Effects of an 8-Week Active Play Intervention on Body Composition and Fundamental Motor Skills in Preschool Children †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurements
2.1.1. General Procedures
2.1.2. Demographics
2.1.3. Height, Weight, and BMI
2.1.4. Body Composition
2.1.5. Fundamental Motor Skills
2.2. Experimental Conditions
2.2.1. Intervention
2.2.2. Control
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fundamental Motor Skills
3.2. Body Composition
3.2.1. FM
3.2.2. FFM
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feldman, R.S. Discovering the Life Span; Pearson Higher Education: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Matłosz, P.; Wyszyńska, J.; Asif, M.; Szybisty, A.; Aslam, M.; Mazur, A.; Herbert, J. Prevalence of overweight, obesity, abdominal obesity, and obesity-related risk factors in Polish preschool children: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, L.E.; Bolger, L.A.; O’Neill, C.; Coughlan, E.; O’Brien, W.; Lacey, S.; Burns, C.; Bardid, F. Global levels of fundamental motor skills in children: A systematic review. J. Sports Sci. 2021, 39, 717–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pate, R.R.; O’Neill, J.R.; Brown, W.H.; Pfeiffer, K.A.; Dowda, M.; Addy, C.L. Prevalence of compliance with a new physical activity guideline for preschool-age children. Child. Obes. 2015, 11, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubans, D.R.; Morgan, P.J.; Cliff, D.P.; Barnett, L.M.; Okely, A.D. Fundamental Movement Skills in Children and Adolescents. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 1019–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallahue, D. Understanding Motor Development; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, J.E.; Metcalfe, J.S. The Mountain of Motor Development: A Metaphor. In Motor Development: Research and Reviews; Clark, J.E., Humphery, J., Eds.; NASPE Publications: Reston, VA, USA, 2002; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kantomaa, M.T.; Stamatakis, E.; Kankaanpää, A.; Kaakinen, M.; Rodriguez, A.; Taanila, A.; Ahonen, T.; Järvelin, M.-R.; Tammelin, T. Physical activity and obesity mediate the association between childhood motor function and adolescents’ academic achievement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1917–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, J.N.P.; Morais, R.L.D.S.; Fernandes, A.C.; Viegas, Â.A.; Figueiredo, P.H.S.; Costa, H.S.; Camargos, A.C.R.; Dias-Peixoto, M.F.; Mendonça, V.A.; Lacerda, A.C.R. Is body fat mass associated with worse gross motor skills in preschoolers? An exploratory study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, K.E.; Carroll, A.V.; Wadsworth, D.D. The relationship in early childhood body composition and physical activity levels regarding fundamental motor skill development. BMC Pediatr. 2023, 23, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodway, J.D.; Ozmun, J.C.; Gallahue, D.L. Understanding Motor Development: Infants, Children, Adolescents, Adults: Infants, Children, Adolescents, Adults; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rebelo, M.; Serrano, J.; Paulo, R.; Duarte-Mendes, P.; Santos, J.; Honório, S.; Petrica, J. The importance of oriented physical activity in the first 48 months: Differences in motor skills. BMC Pediatr. 