loaded In2O3. | [126] |
| 1D porous Pt-doped In2O3 nanofiber structures | Increased sensing response towards acetone Limit of detection: 10 ppb at 180 °C. Fast response/recovery time. Enhanced selectivity towards acetone. Adequate reversibility and time stability (50 days). | [127] |
| In2O3/MWCNT | Increased sensing performance. Limit of detection: 10 ppm at 300 °C. | [128] |
| In2O3 nanowires | Increased response (37.9) at 100 ppm of acetone at 200 °C. Fast response/recovery time. | [129] |
| In2O3/ZrO2 composite | Good response for 100 ppm of acetone. Concise response time (1 s) at 260 °C. | [130] |
| a flower-like WO3-In2O3 hollow heterostructure | Advanced sensing performance towards acetone. | [131] |
| VOC | Production Mechanism | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated Hydrocarbon (aldehyde, ethane, pentane, etc.) | Lipid peroxidation of lipids of the cellular membrane, due to oxidative stress | [141] |
| Oxygen-containing (acetone, etc.) | Lipolysis or lipid peroxidation | [141] |
| Unsaturated hydrocarbon (isoprene, etc.) | Cholesterol synthesis pathways | [142] |
| Nitrogen-containing (ammonia, etc.) | Liver impairment and Uremia | [143] |
| Sulfur-containing (dimethylsulfide, etc.) | Incomplete methionine metabolism | [144] |
| Nanomaterial | Analytes | Sensor Type | Biological System | Controls | Limit of Detection and Response Time | Validation | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic-moleculefunctionalized AuNPs | 42 LC biomarkers | chemiresistor | 40 individuals | 56 individuals | 2–10 ppb for Acetaldehyde Response Time: not provided | Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) | [149] |
| CNT/hexa-perihexabenzocoronene bilayers | octane decane | chemiresistor | not provided | not provided | 15 ppb for octane Response Time: 30 s | GC-MS | [150] |
| AuNPs | 55 VOC biomarkers emitted by NSCLCs (non-small cell LC) | resistance change | cell lines: Calu3, H1650, H4006, H1435, H820, H1975, A549 | growth medium without cells in duplicate | 10 ppb of trimethylbenzene Response time: 10 s | GC-MS | [151] |
| Graphene functionalized with Aptameric GFET | Cytokine IL-6 | electrochemical | not provided | not provided | 2.78 pg/mL Response time: not provided | not provided | [152] |
| AuNPs | IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IFN-γ, and TNF-α | Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance | not provided | not provided | 11.43 (TNF-α), 6.46 (IFN-γ), 20.56 (IL-2), 4.60 (IL-4), 11.29 (IL-6), 10.97 pg/mL (IL-10) | ELISA | [153] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lagopati, N.; Valamvanos, T.-F.; Proutsou, V.; Karachalios, K.; Pippa, N.; Gatou, M.-A.; Vagena, I.-A.; Cela, S.; Pavlatou, E.A.; Gazouli, M.; et al. The Role of Nano-Sensors in Breath Analysis for Early and Non-Invasive Disease Diagnosis. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060317
Lagopati N, Valamvanos T-F, Proutsou V, Karachalios K, Pippa N, Gatou M-A, Vagena I-A, Cela S, Pavlatou EA, Gazouli M, et al. The Role of Nano-Sensors in Breath Analysis for Early and Non-Invasive Disease Diagnosis. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(6):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060317
Chicago/Turabian StyleLagopati, Nefeli, Theodoros-Filippos Valamvanos, Vaia Proutsou, Konstantinos Karachalios, Natassa Pippa, Maria-Anna Gatou, Ioanna-Aglaia Vagena, Smaragda Cela, Evangelia A. Pavlatou, Maria Gazouli, and et al. 2023. "The Role of Nano-Sensors in Breath Analysis for Early and Non-Invasive Disease Diagnosis" Chemosensors 11, no. 6: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060317
APA StyleLagopati, N., Valamvanos, T.-F., Proutsou, V., Karachalios, K., Pippa, N., Gatou, M.-A., Vagena, I.-A., Cela, S., Pavlatou, E. A., Gazouli, M., & Efstathopoulos, E. (2023). The Role of Nano-Sensors in Breath Analysis for Early and Non-Invasive Disease Diagnosis. Chemosensors, 11(6), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060317











