Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes in the Pediatric Age
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes
2.1. APS-1
2.1.1. Epidemiology
2.1.2. Pathogenesis and Autoimmunity
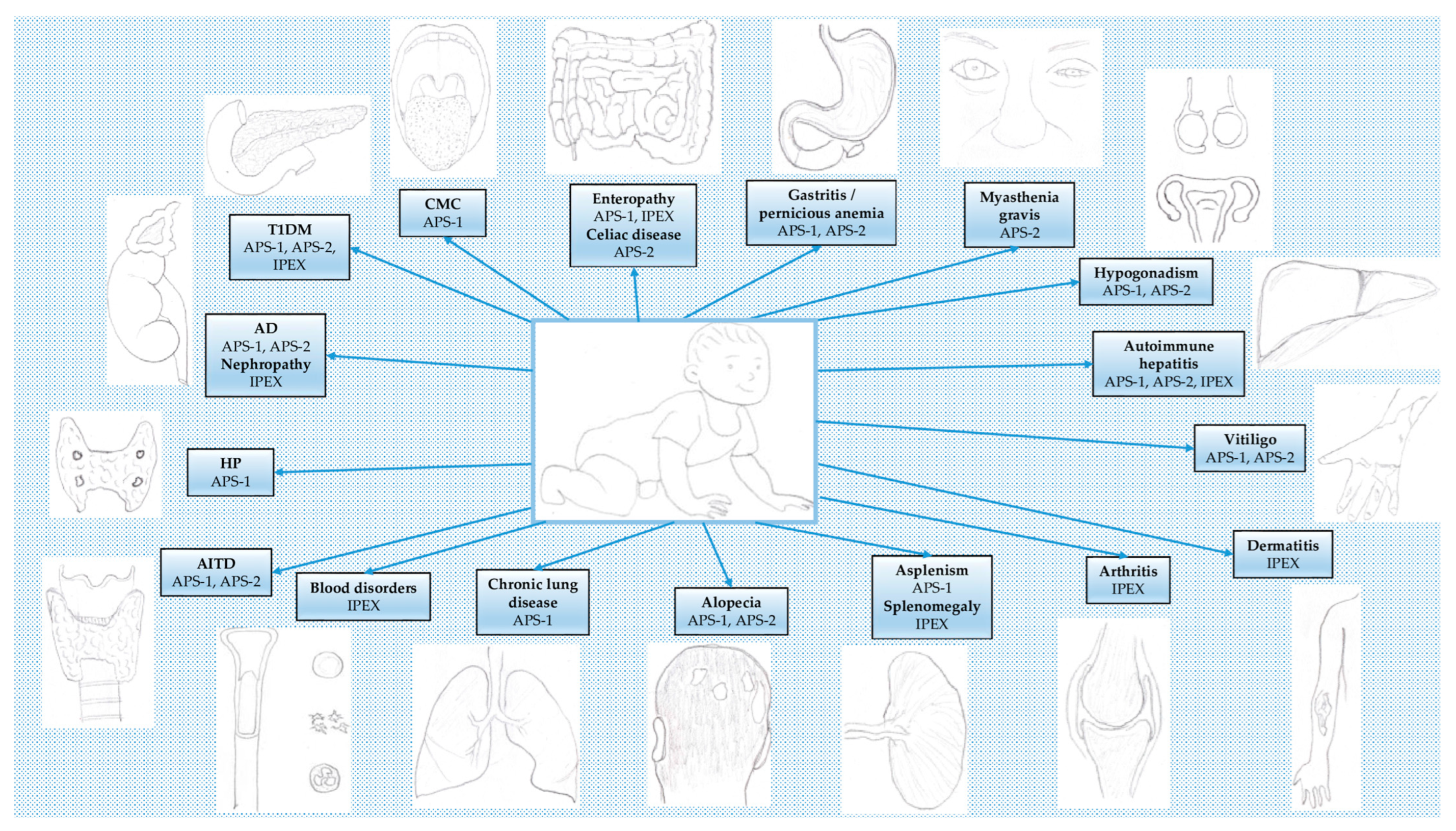
2.1.3. Clinical Features
2.1.4. Treatment
2.2. APS-2
2.2.1. Epidemiology
2.2.2. Pathogenesis and Autoimmunity
2.2.3. Clinical Features
2.2.4. Treatment
2.3. IPEX Syndrome
2.3.1. Epidemiology
2.3.2. Pathogenesis and Autoimmunity
2.3.3. Clinical Features
2.3.4. Treatment
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTH | adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| AD | Addison disease |
| AIRE | autoimmune regulator |
| AITD | autoimmune thyroid disease |
| APECED | autoimmune polyendocrinopathy–candidiasis–ectodermal-dystrophy |
| APS | autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome |
| CaSR | calcium-sensing receptor |
| CGM | continuous glucose monitoring |
| CMC | chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis |
| CTLA-4 | cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 |
| FOXP3 | forkhead box protein P3 |
| GAD-65 | glutamic acid decarboxylase-65 |
| HCL | hybrid closed-loop |
| HLA | human leukocyte antigen |
| HP | hypoparathyroidism |
| HSCT | hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| IA2 | islet antigen 2 |
| IFN-α2-Abs | anti-interferon-α2 antibodies |
| IFN-ω-Abs | anti-interferon-ω antibodies |
| IPEX | immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked |
| MHC | major histocompatibility complex |
| NALP5 | NACHT leucine-rich-repeat protein 5 |
| PTH | parathyroid hormone |
| PTPN22 | protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type |
| P450c17 | 17-alpha-hydroxylase |
| P450c21 | 21-hydroxylase |
| P450scc | side-chain cleavage enzyme |
| QoL | quality of life |
| Tg | thyroglobulin |
| TPO | thyroid peroxidase |
| Tregs | regulatory T-cells |
| TSH | thyrotropin |
| T1DM | type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| ZnT8 | zinc transporter 8 |
References
- Eisenbarth, G.S.; Gottlieb, P.A. Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2068–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufeld, M.; Maclaren, N.; Blizzard, R. Autoimmune polyglandular syndromes. Pediatr. Ann. 1980, 9, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, A.W.; Gottlieb, P.A. Autoimmune polyglandular syndromes. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousfiha, A.; Moundir, A.; Tangye, S.G.; Picard, C.; Jeddane, L.; Al-Herz, W.; Rundles, C.C.; Franco, J.L.; Holland, S.M.; Klein, C.; et al. The 2022 Update of IUIS Phenotypical Classification for Human Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 1508–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.-J.; Leung, P.S.C.; Zhang, W.; Ma, X.; Gershwin, M.E. The immunobiology and clinical features of type 1 autoimmune polyglandular syndrome (APS-1). Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Skowronek, I. IPEX Syndrome: Genetics and Treatment Options. Genes 2021, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profeta, G.; Micangeli, G.; Tarani, F.; Paparella, R.; Ferraguti, G.; Spaziani, M.; Isidori, A.M.; Menghi, M.; Ceccanti, M.; Fiore, M.; et al. Sexual Developmental Disorders in Pediatrics. Clin. Ter. 2022, 173, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micangeli, G.; Menghi, M.; Profeta, G.; Tarani, F.; Mariani, A.; Petrella, C.; Barbato, C.; Ferraguti, G.; Ceccanti, M.; Tarani, L.; et al. The Impact of Oxidative Stress on Pediatrics Syndromes. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraguti, G.; Terracina, S.; Micangeli, G.; Lucarelli, M.; Tarani, L.; Ceccanti, M.; Spaziani, M.; D’Orazi, V.; Petrella, C.; Fiore, M. NGF and BDNF in pediatrics syndromes. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 145, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarani, L.; Rasio, D.; Tarani, F.; Parlapiano, G.; Valentini, D.; Dylag, K.A.; Spalice, A.; Paparella, R.; Fiore, M. Pediatrics for Disability: A Comprehensive Approach to Children withSyndromic Psychomotor Delay. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2022, 18, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahaly, G.J. Polyglandular autoimmune syndromes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 161, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahonen, P.; Myllärniemi, S.; Sipilä, I.; Perheentupa, J. Clinical Variation of Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy–Candidiasis–Ectodermal Dystrophy (APECED) in a Series of 68 Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotogora, J.; Shapiro, M.S. Polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type I among Iranian Jews. J. Med. Genet. 1992, 29, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosatelli, M.C.; Meloni, A.; Meloni, A.; Devoto, M.; Cao, A.; Scott, H.S.; Peterson, P.; Heino, M.; Krohn, K.J.E.; Nagamine, K.; et al. A common mutation in Sardinian autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy patients. Hum. Genet. 1998, 103, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björses, P.; Halonen, M.; Palvimo, J.J.; Kolmer, M.; Aaltonen, J.; Ellonen, P.; Perheentupa, J.; Ulmanen, I.; Peltonen, L. Mutations in the AIRE Gene: Effects on Subcellular Location and Transactivation Function of the Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy-Candidiasis–Ectodermal Dystrophy Protein. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 66, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Chang, L.; Fu, H.; Sun, G.; Yang, W. The Role of Autoimmune Regulator (AIRE) in Peripheral Tolerance. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 3930750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halonen, M.; Eskelin, P.; Myhre, A.-G.; Perheentupa, J.; Husebye, E.S.; Kämpe, O.; Rorsman, F.; Peltonen, L.; Ulmanen, I.; Partanen, J. AIRE Mutations and Human Leukocyte Antigen Genotypes as Determinants of the Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy-Candidiasis-Ectodermal Dystrophy Phenotype. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 2568–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meager, A.; Visvalingam, K.; Peterson, P.; Möll, K.; Murumägi, A.; Krohn, K.; Eskelin, P.; Perheentupa, J.; Husebye, E.; Kadota, Y.; et al. Anti-Interferon Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy Syndrome Type 1. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larosa, M.d.P.; Mackenzie, R.; Burne, P.; Garelli, S.; Barollo, S.; Masiero, S.; Rubin, B.; Chen, S.; Furmaniak, J.; Betterle, C.; et al. Assessment of autoantibodies to interferon-ω in patients with autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1: Using a new immunoprecipitation assay. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. CCLM 2017, 55, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuralieva, N.; Yukina, M.; Sozaeva, L.; Donnikov, M.; Kovalenko, L.; Troshina, E.; Orlova, E.; Gryadunov, D.; Savvateeva, E.; Dedov, I. Diagnostic Accuracy of Methods for Detection of Antibodies against Type I Interferons in Patients with Endocrine Disorders. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliegman, R.; Behrman, R.E.; Nelson, W.E. (Eds.) Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 20th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-4557-7566-8. [Google Scholar]
- Nambam, B.; Winter, W.E.; Schatz, D.A. IgG4 antibodies in autoimmune polyglandular disease and IgG4-related endocrinopathies: Pathophysiology and clinical characteristics. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2014, 26, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrod, H.G. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in childhood and complications of non-Candida infection: A report of the Pediatric Immunodeficiency Collaborative Study Group. J. Pediatr. 1990, 116, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, P.; Perheentupa, J.; Krohn, K.J. Detection of candidal antigens in autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type I. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1996, 3, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Husebye, E.S.; Perheentupa, J.; Rautemaa, R.; Kämpe, O. Clinical manifestations and management of patients with autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 265, 514–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betterle, C.; Zanchetta, R. Update on autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes (APS). Acta Bio-Medica Atenei Parm. 2003, 74, 9–33. [Google Scholar]
- Walser, M.; Robinson, B.H.B.; Duckett, J.W. The Hypercalcemia of Adrenal Insufficiency*. J. Clin. Investig. 1963, 42, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gylling, M.; Kääriäinen, E.; Väisänen, R.; Kerosuo, L.; Solin, M.-L.; Halme, L.; Saari, S.; Halonen, M.; Kämpe, O.; Perheentupa, J.; et al. The Hypoparathyroidism of Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy-Candidiasis-Ectodermal Dystrophy Protective Effect of Male Sex. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4602–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Donohoue, P.A. Adrenal Disorders. In Pediatric Endocrinology: Principles and Practice, 3rd ed.; Allen, D.B., Nadeau, K., Kappy, M.S., Geffner, M.E., Eds.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: http://accesspediatrics.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?aid=1181238347 (accessed on 22 January 2023).