2023, 23, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogman, M.; Garner, A.; Hutchinson, J.; Hirsh-Pasek, K.; Golinkoff, R.M.; Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health; Council on Communications and Media; Baum, R.; Gambon, T.; Lavin, A.; et al. The Power of Play: A Pediatric Role in Enhancing Development in Young Children. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20182058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.; Wright, B.L.; Masterson, M.L.; Willer, B.; Bredekamp, S. Developmentally Appropriate Practice in Early Childhood Programs Serving Children from Birth through Age 8, 4th ed.; National Association for the Education of Young Children: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.; Vaughan, C. Play: How It Shapes the Brain, Opens the Imagination, and Invigorates the Soul; Avery: New York, NY, USA, 2009; 229p. [Google Scholar]
- Elkind, D. The Power of Play: Learning What Comes Naturally; Da Capo Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; 240p. [Google Scholar]
- Whitebread, D.; Basilio, M.; Kuvalja, M.; Verma, M. The Importance of Play; Toy Industries of Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Truelove, S.; Vanderloo, L.M.; Tucker, P. Defining and measuring active play among young children: A systematic review. J. Phys. Act. Health 2017, 14, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.S.; Downing, K.L.; Saelens, B.E.; Christakis, D.A. Two approaches to increase physical activity for preschool children in child care centers: A matched-pair cluster-randomized trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dwyer, M.V.; Fairclough, S.J.; Ridgers, N.D.; Knowles, Z.R.; Foweather, L.; Stratton, G. Effect of a school-based active play intervention on sedentary time and physical activity in preschool children. Health Educ. Res. 2013, 28, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamo, K.B.; Wilson, S.; Harvey, A.L.; Grattan, K.P.; Naylor, P.-J.; Temple, V.A.; Goldfield, G.S. Does intervening in childcare settings impact fundamental movement skill development? Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, L.; Keats, M. Skill-based and planned active play versus free-play effects on fundamental movement skills in preschoolers. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2018, 125, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, L.L.; King, L.; Kelly, B.; Farrell, L.; Howlett, S. Munch and Move: Evaluation of a preschool healthy eating and movement skill program. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfield, G.S.; Harvey, A.L.; Grattan, K.P.; Temple, V.; Naylor, P.-J.; Alberga, A.S.; Ferraro, Z.M.; Wilson, S.; Cameron, J.D.; Barrowman, N.; et al. Effects of child care intervention on physical activity and body composition. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 51, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bander, A.; Murphy-Alford, A.J.; Owino, V.O.; Loechl, C.U.; Wells, J.C.K.; Gluning, I.; Kerac, M. Childhood BMI and other measures of body composition as a predictor of cardiometabolic non-communicable diseases in adulthood: A systematic review. Public Health Nutr. 2023, 26, 323–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G* Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, E.S.; Tucker, P.; Burke, S.M.; Carron, A.V. Effectiveness of physical activity interventions for preschoolers: A meta-analysis. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2013, 84, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, R. Anthropometry. Physiol. Assess. Hum. Fit. 1995, 205, 219. [Google Scholar]
