High-Frequency Percussive Ventilation: A Promising Rescue Strategy in Severe Lung Disease of Extremely Low Gestational Age Neonates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
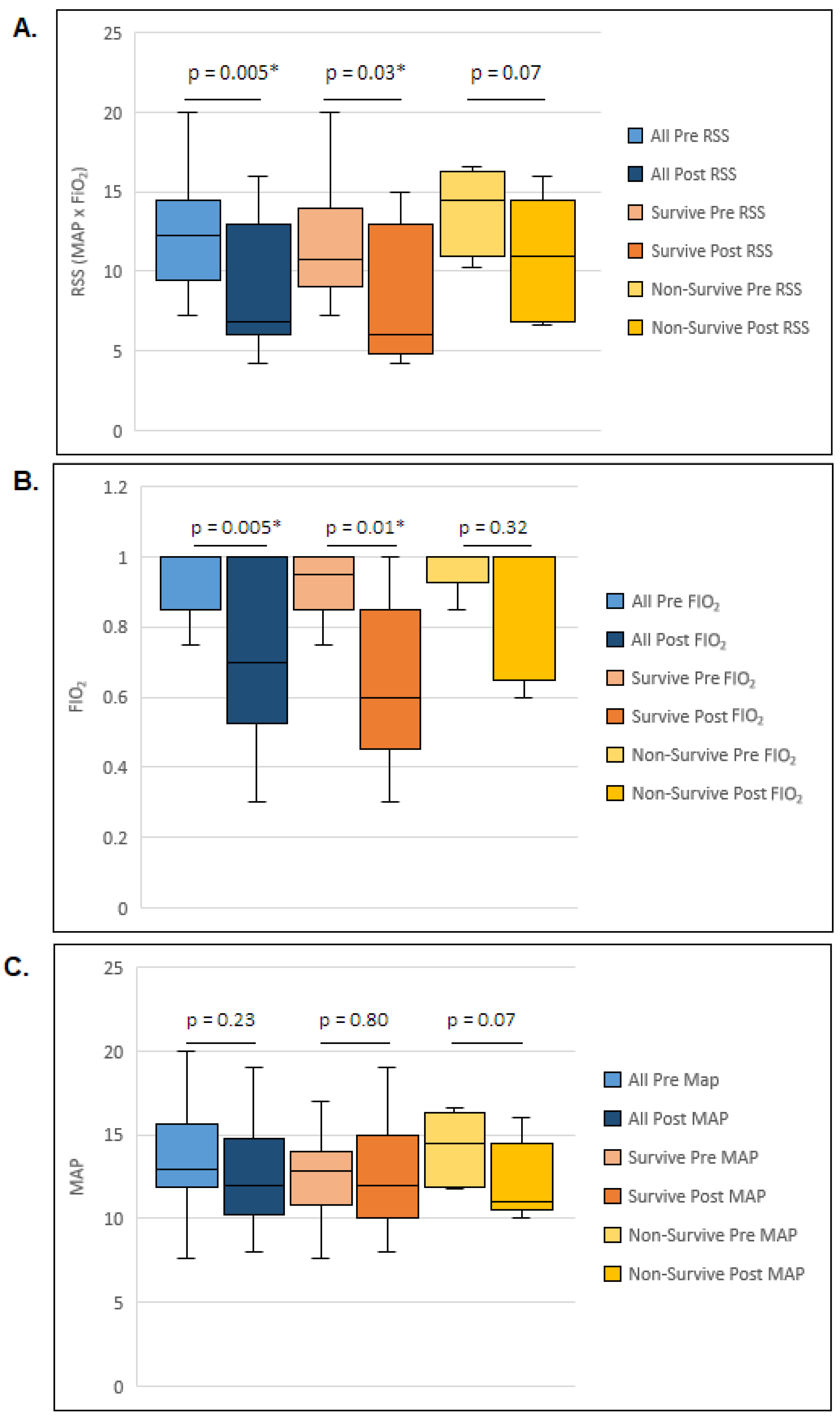
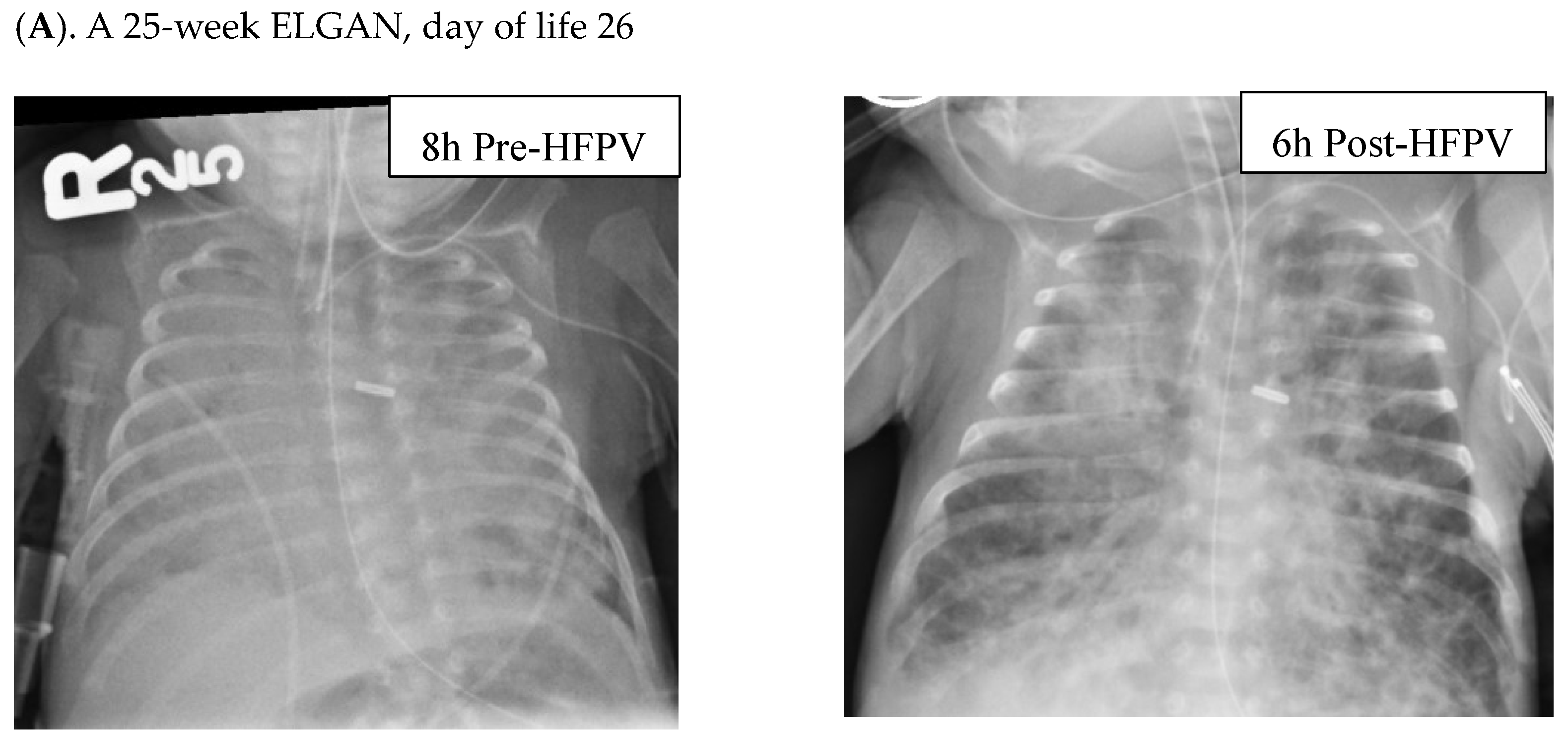
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cioffi, W.G.; Major, M.; Graves, T.A.; Captain, M.; McManus, W.F.; Colonel, M.; Basil, A.P., Jr. High-frequency Percussive Ventilation in Patients with Inhalation Injury. J. Trauma 1989, 29, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucangelo, U.; Fontanesi, L.; Antonaglia, V.; Pellis, T.; Berlot, G.; Liguori, G.; Bird, F.M.; Gullo, A. High frequency percussive ventilation (HFPV) Principles and technique. Minerva Anestesiol. 2003, 69, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salim, A.; Martin, M. High-frequency percussive ventilation. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, s241–s245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfenninger, J.; Gerber, A.C. Intensive Care Medicine High-frequency ventilation (HFV) in hyaline membrane disease-a preliminary report. Intensive Care Med. 1987, 13, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfenninger, J.; Minder, C. Intensive Care Medicine Pressure-volume curves, static compliances and gas exchange in hyaline membrane disease during conventional mechanical and high-frequency ventilation. Intensive Care Med. 1988, 14, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougatef, A.; Casteels, A.; Cools, F.; de Woolf, D.; Foubert, L. High frequency percussive ventilation: Principle and Fifteen Years of Experience in Preterm Infants with Respiratory Distress Syndrome. J. Respir. Care Appl. Technol. 2007, 2, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, K.K.; Wolf, S.E.; Renz, E.M.; Allan, P.F.; Aden, J.K.; Merrill, G.A.; Shelhamer, M.C.; King, B.T.; White, C.E.; Bell, D.G.; et al. High-frequency percussive ventilation and low tidal volume ventilation in burns: A randomized controlled trial. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 1970–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.D.; Dominick, C.L.; Yehya, N. HFPV in Pediatric Acute Respiratory Failure. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioffi, W.G.; Delemos, R.A.; Coalson, J.J.; Gerstmann, D.A.; Pruitt, B.A. Decreased Pulmonary Damage in Primates with Inhalation Injury Treated with High-Frequency Ventilation. Ann. Surg. 1993, 218, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirt, D.; Van Overmeire, B.; Treluyer, J.-M.; Langhendries, J.P.; Marguglio, A.; Eisinger, M.J.; Schepens, P.; Urien, S. An optimized ibuprofen dosing scheme for perterm neonates with PDA, based on a population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 65, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eenjes, E.; Tibboel, D.; Wijnen, R.M.H.; Rottier, R.J. Lung epithelium development and airway regeneration. Front. Cell Devel. Biol. 2022, 10, 1022457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, D. Developmental responses to lung injury: Repair or fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2021, 5 (Suppl. S1), S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carman, B.; Cahill, T.; Warden, G.; McCall, J. A prospective, randomized comparison of the Volume Diffusive Respirator® vs conventional ventilation for ventilation of burned children: 2001 ABA paper. J. Burn. Care Rehabil. 2002, 23, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godet, T.; Jabaudon, M.; Blondonnet, R.; Tremblay, A.; Audard, J.; Rieu, B.; Garcier, J.-M.; Futier, E.; Constantin, J.-M. High frequency percussive ventilation increases alveolar recruitment in early acute respiratory distress syndrome: An experimental, physiological and CT scan study. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizkalla, N.A.; Dominick, C.L.; Fitzgerald, J.C.; Thomas, N.J.; Yehya, N. High-frequency percussive ventilation improves oxygenation and ventilation in pediatric patients with acute respiratory failure. J. Crit. Care 2014, 29, e1–e314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Total | |
