Label-Free Colorimetric Detection of Urine Glucose Based on Color Fading Using Smartphone Ambient-Light Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.3. Method Optimization
2.3.1. TMB and HRP Amount, and Reaction-Time Optimization
2.3.2. Additional H2O2 Quality Optimization
2.3.3. GOD Quality Optimization
2.4. Urine Glucose Determination
2.5. Validation Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis Principle
3.2. Optimized-Experiment Results
3.2.1. TMB and HRP Amount, and Reaction Time
3.2.2. Optimized Results of Additional H2O2 Amount
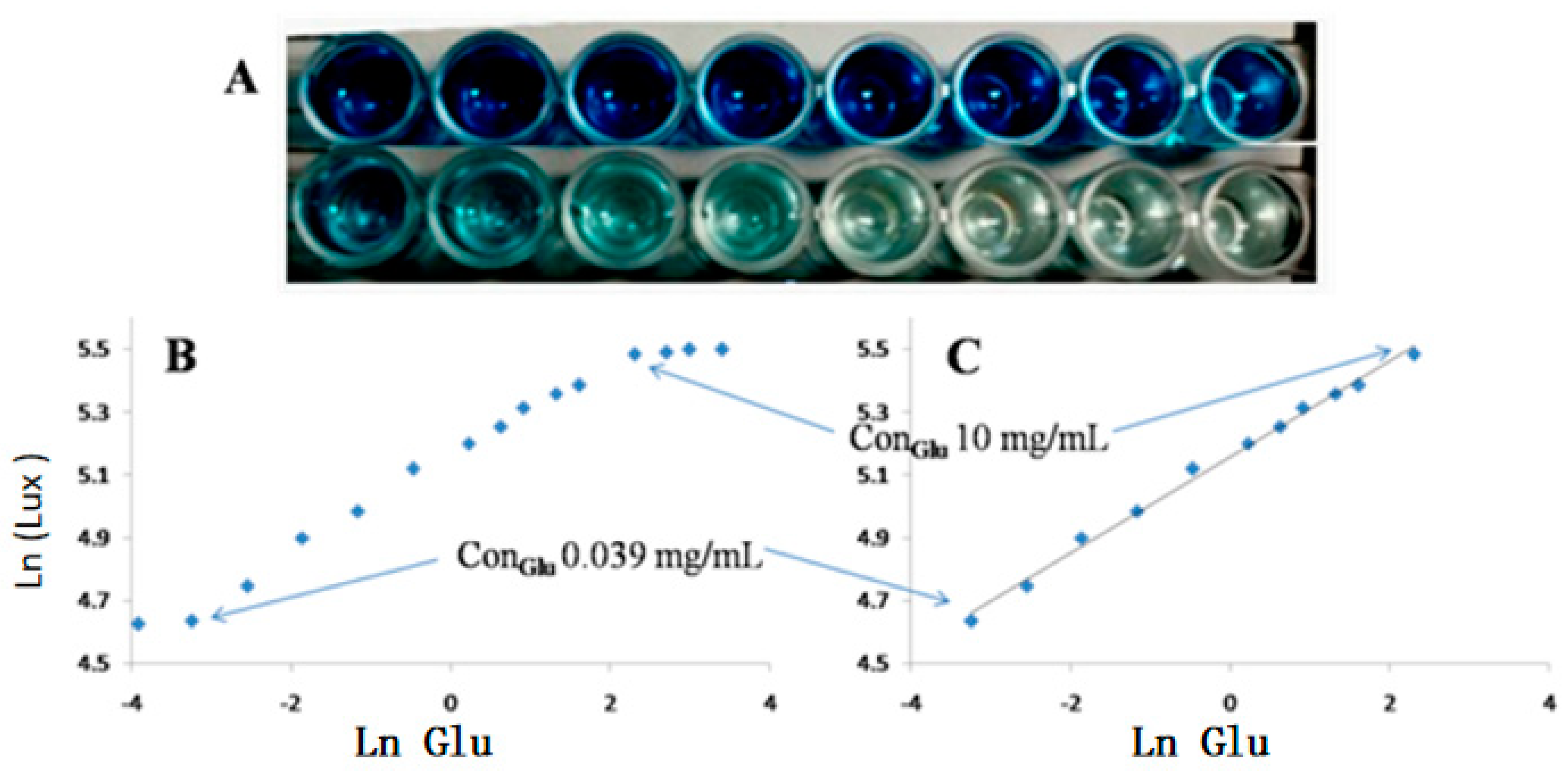
3.3. Method Validation
3.4. Glucose Determination in Urine Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.F.; Foster, J.R. A history of blood glucose meters and their role in self-monitoring of diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 69, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.N.; Anderson, S.R.; Singh, S.; Ramanathan, R.; Bansal, V. Nanostructured silver fabric as a free-standing NanoZyme for colorimetric detection of glucose in urine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Enter, B.J.; von Hauff, E. Challenges and perspectives in continuous glucose monitoring. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 5032–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-L.; Xie, J.; Liang, J.; Dong, G.-T.; Ding, L.-S.; Luo, P.; Qing, L.-S. Competitive Protein Binding Assay of Naproxen by Human Serum Albumin Functionalized Silicon Dioxide Nanoparticles. Molecules 2019, 24, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, L.; Feng, J.; Zhou, X.; Ren, C.; Li, H.; Chen, X. Colorimetric Detection of Urine Glucose Based ZnFe2O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5753–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-H.; Hong, C.P.; Zhu, J.F.; Chen, T.-T.; Chan, C.-T.; Ko, Y.-C.; Lin, T.-L.; Pan, Z.-B.; Sun, N.-K.; Wang, Y.-C.; et al. Ag@Au nanoprism-metal organic framework-based paper for extending the glucose sensing range in human serum and urine. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 6985–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Niu, X.; Chen, X. One-step synthesis of nitrogen, boron co-doped fluorescent carbon nanoparticles for glucose detection. Luminescence 2017, 32, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashist, S.K.; Luong, J.H.T. Commercially Available Smartphone-Based Personalized Mobile Healthcare Technologies. In Point-of-Care Technologies Enabling Next-Generation Healthcare Monitoring and Management; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 10, pp. 81–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kanchi, S.; Sabela, M.I.; Mdluli, P.S.; Inamuddin; Bisetty, K. Smartphone based bioanalytical and diagnosis applications: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.-L.; Huang, W.-X.; Zhang, P.-J.; Chen, L.; Lio, C.-K.; Zhou, H.; Qing, L.