- National Center for Health Statistics. Growth Charts: Age and Gender Specific. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Dooley, E.E.; Pettee Gabriel, K.; Kohl III, H.W.; Durand, C.P.; Hoelscher, D.M.; Byrd-Williams, C.E. Adiposity, cardiovascular, and health-related quality of life indicators and the reallocation of waking movement behaviors in preschool children with overweight and obesity: An isotemporal data analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, E.K.; Sur, I.; Stevens, A.; Robinson, L.E. Associations between body composition and fundamental motor skill competency in children. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyrrell, V.; Richards, G.; Hofman, P.; Gillies, G.; Robinson, E.; Cutfield, W. Foot-to-foot bioelectrical impedance analysis: A valuable tool for the measurement of body composition in children. Int. J. Obes. 2001, 25, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folio, M.; Fewell, R. Peabody Developmental Motor Scales Second Edition; Pro-Ed, Inc.: Austin, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bellows, L.L.; Davies, P.L.; Anderson, J.; Kennedy, C. Effectiveness of a physical activity intervention for Head Start preschoolers: A randomized intervention study. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2013, 67, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.5823. [Google Scholar]
- Searle, S.R.; Speed, F.M.; Milliken, G.A. Population marginal means in the linear model: An alternative to least squares means. Am. Stat. 1980, 34, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, V.; Metgud, D.; Gadre, M.; Kale, S. Effectiveness of Peabody Developmental Motor Scale-2 as an Outcome Measure: A Systematic Review. Indian J. Phys. Ther. Res. 2023, 5, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biino, V.; Tinagli, V.; Borioni, F.; Pesce, C. Cognitively enriched physical activity may foster motor competence and executive function as early as preschool age: A pilot trial. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2023, 28, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddaszadeh, A.; Belcastro, A.N. Guided Active Play Promotes Physical Activity and Improves Fundamental Motor Skills for School-Aged Children. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2021, 20, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth, D.D.; Spring, K.E.; Johnson, J.L.; Carroll, A.V.; Sassi, J.; Suire, K.B.; Pangelinan, M.M.; Rudisill, M.E. Impact of a Fundamental Motor Skill Intervention on Low-Income Preschoolers’ Body Composition. Transl. J. Am. Coll. Sports Med. 2022, 7, e000203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, A.C.; Ravanbakht, S.N.; Skelton, J.A.; Perrin, E.M.; Armstrong, S.C. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity in US children, 1999–2016. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20173459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cliff, D.P.; Okely, A.D.; Morgan, P.J.; Jones, R.A.; Steele, J.R.; Baur, L.A. Proficiency deficiency: Mastery of fundamental movement skills and skill components in overweight and obese children. Obesity 2012, 20, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logue, M.E.; Harvey, H. Preschool teachers’ views of active play. J. Res. Child. Educ. 2009, 24, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivrendi, A. Early childhood teachers’ roles in free play. Early Years 2020, 40, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Gómez, J.M.