Boosting Selectivity and Sensitivity to Biomarkers of Quantum Resistive Vapour Sensors Used for Volatolomics with Nanoarchitectured Carbon Nanotubes or Graphene Platelets Connected by Fullerene Junctions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Hybrid Nanomaterials
2.3. Fabrication of Sensors
2.4. Characterization Techniques
2.5. Dynamic Vapour Sensing
2.6. Biomarkers
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of Hybrid Nanocarbons
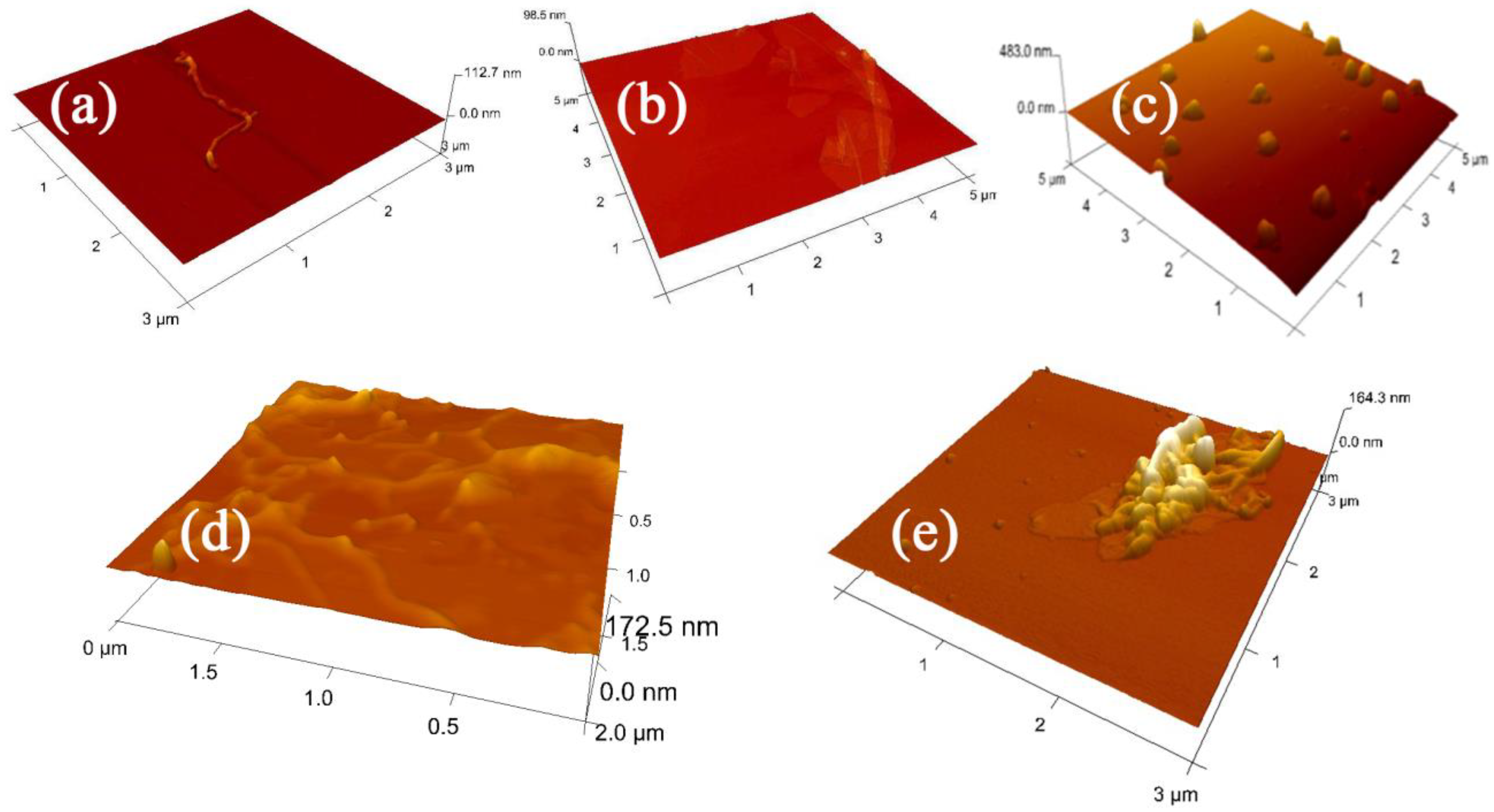
3.1.1. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
3.1.2. Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM)
3.1.3. Thermo Gravimetric Analysis
3.2. Electrical Characterization of the Sensor
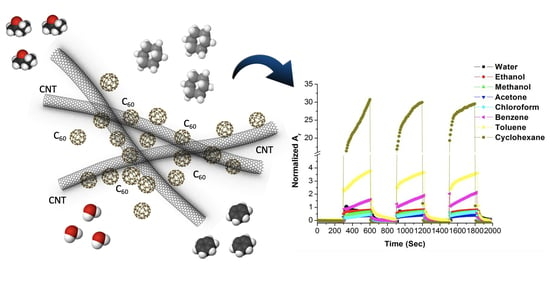
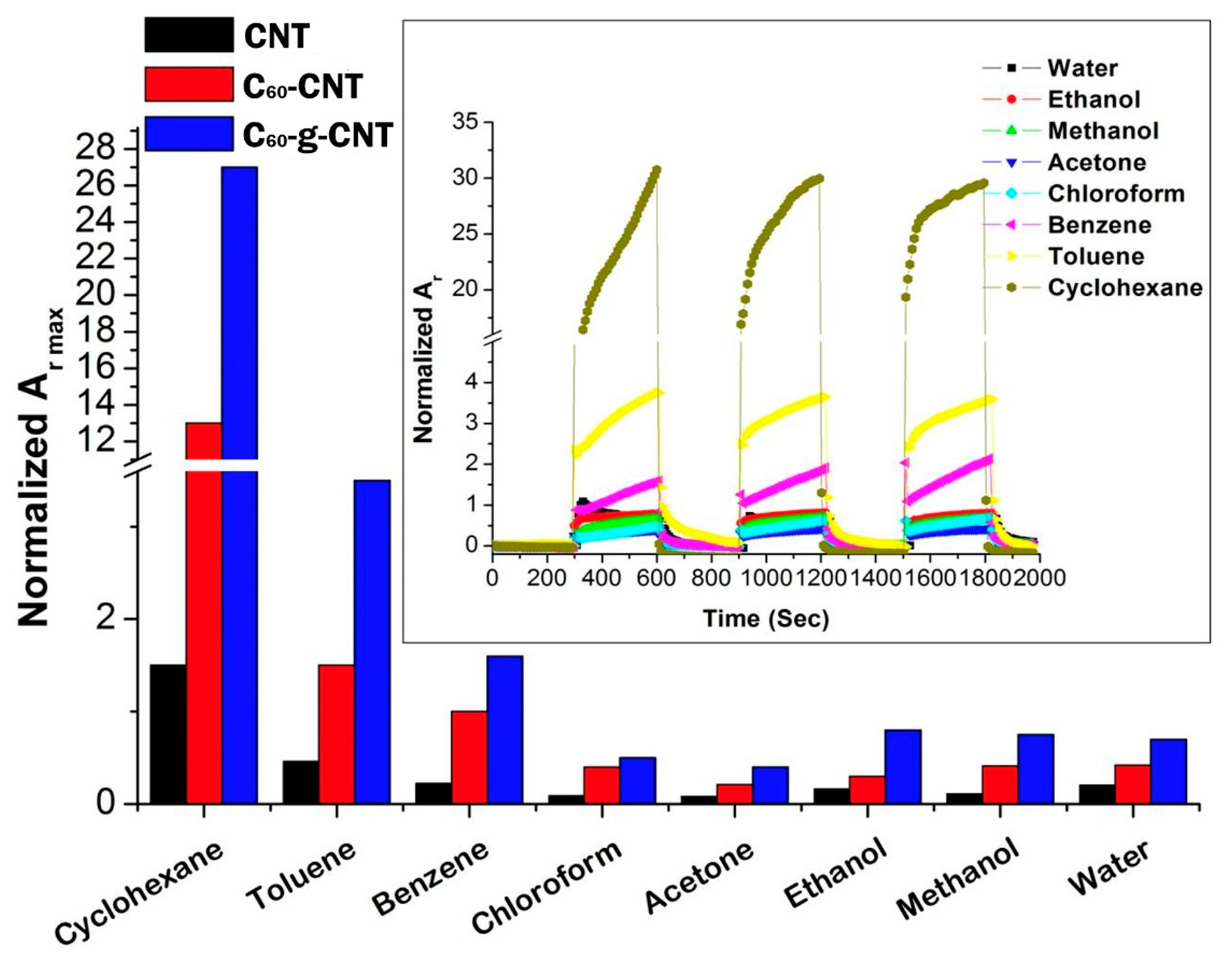
3.2.1. Dynamic Vapour Sensing
3.2.2. Limit of Detection at ppb Level
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haick, H.; Broza, Y.Y.; Mochalski, P.; Ruzsanyi, V.; Amann, A. Assessment, origin, and implementation of breath volatile cancer markers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1423–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.; Yu, J.; Lin, S.; Gao, S.; Yang, H.; Haick, H.; Hua, C.; Deng, S.; Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Nanosensor-based flexible electronic assisted with light fidelity communicating technology for volatolomics-based telemedicine. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 15517–15532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Broza, Y.Y.; Ionsecu, R.; Tisch, U.; Ding, L.; Liu, H.; Song, Q.; Pan, Y.Y.; Xiong, F.X.; Gu, K.S.; et al. A nanomaterial-based breath test for distinguishing gastric cancer from benign gastric conditions. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santonico, M.; Lucantoni, G.; Pennazza, G.; Capuano, R.; Galluccio, G.; Roscioni, C.; La Delfa, G.; Consoli, D.; Martinelli, E.; Paolesse, R.; et al. In situ detection of lung cancer volatile fingerprints using bronchoscopic air-sampling. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhleh, M.K.; Amal, H.; Jeries, R.; Broza, Y.Y.; Aboud, M.; Gharra, A.; Ivgi, H.; Khatib, S.; Badarneh, S.; Har-Shai, L.; et al. Diagnosis and classification of 17 diseases from 1404 subjects via pattern analysis of exhaled molecules. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, K.M.; Sachan, A.; Castro, M.; Choudhary, V.; Sonkar, S.K.; Feller, J.F. Green carbon nanostructured quantum resistive sensors to detect volatile biomarkers. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2018, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Trock, E.; Haick, H. Detecting simulated patterns of lung cancer biomarkers by random network of single-walled carbon nanotubes coated with nonpolymeric organic materials. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3631–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, L.; Nag, S.; Castro, M.; Zaborova, E.; Ménand, M.; Sollogoub, M.; Bennevault, V.; Feller, J.F.; Guégan, P. Chemical Sensors Based on New Polyamides Biobased on (Z) Octadec-9-Enedioic Acid and β-Cyclodextrin. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2016, 217, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Hakim, M.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Tisch, U.; Haick, H. Detection of lung, breast, colorectal, and prostate cancers from exhaled breath using a single array of nanosensors. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.; Knobloch, H.; Richards, J.; Richards, P.; Mottram, T.T.F.; Marlin, D.; Chambers, M.A. Development of a device for sampling cattle breath. Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 112, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruins, M.; Rahim, Z.; Bos, A.; van de Sande, W.W.J.; Endtz, H.P.; van Belkum, A. Diagnosis of active tuberculosis by e-nose analysis of exhaled air. Tuberculosis 2013, 93, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wlodzimirow, K.A.; Abu-Hanna, A.; Schultz, M.J.; Maas, M.A.; Bos, L.D.J.; Sterk, P.J.; Knobel, H.H.; Soers, R.J.T.; Chamuleau, R.A.F.M. Exhaled breath analysis with electronic nose technology for detection of acute liver failure in rats. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.; Tisch, U.; Haick, H. Detection of nonpolar molecules by means of carrier scattering in random networks of carbon nanotubes: Toward diagnosis of diseases via breath samples. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisch, U.; Schlesinger, I.; Ionescu, R.; Nassar, M.; Axelrod, N.; Robertman, D.; Tessler, Y.; Azar, F.; Marmur, A.; Aharon-Peretz, J.; et al. Detection of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease from exhaled breath using nanomaterial-based sensors. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberman, Y.; Tisch, U.; Shuster, G.; Pisula, W.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K.; Haick, H. Carbon nanotube/hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene bilayers for discrimination between nonpolar Volatile Organic Compounds of cancer and humid atmospheres. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4317–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Castro, M.; Feller, J.F. Quantum resistive vapour sensors made of polymer coated carbon nanotubes random networks for biomarkers detection. Chem. Sens. 2013, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mashir, A.; Dweik, R.A. Exhaled breath analysis: The new interface between medicine and engineering. Adv. Powder Technol. 2009, 20, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ionescu, R.; Broza, Y.Y.; Shaltieli, H.; Sadeh, D.; Zilberman, Y.; Feng, X.; Glass-Marmor, L.; Lejbkowicz, I.; Müllen, K.; Miller, A.; et al. Detection of multiple sclerosis from exhaled breath using bilayers of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and single-wall carbon nanotubes. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tran, M.T. Development of Nanocomposite Quantum Resistive Sensors for the Prevention of Bedsores; University of South Brittany (UBS): Lorient, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, T.D.; Prosser, O.; Hulbert, J.N.; Marshall, R.W.; Corcoran, P.; Lowery, P.; Ruck-Keene, E.A.; Heron, S. Detection and simultaneous identification of microorganisms from headspace samples using an electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1997, 44, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming-Jones, M.E.; Smith, R.E. Volatile organic compounds in foods: A five year study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 8120–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, T.T.; Castro, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Suh, K.S.; Feller, J.F. Graphene quantum resistive sensing skin for the detection of alteration biomarkers. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 21754–21766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Robinson, A.; Miller, D.; Davis, M. Overview of sensors and needs for environmental monitoring. Sensors 2005, 5, 4–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamagna, A.; Reich, S.; Rodríguez, D.; Boselli, A.; Cicerone, D. The use of an electronic nose to characterize emissions from a highly polluted river. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 131, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Wu, W.; Gao, J.; Lu, J.; Fan, C. Nanomaterials-based sensors for applications in environmental monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 18101–18110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, A.; Castro, M.; Choudhary, V.; Feller, J.F. vQRS based on hybrids of CNT with PMMA-POSS and PS-POSS copolymers to reach the sub-ppm detection of ammonia and formaldehyde at room temperature despite moisture. ChemoSensors 2017, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekhar, P.K.; Brosha, E.L.; Mukundan, R.; Garzon, F. Chemical sensors for environmental monitoring and homeland security. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2010, 19, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Swager, T.M. Fluorescent detection of chemical warfare agents: Functional group specific ratiometric chemosensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3420–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hou, Z.; Xu, D.; Wei, L.; Kong, E.S.W.; Zhang, Y. Flexible gas sensors with assembled carbon nanotube thin films for DMMP vapor detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laquintinie, P.S.; Sachan, A.; Feller, J.F.; Lahuec, C.; Castro, M.; Seguin, F.; Dupont, L. An electronic nose prototype for the on-field detection of nerve agents. In IEEE Sensors; IEEE: New-Delhi, India, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Haddi, Z.; Mabrouk, S.; Bougrini, M.; Tahri, K.; Sghaier, K.; Barhoumi, H.; El Bari, N.; Maaref, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Bouchikhi, B. E-Nose and e-Tongue combination for improved recognition of fruit juice samples. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobański, T.; Szczurek, A.; Nitsch, K.; Licznerski, B.W.; Radwan, W. Electronic nose applied to automotive fuel qualification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 116, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenho, A.R.V.; Li, R.W.C.; Gruber, J. Polymeric electronic gas sensor for determining alcohol content in automotive fuels. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 136, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cikach, F.S.; Dweik, R.A. Cardiovascular biomarkers in exhaled breath. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 55, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wudl, F. Fullerene materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1959–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, J.F. 6.10 Electrically Conductive Nanocomposites. In Comprehensive Composite Materials II; Beaumont, P.W.R., Zweben, C.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 248–314. [Google Scholar]
- Schedin, F.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Hill, E.W.; Blake, P.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Novoselov, K.S. Detection of individual gas molecules adsorbed on graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Dubonos, S.V.; Firsov, A.A. Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 2005, 438, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Q.; Cui, T. Ultra-sensitive suspended graphene nanocomposite cancer sensors with strong suppression of electrical noise. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, S.; Duarte, L.; Bertrand, E.; Celton, V.; Castro, M.; Choudhary, V.; Guégan, P.; Feller, J.F. Ultrasensitive QRS made by supramolecular assembly of functionalized cyclodextrins and graphene for the detection of lung cancer VOC biomarkers. J. Mater. Chem. B Biol. Med. 2014, 2, 6571–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldoni, A.; Petaccia, L.; Lizzit, S.; Larciprete, R. Sensing gases with carbon nanotubes: A review of the actual situation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, J.F.; Gatt, N.; Kumar, B.; Castro, M. Selectivity of chemoresistive sensors made of chemically functionalized carbon nanotube random networks for volatile organic compounds (VOC). ChemoSensors 2014, 2, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroto, H.W.; Heath, J.R.; O’Brien, S.C.; Curl, R.F.; Smalley, R.E. C60: Buckminsterfullerene. Nature 1985, 318, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krätschmer, W.; Lamb, L.D.; Fostiropoulos, K.; Huffman, D.R. Solid C60: A new form of carbon. Nature 1990, 347, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Curry, R.J.; Sloan, J.; Hatton, R.A.; Chong, L.C.; Blanchard, N.; Stolojan, V.; Kroto, H.W.; Silva, S.R.P. Structural and optoelectronic properties of C60 rods obtained via a rapid synthesis route. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krusic, P.J.; Wasserman, E.; Keizer, P.N.; Morton, J.R.; Preston, K.F. Radical reactions of C60. Science 1991, 254, 1183–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somani, P.R.; Somani, S.P.; Umeno, M. Toward organic thick film solar cells: Three dimensional bulk heterojunction organic thick film solar cell using fullerene single crystal nanorods. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 173503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qu, Y.; Piao, G.; Zhao, J.; Jiao, K. Reduced working electrode based on fullerene C60 nanotubes@DNA: Characterization and application. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 175, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Dillon, A.C.; Heben, M.J.; Zhang, S.B. Hydrogen storage in novel organometallic buckyballs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 155504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohashi, T.; Dai, L. C60 and carbon nanotube sensors. In Carbon Nanotechnology; Dai, L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 525–575. ISBN 9780444518552. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Park, K.; Durstock, M.; Dai, L. Fullerene-grafted graphene for efficient bulk heterojunction polymer photovoltaic devices. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Iqbal, Z.; Mitra, S. A fullerene—Single wall carbon nanotube complex for polymer bulk heterojunction photovoltaic cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 2406–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.B.; Xu, Y.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Chen, Y.S.; Tian, J.G. Porphyrin and fullerene covalently functionalized graphene hybrid materials with large nonlinear optical properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 9681–9686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. Synthesis and characterization of a graphene—C60 hybrid material. Carbon N. Y. 2009, 47, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Shen, Y.; Du, B.; Guo, Z.; Fang, Z. Fabrication of fullerene-decorated carbon nanotubes and their application in flame-retarding polypropylene. Nanoscale 2009, 1, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girifalco, L.A.; Hodak, M.; Lee, R.S. Carbon nanotubes, buckyballs, ropes, and a universal graphitic potential. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 13104–13110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, J.F.; Lu, J.; Zhang, K.; Kumar, B.; Castro, M.; Gatt, N.; Choi, H.J. Novel architecture of carbon nanotube decorated poly(methyl methacrylate) microbead vapour sensors assembled by spray layer by layer. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 4142–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S.; Sachan, A.; Castro, M.; Choudhary, V.; Feller, J.F. Spray layer-by-layer assembly of POSS functionalized CNT quantum chemo-resistive sensors with tuneable selectivity and ppm resolution to VOC biomarkers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, T.T.; Castro, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Suh, K.S.; Feller, J.F. High stability silver nanoparticles–graphene/poly(ionic liquid)-based chemoresistive sensors for volatile organic compounds’ detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3995–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, T.T.; Castro, M.; Pillin, I.; Kim, T.Y.; Suh, K.S.; Feller, J.-F. Graphene–Fe3O4/PIL–PEDOT for the design of sensitive and stable quantum chemo-resistive VOC sensors. Carbon N. Y. 2014, 74, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, T.T.; Feller, J.F.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Yang, W.S.; Suh, K.S. Electromagnetic properties of Fe3O4-functionalized graphene and its composites with a conducting polymer. J. Polym. Sci. A Chem. 2012, 50, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, T.T.; Castro, M.; Feller, J.F. Electronic noses for VOCs detection based on the nanoparticles hybridized graphene composites. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Birmingham, UK, 20–23 August 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Castro, M.; Feller, J.F. An e-nose made of carbon nanotube based quantum resistive sensors for the detection of eighteen polar/nonpolar VOC biomarkers of lung cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S.; Castro, M.; Choudhary, V.; Feller, J.F. Sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) [SPEEK] nanocomposites based on hybrid nanocarbons for the detection and discrimination of some lung cancer VOC biomarkers. J. Mater. Chem. B Biol. Med. 2017, 5, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, T.T.; Pham-Huu, C.; Janowska, I.; Kim, T.Y.; Castro, M.; Feller, J.F. Hybrid films of graphene and carbon nanotubes for high performance chemical and temperature sensing applications. Small 2015, 11, 3485–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, J.F.; Kumar, B.; Castro, M. Conductive biopolymer nanocomposites for sensors. In Nanocomposites with Biodegradable Polymers: Synthesis, Properties & Future Perspectives; Mital, V., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 368–399. ISBN 9780199581924. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Kumar, B.; Castro, M.; Feller, J.F. Vapour sensing with conductive polymer nanocomposites (CPC): Polycarbonate-carbon nanotubes transducers with hierarchical structure processed by spray layer by layer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvrée, A.; Feller, J.-F.; Castro, M.; Grohens, Y.; Rinaudo, M. Conductive Polymer nano-bioComposites (CPC): Chitosan-carbon nanoparticle a good candidate to design polar vapour sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, P. Sniffing out lung cancer. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, A.; Di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R.; Macagnano, A.; Martinelli, E.; Pennazza, G.; Santonico, M.; Bernabei, M.; Roscioni, C.; Gallucio, G. Olfactory systems for medical applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 130, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.L.; Passos, M.; Câmara, J.S. Solid phase microextraction, mass spectrometry and metabolomic approaches for detection of potential urinary cancer biomarkers—A powerful strategy for breast cancer diagnosis. Talanta 2012, 89, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockstein, N.G.; Thaler, E.R.; Torigian, D.; Miller, W.T.; Deffenderfer, O.; Hanson, C.W. Diagnosis of pneumonia with an electronic nose: Correlation of vapor signature with chest computed tomography scan findings. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, N. Investigation of volatile biomarkers in lung cancer blood using solid-phase microextraction and capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 808, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.L.; Xiao, P.; Fang, H.L.; Dai, H.F.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, Y.H. Single-walled carbon nanotube-based biosensors for the detection of volatile organic compounds of lung cancer. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2011, 44, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, H.J.; Gordon, S.N.; O’Neill, M.H.; Gibbons, R.D.; Szidon, J.P. A computerized in lung cancer technique for screening for the presence of breath biomarkers. Clin. Chem. 1988, 34, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, G.B.; Boshier, P.R.; Markar, S.R.; Romano, A. Accuracy and methodologic challenges of volatile organic compound-based exhaled breath tests for cancer diagnosis. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, e182815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomić, M.; Šetka, M.; Vojkůvka, L.; Vallejos, S. VOC sensing by metal oxides, conductive polymers, and carbon-based materials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Heo, G.S.; Shin, S.M. Two-step preconcentration for analysis of exhaled gas of human breath with electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 117, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, P. Solid phase microextraction for analysis of alkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons in human breath. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 826, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.F.; Laskowski, D.; Deffenderfer, O.; Burch, T.; Zheng, S.; Mazzone, P.J.; Mekhail, T.; Jennings, C.; Stoller, J.K.; Pyle, J.; et al. Detection of lung cancer by sensor array analyses of exhaled breath. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dragonieri, S.; van der Schee, M.P.; Massaro, T.; Schiavulli, N.; Brinkman, P.; Pinca, A.; Carratú, P.; Spanevello, A.; Resta, O.; Musti, M.; et al. An electronic nose distinguishes exhaled breath of patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma from controls. Lung Cancer 2012, 75, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, P.; Han, Z.; Piao, G.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Liu, G. A novel approach to fabrication of fullerene C60 nanotubes: Using C60—Pyridine colloid as a precursor. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Han, Z.; Piao, G.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Liu, G. To distinguish fullerene C60 nanotubes and C60 nanowhiskers using Raman spectroscopy. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2009, 163, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, M.; Miyazawa, K. Synthesis and characterization of fullerene nanowhiskers by liquid-liquid interfacial precipitation: Influence of C60 solubility. Molecules 2012, 17, 3858–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feller, J.F.; Castro, M.; Kumar, B. Polymer-carbon nanotube conductive nanocomposites for sensing. In Polymer-Carbon Nanotube Composites: Preparation, Properties and Applications; McNally, T., Pötschke, P., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 760–803. ISBN 1845697618. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, B.; Castro, M.; Feller, J.F. Controlled conductive junction gap for chitosan-carbon nanotube quantum resistive vapour sensors. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 10656–10664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, A.; Castro, M.; Choudhary, V.; Feller, J.F. Influence of water molecules on the detection of volatile organic compounds (VOC) cancer biomarkers by nanocomposite quantum resistive vapor sensors vQRS. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, T.; Woodka, M.D.; Brunschwig, B.S.; Lewis, N.S. Chemiresistors for array-based vapor sensing using composites of carbon black with low volatility organic molecules. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 5193–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Nature | Process | R0 (kΩ) |
|---|---|---|
| CNT | 2 layers of CNT solution in chloroform sprayed | 5 ± 2 |
| CNT-g-C60 | 2 layers of C60-g-CNT solution in chloroform sprayed | 8 ± 3 |
| CNT-l-C60 | 1 layer of CNT solution in chloroform sprayed followed by spray of 1 layer of C60 solution in toluene | 4 ± 2 |
| rGO | 5 layers of rGO solution in acetone sprayed | 10 ± 4 |
| rGO-g-C60 | 5 layers of C60-g-rGO solution in acetone sprayed | 10 ± 5 |
| VOC Type | Representative Vapour Biomarkers | Concentration Range in Exhaled Breath (ppb) |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohols | Methanol Ethanol 1-Propanol | 157–344 96–2848 4–13 |
| Aldehydes | Pentanal Heptanal Nonanal | 2–7 2–7 2–107 |
| Alkanes | Pentane 4-Methyloctane Cyclohexane | 2–18 16–19 0.1–15 |
| Halo hydrocarbons | Chloroform | 10 |
| Ketones | Acetone 2-Butanone 3-Hydroxy-2- Butanone | 35–1000 0.002–3 0.002–0.05 |
| Alkenes | Isoprene | 41–109 |
| Aromatics | Ethyl benzene Benzene Toluene | 1–18 1.1–3.5 1–37 |
| VOC | S/N [rGO] | S/N [C60-g-rGO] |
|---|---|---|
| Toluene | 61 | 109 |
| Methanol | 30 | 224 |
| Benzene | 18 | 231 |
| Water | 19 | 153 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nag, S.; Castro, M.; Choudhary, V.; Feller, J.-F. Boosting Selectivity and Sensitivity to Biomarkers of Quantum Resistive Vapour Sensors Used for Volatolomics with Nanoarchitectured Carbon Nanotubes or Graphene Platelets Connected by Fullerene Junctions. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9040066
Nag S, Castro M, Choudhary V, Feller J-F. Boosting Selectivity and Sensitivity to Biomarkers of Quantum Resistive Vapour Sensors Used for Volatolomics with Nanoarchitectured Carbon Nanotubes or Graphene Platelets Connected by Fullerene Junctions. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(4):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9040066
Chicago/Turabian StyleNag, Sananda, Mickaël Castro, Veena Choudhary, and Jean-Francois Feller. 2021. "Boosting Selectivity and Sensitivity to Biomarkers of Quantum Resistive Vapour Sensors Used for Volatolomics with Nanoarchitectured Carbon Nanotubes or Graphene Platelets Connected by Fullerene Junctions" Chemosensors 9, no. 4: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9040066
APA StyleNag, S., Castro, M., Choudhary, V., & Feller, J.-F. (2021). Boosting Selectivity and Sensitivity to Biomarkers of Quantum Resistive Vapour Sensors Used for Volatolomics with Nanoarchitectured Carbon Nanotubes or Graphene Platelets Connected by Fullerene Junctions. Chemosensors, 9(4), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9040066