Stand-Off Chemical Detection Using Photoacoustic Sensing Techniques—From Single Element to Phase Array
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Consideration
- p
- represents the amplitude
- k
- is the wave number i.e., analogous to w
- w
- is the angular frequency
- t
- represents the time instance for the signal
- x
- represents the distance between the microphone and the acoustic source.
- = signal, and
- = signal-independent noise
- t = time instance
- T = sampling time interval,
- l describes the L-range samples recorded during T such that , and
- m is the M-sequential A-lines recorded in a frame such that .
- N signifies the number of microphones in the acoustic beam array
- = Signal to Noise Ratio from an acoustic beam array with N microphone elements.
- = signal received by the acoustic beam array
- = noise signal received by the beam array
2.2. Implementation and Measurement
2.2.1. Preliminary Work Review
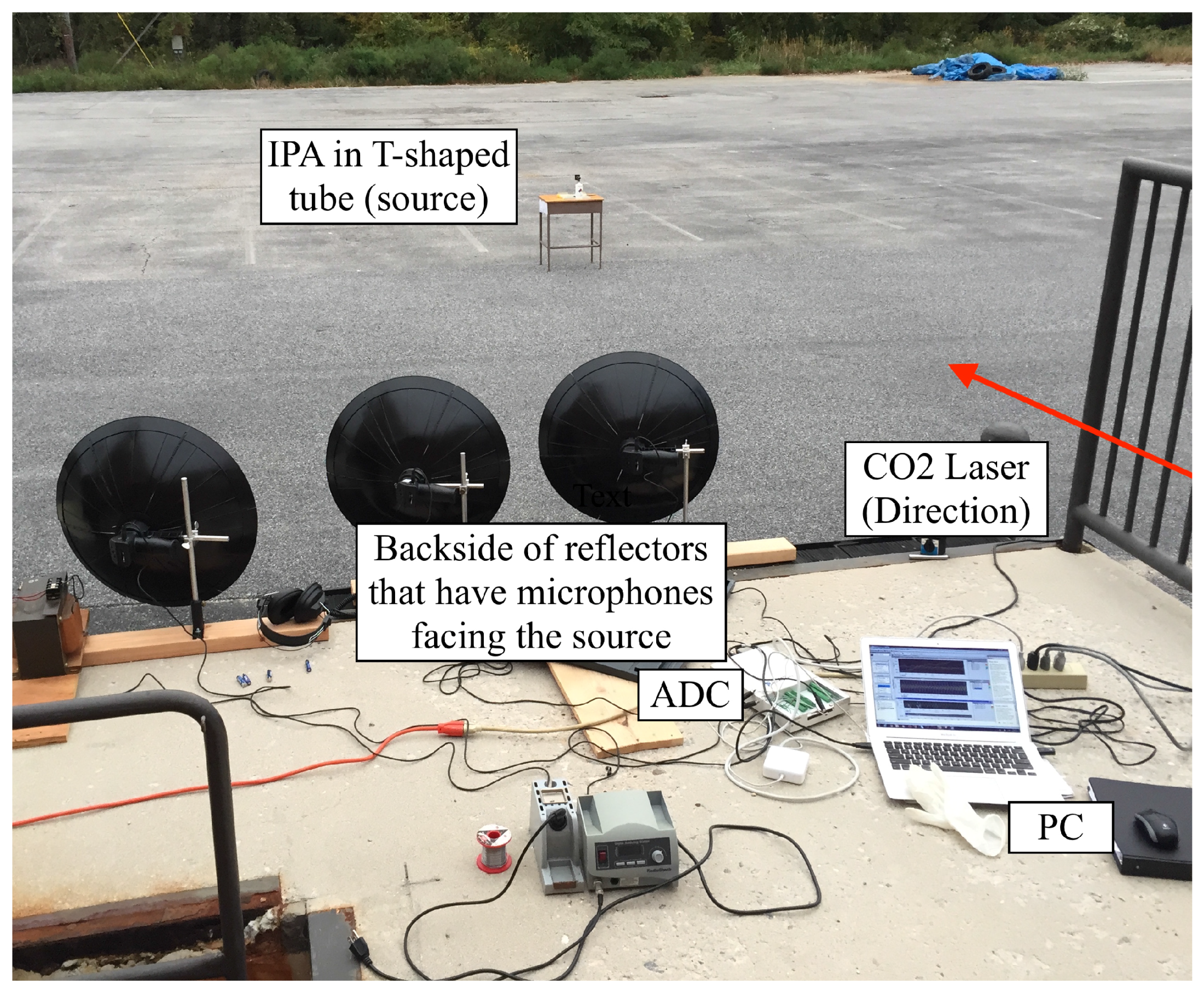
2.2.2. Outdoor Photoacoustic Sensing Implementation
2.2.3. Acoustic Beam Array Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PA | Photoacoustic |
| QCL | Quantum Cascade Laser |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| LD | linear dichroism |
References
- Pao, Y.-H. Optoacoustic Spectroscopy and Detection; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Rosencwaig, A. Photoacoustics and Photoacoustic Spectroscopy; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, A.G. Upon the Production of Sound by Radiant Energy; Gibson Brothers, Printers: Washington, DC, USA, 1881. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, R.L.; Prasad, R.; Bhar, G.C.; Thakur, S.N. Photoacoustic spectra and modes of vibration of tnt and rdx at CO2 laser wavelengths. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2002, 58, 3093–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giubileo, G.; Puiu, A. Photoacoustic spectroscopy of standard explosives in the mir region. Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2010, 623, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, K.T.; Yury, B.; Anatoliy, A.K.; Gerard, W. Recent advances in trace gas detection using quantum and interband cascade lasers. Rev. Laser Eng. 2006, 34, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki, G.; Curl, R.F.; Tittel, F.K.; Maulini, R.; Bulliard, J.-M.; Faist, J. Widely tunable mode-hop free external cavity quantum cascade laser for high resolution spectroscopic applications. Appl. Phys. B 2005, 81, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, N.; Chen, M.; Sengupta, S.; Slivken, S.; Razeghi, M. Ultra-broadband quantum cascade laser, tunable over 760 cm−1, with balanced gain. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 21159–21164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuzer, L.B. Ultralow gas concentration infrared absorption spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 1971, 42, 2934–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Cantu, A.A.; Chow, A.W.; Fussell, P.S.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Parmeter, J.E.; Sayler, G.S.; Shreeve, J.M.; Slusher, R.E.; Story, M.; et al. Existing and Potential Standoff Explosives Detection Techniques; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, C.K.N. Laser photoacoustic spectroscopy helps fight terrorism: High sensitivity detection of chemical warfare agent and explosives. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2008, 153, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagli, L.; Gaft, M. Raman scattering spectroscopy for explosives identification. In Proceedings of the Defense and Security Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 9–13 April 2008; p. 65520Z. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, A.; Von der Porten, S.; Patel, C.K.N. Standoff detection of explosive substances at distances of up to 150 m. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furstenberg, R.; Kendziora, C.A.; Stepnowski, J.; Stepnowski, S.V.; Rake, M.; Papantonakis, M.R.; Nguyen, V.; Hubler, G.K.; McGill, R.A. Stand-off detection of trace explosives via resonant infrared photothermal imaging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 224103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, A.; Franco, C.D.; Spagnolo, V.; Lugarà, P.M.; Scamarcio, G. Quantum cascade laser-based photoacoustic sensor for trace detection of formaldehyde gas. Sensors 2009, 9, 2697–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holthoff, E.; Bender, J.; Pellegrino, P.; Fisher, A. Quantum cascade laser-based photoacoustic spectroscopy for trace vapor detection and molecular discrimination. Sensors 2010, 10, 1986–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brassington, D.J. Photo-acoustic detection and ranging—A new technique for the remote detection of gases. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1982, 15, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olender, F.T.; Woody, B.A.; Newman, L.A. Photo-Acoustic Leak Detector with Multiple Beams. U.S. Patent 5,834,632, 10 November 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, U. History of acoustic beamforming. In Proceedings of the 1st Berlin Beamforming Conference, BeBeC, Berlin, 21–22 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fenn, A.J.; Temme, D.H.; Delaney, W.P.; Courtney, W.E. The development of phased-array radar technology. Linc. Lab. J. 2000, 12, 321–340. [Google Scholar]
- Yonak, S.H.; Dowling, D.R. Multiple Microphone Photoacoustic Leak Detection and Localization System and Method. U.S. Patent 6,227,036, 8 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yönak, S.H.; Dowling, D.R. Parametric dependencies for photoacoustic leak localization. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggeroer, A.B.; Kuperman, W.A.; Schmidt, H. Matched field processing: Source localization in correlated noise as an optimum parameter estimation problem. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1988, 83, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Janssen, D.; Kostov, D.; Choa, F.-S. Standoff chemical detection using quantum cascade lasers and photoacoustic sensing techniques. In Proceedings of the Quantum Electronics and Laser Science Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 1–6 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Guo, D.; Choa, F.-S.; Wang, C.-C.; Trivedi, S.; Snyder, A.P.; Ru, G.; Fan, J. Standoff photoacoustic detection of explosives using quantum cascade laser and an ultrasensitive microphone. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 2626–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cheng, L.; Guo, D.; Kostov, Y.; Choa, F.-S. Quantum cascade laser based standoff photoacoustic chemical detection. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 20251–20257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Choa, F.-S.; Holthoff, E.; Pellegrino, P.; Fan, J. Standoff chemical detection with parts per million level calibrated detection sensitivity. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 April–3 May 2013; p. 871007. [Google Scholar]
- Choa, F.-S.; Wang, C.-C.; Khurgin, J.; Samuels, A.; Trivedi, S.; Gupta, D. Standoff photoacoustic detections with high-sensitivity microphones and acoustic arrays. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense + Security, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–21 April 2016; p. 98240M. [Google Scholar]
- Graninger, A.; Chen, X.; Choa, F.-S. Stand-off chemical detection using acoustic beam forming & photoacoustic sensing. In Proceedings of the 16th International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Kraków, Poland, 5–9 July 2009; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lay, J.; Chen, X.; Choa, F.-S. Performance comparison of microphone and reflector array structures for real-time and outdoor photoacoustic chemical sensing. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 April–3 May 2013; p. 871009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kim, K.-S.; Insana, M.F. Snr comparisons of beamforming strategies. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2007, 54, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trees, H.L.V. Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]










© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.-C.; Trivedi, S.; Choa, F.-S. Stand-Off Chemical Detection Using Photoacoustic Sensing Techniques—From Single Element to Phase Array. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6010006
Gupta D, Chen X, Wang C-C, Trivedi S, Choa F-S. Stand-Off Chemical Detection Using Photoacoustic Sensing Techniques—From Single Element to Phase Array. Chemosensors. 2018; 6(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Deepa, Xing Chen, Chen-Chia Wang, Sudhir Trivedi, and Fow-Sen Choa. 2018. "Stand-Off Chemical Detection Using Photoacoustic Sensing Techniques—From Single Element to Phase Array" Chemosensors 6, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6010006
APA StyleGupta, D., Chen, X., Wang, C.-C., Trivedi, S., & Choa, F.-S. (2018). Stand-Off Chemical Detection Using Photoacoustic Sensing Techniques—From Single Element to Phase Array. Chemosensors, 6(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6010006




