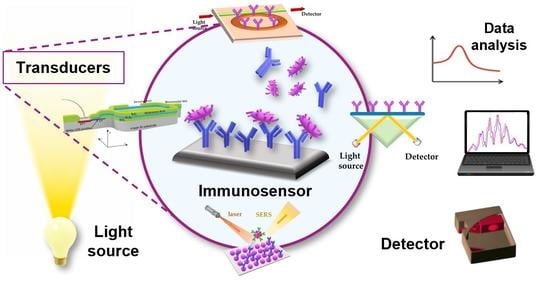
Optical Immunosensors for Bacteria Detection in Food Matrices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
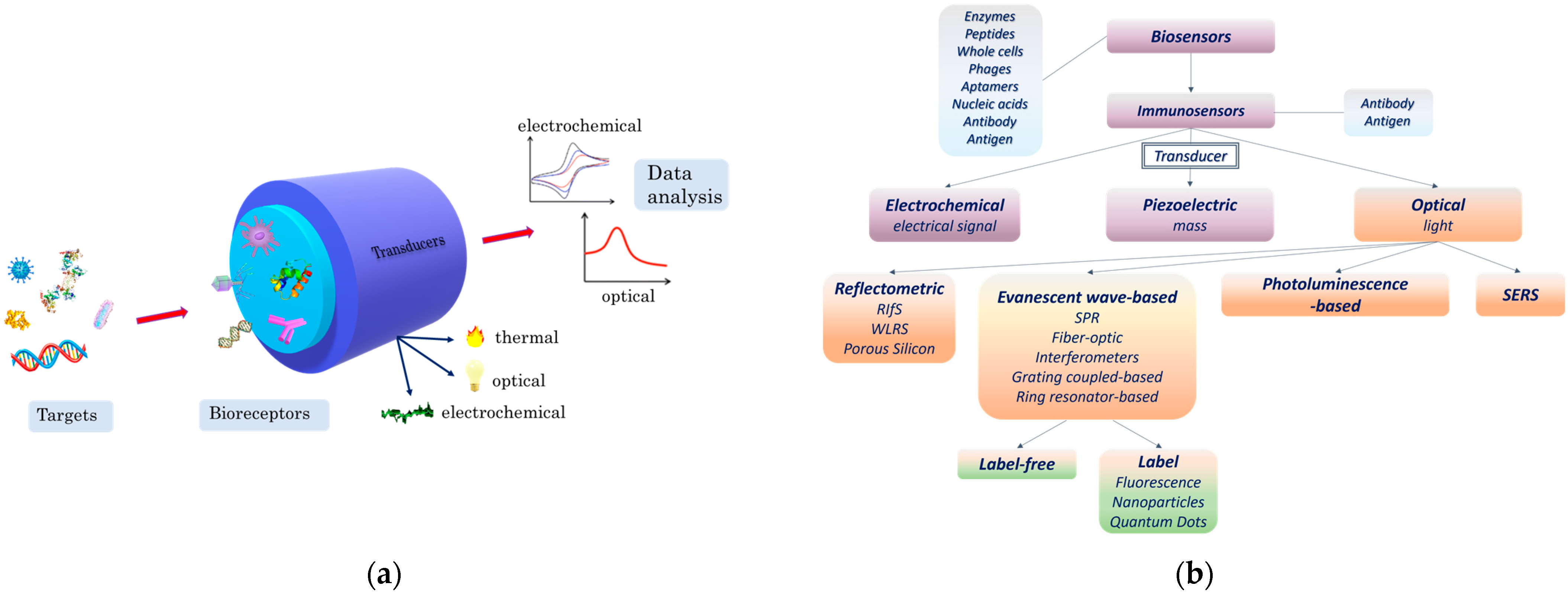
2. Principles of Optical Immunosensors
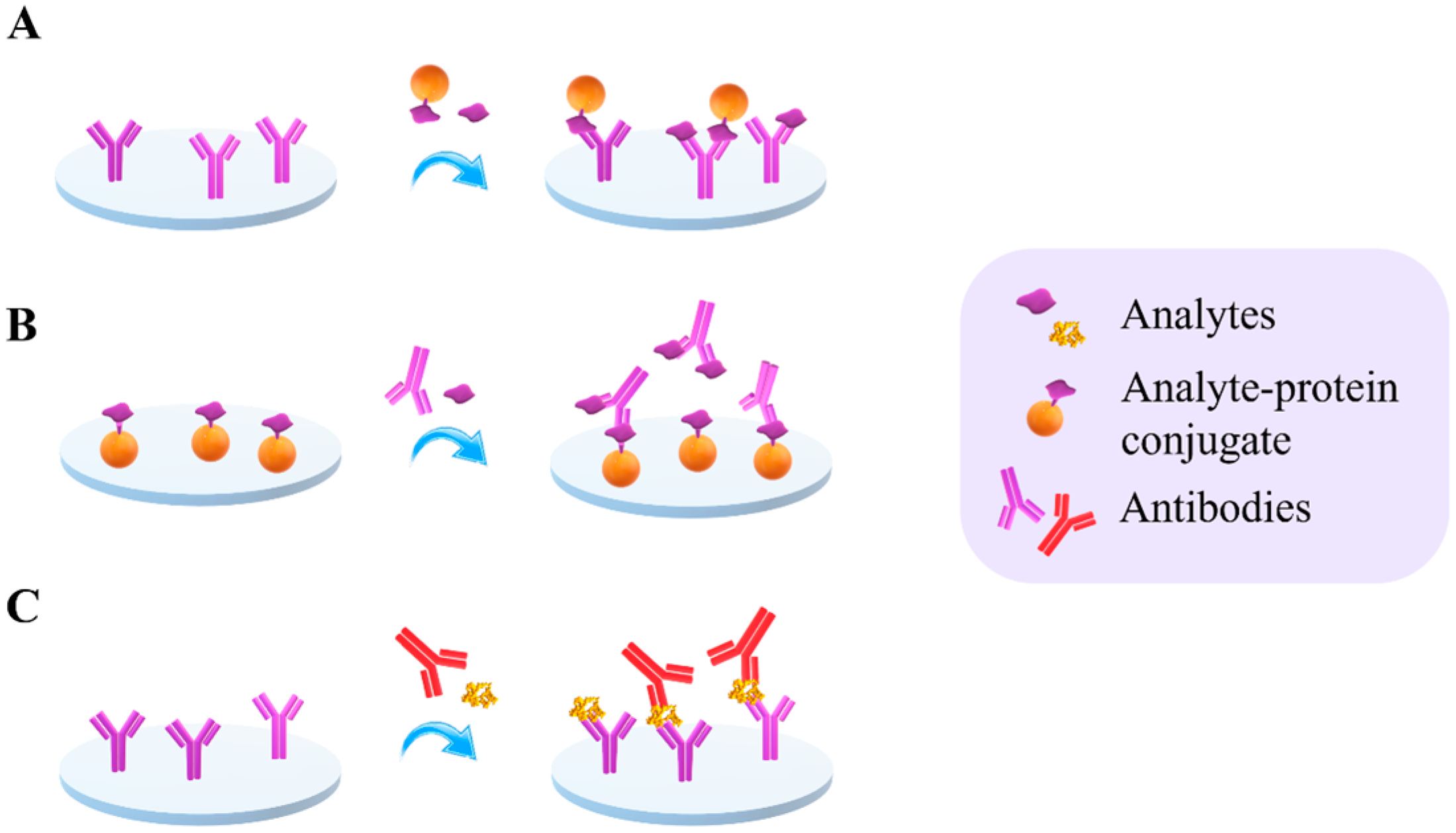
2.1. Assay Formats
2.2. Main Optical Transduction Principles
2.2.1. Detection Using Labels
2.2.2. Label-Free Detection
3. Application of Optical Sensors for Bacteria Detection
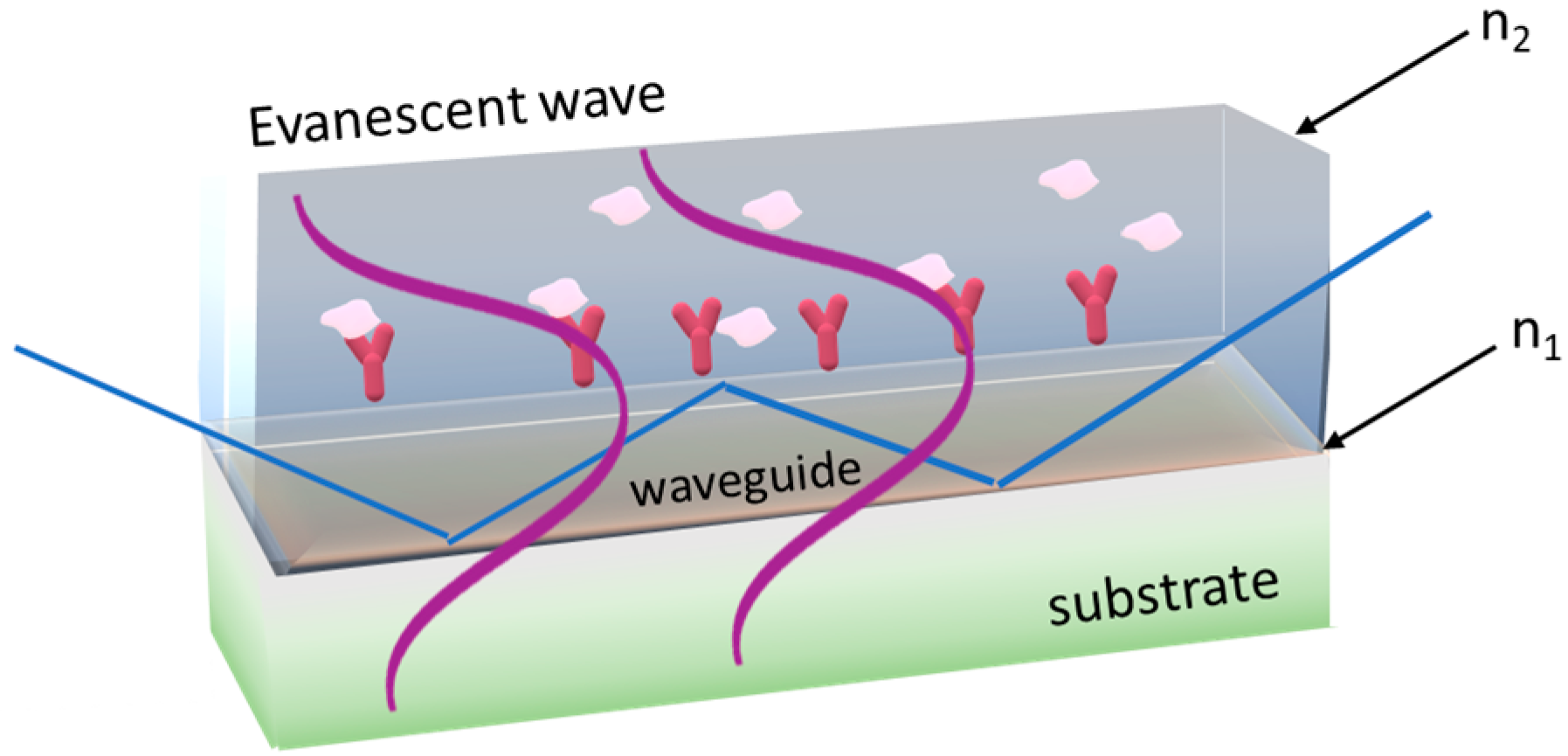
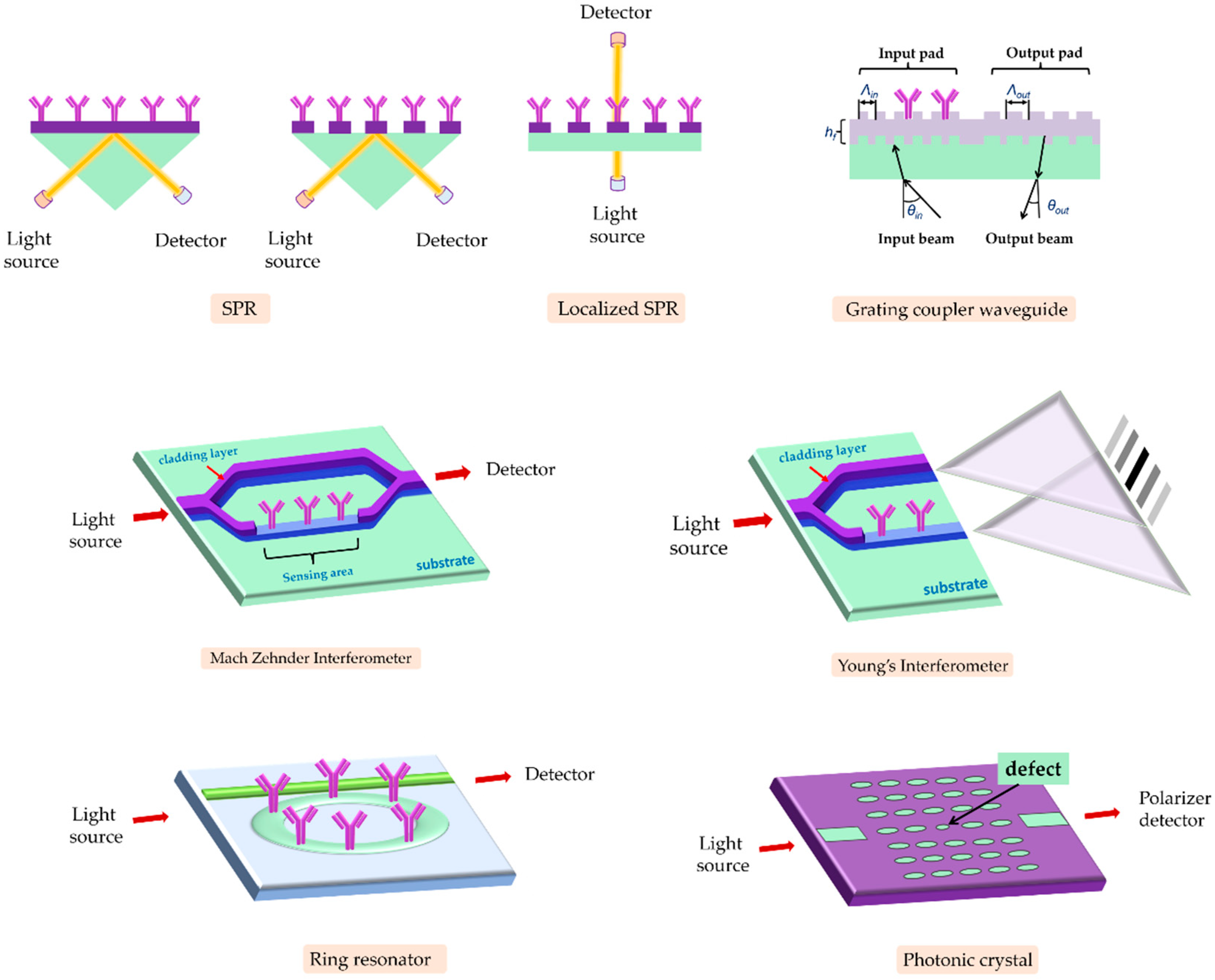
3.1. Evanescent-Wave-Based Biosensors
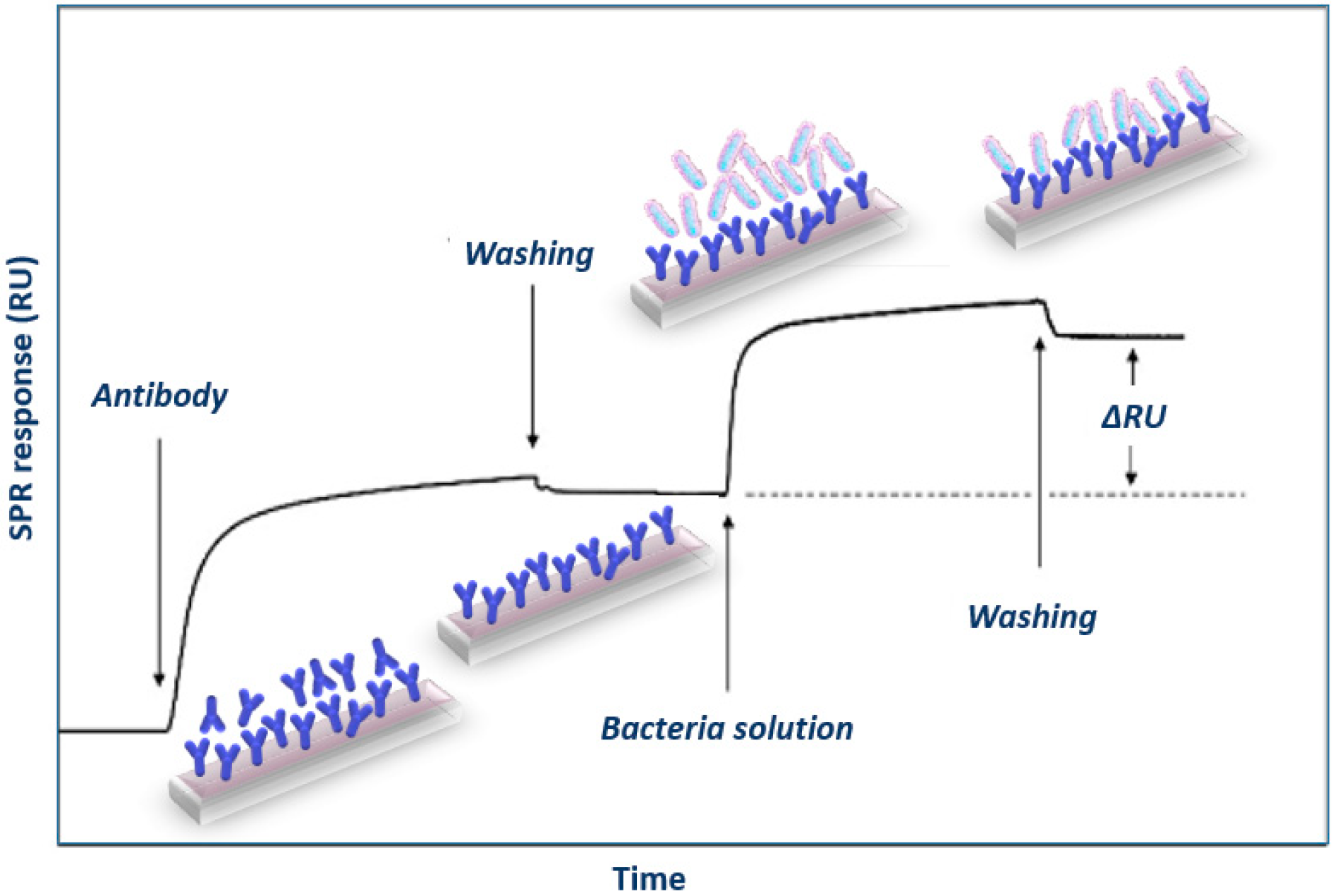
