Application of the Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Combined with Microfluidic System and Calibration Readout Circuit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the CZO Sensor
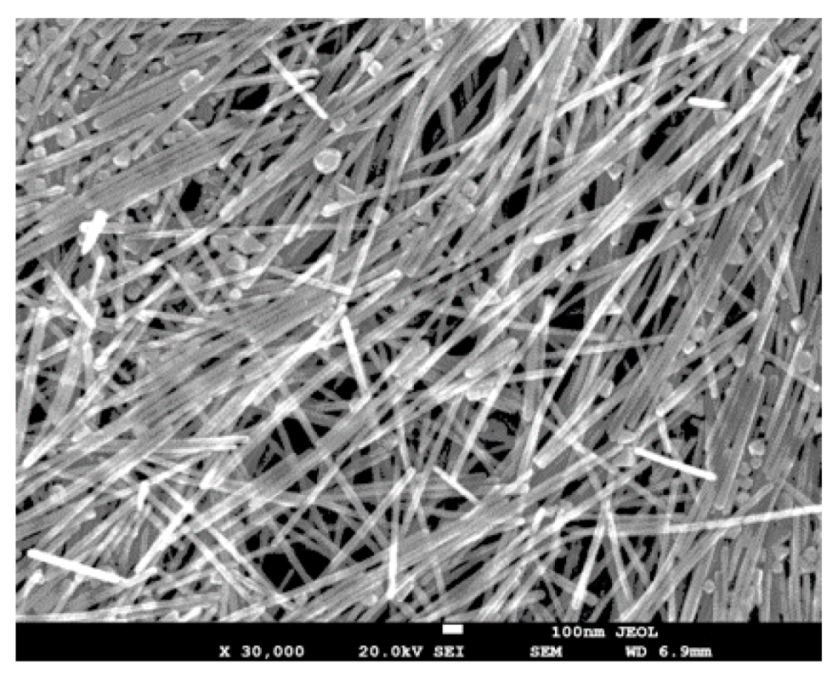
2.3. Fabrication of the AgNWs
3. Results
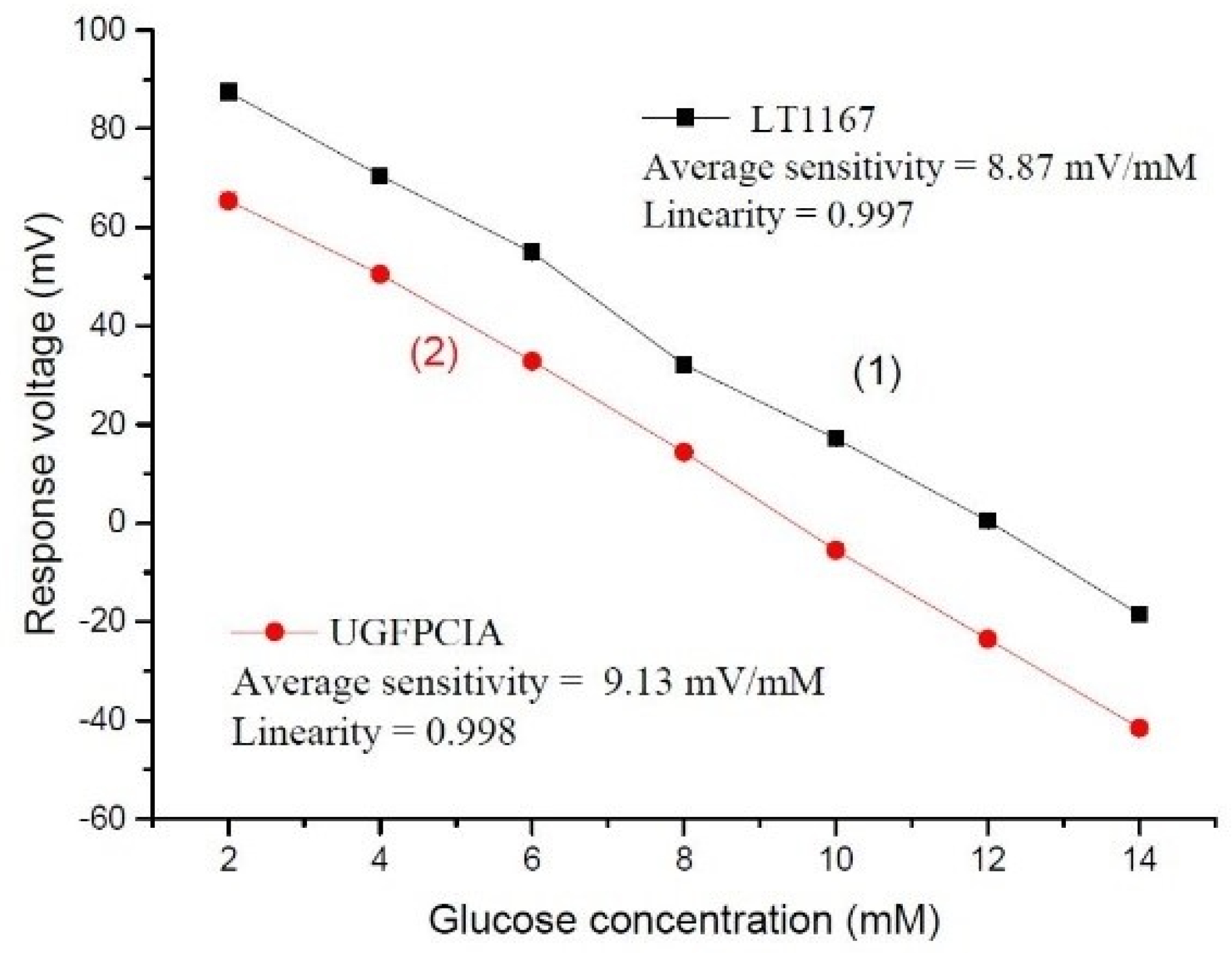
3.1. Sensing Performances of the Sensor
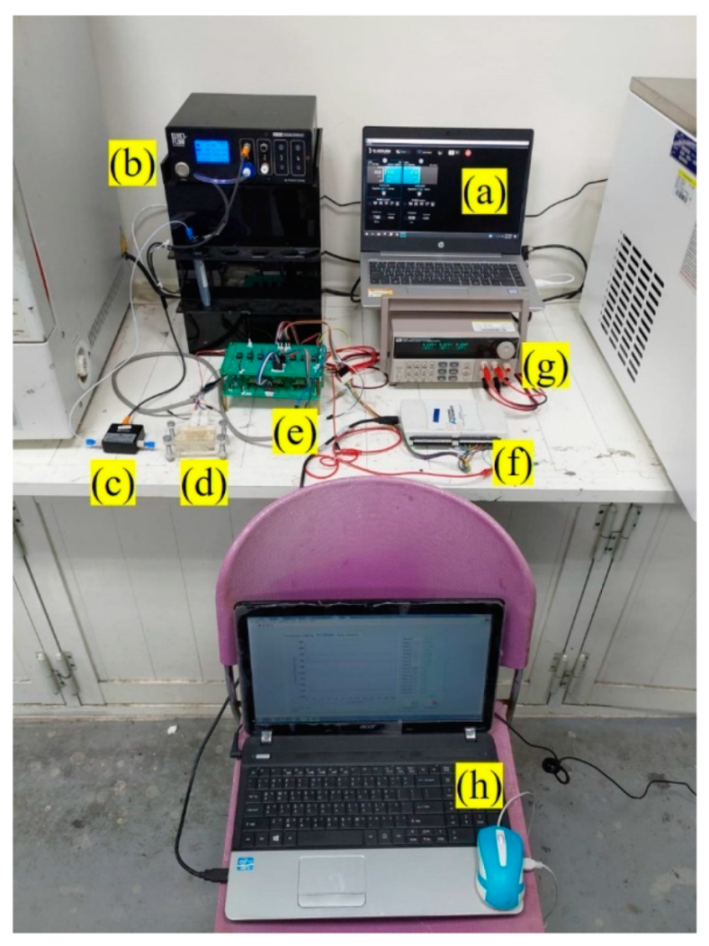
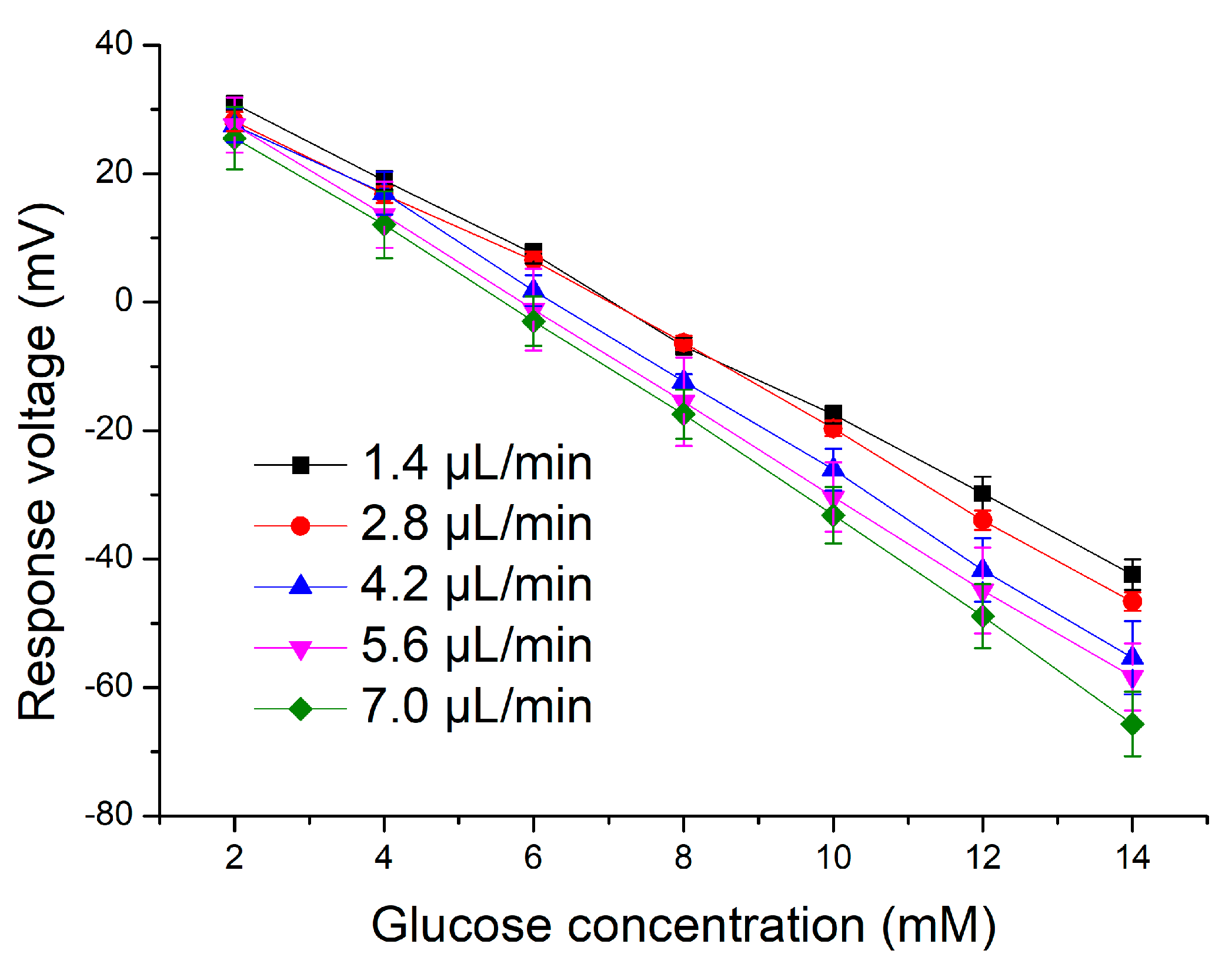
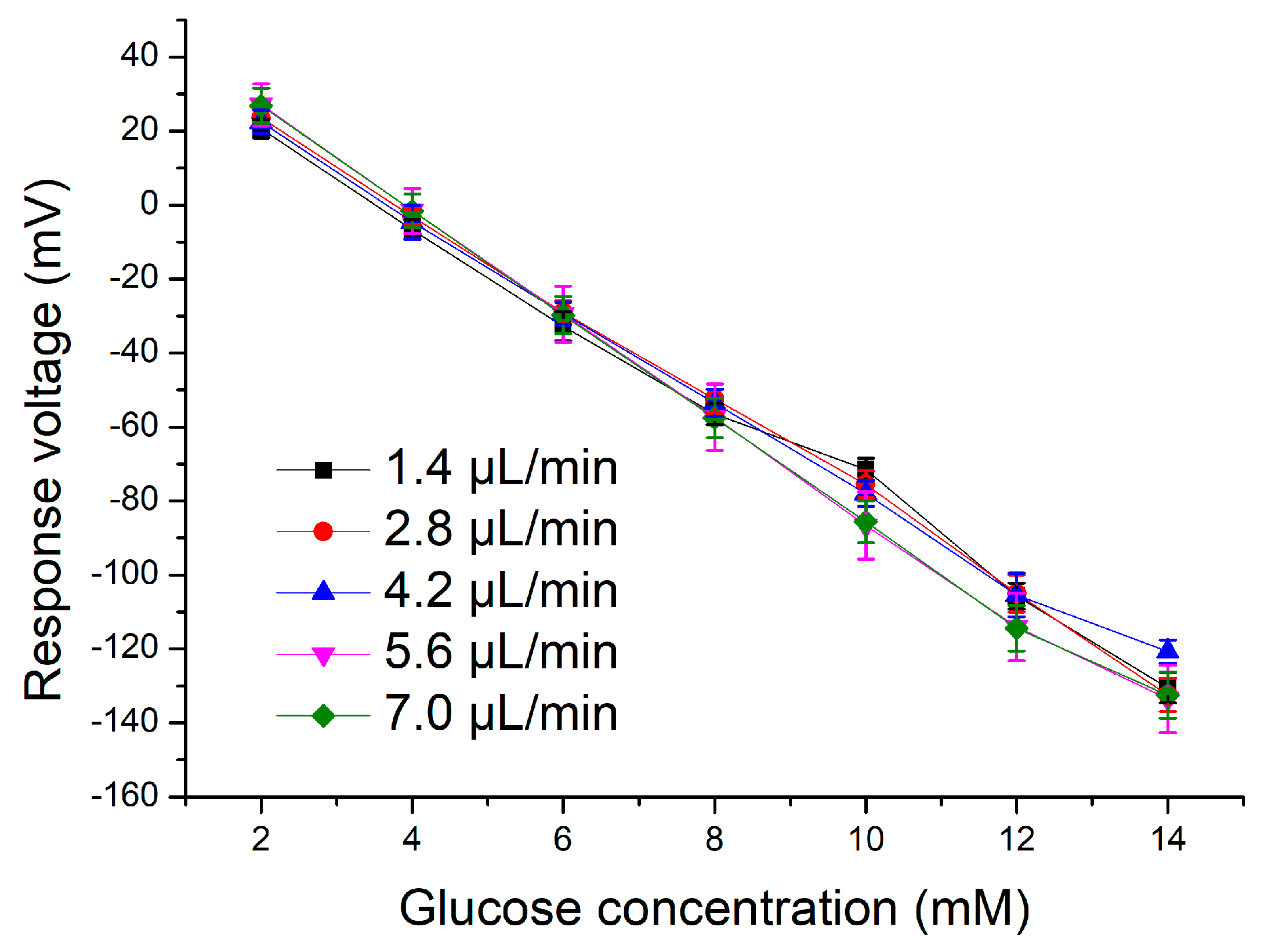
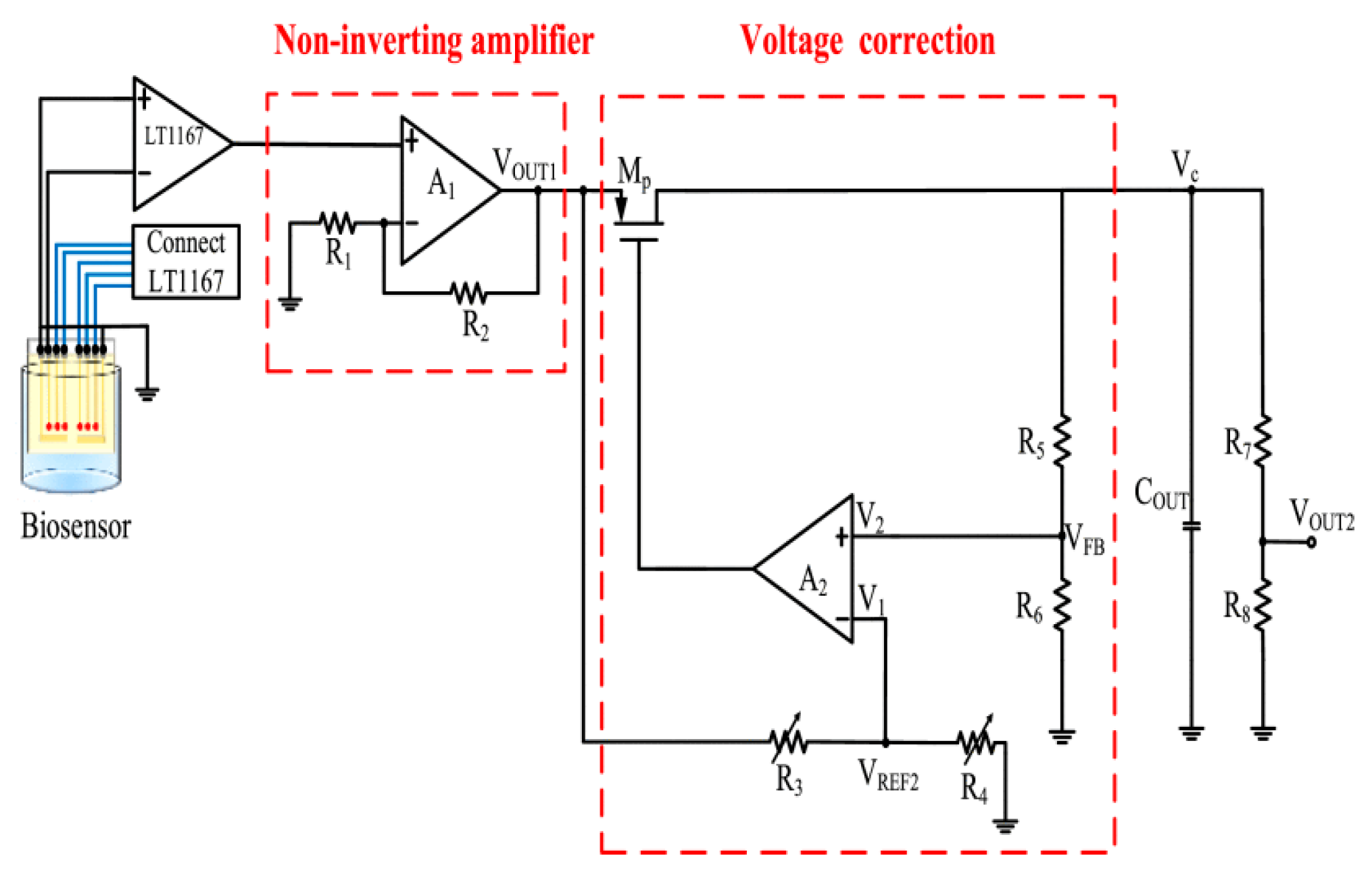
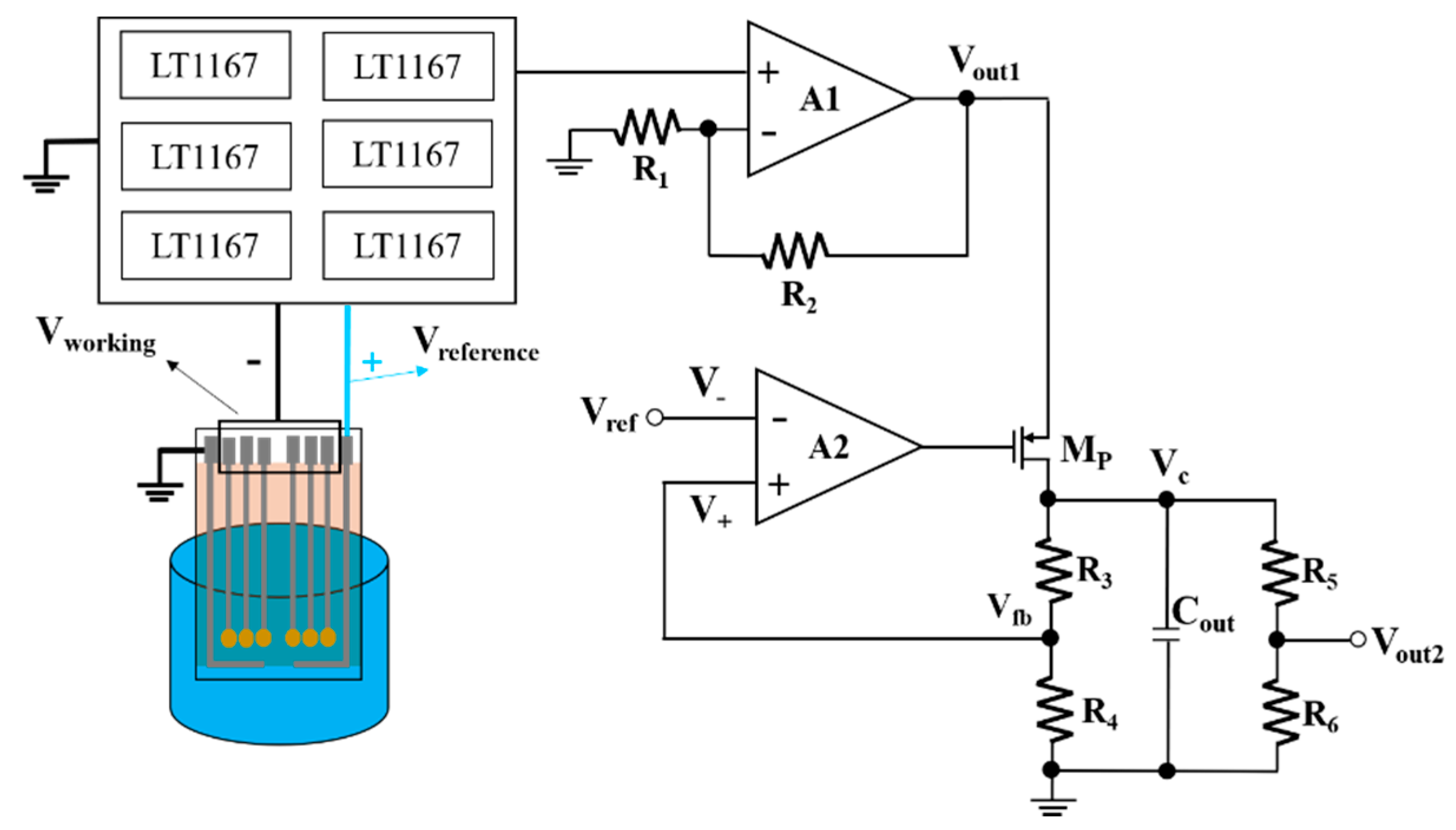
3.2. Application of the Microfluidic System
3.3. Drift Effects of the Sensor
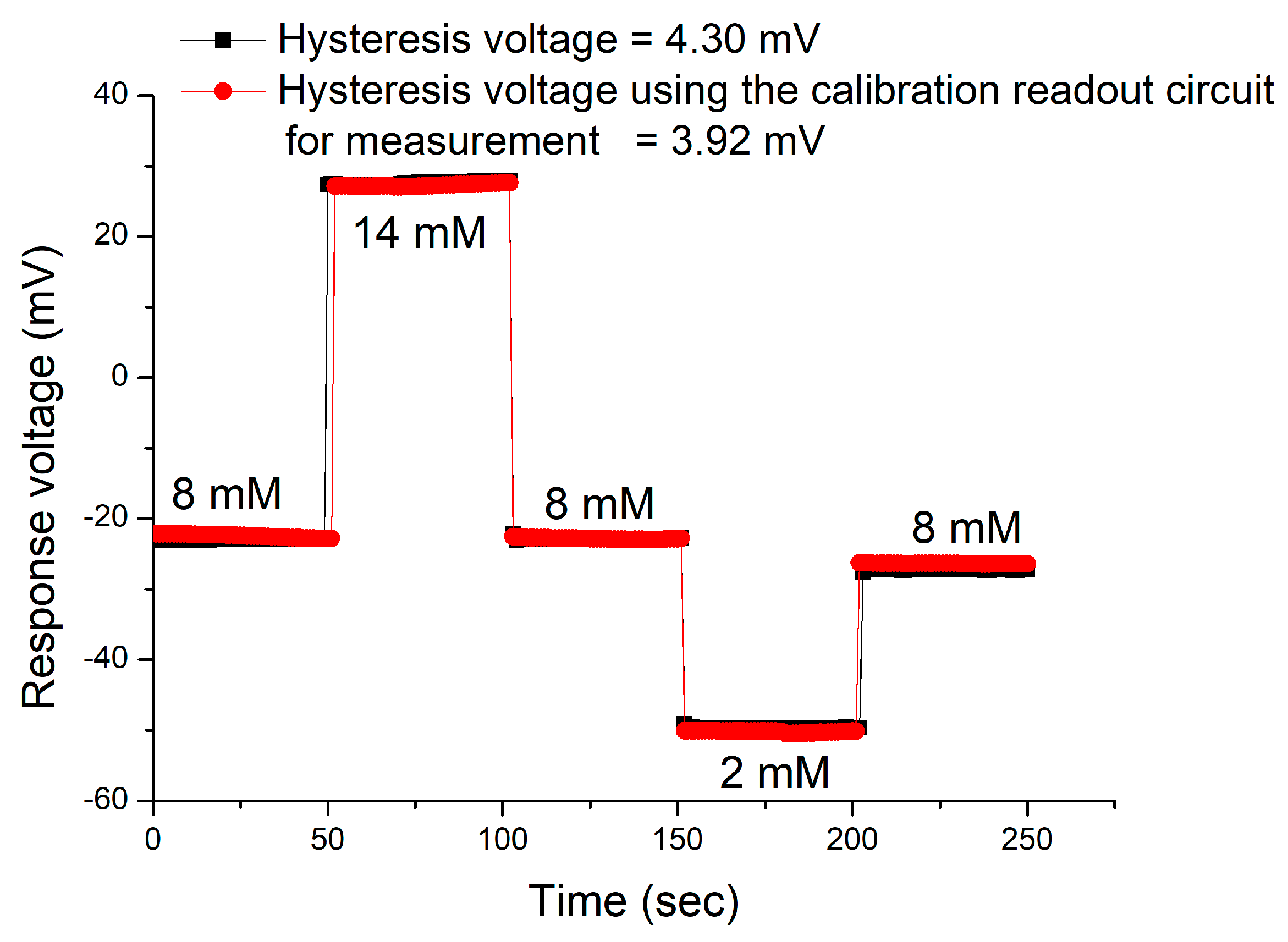
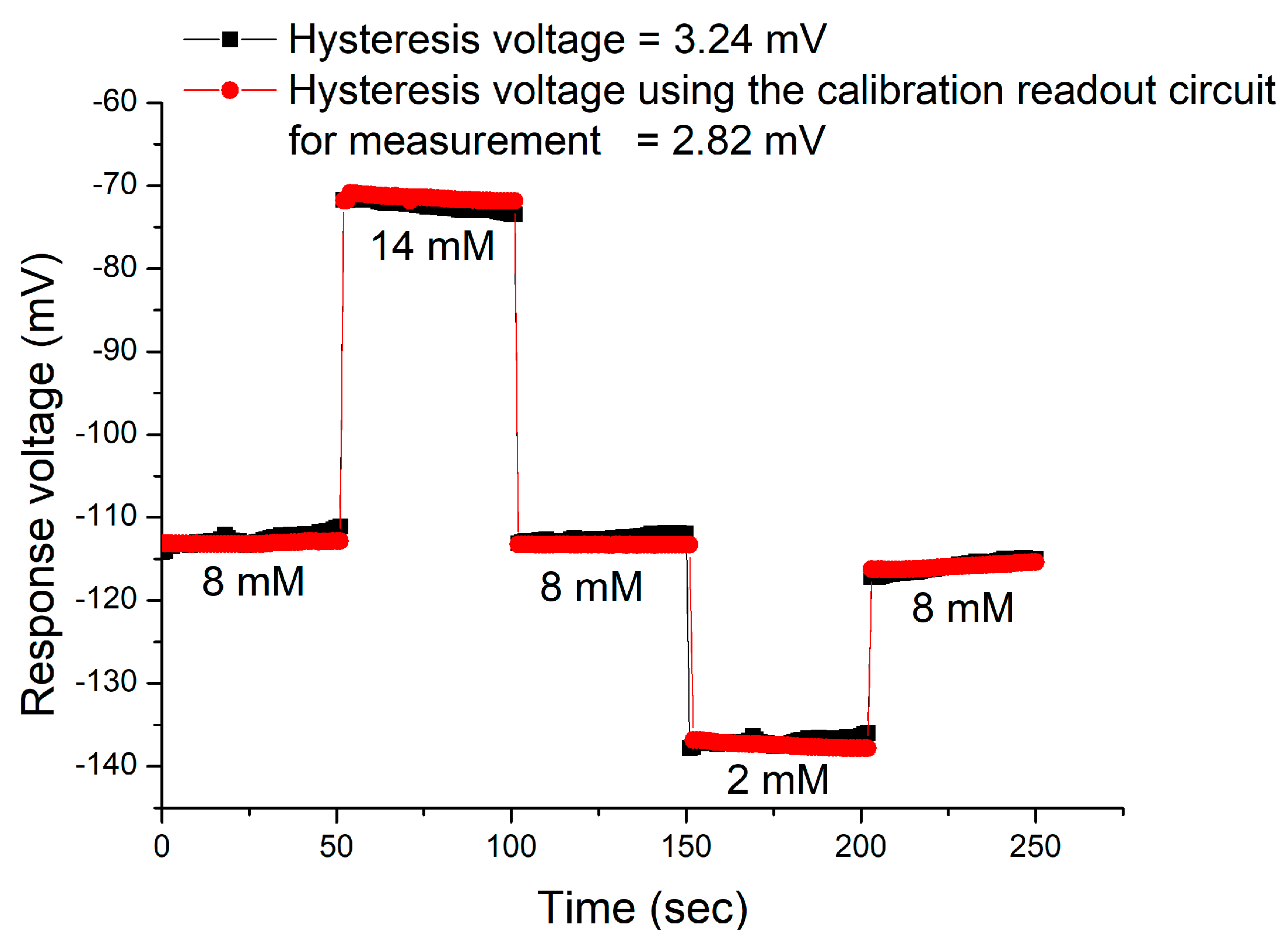
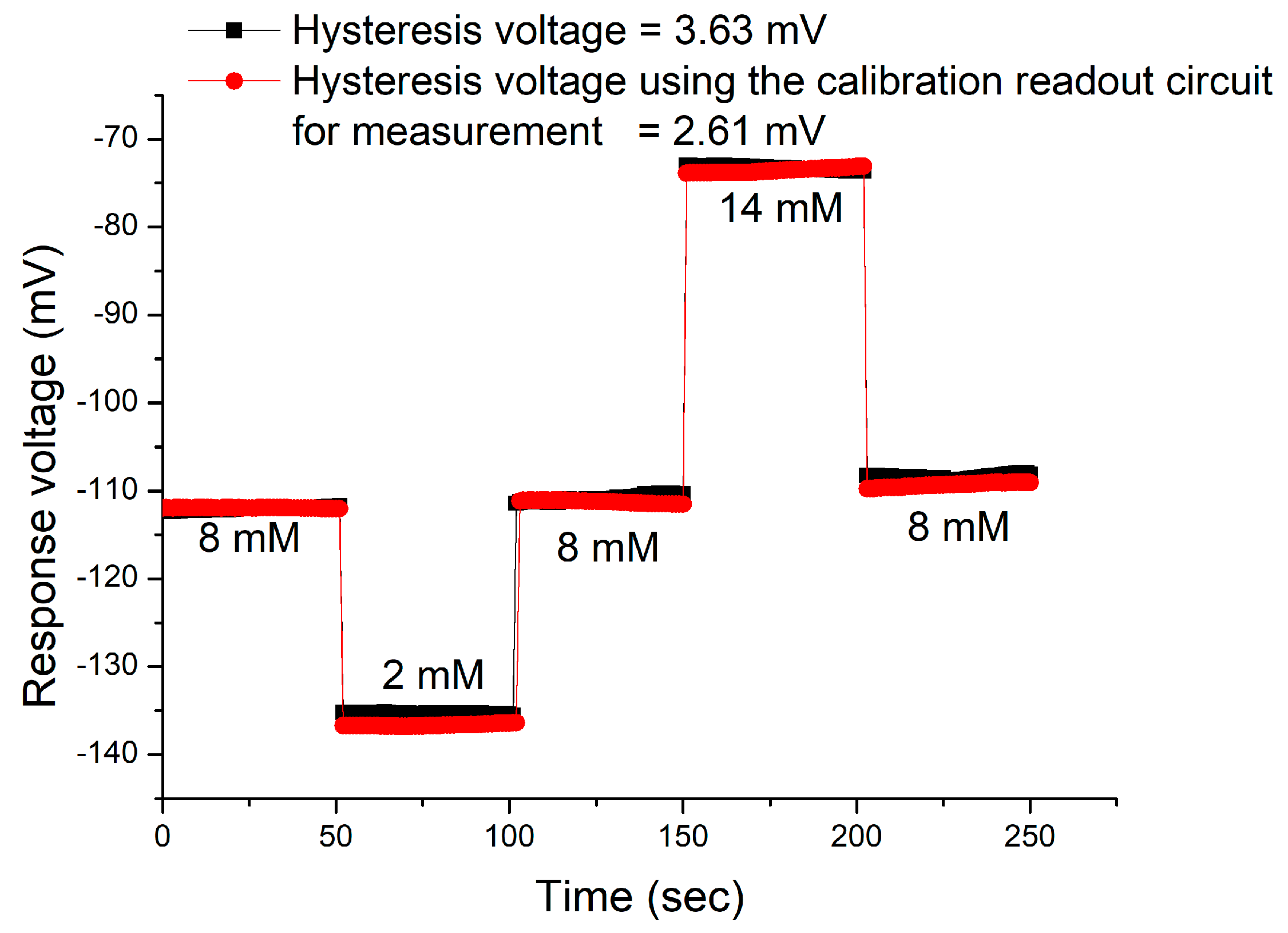
3.4. Hysteresis Effects of the Sensor
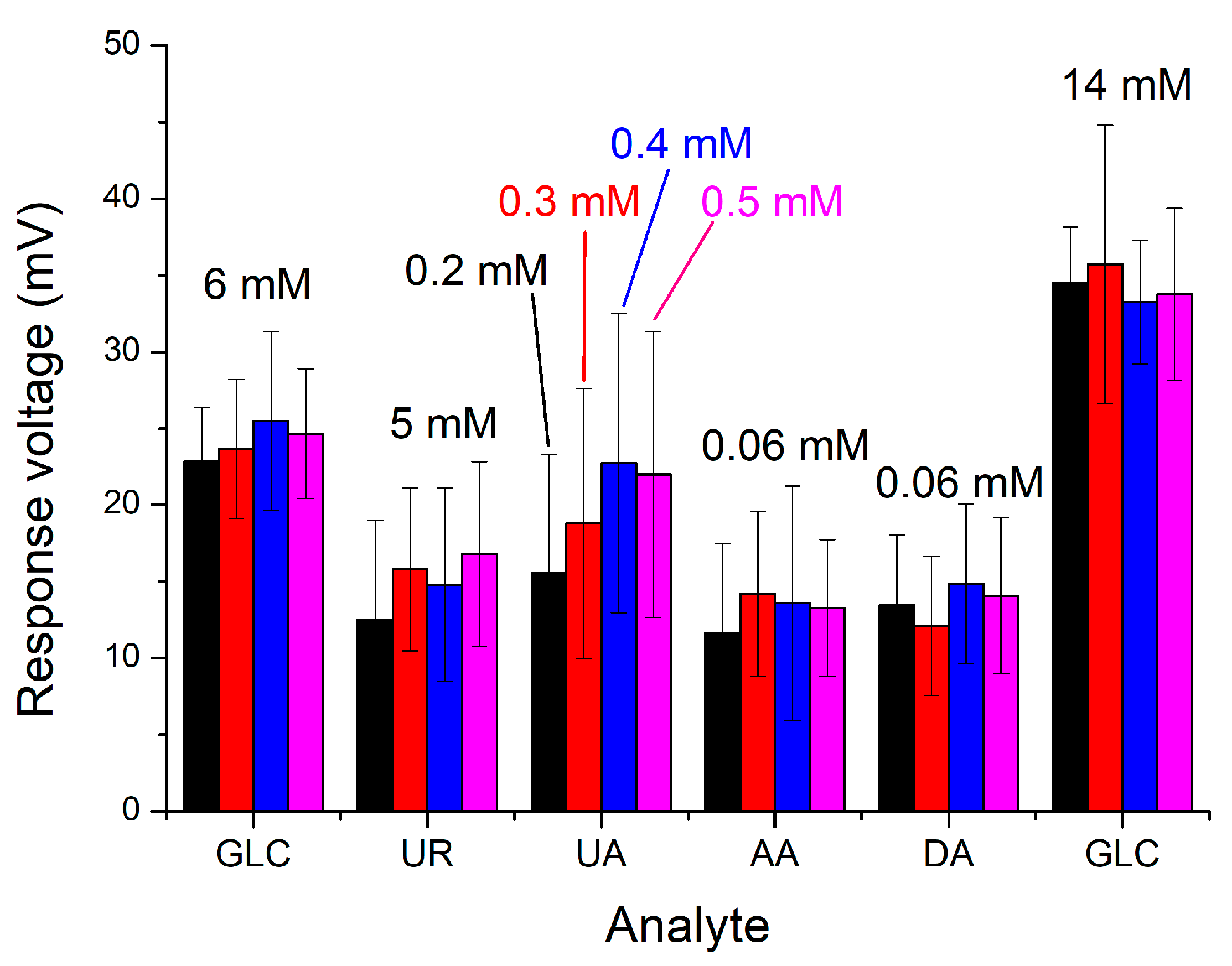
3.5. Interference Effects of the Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Villena Gonzales, W.; Mobashsher, A.T.; Abbosh, A. The progress of glucose monitoring—A review of invasive to minimally and non-invasive techniques, devices and sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garg, S.K.; Akturk, H.K. A new era in continuous glucose monitoring: Food and drug administration creates a new category of factory-calibrated nonadjunctive, interoperable class II medical devices. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rickels, M.R.; Peleckis, A.J.; Dalton-Bakes, C.; Naji, J.R.; Ran, N.A.; Nguyen, H.