Genetic Pleiotropy and Causal Pathways Linking Glycemic Traits to Asthma: An Integrated Proteogenomic Investigation
Highlights
- Obesity (BMI) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) show significant genetic correlations and causal effects on asthma risk.
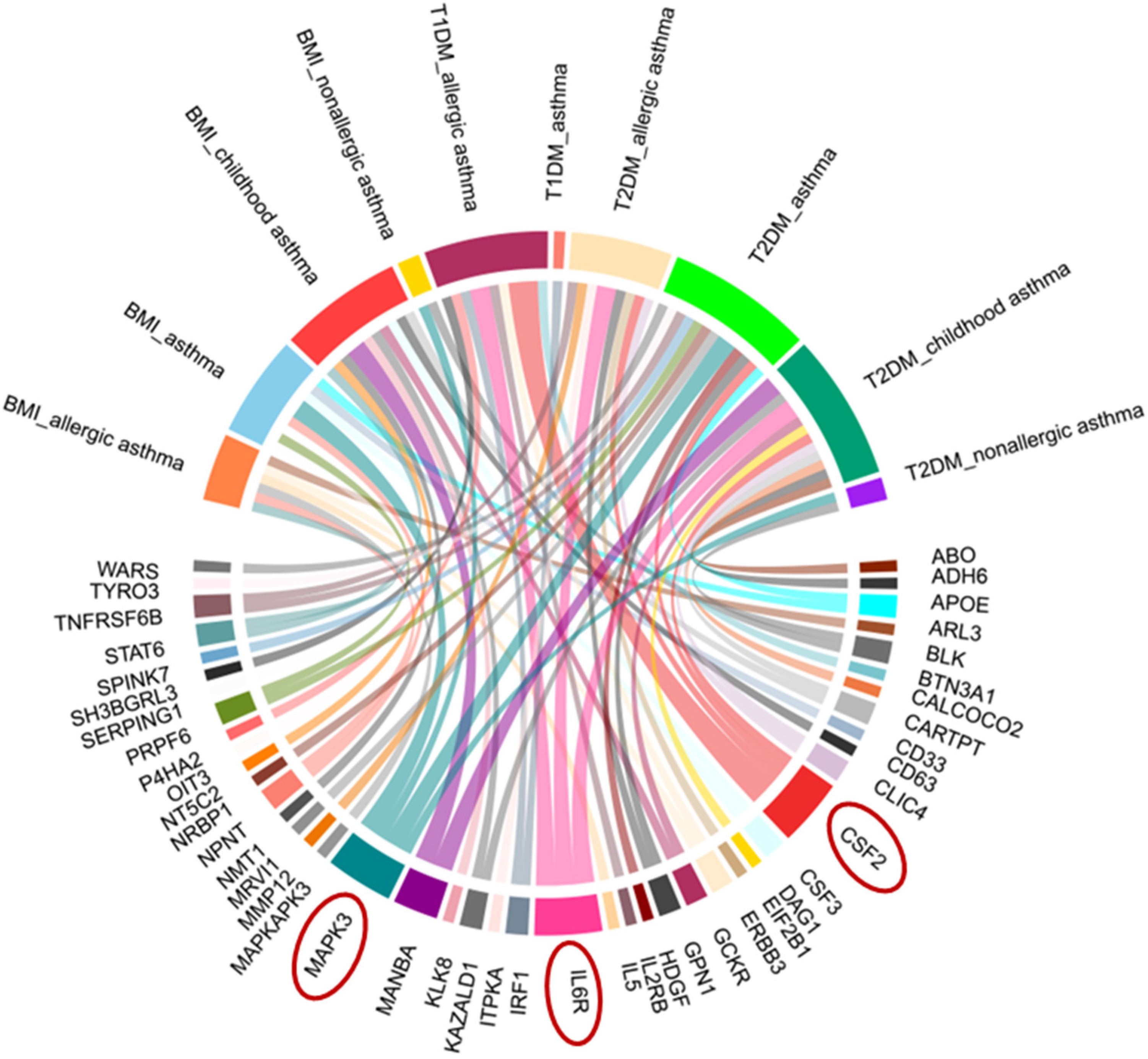
- Shared pleiotropic loci and key proteins (e.g., IL6R, MAPK3, CSF2) link diabetes/glycemic traits with asthma through inflammatory pathways.
- These findings suggest that metabolic dysfunction contributes to asthma pathogenesis via shared genetic and immunological mechanisms.
- Targeting colocalized proteins and pathways such as JAK-STAT signaling may provide novel therapeutic strategies for comorbid diabetes and asthma.
