Do You Want to Increase Physical Activity in Adolescents? A School-Based Physical Activity Program Could Be an Efficient Way
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Instruments
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results Data
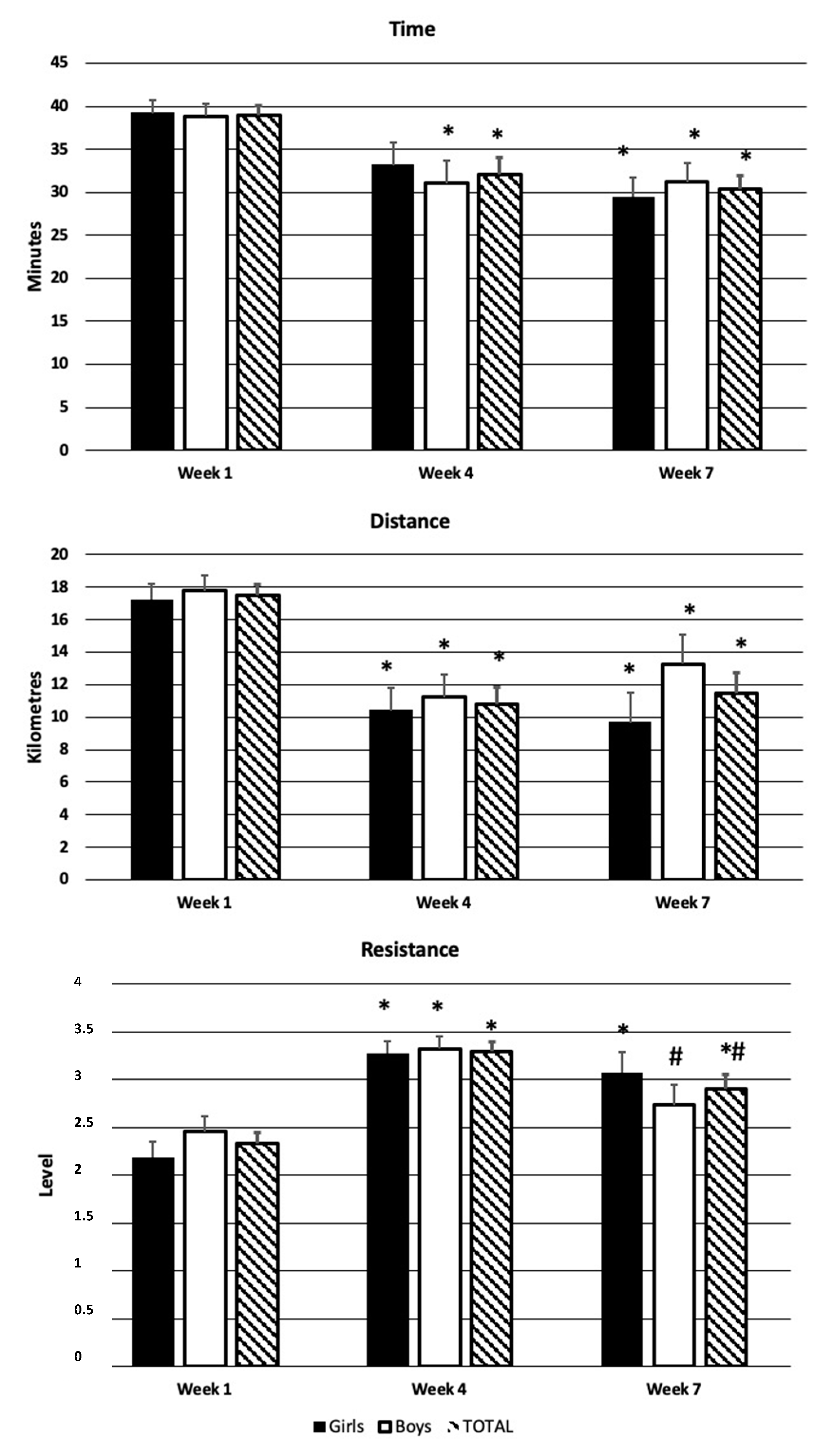
3.1.1. Participants’ Characteristics and Pedaling
3.1.2. Cardiorespiratory Fitness
3.1.3. Physical Activity
3.1.4. Language Competence
3.1.5. Attention
3.1.6. Heart Rate
3.1.7. Additional Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abarca-Gómez, L.; Abdeen, Z.A.; Hamid, Z.A.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.; Acosta-Cazares, B.; Acuin, C.; Adams, R.J.; Aekplakorn, W.; Afsana, K.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; et al. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 1289 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.B.; Artero, E.G.; Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Ruiz, J.R. Role of physical activity and fitness in the promotion of metabolic and overall health. Eur. J. Hum. Mov. 2018, 41, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.S.; LeBlanc, A.G.; Kho, M.E.; Saunders, T.J.; Larouche, R.; Colley, R.C.; Goldfield, G.; Gorber, S. Systematic review of sedentary behaviour and health indicators in school-aged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Wang, D.; Shen, H.; Yu, L.; Gao, Q.; Mao, L.; Jiang, F.; Luo, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Physical activity and health in Chinese children and adolescents: Expert consensus statement (2020). Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriemler, S.; Meyer, U.; Martin, E.; van Sluijs, E.M.; Andersen, L.B.; Martin, B.W. Effect of school-based interventions on physical activity and fitness in children and adolescents: A review of reviews and systematic update. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, Y.; Höner, O. Physical activity interventions in the school setting: A systematic review. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2012, 13, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly-Smith, A.; Quarmby, T.; Archbold, V.S.; Routen, A.C.; Morris, J.L.; Gammon, C.; Bartholomew, J.B.; Resaland, G.K.; Llewellyn, B.; Allman, R.; et al. Implementing physically active learning: Future directions for research, policy, and practice. J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, J.A.; Carriedo, A. Effects of an Interdisciplinary Approach Integrating Mathematics and Physical Education on Mathematical Learning and Physical Activity Levels. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2020, 39, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, M.M.C.; Chin, M.-K.; Korcz, A.; Popeska, B.; Edginton, C.R.; Uzunoz, F.S.; Podnar, H.; Coetzee, D.; Georgescu, L.; Emeljanovas, A.; et al. Brain Breaks® Physical Activity Solutions in the Classroom and on Attitudes toward Physical Activity: A Randomized Controlled Trial among Primary Students from Eight Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbeyns, T.; de Geus, B.; Bailey, S.; Decroix, L.; Van Cutsem, J.; De Pauw, K.; Meeusen, R. Bike Desks in the Classroom: Energy Expenditure, Physical Health, Cognitive Performance, Brain Functioning, and Academic Performance. J. Phys. Act. Health 2017, 14, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollo, S.; Crutchlow, L.; Nagpal, T.S.; Sui, W.; Prapavessis, H. The effects of classroom-based dynamic seating interventions on academic outcomes in youth: A systematic review. Learn. Environ. Res. 2019, 22, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedewa, A.L.; Abel, M.; Erwin, H.E. The effects of using stationary bicycle desks in classrooms on adolescents’ physical activity. J. Occup. Ther. Sch. Early Interv. 