3.1.1. SPR Immunosensors
3.1.2. Fiber Optic Immunosensors
3.1.3. Interferometric Immunosensors
3.1.4. Grating-Coupler-Based Immunosensors
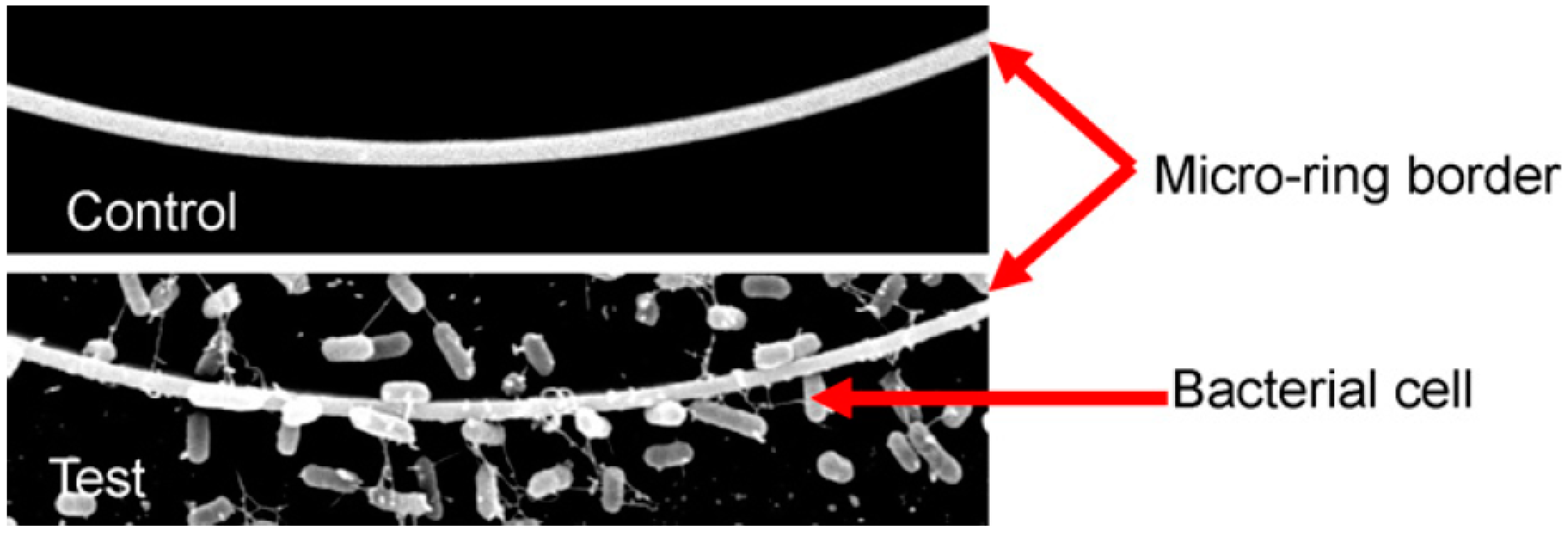
3.1.5. Ring-Resonator-Based Immunosensors
3.2. Reflectrometric Immunosensors
3.3. Photoluminescence-Based Immunosensors
3.4. Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS)-Based Immunosensors
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Foodborne Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/foodborne-diseases#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 18 June 2023).