Abstract
1. Introduction
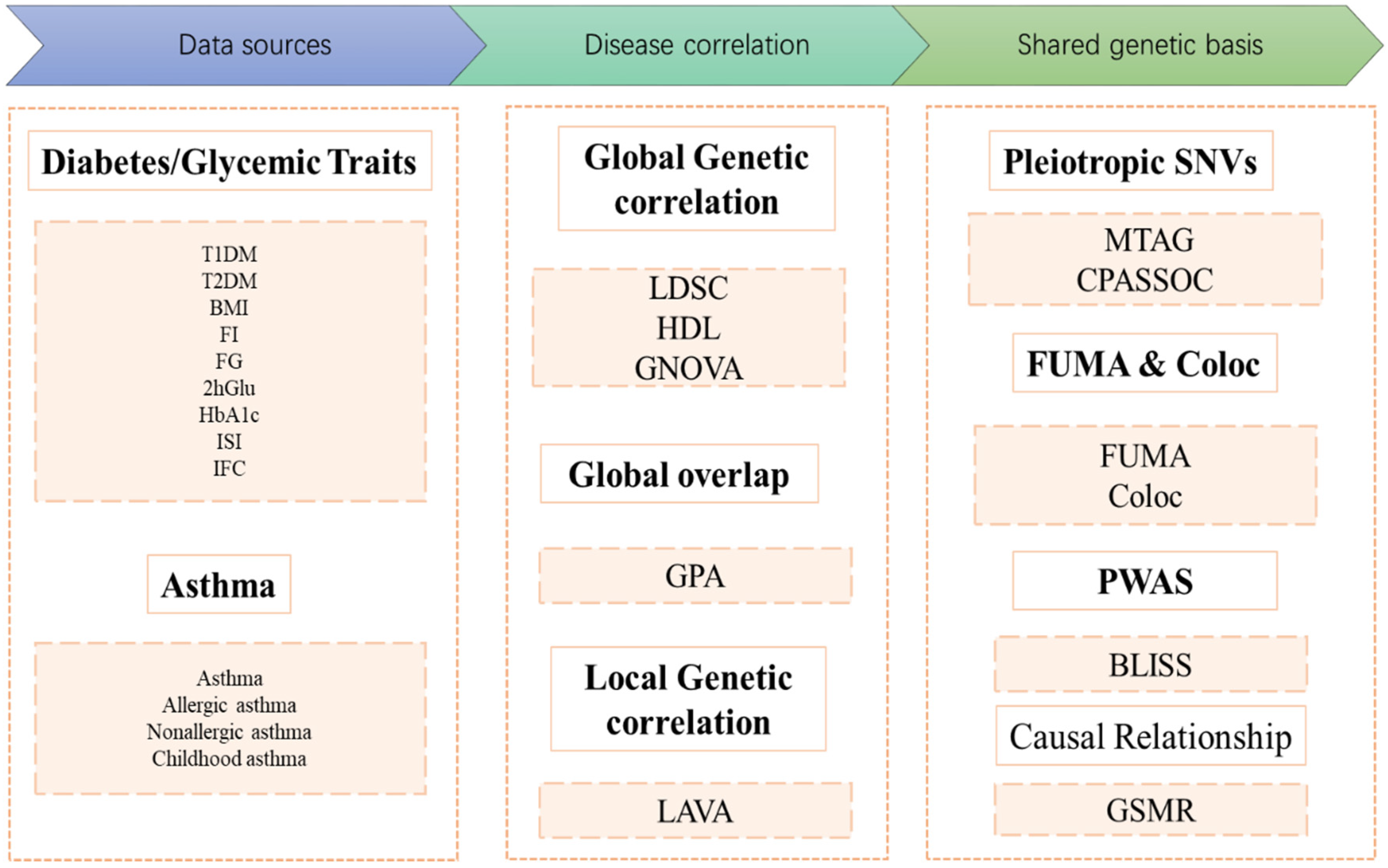
2. Method
2.1. Study Population and Design
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Genetic Correlation Analysis
2.4. Genome-Wide Genetic Overlap
2.5. Local Genetic Correlations
2.6. Identification of Pleiotropic Loci
2.7. Colocalization Analysis
2.8. Biomarker Expression Level Imputation via Summary-Level Statistics
2.9. GSMR
3. Results
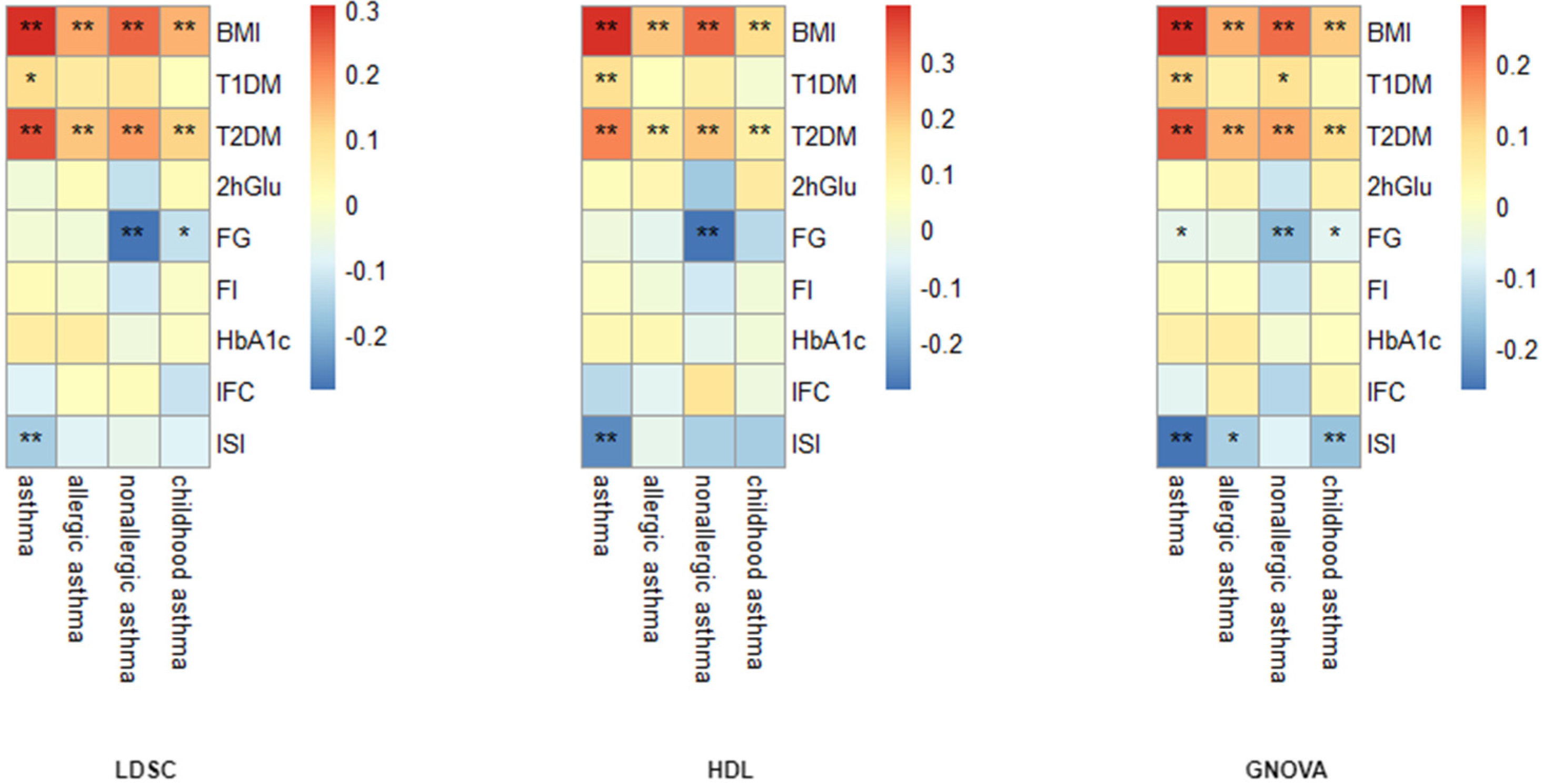
3.1. Global Genetic Correlation Analysis
3.2. Genome-Wide Genetic Overlap Analysis
3.3. Local Genetic Correlation Analysis
3.4. GSMR
3.5. Cross-Trait Loci and Causal Variant Analysis
3.6. Identification of Proteins Associated with Comorbid Glucose Metabolism Traits and Asthma
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGEs | Advanced Glycation End Products |
| AHR | Airway Hyperresponsiveness |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BLISS | Biomarker Expression Level Imputation using Summary Statistics |
| COLOC | Colocalization |
| CPASSOC | Cross-Phenotype Association |
| DM | Diabetes Mellitus |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| FG | Fasting Glucose |
| FI | Fasting Insulin |
| FUMA | Functional Mapping and Annotation of Genetic Associations |
| GNOVA | Genetic Covariance Analysis |
| GSMR | Generalized Summary-Data-Based Mendelian Randomization |
| GWAS | Genome-Wide Association Study |
| HDL | High-Definition Likelihood Analysis |
| HEIDI | Heterogeneity in Dependent Instruments |
| ICS | Inhaled Corticosteroids |
| IFC | Insulin Fold Change after Oral Glucose Tolerance Test |
| ISI | Insulin Sensitivity Index |
| LABA | Long-Acting Beta-Adrenoceptor Agonists |
| LD | Linkage Disequilibrium |
| LDSC | Linkage Disequilibrium Score Regression |
| LAVA | Local Genetic Variant Association Analysis |
| MCC | Maximal Clique Centrality |
| MTAG | Multitrait Analysis of GWAS |
| PAR | Pleiotropy Association Ratio |
| PPI | Protein‒Protein Interaction |
| PWAS | Proteome-Wide Association Study |
| RAGE | Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproducts |
| SNPs | Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms |
| T1DM | Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| 2hGlu | 2 Hour Postprandial Glucose |
References