2017, 10, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedewa, A.; Cornelius, C.; Whitney, E.; Ahn, S.; Comis, M. The use of bicycle desks to increase physical activity in two special education classrooms. Health Psychol. Rep. 2018, 6, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kulinna, P.; Mulhearn, S.; Griffo, J.; McLeod, C. High School Students’ Perceptions of Using Desk Cycles. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2019, 90, A67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontifex, M.B.; Saliba, B.J.; Raine, L.B.; Picchietti, D.L.; Hillman, C.H. Exercise Improves Behavioral, Neurocognitive, and Scholastic Performance in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, J.E.; Lambourne, K. Classroom-based physical activity, cognition, and academic achievement. Prev. Med. 2011, 52 (Suppl. S1), S36–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelius, C. A Classroom-Based Physical Activity Intervention for Adolescents: Is There a Relationship with Self-Efficacy, Physical Activity, and On-Task Behavior? Ph.D. Thesis, Educational School and Counseling Psychology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Polo-Recuero, B.; Rojo-Tirado, M.; Ordóñez-Dios, A.; Breitkreuz, D.; Lorenzo, A. The Effects of Bike Desks in Formal Education Classroom-Based Physical Activity: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, L.A.; Mercier, D.; Gadoury, C.; Lambert, J. The multistage 20 metre shuttle run test for aerobic fitness. J. Sports Sci. 1988, 6, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resolución de 8 de marzo de 2019, de las Viceconsejerías de Política Educativa y Ciencia, y de Organización Educativa, por la que se dictan instrucciones para la celebración de las pruebas correspondientes a la evaluación final de los alumnos de cuarto curso de Educación Secundaria Obligatoria, para el curso académico 2018–2019. Boletín Oficial de la Comunidad de Madrid, 63, de 15 de marzo de 2019, 149–160. Available online: https://www.comunidad.madrid/sites/default/files/doc/educacion/sgea_eval_6ep_2019_pruebas_bocm-20190308-26.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Brickenkamp, R.; Cubero, N.S. D2: Test de Atención; TEA Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.L.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-Country Reliability and Validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, S.D.; Pfeiffer, K.A. New Data for an Updated Youth Energy Expenditure Compendium: An Introduction. J. Phys. Act. Health 2016, 13, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, H.W.; Fulton, J.E.; Caspersen, C.J. Assessment of Physical Activity among Children and Adolescents: A Review and Synthesis. Prev. Med. 2000, 31, S54–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, N.; Welsman, J.R. The Physical Activity Patterns of European Youth with Reference to Methods of Assessment. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 1067–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Revised edition; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Polo-Recuero, B.; Moreno-Barrio, A.; Ordóñez-Dios, A.F. Lecciones activas: Estrategia para aumentar la actividad física de los escolares durante la jornada lectiva. RICYDE Rev. Int. Cienc. Deporte 2020, 62, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemes, S.A.; Barber, S.E.; Bingham, D.D.; Ridgers, N.D.; Fletcher, E.; Pearson, N.; Salmon, J.; Dunstan, D.W. Reducing children’s classroom sitting time using sit-to-stand desks: Findings from pilot studies in UK and Australian primary schools. J. Public Health 2015, 38, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.; Coenen, P.; Howie, E.; Williamson, A.; Straker, L. The musculoskeletal and cognitive effects of under-desk cycling compared to sitting for office workers. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 79, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Úbeda-Palomares, A.B.; Hernández-Álvarez, J.L. Incremento de sesiones de educación física, motivación y eficacia motriz percibida en adolescentes. Rev. Int. Med. Cienc. Act. Física Deporte 2020, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.; Rosengren, B.E.; Dencker, M.; Karlsson, C.; Karlsson, M.K. A seven-year physical activity intervention for children increased gains in bone mass and muscle strength. Acta Paediatr. 2016, 105, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gråstén, A. School-based physical activity interventions for children and youth: Keys for success. J. Sport Health Sci. 2017, 6, 290–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherry, A.P.; Pearson, N.; Clemes, S.A. The effects of standing desks within the school classroom: A systematic review. Prev. Med. Rep. 2016, 3, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, L.; Kilgas, M.; Riley, A.; Gautam, Y.; Donath, L. y Drum, S. In-Class Cycling to Augment College Student Academic Performance and Reduce Physical Inactivity: Results from an RCT. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Hu, X.; Ma, G.; Cui, Z.; Pan, Y.; Chang, S.; Zhao, W.; Chen, C. Evaluation of a classroom-based physical activity promoting programme. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, D.P.; Fairclough, S.J.; Savory, L.A.; Denton, S.J.; Pang, D.; Deane, C.S.; Kerr, C.J. Accelerometry-assessed sedentary behaviour and physical activity levels during the segmented school day in 10–14-year-old children: The HAPPY study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.; Schofield, G.; McEvoy, E. An Integrated Curriculum Approach to Increasing Habitual Physical Activity in Children: A Feasibility Study. J. Sch. Health 2006, 76, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Brinthaupt, T.M. Effects of group and individual-based step goals on children’s physical activity levels in school. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2009, 21, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PEDAL Group | Control Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Girls | Boys | Total | Girls | Boys | Total | ||
| CF pre | 4.23 ± 0.48 | 8.62 § ± 0.48 | 6.42 ± 0.34 | 4.64 ± 0.52 | 8.59 § ± 0.52 | 6.61 ± 0.37 | |
| CF post | 5.42 * ± 0.42 | 9.19 *§ ± 0.42 | 7.30 * ± 0.30 | 5.50 * ± 0.46 | 8.77 § ± 0.46 | 7.14 * ± 0.32 | |
| IPAQ-SF | METs pre | 1683.27 ± 293.00 | 2898.47 § ± 259.72 | 2290.87 ± 195.77 | 2072.21 ± 280.53 | 2539.75 ± 280.53 | 2305.98 ± 198.36 |
| METs post | 2825.68 * ± 406.53 | 3671.40 * ± 360.35 | 3248.54 *# ± 271.62 | 1737.83 ± 389.22 | 2925.08 § ± 389.22 | 2331.46 ± 275.22 | |
| Sedentary time pre | 505.91 ± 36.00 | 499.29 ± 31.91 | 502.60 ± 24.06 | 501.25 ± 34.47 | 490.91 ± 36.00 | 496.08 ± 24.92 | |