- World Health Organization. The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 18 June 2023).
- World Health Organization. Estimating the Burden of Foodborne Diseases: A Practical Handbook for Countries; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Addis, M.; Sisay, D. A review on major food borne bacterial illnesses. J. Trop. Dis. 2015, 3, 1000176. [Google Scholar]
- Madigan, M.; Martinko, J.; Stahl, D.; Clark, D.P. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 13th ed.; Benjamin Cummings: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 1022–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Zourob, M.; Elwary, S.; Turner, A. Principles of Bacterial Detection: Biosensors, Recognition Receptors and Microsystems, 1st ed.; Springer Science+Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Hemavathy, R.V.; Jeevanantham, S.; Kamalesh, R.; Sneha, S.; Yaashikaa, P.R. Methods of detection of food-borne pathogens: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracias, K.S.; McKillip, J.L. A review of conventional detection and enumeration methods for pathogenic bacteria in food. Can. J. Microbiol. 2004, 50, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Lin, C.W.; Wang, J.; Oh, D.H. Advances in rapid detection methods for foodborne pathogens. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Salazar, J.K. Culture-independent rapid detection methods for bacterial pathogens and toxins in food matrices. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Maestu, A.; Tomás Fornés, D.; Prado Rodríguez, M. The use of multiplex real-time PCR for the simultaneous detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens. In Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens: Methods and Protocols; Bridier, A., Ed.; Springer Science+Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1918, pp. 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, T.; Dong, Q.; Li, J.; Niu, C. Detection of 12 common food-borne bacterial pathogens by Taq Man real-time PCR using a single set of reaction conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Oh, S.-W. A review of isothermal amplification methods and food-origin inhibitors against detecting food-borne pathogens. Foods 2022, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliulo, M.; Simoni, P.; Guardigli, M.; Michelini, E.; Luciani, M.; Lelli, R.; Roda, A. A rapid multiplexed chemiluminescent immunoassay for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Yersinia enterocolitica, Salmonella typhimurium, and Listeria monocytogenes pathogen bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4933–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaiuolo, M.; Paramithiotis, S.; Drosinos, E.H.; Ferrante, A. Development and optimization of an ELISA based method to detect Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157 in fresh vegetables. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 4622–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; He, J.; Cao, X.; Huang, K.; Luo, Y.; Xu, W. Development of a double-antibody sandwich ELISA for rapid detection of Bacillus cereus in food. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 16092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hochel, I.; Slavíčková, D.; Viochna, D.; Škvor, J.; Steinhauserová, I. Detection of Campylobacter species in foods by indirect competitive ELISA using hen and rabbit antibodies. Food Agric. Immunol. 2007, 18, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohde, A.; Hammerl, J.A.; Boone, I.; Jansen, W.; Fohler, S.; Klein, G.; Dieckmann, R.; Al Dahouk, S. Overview of validated alternative methods for the detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens. Trend Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.W.F.; Mutalib, N.S.A.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Rapid methods for the detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens: Principles, applications, advantages and limitations. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khansili, N.; Rattu, G.; Krishna, P.M. Label-free optical biosensors for food and biological sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 265, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Fu, Y.; Lei, C.; Li, Y. Advances in antimicrobial peptides-based biosensing methods for detection of foodborne pathogens: A review. Food Control 2020, 112, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.A.; Halpern, J.M. Guide to selecting a biorecognition element for biosensors. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 3231–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, N.; Zhang, W. Review of electrochemical DNA biosensors for detecting food borne pathogens. Sensors 2019, 19, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansari, N.; Yazdian-Robati, R.; Shahdordizadeh, M.; Wang, Z.; Ghazvini, K. Aptasensors for quantitative detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 533, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawil, N.; Sacher, E.; Mandeville, R.; Meunier, M. Surface plasmon resonance detection of E. coli and methicillin-resistant S. aureus using bacteriophages. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 37, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Wang, R.; Sotero, A.; Li, Y. A portable impedance immunosensing system for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Sensors 2017, 17, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viswanathan, S.; Rani, C.; Ho, J.A.A. Electrochemical immunosensor for multiplexed detection of food-borne pathogens using nanocrystal bioconjugates and MWCNT screen-printed electrode. Talanta 2012, 94, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulgione, A.; Cimafonte, M.; Della Ventura, B.; Iannaccone, M.; Ambrosino, C.; Capuano, F.; Proroga, Y.T.R.; Velotta, R.; Capparelli, R. QCM-based immunosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium in food. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, Y.; Guo, H.; Sun, X. Recent progress on cell-based biosensors for analysis of food safety and quality control. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 389–404. [Google Scholar]
- Templier, V.; Roux, A.; Roupioz, Y.; Livache, T. Ligands for label-free detection of whole bacteria on biosensors: A review. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, M.; Hashmi, M.S.J. An overview of biosensors and devices. Ref. Mod. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. 2017, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, M.; Maa, Q.; Ai, S. A label-free electrochemical impedance immunosensor based on AuNPs/PAMAM-MWCNT-Chi nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode for detection of Salmonella typhimurium in milk. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chuang, Y.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Shen, T.Y.; Chang, C.A.; Lin, C.S. Disposable amperometric immunosensing strips fabricated by Au nanoparticles-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes for the detection of foodborne pathogen Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathelié-Guinlet, M.; Cohen-Bouhacina, T.; Gammoudi, I.; Martin, A.; Béven, L.; Delville, M.H.; Grauby-Heywang, C. Silica nanoparticles-assisted electrochemical biosensor for the rapid, sensitive and specific detection of Escherichia coli. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 292, 314–320. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.H.; Wu, V.C.H.; Chuang, Y.C.; Lin, C.S. Using oligonucleotide-functionalized Au nanoparticles to rapidly detect foodborne pathogens on a piezoelectric biosensor. J. Microbiol. Method 2008, 73, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalograiaki, I.; Euba, B.; Proverbio, D.; Campanero-Rhodes, M.A.; Aastrup, T.; Garmendia, J.; Solís, D. Combined bacteria microarray and quartz crystal microbalance approach for exploring glycosignatures of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae and recognition by host lectins. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5950–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, S.M.; Lee, S.Y. Optical biosensors for the detection of pathogenic microorganisms. Trend Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, R.; Lee, N.Y. Recent advances in airborne pathogen detection using optical and electrochemical biosensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1234, 340297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudak, F.C.; Boyaci, I.H. Rapid and label-free bacteria detection by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensors. Biotechnol. J. 2009, 4, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, A.K. Biosensors and bio-based methods for the separation and detection of foodborne pathogens. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2008, 54, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J. Optical biosensors: An exhaustive and comprehensive review. Analyst 2020, 145, 1605–1628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Kakabakos, S.; Petrou, P. Label-free biosensors based onto monolithically integrated onto silicon optical transducers. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanvicens, N.; Pastells, C.; Pascual, N.; Marco, M.P. Nanoparticle-based biosensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Fiber-optic chemical sensors and biosensors (2008–2012). Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 487–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-Peña, E.; Valdés, M.G.; Glahn-Martínez, B.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Fluorescence based fiber optic and planar waveguide biosensors. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 943, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taitt, C.R.; Anderson, G.P.; Ligler, F.S. Evanescent wave fluorescence biosensors: Advances of the last decade. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashist, S.K.; Luppa, P.B.; Yeo, L.Y.; Ozcan, A.; Luong, J.H.T. Emerging technologies for next-generation Point-of-Care testing. Trend Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauglitz, G. Direct optical detection in bioanalysis: An update. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, E.; Shoman, H.; Ratner, D.M.; Cheung, K.C.; Chrostowski, L. Silicon photonic biosensors using label-free detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.; Hwang, J.; Seo, Y.; Gilad, A.A.; Choi, J. Optical immunosensors for the efficient detection of target biomolecules. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 2018, 23, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas, C.S.; Calvo-Lozano, O.; Mitchell, A.; Lechuga, L.M. Advanced evanescent-wave optical biosensors for the detection of nucleic acids: An analytic perspective. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauglitz, G.; Nahm, W. Observation of spectral interferences for the determination of volume and surface effects of thin films. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1991, 341, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothmund, M.; Schütz, A.; Brecht, A.; Gauglitz, G.; Berthel, G.; Gräfe, D. Label free binding assay with spectroscopic detection for pharmaceutical screening. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1997, 359, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleher, O.; Schindler, A.; Yin, M.X.; Holmes, A.B.; Luppa, P.B.; Gauglitz, G.; Proll, G. Development of a new parallelized, optical biosensor platform for label-free detection of autoimmunity-related antibodies multiplex platforms in diagnostics and bioanalytics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3305–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.P.; Alvarez, S.D.; Sailor, M.J. A Porous SiO2 interferometric biosensor for quantitative determination of protein interactions: Binding of protein A to immunoglobulins derived from different species. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsang, C.K.; Kelly, T.L.; Sailor, M.J.; Li, Y.Y. Highly stable porous silicon-carbon composites as label-free optical biosensors. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 10546–10554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, K.S.; Alvarez, S.D.; Choi, W.Y.; Sailor, M.J. A Stable, label-free optical interferometric biosensor based on TiO2 nanotube arrays. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2070–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrou, P.S.; Ricklin, D.; Zavali, M.; Raptis, I.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Misiakos, K.; Lambris, J.D. Real-time label-free detection of complement activation products in human serum by White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3359–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsounidi, D.; Koukouvinos, G.; Petrou, P.; Misiakos, K.; Zisis, G.; Goustouridis, D.; Raptis, I.; Kakabakos, S.E. Rapid and sensitive label-free determination of aflatoxin M1 levels in milk through a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy immunosensor. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 282, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouvinos, G.; Petrou, P.; Goustouridis, D.; Misiakos, K.; Kakabakos, S.; Raptis, I. Development and bioanalytical applications of a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy label-free sensing platform. Biosensors 2017, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurihara, Y.; Takama, M.; Masubuchi, M.; Ooya, T.; Takeuchi, T. Microfluidic reflectometric interference spectroscopy-based sensing for exploration of protein-protein interaction conditions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratamico, P.M.; Strobaugh, T.R.; Medina, M.B.; Gehring, A.G. Detection of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Biotechnol. Technique 1998, 12, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoung, J.-Y.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, W.; Choi, J.W. Immunosensor for the detection of Vibrio cholerae O1 using surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, W.; Bae, Y.M.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, J.W. Immunosensor for detection of Legionella pneumophila using surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waswa, J.W.; Debroy, C.; Irudayaraj, J. Rapid detection of Salmonella Enteritidis and Escherichia Coli using surface plasmon resonance biosensor. J. Food Proc. Eng. 2006, 29, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokken, G.C.A.M.; Corbee, R.J.; Van Knapen, F.; Bergwerff, A.A. Immunochemical detection of Salmonella group B, D and E using an optical surface plasmon resonance biosensor. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 222, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, A.; Irudayaraj, J.; Ryan, T. Mono and dithiol surfaces on surface plasmon resonance biosensors for detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 114, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Irudayaraj, J.; Ryan, T. A Mixed self-assembled monolayer-based surface plasmon immunosensor for detection of E. coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.K.; Lee, W.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, J.W. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor using self-assembled protein G for the detection of Salmonella paratyphi. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 111, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisocherová-Lísalová, H.; Víšová, I.; Ermini, M.L.; Špringer, T.; Song, X.C.; Mrázek, J.; Lamačová, J.; Scott Lynn, N.; Šedivák, P.; Homola, J. Low-fouling surface plasmon resonance biosensor for multi-step detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens in complex food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masdor, N.A.; Altintas, Z.; Tothill, I.E. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for the detection of Campylobacter jejuni. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poltronieri, P.; De Blasi, M.D.; D’Urso, O.F. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes through real-time PCR and biosensor methods. Plant Soil Environ. 2009, 55, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linman, M.J.; Sugerman, K.; Cheng, Q. Detection of low levels of Escherichia coli in fresh spinach by surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy with a TMB-based enzymatic signal enhancement method. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 145, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhneva, E.; Farka, Z.; Skládal, P.; Zajíčková, L. Cyclopropylamine plasma polymer surfaces for label-free SPR and QCM immunosensing of Salmonella. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 276, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.D.; Yu, Q.; Chen, S.; Homola, J.; Jiang, S. Comparison of E. coli O157:H7 preparation methods used for detection with surface plasmon resonance sensor. Sens. Actuators B 2005, 107, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waswa, J.; Irudayaraj, J.; DebRoy, C. Direct detection of E. coli O157:H7 in selected food systems by a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, S.D.; Hartmann, M.; Kämpfer, P.; Keusgen, M. Rapid method for detection of Salmonella in milk by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2040–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, P.; Hearty, S.; Quinn, J.; O’Kennedy, R. A generic approach for the detection of whole Listeria monocytogenes cells in contaminated samples using surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Si, C.; Ying, Y. Subtractive inhibition assay for the detection of E. coli O157:H7 using surface plasmon resonance. Sensors 2011, 11, 2728–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.B.; Bi, L.J.; Zhang, Z.P.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, R.F.; Wei, H.P.; Zhou, Y.F.; Zhang, X.E. Label-free detection of B. anthracis spores using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Analyst 2009, 134, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skottrup, P.D.; Nicolaisen, M.; Justesen, A.F. Towards on-site pathogen detection using antibody-based sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skottrup, P.; Nicolaisen, M.; Justesen, A.F. Rapid determination of Phytophthora infestans sporangia using a surface plasmon resonance immunosensor. J. Microbiol. Method 2007, 68, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skottrup, P.; Hearty, S.; Frøkiær, H.; Leonard, P.; Hejgaard, J.; O’Kennedy, R.; Nicolaisen, M.; Justesen, A.F. Detection of fungal spores using a generic surface plasmon resonance immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2724–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.D.; Cao, C.; Lee, J.; Choi, I.S.; Kim, B.W.; Sim, S.J. Surface plasmon resonance-based inhibition assay for real-time detection of Cryptosporidium parvum oocyst. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, P.; Hearty, S.; Wyatt, G.; Quinn, J.; O’Kennedy, R. Development of a surface plasmon resonance-based immunoassay for Listeria monocytogenes. J. Food Protect. 2005, 68, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.K.; Lee, W.; Chun, B.S.; Bae, Y.M.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, J.W. The fabrication of protein chip based on surface plasmon resonance for detection of pathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1847–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.D.; Ladd, J.; Yu, Q.; Chen, S.; Homola, J.; Jiang, S. Quantitative and simultaneous detection of four foodborne bacterial pathogens with a multi-channel SPR sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlay, A.; Duquenoy, A.; Piat, F.; Calemczuk, R.; Mercey, T.; Livache, T.; Roupioz, Y. Label-free immuno-sensors for the fast detection of Listeria in Food. Measurement 2017, 98, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
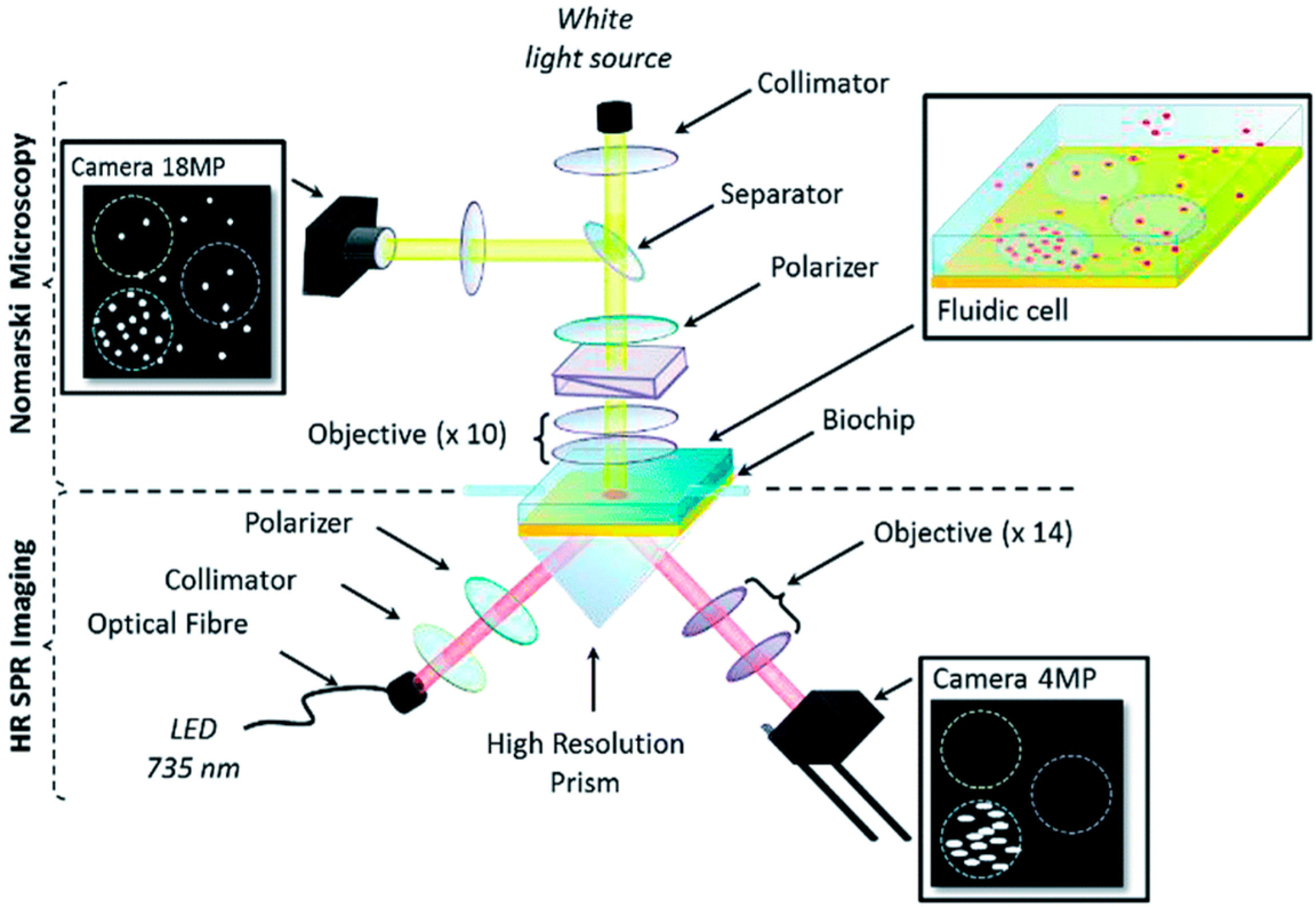
- Chen, J.; Park, B. Label-free screening of foodborne Salmonella using surface plasmon resonance imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5455–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.; Wang, B.; Chen, J. Label-free immunoassay for multiplex detections of foodborne bacteria in chicken carcass rinse with surface plasmon resonance imaging. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulade, M.; Morlay, A.; Piat, F.; Roupioz, Y.; Livache, T.; Charette, P.G.; Canva, M.; Leroy, L. Early detection of bacteria using SPR imaging and event counting: Experiments with Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15554–15560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Oyarzabal, O.A.; Huang, T.S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Sista, S.; Simonian, A.L. Development of a surface plasmon resonance biosensor for the identification of Campylobacter jejuni. J. Microbiol. Method 2007, 69, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeusen, C.A.; Alocilja, E.C.; Osburn, W.N. Detection of E. coli O157:H7 using a miniaturized surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Transact. ASAE 2005, 48, 2409–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudak, F.C.; Boyaci, I.H. Development of an immunosensor based on surface plasmon resonance for enumeration of Escherichia coli in water samples. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.-B.; Wang, S.-Z.; Yin, Y.-G.; Hoffmann, W.C.; Zheng, X.-Z. Using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium in chicken carcass. J. Bionic Eng. 2008, 5, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torun, Ö.; Hakki Boyaci, I.; Temür, E.; Tamer, U. Comparison of sensing strategies in SPR biosensor for rapid and sensitive enumeration of bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 37, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokel, O.; Yildiz, U.H.; Inci, F.; Durmus, N.G.; Ekiz, O.O.; Turker, B.; Cetin, C.; Rao, S.; Sridhar, K.; Natarajan, N.; et al. Portable microfluidic integrated plasmonic platform for pathogen detection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Yi, S.Y.; Woubit, A.; Kim, M. A portable surface plasmon resonance biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Appl. Sci. Converg. Technol. 2016, 25, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.; Lee, J.; Son, J.; Choi, J. Noble metal-assisted surface plasmon resonance immunosensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopez, G.A.; Estevez, M.C.; Soler, M.; Lechuga, L.M. Recent advances in nanoplasmonic biosensors: Applications and lab-on-a-chip integration. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, J.; Park, B.; Zhao, Y. Limitation of a localized surface plasmon resonance sensor for Salmonella detection. Sens. Actuators B 2009, 141, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, T. Amplifying the signal of localized surface plasmon resonance sensing for the sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghubi, F.; Zeinoddini, M.; Saeedinia, A.R.; Azizi, A.; Samimi Nemati, A. Design of localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) biosensor for immunodiagnostic of E. coli O157:H7 using gold nanoparticles conjugated to the chicken antibody. Plasmonics 2020, 15, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Knoll, W.; Dostalek, J. Bacterial pathogen surface plasmon resonance biosensor advanced by long range surface plasmons and magnetic nanoparticle assays. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8345–8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Mutharasan, R. Review of biosensors for foodborne pathogens and toxins. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 183, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijal, K.; Leung, A.; Shankar, P.M.; Mutharasan, R. Detection of pathogen Escherichia coli O157:H7 at 70 cells/mL using antibody-immobilized biconical tapered fiber sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiejata, P.J.; Shankar, P.M.; Mutharasan, R. Fluorescent sensing using biconical tapers. Sens. Actuators B 2003, 96, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Lang, T.; Bian, J.; Kong, W. Label-free fiber optic biosensor based on thin-core modal interferometer. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 228, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bharadwaj, R.; Sai, V.V.R.; Thakare, K.; Dhawangale, A.; Kundu, T.; Titus, S.; Verma, P.K.; Mukherji, S. Evanescent wave absorbance based fiber optic biosensor for label-free detection of E. coli at 280 nm wavelength. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3367–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandemur, G.; Rodrigues, D.; Allil, R.; Queiroz, V.; Peixoto, R.; Werneck, M.; Miguel, M. Plastic optical fiber-based biosensor platform for rapid cell detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Pivarnik, P.; Auger, S.; Rand, A.; Letcher, S. A compact fiber-optic immunosensor for Salmonella based on evanescent wave excitation. Sens. Actuators B 1997, 42, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Uknalis, J.; Tu, S.I.; Bhunia, A.K. Fiber-optic biosensor employing Alexa-Fluor conjugated antibody for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from ground beef in four hours. Sensors 2006, 6, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.F.; Lim, D.V. A rapid and automated fiber optic-based biosensor assay for the detection of Salmonella in spent irrigation water used in the sprouting of sprout seeds. J. Food Protect. 