- Maspero, J.; Adir, Y.; Al-Ahmad, M.; Celis-Preciado, C.A.; Colodenco, F.D.; Giavina-Bianchi, P.; Lababidi, H.; Ledanois, O.; Mahoub, B.; Perng, D.-W.; et al. Type 2 inflammation in asthma and other airway diseases. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00576–02021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Li, R.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Nie, H.; Liu, L.; Zou, X.; Zhong, J.; Zheng, B.; Gong, Q. The role of B cells in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1450366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Tian, Y.; Shi, W.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Qian, L. beta-cell neogenesis: A rising star to rescue diabetes mellitus. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 62, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, K.; Wilczopolski, P.; Bulawska, D.; Mlynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. The Importance of SGLT-2 Inhibitors as Both the Prevention and the Treatment of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, M.; Prattichizzo, F.; La Grotta, R.; Matacchione, G.; Scisciola, L.; Fontanella, R.A.; Tortorella, G.; Benedetti, R.; Carafa, V.; Marfella, R.; et al. Is it time to revise the fighting strategy toward type 2 diabetes? Sex and pollution as new risk factors. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 99, 102405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stene, L.C.; Nafstad, P. Relation between occurrence of type 1 diabetes and asthma. Lancet 2001, 357, 607–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Chen, G.; Liang, T.; Li, A.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Kuang, X.; Han, D.; Liao, W.; et al. Childhood asthma and type 1 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 33, e13858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yang, Y.; Yu, L.; Song, L.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Wu, L.; Ma, W.; Zhang, B. The association between type 2 diabetes and asthma incidence: A longitudinal analysis considering genetic susceptibility. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, M.D.; Gavrilova, T. Understanding the immunology of asthma: Pathophysiology, biomarkers, and treatments for asthma endotypes. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2020, 36, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwell, J.R.; Fitzpatrick, A.M. Asthma Phenotypes and Biomarkers. Respir. Care 2025, 70, 649–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuramoto, K.; Morishima, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Ano, S.; Kawashima, K.; Yabuuchi, Y.; Sakai, C.; Matsumura, S.; Nishino, K.; Yazaki, K.; et al. Nrf2 Deficiency Accelerates IL-17-Dependent Neutrophilic Airway Inflammation in Asthmatic Mice. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Morgan, S.B.; Donachie, G.E.; Horton, K.L.; Pavord, I.D.; Arancibia-Carcamo, C.V.; Hinks, T.S.C. Epithelial immune activation and intracellular invasion by non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1141798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Qin, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Kang, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, H.; Wu, T.; Chen, D.; et al. Identification of shared genetic etiology of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases through common cardiometabolic risk factors. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, R.; Yu, B.; Yu, Y.; Luo, X.; Yin, S.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, J.; Ai, S. Dissecting shared genetic architecture between depression and body mass index. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, D.; Gao, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Dong, G. Shared genetic architecture between COVID-19 and irritable bowel syndrome: A large-scale genome-wide cross-trait analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1442693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Finucane, H.K.; Anttila, V.; Gusev, A.; Day, F.R.; Loh, P.R.; Duncan, L.; Perry, J.R.B.; Patterson, N.; Robinson, E.B.; et al. An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Z.; Pawitan, Y.; Shen, X. High-definition likelihood inference of genetic correlations across human complex traits. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Li, B.; Ou, D.; Erlendsdottir, M.; Powles, R.L.; Jiang, T.; Hu, Y.; Chang, D.; Jin, C.; Dai, W.; et al. A Powerful Approach to Estimating Annotation-Stratified Genetic Covariance via GWAS Summary Statistics. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 939–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.; Yang, C.; Li, C.; Gelernter, J.; Zhao, H. GPA: A statistical approach to prioritizing GWAS results by integrating pleiotropy and annotation. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werme, J.; van der Sluis, S.; Posthuma, D.; de Leeuw, C.A. An integrated framework for local genetic correlation analysis. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhu, X. Cross-Phenotype Association Analysis Using Summary Statistics from GWAS. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1666, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Turley, P.; Walters, R.K.; Maghzian, O.; Okbay, A.; Lee, J.J.; Fontana, M.A.; Nguyen-Viet, T.A.; Wedow, R.; Zacher, M.; Furlotte, N.A.; et al. Multi-trait analysis of genome-wide association summary statistics using MTAG. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Taskesen, E.; van Bochoven, A.; Posthuma, D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambartolomei, C.; Vukcevic, D.; Schadt, E.E.; Franke, L.; Hingorani, A.D.; Wallace, C.; Plagnol, V. Bayesian test for colocalisation between pairs of genetic association studies using summary statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Liu, F.; Hu, C.; Hu, J. Multi-trait analysis reveals risk loci for heart failure and the shared genetic etiology with blood lipids, blood pressure, and blood glucose. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhao, B. Large-scale imputation models for multi-ancestry proteome-wide association analysis. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferkingstad, E.; Sulem, P.; Atlason, B.A.; Sveinbjornsson, G.; Magnusson, M.I.; Styrmisdottir, E.L.; Gunnarsdottir, K.; Helgason, A.; Oddsson, A.; Halldorsson, B.V.; et al. Large-scale integration of the plasma proteome with genetics and disease. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dutta, D.; Köttgen, A.; Tin, A.; Schlosser, P.; Grams, M.E.; Harvey, B.; CKDGen Consortium; Yu, B.; Boerwinkle, E.; et al. Plasma proteome analyses in individuals of European and African ancestry identify cis-pQTLs and models for proteome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.; Trzaskowski, M.; Maier, R.; Robinson, M.R.; McGrath, J.J.; Visscher, P.M.; Wray, N.R.; et al. Causal associations between risk factors and common diseases inferred from GWAS summary data. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; Guo, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Yan, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Xue, F.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, Z. Role of the Gut-Brain Axis in the Shared Genetic Etiology Between Gastrointestinal Tract Diseases and Psychiatric Disorders: A Genome-Wide Pleiotropic Analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2023, 80, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.Y.; Lee, S.E.; Han, K.; Koh, E.H. Association between diabetes and asthma: Evidence from a nationwide Korean study. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.K.; Pedersen, C.T.; Fischer-Rasmussen, K.; Melgaard, M.E.; Brustad, N.; Kyvsgaard, J.N.; Vahman, N.; Schoos, A.-M.M.; Stokholm, J.; Chawes, B.; et al. Genetic predisposition to high BMI increases risk of early life respiratory infections and episodes of severe wheeze and asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 64, 2400169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Shu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, L. AMPK Regulates M1 Macrophage Polarization through the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway to Attenuate Airway Inflammation in Obesity-Related Asthma. Inflammation 2025, 48, 372–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zi, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G.; Xiong, J. Genetic correlation, pleiotropic loci and shared risk genes between major depressive disorder and gastrointestinal tract disorders. J. Affect. Disord. 2025, 374, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akirav, E.M.; Henegariu, O.; Preston-Hurlburt, P.; Schmidt, A.M.; Clynes, R.; Herold, K.C. The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) affects T cell differentiation in OVA induced asthma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Gong, Z.; Hao, X.; Liu, L. Genetic perturbation of IL-6 receptor signaling pathway and risk of multiple respiratory diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Kuai, S.