- Huecker, M.R.; Bhutta, B.S.; Dominique, E. Adrenal Insufficiency. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022; Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441832/ (accessed on 22 January 2023).
- Chen, S.; Sawicka, J.; Betterle, C.; Powell, M.; Prentice, L.; Volpato, M.; Rees Smith, B.; Furmaniak, J. Autoantibodies to steroidogenic enzymes in autoimmune polyglandular syndrome, Addison’s disease, and premature ovarian failure. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 1871–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Betterle, C.; Volpato, M.; Rees Smith, B.; Furmaniak, J.; Chen, S.; Zanchetta, R.; Greggio, N.A.; Pedini, B.; Boscaro, M.; Presotto, F., II. Adrenal Cortex and Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Autoantibodies in Children with Organ-Specific Autoimmune Diseases: Markers of High Progression to Clinical Addison’s Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, T.C.; Thomas, P.M.; Fleisher, T.A.; Feuillan, P.; Parker, R.I.; Cassorla, F.; Chrousos, G.P. Frequent occurrence of asplenism and cholelithiasis in patients with autoimmune polyglandular disease type I. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzise, M.; Alessi, L.; Bruno, E.; Cama, V.; Costanzo, D.; Genovese, C.; Mignosa, C.; Scuderi, V.; DE Luca, F. APECED syndrome in childhood: Clinical spectrum is enlarging. Minerva Pediatr. 2016, 68, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valenzise, M.; Aversa, T.; Salzano, G.; Zirilli, G.; De Luca, F.; Su, M. Novel insight into Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polineuropathy in APECED syndrome: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications in children. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2017, 43, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winer, K.K.; Sinaii, N.; Peterson, D.; Sainz, B.; Cutler, G.B. Effects of Once Versus Twice-Daily Parathyroid Hormone 1–34 Therapy in Children with Hypoparathyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3389–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, S.R.; Bryce, J.; Haghpanahan, H.; Lewsey, J.D.; Tan, L.E.; Atapattu, N.; Birkebaek, N.H.; Blankenstein, O.; Neumann, U.; Balsamo, A.; et al. Real-World Estimates of Adrenal Insufficiency-Related Adverse Events in Children With Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e192–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.S.; Sandhu, C.S.; Singh, N.; Evans, T. Initiation of levothyroxine in a patient with hypothyroidism inducing adrenal crisis requiring VA ECMO: A tale of preventable disaster. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e230601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, L.G.; Schaffner, W. Care of the Asplenic Patient. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husebye, E.S.; Anderson, M.S.; Kämpe, O. Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahaly, G.J.; Frommer, L. Polyglandular autoimmune syndromes. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2018, 41, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, S.Y. The HLA System: Genetics, Immunology, Clinical Testing, and Clinical Implications. Yonsei Med. J. 2007, 48, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maclaren, N.K.; Riley, W.J. Inherited Susceptibility to Autoimmune Addison’s Disease Is Linked to Juman Leukocyte Antigens-DR3 and/or DR4, except when Associated with Type I Autoimmune Poluglandular Syndrome*. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1986, 62, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dultz, G.; Matheis, N.; Dittmar, M.; Bender, K.; Kahaly, G. CTLA-4 CT60 Polymorphism in Thyroid and Polyglandular Autoimmunity. Horm. Metab. Res. 2009, 41, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dultz, G.; Matheis, N.; Dittmar, M.; Röhrig, B.; Bender, K.; Kahaly, G.J. The Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Non-Receptor Type 22 C1858T Polymorphism Is a Joint Susceptibility Locus for Immunthyroiditis and Autoimmune Diabetes. Thyroid 2009, 19, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourati, H.; Bouzid, D.; Abida, O.; Kharrat, N.; Mnif, F.; Haddouk, S.; Fesel, C.; Costa, J.; Ayed, M.B.; Abid, M.; et al. Non-HLA autoimmunity genetic factors contributing to Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndrome type II in Tunisian patients. Hum. Immunol. 2012, 73, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- “Percorso Diagnostico Terapeutico Assistenziale ospedale territorio per la gestione ed il trattamento del paziente con diabete in età pediatrica.” Società Italiana di Endocrinologia e Diabetologia Pediatrica SIEDP. 2018. Available online: http://www.siedp.it/pagina/905/pdta+diabete+in+et%C3%80+pediatrica (accessed on 11 March 2023).