2004, 67, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leskinen, S.D.; Lim, D.V. Rapid ultrafiltration concentration and biosensor detection of Enterococci from large volumes of Florida recreational water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4792–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, T.; Morgan, M.T.; Bhunia, A.K. Detection of low levels of Listeria monocytogenes cells by using a fiber-optic immunosensor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6138–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohk, S.H.; Koo, O.K.; Sen, T.; Yamamoto, C.M.; Bhunia, A.K. Antibody-aptamer functionalized fibre-optic biosensor for specific detection of Listeria monocytogenes from food. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanduri, V.; Kim, G.; Morgan, M.T.; Ess, D.; Hahm, B.K.; Kothapalli, A.; Valadez, A.; Geng, T.; Bhunia, A.K. Antibody immobilization on waveguides using a flow–through system shows improved Listeria monocytogenes detection in an automated fiber optic biosensor: RAPTORTM. Sensors 2006, 6, 808–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohk, S.H.; Bhunia, A.K. Multiplex fiber optic biosensor for detection of Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella enterica from ready-to-eat meat samples. Food Microbiol. 2013, 33, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.; Grant, S.A. A Novel FRET-based optical fiber biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, H.; Asadishad, T.; Parsanasab, G.M.; Harun, S.W.; Mohammed, W.S.; Yasin, M. Optical fiber biosensor toward E. coli bacterial detection on the pollutant water. Eng. J. 2021, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Tsao, Y.C.; Tsai, W.H.; Yang, Y.W.; Yan, T.R.; Sheu, B.C. Development and application of side-polished fiber immunosensor based on surface plasmon resonance for the detection of Legionella pneumophila with halogens light and 850 nm-LED. Sens. Actuators A 2007, 138, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; Tiwari, U.K.; Pal, S.S.; Sinha, R.K. Rapid detection of Escherichia coli using fiber optic surface plasmon resonance immunosensor based on biofunctionalized molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, P.; Kehl, F.; Ehrentreich-Förster, E.; Stamm, C.; Bier, F.F. Integrated planar optical waveguide interferometer biosensors: A comparative review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 58, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarona, E.; Petrou, P.; Kakabakos, S.; Misiakos, K.; Raptis, I. Point-of-need bioanalytics based on planar optical interferometry. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Gunda, N.S.K.; Jamal, I.; Mitra, S.K. Optical biosensors with an integrated Mach-Zehnder interferometer for detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Biomed. Microdev. 2014, 16, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathesz, A.; Valkai, S.; Újvárosy, A.; Aekbote, B.; Sipos, O.; Stercz, B.; Kocsis, B.; Szabó, D.; Dér, A. Integrated optical biosensor for rapid detection of bacteria. Optofluid. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2016, 2, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Petrou, P.; Misiakos, K.; Raptis, I.; Kakabakos, S. Simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in drinking water and milk with Mach–Zehnder interferometers monolithically integrated on silicon chips. Biosensors 2022, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ymeti, A.; Greve, J.; Lambeck, P.V.; Wink, T.; Van Novell, S.W.F.M.; Beumer, T.A.M.; Wijn, R.R.; Heideman, R.G.; Subramaniam, V.; Kanger, J.S. Fast, ultrasensitive virus detection using a Young interferometer sensor. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, B.H.; Edwards, J.G.; Hartman, N.F. Hartman interferometer: Versatile integrated optic sensor for label- free, real-time quantification of nucleic acids, proteins, and pathogens. Clin. Chem. 1997, 43, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.H.; Brackett, R.E.; Hartman, N.F.; Campbell, D.P. Development of a rapid response biosensor for detection of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Food Protect. 1999, 62, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, T.; Ehrentreich-Förster, E.; Singh, M.; Schmitt, K.; Brandenburg, A.; Berka, A.; Bier, F.F. Direct detection of Tuberculosis infection in blood serum using three optical label-free approaches. Sens. Actuators B 2008, 129, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, J.; González-Guerrero, A.B.; Domínguez, C.; Lechuga, L.M. Label-free bimodal waveguide immunosensor for rapid diagnosis of bacterial infections in cirrhotic patients. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maldonado, J.; González-Guerrero, A.B.; Fernández-Gavela, A.; González-López, J.J.; Lechuga, L.M. Ultrasensitive label-free detection of unamplified multidrug-resistance bacteria genes with a bimodal waveguide interferometric biosensor. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grego, S.; McDaniel, J.R.; Stoner, B.R. Wavelength interrogation of grating-based optical biosensors in the input coupler configuration. Sens. Actuators B 2008, 131, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, J.; Pasche, S.; Diserens, J.M.; Sánchez-Baeza, F.; Gao, H.; Marco, M.P.; Voirin, G. Waveguide interrogated optical immunosensor (WIOS) for detection of sulfonamide antibiotics in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3340–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, F.; Etlinger, G.; Gartmann, T.E.; Tscharner, N.S.R.U.; Heub, S.; Follonier, S. Introduction of an angle interrogated, MEMS-based, optical waveguide grating system for label-free biosensing. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 226, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, P.; Hamori, A.; Cottier, K.; Kurunczi, S.; Horvath, R. Grating coupled interferometry for optical sensing. Appl. Phys. B 2009, 97, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teotia, P.K.; Kaler, R.S. Multilayer with Periodic Grating Based High Performance SPR Waveguide Sensor. Opt. Commun. 2017, 395, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusov, G.; Sweatt, A.; Pietrosimone, K.; Benson, D.; Geary, S.J.; Silbart, L.K.; Challa, S.; Lagoy, J.; Lawrence, D.A.; Lynes, M.A. A microarray biosensor for multiplexed detection of microbes using grating-coupled surface plasmon resonance imaging. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, E.; Viitala, R.; Salomäki, M.; James, S.W.; Tatam, R.P. Optical fibre long-period grating sensors: Characteristics and application. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, R49. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Yun, H.; Lin, C.; Chrostowski, L.; Jaeger, N.A.F. Grating-coupled silicon microring resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 121118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, R.; Pedersen, H.C.; Skivesen, N.; Selmeczi, D.; Larsen, N.B. Optical waveguide sensor for on-line monitoring of bacteria. Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandara, A.B.; Zuo, Z.; Ramachandran, S.; Ritter, A.; Heflin, J.R.; Inzana, T.J. Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococci by biosensor assay consisting of nanoscale films on optical fiber long-period gratings. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chang, T.L.; Liu, T.; Wu, D.; Du, H.; Liang, J.; Tian, F. Label-free detection of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria using long-period fiber gratings with functional polyelectrolyte coatings. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 133, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; Tiwari, U.; Nilima; Prashar, S.; Das, B.; Sinha, R.K. Label-free detection of Escherichia coli bacteria by cascaded chirped long period gratings immunosensor. Rev. Sci. Instr. 