Incomplete Kawasaki Disease with Peripheral Facial Nerve Palsy and Lung Nodules: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
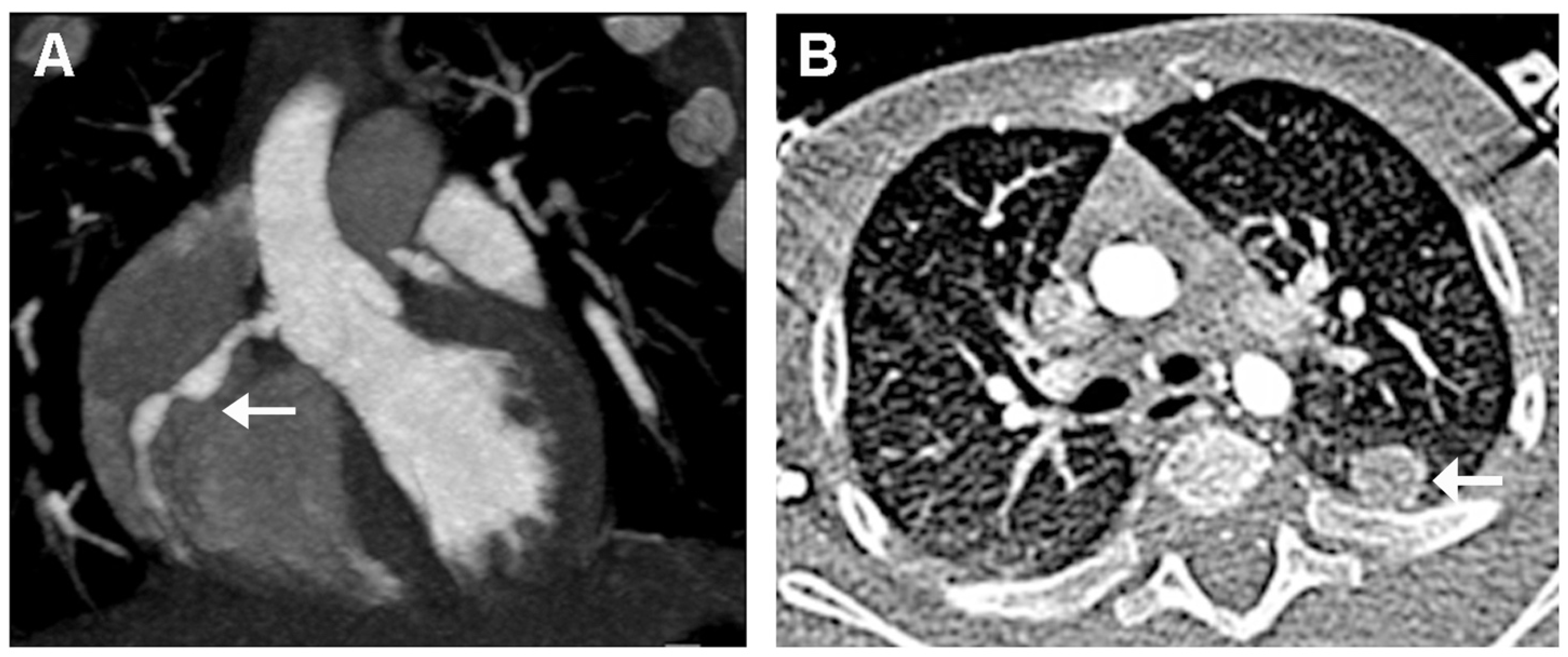
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| KD | Kawasaki disease |
| CALs | coronary artery lesions |
| FNP | facial nerve palsy |
| CT | computed tomography |
| WBC | white blood cells |
| CRP | c-reactive protein |
| PCT | procalcitonin |
| BNP | brain natriuretic peptide |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| IL | interleukin |
| SARS-CoV-2 | acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| HSV | herpes simplex virus |
| ECG | electrocardiogram |
| ASA | acetyl salicylic acid |
| intravenous immunoglobulin | IVIG |
| CAA | coronary artery aneurysm |
| CA | coronary artery |
| CNS | central nervous system |
References
- Marchesi, A.; Tarissi de Jacobis, I.; Rigante, D.; Rimini, A.; Malorni, W.; Corsello, G.; Bossi, G.; Buonuomo, S.; Cardinale, F.; Cortis, E.; et al. Kawasaki disease: Guidelines of the Italian Society of Pediatrics, part I—Definition, epidemiology, etiopathogenesis, clinical expression and management of the acute phase. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rife, E.; Gedalia, A. Kawasaki Disease: An Update. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, M.; Minami, T. Kawasaki Disease: Pathology, Risks, and Management. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2022, 18, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, G.; Cimaz, R.; Calabri, G.B.; Simonini, G.; Lasagni, D.; Resti, M.; Trapani, S. Kawasaki disease in infants less than one year of age: An Italian cohort from a single center. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, A.P. High risk of coronary artery aneurysms in infants younger than 6 months with Kawasaki disease. J. Pediatr. 2017, 185, 112–116.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizard, E.J. Complications of Kawasaki disease. Curr. Paediatr. 2005, 15, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, J. An autopsy case of acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome with coronary embolism. Acta Paediatr. Jpn. 1974, 78, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Terasawa, K.; Ichinose, E.; Matsuishi, T.; Kato, H. Neurological complications in Kawasaki disease. Brain Dev. 1983, 5, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Tokugawa, K.; Fukushige, J.; Tasaki, H.; Nanri, T.; Ueda, K. Facial palsy in Kawasaki disease. Report of two cases and a review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1987, 146, 601–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, H.M.; Yang, J.S.; Lim, B.K.; Kim, J.S. Facial nerve paralysis associated with Kawasaki disease. Yonsei Med. J. 1991, 32, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushara, K.; Wilson, A.; Rust, R.S. Facial Palsy in Kawasaki syndrome. Pediatr. Neurol. 