Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Pediatric Tumors: Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment
Abstract
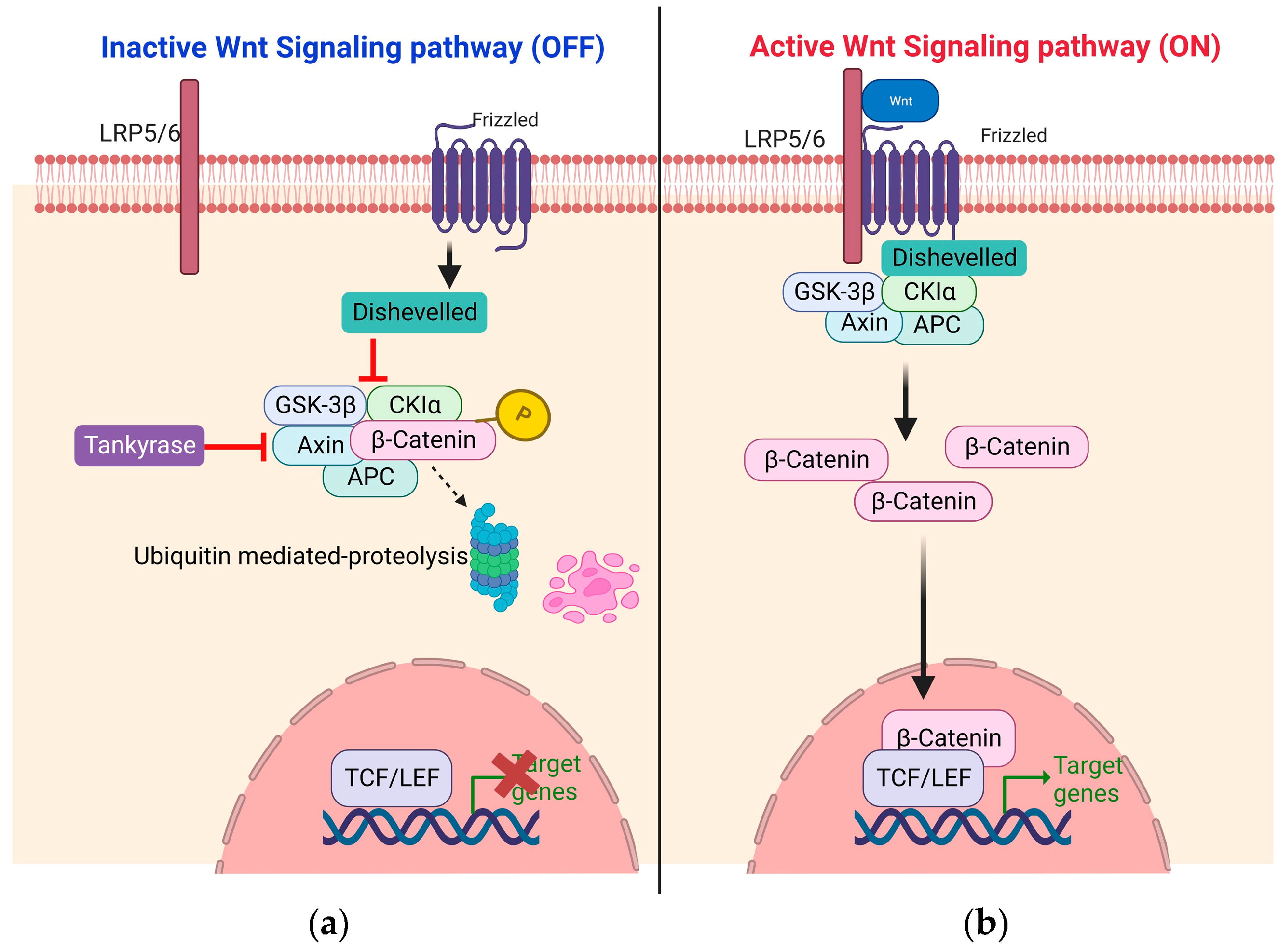
1. Introduction
2. Pediatric Tumors
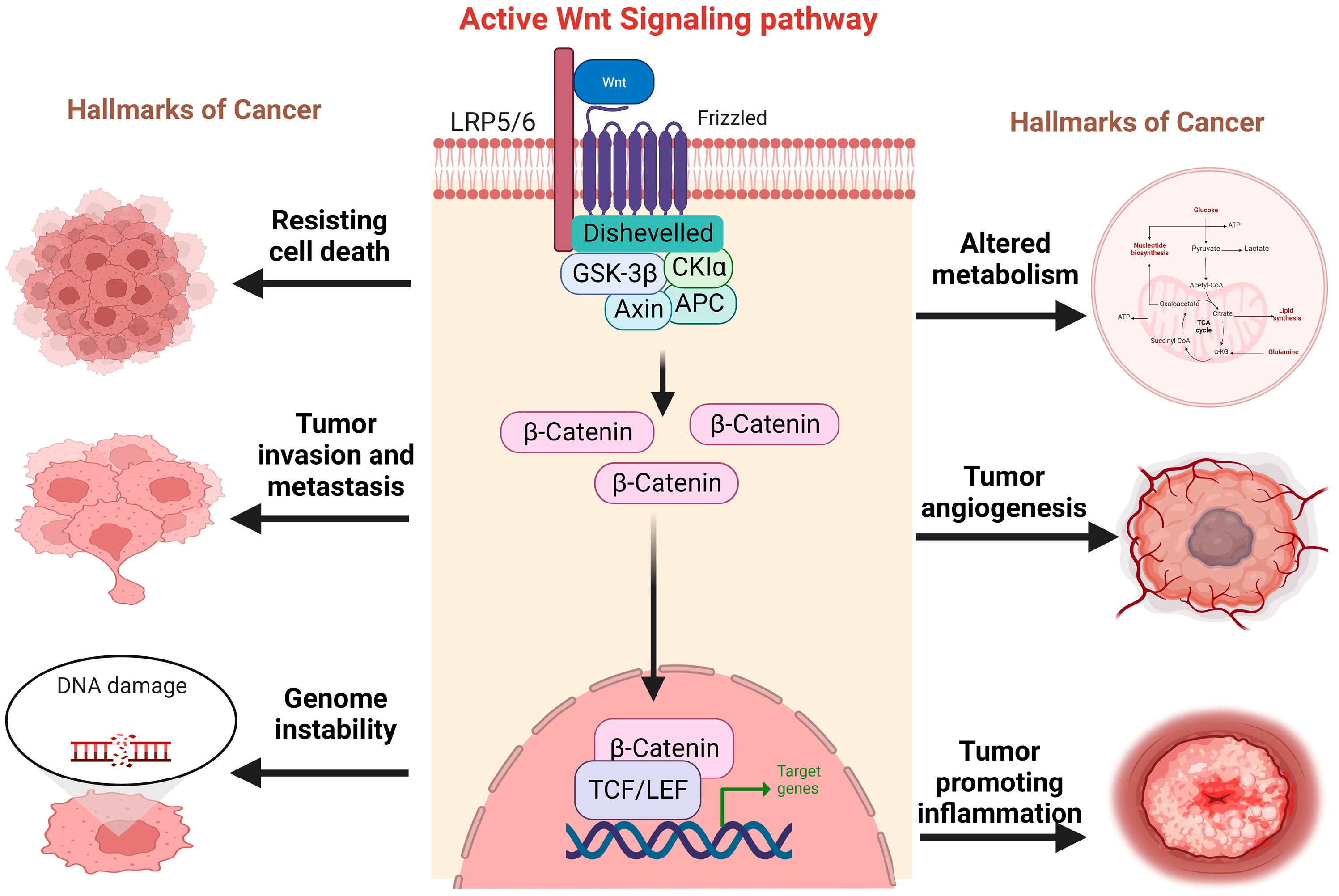
3. Implications of Wnt/b-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Pediatric Tumors
4. Wnt Signaling in Retinoblastoma
5. Wnt Signaling in Neuroblastoma
6. Wnt Signaling in Rhabdomyosarcoma
7. Wnt Signaling in Wilms Tumor (Nephroblastoma)
8. Challenges of Wnt/β-Catenin Targeted Therapies in Pediatric Tumors
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, F.; Yu, C.; Li, F.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Ye, L. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2021, 6, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusse, R.; Varmus, H.E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell 1982, 31, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ooyen, A.; Kwee, V.; Nusse, R. The nucleotide sequence of the human int-1 mammary oncogene; evolutionary conservation of coding and non-coding sequences. EMBO J. 1985, 4, 2905–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Komiya, Y.; Habas, R. Wnt signal transduction pathways. Organogenesis 2008, 4, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salik, B.; Yi, H.; Hassan, N.; Santiappillai, N.; Vick, B.; Connerty, P.; Duly, A.; Trahair, T.; Woo, A.J.; Beck, D.; et al. Targeting RSPO3-LGR4 Signaling for Leukemia Stem Cell Eradication in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 263–278.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleas, J.P.; D’Arcangelo, E.; Huang, L.; Karoubi, G.; Nostro, M.C.; McGuigan, A.P.; Waddell, T.K. Assembly of lung progenitors into developmentally-inspired geometry drives differentiation via cellular tension. Biomaterials 2020, 254, 120128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.R.; Cave, C.; Na, C.H.; Sockanathan, S. GDE2-Dependent Activation of Canonical Wnt Signaling in Neurons Regulates Oligodendrocyte Maturation. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parsons, M.J.; Tammela, T.; Dow, L.E. WNT as a Driver and Dependency in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2413–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Tang, S. WNT/β-catenin signaling in the development of liver cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajos-Michniewicz, A.; Czyz, M. WNT Signaling in Melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Weng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ni, S.; Tan, C.; Xu, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, C.; Wei, P.; et al. The lncRNA NEAT1 activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes colorectal cancer progression via interacting with DDX5. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Wang, X. Role of Wnt canonical pathway in hematological malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2010, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.Q.; You, A.B.; Zhu, X.D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.Z.; Zhang, K.W.; Cai, H.; Shi, W.K.; Li, X.L.; et al. miR-182-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing FOXO3a. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusse, R. The Wnt Homepage. Available online: https://web.stanford.edu/group/nusselab/cgi-bin/wnt/ (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- Rim, E.Y.; Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. The Wnt Pathway: From Signaling Mechanisms to Synthetic Modulators. