Origami Paper-Based Electrochemical Immunosensor with Carbon Nanohorns-Decorated Nanoporous Gold for Zearalenone Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Equipment
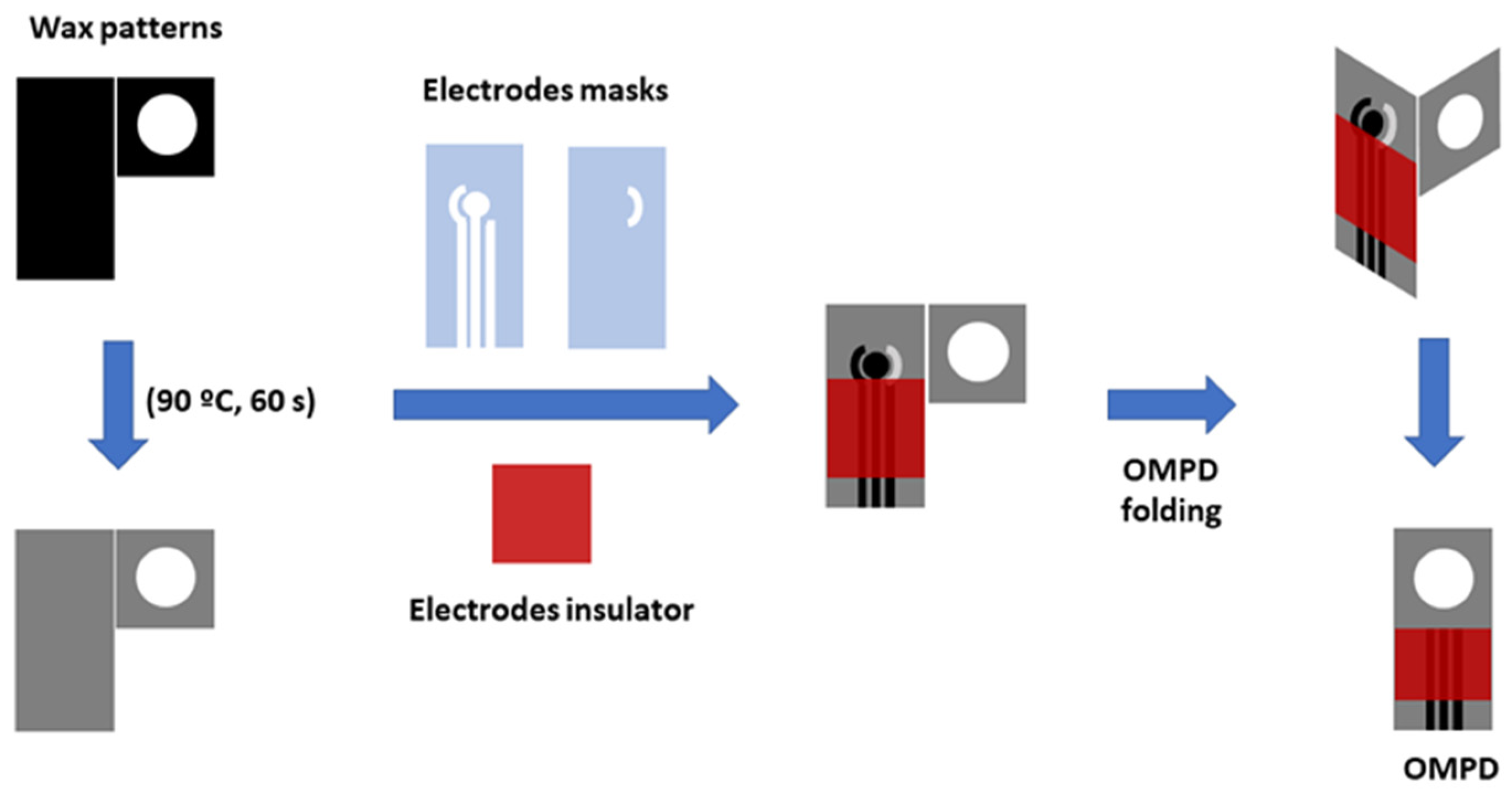
2.3. Design and Fabrication of the OMPDs with Electrochemical Detection
2.4. Modification of the GPE Working Electrode with the CNH/GNP Nanocomposite
2.5. Functionalization and Immobilization of the OMPD Microzones
2.6. Sample Preparation and Extraction
2.7. Analytical Procedure Detail for ZEA Determination on the OMPDs—GPE/CNH/GNP
2.8. Commercial ELISA Kit ZEA
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the GPE/CNH/GNP Working Electrode
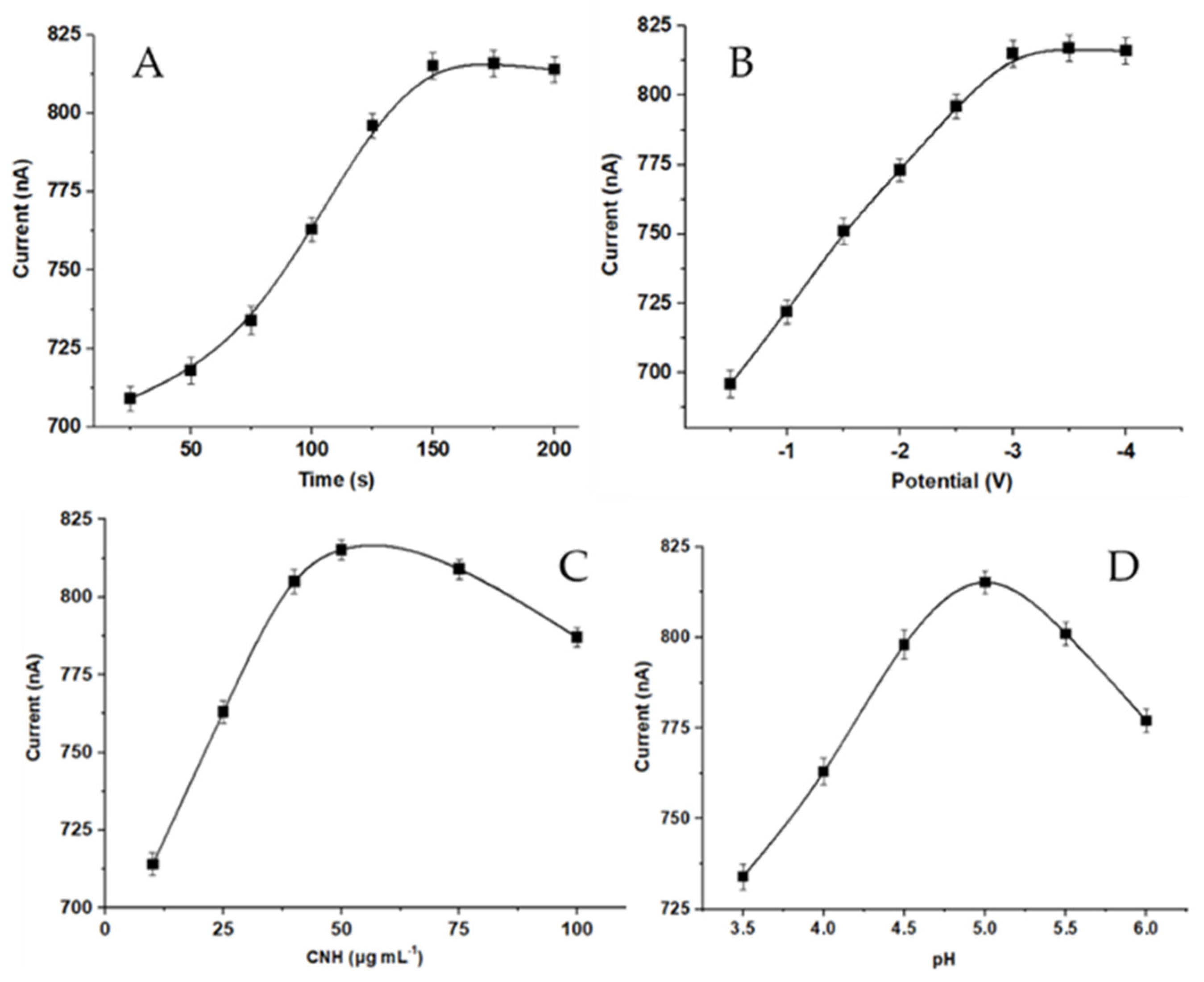
3.2. Analytical Optimization of Experimental Parameters
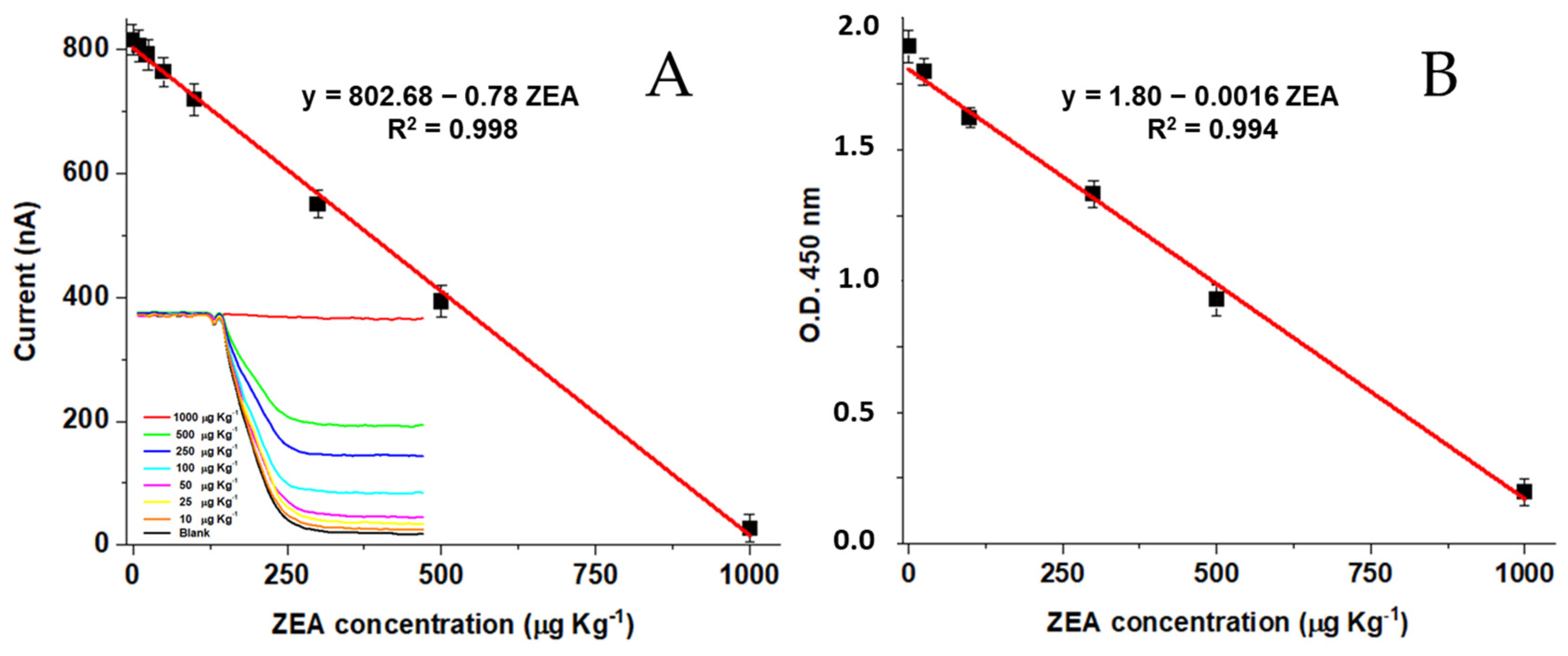
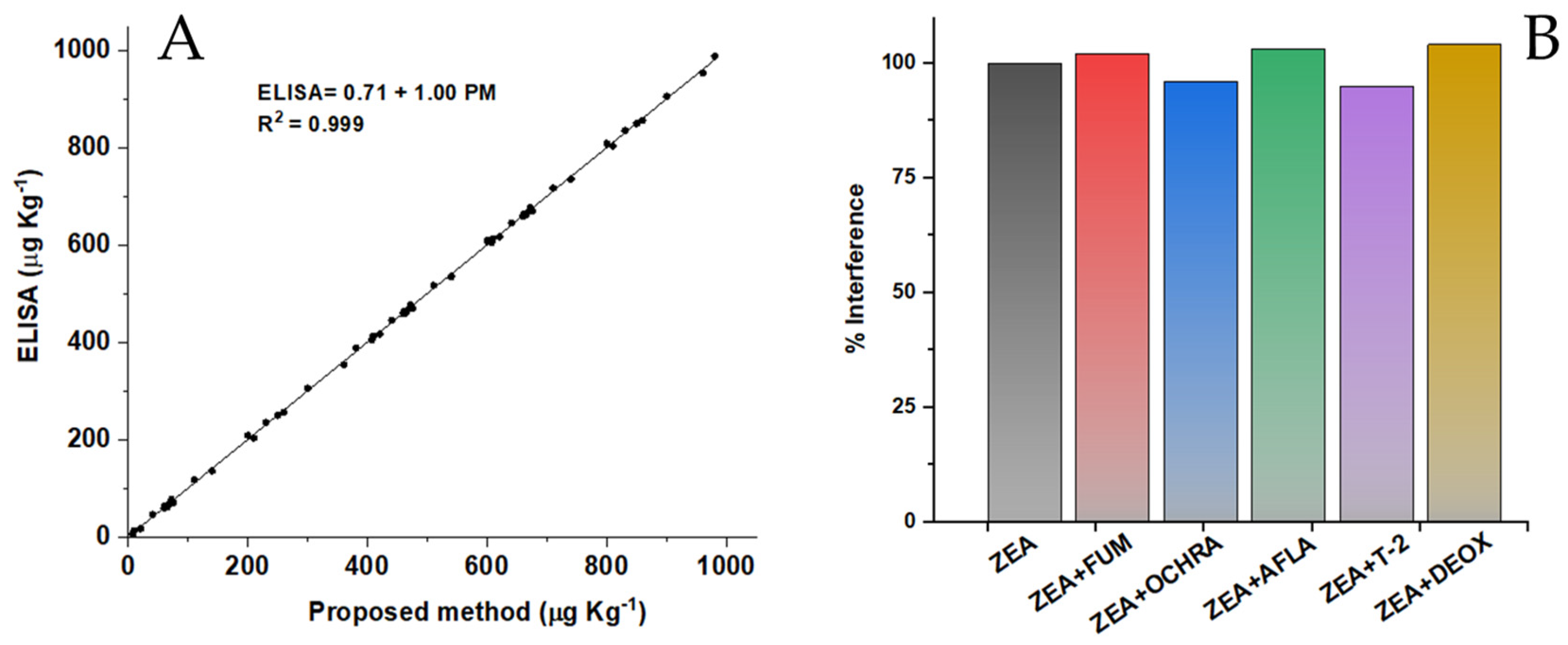
3.3. Analytical Performance of the OMPDs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, K.; Fan, Y.; Hebda, M.; Zhang, Y. Origami Microfluidics: A Review of Research Progress and Biomedical Applications. Biomed. Mater. Devices 2022, 1, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, F. Electrochemical paper-based devices: When the simple replacement of the support to print ecodesigned electrodes radically improves the features of the electrochemical devices. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 35, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colozza, N.; Di Meo, E.; Mucaria, A.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. An origami paper-based electrochemical biosensing platform for quality control of agri-food waste in the valorization strategy. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, F.; Cinti, S.; Caratelli, V.; Amendola, L.; Palleschi, G.; Moscone, D. Origami multiple paper-based electrochemical biosensors for pesticide detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Aziz, A.U.R.; Wu, B.