- Michels, A.W.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS-1) as a model for understanding autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 2 (APS-2). J. Intern. Med. 2009, 265, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didriksen, N.M.; Sævik, Å.B.; Sortland, L.S.; Øksnes, M.; Husebye, E.S. Sex-Specific Limitations in Physical Health in Primary Adrenal Insufficiency. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 718660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensing, S.; Hulting, A.-L.; Husebye, E.S.; Kämpe, O.; Løvås, K. MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Epidemiology, quality of life and complications of primary adrenal insufficiency: A review. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 175, R107–R116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Løvås, K.; Curran, S.; Øksnes, M.; Husebye, E.S.; Huppert, F.A.; Chatterjee, V.K.K. Development of a Disease-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire in Addison’s Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fröhlich, E.; Wahl, R. Thyroid Autoimmunity: Role of Anti-thyroid Antibodies in Thyroid and Extra-Thyroidal Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuomilehto, J. The Emerging Global Epidemic of Type 1 Diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2013, 13, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.P.; Matheis, N.; Kahaly, G.J. Type 1 diabetes and polyglandular autoimmune syndrome: A review. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-Y.; Chen, I.-W.; Chen, S.-T.; Wang, C.-C. Association of stiff-person syndrome with autoimmune endocrine diseases. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 2942–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Jialal, I. Polyglandular Autoimmune Syndrome Type II. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022; Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525992/ (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Bassi, M.; Patti, L.; Silvestrini, I.; Strati, M.F.; Ponzano, M.; Minuto, N.; Maggi, D. One-year follow-up comparison of two hybrid closed-loop systems in Italian children and adults with type 1 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1099024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffini, R.; Deodati, A.; Nicoletti, M.C.; Carducci, C.; Ciampalini, P.; Lorubbio, A.; Matteoli, M.C.; Pampanini, V.; Patera, I.P.; Rapini, N.; et al. Comparison of two advanced hybrid closed loop in a pediatric population with type 1 diabetes: A real-life observational study. Acta Diabetol. 2022, 59, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.M.; Katkat, N.; Day, H.; Hubbard, R.; Quinn, M.; Finnigan, L. Real-world prospective observational single-centre study: Hybrid closed loop improves HbA1c, time-in-range and quality of life for children, young people and their carers. Diabet. Med. 2022, 39, e14863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warshauer, J.T.; Bluestone, J.A.; Anderson, M.S. New Frontiers in the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Olsen, N.; Zheng, S.G. The progress and prospect of regulatory T cells in autoimmune diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 111, 102461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzaghi, F.; Passerini, L. IPEX Syndrome: Improved Knowledge of Immune Pathogenesis Empowers Diagnosis. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 612760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampasona, V.; Passerini, L.; Barzaghi, F.; Lombardoni, C.; Bazzigaluppi, E.; Brigatti, C.; Bacchetta, R.; Bosi, E. Autoantibodies to Harmonin and Villin Are Diagnostic Markers in Children with IPEX Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambineri, E.; Ciullini Mannurita, S.; Hagin, D.; Vignoli, M.; Anover-Sombke, S.; DeBoer, S.; Segundo, G.R.S.; Allenspach, E.J.; Favre, C.; Ochs, H.D.; et al. Clinical, Immunological, and Molecular Heterogeneity of 173 Patients With the Phenotype of Immune Dysregulation, Polyendocrinopathy, Enteropathy, X-Linked (IPEX) Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Jeon, B.; Ochs, H.D.; Lee, J.S.; Gee, H.Y.; Seo, S.; Geum, D.; Piccirillo, C.A.; Eisenhut, M.; et al. Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) syndrome: A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabi-Tawil, M.; Ruemmele, F.M.; Fraitag, S.