1997, 17, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Buttery, J.; Pike, M. Neurological complications of Kawasaki disease. Arch. Dis. Child. 1998, 79, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, L.K.H.; Lun, K.S.; Ng, Y.M. Facial nerve palsy and Kawasaki disease. HKMJ 2000, 6, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biezeveld, M.H.; Voorbrood, B.S.; Clur, S.A.; Kuijpers, T.W. Facial nerve palsy in a thirteen-year-old male youth with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2002, 21, 442–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larralde, M.; Santos-Muñoz, A.; Rutiman, R. Kawasaki disease with facial nerve paralysis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2003, 20, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, H.; Waddington, C.; Geddes, J.; Newburger, J.W.; Burgner, D. Facial nerve palsy complicating Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 2008, 122, e783–e785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.T.; Chiu, N.C.; Ho, C.S.; Chen, M.R. Facial palsy in Kawasaki disease: Report of two cases. Acta Paediatr. Taiwan 2008, 49, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.C.; Yeo, W.S.; Loke, K.Y.; Quek, S.C. Bilateral facial nerve palsy in Kawasaki disease. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2009, 38, 737–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kulkarni, K.P.; Dubey, P.N. Facial palsy in a 2-month-old infant with Kawasaki disease. Rheumatol. Int. 2010, 30, 1407–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, N.R.; Magalhães, C.M.; Almeida, R.d.F.; Santos, R.C.; Gandolfi, L.; Pratesi, R. Prospective study of Kawasaki disease complications: Review of 115 cases. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2011, 57, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khubchandani, R.P.; Dhanrajani, A. Facial nerve palsy complicating a case of Kawasaki disease. Indian J. Pediatr. 2014, 81, 406–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowe, R.C. Facial nerve palsy, Kawasaki disease and coronary artery aneurysm. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2015, 19, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Gonzalez, M.; Castellano-Martinez, A.; Perez-Reviriego, A.A. Atypical Presentation of Incomplete Kawasaki Disease: A Peripheral Facial Nerve Palsy. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 55, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgun, A.; Karagöl, C.; Pamuk, U.; Gürsu, H.A.; Çetin, İ. A rare cause of facial nerve palsy in a young infant: Kawasaki disease. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2018, 60, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lu, N. Facial nerve palsy presenting as rare neurological complication of Kawasaki disease: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e16888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, N.; Li, H.; Liang, J. Kawasaki disease manifesting as bilateral facial nerve palsy and meningitis: A case report and literature review. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 4014–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, N.; Wang, M.; Sun, L. Kawasaki disease complicating bilateral facial nerve palsy and giant coronary artery aneurysms: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, 14395–14399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Juárez, A.; Medina-Andrade, M.A.; Olivares, I.E.R.; Colín-Ortíz, J.L.; Yamazaki-Nakashimada, M.A.; Garrido-Garcia, L.M. Multiresistant Kawasaki Disease Complicated with Facial Nerve Palsy, Bilateral Giant Coronary Artery Aneurysms, and Stenosis of the Right Coronary Artery in an Infant. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, S351–S354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Hu, W.; Xu, Y.; Deng, J. Facial nerve palsy may indicate coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellis, L.; Castellanos, D.A.; Oduor, R.; Gauvreau, K.; Dionne, A.; Newburger, J.; Friedman, K.G. Comparison of coronary artery measurements between echocardiograms and cardiac CT in Kawasaki disease patients with aneurysms. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2022, 16, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Liu, X. Kawasaki disease with pulmonary nodules: Two case reports and literature review. Transl. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 1952–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, A.F.; Crawford, S.E.; Finn, L.S.; López-Andreu, J.A.; Ferrando-Monleón, S.; Pérez-Tamarit, D.; Cornwall, M.L.; Shulman, S.T.; Rowley, A.H. Inflammatory pulmonary nodules in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2003, 36, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.C.; Franco, A. The immunomodulatory effects of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in Kawasaki disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, A.; Rigante, D.; Cimaz, R.; Ravelli, A.; Tarissi de Jacobis, I.; Rimini, A.; Cardinale, F.; Cattalini, M.; De Zorzi, A.; Dellepiane, R.M.; et al. Revised recommendations of the Italian Society of Pediatrics about the general management of Kawasaki disease. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelik, M.; Chung, S.A.; Ardalan, K.; Binstadt, B.A.; Friedman, K.; Hayward, K.; Imundo, L.F.; Lapidus, S.K.; Kim, S.; Son, M.B.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Kawasaki Disease. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2022, 74, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrindle, B.W.; Rowley, A.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Burns, J.C.; Bolger, A.F.; Gewitz, M.; Baker, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Takahashi, M.; Shah, P.B.; et al. Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Management of Kawasaki Disease: A Scientific Statement for Health Professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e927–e999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egami, K.; Muta, H.; Ishii, M.; Suda, K.; Sugahara, Y.; Iemura, M.; Matsuishi, T. Prediction of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease. J. Pediatr. 2006, 149, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Inoue, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Okada, Y.; Tamura, K.; Tomomasa, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Morikawa, A. Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in patients with Kawasaki disease. Circulation 2006, 113, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

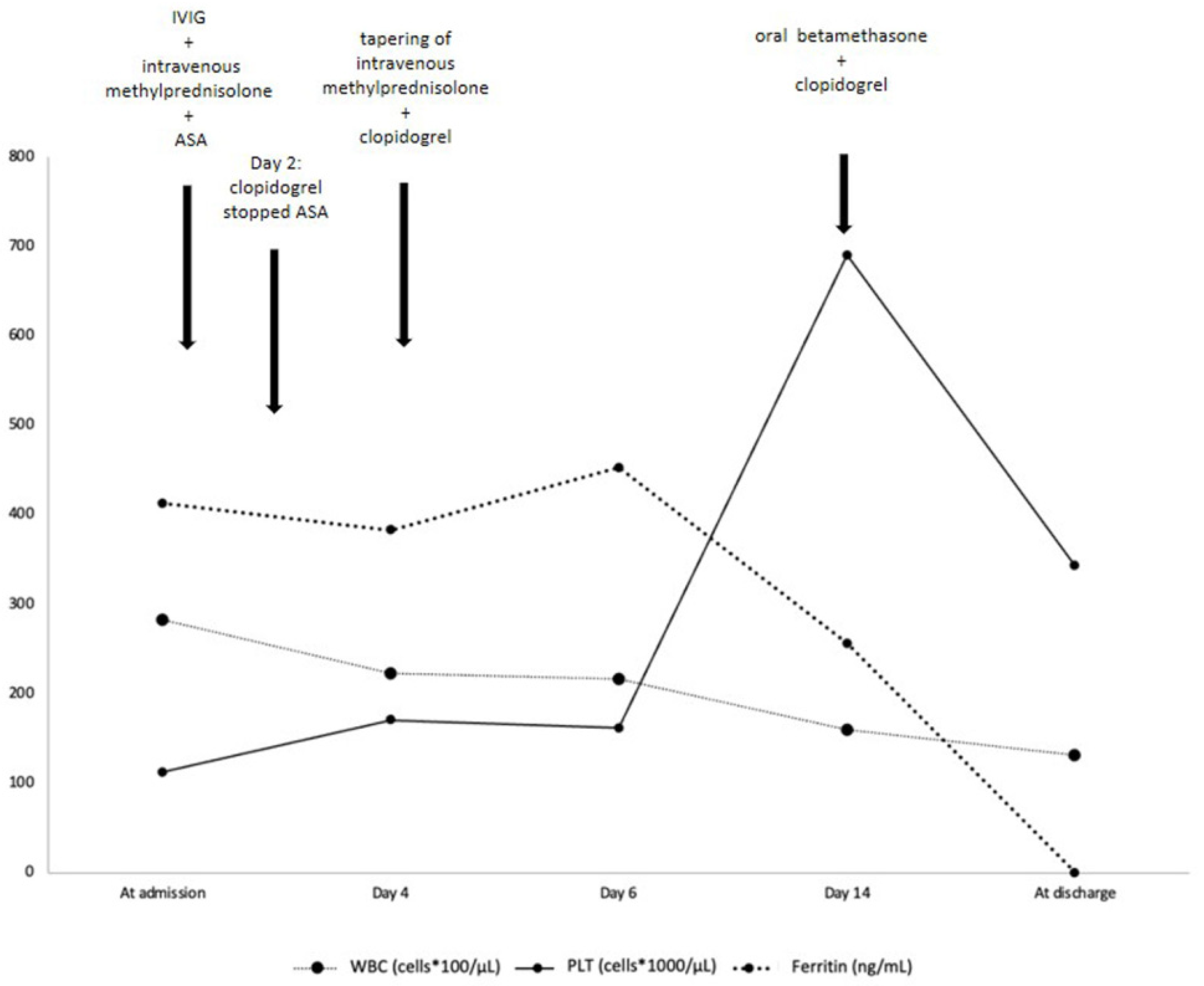

| At Admission | Day 2 | Day 4 | Day 6 | Day 14 | At Discharge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hb (g/dl) | 8.6 | 9.1 | 10.9 | 11.4 | 11.8 | |
| CRP (mg/L) (reference value < 5) | 111.31 | 8.48 | 1.77 | 0.30 | 0.44 | |
| ESR (mm/h) | 54 | 23 | ||||
| AST (U/L) (reference value < 48) | 20 | 18 | 27 | 42 | 30 | 36 |
| ALT (U/L) (reference value < 50) | 14 | 14 | 22 | 44 | 27 | 17 |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) (reference value < 320) | 412.9 | 383.2 | 453.30 | 256.8 | ||
| Troponin (ng/L) (reference value < 14) | 9 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 7 | |
| BNP (pg/mL) (reference value < 100) | 48.2 | 28.4 | 8.3 | <5 |
| Cytokine | Patient’s Value | Reference Value |
|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ (pg/mL) | 0.73 | 0.54–2.72 |
| IL-1-β (pg/mL) | 0.58 | <0.16 |
| IL-4 (pg/mL) | 0.35 | <0.5 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 3.54 | 0.76–6.38 |
| IL-10 (pg/mL) | 4.64 | 1.77–3.76 |
| IL-12p70 (pg/mL) | 0.78 | 0.60–7.96 |
| IL-17A (pg/mL) | 1.54 | <1.05 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 16.9 | 7.78–12.2 |
| Author | Article Type | Patient’s Age (Months) | No. of Included Patients | FNP Onset (Day of Illness) | Coronary Involvement | Therapy | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terasawa, 1983 [8] | Case report | 12 | 3 | 22 | No | ASA (30 mg/kg) | Full recovery of FNP within 2 weeks |
| Hattori, 1987 [9] | Case report | 6; 9 | 2 | 16; 19 | No | ASA (50 and 80 mg/kg/d, respectively) | Full recovery of FNP within 1 and 2 months, respectively |