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z. The road to unconventional detections: Paper-based microfluidic chips. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Neto, H.A.; Rocha, D.S.; Pradela-Filho, L.A.; Paixão, T.R.; Coltro, W.K.T. (Bio)electrodes on Paper Platforms as Simple and Portable Analytical Tools for Bioanalytical Applications. In Advances in Bioelectrochemistry; Crespilho, F.N., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; Volume 5, pp. 181–202. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chang, H.; Zhang, N.; He, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, B.; Fang, Y. Recent advances in enzyme inhibition based-electrochemical biosensors for pharmaceutical and environmental analysis. Talanta 2022, 253, 124092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, H. A portable 3D microfluidic origami biosensor for cortisol detection in human sweat. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3526–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, J.F.C.; Ho, A.H.P.; Mak, W.C. Printed microfluidic biosensors and their biomedical applications. In Microfluidic Biosensors; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ozer, T.; Henry, C.S. Paper based analytical devices for virus detection: Recent strategies for current and future pandemics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 144, 116424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagkaris, A.S.; Nelis, J.L.; Campbell, K.; Elliott, C.T.; Pulkrabova, J.; Hajslova, J. Smartphone and microfluidic systems in medical and food analysis. In Microfluidic Biosensors; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 233–257. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Mao, K.; Hui, Q.; Wang, B.; Cooper, J.; Yang, Z. Paper based devices for rapid diagnosis and wastewater surveillance. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.S.; Brasel, J.M. Toxicity, metabolism, and impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. Toxicology 2001, 167, 101–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cui, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Jia, Z.; Gao, C.; Zhang, H. Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices for the Determination of Food Contaminants: Developments and Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8188–8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglayan, M.O.; Şahin, S.; Üstündağ, Z. Detection strategies of zearalenone for food safety: A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari-Nodoushan, A.A. Zearalenone, an abandoned mycoestrogen toxin, and its possible role in human infertility. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2022, 20, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Yu, J.; Ye, Y.; Sheng, L.; Fang, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, X. Biodegradation methods and product analysis of zearalenone and its future development trend: A review. Food Control 2022, 145, 109469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer-Baranyi, K.; Adányi, N.; Székács, A. Biosensors for deoxynivalenol and zearalenone determination in feed quality control. Toxins 2021, 13, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Mu, G.D.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.L.; Lu, D.J.; Chen, F.M.; Yang, M.L.; He, M.Y.; Liu, T. Fast construction of core-shell structured magnetic covalent organic framework as sorbent for solid-phase extraction of zearalenone and its derivatives prior to their determination by UHPLC-MS/MS. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijalem, Y.G.; Gab-Allah, M.A.; Choi, K.; Kim, B. Development of isotope dilution-liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry for the accurate determination of zearalenone and its metabolites in corn. Food Chem. 2022, 384, 132483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z.; Fu, X.; Du, D. High-performance liquid chromatography for the sensitive zearalenone determination by the automated immunomagnetic beads purifier for one-step sample pre-treatment. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Peng, J.; Cui, Y.; Shi, Y.; He, H. Magnetic hyperbranched molecularly imprinted polymers for selective enrichment and determination of zearalenone in wheat proceeded by HPLC-DAD analysis. Talanta 2020, 209, 120555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, D.; Huang, Q.; Yang, J. Microfluidics-Based Time-Resolved Fluorescence Immunoassay for the On-Site Detection of Aflatoxins B1 Zearalenone and Deoxynivalenol in Cereals. Foods 2022, 11, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Hua, M.Z.; Roopesh, M.S.; Lu, X. Rapid detection of three mycotoxins in animal feed materials using competitive ELISA-based origami microfluidic paper analytical device (μPAD). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, C.; Tong, X.; Duan, N.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S. A portable paper-based aptasensor for simultaneous visual detection of two mycotoxins in corn flour using dual-color upconversion nanoparticles and Cu-TCPP nanosheets. Food Chem. 2023, 404 Pt B, 134750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Liu, W.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, H.; Yu, H.; Dong, C.; Wu, M. Recent Advances in Electrochemiluminescence Biosensors for Mycotoxin Assay. Biosensors 2023, 13, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felici, E.; Regiart, M.D.; Pereira, S.V.; Ortega, F.G.; Angnes, L.; Messina, G.A.; Fernández-Baldo, M.A. Microfluidic Platform Integrated with Carbon Nanofibers-Decorated Gold Nanoporous Sensing Device for Serum PSA Quantification. Biosensors 2023, 13, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenga, Y.; Camarada, M.B.; Lu, X.; Tanga, K.; Lia, W.; Qiu, D.; Wen, Y.; Wu, G.; Luo, Q.; Bai, L. Detection and electrocatalytic mechanism of zearalenone using nanohybrid sensor based on copper-based metal-organic framework/magnetic Fe3O4-graphene oxide modified electrode. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liang, N.; Zhao, L. Fluorescence Sensor for Zearalenone Detection Based on Oxidized Single-walled Carbon Nanohorns/N-doped Carbon Quantum Dots-aptamer. J. Fluoresc. 2023, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Cavas, T.; Navarro-Villoslada, F.; Urraca, J.L.; Serrano, L.A.; Orellana, G.; Moreno-Bondia, M.C. Simultaneous determination of zearalenone and alternariol mycotoxins in oil samples using mixed molecularly imprinted polymer beads. Food Chem. 2023, 412, 135538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Fan, K.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Cao, H.; Zhao, Z.; Tangni, E.K.; Zheng, H. Development of a reliable UHPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of zearalenone and zearalenone-14-glucoside in various feed products. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 955266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | CV % a Within-Assay | CV % a Between-Assay | Linear Range b | LOD b | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | 6.19 | 7.14 | 25–1000 | 20 | >20 |
| OMPD | 4.24 | 4.89 | 10–1000 | 4.4 | 10 |
| ZEA a | ELISA | Recovery (%) c | OMPD | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 9.1 ± 0.6 b | 91 | 9.9 ± 0.3 | 99 |
| 25 | 23.5 ± 1.4 | 94 | 25.3 ± 1.1 | 101.2 |
| 100 | 96.2 ± 6.5 | 96.2 | 102.7 ± 4.6 | 102.7 |
| 300 | 315.8 ± 19.7 | 105.2 | 298.2 ± 14.5 | 99.4 |
| 500 | 522.9 ± 33.9 | 104.5 | 494.1 ± 21.7 | 98.8 |
| 1000 | 1025.8 ± 69.2 | 102.58 | 987.87 ± 45.1 | 98.7 |
| N-C d | <20 | N.A. | <4.40 | N.A. |
