Swelling Properties of Hydrogels Containing Phenylboronic Acids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
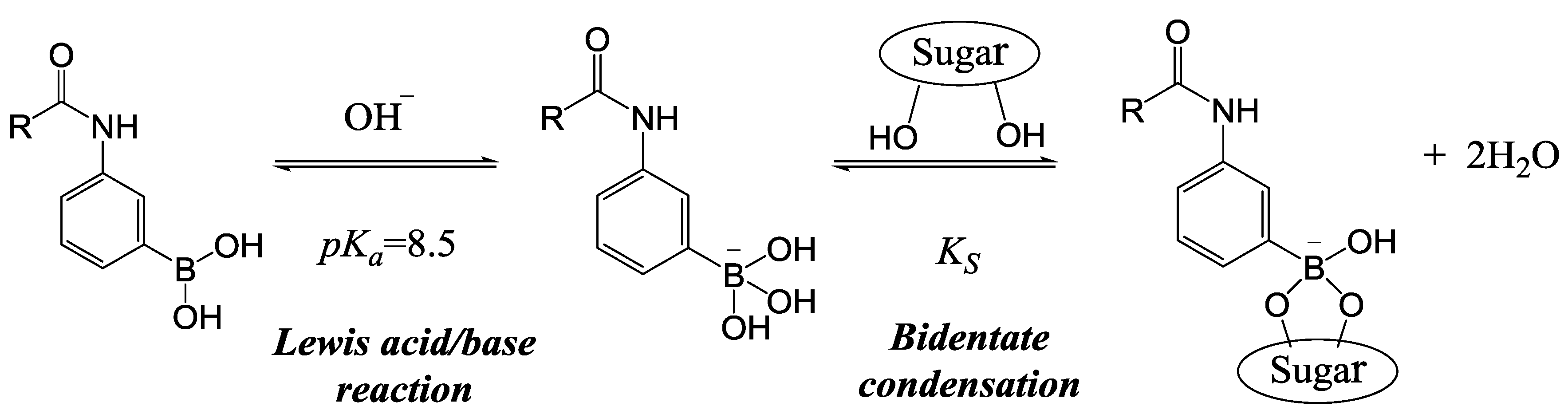


2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis of MPBA
2.2. p(MPBA-co-AAm) Hydrogels
2.3. p(MPBA-co-DMP-co-AAm) Hydrogels
2.4. Swelling Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. p(MPBA-co-AAm) Hydrogels