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.-C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis—Part II: Utilization in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1430–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health (US). Office of Medical Applications of Research. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Body Composition Measurement: National Institutes of Health Technology Assessment Conference Statement, December 12–14, 1994. Nutrition 1996, 12, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deurenberg, P.; Weststrate, J.; Paymans, I.; Van der Kooy, K. Factors affecting bioelectrical impedance measurements in humans. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1988, 42, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Brantlov, S.; Ward, L.C.; Jødal, L.; Rittig, S.; Lange, A. Critical factors and their impact on bioelectrical impedance analysis in children: A review. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2017, 41, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Baseline | Post-Intervention | Follow-Up | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention (n = 25) | Control (n = 25) | Intervention (n = 25) | Control (n = 25) | Intervention (n = 24) | Control (n = 18) | |
| Age (years) | 3.91 (±0.53) [3.69–4.14] | 3.69 (±0.81) [3.35–4.03] | 4.13 (±0.54) [3.90–4.36] | 3.86 (±0.81) [3.52–4.20] | 4.47 (±0.59) [4.23–4.72] | 4.27 (±0.88) [3.83–4.70] |
| Height (cm) | 101.14 (±5.88) [98.77–103.52] | 99.62 (±5.94) [97.24–101.99] | 102.57 (±5.63) [1.41%] [100.22–104.92] | 101.09 (±6.05) [1.48%] [98.74–103.44] | 103.94 (±6.27) [2.77%] [101.50–106.38] | 104.01 (±5.73) [4.41%] [101.21 = 106.80] |
| Weight (kg) | 15.46 (±1.96) [14.59–16.34] | 15.89 kg (±2.38) [15.02–16.77] | 15.94 (±2.00) [3.10%] [15.04–16.84] | 16.26 (±2.46) [2.33%] [15.36–17.16] | 16.70 (±2.2) [8.02%] [15.76–17.65] | 17.14 (±7.84) [7.87%] [16.08–18.49] |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 15.08 (±0.88) [14.66–15.50] | 15.95 (±1.19) [15.53–16.37] | 15.12 (±0.99) [0.27%] [14.70–15.54] | 15.84 (±1.10) [−0.69%] [15.42–16.37] | 15.43(±1.24) [2.32%] [14.96–15.91] | 15.92 (±1.08) [−0.19%] [15.38–16.46] |
| BMI% | 37.12 (±23.46%) [26.41–47.83] | 53.56 (±29.48%) [42.85–64.27] | 39.04 (±24.99) [5.17%] [27.99–50.08] | 53.24 (±29.72) [−0.60%] [42.20–64.28] | 47.14 (±28.42) [26.99%] [36.10–58.22] | 58.10 (±25.99) [8.48%] [45.42–70.79] |
| F% | 19.36 (±4.5%) [17.84–20.88] | 21.64 (±2.85%) [20.12–23.16] | 20.06 (±3.22) [3.62%] [18.88–21.25] | 21.17 (±2.64) [−2.17%] [19.99–22.36] | 20.94 (±3.31) [8.16%] [19.78–22.11] | 21.67 (±2.21) [0.14%] [20.34–23.01] |
| FM (kg) | 3.03 (±0.92) [2.66–3.39] | 3.50 (±0.91) [3.13–3.87] | 3.21 (±0.76) [5.94%] [2.88–3.54] | 3.47 (±0.87) [−0.86%] [3.15–3.80] | 3.51 (±0.89) [15.84%] [3.14–3.87] | 3.74 (±0.86) [6.86%] [3.32–4.16] |
| FFM (kg) | 12.44 (±1.37) [11.84–13.04] | 12.40 (±1.60) [11.80 = 12.99] | 12.72 (±1.51) [2.25%] [12.09–13.38] | 12.78 (±1.70) [3.06%] [12.13–13.43] | 13.19 (±1.65) [6.03%] [12.50–13.88] | 13.44 (±1.73) [8.39%] [12.64–14.24] |