| Method | Linear Range (µg Kg−1) | LOD (µg Kg−1) | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microfluidics-Based Time-Resolved Fluorescence | 1.5–375 | 5 | Cereals | [23] |
| ELISA-based origami microfluidic paper | 0–40 | 1000 | Animal feed | [24] |
| Portable paper-based aptasensor | 0.5–100 | 0.44 | Corn flour | [25] |
| Sensor Metal-Organic | 159–2865 | 23.14 | Breakfast cereal, maize powder and rice flour | [28] |
| Fluorescence Sensor | 20–100 | 18.0 | Corn and flour | [29] |
| HPLC-FLD/MIP | 100–500 | 5.0 | Refined corn oil | [30] |
| UHPLC-MS/MS | 0.50–200 | 0.15 | Feed | [31] |
| OMPD | 10–1000 | 4.40 | Corn | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laza, A.; Pereira, S.V.; Messina, G.A.; Fernández-Baldo, M.A.; Raba, J.; Regiart, M.D.; Bertolino, F.A. Origami Paper-Based Electrochemical Immunosensor with Carbon Nanohorns-Decorated Nanoporous Gold for Zearalenone Detection. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12010010
Laza A, Pereira SV, Messina GA, Fernández-Baldo MA, Raba J, Regiart MD, Bertolino FA. Origami Paper-Based Electrochemical Immunosensor with Carbon Nanohorns-Decorated Nanoporous Gold for Zearalenone Detection. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaza, Anabel, Sirley V. Pereira, Germán A. Messina, Martín A. Fernández-Baldo, Julio Raba, Matías D. Regiart, and Franco A. Bertolino. 2024. "Origami Paper-Based Electrochemical Immunosensor with Carbon Nanohorns-Decorated Nanoporous Gold for Zearalenone Detection" Chemosensors 12, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12010010
APA StyleLaza, A., Pereira, S. V., Messina, G. A., Fernández-Baldo, M. A., Raba, J., Regiart, M. D., & Bertolino, F. A. (2024). Origami Paper-Based Electrochemical Immunosensor with Carbon Nanohorns-Decorated Nanoporous Gold for Zearalenone Detection. Chemosensors, 12(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12010010