| Park, 1991 [10] | Case report | 4 | 1 | 17 | Not reported | IVIG (400 mg/kg/d for 5 days), ASA (100 mg/kg/d) | Full recovery of FNP within 40 days |
| Bushara, 1997 [11] | Case report | 3 | 1 | 22 | Aneurysmal dilatation of both right and left CAs | IVIG (2 g/kg), ASA (100 mg/kg/d), heparin | Improvement of CAA |
| McDonald, 1998 [12] | Case report | 3 and 2 weeks | 1 | 11 | Aneurysms of the left anterior descending and circumflex CAs | Not reported | Not reported |
| Poon, 2000 [13] | Case report | 24 | 1 | >15 days | No | IVIG (2 g/kg) and ASA (30 mg/kg/d) | Full recovery of FNP within 1 month |
| Biezeveld, 2002 [14] | Case report | 156 | 1 | 12 | Right CAA | IVIG (2 g/kg), ASA (80 mg/kg/d) | Resolution of CAA within 1 month |
| Larralde, 2003 [15] | Case report | 5 | 1 | >11 | Right CAA and fusiform enlargement of the left CA | IVIG (2 g/kg), ASA (100 mg/kg/d) | Complete recovery |
| Wright, 2008 [16] | Case report | 3; 7 | 2 | 6; not reported | “Beaded” appearance of the right CA, ectasia of proximal right CA and left anterior descending CA, severe bilateral axillary artery involvement | IVIG (2 g/kg), ASA (75 mg/kg/d), warfarin, ASA (started after the acute phase of KD) | Minimal residual dilatation of the right CA and slight ectasia of the other CAs at the 6th month post discharge; stable at 9-year follow-up |
| Li, 2008 [17] | Case report | - | 2 | - | CAAs | IVIG | Complete resolution of CAA in one case; persistence of CAA in the other case |
| Lim, 2009 [18] | Case report | 72 | 1 | 10 | Aneurysm of the left and right CAs, left anterior descending CA, left circumflex CA; giant left anterior descending CA aneurysm on day 13 of illness | IVIG (2 g/kg, 2 doses), ASA (100 mg/kg/d), warfarin and prednisolone (1 mg/kg/d) | No symptoms of myocardial ischemia on exertion |
| Kaur, 2010 [19] | Case report | 2 | 1 | 12 | Dilatation of right and left CAs and left anterior descending CA | IVIG (2 g/kg), ASA (75 mg/kg/d) | Resolution of FNP within 2 days |
| Alves, 2011 [20] | Prospective study | 38 (mean age) | 115, FNP in one case | 26 | Small left CAA | IVIG (2 g/kg) | FNP improvement within 30 days |
| Khubchandani, 2014 [21] | Case report | 36 | 1 | 27 | Diffuse dilatation of all CAs and aneurysm of left anterior descending and proximal right CA | IVIG (2 g/kg, 2 doses) | Full recovery of FNP within 3 weeks |
| Stowe, 2015 [22] | Case report | 15 | 1 | 6 | Right CA dilatation | IVIG (2 g/kg), high-dose ASA, i.v. methylprednisolone (30 mg/kg/d) | Full recovery |
| Rodriguez-Gonzalez, 2018 [23] | Case report | 5 | 1 | 12 | Aneurysms of the left and right main CAs, left anterior descending CA, and left circumflex CA | IVIG (2 g/kg), ASA (100 mg/kg/d), steroids | Full recovery of FNP and improvement of CAA |