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2022, 91, 571–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M.; Katoh, M. WNT signaling and cancer stemness. Essays Biochem. 2022, 66, 319–331. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J.; Sanci, L.; Haller, D. Global adolescent health: Is there a role for general practice? Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2012, 62, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sweet-Cordero, E.A.; Biegel, J.A. The genomic landscape of pediatric cancers: Implications for diagnosis and treatment. Science 2019, 363, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, S.M.; Reyes-Múgica, M.; Chan, J.K.; Hasle, H.; Lazar, A.J.; Rossi, S.; Ferrari, A.; Jarzembowski, J.A.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; Hill, D.A.; et al. A Summary of the Inaugural WHO Classification of Pediatric Tumors: Transitioning from the Optical into the Molecular Era. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 331–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtutman, M.; Zhurinsky, J.; Simcha, I.; Albanese, C.; D’Amico, M.; Pestell, R.; Ben-Ze’ev, A. The cyclin D1 gene is a target of the beta-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5522–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Vega, F.; Mina, M.; Armenia, J.; Chatila, W.K.; Luna, A.; La, K.C.; Dimitriadoy, S.; Liu, D.L.; Kantheti, H.S.; Saghafinia, S.; et al. Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in The Cancer Genome Atlas. Cell 2018, 173, 321–337.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhou, S.; Glowacki, J. Effects of age and gender on WNT gene expression in human bone marrow stromal cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2009, 106, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ilyas, M. Wnt signalling and the mechanistic basis of tumour development. J. Pathol. 2005, 205, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimaras, H.; Corson, T.W.; Cobrinik, D.; White, A.; Zhao, J.; Munier, F.L.; Abramson, D.H.; Shields, C.L.; Chantada, G.L.; Njuguna, F.; et al. Retinoblastoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixo, R.; Laranjo, M.; Abrantes, A.M.; Brites, G.; Serra, A.; Proença, R.; Botelho, M.F. Retinoblastoma: Might photodynamic therapy be an option? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Yu, S.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Z.; Huang, S.; Wang, P. The emerging role of circRNAs and their clinical significance in human cancers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2018, 1870, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Lee, H.J.; Zheng, J.J. Genome-wide network analysis of Wnt signaling in three pediatric cancers. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Silva, A.K.; Yi, H.; Hayes, S.H.; Seigel, G.M.; Hackam, A.S. Lithium chloride regulates the proliferation of stem-like cells in retinoblastoma cell lines: A potential role for the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Beta, M.; Chitipothu, S.; Khetan, V.; Biswas, J.; Krishnakumar, S. Hypermethylation of adenomatosis polyposis coli-2 and its tumor suppressor role in retinoblastoma. Curr. Eye Res. 2015, 40, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lu, X. Decreased expression of MEG3 contributes to retinoblastoma progression and affects retinoblastoma cell growth by regulating the activity of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 1461–1469, Erratum in Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J. LncRNA MEG3 inhibits retinoblastoma invasion and metastasis by inducing β-catenin degradation. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 3111–3127. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, G.; Huang, Y.; Mao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin by anthelmintic drug niclosamide effectively targets growth, survival, and angiogenesis of retinoblastoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 3776–3786. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, L.L.; Han, F.; Zhang, X.M.; Li, Y.Y. LncRNA MT1JP acts as a tumor inhibitor via reciprocally regulating Wnt/β-Catenin pathway in retinoblastoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4204–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.; Singh, L.; Sen, S.; Pushker, N.; Sharma, A.; Ahamad, F.C.; Chawla, B.; Kashyap, S. Role of High-mobility Group Protein A Isoforms and Their Clinicopathologic Significance in Primary Retinoblastoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2017, 25, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhao, L. MicroRNA-98 targets HMGA2 to inhibit the development of retinoblastoma through mediating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 25, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Qin, M. Long non-coding RNA LEF1-AS1 is involved in the progression of retinoblastoma through regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyv, X.; Wu, F.; Zhang, H.; Lu, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y. Long Noncoding RNA ZFPM2-AS1 Knockdown Restrains the Development of Retinoblastoma by Modulating the MicroRNA-515/HOXA1/Wnt/β-Catenin Axis. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fu, C.; Wang, S.; Jin, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, M. CircTET1 Inhibits Retinoblastoma Progression via Targeting miR-492 and miR-494-3p through Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway. Curr. Eye Res. 2021, 46, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tell, S.; Yi, H.; Jockovich, M.E.; Murray, T.G.; Hackam, A.S. The Wnt signaling pathway has tumor suppressor properties in retinoblastoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Zhu, Y. Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of indomethacin on human retinoblastoma cell line Y79 and the involvement of β-catenin, nuclear factor-κB and Akt signaling pathways. Ophthalmic. Res. 2014, 51, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolucci, D.; Montemurro, L.; Raieli, S.; Lampis, S.; Pession, A.; Hrelia, P.; Tonelli, R. MYCN Impact on High-Risk Neuroblastoma: From Diagnosis and Prognosis to Targeted Treatment. Cancers 2022, 14, 4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Gu, W.; Liu, F.; Yu, L.; Shu, Y.; Liu, L.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Mao, J. Prominent Staining of MYCN Immunohistochemistry Predicts a Poor Prognosis in MYCN Non-Amplified Neuroblastoma. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2023, 26, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.H.; Ghosh, B.; Rizvi, M.A.; Ali, M.; Kaur, L.; Mondal, A.C. Neural crest cells development and neuroblastoma progression: Role of Wnt signaling. J. Cell Physiol. 2023, 238, 306–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garikapati, K.R.; Patel, N.; Makani, V.K.K.; Cilamkoti, P.; Bhadra, U.; Bhadra, M.P. Down-regulation of BORIS/CTCFL efficiently regulates cancer stemness and metastasis in MYCN amplified neuroblastoma cell line by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 484, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ohira, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, T.; Luo, W.; Yang, C.; Li, X.; Gao, Z.; Zhou, R.