|---|---|
| N = 16 | |
| Birth Weight (median, IQR) | 640 (535, 773) |
| Gestational Age (median, IQR) | 25 (24, 26) |
| C/S (n, %) | 16 (100%) |
| Male (n, %) | 8 (50%) |
| SGA (n, %) | 3 (19%) |
| Prenatal Steroids (n, %) | 15 (94%) |
| Surfactant (n, %) | 16 (100%) |
| APGAR 1 min ≤ 7 (n, %) | 15 (94%) |
| APGAR 5 min ≤ 7 (n, %) | 10 (63%) |
| Sepsis (n, %) | 9 (56%) |
| PDA (n, %) | 15 (94%) |
| IVH Grade 3/4 (n, %) | 1 (6%) |
| Pneumothorax (n, %) | 2 (13%) |
| iNO (n, %) | 12 (75%) |
| HFJV (n, %) | 15 (94%) |
| HFOV (n, %) | 12 (75%) |
| Total | |
|---|---|
| N = 16 | |
| DOL when HFPV was Started (median, IQR) | 46 (27, 61) |
| DOL when HFPV was Stopped (median, IQR) | 86 (52, 110) |
| Days on HFPV (median, IQR) | 40 (12, 64) |
| Pre-HFPV FiO2 (median, IQR) | 1 (0.85, 1) |
| Post-HFPV FiO2 (median, IQR) | 0.7 (0.53, 1) |
| Pre-HFPV MAP (median, IQR) | 13 (12, 16) |
| Post- HFPV MAP (median, IQR) | 12 (10, 15) |
| Pre-HFPV RSS (median, IQR) | 12 (9, 15) |
| Post-HFPV RSS (median, IQR) | 7 (6, 13) |
| RSS Change (median, IQR) | 3 (0.65, 8) |
| Survived | Non-Survived | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (11) | N (5) | ||
| Birth Weight (median, IQR) | 650 (610, 790) | 520 (345, 772) | 0.36 |
| Gestational Age (median, IQR) | 24 (23, 26) | 26 (25, 28) | 0.04 * |
| C/S (n, %) | 11 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 1 |
| Male (n, %) | 6 (55%) | 2 (40%) | 1 |
| SGA (n, %) | 0 (0%) | 3 (60%) | 0.02 * |
| Prenatal Steroids (n, %) | 11 (100%) | 4 (80%) | 0.31 |
| Surfactant (n, %) | 11 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 1 |
| APGAR 1 min ≤ 7 (n, %) | 10 (91%) | 5 (100%) | 1 |
| APGAR 5 min ≤ 7 (n, %) | 8 (73%) | 2 (40%) | 1 |
| Sepsis (n, %) | 5 (45%) | 4 (80%) | 0.31 |
| PDA (n, %) | 10 (91%) | 5 (100%) | 1 |
| IVH Grade 3/4 (n, %) | 1 (9%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| Pneumothorax (n, %) | 1 (9%) | 1 (20%) | 1 |
| iNO (n, %) | 8 (73%) | 4 (80%) | 0.51 |
| HFJV (n, %) | 10 (91%) | 5 (100%) | 1 |