-S.; Luo, P. Colorimetric determination of the early biomarker hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) in circulating exosomes by using a gold seed-coated with aptamer-functionalized Au@Au core-shell peroxidase mimic. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Vandevoorde, K.; Wouters, N.; Kayacan, E.; De Baerdemaeker, J.G.; Saeys, W. Detection of red and bicoloured apples on tree with an RGB-D camera. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 146, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, F.; Cai, Z.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; He, J. Sensitive colorimetric assay for uric acid and glucose detection based on multilayer-modified paper with smartphone as signal readout. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J. A portable system for on-site quantification of formaldehyde in air based on G-quadruplex halves coupled with A smartphone reader. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.-T.; Lio, C.k.; Huang, H.; Wang, R.-Y.; Zhou, H.; Luo, P.; Qing, L.-S. A feasible image-based colorimetric assay using a smartphone RGB camera for point-of-care monitoring of diabetes. Talanta 2020, 206, 120211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S. Point of care sensing and biosensing using ambient light sensor of smartphone: Critical review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.M.; Han, Y.D.; Chun, H.J.; Yoon, H.C. Ambient light-based optical biosensing platform with smartphone-embedded illumination sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, Q.; Li, D.; Xie, J.; Ke, D.; Song, Q.; Tang, Y.; Wang, H. A smartphone colorimetric reader integrated with an ambient light sensor and a 3D printed attachment for on-site detection of zearalenone. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6567–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Yao, C.; Yu, S.; Xiao, W.; Tang, Y. Novel versatile smart phone based Microplate readers for on-site diagnoses. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.-L.; Li, J.; Li, X.-D.; Ding, L.-S.; Xie, J.; Qing, L.-S. A simple nano-SiO2-based ELISA method for residue detection of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in bean sprouts. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-L.; Li, J.; Li, X.-D.; Tao, W.-J.; Ding, L.-S.; Luo, P.; Qing, L.-S. An efficient direct competitive nano-ELISA for residual BSA determination in vaccines. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4607–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-L.; Xie, J.; Li, X.-D.; Ding, L.-S.; Liang, J.; Luo, P.; Qing, L.