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Genomic analysis-integrated whole-exome sequencing of neuroblastomas identifies genetic mutations in axon guidance pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56684–56697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Flahaut, M.; Meier, R.; Coulon, A.; Nardou, K.A.; Niggli, F.K.; Martinet, D.; Beckmann, J.S.; Joseph, J.M.; Mühlethaler-Mottet, A.; Gross, N. The Wnt receptor FZD1 mediates chemoresistance in neuroblastoma through activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2245–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szemes, M.; Greenhough, A.; Melegh, Z.; Malik, S.; Yuksel, A.; Catchpoole, D.; Gallacher, K.; Kollareddy, M.; Park, J.H.; Malik, K. Wnt Signalling Drives Context-Dependent Differentiation or Proliferation in Neuroblastoma. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, S.; Furfaro, A.L.; Caggiano, R.; Brondolo, L.; Garibaldi, S.; Ivaldo, C.; Marinari, U.M.; Pronzato, M.A.; Faraonio, R.; Nitti, M. microRNA-494 Favors HO-1 Expression in Neuroblastoma Cells Exposed to Oxidative Stress in a Bach1-Independent Way. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.J.; Zhou, C.L.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhao, Y.M.; Deng, C.M.; Wu, H.Y.; Zhuo, Z.J.; He, J. Association Between miR-492 rs2289030 G>C and Susceptibility to Neuroblastoma in Chinese Children from Jiangsu Province. Cancer Screen. Prev. 2023, 2, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villablanca, J.G.; Khan, A.A.; Avramis, V.I.; Seeger, R.C.; Matthay, K.K.; Ramsay, N.K.; Reynolds, C.P. Phase I trial of 13-cis-retinoic acid in children with neuroblastoma following bone marrow transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, K.K.; Villablanca, J.G.; Seeger, R.C.; Stram, D.O.; Harris, R.E.; Ramsay, N.K.; Swift, P.; Shimada, H.; Black, C.T.; Brodeur, G.M.; et al. Treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma with intensive chemotherapy, radiotherapy, autologous bone marrow transplantation, and 13-cis-retinoic acid. Children’s Cancer Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, J.; Yang, J. Promising Molecular Targets and Novel Therapeutic Approaches in Neuroblastoma. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 9, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, I.; Qaddoumi, I.; Yaser, S.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Ferrari, A. Comparing adult and pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma in the surveillance, epidemiology and end results program, 1973 to 2005: An analysis of 2,600 patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3391–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, L.H. Rhabdomyosarcoma and the Undifferentiated Sarcomas. In Principles and Practice of Pediatric Oncology, 2006th ed.; LWW: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 971–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Raney, R.B.; Maurer, H.M.; Anderson, J.R.; Andrassy, R.J.; Donaldson, S.S.; Qualman, S.J.; Wharam, M.D.; Wiener, E.S.; Crist, W.M. The Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group (IRSG): Major Lessons From the IRS-I Through IRS-IV Studies as Background for the Current IRS-V Treatment Protocols. Sarcoma 2001, 5, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dm, P.; Da, E. Rhabdomyosarcomas in Adults and Children: An Update. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2006, 130. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17090187/ (accessed on 11 August 2023).