| Intervention (n = 24) | Control (n = 24) | Intervention (n = 24) | Control (n = 24) | Intervention (n = 23) | Control (n = 17) | |
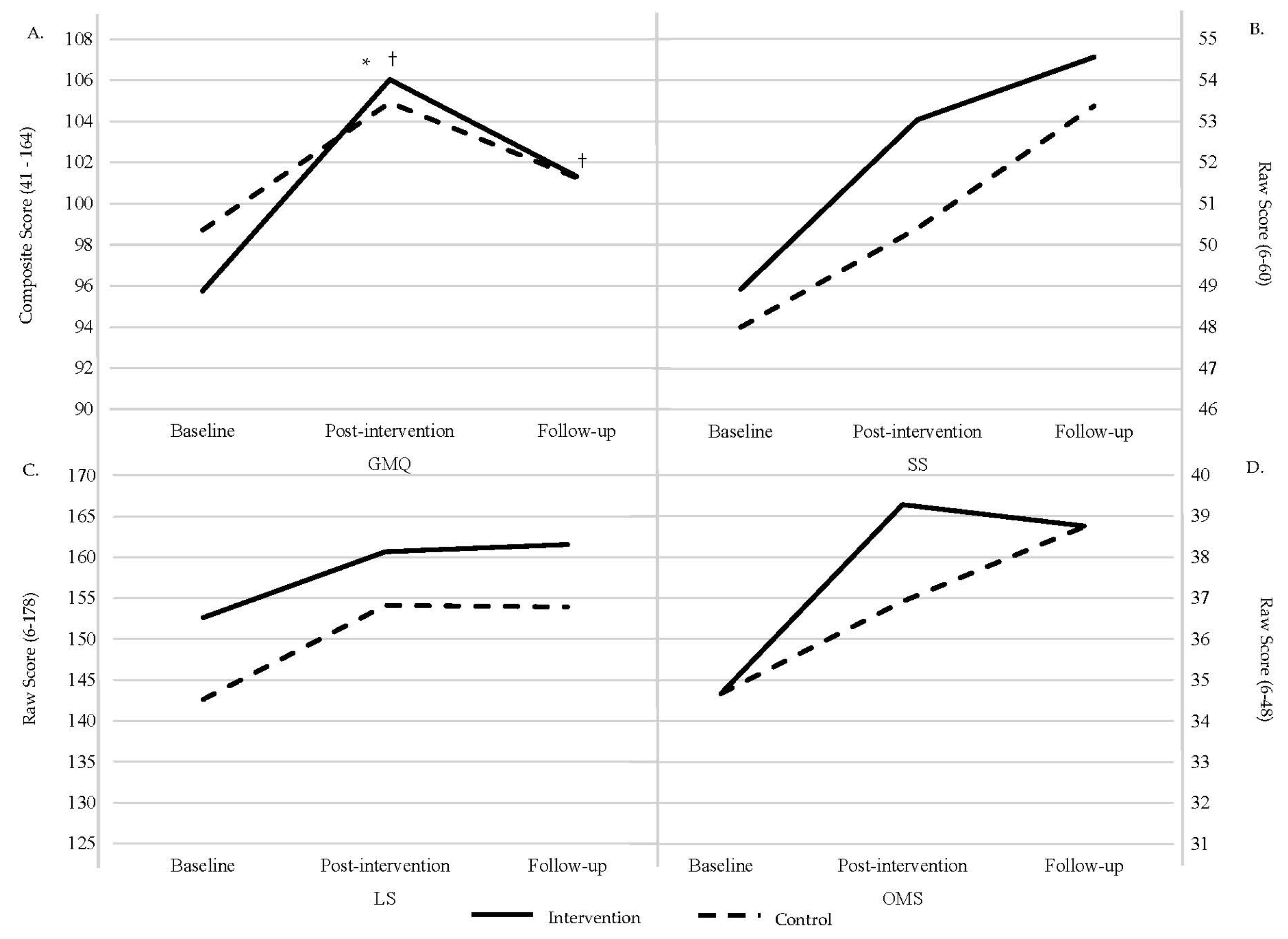
| SS | 48.96 (±5.90) [46.51–51.32] | 48.00 (±5.8) [45.60–50.40] | 53.04 (±4.27) [8.33%] [51.56–55.11] | 50.40 (±4.48) [5.00%] [48.72–52.28] | 54.52 (±3.37) [11.36%] [53.20–55.85] | 53.59 (±2.79) [11.65%] [52.05–55.13] |
| LS | 152.63 (±16.28) [141.36–163.89] | 137.71 (±35.19) [126.44–148.97] | 160.68 (±17.77) [5.27%] [155.28–169.06] | 154.12 (±18.06) [11.92%] [148.97–162.29] | 162.30 (±15.63) [6.34%] [154.05–170.56] | 154.18 (±23.93) [11.96%] [144.57–164.63] |
| OMS | 34.67 (±6.48) [31.97–37.37] | 34.67 (±6.66) [31.97–37.37] | 39.28 (±4.63) [13.30%] [37.40–41.52] | 36.92 (±5.40) [6.49%] [35.10–39.23] | 39.13 (±4.91) [12.86%] [37.19–41.07] | 39.22 (±4.54) [13.12%] [37.10–41.61] |
| GMQ | 95.75 (±12.28) [90.99–100.51] | 98.71 (±10.87) [93.95–103.47] | 106.04 (±9.41) [10.75%] [101.86–110.23] | 104. 93 (±23.36) [6.30%] [100.40 = 108.77] | 100.70 (±8.33) [5.17%] [96.85–104.54] | 101.00 (±10.10) [2.34%] [96.53–105.48] |
| EMM | df | SE | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Intervention | −5.55 | 72.8 | 2.12 | [−9.78, −1.31] |
| Control | −2.20 | 72.8 | 2.11 | [−6.43, 2.04] | |
| Post-Intervention | Intervention | 4.80 | 71.1 | 2.12 | [0.60, 9.01] |
| Control | 3.68 | 71.1 | 2.12 | [−0.52, 7.89] | |
| Follow-up | Intervention | 0.07 | 72.8 | 2.11 | [−4.16, 4.3] |
| Control | −0.47 | 86.5 | 2.25 | [−4.93, 4.00] |
| EMM | df | SE | 95% CI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Intervention | FM | −0.37 | 62.7 | 0.17 | [−0.071, −0.02] |
| FFM | −0.36 | 55.3 | 0.32 | [−0.99, 0.28] | ||
| Control | FM | 0.10 | 62.7 | 0.17 | [−0.24, 0.45] | |
| FFM | −0.40 | 55.3 | 0.32 | [−1.04, 0.24] | ||
| Post-Intervention | Intervention | FM | −0.18 | 62.7 | 0.17 | [−0.53, 0.16] |
| FFM | −0.07 | 55.3 | 0.32 | [−0.70, 0.57] | ||
| Control | FM | 0.08 | 62.7 | 0.17 | [−0.26, 0.43] | |
| FFM | −0.14 | 55.3 | 0.32 | [−0.65, 0.62] | ||
| Follow-up | Intervention | FM | 0.13 | 63.7 | 0.17 | [−0.22, 0.47] |
| FFM | 0.40 | 55.7 | 0.32 | [−0.24, 1.04] | ||
| Control | FM | 0.39 | 72.0 | 0.18 | [0.03, 0.75] | |
| FFM | 0.65 | 58.3 | 0.32 | [0.01, 1.29] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spring, K.E.; Lang, D.; Pangelinan, M.M.; Wadsworth, D.D. Effects of an 8-Week Active Play Intervention on Body Composition and Fundamental Motor Skills in Preschool Children. Children 2024, 11, 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101173
Spring KE, Lang D, Pangelinan MM, Wadsworth DD. Effects of an 8-Week Active Play Intervention on Body Composition and Fundamental Motor Skills in Preschool Children. Children. 2024; 11(10):1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101173
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpring, Katherine E., Danielle Lang, Melissa M. Pangelinan, and Danielle D. Wadsworth. 2024. "Effects of an 8-Week Active Play Intervention on Body Composition and Fundamental Motor Skills in Preschool Children" Children 11, no. 10: 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101173
APA StyleSpring, K. E., Lang, D., Pangelinan, M. M., & Wadsworth, D. D. (2024). Effects of an 8-Week Active Play Intervention on Body Composition and Fundamental Motor Skills in Preschool Children. Children, 11(10), 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101173






