Assessment of Cypermethrin Residues in Tobacco by a Bioelectric Recognition Assay (BERA) Neuroblastoma Cell-Based Biosensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological and Chemical Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation for the Cell-Based Biosensor Assessment
2.3. Cell Membrane Potential Measurements: Biosensor Set-Up
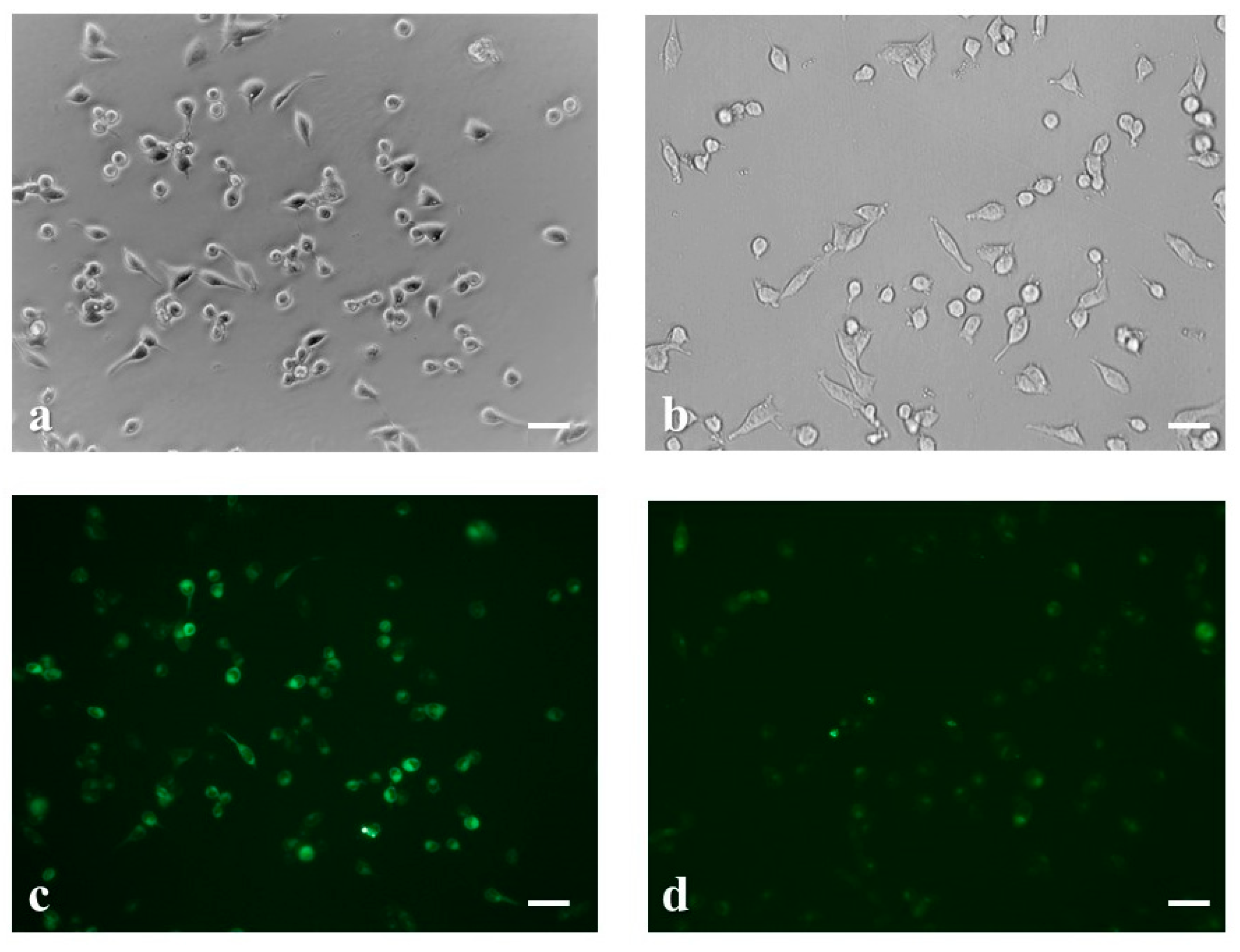
2.4. Intracellular Ca2+ Uptake Analysis by Fluorescence Imaging
2.5. Nicotine Chemical Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis and Experimental Design
2.7. Chromatographic Analysis of Cypermethrin Residues in Tobacco Leaves
3. Results
Neuroblastoma Cell-Based Biosensor Response against Cypermethrin Standard Solution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bilal, M.; Rasheed, T.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Raza, A.; Nabeel, F.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Biosorption: An Interplay between Marine Algae and Potentially Toxic Elements—A Review. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Zuberi, A.; Alagawany, M.; Farag, M.R.; Dadar, M.; Karthik, K.; Tiwari, R.; Dhama, K.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Cypermethrin induced toxicities in fish and adverse health outcomes: Its prevention and control measure adaptation. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 206, 863–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Rahman, M.; Hossain, S. Cypermethrin residue analysis of fruit and soil samples in eggplant ecosystem in Bangladesh. Sci. Lett. 2015, 3, 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Drossopoulos, J.; Bouranis, D.; Kintzios, S.; Aivalakis, G.; Triposkoufi, A. Distribution profiles of selected micronutrients in oriental field-grown tobacco plants as affected by nitrogen fertilization. J. Plant Nutr. 1998, 21, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgman, A.; Perfetti, T.A. The Chemical Components of Tobacco and Tobacco Smoke; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen, C.D.; Amdur, M.O.; Doull, J. Casarett & Doull’s Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poisons; McGraw-Hill: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wolansky, M.J.; Harrill, J.A. Neurobehavioral toxicology of pyrethroid insecticides in adult animals: A critical review. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2008, 30, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.L.; Casida, J.E. Pyrethroid toxicology:mouse intracerebral structure-toxicity relationships. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1982, 18, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Ares, I.; Ramos, E.; Castellano, V.; Martínez, M.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Anadón, A.; Martínez, M.A. Evidence for dose-additive effects of a type II pyrethroid mixture. In vitro assessment. Environ. Res. 2015, 138, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkiewicz, K.; Koteras, M.; Folkesson, R.; Brzezinski, J.; Winblad, B.; Szutowski, M.; Benedikz, E. Cypermethrin alters Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein levels in the rat brain. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 21, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raszewski, G.; Lemieszek, M.K.; Łukawski, K. Cytotoxicity induced by cypermethrin in human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2016, 23, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Ramos, E.; Ares, I.; Castellano, V.; Martínez, M.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Anadón, A.; Martínez, M.A. Oxidative stress and gene expression profiling of cell death pathways in alpha-cypermethrin-treated SH-SY5Y cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 91, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, S.K.; Mishra, J.; Tripathi, V.K.; Sharma, R.; Siddiqui, M.H. Cypermethrin induces astrocyte damage: Role of aberrant Ca(2+), ROS, JNK, P38, matrix metalloproteinase 2 and migration related reelin protein. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 111, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soderlund, D. Molecular mechanisms of pyrethroid insecticide neurotoxicity: Recent advances. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, M.; Dingemans, M.M.; Berg, M.V.D.; Westerink, R.H. Inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels as common mode of action for (mixtures of) distinct classes of insecticides. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 141, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, M.; Brandsema, J.A.; Nieuwenhuis, D.; Wijnolts, F.M.; Dingemans, M.M.; Westerink, R.H. Inhibition of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels After Subchronic and Repeated Exposure of PC12 Cells to Different Classes of Insecticides. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 147, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.G. The neurotoxicity of organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticides. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 131, 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.M.; Liu, J.; Richardson, J.R. Pyrethroid Insecticides Directly Activate Microglia Through Interaction with Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 155, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taju, G.; Majeed, S.A.; Nambi, K.S.; Farook, M.A.; Vimal, S.; Hameed, A.S.S. In vitro cytotoxic, genotoxic and oxidative stress of cypermethrin on five fish cell lines. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 113, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrikou, S.; Flampouri, K.; Moschopoulou, G.; Mangana, O.; Michaelides, A.; Kintzios, S. Assessment of Organophosphate and Carbamate Pesticide Residues in Cigarette Tobacco with a Novel Cell Biosensor. Sensors 2008, 8, 2818–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiades, M.; Lehotay, S.J. Fast and easy multiresidue methods employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412–413. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, Q.; Han, L.; Hou, C.; Wang, F.; Liu, A. A sensitive acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on gold nanorods modified electrode for detection of organophosphate pesticide. Talanta 2016, 156, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.; Momtaz, S.; Vakhshiteh, F.; Maghsoudi, A.S.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Abdollahi, M. Biosensors and their applications in detection of organophosphorus pesticides in the environment. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 91, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschopoulou, G.; Dourou, A.M.; Fidaki, A.; Kintzios, S. Assessment of pesticides cytoxicity by means of bioelectric profiling of mammalian cells. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 8, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintzios, S.; Pistola, E.; Panagiotopoulos, P.; Bomsel, M.; Alexandropoulos, N.; Bem, F.; Ekonomou, G.; Biselis, J.; Levin, R. Bioelectric recognition assay (BERA). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flampouri, K.; Mavrikou, S.; Kintzios, S.; Miliadis, G.; Aplada-Sarlis, P. Development and validation of a cellular biosensor detecting pesticide residues in tomatoes. Talanta 2010, 80, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferentinos, K.P.; Yialouris, C.P.; Blouchos, P.; Moschopoulou, G.; Kintzios, S. Pesticide Residue Screening Using a Novel Artificial Neural Network Combined with a Bioelectric Cellular Biosensor. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 813519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard, B. Foods of Plant Origin—Determination of Pesticide Residues Using GC-MS and/or LC-MS/MS Following Acetonitrile Extraction/Partitioning and Clean-up by Dispersive SPE—QuEChERS Method. Available online: https://standards.globalspec.com/std/10387667/EN%2015662 (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- Instruments, T. Amplifiers for Any System. Available online: https://www.ti.com/amplifier-circuit/overview.html (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Ungvari, Z.; Labinskyy, N.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Pinto, J.T.; Bagi, Z.; Ballabh, P.; Zhang, C. Resveratrol attenuates mitochondrial oxidative stress in coronary arterial endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. 2009, 297, H1876–H1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambwekar, K.R.; Kakariya, R.B.; Garg, S. A validated high performance liquid chromatographic method for analysis of nicotine in pure form and from formulations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 32, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardous, Z.; Islam, M.N.; Hoque, S.M.; Chowdhury, M.A.Z.; Rahman, M.A. Determination of some selected pesticide residues in tomato from different locations of Bangladesh. Int. J. Sustain. Agric. Technol. 2007, 3, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, A.Z.; Jahan, S.A.; Islam, M.N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Alam, M.K.; Zaman, M.A.; Karim, N.; Gan, S.H. Occurrence of organophosphorus and carbamate Pesticide residues in surface water samples from the Rangpur district of Bangladesh. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, B.; Mohammad, A.B.; Nahlé, A.; Vats, M.; Assaf, O.A.; Al-Zarooni, H. Analytical Determination of Nicotine and Tar Levels in Various Dokha and Shisha Tobacco Products. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 42, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, S.; Khashyarmanesh, Z.; Moalemzadeh-Haghighi, H. Nicotine content of domestic cigarettes, imported cigarettes and pipe tobacco in iran. Addict. Health 2012, 4, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pundir, C.S.; Chauhan, N. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition-based biosensors for pesticide determination: A review. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 429, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.; Bhardwaj, A. Biosensor technology for pesticides—A review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 3093–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zheng, Z.; Li, X. Advances in pesticide biosensors: Current status, challenges, and future perspectives. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 63–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedler, J.L.; Roffler-Tarlov, S.; Schachner, M.; Freedman, L.S. Multiple neurotransmitter synthesis by human neuroblastoma cell lines and clones. Cancer Res. 1978, 38, 3751–3757. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chrysafides, S.M.; Sharma, S. Physiology, Resting Potential; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, K.S.; Du, Y.; Nomura, Y.; Oliveira, E.E.; Salgado, V.L.; Zhorov, B.S.; Dong, K. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels as Insecticide Targets. Adv. Insect Physiol. 2014, 46, 389–433. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, R.E.; Ross, S.A.; Drago, J.; Loiacono, R.E. Dose-related neuroprotective effects of chronic nicotine in 6-hydroxydopamine treated rats, and loss of neuroprotection in alpha4 nicotinic receptor subunit knockout mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 132, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, X.; Gerzanich, V.; Anand, R.; Wang, F.; Lindstrom, J. Chronic nicotine treatment up-regulates alpha3 and alpha7 acetylcholine receptor subtypes expressed by the human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Nelson, M.E.; Kuryatov, A.; Olale, F.; Cooper, J.; Keyser, K.; Lindstrom, J. Chronic nicotine treatment up-regulates human alpha3 beta2 but not alpha3 beta4 acetylcholine receptors stably transfected in human embryonic kidney cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 28721–28732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokolova, E.; Matteoni, C.; Nistri, A. Desensitization of neuronal nicotinic receptors of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells during short or long exposure to nicotine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambrose, V.; Miller, J.H.; Dickson, S.J.; Hampton, S.; Truman, P.; Lea, R.A.; Fowles, J. Tobacco particulate matter is more potent than nicotine at upregulating nicotinic receptors on SH-SY5Y cells. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2007, 9, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buisson, B.; Bertrand, D. Chronic exposure to nicotine upregulates the human (alpha)4(beta)2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.N.; Amin, J.; Weiss, D.S.; Wecker, L. Sustained nicotine exposure differentially affects alpha 3 beta 2 and alpha 4 beta 2 neuronal nicotinic receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinari, E.J.; Delbono, O.; Messi, M.L.; Renganathan, M.; Arneric, S.P.; Sullivan, J.P.; Gopalakrishnan, M. Up-regulation of human alpha7 nicotinic receptors by chronic treatment with activator and antagonist ligands. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 347, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, D.L.; Pakkanen, J.; Wonnacott, S. Effects of chronic drug treatments on increases in intracellular calcium mediated by nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in SH-SY5Y cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Sample | Spiking Amount in 2 g of Leaf Sample (μg) | Spiking Level (μg mL−1) | Measured (μg mL−1) | Mean Recovery % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 657 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 658 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 659 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 660 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 940 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 80 |
| 941 | 1.75 | 1.75 | 1.5 | 85.7 |
| 942 | 2 | 2 | 1.5 | 75 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apostolou, T.; Mavrikou, S.; Denaxa, N.-K.; Paivana, G.; Roussos, P.A.; Kintzios, S. Assessment of Cypermethrin Residues in Tobacco by a Bioelectric Recognition Assay (BERA) Neuroblastoma Cell-Based Biosensor. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040058
Apostolou T, Mavrikou S, Denaxa N-K, Paivana G, Roussos PA, Kintzios S. Assessment of Cypermethrin Residues in Tobacco by a Bioelectric Recognition Assay (BERA) Neuroblastoma Cell-Based Biosensor. Chemosensors. 2019; 7(4):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040058
Chicago/Turabian StyleApostolou, Theofylaktos, Sophia Mavrikou, Nikoleta-Kleio Denaxa, Georgia Paivana, Peter A. Roussos, and Spyridon Kintzios. 2019. "Assessment of Cypermethrin Residues in Tobacco by a Bioelectric Recognition Assay (BERA) Neuroblastoma Cell-Based Biosensor" Chemosensors 7, no. 4: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040058
APA StyleApostolou, T., Mavrikou, S., Denaxa, N.-K., Paivana, G., Roussos, P. A., & Kintzios, S. (2019). Assessment of Cypermethrin Residues in Tobacco by a Bioelectric Recognition Assay (BERA) Neuroblastoma Cell-Based Biosensor. Chemosensors, 7(4), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040058