- Davicioni, E.; Anderson, M.J.; Finckenstein, F.G.; Lynch, J.C.; Qualman, S.J.; Shimada, H.; Schofield, D.E.; Buckley, J.D.; Meyer, W.H.; Sorensen, P.H.; et al. Molecular classification of rhabdomyosarcoma--genotypic and phenotypic determinants of diagnosis: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soglio, D.B.; Rougemont, A.L.; Absi, R.; Giroux, L.M.; Sanchez, R.; Barrette, S.; Fournet, J.C. Beta-catenin mutation does not seem to have an effect on the tumorigenesis of pediatric rhabdomyosarcomas. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2009, 12, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Vinson, C.; Gurley, C.M.; Nolen, G.T.; Beggs, M.L.; Nagarajan, R.; Wagner, E.F.; Parham, D.M.; Peterson, C.A. Impaired Wnt signaling in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma cells from p53/c-fos double mutant mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2055–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, N.; Yu, Y.; Duan, C.; Wei, J.; Sun, W.; Jiang, C.; Jian, B.; Cao, W.; Jia, L.; Ma, X. Quantitative proteomics identifies and validates urinary biomarkers of rhabdomyosarcoma in children. Clin. Proteomics. 2023, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Y.; DeRan, M.T.; Ignatius, M.S.; Grandinetti, K.B.; Clagg, R.; McCarthy, K.M.; Lobbardi, R.M.; Brockmann, J.; Keller, C.; Wu, X.; et al. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors induce the canonical WNT/β-catenin pathway to suppress growth and self-renewal in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5349–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.L.P.; Saad, S.T.O.; Roversi, F.M. WNT5A in tumor development and progression: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, N.; Viehweger, F.; Bauer, J.; Geyer, N.; Yang, M.; Seils, A.; Belharazem, D.; Brembeck, F.H.; Schildhaus, H.U.; Marx, A.; et al. Canonical WNT/β-Catenin Signaling Plays a Subordinate Role in Rhabdomyosarcomas. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieśla, M.; Dulak, J.; Józkowicz, A. MicroRNAs and epigenetic mechanisms of rhabdomyosarcoma development. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 53, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missiaglia, E.; Shepherd, C.J.; Patel, S.; Thway, K.; Pierron, G.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; Renard, M.; Sciot, R.; Rao, P.; Oberlin, O. MicroRNA-206 expression levels correlate with clinical behaviour of rhabdomyosarcomas. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Dong Xda, E.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Qu, J.; Tu, L. MicroRNA-1/206 targets c-Met and inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma development. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 29596–29604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giralt, I.; Gallo-Oller, G.; Navarro, N.; Zarzosa, P.; Pons, G.; Magdaleno, A.; Segura, M.F.; Sábado, C.; Hladun, R.; Arango, D.; et al. Dickkopf-1 Inhibition Reactivates Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Rhabdomyosarcoma, Induces Myogenic Markers In Vitro and Impairs Tumor Cell Survival In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Physiological Functions of Wilms’ Tumor 1-Associating Protein and Its Role in Tumourigenesis. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30756410/ (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Cone, E.B.; Dalton, S.S.; Van Noord, M.; Tracy, E.T.; Rice, H.E.; Routh, J.C. Biomarkers for Wilms Tumor: A Systematic Review. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakumatha, E.; Weijers, J.; Banda, K.; Bailey, S.; Molyneux, E.; Chagaluka, G.; Israels, T. Outcome at the end of treatment of patients with common and curable childhood cancer types in Blantyre, Malawi. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surgical Concepts in the Treatment of Wilms Tumor: An Update. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26704280/ (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Spreafico, F.; Pritchard Jones, K.; Malogolowkin, M.H.; Bergeron, C.; Hale, J.; De Kraker, J.; Dallorso, S.; Acha, T.; De Camargo, B.; Dome, J.S.; et al. Treatment of relapsed Wilms tumors: Lessons learned. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2009, 9, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- lncRNA MSC-AS1 Activates Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway to Modulate Cell Proliferation and Migration in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma via miR-3924/WNT5A. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31916281/ (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Akpa, M.M.; Iglesias, D.M.; Chu, L.L.; Cybulsky, M.; Bravi, C.; Goodyer, P.R. Wilms Tumor Suppressor, WT1, Suppresses Epigenetic Silencing of the β-Catenin Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 2279–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhme, C.; Busch, M.; Heine, E.; de Torres, C.; Mora, J.; Royer-Pokora, B. WT1-Mutant Wilms Tumor Progression Is Associated With Diverting Clonal Mutations of CTNNB1. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 43, e180-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhu, J. DEPDC1 is a novel cell cycle related gene that regulates mitotic progression. BMB Rep. 2015, 48, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Huang, R.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Liu, F.; Liang, H.; Mo, Z. Myelin and lymphocyte protein serves as a prognostic biomarker and is closely associated with the tumor microenvironment in the nephroblastoma. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Li, W.; Chang, G.Z.; Li, Y.M. Long noncoding RNA KTN1 antisense RNA 1exerts an oncogenic function in lung adenocarcinoma by regulating DEP domain containing 1 expression via activating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Anticancer Drugs 2021, 32, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Chu, H.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; Gong, B.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; et al. DEPDC1 upregulation promotes cell proliferation and predicts poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2021, 30, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, S.; Huang, P.; Xu, S.; Zhang, G.; He, H.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, C.X.; Kim, H.; Tan, Y. NNK-mediated upregulation of DEPDC1 stimulates the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting CYP27B1 expression. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 1745–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Liu, J.; Ma, G.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y. DEP Domain Containing 1 Promotes Proliferation, Invasion, and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer by Enhancing Expression of Suppressor of Zest 12. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2021, 36, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Yu, M.; Sui, L.; Gong, B.; Zhou, B.; Chen, J.; Gong, Z.; Hao, C. High Expression of DEPDC1 Promotes Malignant Phenotypes of Breast Cancer Cells and Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhong, W.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Ma, F.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Artemisia argyi Essential Oil Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis via Suppression of DEPDC1 Dependent Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2021.664791 (accessed on 12 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; Li, Q.; Guo, X.; Ni, Q.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ming, M. FOXO3a-modulated DEPDC1 promotes malignant progression of nephroblastoma via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 26, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, D.M.; Ramalho, R.F.; Maschietto, M. Gene Expression in Wilms Tumor: Disturbance of the Wnt Signaling Pathway and MicroRNA Biogenesis. In Wilms Tumor; Codon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashihara, E.; Takada, T.; Maekawa, T. Targeting the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hematological malignancies. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiheisel, A.; Kaur, M.; Ma, N.; Havard, P.; Shenoy, A.K. Wnt pathway modulators in cancer therapeutics: An update on completed and ongoing clinical trials. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M. Canonical and non-canonical WNT signaling in cancer stem cells and their niches: Cellular heterogeneity, omics reprogramming, targeted therapy and tumor plasticity. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoerger, B.; Kang, H.J.; Yalon-Oren, M.; Marshall, L.V.; Vezina, C.; Pappo, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Petrilli, A.S.; Ebinger, M.; Toporski, J.; et al. Pembrolizumab in paediatric patients with advanced melanoma or a PD-L1-positive, advanced, relapsed, or refractory solid tumour or lymphoma (KEYNOTE-051): Interim analysis of an open-label, single-arm, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srimongkol, A.; Laosillapacharoen, N.; Saengwimol, D.; Chaitankar, V.; Rojanaporn, D.; Thanomchard, T.; Borwornpinyo, S.; Hongeng, S.; Kaewkhaw, R. Sunitinib efficacy with minimal toxicity in patient-derived retinoblastoma organoids. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Tian, R.; Chen, J.; Gao, H.; Xie, C.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, S.; Xu, M. The protective autophagy activated by GANT-61 in MYCN amplified neuroblastoma cells is mediated by PERK. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 14413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Widemann, B.C.; Krailo, M.; Jayaprakash, N.; Fox, E.; Weigel, B.; Blaney, S.M. Phase 2 trial of sorafenib in children and young adults with refractory solid tumors: A report from the Children's Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.C.; Huang, C.C.; Wang, P.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Hsu, W.M.; Chuang, J.H.; Chuang, H.C. ONC201 Suppresses Neuroblastoma Growth by Interrupting Mitochondrial Function and Reactivating Nuclear ATRX Expression While Decreasing MYCN. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfreda, L.; Rampazzo, E.; Persano, L. Wnt signaling in brain tumors: A challenging therapeutic target. Biology 2023, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, C.L.; Van den Heuvel, A.P.; Allen, J.E.; Prabhu, V.V.; Dicker, D.T.; El-Deiry, W.S. ONC201 kills solid tumor cells by triggering an integrated stress response dependent on ATF4 activation by specific eIF2α kinases. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugolkov, A.V.; Bondarenko, G.I.; Dubrovskyi, O.; Berbegall, A.P.; Navarro, S.; Noguera, R.; O’Halloran, T.V.; Hendrix, M.J.; Giles, F.J.; Mazar, A.P. 9-ING-41, a small-molecule glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor, is active in neuroblastoma. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2018, 29, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoerger, B.; Kieran, M.W.; Grupp, S.; Perek, D.; Clancy, J.; Krygowski, M.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Boni, J.P.; Berkenblit, A.; Spunt, S.L. Phase II trial of temsirolimus in children with high-grade glioma, neuroblastoma and rhabdomyosarcoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Fan, S.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y. Growth inhibition and suppression of the mTOR and Wnt/β-catenin pathways in T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia by rapamycin and MYCN depletion. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Han, L.; Weng, J.; Wang, K.; Chen, T. Rapamycin inhibits proliferation and induces autophagy in human neuroblastoma cells. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20181822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M.; Elliott, R.; Bowers, L.; Balan, N.; Rafiq, R.; Costa-Cabral, S.; Munkonge, F.; Trinidade, I.; Porter, R.; Campbell, A.D.; et al. A novel tankyrase inhibitor, MSC2504877, enhances the effects of clinical CDK4/6 inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodge, M.E.; Lum, L. Drugging the cancer stem cell compartment: Lessons learned from the hedgehog and Wnt signal transduction pathways. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 51, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.H.; Hou, W.J.; Fang, Y.; Fan, J.; Tong, H.; Bai, S.L.; Chen, Q.; Xu, H.; Li, Y. XAV939, a tankyrase 1 inhibitior, promotes cell apoptosis in neuroblastoma cell lines by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabal, P.; Zhou, F.; Ma, X.; Bondra, K.M.; Blackman, B.; Weintraub, S.T.; Chen, Y.; Chévez-Barrios, P.; Houghton, P.J.; Gallie, B.; et al. Nitric oxide suppression by secreted frizzled-related protein 2 drives retinoblastoma. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.Y.; Kim, J. Cyclic pentapeptide cRGDfK enhances the inhibitory effect of sunitinib on TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Liu, B. GANT61 exerts anticancer cell and anticancer stem cell capacity in colorectal cancer by blocking the Wnt/β-catenin and Notch signalling pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 48, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesha, S.; Manzella, G.; Bovay, A.; Casanova, E.A.; Bode, P.K.; Belle, R.; Feuchtgruber, S.; Jaaks, P.; Dogan, N.; Koscielniak, E.; et al. Targeting hedgehog signaling reduces self-renewal in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualtrough, D.; Rees, P.; Speight, B.; Williams, A.C.; Paraskeva, C. The hedgehog inhibitor cyclopamine reduces β-catenin-Tcf transcriptional activity, induces E-cadherin expression, and reduces invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Cancers 2015, 7, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruwge, W.; D’Arcy, P.; Folin, A.; Brnjic, S.; Wejde, J.; Davis, A.; Erlandsson, F.; Bergh, J.; Brodin, B. Sorafenib inhibits tumor growth and vascularization of rhabdomyosarcoma cells by blocking IGF-1R-mediated signaling. OncoTargets Ther. 2008, 1, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polosukhina, D.; Love, H.D.; Moses, H.L.; Lee, E.; Zent, R.; Clark, P.E. Pharmacologic inhibition of β-catenin with Pyrvinium inhibits murine and human models of Wilms tumor. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pode-Shakked, N.; Harari-Steinberg, O.; Haberman-Ziv, Y.; Rom-Gross, E.; Bahar, S.; Omer, D.; Metsuyanim, S.; Buzhor, E.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Goldstein, R.S.; et al. Resistance or sensitivity of Wilms’ tumor to anti-FZD7 antibody highlights the Wnt pathway as a possible therapeutic target. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1664–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M. Can we safely target the WNT pathway? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: Function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Luo, H.; Meng, X.; Chen, M.; Zhu, D. Wnt signaling pathway in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2022, 525, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsken, J.; Birchmeier, W. New aspects of Wnt signaling pathways in higher vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001, 11, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusse, R.; van Ooyen, A.; Cox, D.; Fung, Y.K.; Varmus, H. Mode of proviral activation of a putative mammary oncogene (int-1) on mouse chromosome 15. Nature 1984, 307, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koni, M.; Pinnarò, V.; Brizzi, M.F. The Wnt Signalling Pathway: A Tailored Target in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, R.B.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

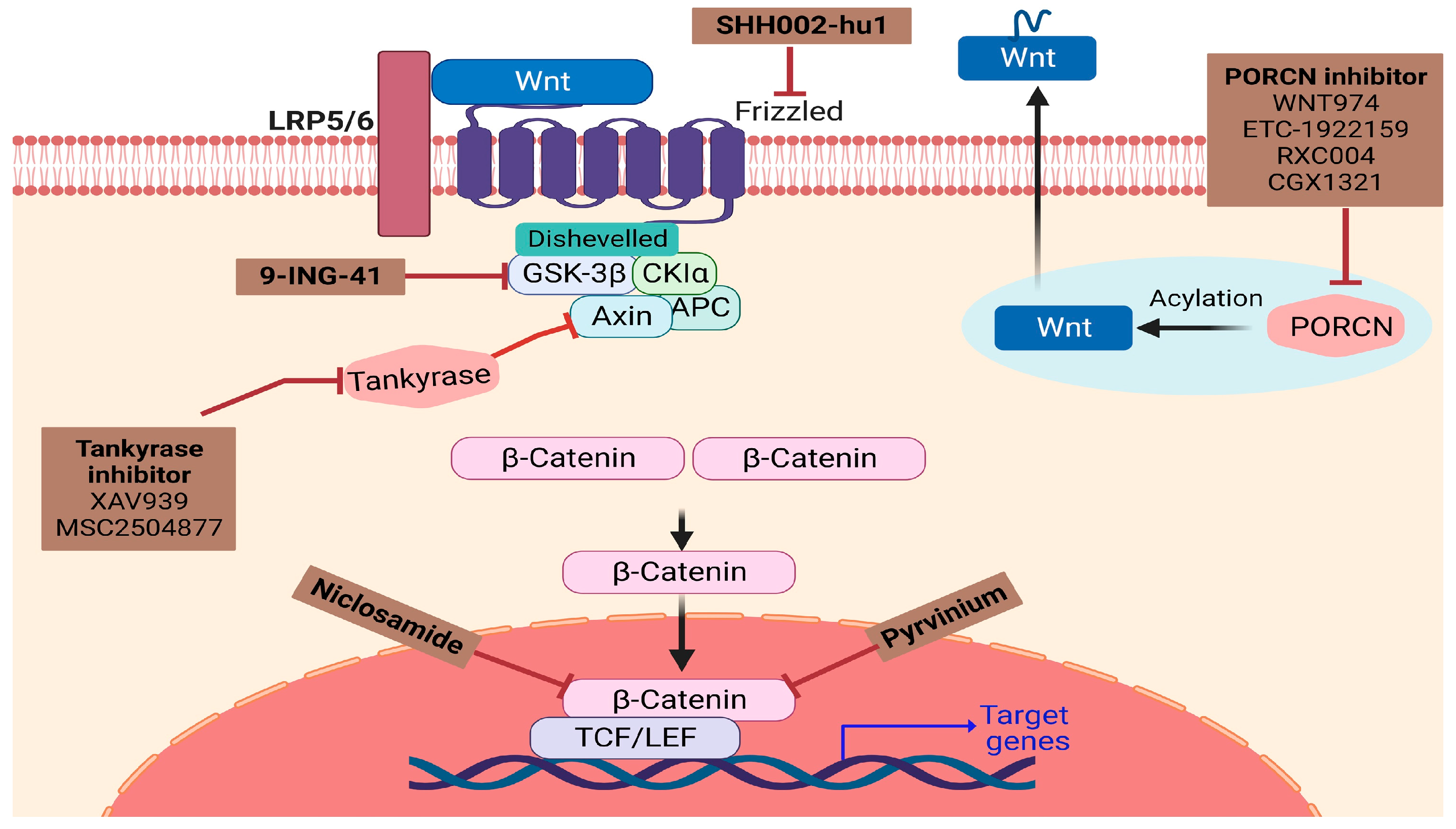
| Drug | Mechanism of Action | Disease | Literature | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ETC-1922159 + Pembrolizumab | PORCN inhibitor, inhibits the extracellular secretion of Wnt | Solid Tumors | [90] |
| 2 | ONC201 | Reduces the expression of several Wnt pathway components | Solid tumors Neuroblastoma | [94,95,96] |
| 3 | 9-ING-41 | Maleimide-based ATP-competitive small molecule GSK-3 inhibitor | Pediatric cancer, Neuroblastoma | [88,97] |
| 4 | Rapamycin | Suppresses the mTOR and Wnt/β-catenin pathways, induces autophagy | Neuroblastoma | [98,99,100] |
| 5 | MSC2504877 | Tankyrase inhibitor | Neuroblastoma | [101] |
| 6 | IWP Compounds | PORCN inhibitor | Neuroblastoma | [102] |
| 7 | XAV939 | Tankyrase 1(TNKS1) inhibitor | Neuroblastoma, Retinoblastoma | [103,104] |
| 8 | Sunitinib | Inhibits TGF-β1-induced Wnt signaling | Neuroblastoma, Retinoblastoma | [1,105] |
| 9 | GANT-61 | Inhibits Wnt/β-catenin and Notch signaling pathways | Neuroblastoma Rhabdomyosarcoma | [92,106] |
| 10 | Niclosamide | Inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling | Retinoblastoma | [32] |
| 11 | * CircTET1 | Inhibits WNT/β-catenin signaling | Retinoblastoma | [38] |
| 12 | Cyclopamine | Inhibits β-catenin | Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma | [107,108] |
| 13 | Sorafenib | Inhibits WNT/β-catenin signaling | Rhabdomyosarcoma, Wilms Tumor | [93,109] |
| 14 | Pyrvinium | Inhibition of β-catenin gene transcription | Wilms tumor | [110] |
| 15 | SHH002-hu1 | FZD7 inhibitor | Wilms Tumor | [111] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choudhary, S.; Singh, M.K.; Kashyap, S.; Seth, R.; Singh, L. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Pediatric Tumors: Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment. Children 2024, 11, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11060700
Choudhary S, Singh MK, Kashyap S, Seth R, Singh L. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Pediatric Tumors: Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment. Children. 2024; 11(6):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11060700
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoudhary, Sahar, Mithalesh Kumar Singh, Seema Kashyap, Rachna Seth, and Lata Singh. 2024. "Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Pediatric Tumors: Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment" Children 11, no. 6: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11060700
APA StyleChoudhary, S., Singh, M. K., Kashyap, S., Seth, R., & Singh, L. (2024). Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Pediatric Tumors: Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment. Children, 11(6), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11060700