3.2. p(MPBA-co-DMP-co-AAm) Hydrogels



4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Diabetes Fact Sheet, 2011. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/pdf/ndfs_2011.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2013).
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, D.A.; Armour, J.C.; Baker, D.A. Advances and prospects in glucose assay technology. Diabetologia 1997, 40, S1025–S1107. [Google Scholar]
- Klonoff, D. Noninvasive blood glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 433–437. [Google Scholar]
- Koschwanez, H.E.; Reichert, W.M. In vitro, in vivo and post explantation testing of glucose-detecting biosensors: Current methods and recommendations. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3687–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, D.A.; Kumosa, L.S.; Routh, T.L.; Lin, J.T.; Lucisano, J.Y. Function of an implantanted tissue glucose sensor for more than 1 year in animals. Science Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Alexeev, V.; Das, S.; Finegold, D.; Asher, S. Photonic crystal glucose-sensing material for noninvasive monitoring of glucose in tear fluid. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 2353–2360. [Google Scholar]
- Alexeev, V.L.; Sharma, A.C.; Goponenko, A.V.; Das, S.; Lebedev, I.K.; Wilcox, C.S.; Finegold, D.N.; Asher, S.A. High ionic strength glucose-sensing photonic crystal. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 2316–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, S.A.; Alexeev, V.L.; Goponenko, A.V.; Sharma, A.C.; Lednev, I.K.; Wilcox, C.S.; Finegold, D.N. Photonic crystal carbohydrate sensors: Low ionic strength sugar sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3322–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscatello, M.; Stunja, L.E.; Asher, S.A. Polymerized crystalline colloidal array sensing of high glucose concentration. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4978–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Pruzinsky, S.A.; Braun, P.V. Glucose-sensitive inverse hydrogel opals: Analysis of optical diffraction response. Langmuir 2004, 20, 3096–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, A.M.; Marshall, A.J.; Kew, S.J.; Dean, K.E.S.; Creasey, C.D.; Kabilan, S. Crosslinking of phenylboronic acid receptors as a means of glucose selective holographic detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabilan, S.; Marshall, A.J.; Sartain, F.K.; Lee, M.-C.; Hussain, A.; Yang, X.; Blyth, J.; Karangu, N.; James, K.; Zeng, J.; Smith, D.; Domschke, A.; Lowe, C.R. Holographic glucose sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, S.; Falch, B.M.; Hjelme, D.R.; Stokke, B.T. Determination of glucose levels using a functionalized hydrogel-optical fiber biosensor: Toward continuous monitoring of blood glucose in vivo. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3630–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, S.; Volden, S.; Stokke, B.T. Glucose sensors based on a responsive gel incorporated as a fabry-perot cavity on a fiber-optic readout platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2034–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Chang, S.F.; Hao, H.; Tathireddy, P.; Orthner, M.; Magda, J.J.; Solzbacher, F. Osmotic swelling pressure response of smart hydrogels suitable for chronically implantable glucose sensors. Sens. Act. B 2010, 144, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orthner, M.; Lin, G.; Avula, M.; Buetefisch, S.; Magda, J.J.; Rieth, L.W.; Solzbacher, F. Hydrogel based sensor arrays (2×2) with perforated piezoresistive diaphragms for metabolic monitoring (in vitro). Sens. Act. B. 2010, 145, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, M.; Gerlach, G.; Wallmersperger, T. Piezoresistive biochemical sensors based on hydrogels. Microsyst. Technol. 2010, 16, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Baldi, A.; Nuxoll, E.; Siegel, R.A.; Ziaie, B. A hydrogel based implantable micromachined transponder for wireless glucose measurement. Diabet. Technol. Therap. 2006, 8, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.A.; Gu, Y.; Lei, M.; Baldi, A.; Nuxoll, E.; Ziaie, B. Hard and soft micro- and nanofabrication: An integrated approach to hydrogel based sensing and drug delivery. J. Control. Rel. 2010, 141, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Miyazaki, H.; Bunya, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y. Totally synthetic polymer gels responding to external glucose concentration: Their preparation and appliation to on-off regulation of insulin release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 12694–12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Yoshida, M.; Kataoka, K.; Aoyagi, T.; Miyahara, Y. A totally synthetic glucose responsive gel operating in physiological aqueous conditions. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 2203–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Yoshida, R.; Kataoka, K. Glucose-responsive polymer gel bearing phenylborate derivative as a glucose-sensing moiety operating at physiological pH. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiino, D.; Murata, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Koyama, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y. Preparation and characterization of a glucose-responsive insulin-releasing polymer device. Biomaterials. 1994, 15, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springsteen, G.; Wang, B. A detailed examination of boronic acid-diol complexation. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 5291–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Springsteen, G.; Deeter, S.; Wang, B. The relationship among pKa, pH, and binding constants in the interactions between boronic acids and diols—It is not as simple as it appears. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 11205–11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.A.; Gu, Y.; Baldi, A.; Ziaie, B. Novel swelling/shrinking behaviors of glucose-binding hydrogels and their potential use in a microfluidic delivery system. Macromol. Symp. 2004, 208, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Yang, X.; Lowe, C.R. Evidence for a cross-linked mechanism underlying glucose-induced contraction of phenylboronate hydrogel. J. Mol. Recognit. 2008, 21, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancla, C.; Lapeyre, V.; Gosse, I.; Catargi, B.; Ravaine, V. Designed glucose-responsive microgels with selective shrinking behavior. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12693–12701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiino, D.; Kubo, A.; Murata, Y.; Koyama, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Kikuchi, A.; Sakurai, Y.; Okano, T. Amine effect on phenylboronic acid complex with glucose under physiological pH in aqueous solution. J. Biomater. Sci. Polymer Ed. 1996, 7, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, S.; Hisamitsu, I.; Koyama, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y. Effect of the incorporation of amino groups in a glucose-responsive polymer complex having phenylboronic acid moieties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 1991, 2, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisamitsu, I.; Kataoka, K.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y. Glucose-responsive gel from phenylborate polymer and poly(vinyl alcohol): Prompt response at physiological pH through the interaction of borate with amino group in the gel. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiino, D.; Koyama, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y. Design of glucose responsive, insulin releasing device using polymers containing boronic acid groups. J. Artif. Org. 1992, 21, 1196–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y. Swelling Properties of Phenylboronic Acid-Containing Hydrogels and Their Applications in Microfluidic Drug Delivery Devices. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.; Stephens, D.; Blanch, H.; Prausnitz, J. Swelling equilibra for acrylamide based polyampholyte hydrogels. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 1955–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, A.; Mafe, S.; Mazanares, J.A.; Yu, X.; Grosberg, A.Y.; Tanaka, T. Equilibrium swelling properties of polyampholytic hydrogels. J. Chem. Phys. 1996, 104, 8713–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, T.; Pelton, R. Charge-switching, amphoteric glucose-responsive microgels with physiological swelling activity. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujumdar, S.K. Stimuli Sensitive Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery and Sensing Applications; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, T.; Ahanuma, H.; Yamanouchi, T. Increased fructose concentrations in blood and urine in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 353–357. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, A.; Mujumdar, S.K.; Siegel, R.A. Swelling Properties of Hydrogels Containing Phenylboronic Acids. Chemosensors 2014, 2, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors2010001
Kim A, Mujumdar SK, Siegel RA. Swelling Properties of Hydrogels Containing Phenylboronic Acids. Chemosensors. 2014; 2(1):1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Arum, Siddharthya K. Mujumdar, and Ronald A. Siegel. 2014. "Swelling Properties of Hydrogels Containing Phenylboronic Acids" Chemosensors 2, no. 1: 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors2010001
APA StyleKim, A., Mujumdar, S. K., & Siegel, R. A. (2014). Swelling Properties of Hydrogels Containing Phenylboronic Acids. Chemosensors, 2(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors2010001