-S. Development of a nano-SiO2 based enzyme-linked ligand binding assay for the determination of ibuprofen in human urine. Talanta 2017, 167, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnao, M.B.; Acosta, M.; Rio, J.A.D.; Varón, R.; García-Cánovas, F. A kinetic study on the suicide inactivation of peroxidase by hydrogen peroxide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1041, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.F.; Park, J.Y. Plain to point network reduced graphene oxide - activated carbon composites decorated with platinum nanoparticles for urine glucose detection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, Z.B.; Wang, Y.C.; Chakkaradhari, G.; Zhu, J.F.; He, R.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Koshevoy, I.O.; Chou, P.T.; Pan, S.W. A silver metal complex as a luminescent probe for enzymatic sensing of glucose in blood plasma and urine. Dalton Transactions 2018, 10, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabriel, E.F.M.; Garcia, P.T.; Cardoso, T.M.G.; Lopes, F.M.; Martins, F.T.; Coltro, W.K.T. Highly sensitive colorimetric detection of glucose and uric acid in biological fluids using chitosan-modified paper microfluidic devices. The Analyst 2016, 141, 4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciucu, A.A. Chemically Modified Electrodes in Biosensing. J. Biosen. Bioelectron. 2014, 5, 1000154. [Google Scholar]


| Analyte | Probe | Detection Method | Linear Response Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | GRGO/AC a | Cyclic voltammetry method | 0.002–10 mM | 2 μM | [24] |
| Ag@Au-Ir-Zne MOFs b | Phosphorescence intensity | 0.05–30.0 mM | 0.038 mM | [7] | |
| Ag3 | Phosphorescence intensity | 1.0–35 mM | 0.09 mM | [25] | |
| NB-CNPs c | Fluorescence quenching | 0–900 μM | 1.8 μM | [8] | |
| ZnFe2O4 MNPs d | Colorimetric detection | 1.25–18.75 μM | 0.3 μM | [6] | |
| µPADs with chitosan e | Colorimetric detection | 130–380 µM. | 27 μM | [26] | |
| GR-CNT-ZnO f | Electrochemistry | - | 4.5 μM | [27] | |
| - | Phone ALS detection g | 0.2–55.6 μM | 0.03 μM | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.-T.; Guo, K.; Hu, X.-M.; Liang, J.; Li, X.-D.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Xie, J. Label-Free Colorimetric Detection of Urine Glucose Based on Color Fading Using Smartphone Ambient-Light Sensor. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8010010
Wang T-T, Guo K, Hu X-M, Liang J, Li X-D, Zhang Z-F, Xie J. Label-Free Colorimetric Detection of Urine Glucose Based on Color Fading Using Smartphone Ambient-Light Sensor. Chemosensors. 2020; 8(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tian-Tian, Kun Guo, Xue-Mei Hu, Jian Liang, Xing-De Li, Zhi-Feng Zhang, and Jing Xie. 2020. "Label-Free Colorimetric Detection of Urine Glucose Based on Color Fading Using Smartphone Ambient-Light Sensor" Chemosensors 8, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8010010
APA StyleWang, T.-T., Guo, K., Hu, X.-M., Liang, J., Li, X.-D., Zhang, Z.-F., & Xie, J. (2020). Label-Free Colorimetric Detection of Urine Glucose Based on Color Fading Using Smartphone Ambient-Light Sensor. Chemosensors, 8(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8010010