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Wang, T.; Cui, Y. Diagnostic value of IL-6 for patients with asthma: A meta-analysis. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2023, 19, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Nogues, I.E.; Chen, T.; Xiong, X.; Bonzel, C.L.; Zhang, H.; Hong, C.; Xia, Y.; Dahal, K.; et al. Heterogeneous associations between interleukin-6 receptor variants and phenotypes across ancestries and implications for therapy. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, F.; Hua, M.; Liang, M.; Song, C. Role of GM-CSF in lung balance and disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1158859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, L.; Sengupta, S.; Purawarga Matada, G.S.; Teli, G.; Biswas, G.; Das, P.K.; Mudgal, M.P. Medicinal chemistry perspective of JAK inhibitors: Synthesis, biological profile, selectivity, and structure activity relationship. Mol. Divers. 2024, 28, 4467–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobs, S.P.; Pohlmeier, L.; Li, F.; Kayhan, M.; Becher, B.; Kopf, M. GM-CSF instigates a dendritic cell-T-cell inflammatory circuit that drives chronic asthma development. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 2118–2133.e2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
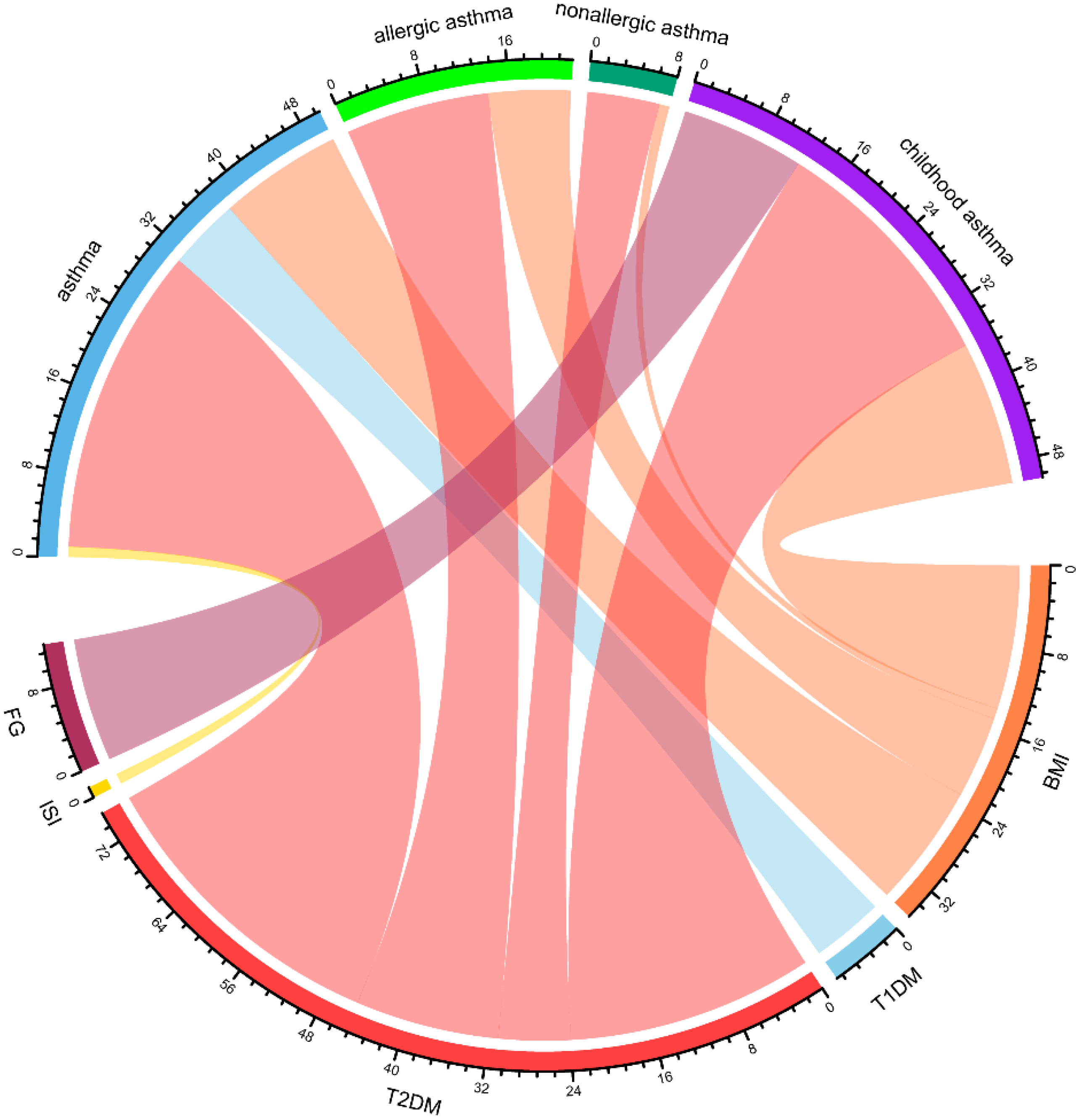
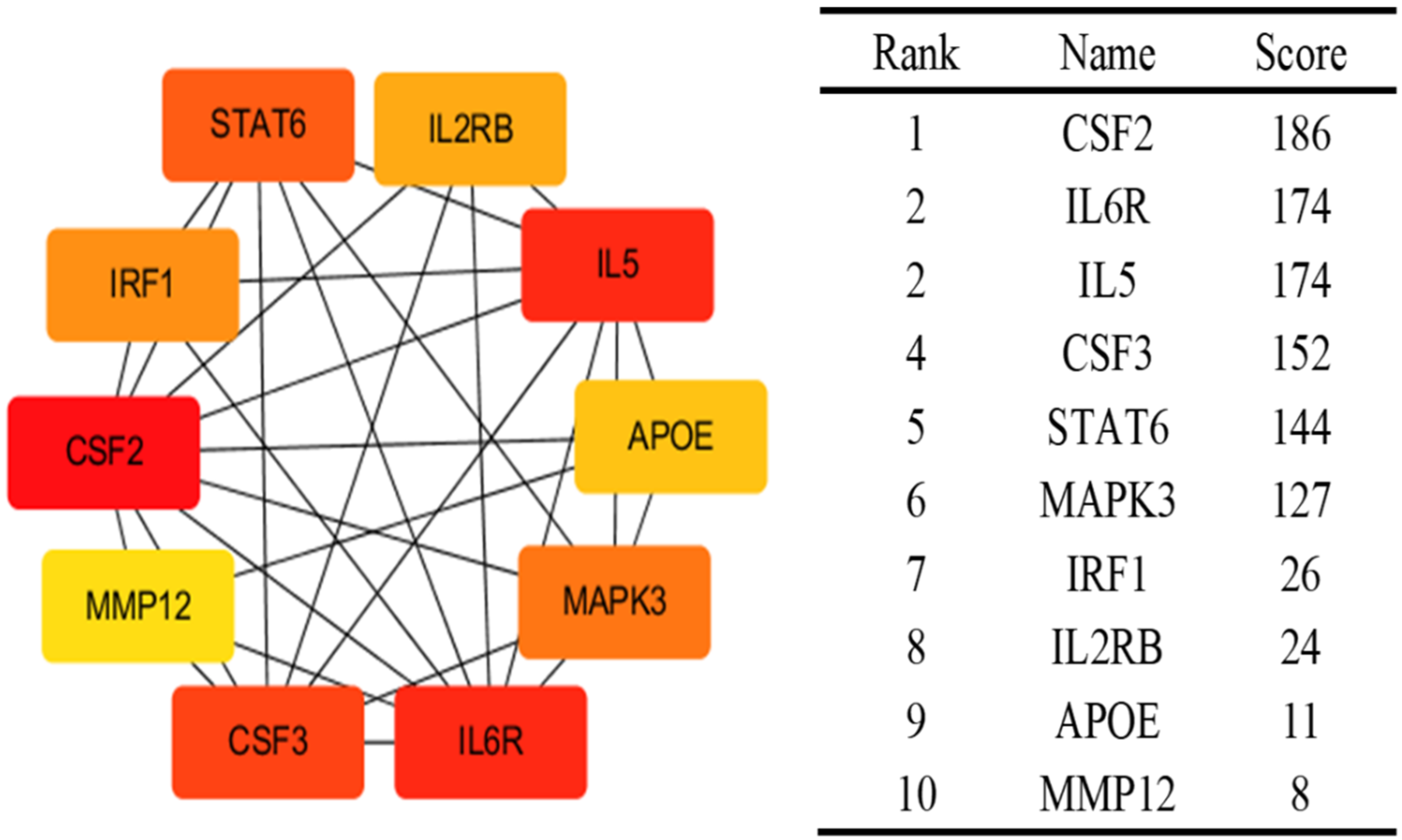
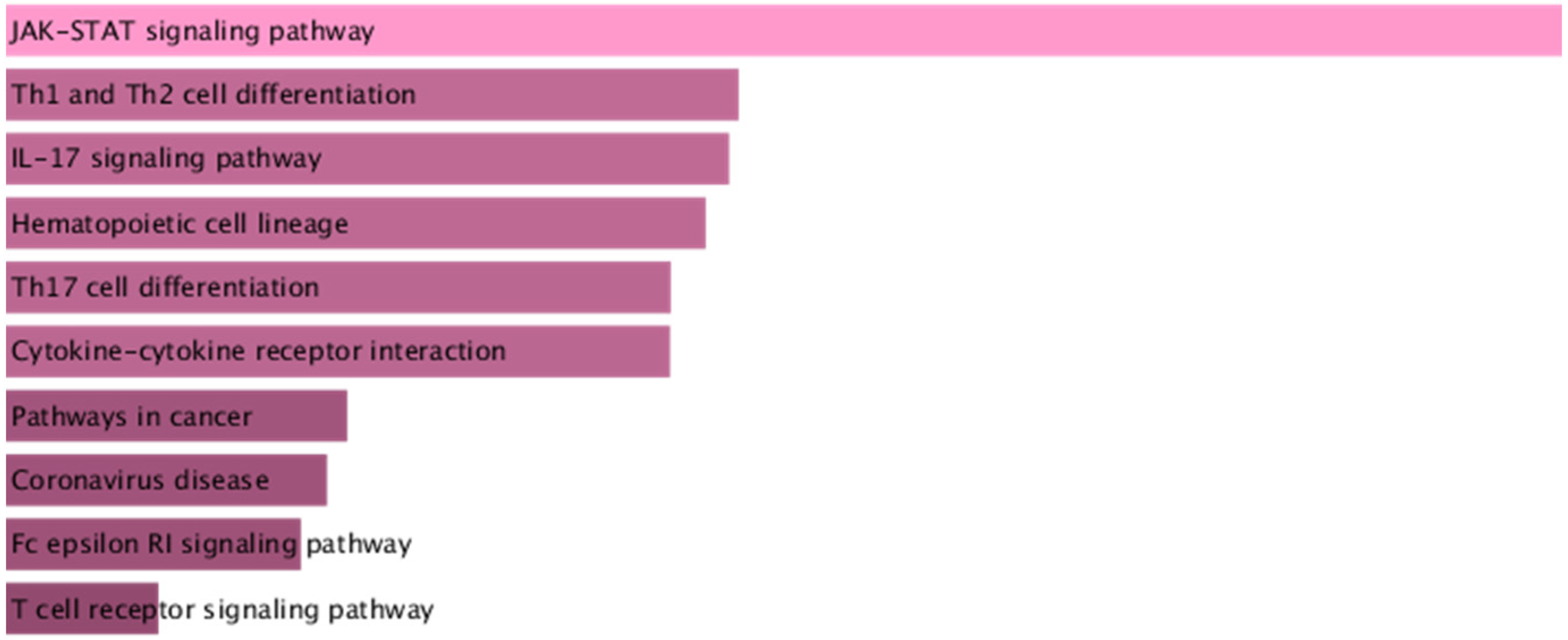
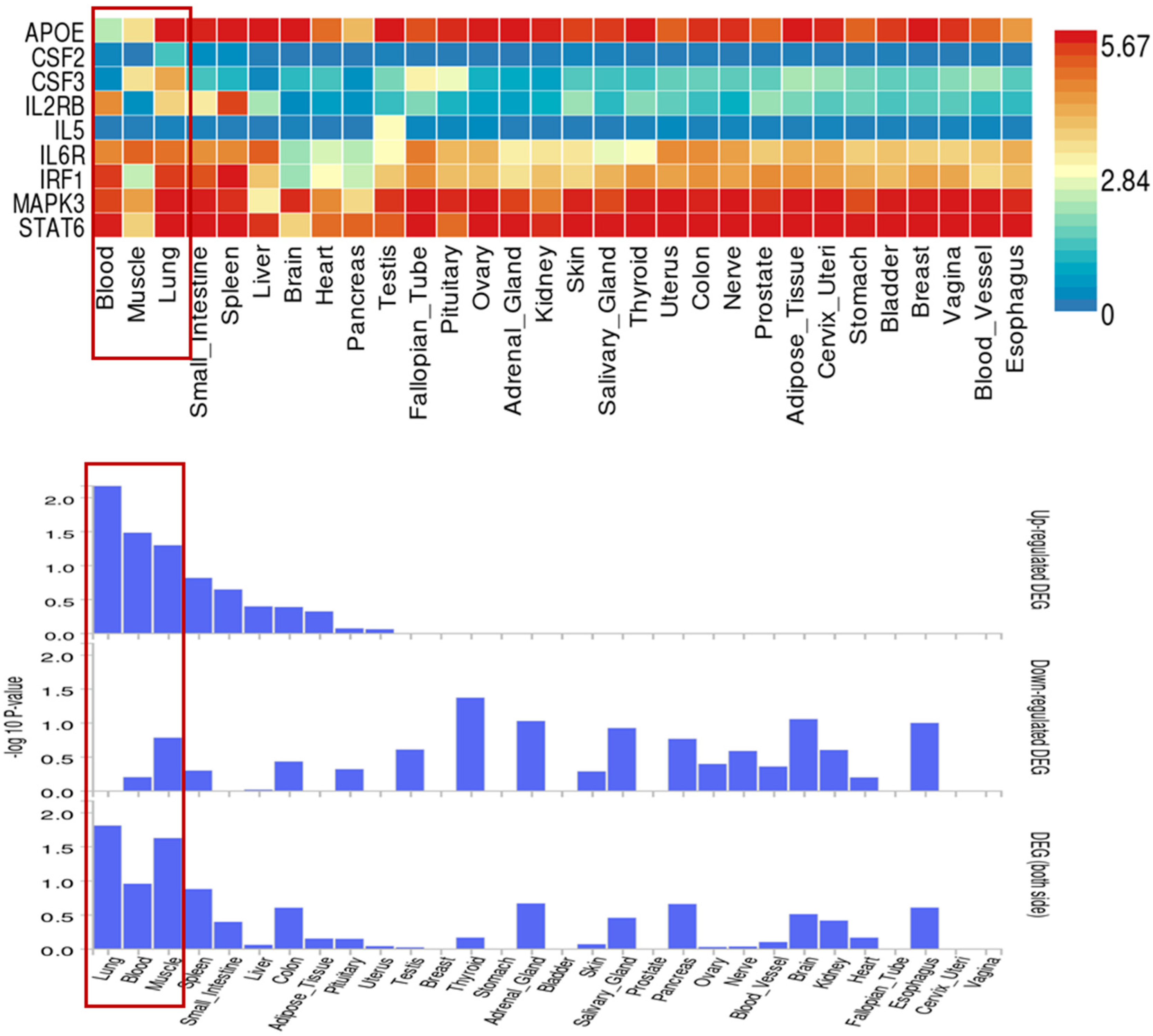
| Trait Pairs | PM 11 | PAR | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI–allergic asthma | 0.100 | 0.219 | <0.001 |
| T2DM–allergic asthma | 0.086 | 0.228 | <0.001 |
| BMI–childhood asthma | 0.079 | 0.176 | <0.001 |
| FG–childhood asthma | 0.012 | 0.077 | <0.001 |
| T2DM–childhood asthma | 0.072 | 0.196 | <0.001 |
| BMI–non-allergic asthma | 0.165 | 0.332 | <0.001 |
| FG–non-allergic asthma | 0.014 | 0.048 | 4.21 × 10−34 |
| T2DM–non-allergic asthma | 0.132 | 0.304 | <0.001 |
| BMI–asthma | 0.189 | 0.377 | <0.001 |
| T1DM–asthma | 0.043 | 0.143 | <0.001 |
| ISI–asthma | 0.033 | 0.111 | 9.66 × 10−202 |
| T2DM–asthma | 0.155 | 0.353 | <0.001 |
| Exposure | Outcome | OR | Lower 95%CI | Upper 95%CI | FDR | nsnp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | Asthma | 1.47 | 1.42 | 1.53 | 5.46 × 10−92 | 1369 |