-L.; O’Brien, S.; Chen, S.; Lee, I.; Schutta, M.H. Continuous glucose monitoring for hypoglycemia avoidance and glucose counterregulation in long-standing type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Shao, Q.; Xu, Q.; Shi, H.; Li, L. Art therapy alleviates the levels of depression and blood glucose in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabnam, L.; Faisal, S.N.; Roy, A.K.; Haque, E.; Minett, A.I.; Gomes, V.G. Doped graphene/Cu nanocomposite: A high sensitivity non-enzymatic glucose sensor for food. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.M.; Batista, K.d.A.; Batista, G.L.A.; Fernandes, K.F. Technology. Biosensor for determination of glucose in real samples of beverages. Food Sci. 2012, 32, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Noreen, F.; Kanwal, S.; Iqbal, A.; Hussain, G. Green synthesis of ZnO and Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles from leaf extracts of Abutilon indicum, Clerodendrum infortunatum, Clerodendrum inerme and investigation of their biological and photocatalytic activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 82, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboud, A.A.; Shaban, M.; Revaprasadu, N. Effect of Cu, Ni and Pb doping on the photo-electrochemical activity of ZnO thin films. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 7729–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shetti, N.P.; Bukkitgar, S.D.; Reddy, K.R.; Reddy, C.V.; Aminabhavi, T.M. ZnO-based nanostructured electrodes for electrochemical sensors and biosensors in biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, D.; Singh, U.; Gupta, S.; Singhal, R.; Kulriya, P.; Singh, F.; Tripathi, A.; Singh, J.; Joshi, U.; Avasthi, D.K. Enhanced room temperature ferromagnetism and green photoluminescence in Cu doped ZnO thin film synthesised by neutral beam sputtering. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathy, N.; Kim, D.H. Metal oxide modified ZnO nanomaterials for biosensor applications. Nano Converg. 2018, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, M.; Lin, S.; Liu, J.; Lei, M.; Wu, H.; Dai, C.; Wei, Z.Y. Synthesis of high quality silver nanowires and their applications in ultrafast photonics. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 16440–16448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff, A.; Wagner, D.; Ditlbacher, H.; Kreibig, U. Silver nanowires. Eur. Phys. J. D 2005, 34, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengbo, S.; Lihua, L.; Aoqun, J.; Qianqian, D.; Jianlong, J.; Qiang, Z.; Wendong, Z. Highly sensitive wearable strain sensor based on silver nanowires and nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 255202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, P.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y. A novel low unity-gain frequency and low power consumption instrumentation amplifier design for RuO2 uric acid biosensor measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.-Y.; Dong, Z.