2019, 90, 25003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Park, I.S.; Kim, W.Y. Salmonella detection with a direct-binding optical grating coupler immunosensor. Sens. Actuators B 2007, 121, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, I.R.; Meikle, S.T.; Standen, G.; Hanlon, G.W.; Santin, M. The rapid and specific real-time detection of Legionella pneumophila in water samples using optical waveguide lightmode spectroscopy. J. Microbiol. Method 2009, 78, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Chan Eom, S.; Soo Chang, J.; Huh, C.; Yong Sung, G.; Shin, J.H. A silicon nitride microdisk resonator with a 40-nm-thin horizontal air slot. Opt. Exp. 2010, 18, 11209–11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Vos, K.; Bartolozzi, I.; Schacht, E.; Bienstman, P.; Baets, R. Silicon-on-insulator microring resonator for sensitive and label-free biosensing. Opt. Exp. 2007, 15, 7610–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armani, D.K.; Kippenberg, T.J.; Spillane, S.M.; Vahala, K.J. Ultra-high-Q toroid microcavity on a chip. Nature 2003, 421, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Wang, S.; Clarke, J.; Ja, S.J.; Goad, D.; Wald, L.; Flood, E.M.; Knobbe, E.; Hryniewicz, J.V.; Chu, S.T.; et al. A universal biosensing platform based on optical micro-ring resonators. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, H.; Chibli, H.; Nadeau, J.L.; Bianucci, P.; Peter, Y.A. Real-time detection of Staphylococcus aureus using whispering gallery mode optical microdisks. Biosensors 2016, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merkl, S.; Vornicescu, D.; Dassinger, N.; Keusgen, M. Detection of whole cells using reflectometric interference spectroscopy. Phys. Status Solidi A 2014, 211, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Tzialla, K.; Voulgari, A.; Dikeoulia, M.; Raptis, I.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Petrou, P. Rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium in drinking water by a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy immunosensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massad-Ivanir, N.; Shtenberg, G.; Tzur, A.; Krepker, M.A.; Segal, E. Engineering nanostructured porous SiO2 surfaces for bacteria detection via “direct cell capture”. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3282–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massad-Ivanir, N.; Shtenberg, G.; Segal, E. Optical detection of E. coli Bacteria by Mesoporous Silicon Biosensors. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 81, e50805. [Google Scholar]
- Massad-Ivanir, N.; Shtenberg, G.; Raz, N.; Gazenbeek, C.; Budding, D.; Bos, M.P.; Segal, E. Porous silicon-based biosensors: Towards real-time optical detection of target bacteria in the food industry. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massad-Ivanir, N.; Shtenberg, G.; Segal, E. Advancing nanostructured porous Si-based optical transducers for label free bacteria detection. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 733, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Li, Z.; Luo, Q.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. Bacteria detection based on its blockage effect on silicon nanopore array. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaraee, N.; Kanik, F.E.; Bhuiya, A.M.; Gong, E.S.; Geib, M.T.; Lortlar Ünlü, N.; Ozkumur, A.Y.; Dupuis, J.R.; Ünlü, M.S. Highly sensitive and label-free digital detection of whole cell E. coli with interferometric reflectance imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 162, 112258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, K.F.; Zhong, Z.; Lear, K.L. Environmental applications of photoluminescence-based biosensors. In Optical Sensor Systems in Biotechnology; Rao, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 116, pp. 99–123. [Google Scholar]
- Viter, R.; Tereshchenko, A.; Smyntyna, V.; Ogorodniichuk, J.; Starodub, N.; Yakimova, R.; Khranovskyy, V.; Ramanavicius, A. Toward development of optical biosensors based on photoluminescence of TiO2 nanoparticles for the detection of Salmonella. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 252, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taitt, C.R.; Shubin, Y.S.; Angel, R.; Ligler, F.S. Detection of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium by using a rapid, array-based immunosensor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapsford, K.E.; Rasooly, A.; Taitt, C.R.; Ligler, F.S. Detection of Campylobacter and Shigella Species in Food Samples Using an Array Biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapsford, K.E.; Ngundi, M.M.; Moore, M.H.; Lassman, M.E.; Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Taitt, C.R.; Ligler, F.S. Rapid detection of foodborne contaminants using an array biosensor. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 113, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Turner, S.; Taitt, C.R. Rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 spiked into food matrices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 584, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, Z.; Mohammadnejad, J.; Hosseini, M.; Bakhshi, B.; Rezayan, A.H. Whole cell FRET immunosensor based on graphene oxide and graphene dot for Campylobacter jejuni detection. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zong, S.; Wu, L.; Zhu, D.; Cui, Y. SERS-activated platforms for immunoassay: Probes, encoding methods, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7910–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier-Boss, P.A. Review on SERS of bacteria. Biosensors 2017, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Hu, Z.; Yang, D.; Xie, S.; Jiang, Z.; Niessner, R.; Haisch, C.; Zhou, H.; Sun, P. Bacteria detection: From powerful SERS to its advanced compatible techniques. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.L.; Ying, Y.L.; Yu, R.J.; Long, Y.T. In situ food-borne pathogen sensors in a nanoconfined space by surface enhanced Raman scattering. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 201. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.W. Recent advances in nanofabrication techniques for SERS substrates and their applications in food safety analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2800–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, M.; Ivleva, N.P.; Liu, X.; Niessner, R.; Haisch, C. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based label-free microarray readout for the detection of microorganisms. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2766–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knauer, M.; Ivleva, N.P.; Niessner, R.; Haisch, C. A flow-through microarray cell for the online SERS detection of antibody-captured E. coli bacteria. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 2663–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.H.; Bhandari, P.; Patel, P.; Irudayaraj, J. Membrane filter-assisted surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy for the rapid detection of E. coli O157:H7 in ground beef. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Shen, A.; Hu, J. A sensitive SERS-based sandwich immunoassay platform for simultaneous multiple detection of foodborne pathogens without interference. Anal. Method 2020, 12, 4885–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Hudson, J.; Sharma, A.; Banerjee, P. Development of a rapid capture-cum-detection method for Escherichia coli O157 from apple juice comprising nano-immunomagnetic separation in tandem with surface enhanced Raman scattering. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 189, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, H.; Goodacre, R.; Jamieson, L.E.; Graham, D.; Faulds, K. SERS detection of multiple antimicrobial-resistant pathogens using nanosensors. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12666–12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, C.; Rong, Z.; Ding, H.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Shao, N.; Dong, P.; Xiao, R.; et al. Facile synthesis of Au-coated magnetic nanoparticles and their application in bacteria detection via a SERS method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2016, 8, 19958–19967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamer, U.; Boyaci, I.H.; Temur, E.; Zengin, A.; Dincer, I.; Elerman, Y. Fabrication of magnetic gold nanorod particles for immunomagnetic separation and SERS application. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 3167–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temur, E.; Boyaci, I.H.; Tamer, U.; Unsal, H.; Aydogan, N. A Highly Sensitive detection platform based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering for Escherichia coli enumeration. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven, B.; Basaran-Akgul, N.; Temur, E.; Tamer, U.; Boyaci, I.H. SERS-based sandwich immunoassay using antibody coated magnetic nanoparticles for Escherichia coli enumeration. Analyst 2011, 136, 740–748. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.Y.; Huang, C.H.; Hsieh, W.H.; Liu, L.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Chu, C.C.; Wang, S.T.; Kuo, I.T.; Chau, L.K.; Yang, C.Y. On-line SERS detection of single bacterium using novel SERS nanoprobes and a microfluidic dielectrophoresis device. Small 2014, 10, 4700–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z. Simultaneous detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella typhimurium by a SERS-based lateral flow immunochromatographic assay. Food Anal. Method 2019, 12, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-B.; Du, X.-J.; Zang, Y.-X.; Li, P.; Wang, S. SERS-based lateral flow strip biosensor for simultaneous detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica serotype enteritidis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10290–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-B.; Chen, C.-Y.; Zhang, C.-N.; Du, X.-J.; Li, P.; Wang, S. Functionalized AuMBA@Ag nanoparticles as an optical and SERS dual probe in a lateral flow strip for the quantitative detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2916–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
