Ascorbic Acid Rejection Characteristics of Modified Platinum Electrodes: A Shelf Life Investigation
Abstract
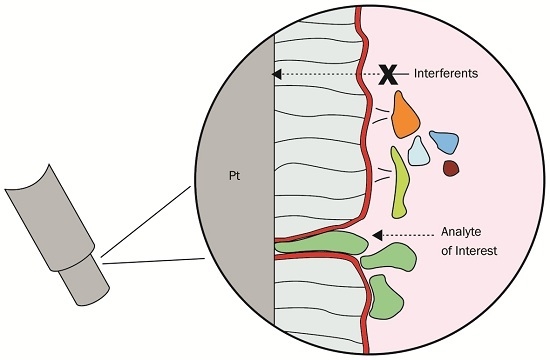
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Sensor Manufacture
2.3. Storage Conditions
2.4. AA Calibrations
2.5. Instrumentation and Software
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Shelf-Life Studies—Effect of Repeated AA Calibrations


 ” denotes level of significance against day 1. “ns” denotes no significant change.
” denotes level of significance against day 1. “ns” denotes no significant change.
| Pt-PPD | Pt-Nafion® (5/2) | Pt-Nafion® (1/2)-PPD | Pt-Nafion® (2/1)-PPD | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | Mean I (pA) | SEM | Stats | Mean I (pA) | SEM | Stats | Mean I (pA) | SEM | Stats | Mean I (pA) | SEM | Stats |
| 1 | 138 | 19 | 131 | 29 | −59 | 10 | 2 | 10 | ||||
| 3 | 147 | 10 | ns | 260 | 211 | ns | 141 | 107 | ns | 8 | 1 | ns |
| 7 | 150 | 53 | ns | 592 | 328 | ns | 2583 | 944 |  | 473 | 156 |  |
| 14 | 590 | 224 | ns | 1254 | 902 | ns | 2910 | 1000 |  | 1328 | 408 |  |
| 28 | 1847 | 684 |  | 1598 | 1099 | ns | 3299 | 1049 |  | 2231 | 594 |   |
| 56 | 2707 | 1031 |  | 3239 | 1175 |  | 6539 | 1504 |   | 4434 | 665 |    |

3.2. Shelf-Life Studies—Effect of Single AA Calibration


3.3. Effect of Various Storage Conditions on Shelf Life of Pt-PPD Electrodes
 ” denotes level of significance against day 1. “ns” denotes no significant change.
” denotes level of significance against day 1. “ns” denotes no significant change.
| 4 °C | 4 °C /N2 Saturated PBS | 4 °C /N2 Saturated | −20 °C | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | Mean I (pA) | SEM | Stats | Mean I (pA) | SEM | Stats | Mean I (pA) | SEM | Stats | Mean I (pA) | SEM | Stats |
| 1 | 19 | 4 | 18 | 7 | 251 | 27 | 139 | 23 | ||||
| 56 | 24 | 2 | ns | 1123 | 121 |    | 295 | 105 | ns | 804 | 302 |  |
| 168 | 3490 | 1276 |  | 4057 | 122 |    | 222 | 131 | ns | 1706 | 615 |  |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lowry, J.P.; O’Neill, R.D. Neuroanalytical chemistry in vivo using electrochemical sensors. Encycl. Sens. 2006, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Miele, M.; Fillenz, M. In vivo determination of extracellular brain ascorbate. J. Neurosci. Methods 1996, 70, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpat, S.; Alpat, S.K.; Telefoncu, A. A sensitive determination of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid using a Nafion-coated clinoptilolite-modified carbon paste electrode. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cass, W.A.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Mayfield, R.D.; Curella, P.; Zahniser, N.R. Differences in dopamine clearance and diffusion in rat striatum and nucleus accumbens following systemic cocaine adminstration. J. Neurochem. 1992, 59, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedemann, M.N.; Gerhardt, G.A. Regional effects of aging on dopaminergic function in the fischer-344 rat. Neurobiol. Aging 1992, 13, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedemann, M.N.; Robinson, S.W.; Gerhardt, G.A. O-phenylenediamine-modified carbon fiber electrodes for the detection of nitric oxide. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 2621–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, F.O.; Lowry, J.P. Microelectrochemical sensors for in vivo brain analysis: An investigation of procedures for modifying pt electrodes using Nafion. Analyst 2003, 128, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, F.O.; Finnerty, N.J.; Lowry, J.P. Nitric oxide monitoring in brain extracellular fluid: Characterisation of Nafion®-modified Pt electrodes in vitro and in vivo. Analyst 2009, 134, 2012–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariffin, A.A.; O’Neill, R.D.; Yahya, M.Z.A.; Zain, Z.M. Electropolymerization of ortho-phenylenediamine and its use for detection on hydrogen peroxide and ascorbic acid by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 10154–10163. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, J.P.; McAteer, K.; el Atrash, S.S.; Duff, A.; O’Neill, R.D. Characterisation of glucose oxidase modified poly (phenylenediamine) coated electrodes in vitro and in vivo: Homogenous interference by ascorbic acid in hydrogen peroxide detection. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.P.; Rocchitta, G.; Kirwan, S.M.; Killoran, S.J.; Serra, P.A.; Lowry, J.P.; O’Neill, R.D. Oxygen tolerance of an implantable polymer/enzyme composite glutamate biosensor displaying polycation-enhanced substrate sensitivity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malitesta, C.; Palmisano, F.; Torsi, L.; Zambonin, P.G. Glucose fast-response amperometric sensor based on glucose-oxidase immobilised in an electropolymerized poly(ortho-phenylenediamine) film. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, K.; Ohsaka, T.; Ohnuki, Y.; Oyama, N. Electrochemical preparation of a ladder polymer containing phenazine rings. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1987, 219, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, J. Electrochemical and structural studies on soluble and conducting polymer from o-phenylenediamine. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1995, 33, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losito, I.; Palmisano, F.; Zambonin, P.G. O-phenylenediamine electropolymerization by cyclic voltammetry combined with electrospray ionization-ion trap mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4988–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.R.; Ledo, A.; Frade, J.G.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Laranjinha, J.; Barbosa, R.M. Electrochemical measurement of endogenously produced nitric oxide in brain slices using Nafion/o-phenylenediamine modified carbon fiber microelectrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 535, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Tran, P.H.; Chao, J.K.; Ghodadra, R.; Rangarajan, R.; Thakor, N.V. In vivo nitric oxide sensor using non-conducting polymer-modified carbon fiber. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1998, 13, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, F.O.; Finnerty, N.J.; Bolger, F.B.; Millar, J.; Lowry, J.P. Calibration of no sensors for in vivo voltammetry: Laboratory synthesis of NO and the use of UV-visible spectroscopy for determining stock concentrations. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 381, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerty, N.J.; O’Riordan, S.L.; Brown, F.O.; Serra, P.A.; O’Neill, R.D.; Lowry, J.P. In vivo characterisation of a Nafion®-modified Pt electrode for real-time nitric oxide monitoring in brain extracellular fluid. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerty, N.J.; O’Riordan, S.L.; Palsson, E.; Lowry, J.P. Brain nitric oxide: Regional characterisation of a real-time microelectrochemical sensor. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 209, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, A.M.; Reid, C.H.; Finnerty, N.J. In vitro characterisation of ortho phenylenediamine and Nafion®-modified pt electrodes for measuring brain nitric oxide. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 732, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, F.B.; Bennett, R.; Lowry, J.P. An in vitro characterisation comparing carbon paste and Pt microelectrodes for real-time detection of brain tissue oxygen. Analyst 2011, 136, 4028–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, P.A.; Hebel, M.; Rocchitta, G.; Tate, R.F. Biotelemetry NET for Neurochemical Biosensor and Microsensor Applications: Design, Construction and Validation; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 119–144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, W.; Tian, X.; Yan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Preparation and characterization of a poly-o-phenylenediamine film modified glassy carbon electrode as a H2O2 sensor. Can. J. Chem. Revue Can. Chim. 2013, 91, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.B.; Killoran, S.J.; O’Neill, R.D.; Lowry, J.P. Development and characterization in vitro of a catalase-based biosensor for hydrogen peroxide monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2994–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, S.A.; Killoran, S.J.; O’Neill, R.D. Enzyme immobilization strategies and electropolymerization conditions to control sensitivity and selectivity parameters of a polymer-enzyme composite glucose biosensor. Sensors 2010, 10, 6439–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, S.A.; O’Neill, R.D. Effects of applied potential on the mass of non-conducting poly(ortho-phenylenediamine) electro-deposited on eqcm electrodes: Comparison with biosensor selectivity parameters. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 5413–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killoran, S.J.; O’Neill, R.D. Characterization of permselective coatings electrosynthesized on Pt-Ir from the three phenylenediamine isomers for biosensor applications. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7303–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, S.M.; Rocchitta, G.; McMahon, C.P.; Craig, J.D.; Killoran, S.J.; O’Brien, K.B.; Serra, P.A.; Lowry, J.P.; O’Neill, R.D. Modifications of poly(o-phenylenediamine) permselective layer on Pt-Ir for biosensor application in neurochemical monitoring. Sensors 2007, 7, 420–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, J.P.; O’Neill, R.D. Partial characterisation of in vitro glucose oxidase-modified poly(phenylenediamine)-coated electrodes for neurochemical analysis in vivo. Electroanalysis 1994, 6, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, R.J.; Adams, J.M.; Barone, N.J.; Yacynych, A.M. Electropolymerized films to prevent interferences and electrode fouling in biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1991, 6, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, P.; Dankoski, E.C.; Petrovic, J.; Keithley, R.B.; Wightman, R.M. Voltammetric detection of 5-hydroxytryptamine release in the rat brain. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9462–9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.; Ilgen, T.J.; Gordon, S.; Ranasinghe, A.D.; McFarland, E.W.; Metiu, H.; Buratto, S.K. Investigation of the enhanced signals from cations and dopamine in electrochemical sensors coated with Nafion. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2009, 632, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, F.; Mobius, C. In vivo selective monitoring of basal levels of cerebral dopamine using voltammetry with Nafion modified (NA-CRO) carbon fiber microelectrodes. J. Neurosci. Methods 1992, 42, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazell, M.P.; Kasser, R.J.; Renner, K.J.; Feng, J.; Moghaddam, B.; Adams, R.N. Electrocoating carbon-fiber microelectrodes with Nafion improves selectivity for electroactive neurotransmitters. J. Neurosci. Methods 1987, 22, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zook, L.A.; Leddy, J. Density and solubility of Nafion: Recast, annealed, and commercial films. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 3793–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.H.; Harrison, D.J. Permeability of glucose and other neutral species through recast perfluorosulfonated ionmer films. Anal. Chem. 1992, 64, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, R.C.; Moussy, F. In vitro and in vivo mineralization of Nafion membrane used for implantable glucose sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1998, 13, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, R.M.; Lourenco, C.F.; Santos, R.M.; Pomerleau, F.; Huettl, P.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Laranjinha, J. In vivo real-time measurement of nitric oxide in anesthetized rat brain. In Nitric Oxide, Part G: Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress in Redox Regulation of Cell Signaling; Cadenas, E., Packer, L., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; Volume 441, pp. 351–367. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, J.D.; O’Neill, R.D. Comparison of simple aromatic amines for electrosynthesis of permselective polymers in biosensor fabrication. Analyst 2003, 128, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.P.; Rocchitta, G.; Serra, P.A.; Kirwan, S.M.; Lowry, J.P.; O’Neill, R.D. Control of the oxygen dependence of an implantable polymer/enzyme composite biosensor for glutamate. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 2352–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, M.E.; Nicholson, C. Measurement of nanomolar dopamine diffusion using low-noise perfluorinated ionomer coated carbon-fiber microelectrodes and high-speed cyclic voltammetry. Anal. Chem. 1989, 61, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, S.; Bartroli, J.; Fabregas, E. Amperometric biosensor for the determination of histamine in fish samples. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, F.; Ustabas, S.; Arslan, H. An amperometric biosensor for glucose determination prepared from glucose oxidase immobilized in polyaniline-polyvinylsulfonate film. Sensors 2011, 11, 8152–8163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyurcsanyi, R.E.; Cristalli, A.; Nagy, G.; Nagy, L.; Corder, C.; Pendley, B.D.; Ufer, S.; Nagle, H.T.; Neuman, M.R.; Lindner, E. Analytical perfomance characteristics of thin and thick film amperometric microcells. Fresnius J. Anal. Chem. 2001, 369, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasso, S.V.; Pierce, R.J.; Walla, R.; Yacynych, A.M. Electropolymerized 1,2-diaminobenzene as a means to prevent interferences and fouling and to stabilize immobilized enzyme in electrochemical biosensors. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wynne, A.M.; Finnerty, N.J. Ascorbic Acid Rejection Characteristics of Modified Platinum Electrodes: A Shelf Life Investigation. Chemosensors 2015, 3, 55-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3020055
Wynne AM, Finnerty NJ. Ascorbic Acid Rejection Characteristics of Modified Platinum Electrodes: A Shelf Life Investigation. Chemosensors. 2015; 3(2):55-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3020055
Chicago/Turabian StyleWynne, Andrea M., and Niall J. Finnerty. 2015. "Ascorbic Acid Rejection Characteristics of Modified Platinum Electrodes: A Shelf Life Investigation" Chemosensors 3, no. 2: 55-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3020055
APA StyleWynne, A. M., & Finnerty, N. J. (2015). Ascorbic Acid Rejection Characteristics of Modified Platinum Electrodes: A Shelf Life Investigation. Chemosensors, 3(2), 55-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3020055