-X. A new calibration circuit design to reduce drift effect of RuO2 urea biosensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuo, P.-Y.; Dong, Z.-X.; Chen, Y.-Y. The Hysteresis reduction approach for urea biosensor modified by silver nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2021, 20, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd-Moss, M.; Baratchi, S.; Di Venere, M.; Khoshmanesh, K. Self-contained microfluidic systems: A review. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3177–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Liang, B.; Tu, T.; Wei, J.; Fang, L.; Ye, X. Three-dimensional paper-based microfluidic electrochemical integrated devices (3D-PMED) for wearable electrochemical glucose detection. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 5674–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, T.; Gu, C.; Gan, Y.; Wu, Q.; He, C.; Tu, J.; Pan, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Kong, L.; Wan, H.; et al. Microfluidic chip system integrated with light addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS) for real-time extracellular acidification detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 127004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinke, C.; Wosgrau, V.; Oliveira, P.R.; Oliveira, G.A.; Martins, G.; Mangrich, A.S.; Bergamini, M.F.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H. Green method for glucose determination using microfluidic device with a non-enzymatic sensor based on nickel oxyhydroxide supported at activated biochar. Talanta 2019, 200, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, S.; Aksoy, B.; Unalan, H.E. Polyol synthesis of silver nanowires: An extensive parametric study. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 4963–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Echabaane, M.; Omri, K.; El Mir, L.; Chaabane, R.B. Development of an impedimetric non enzymatic sensor based on ZnO and Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles for the detection of glucose. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 786, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Jin, L.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Lin, X. Amperometric glucose biosensor based on silver nanowires and glucose oxidase. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 176, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Kang, H.W.; Lee, W. Ultra-sensitive non-enzymatic amperometric glucose sensors based on silver nanowire/graphene hybrid three-dimensional nanostructures. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102761. [Google Scholar]
- Korotcenkov, G.; Cho, B.K. Instability of metal oxide-based conductometric gas sensors and approaches to stability improvement (short survey). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 156, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbioli, M.; Morf, W.E.; Badertscher, M.; de Rooij, N.F.; Pretsch, E. Potential drifts of solid-contacted ion-selective electrodes due to zero-current ion fluxes through the sensor membrane. Electroanalysis 2000, 12, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.