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Neven, B.; Brousse, N.; De Prost, Y.; Fischer, A.; Goulet, O.; Bodemer, C. Cutaneous manifestations of immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 160, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzaghi, F.; Passerini, L.; Bacchetta, R. Immune Dysregulation, Polyendocrinopathy, Enteropathy, X-Linked Syndrome: A Paradigm of Immunodeficiency with Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacchetta, R.; Barzaghi, F.; Roncarolo, M.-G. From IPEX syndrome to FOXP3 mutation: A lesson on immune dysregulation: IPEX syndrome and FOXP3. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1417, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedetti, F.; Insalaco, A.; Diamanti, A.; Cortis, E.; Muratori, F.; Lamioni, A.; Carsetti, R.; Cusano, R.; De Vito, R.; Perroni, L.; et al. Mechanistic Associations of a Mild Phenotype of Immunodysregulation, Polyendocrinopathy, Enteropathy, X-Linked Syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Torgerson, T.R.; Selmi, C.; Gambineri, E.; Carneiro-Sampaio, M.; Mannurita, S.C.; Leung, P.S.C.; Norman, G.L.; Gershwin, M.E. The spectrum of autoantibodies in IPEX syndrome is broad and includes anti-mitochondrial autoantibodies. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 35, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzaghi, F.; Amaya Hernandez, L.C.; Neven, B.; Ricci, S.; Kucuk, Z.Y.; Bleesing, J.J.; Nademi, Z.; Slatter, M.A.; Ulloa, E.R.; Shcherbina, A.; et al. Long-term follow-up of IPEX syndrome patients after different therapeutic strategies: An international multicenter retrospective study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1036–1049.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borna, S.; Lee, E.; Sato, Y.; Bacchetta, R. Towards gene therapy for IPEX syndrome. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 52, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| APS-1 | APS-2 | IPEX | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence | <1:100,000/year | 1-2:100,000/year | <1:1,000,000 (prevalence) |
| Age of onset | Infancy/early childhood | Late childhood/early adulthood | Perinatally/within the first few weeks or months of life |
| Gene and inheritance | Monogenic (AIRE, chromosome 21q22.3), autosomal recessive | Polygenic, associated with HLA and non-HLA genes | Monogenic (FOXP3, chromosome Xp11.23), X-linked recessive |
| Autoantibodies | Anti-interferon-ω/α2 | Organ-specific | Anti-harmonin, anti-villin |
| Common phenotype | Candidiasis, hypoparathyroidism, Addison disease | Addison disease, type 1 diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroid disease | Enteropathy, type 1 diabetes mellitus, dermatitis |
| Main treatments | Antifungal therapy, calcium and vitamin D, hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone | Hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone, insulin, levothyroxine | Nutritional treatment, insulin, levothyroxine, immunosuppressive agents, HSCT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paparella, R.; Menghi, M.; Micangeli, G.; Leonardi, L.; Profeta, G.; Tarani, F.; Petrella, C.; Ferraguti, G.; Fiore, M.; Tarani, L. Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes in the Pediatric Age. Children 2023, 10, 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030588
Paparella R, Menghi M, Micangeli G, Leonardi L, Profeta G, Tarani F, Petrella C, Ferraguti G, Fiore M, Tarani L. Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes in the Pediatric Age. Children. 2023; 10(3):588. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030588
Chicago/Turabian StylePaparella, Roberto, Michela Menghi, Ginevra Micangeli, Lucia Leonardi, Giovanni Profeta, Francesca Tarani, Carla Petrella, Giampiero Ferraguti, Marco Fiore, and Luigi Tarani. 2023. "Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes in the Pediatric Age" Children 10, no. 3: 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030588
APA StylePaparella, R., Menghi, M., Micangeli, G., Leonardi, L., Profeta, G., Tarani, F., Petrella, C., Ferraguti, G., Fiore, M., & Tarani, L. (2023). Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes in the Pediatric Age. Children, 10(3), 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030588