| T2DM | Asthma | 1.06 | 1.04 | 1.08 | 2.54 × 10−11 | 1101 |
| FG | Asthma | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.97 | 4.30 × 10−2 | 115 |
| FI | Asthma | 0.68 | 0.56 | 0.83 | 7.13 × 10−4 | 37 |
| HbA1c | Asthma | 0.98 | 0.85 | 1.12 | 8.80 × 10−1 | 111 |
| 2hGlu | Asthma | 1.03 | 0.96 | 1.11 | 8.80 × 10−1 | 15 |
| T1DM | Asthma | 1.01 | 1.00 | 1.03 | 2.20 × 10−1 | 121 |
| IFC | Asthma | 1.24 | 1.04 | 1.49 | 6.94 × 10−2 | 5 |
| Asthma | BMI | 1.01 | 1.00 | 1.03 | 3.16 × 10−1 | 29 |
| Asthma | T2DM | 1.02 | 0.99 | 1.05 | 8.07 × 10−1 | 31 |
| Asthma | FG | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 8.07 × 10−1 | 36 |
| Asthma | FI | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 36 |
| Asthma | HbA1c | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 36 |
| Asthma | 2hGlu | 0.99 | 0.94 | 1.05 | 1.00 | 36 |
| Asthma | T1DM | 1.06 | 0.96 | 1.18 | 1.00 | 34 |
| Asthma | IFC | 0.97 | 0.93 | 1.01 | 8.07 × 10−1 | 37 |
| Asthma | ISI | 1.02 | 0.98 | 1.07 | 1.00 | 37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Lin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Kong, Z.; Qiu, C.; Peng, K.; Liu, H.; Luo, Z. Genetic Pleiotropy and Causal Pathways Linking Glycemic Traits to Asthma: An Integrated Proteogenomic Investigation. Children 2025, 12, 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111443
Chen L, Lin J, Zhao Y, Zhang G, Kong Z, Qiu C, Peng K, Liu H, Luo Z. Genetic Pleiotropy and Causal Pathways Linking Glycemic Traits to Asthma: An Integrated Proteogenomic Investigation. Children. 2025; 12(11):1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111443
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lin, Juntao Lin, Yan Zhao, Guangli Zhang, Zhenxuan Kong, Chunlan Qiu, Kaicheng Peng, Hui Liu, and Zhengxiu Luo. 2025. "Genetic Pleiotropy and Causal Pathways Linking Glycemic Traits to Asthma: An Integrated Proteogenomic Investigation" Children 12, no. 11: 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111443
APA StyleChen, L., Lin, J., Zhao, Y., Zhang, G., Kong, Z., Qiu, C., Peng, K., Liu, H., & Luo, Z. (2025). Genetic Pleiotropy and Causal Pathways Linking Glycemic Traits to Asthma: An Integrated Proteogenomic Investigation. Children, 12(11), 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111443