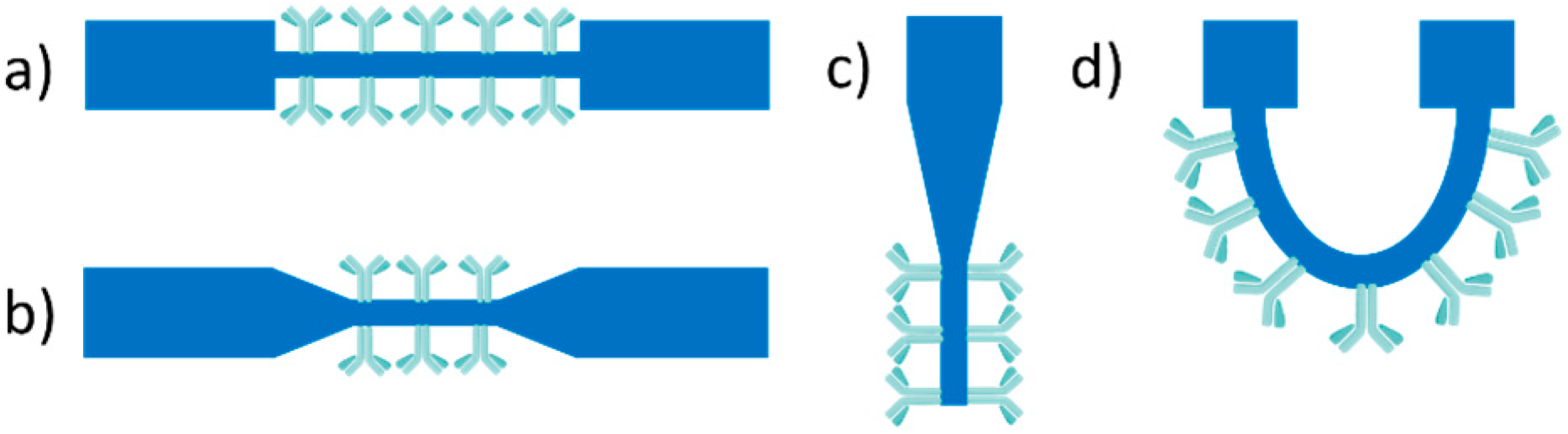
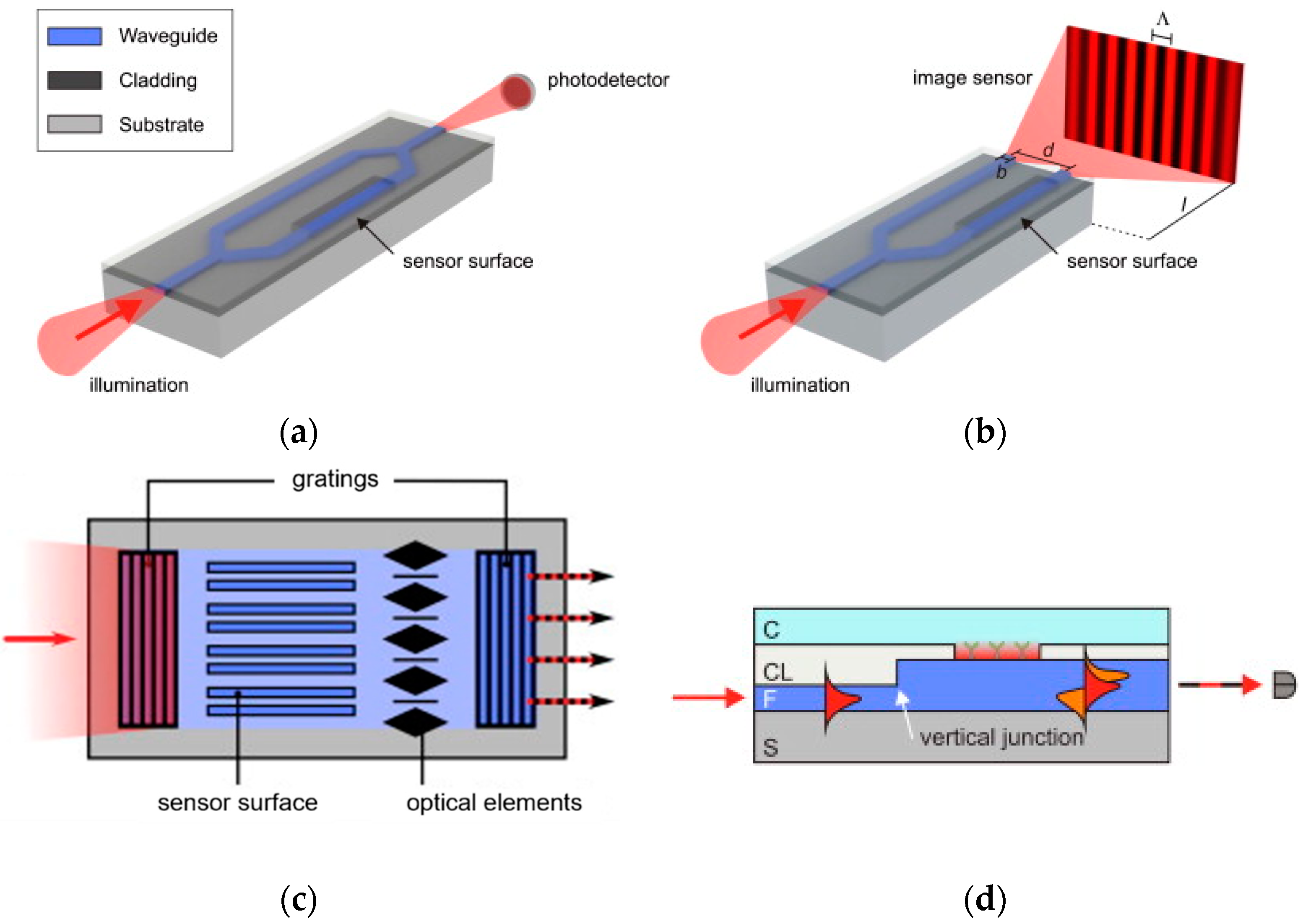
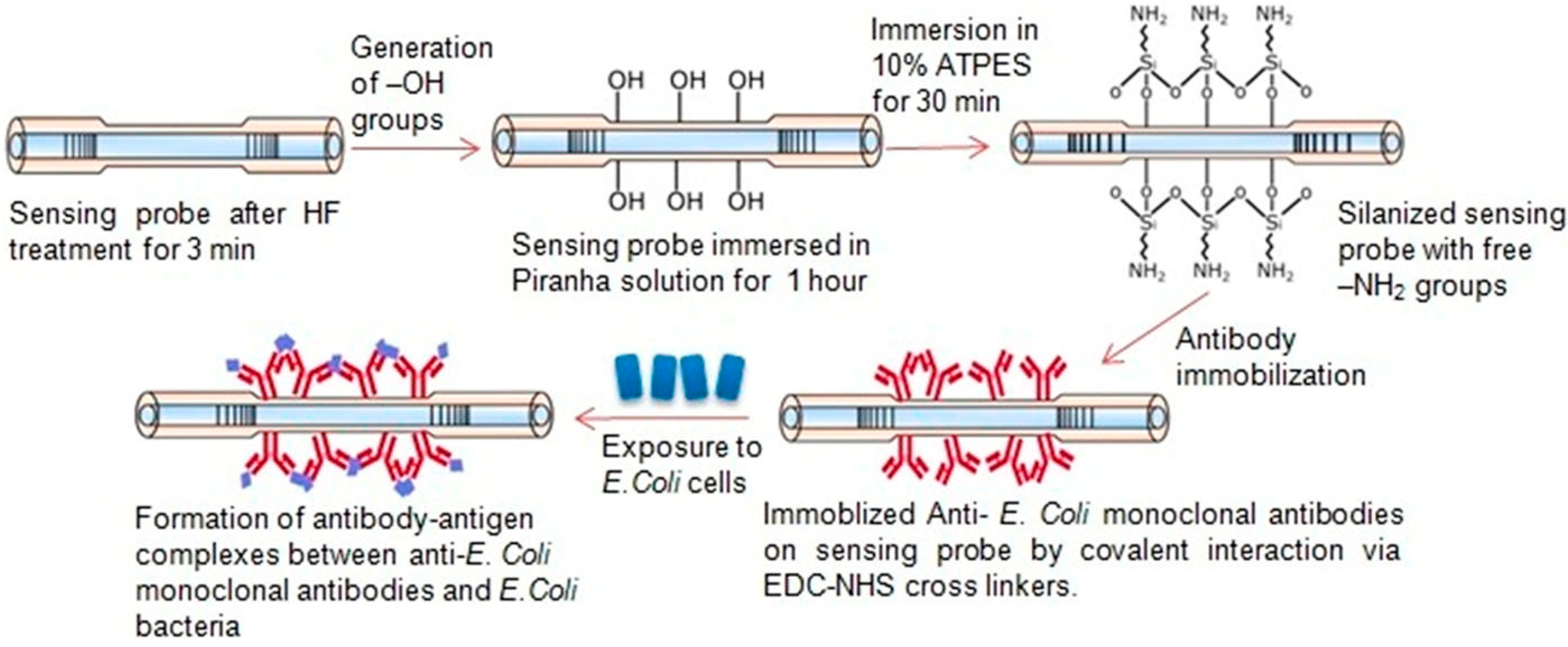

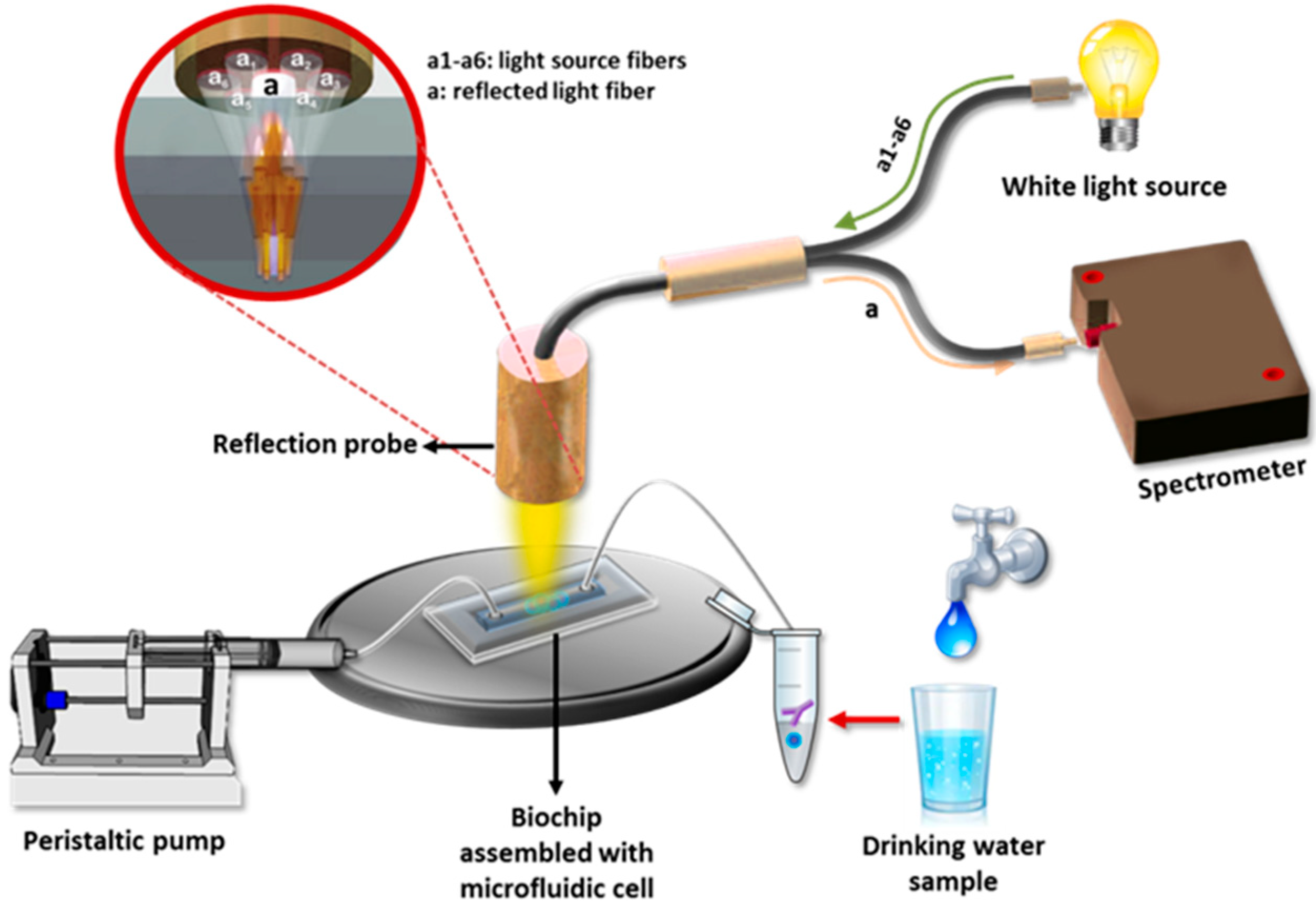
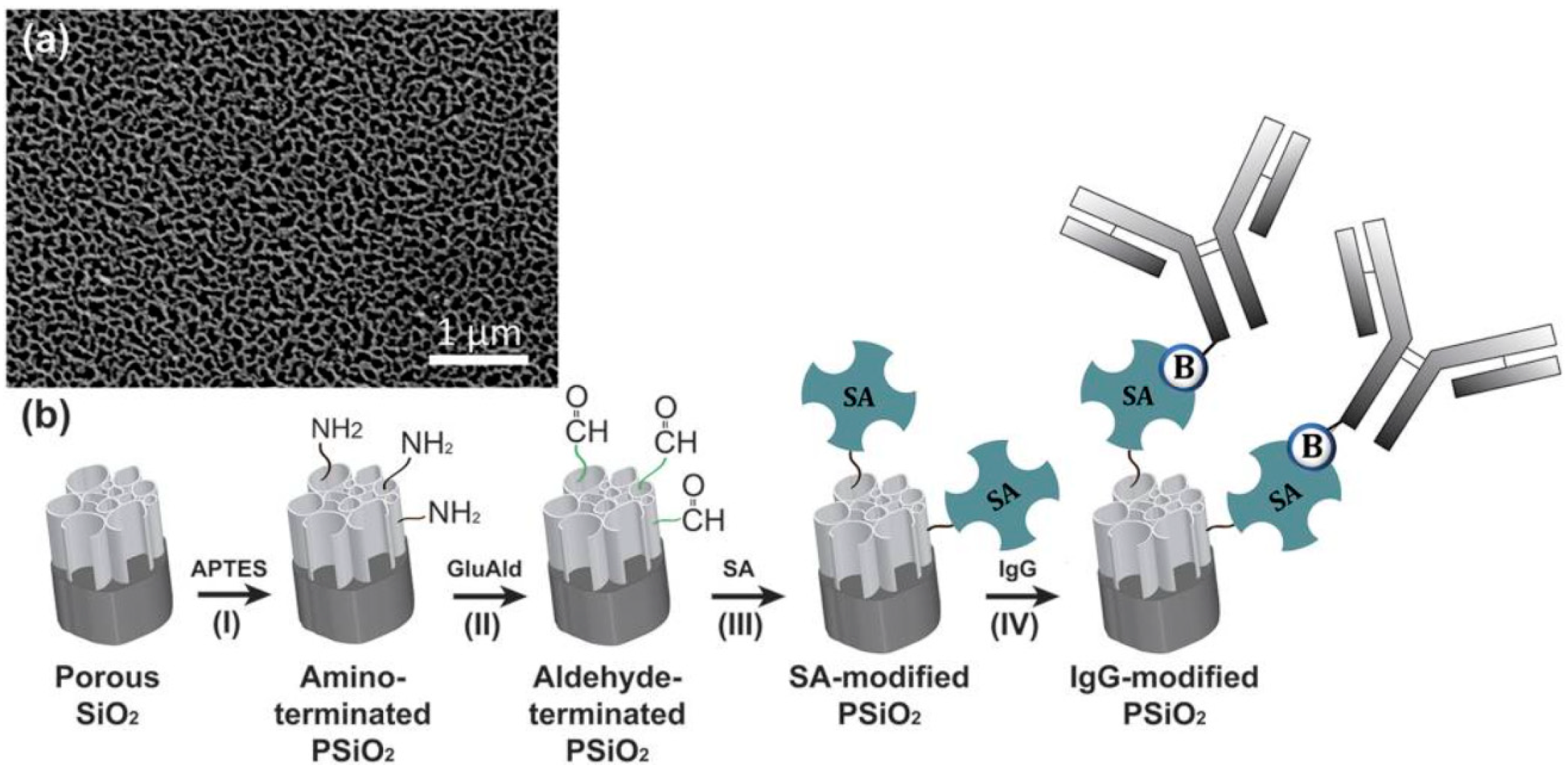


| Analyte | Detection Principle | Assay Type | Sample Type | Assay Duration | LOD | Ref. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | SPR | direct | milk | 5–7 min | 23 cfu/mL | [66] |
| S. enteritidis | 25 cfu/mL | |||||
| E. coli O157:H7 Salmonella sp. | SPR | sandwich with biotinylated detection antibody and streptavidin labeled with gold nanoparticles | hamburger/ cucumber | ~1 h | 57/17 cfu/mL 7.4 × 103/11.7 × 103 cfu/mL | [71] |
| E. coli | SPR | sandwich with detection antibody labeled with peroxidase + TMB substrate | fresh spinach | ~2 h | 104 cfu/mL | [74] |
| E. coli O157:H7 | SPR | direct | milk apple juice ground beef | 30 min | 102–103 cfu/mL | [77] |
| S. typhimurium | SPR | sandwich | milk | 1 h | 1.25 × 105 cfu/mL | [78] |
| C. parvum oocysts | SPR | subtractive inhibition | water | 30 min | 102 oocysts/mL | [85] |
| L. monocytogenes | SPR | inhibition | chocolate milk | 30 min | 2 × 105 cfu/mL | [86] |
| L. monocytogenes | SPR imaging | direct | apple juice | 30 min | 3.5 × 103 cfu/mL | [88] |
| E. coli O157:H7 | 1.4 × 104 cfu/mL | |||||
| C. jejuni | 1.1 × 105 cfu/mL | |||||
| S. typhimurium | 4.4 × 104 cfu/mL | |||||
| L. monocytogenes | SPR imaging | direct | lettuce | 30 min | 107 cfu/mL | [89] |
| S. typhimurium | SPR imaging | direct | chicken carcass rinse | ~20 min | 7.6 × 106 cfu/mL | [90] |
| Salmonella spp. Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli L. monocytogenes | SPR imaging | direct | chicken carcass rinse | 106 cfu/mL | [91] | |
| C. jejuni | Portable SPR | direct | broiler meat | <30 min | 103 cfu/mL | [93] |
| E. coli | Portable SPR | direct | water | ~17 min | 90 cfu/mL | [95] |
| S. typhimurium | Portable SPR | direct | chicken carcass | 3 min | 106 cfu/mL | [96] |
| E. coli | SPR | direct | lake, river, puddle, and tap water | 20 min | 3 cfu/mL | [97] |
| Analyte | Detection Principle | Assay Type | Sample Type | Assay Duration | LOD | Ref. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli O157:H7 | fiber optic fluorescence | sandwich | ground beef | 2.5 h | 103 cfu/mL | [113] |
| S. typhimurium | plastic fiber optic fluorescence | sandwich | sprouted alfalfa seeds rinse water | ~30 min | 105 cfu/mL 50 cfu/g (67 h) * | [114] |
| E. faecalis | plastic fiber optic fluorescence | indirect | ambient water | 2.5 h | 105 cfu/mL | [115] |
| L. monocytogenes | plastic fiber optic fluorescence | sandwich | hot dog bologna | 2.5 h | 4.3 × 103 cfu/mL 10 cfu/g (24 h) * | [116] |
| L. monocytogenes | plastic fiber optic fluorescence | sandwich | meat products | 4.0 h | 103 cfu/mL 102 cfu/g (18 h) * | [117] |
| L. monocytogenes | plastic fiber optic fluorescence | sandwich | frankfurter | 12 min | 5 × 105 cfu/mL | [118] |
| L. monocytogenes | plastic fiber optic fluorescence | sandwich | beef chicken turkey | 4.0 h | 103 cfu/mL 4 cfu/g (18 h) * | [119] |
| E. coli O157:H7 | ||||||
| S. enterica | ||||||
| S. typhimurium | FRET-based optical fiber | direct | buffer | 5 min | 103 cells/mL | [120] |
| ground pork | 105 cfu/g | |||||
| E. coli | fiber optic with a gold layer and ZnO nanorods | direct | water | 3 s | 103 cfu/mL | [121] |
| E. coli O157:H7 | fiber optic SPR | direct | drinking water | ~15 min | 94 cfu/mL | [123] |
| Analyte | Detection Principle | Assay Type | Sample Type | Assay Duration | LOD | Ref. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. typhimurium | Hartman interferometer | sandwich and direct | buffer | 10 min | 104 cfu/mL 20 cfu/mL (12 h) * | [132] |
| chicken carcass | ||||||
| S. typhimurium E. coli | MZI | competitive with biotinylated secondary antibodies and streptavidin | water milk | 10 min | 40 cfu/mL 110 cfu/mL 1 cfu/25 g (7.5 h) * | [128] |
| E. coli | Bimodal interferometer | direct | buffer | 25 min | 40 cfu/mL | [133] |
| B. cereus | 12.5 min | 70 cfu/mL |
| Analyte | Detection Principle | Assay Type | Sample Type | Assay Duration | LOD | Ref. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. typhimurium | WLRS | competitive | drinking water | 15 min | 320 cfu/mL | [155] |
| E. coli | reflectance spectroscopy on porous silicon | direct | water | 45 min | 103 cells/mL | [158] |
| E. coli | reflectance spectroscopy imaging | direct | tap water | 2 h | 2.2 cfu/mL | [161] |
| Analyte | Detection Principle | Assay Type | Sample Type | Assay Duration | LOD | Ref. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. typhimurium | fluorescence | sandwich | sausage cantaloupe whole liquid egg alfalfa sprouts chicken carcass rinse chicken excretal samples | 15 min 1 h | 8 × 104 cfu/mL 8 × 103 cfu/mL or cfu/g | [164] |
| Shigella dysenteriae C. jejuni | fluorescence | sandwich | buffer chicken carcass rinse ground turkey buffered milk lettuce leaf rinse | 25 min | 4.9 × 104 cfu/mL 9.7 × 102 cfu/mL | [165] |
| C. jejuni | fluorescence | sandwich | ground turkey sausage ham carnation non-fat dried milk vanilla fat-free yogurt | 25 min | 500 cells/mL | [166] |
| E. coli | fluorescence | sandwich | ground beef turkey sausage carcass wash apple juice | 30 min | 1–5 × 104 cells/mL | [167] |
| C. jejuni | homogeneous FRET | direct | poultry liver | 1.5 h | 100 cfu/mL | [168] |
| Analyte | Detection Principle | Assay Type | Sample Type | Assay Duration | LOD | Ref. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. pneumophila S. typhimurium | SERS | direct | water | 65 min | 106 cfu/mL 108 cfu/mL | [174] |
| E. coli O157:H7 | SERS | direct | water | >60 min | 4.3 × 103 cfu/mL | [175] |
| E. coli O157:H7 | SERS | sandwich | ground beef | ~2 h | 10 cfu/mL | [176] |
| E. coli S. aureus | SERS | sandwich | bottled water milk | ~2 h | 10 cfu/mL 25 cfu/mL | [177] |
| E. coli O157 | SERS | sandwich | apple juice | <1 h | 102 cfu/mL | [178] |
| E. coli | SERS | sandwich | water | 70 min | 8 cfu/mL | [183] |
| L. monocytogenes S. typhimurium | LFIA SERS | sandwich | milk | 10 min | 75 cfu/mL | [185] |
| S. enteritidis/ L. monocytogenes | LFIA SERS | sandwich | buffer chicken breast beef milk | 30 min | 27/19 cfu/mL 35/29 cfu/mL 35/22 cfu/mL 31/36 cfu/mL | [186] |
| E. coliO157:H7 | LFIA SERS | sandwich | milk chicken breast beef | 15 min | 5 × 104 cfu/mL | [187] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kourti, D.; Angelopoulou, M.; Petrou, P.; Kakabakos, S. Optical Immunosensors for Bacteria Detection in Food Matrices. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11080430
Kourti D, Angelopoulou M, Petrou P, Kakabakos S. Optical Immunosensors for Bacteria Detection in Food Matrices. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(8):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11080430
Chicago/Turabian StyleKourti, Dimitra, Michailia Angelopoulou, Panagiota Petrou, and Sotirios Kakabakos. 2023. "Optical Immunosensors for Bacteria Detection in Food Matrices" Chemosensors 11, no. 8: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11080430
APA StyleKourti, D., Angelopoulou, M., Petrou, P., & Kakabakos, S. (2023). Optical Immunosensors for Bacteria Detection in Food Matrices. Chemosensors, 11(8), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11080430