| Orgun, 2018 [24] | Case report | 4 | 1 | 7 | Left CA, proximal right CA and CA ectasia at all segments, saccular aneurysm in proximal right CA | IVIG (2 g/kg/12 h), ASA (80 mg/kg/d), enalapril (0.1 mg/kg/d), subcutaneous enoxaparin | FNP recovered 7 days after IVIG treatment, resolution of CAAs, minimal improvement of CA ectasia |
| Yuan, 2019 [25] | Case report | 3 | 1 | 8 | Left CA dilatation | IVIG (2 g/kg/16 h), ASA (50 mg/kg/d) | Full recovery |
| Zhang, 2019 [26] | Case report | 6 | 1 | 6 | Bilateral dilatation of CAs and CAA | IVIG (2 g/kg), ASA (four doses of 30–50 mg/kg/d) | Persistence of FNP during the 18-month follow-up |
| Yu, 2019 [27] | Case report | 7 | 1 | 14 | Dilatation of all CAs, in addition to aneurysms of the middle of the right and left CAs | IVIG (2 g/kg), high-dose ASA | Partial FNP improvement during the follow-up period |
| Peña-Juárez, 2021 [28] | Case report | 9 | 1 | 29 | Bilateral giant CAAs | IVIG (2 g/kg), high-dose ASA, methylprednisolone (30 mg/kg) | - |
| Chen, 2021 [29] | Retrospective observational study | 88.9% of patients <24 and 55.6% <12 | 9 | 10 (median time) | In 8 out of 9 patients: CAA in 4 cases and CA dilatation in 4 cases | IVIG (2 g/kg), ASA (30–50 mg/kg/d), short-term dexamethasone | Full remission of CALs in an average time of 66 days |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maglione, M.; Barlabà, A.; Grieco, M.; Cosimi, R.; Di Nardo, G.; Di Marco, G.M.; Gelzo, M.; Castaldo, G.; Tucci, C.; Iodice, R.M.; et al. Incomplete Kawasaki Disease with Peripheral Facial Nerve Palsy and Lung Nodules: A Case Report and Literature Review. Children 2023, 10, 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040679
Maglione M, Barlabà A, Grieco M, Cosimi R, Di Nardo G, Di Marco GM, Gelzo M, Castaldo G, Tucci C, Iodice RM, et al. Incomplete Kawasaki Disease with Peripheral Facial Nerve Palsy and Lung Nodules: A Case Report and Literature Review. Children. 2023; 10(4):679. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040679
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaglione, Marco, Annalisa Barlabà, Michela Grieco, Rosaria Cosimi, Giangiacomo Di Nardo, Giovanni Maria Di Marco, Monica Gelzo, Giuseppe Castaldo, Celeste Tucci, Raffaella Margherita Iodice, and et al. 2023. "Incomplete Kawasaki Disease with Peripheral Facial Nerve Palsy and Lung Nodules: A Case Report and Literature Review" Children 10, no. 4: 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040679
APA StyleMaglione, M., Barlabà, A., Grieco, M., Cosimi, R., Di Nardo, G., Di Marco, G. M., Gelzo, M., Castaldo, G., Tucci, C., Iodice, R. M., Lonardo, M. C., Tipo, V., & Giannattasio, A. (2023). Incomplete Kawasaki Disease with Peripheral Facial Nerve Palsy and Lung Nodules: A Case Report and Literature Review. Children, 10(4), 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040679