-L.; Jan, S.-S.; Chou, J.-C.; Chen, Y.-C. Study on the temperature effect, hysteresis and drift of pH-ISFET devices based on amorphous tungsten oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 76, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nien, Y.-H.; Su, T.-Y.; Chou, J.-C.; Kuo, P.-Y.; Lai, C.-H.; Ho, C.-S.; Dong, Z.-X.; Kang, Z.-X.; Lai, T.-Y. Improving the drift effect and hysteresis effect of urea biosensor based on graphene oxide/nickel oxide sensing film modified either by Au nanoparticles or γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles using back-end calibration circuit. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2021, 9, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.-C.; Yan, S.-J.; Liao, Y.-H.; Lai, C.-H.; Chen, J.-S.; Chen, H.-Y.; Tseng, T.-W.; Wu, T.-Y. Characterization of flexible arrayed pH sensor based on nickel oxide films. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 18, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.-C.; Yan, S.-J.; Liao, Y.-H.; Lai, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-X.; Wu, C.-Y. Remote detection for glucose and lactate based on flexible sensor array. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 3467–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Lou, B.-S.; Her, J.-L.; Pang, S.-T.; Pan, T.-M. Super Nernstian pH response and enzyme-free detection of glucose using sol-gel derived RuOx on PET flexible-based extended-gate field-effect transistor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Electrode | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZO/PET | AgNWs/CZO/PET | |||
| Standard Deviation | ||||
| Glucose Concentration (mM) | LT1167 (mV) | UGFPCIA (mV) | LT1167 (mV) | UGFPCIA (mV) |
| 2 | 2.42 | 2.36 | 1.59 | 1.55 |
| 4 | 2.08 | 1.06 | 1.07 | 1.03 |
| 6 | 0.96 | 0.41 | 1.26 | 1.09 |
| 8 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 1.15 | 1.05 |
| 10 | 0.52 | 0.48 | 1.35 | 1.28 |
| 12 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 1.29 | 1.24 |
| 14 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 1.18 | 1.09 |
| Electrode | Flow Rate (µL/min) | Average Sensitivity (mV/mM) | Linearity |
|---|---|---|---|
| CZO/PET | 1.4 | 6.11 | 0.998 |
| 2.8 | 6.96 | 0.996 | |
| 4.2 | 6.90 | 0.997 | |
| 5.6 | 7.21 | 0.997 | |
| 7.0 | 7.59 | 0.998 |
| Electrode | Flow Rate (µL/min) | Average Sensitivity (mV/mM) | Linearity |
|---|---|---|---|
| AgNWs/CZO/PET | 1.4 | 12.28 | 0.994 |
| 2.8 | 12.75 | 0.998 | |
| 4.2 | 12.01 | 0.997 | |
| 5.6 | 13.71 | 0.998 | |
| 7.0 | 13.63 | 0.997 |
| Cycle | Hysteresis Voltage that Using the V-T Measurement System (mV) | Hysteresis Voltage that Using the Calibration Readout Circuit (mV) | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AgNWs/CZO/PET | 1.03 | 3.24 | This work |
| 3.63 | |||
| Nafion-GOD-MBs/GO/NiO | 3.70 | N/A | [31] 2018 |
| RuOx | 2.08 | 1.00 | [32] 2019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chou, J.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Kuo, P.-Y.; Lai, C.-H.; Nien, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Kang, Z.-X.; Lee, K.-T. Application of the Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Combined with Microfluidic System and Calibration Readout Circuit. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120351
Chou J-C, Huang Y-H, Kuo P-Y, Lai C-H, Nien Y-H, Chen Y-Y, Kang Z-X, Lee K-T. Application of the Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Combined with Microfluidic System and Calibration Readout Circuit. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(12):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120351
Chicago/Turabian StyleChou, Jung-Chuan, Yu-Hao Huang, Po-Yu Kuo, Chih-Hsien Lai, Yu-Hsun Nien, Yung-Yu Chen, Zhi-Xuan Kang, and Kun-Tse Lee. 2021. "Application of the Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Combined with Microfluidic System and Calibration Readout Circuit" Chemosensors 9, no. 12: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120351
APA StyleChou, J.-C., Huang, Y.-H., Kuo, P.-Y., Lai, C.-H., Nien, Y.-H., Chen, Y.-Y., Kang, Z.-X., & Lee, K.-T. (2021). Application of the Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Combined with Microfluidic System and Calibration Readout Circuit. Chemosensors, 9(12), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9120351