| Sedentary time post | 468.18 ± 30.02 | 447.86 # ± 26.61 | 458.02 # ± 20.06 | 522.50 ± 28.74 | 545.46 ± 30.02 | 533.98 ± 20.78 | |
| Language competence pre | 6.20 ± 0.43 | 5.37 ± 0.41 | 5.78 ± 0.30 | 6.29 ± 0.45 | 5.40 ± 0.47 | 5.84 ± 0.32 | |
| Language competence post | 6.37 ± 0.34 | 5.23 § ± 0.33 | 5.80 ± 0.24 | 5.50 * ± 0.36 | 5.60 ± 0.37 | 5.55 ± 0.26 | |
| Attention | TOT pre | 439.50 ± 19.23 | 405.36 ± 17.80 | 422.43 ± 13.10 | 398.00 ± 17.80 | 388.67 ± 22.21 | 393.33 ± 14.23 |
| TOT post | 487.25 * ± 22.71 | 451.71 * ± 21.03 | 469.48 * ± 15.48 | 460.71 * ± 21.03 | 442.00 * ± 26.23 | 451.36 * ± 16.81 | |
| CON pre | 171.67 ± 7.89 | 157.71 ± 7.30 | 164.69 ± 5.38 | 151.43 ± 7.30 | 148.11 ± 9.11 | 149.77 ± 5.84 | |
| CON post | 202.50 * ± 10.62 | 183.29 * ± 9.83 | 192.89 * ± 7.23 | 184.64 * ± 9.83 | 174.33 * ± 12.26 | 179.49 * ± 7.86 | |
| PEDAL Group | Control Group | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Intervention | Week 1 | Week 4 | Week 7 | Pre-Intervention | Week 1 | Week 4 | Week 7 | ||
| HRweek | Girls | 90.92 ± 4.47 | 87.96 ± 4.65 | 92.62 ± 4.92 | 96.63 ± 4.64 | 90.65 ± 5.00 | 84.95 ± 5.20 | 87.40 ± 5.50 | 89.69 ± 5.19 |
| Boys | 93.70 ± 5.00 | 88.12 ± 5.20 | 98.28 ± 5.50 | 97.00 ± 5.19 | 94.30 ± 5.00 | 91.25 ± 5.20 | 98.98 ± 5.50 | 99.00 ± 5.20 | |
| Total | 92.31 ± 3.35 | 88.04 ± 3.49 | 95.45 ± 3.69 | 96.82 b ± 3.48 | 92.48 ± 3.53 | 88.10 ± 3.68 | 93.19 ± 3.89 | 94.34 ± 3.67 | |
| HR (LA lessons) | Girls | 86.90 ± 4.68 | 98.25 a# ± 4.27 | 94.12 # ± 5.51 | 99.07 a ± 5.10 | 84.38 ± 5.24 | 79.25 ± 4.77 | 76.29 ± 6.16 | 84.29 ± 5.70 |
| Boys | 88.44 ± 5.24 | 96.23 ± 4.77 | 93.78 ± 6.16 | 94.94 ± 5.70 | 88.69 ± 5.24 | 89.56 ± 4.77 | 90.83 ± 6.16 | 91.46 ± 5.70 | |
| Total | 87.67 ± 3.51 | 97.24 a# ± 3.20 | 93.95 ± 4.13 | 97.00 a ± 3.82 | 86.53 ± 3.70 | 84.41 ± 3.37 | 83.56 ± 4.35 | 87.87 ± 4.03 | |
| HR (PE lessons) | Girls | 129.30 ± 4.43 | 122.30 ± 4.53 | 141.30 b ± 5.28 | 123.10 ± 4.33 | 121.25 ± 4.95 | 119.88 ± 5.07 | 127.25 ± 5.91 | 127.25 ± 4.84 |
| Boys | 132.13 ± 4.95 | 119.88 ± 5.07 | 129.38 ± 5.91 | 130.38 ± 4.84 | 143.50 § ± 4.95 | 124.50 a ± 5.07 | 128.25 ± 5.91 | 129.75 ± 4.84 | |
| Total | 130.71 ± 3.32 | 121.09 ± 3.40 | 135.34 b ± 3.96 | 126.74 ± 3.25 | 132.38 ± 3.50 | 122.19 ± 3.58 | 127.75 ± 4.18 | 128.50 ± 3.42 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polo-Recuero, B.; Ordóñez-Dios, A.; Rojo-Tirado, M.Á.; Lorenzo, A. Do You Want to Increase Physical Activity in Adolescents? A School-Based Physical Activity Program Could Be an Efficient Way. Children 2023, 10, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101641
Polo-Recuero B, Ordóñez-Dios A, Rojo-Tirado MÁ, Lorenzo A. Do You Want to Increase Physical Activity in Adolescents? A School-Based Physical Activity Program Could Be an Efficient Way. Children. 2023; 10(10):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101641
Chicago/Turabian StylePolo-Recuero, Beatriz, Alfonso Ordóñez-Dios, Miguel Ángel Rojo-Tirado, and Alberto Lorenzo. 2023. "Do You Want to Increase Physical Activity in Adolescents? A School-Based Physical Activity Program Could Be an Efficient Way" Children 10, no. 10: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101641
APA StylePolo-Recuero, B., Ordóñez-Dios, A., Rojo-Tirado, M. Á., & Lorenzo, A. (2023). Do You Want to Increase Physical Activity in Adolescents? A School-Based Physical Activity Program Could Be an Efficient Way. Children, 10(10), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101641