| HFOV (n, %) | 7 (64%) | 5 (100%) | 0.25 |
| Survived | Non-Survived | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (11) | N (5) | ||
| DOL when HFPV was Started (median, IQR) | 46 (30, 61) | 41 (19, 123) | 0.72 |
| DOL when HFPV was Stopped (median, IQR) | 69 (50, 105) | 90 (50, 205) | 0.49 |
| Number of Days on HFPV (median, IQR) | 38 (11, 45) | 66 (21, 84) | 0.19 |
| Pre-HFPV FiO2 (median, IQR) | 0.95 (0.85, 1) | 1 (1, 1) | 0.31 |
| Post-HFPV FiO2 (median, IQR) | 0.6 (0.4, 0.9) | 1 (0.7, 1) | 0.12 |
| Pre-HFPV MAP (median, IQR) | 13 (10.8, 14) | 15 (11.9, 16.3) | 0.49 |
| Post-HFPV MAP (median, IQR) | 12 (10, 15) | 11 (10.5, 14.5) | 0.89 |
| Pre-HFPV RSS (median, IQR) | 11 (9, 14) | 15 (11, 16) | 0.17 |
| Post-HFPV RSS (median, IQR) | 6 (4.8, 13) | 11 (6.8, 14.5) | 0.12 |
| RSS Change (median, IQR) | 3 (0, 8.5) | 2 (0.7, 6.3) | 0.77 |
| HFJV (n, %) | 10 (91%) | 5 (100%) | 1 |
| HFOV (n, %) | 7 (64%) | 5 (100%) | 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Louie, K.; Ericksen, K.; Parton, L.A. High-Frequency Percussive Ventilation: A Promising Rescue Strategy in Severe Lung Disease of Extremely Low Gestational Age Neonates. Children 2024, 11, 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101239
Louie K, Ericksen K, Parton LA. High-Frequency Percussive Ventilation: A Promising Rescue Strategy in Severe Lung Disease of Extremely Low Gestational Age Neonates. Children. 2024; 11(10):1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101239
Chicago/Turabian StyleLouie, Kevin, Kristina Ericksen, and Lance A. Parton. 2024. "High-Frequency Percussive Ventilation: A Promising Rescue Strategy in Severe Lung Disease of Extremely Low Gestational Age Neonates" Children 11, no. 10: 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101239
APA StyleLouie, K., Ericksen, K., & Parton, L. A. (2024). High-Frequency Percussive Ventilation: A Promising Rescue Strategy in Severe Lung Disease of Extremely Low Gestational Age Neonates. Children, 11(10), 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11101239






